Cardio/Renal 12 - Physical Examination of the Cardiovascular System (Dr. Shaikhi)
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
Cardiovascular System Physical Examination consists of:
Examination of Extremities, Vital signs (Pulse & BP) & Heart

What part of the physical examination is known as "see"?
Inspection
What part of the physical examination is known as "feel"?
Palpation
What part of the physical examination is known as "tap"?
Percussion
What part of the physical examination is known as "hear"?
Auscultation
Druing auscultation, listen for Carotid Bruit if partial ...
carotid block is evident by R & L pulse rate disparity
normal pulse rate range:
60-80 beats/min

Final BP recorded is average of _____ readings
2-4

patients height is logged in:
feet and inches

patients weight is logged in _____ in chart
lbs

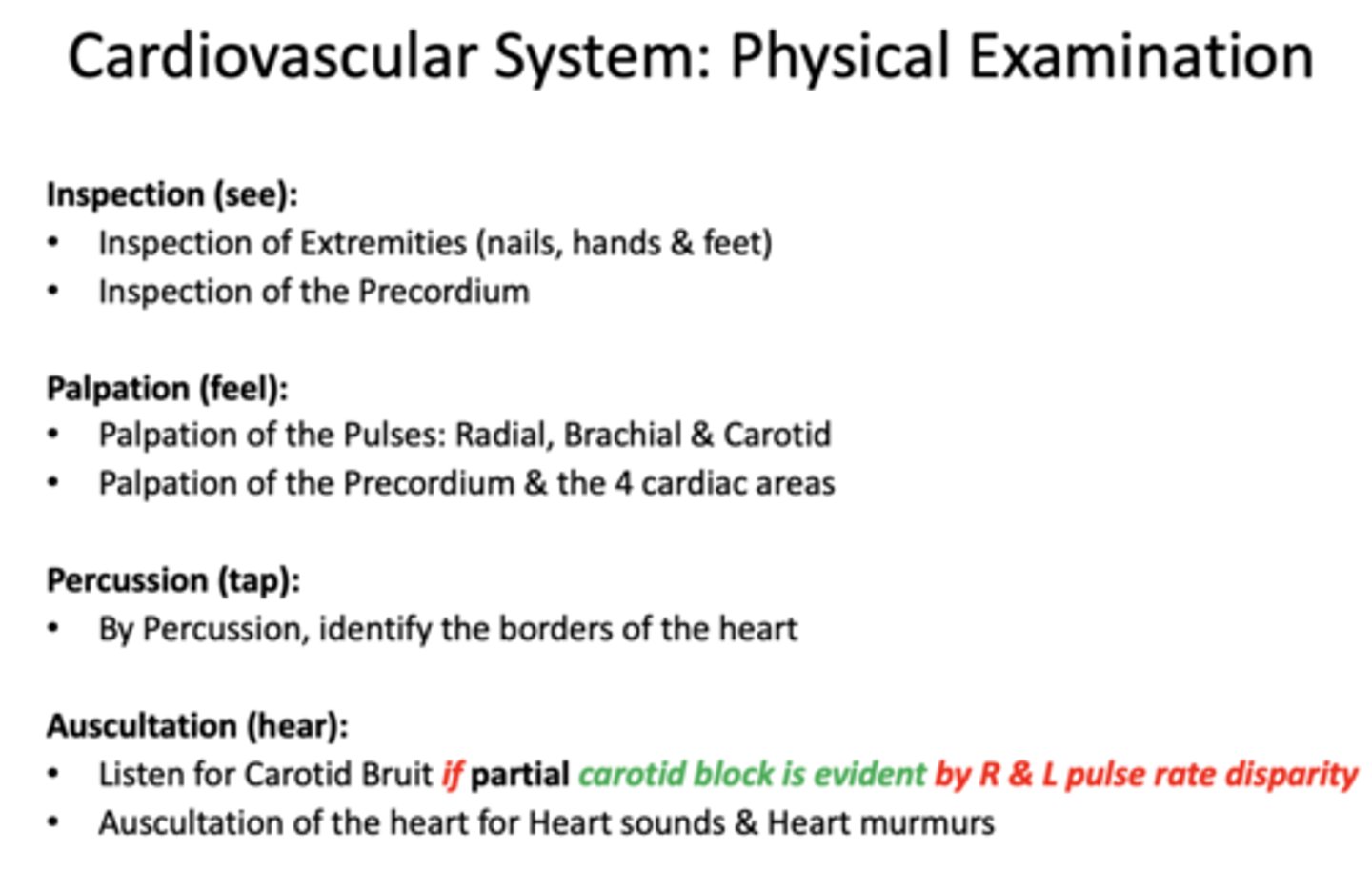
What are 3 things to note when taking pulse?
- Rate
- Rhythm
- Volume
patients weight is logged in _____ during medical emergency
kg

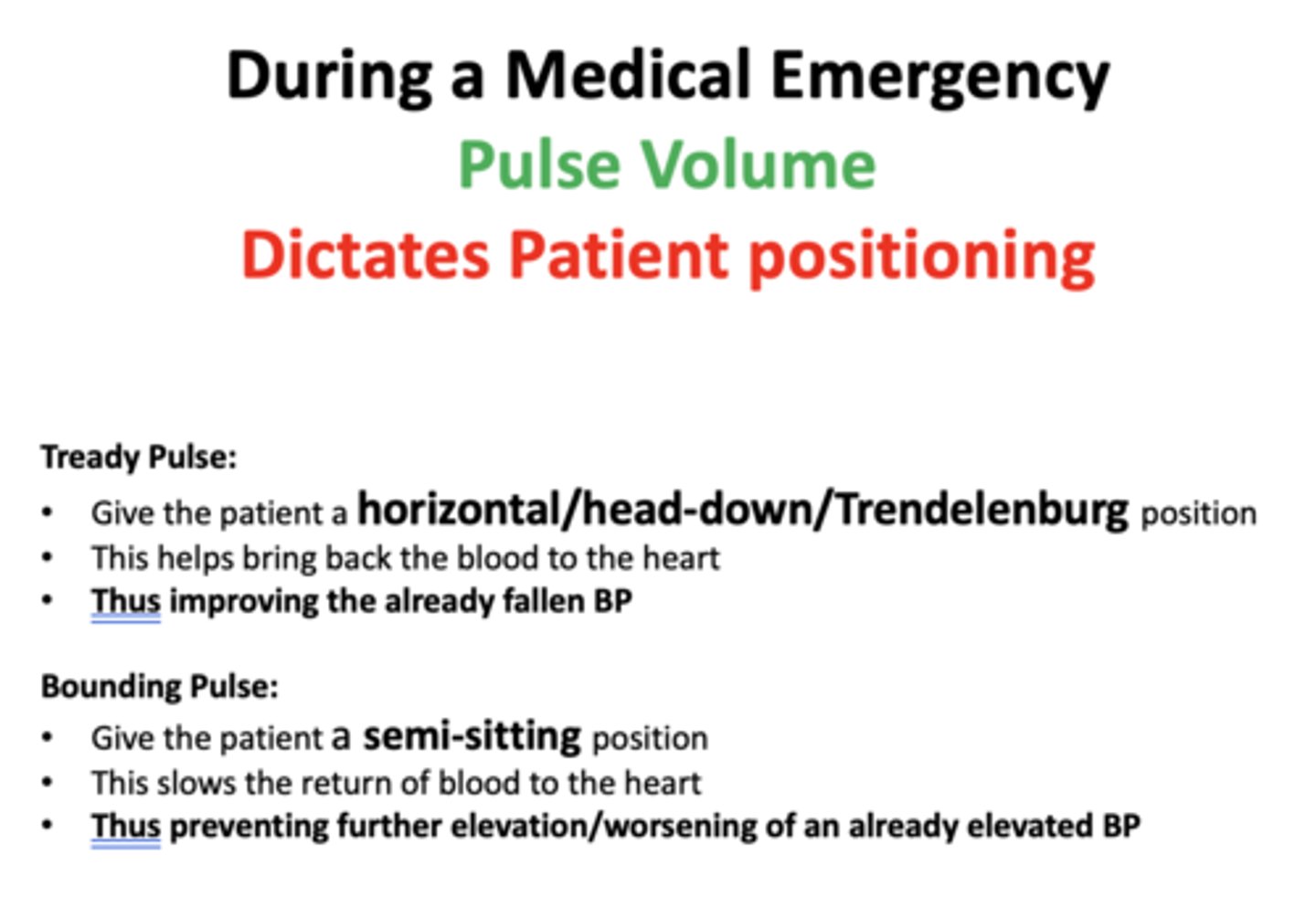
A “low volume” pulse is also called a ___________ pulse
"Tready" or "weak"

A Tready pulse indicates a _________ Blood Pressure (BP)
lowered

A “high volume” pulse is called a __________ pulse
"Bounding" or "strong"

A Bounding pulse indicates an _________ BP
elevated

if a patient presents to the dental office with a "tready" pulse, what positions should you sit them in to bring back blood to heart and raise BP?
horizontal/head-down/Trendelenburg
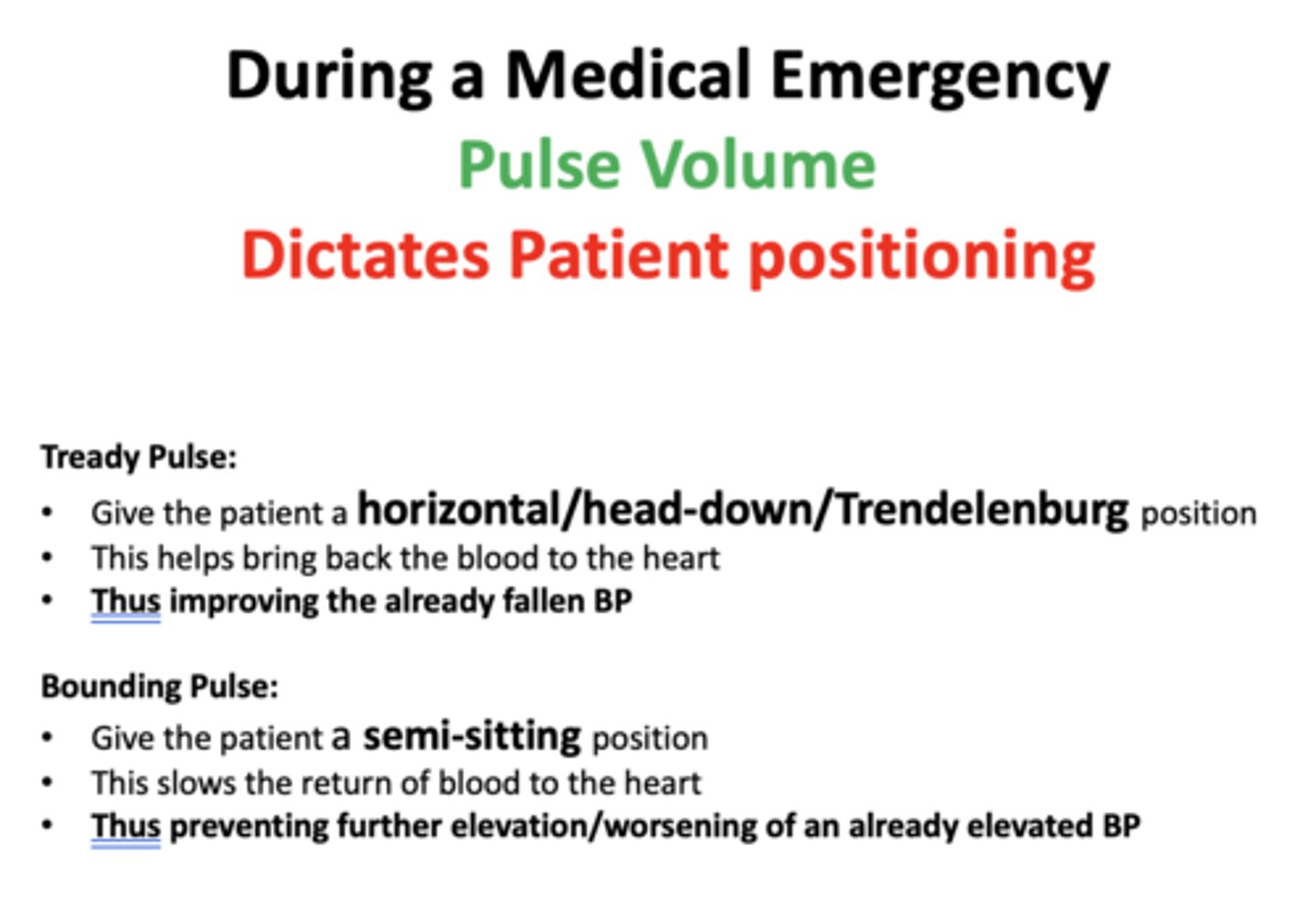
if a patient presents to the dental office with a "bounding" pulse, what positions should you sit them in to slow return of blood to the heart & prevent further elevation of BP?
semi-sitting
Pulse Rate less than 60/min:
bradycardia

Pulse Rate more than 100/min:
tachycardia

_________ can lead to a lowered HR and it is NORMAL:
regular exercise

these drugs are typically used for BP management, decrease the heart rate:
beta blockers

Rhythm is the ________ pattern of the Pulse
sequential

Sudden anxiety, fear or noise can temporarily _____ pulse rate
increase

Persistent irregularity especially with symptoms prompts =
immediate MD consult

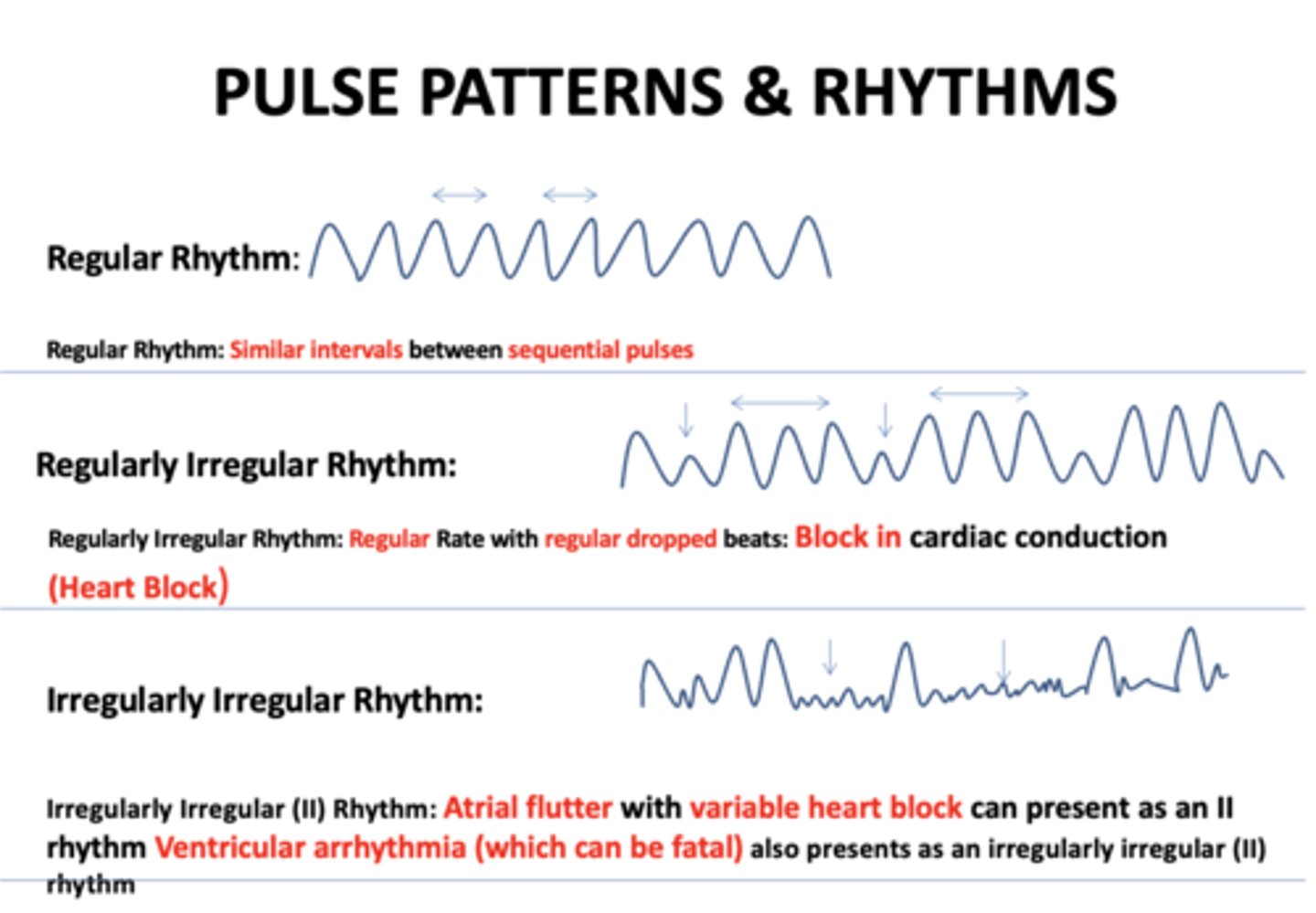
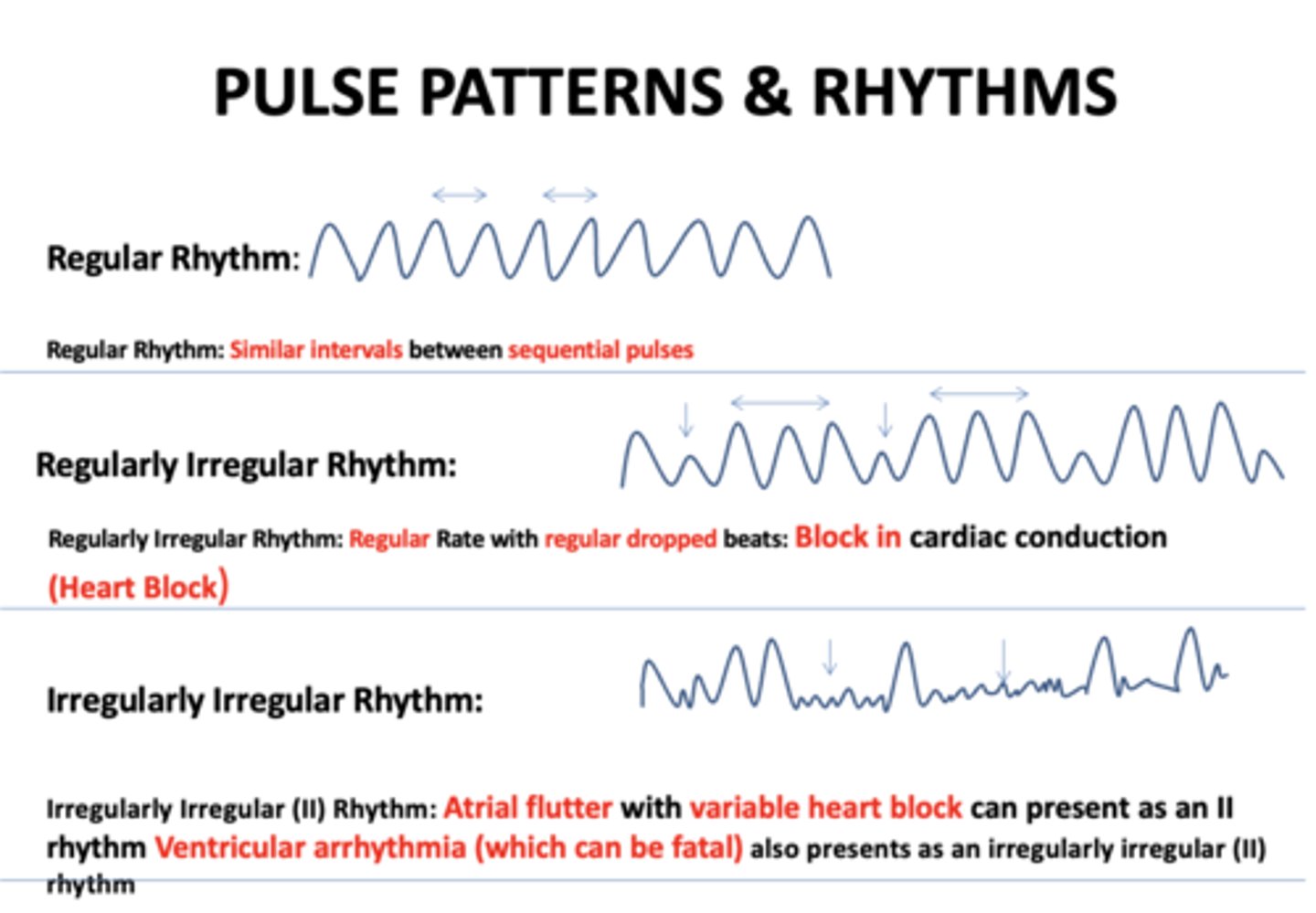
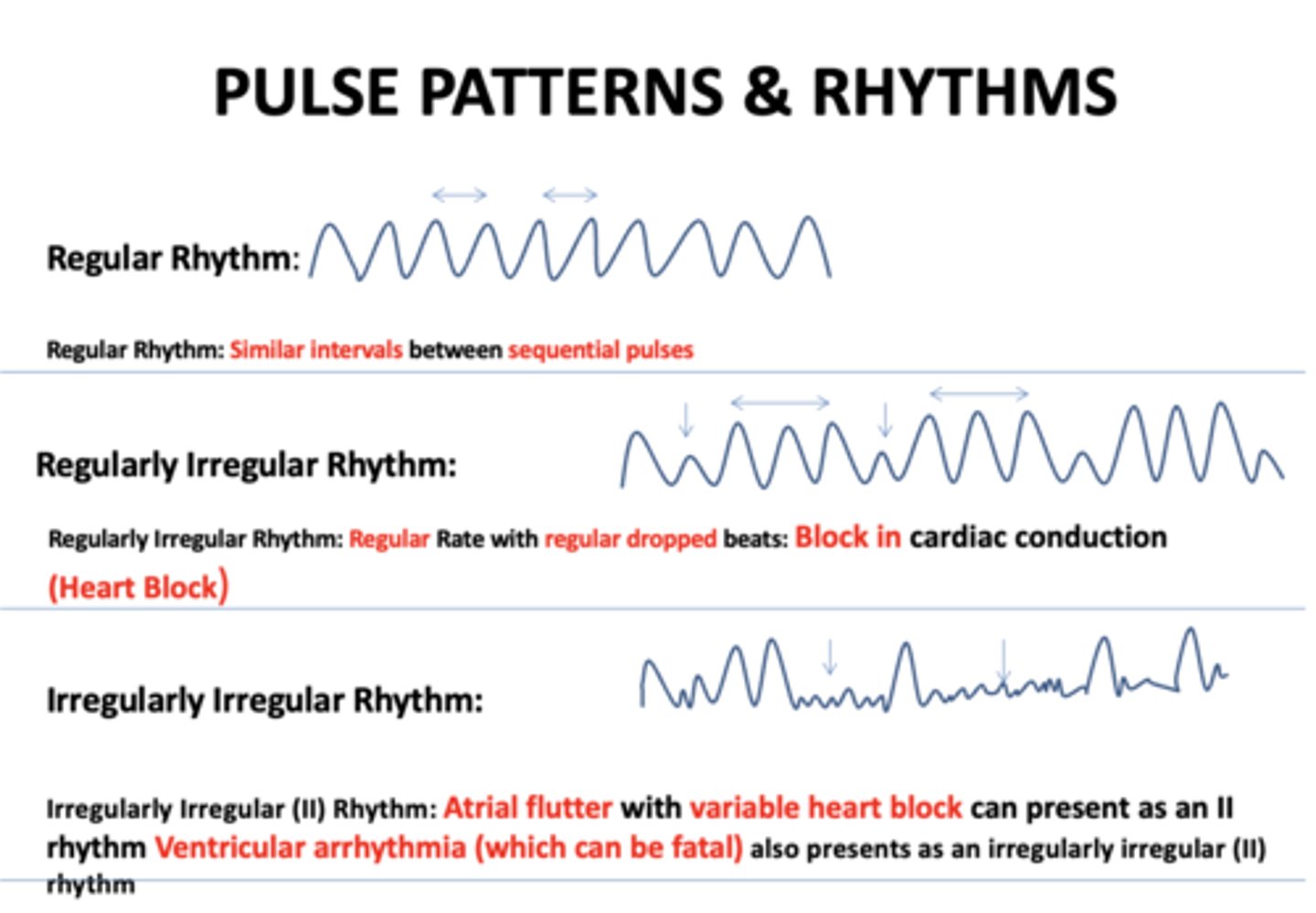
Similar intervals between sequential pulses:
regular rhythm
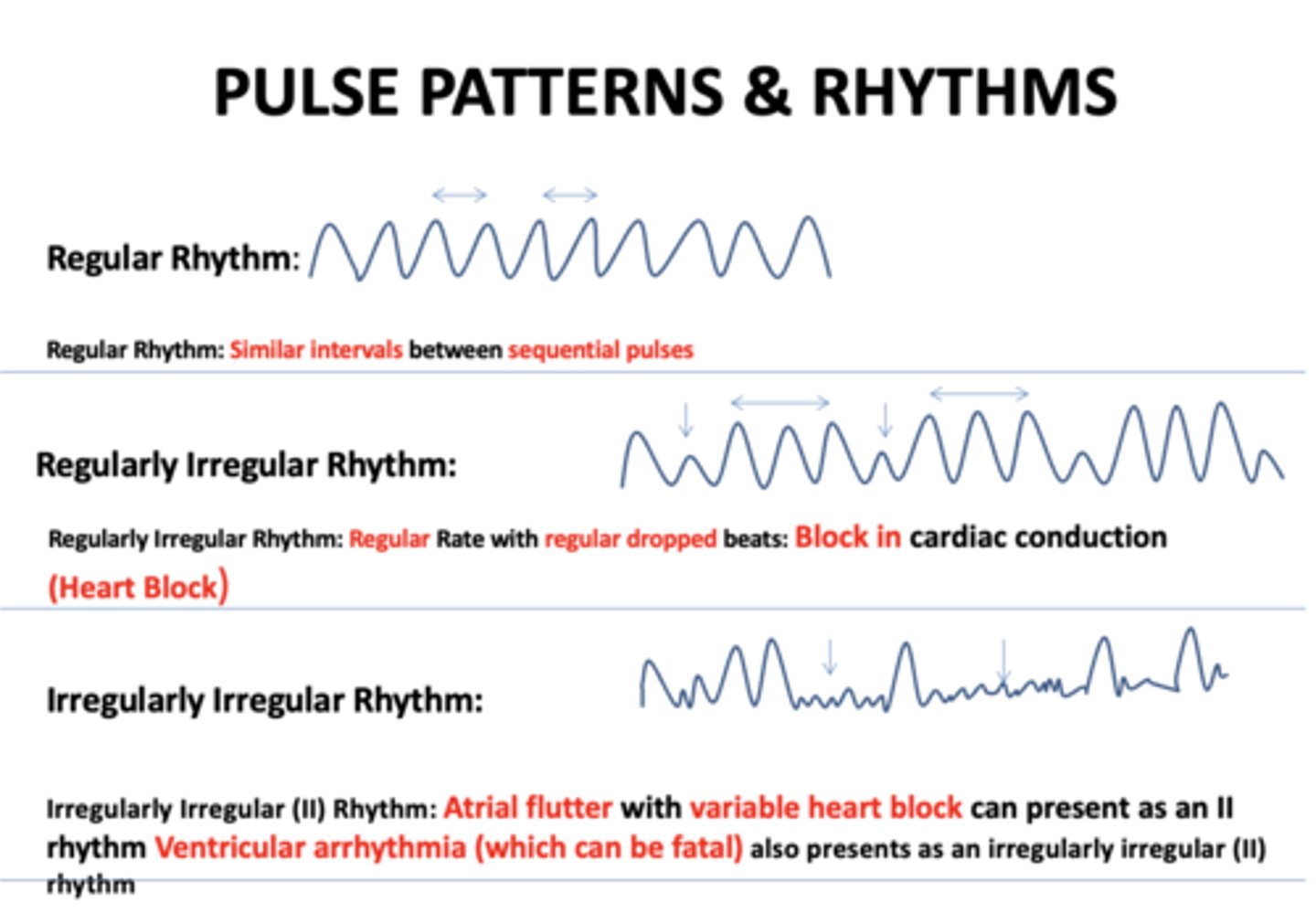
Regular Rate with regular dropped beats...
regularly irregular rhythm
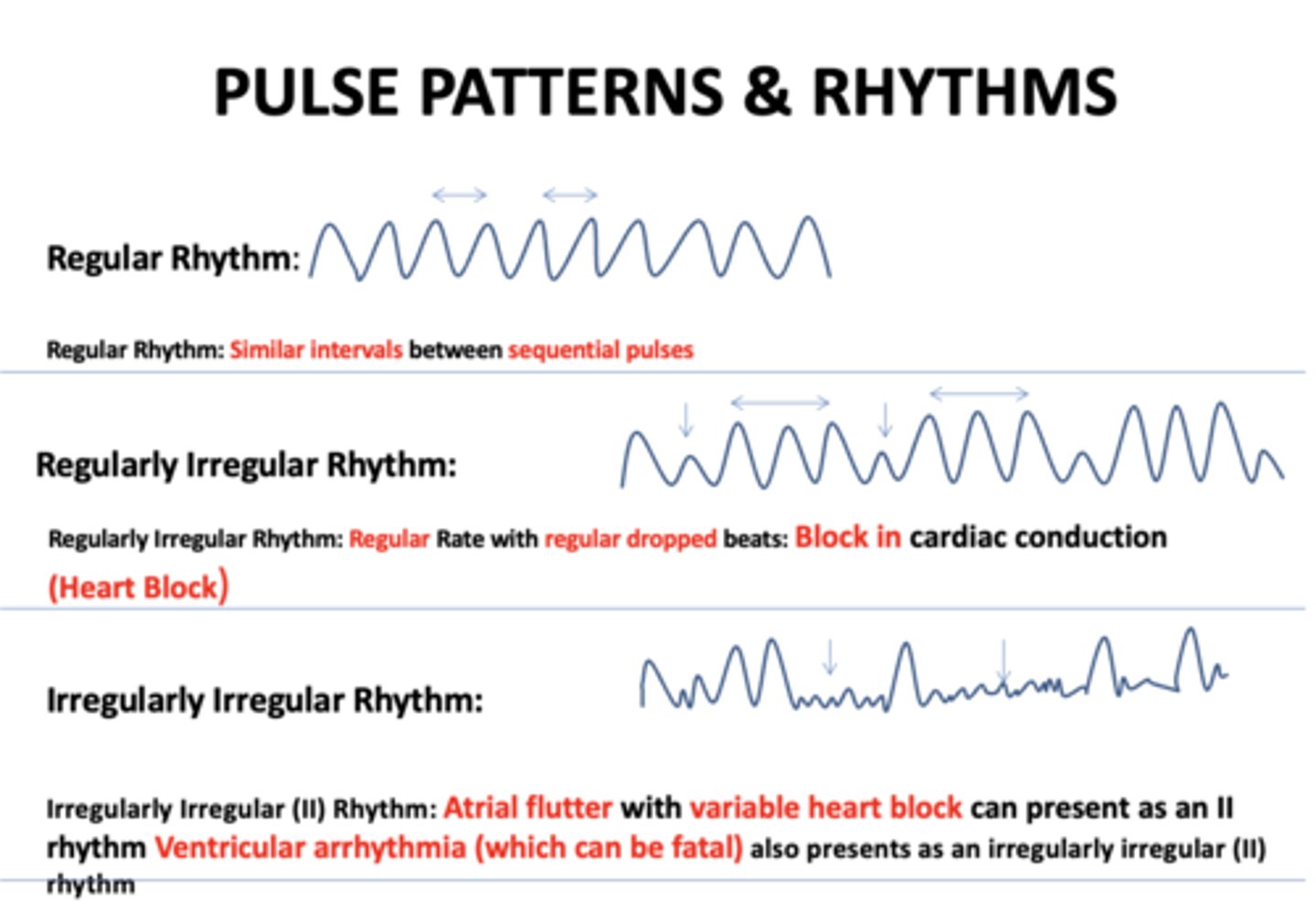
Regular Rate with regular dropped beats indicates...
block in cardiac conduction
Regular rate with regular dropped beats and block in cardiac conduction (Heart block) is referred to as...
regularly irregular rhythm
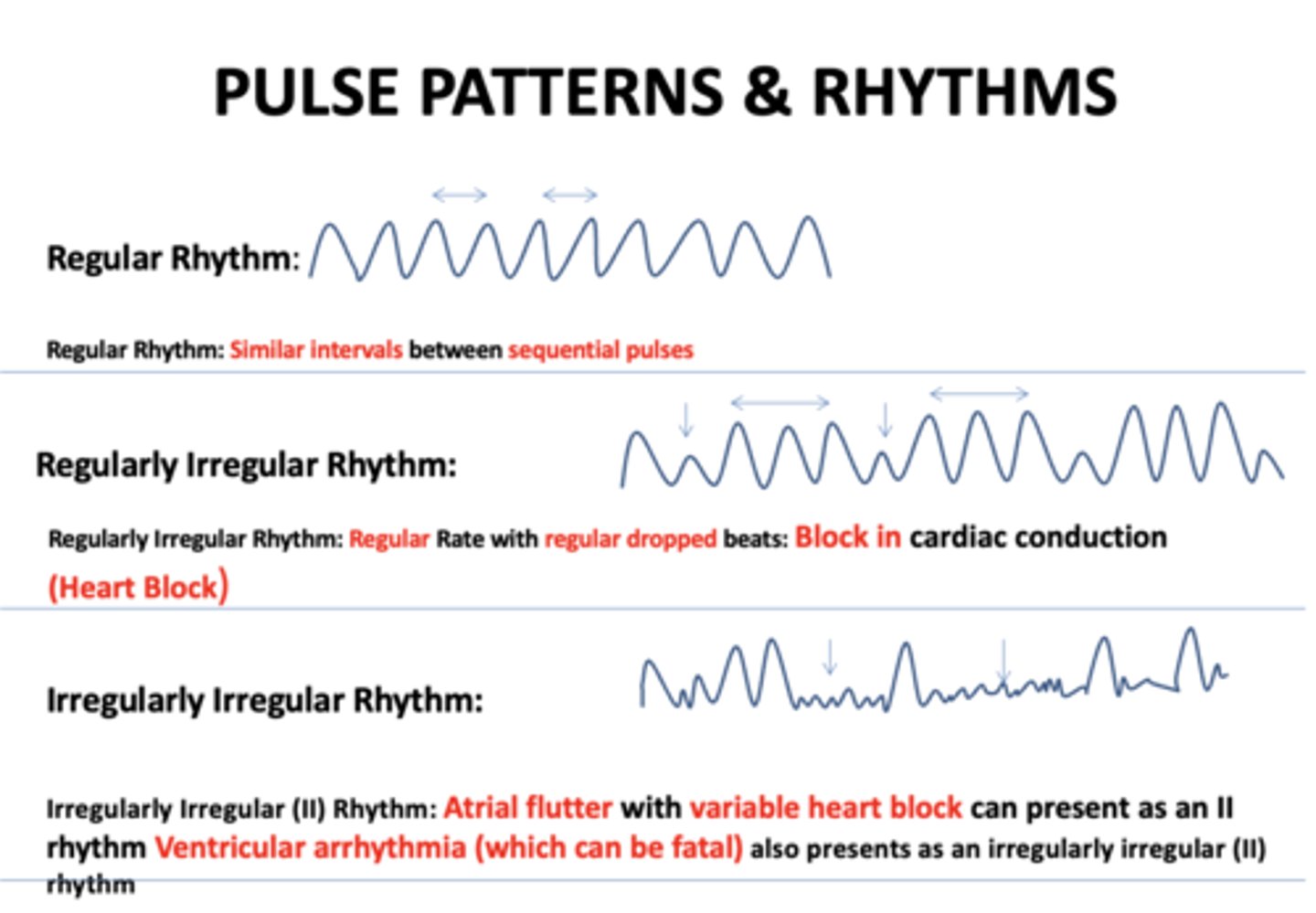
Atrial flutter with variable heart block can present as an II rhythm Ventricular arrhythmia (which can be fatal):
Irregularly irregular rhythm
Two examples of Irregularly Irregular Rhythm
Atrial flutter
Ventricular Arrhytmia
What has the following characteristics:
Normal SA node generated impulses are overwhelmed by disorganized electrical impulses usually originating in the roots of the pulmonary veins -> irregular conduction to ventricles
atrial fibrillation
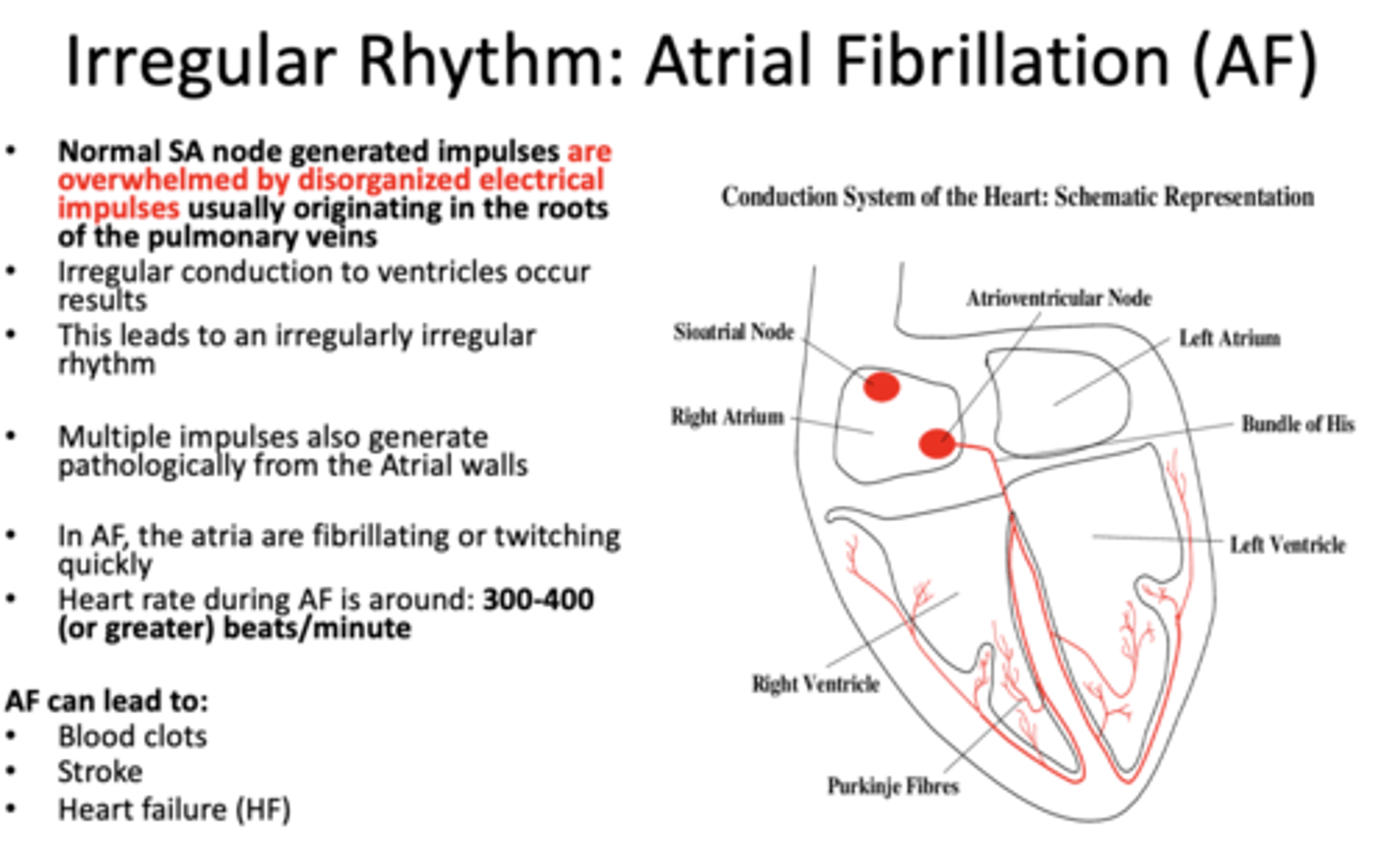
Heart rate during atrial fibrillation is around ________ beats/minute
300-400 (or greater)
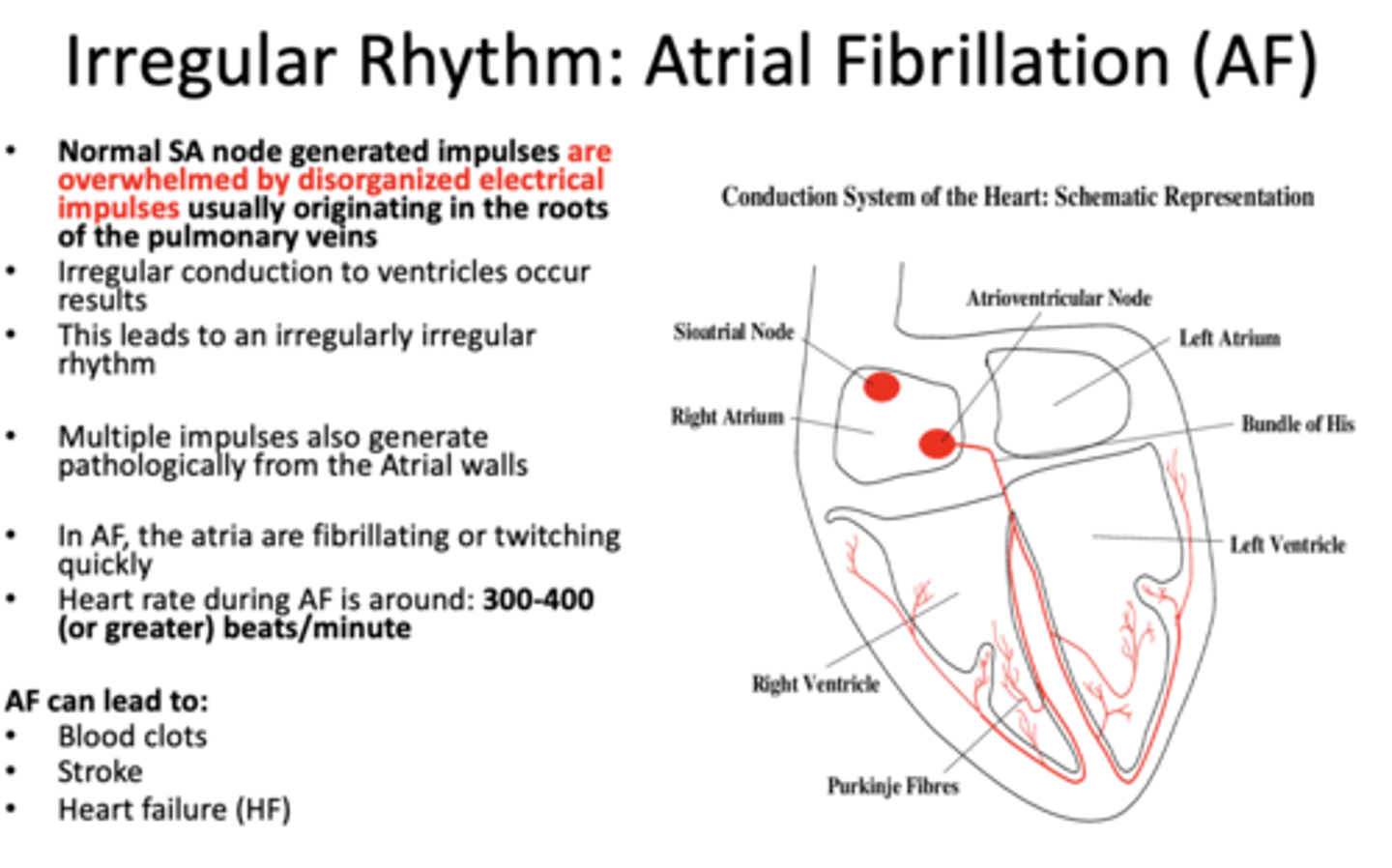
Atrial Fibrillation can lead to (3):
- Blood clots
- Stroke
- Heart failure (HF)
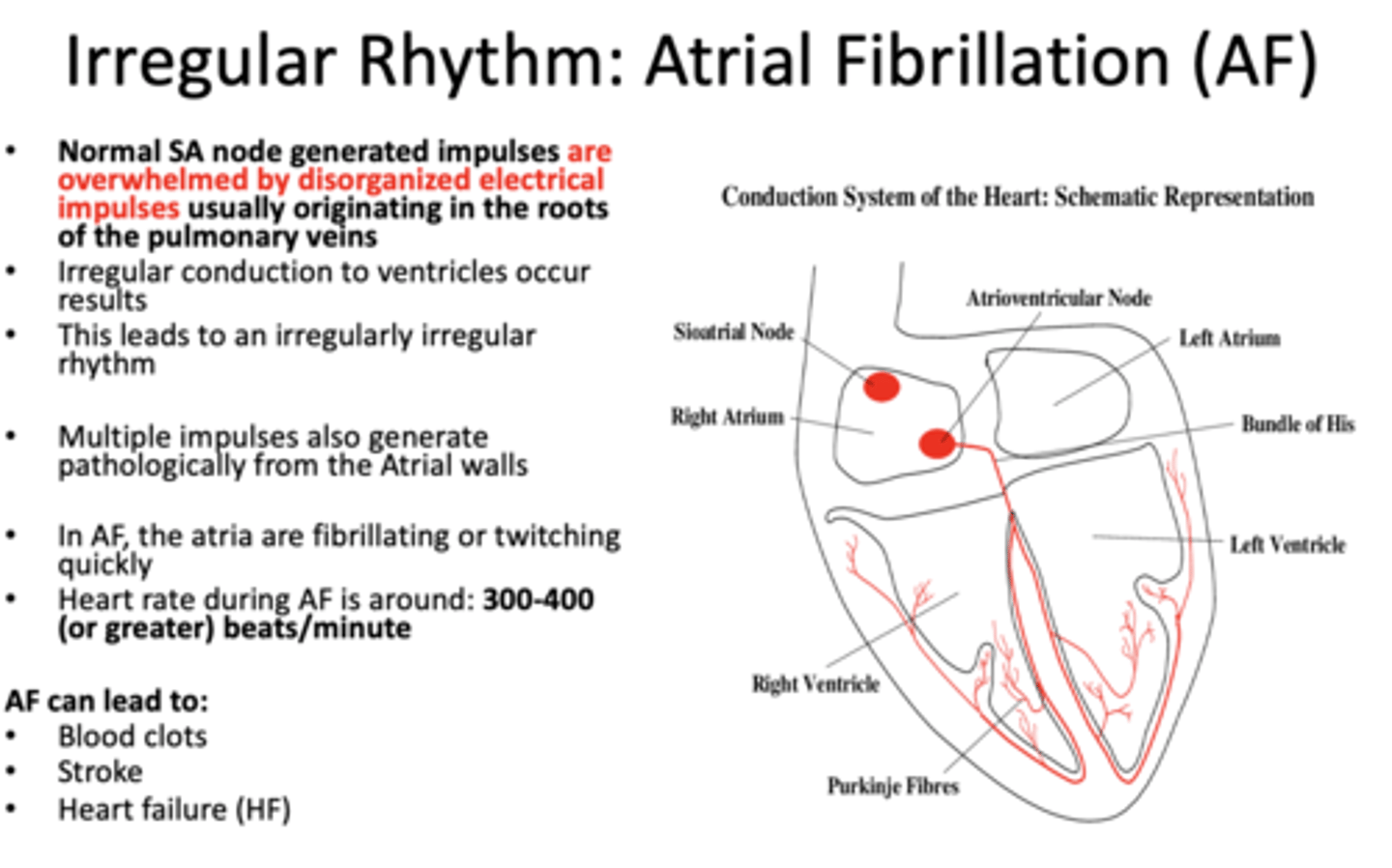
Always feel the pulse with at least 2 fingers. What two fingers should you use?
index and middle fingers

_________ patients have thickened arteries due to atherosclerosis, this causes the arteries to be whip-cord like and slippery
Older

what finger has its own pulse/pulsations and should NEVER be used to take a pulse?
thumb

where is the radial pulse felt?
wrist just BELOW the thumb
Which pulse is this?
- Start counting the pulse only after pt is relaxed
- Count pulse for a minute and note presence of irregularities
- Irregularities may be missed if pulse felt for only 10/15 secs
radial pulse

the carotid pulse can be felt on the anterior boarder of the _______
sternocleidomastoid

when taking a carotid pulse, where should you place your fingers?
along the border (of STM) in the middle of the neck

When taking a carotid pulse, the platysma can be relaxed by having the patient:
flex the neck

Where should you never take the Carotid pulse?
- At the angle of the mandible
- Both sides at the same time (can be dangerous esp to elderlu)

taking a pulse at the ________ can massage the Carotid sinus thus slowing the pulse
angle of mandible

taking a pulse at _________ can cause a patient to pass out, especially elderly patients
both sides at the same time

which pulse is most frequently felt during a medical emergency?
carotid

Auscultate for _______ if the rate is not the same on both sides
carotid bruit
Carotid Bruit is heard over the Carotid with the _______ pulsation
lesser
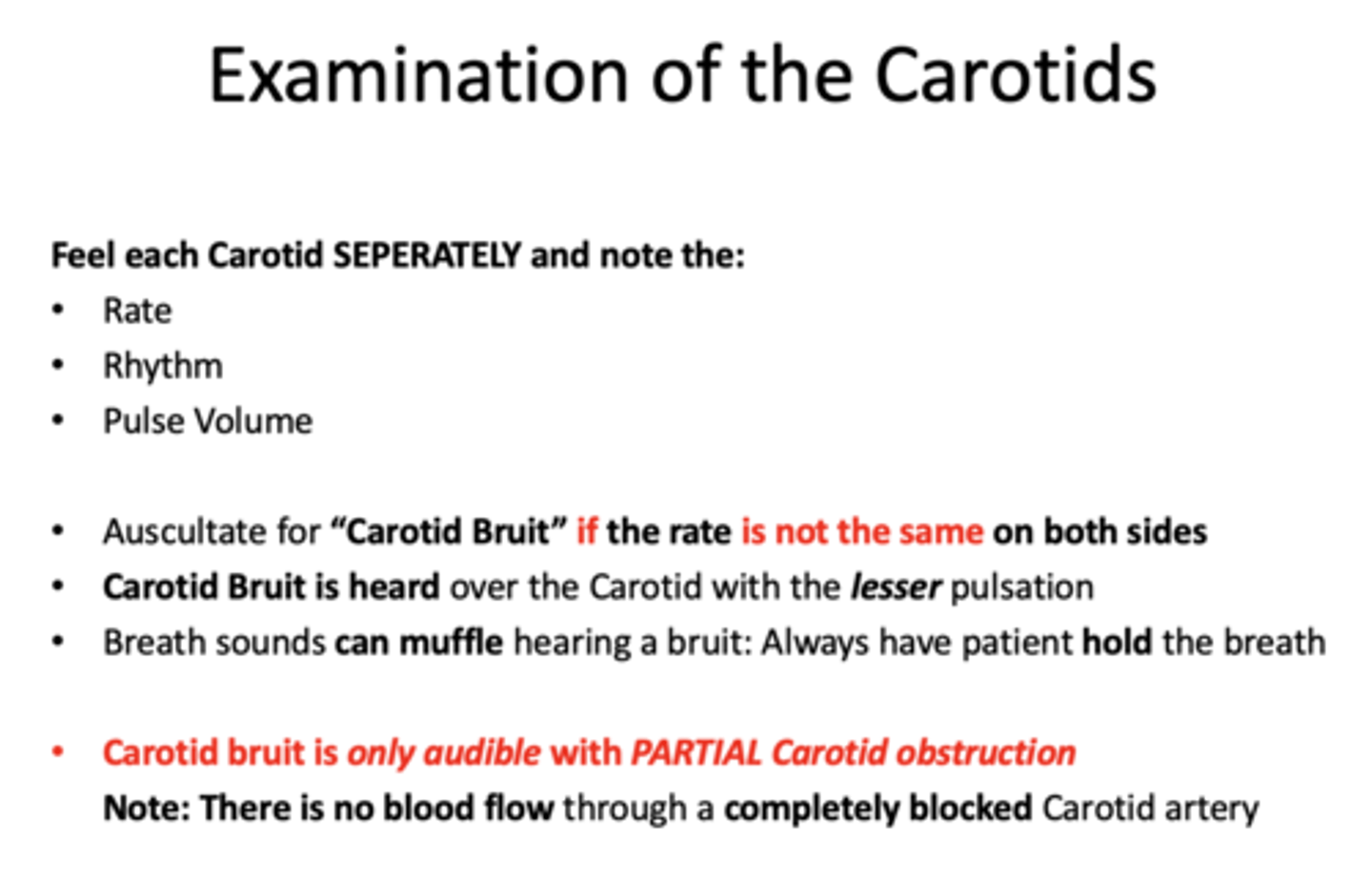
t/f: there is blood flow through a completely blocked carotid artery
false, no blood flow
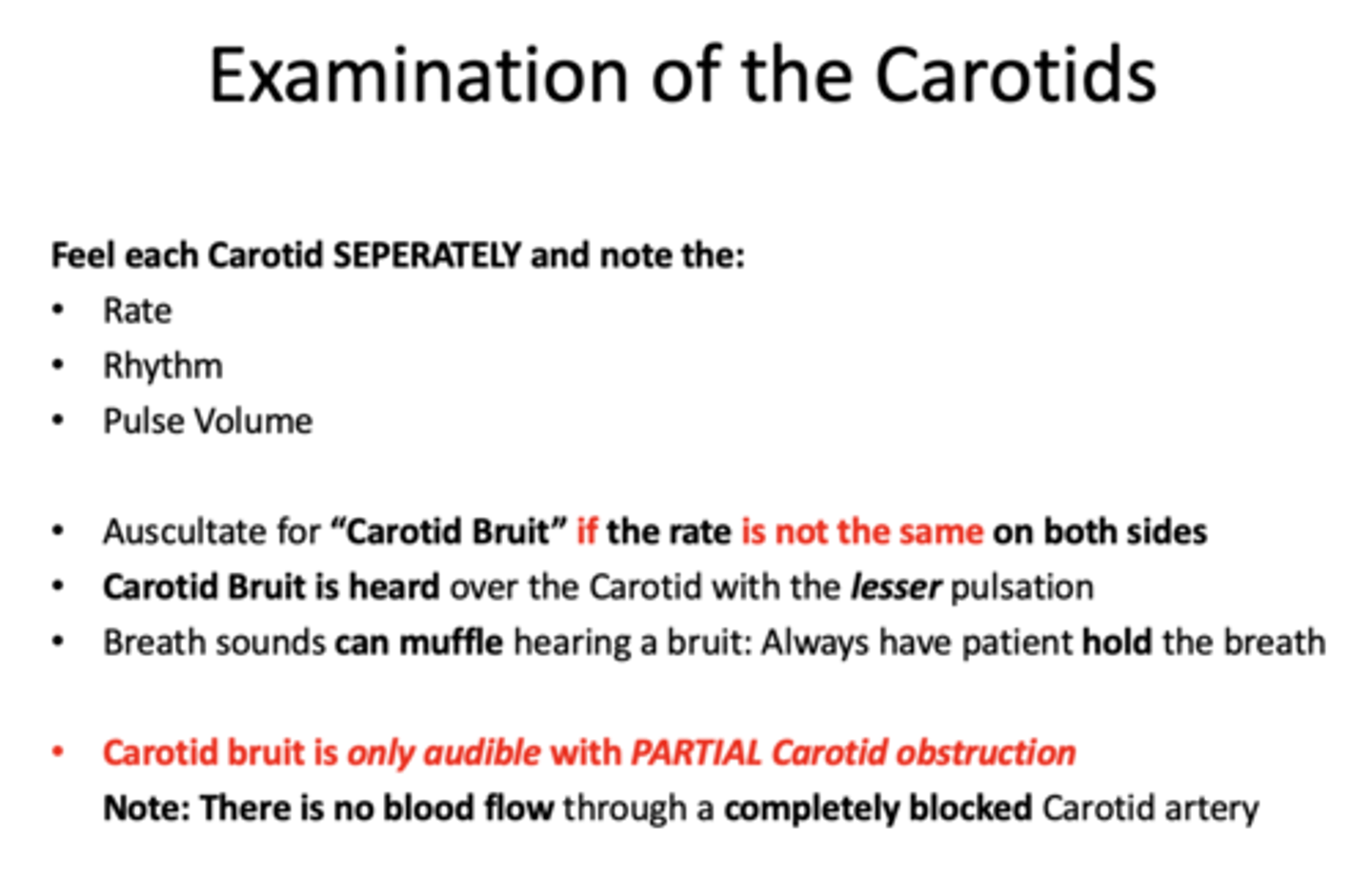
t/f: breath sounds can muffle hearing a bruit -> always have patient hold the breathe when ascultating for carotid bruit
true
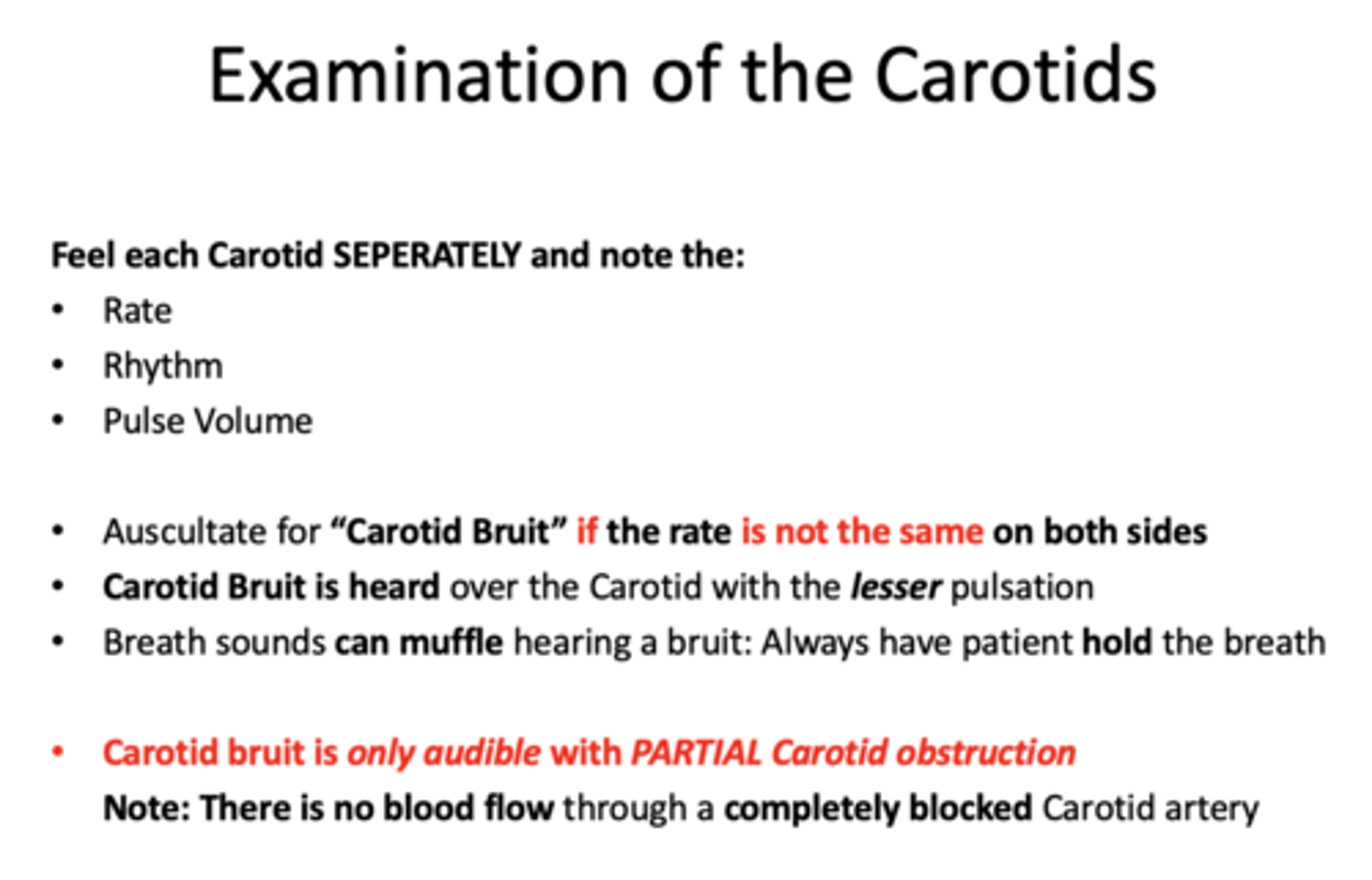
Carotid bruit is only audible with ______Carotid obstruction
partial
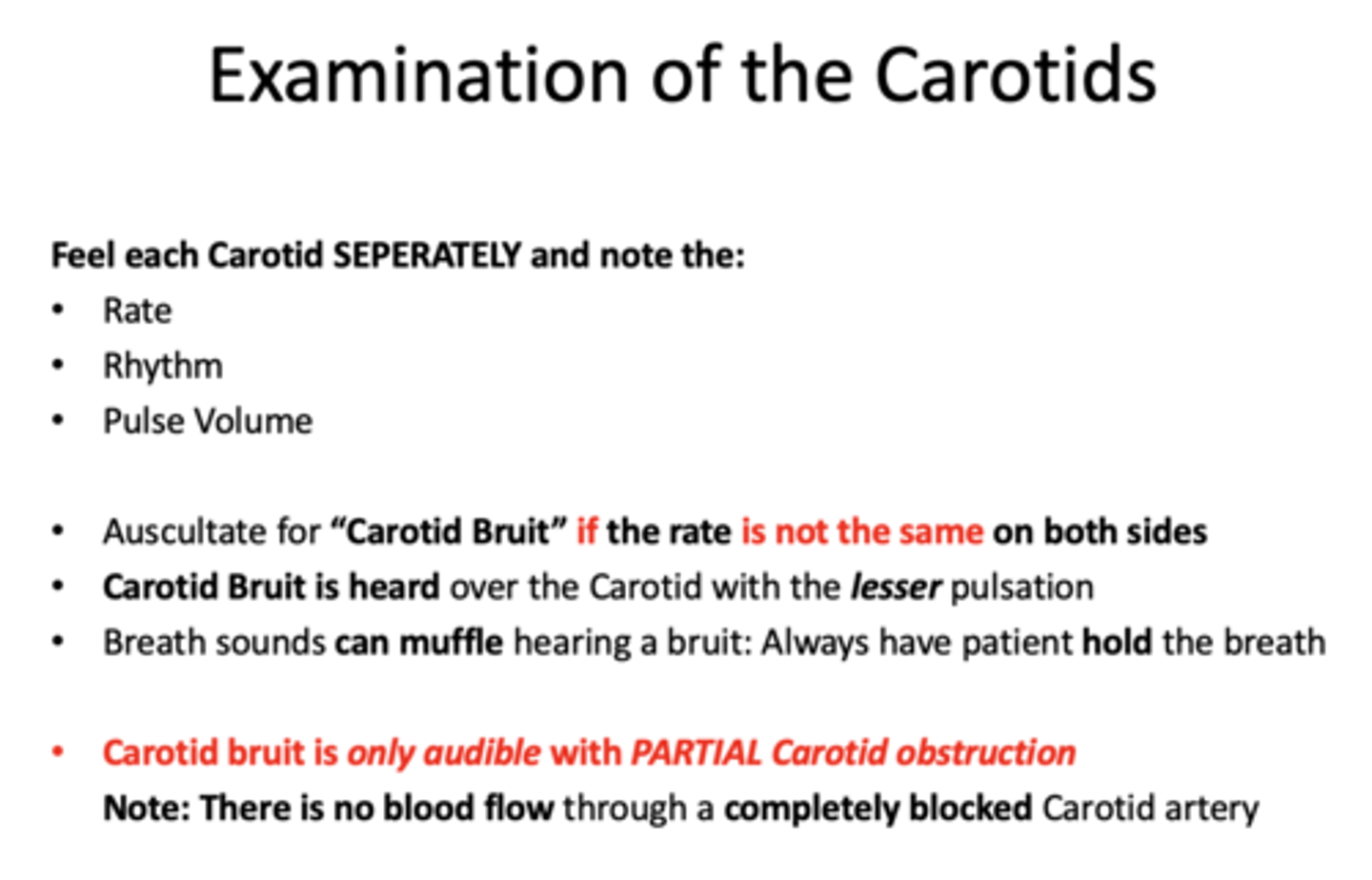
•Place the stethoscope over the Carotid in the middle of the neck
•Ask the patient to hold his/her breath
•Listen for a “swooshing sound” caused by turbulence of the blood flow through a narrowed or partially obstructed arterial lumen
•Auscultation of a swooshing sound confirms presence of a __________
carotid bruit

Obstructive blood flow leads to compromised circulation to the
brain

In the presence of Carotid Bruits always assess for (2)
•TIAs: Transient Ischemic Attacks
•CVAs: Cerebrovascular Accidents/Strokes

during a medical emergency with a child, which pulse it taken?
brachial pulse
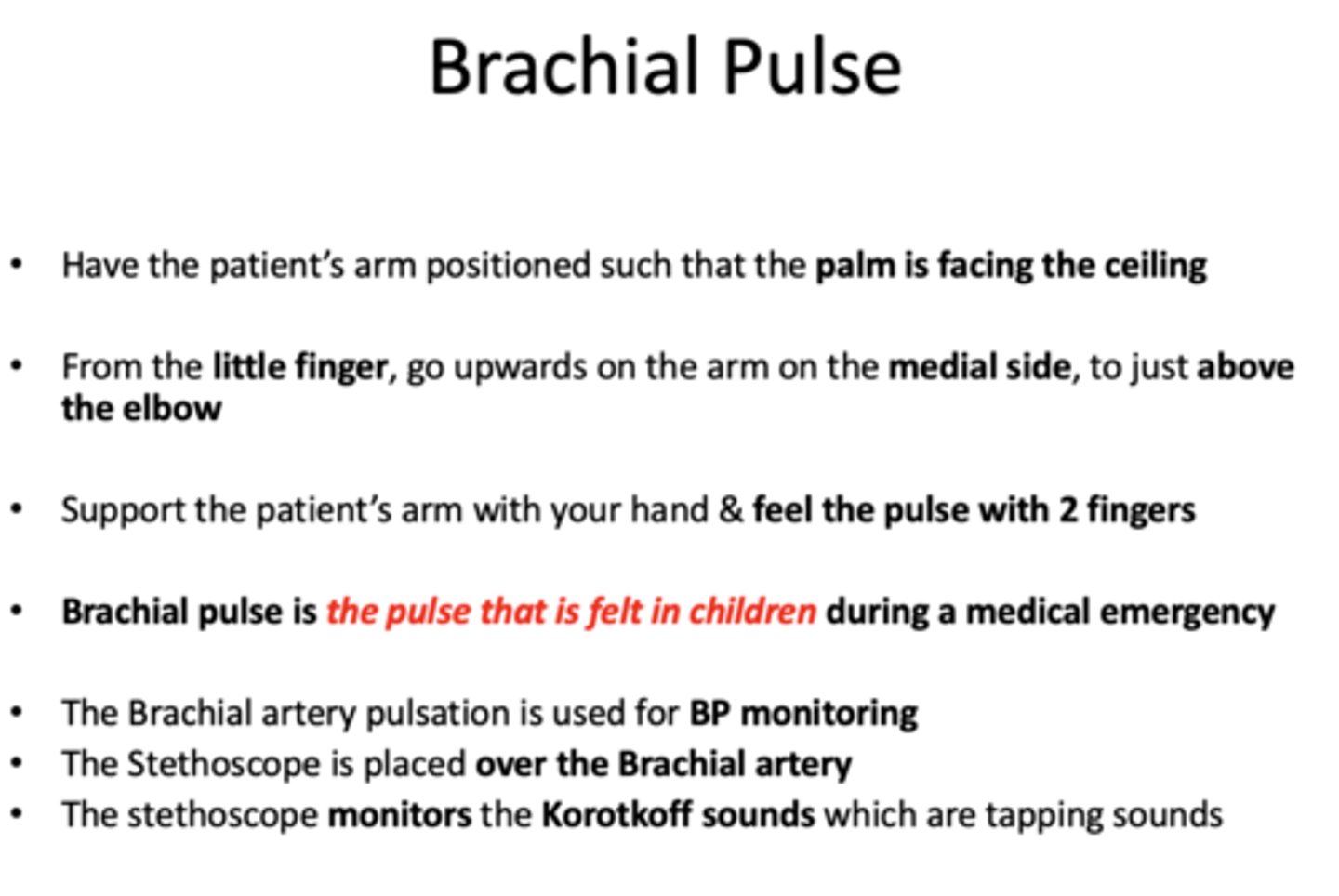
where is a brachial pulse taken?
the arm on the medial side, just above the elbow
Brachial artery pulsation is used for
BP monitoring
When taking brachial pulse, stethoscope is placed over brachial artery, which monitors the ______ which are tapping sounds.
Korotkoff sounds
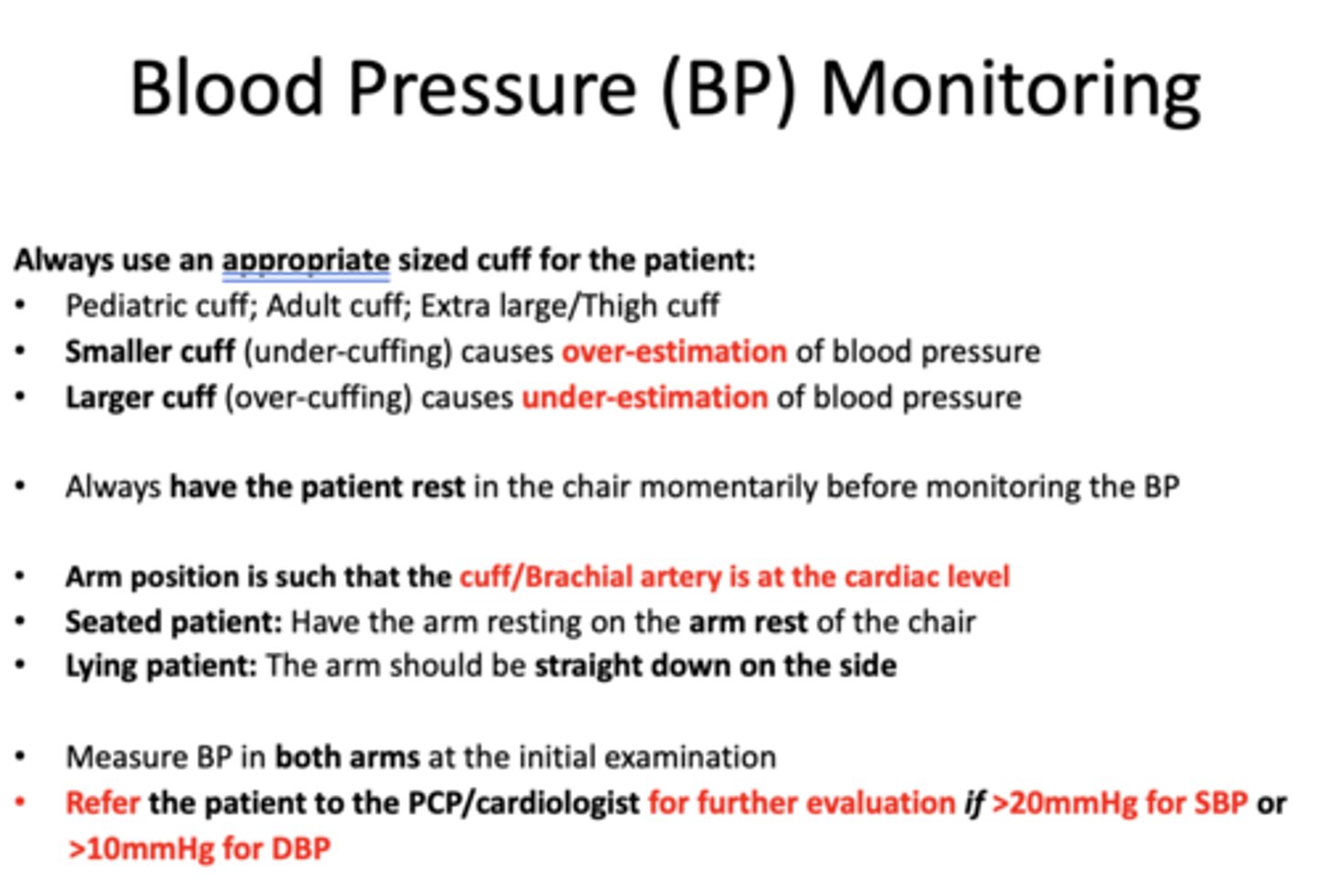
using a smaller cuff (under-cuffing) causes an __________ of blood pressure
over-estimation
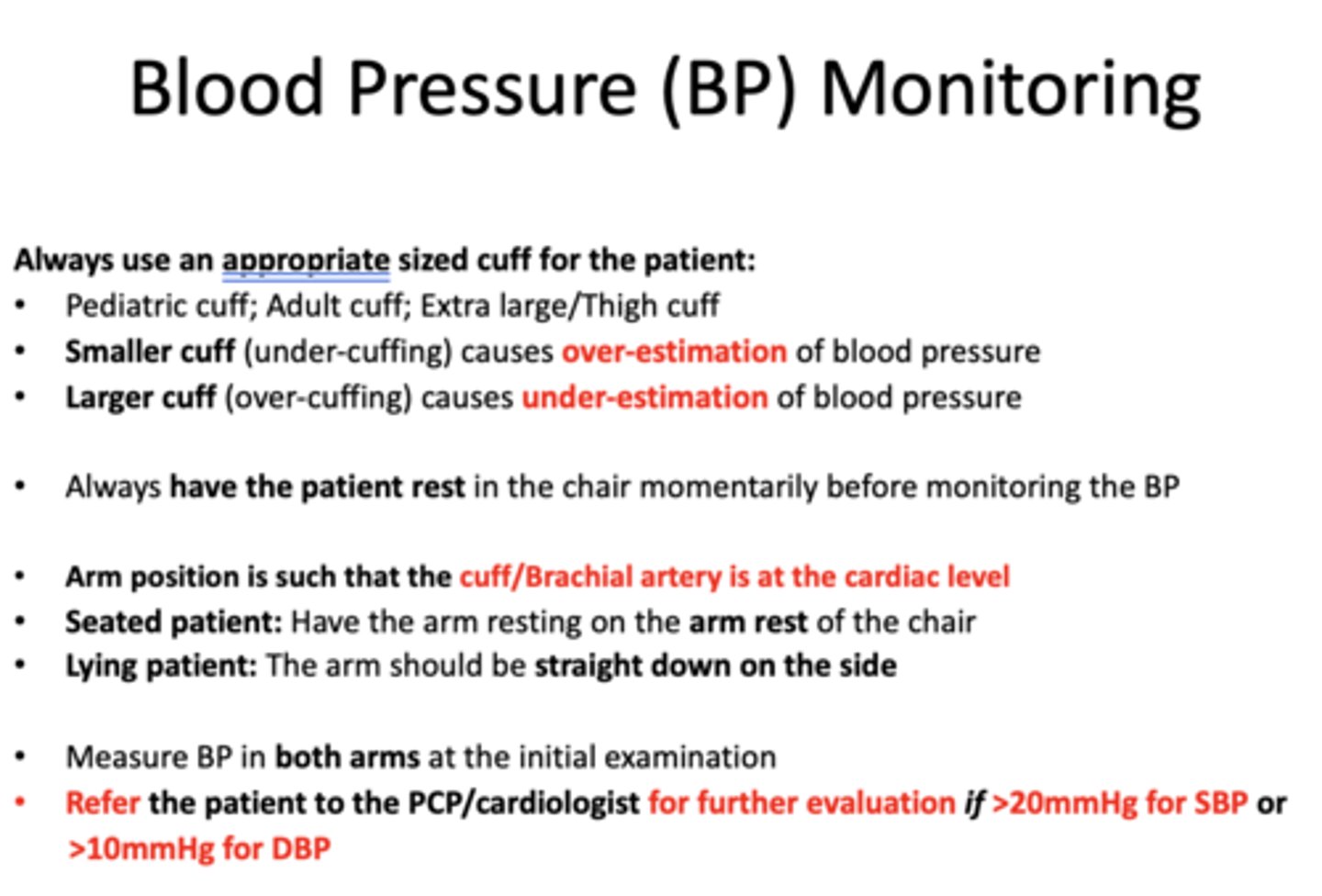
using a larger cuff (over-cuffing) causes an ________ of blood pressure
under-estimation
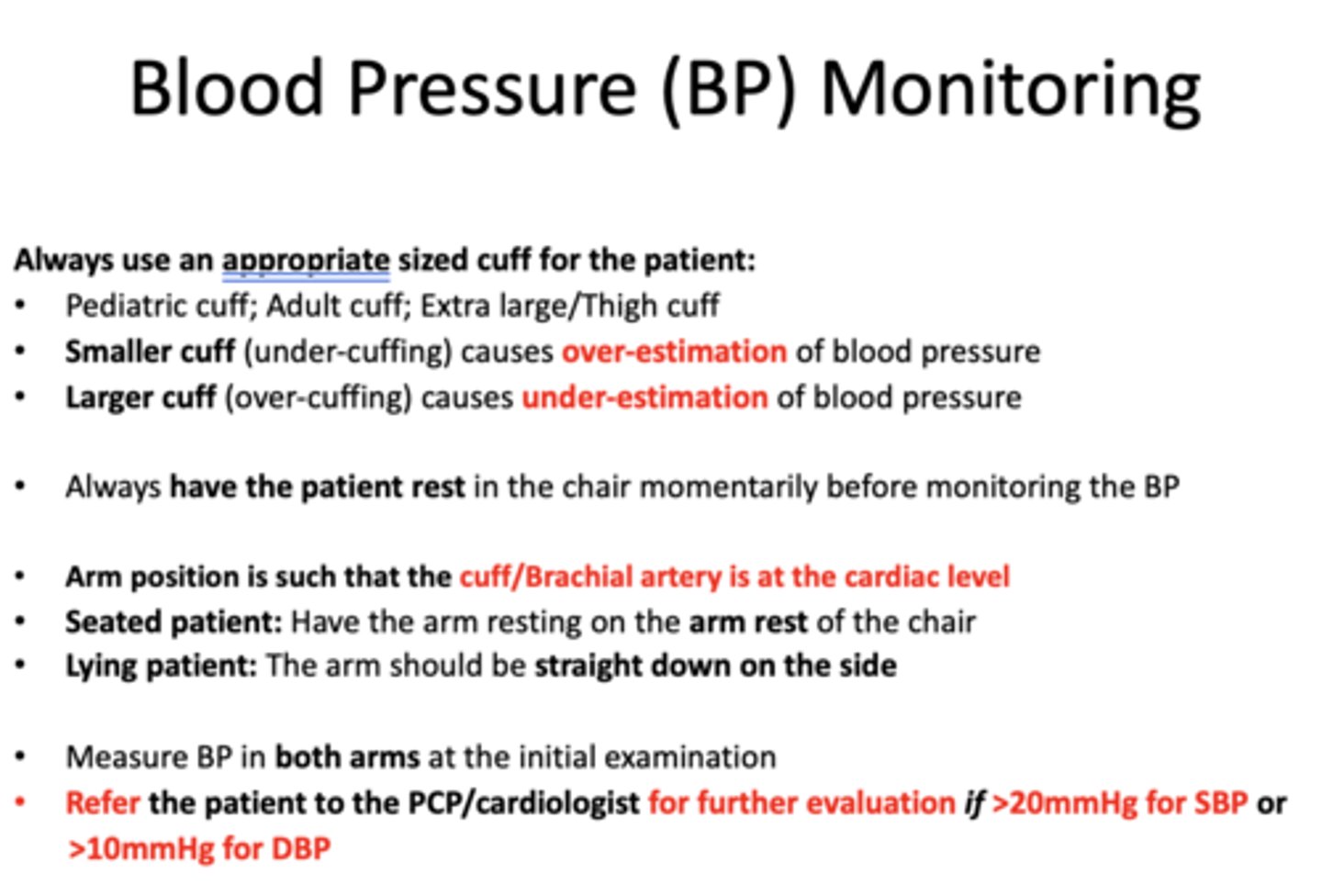
t/f: you should always have the patient rest in the chair for a little before monitoring BP
true
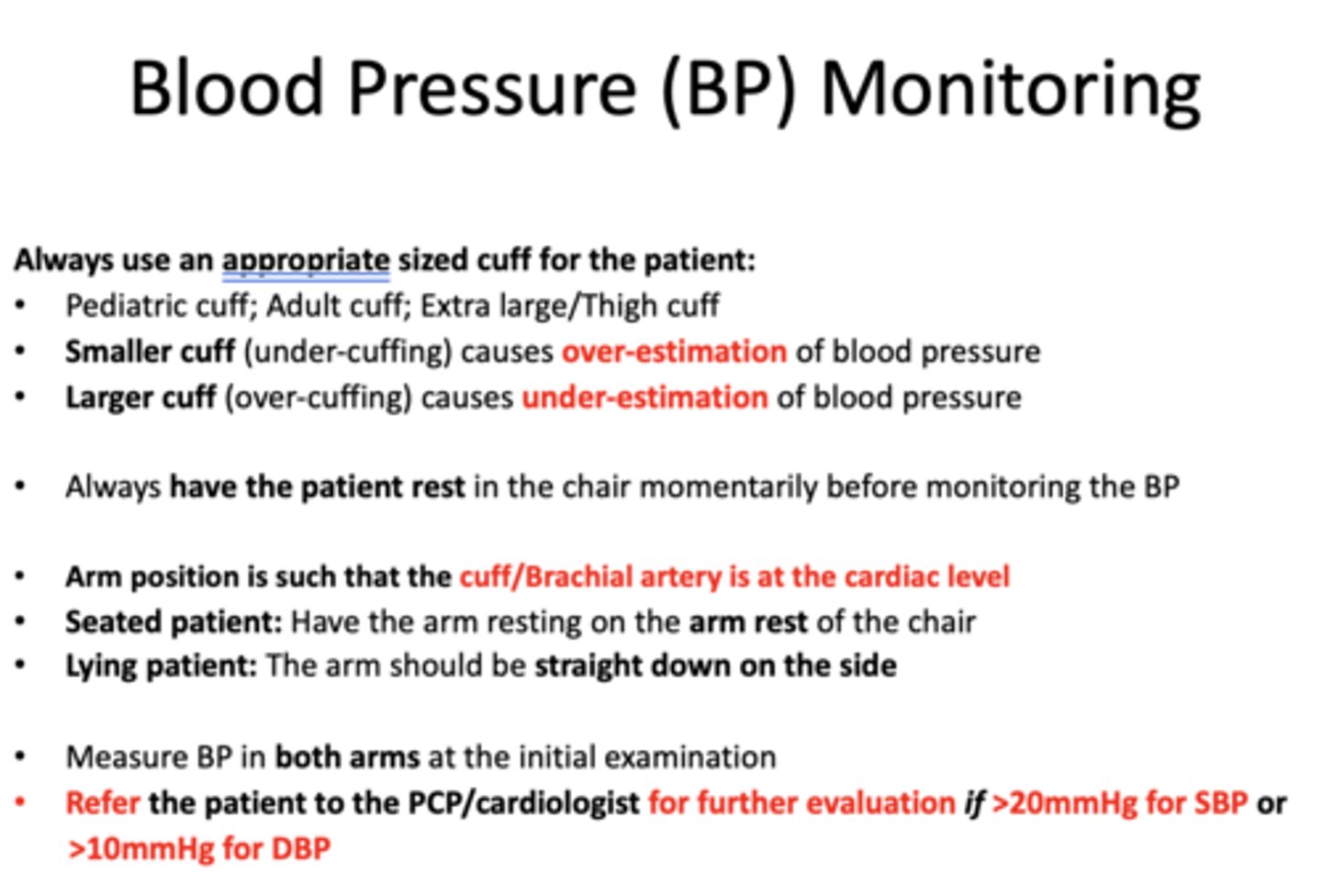
when taking a BP, the cuff/Brachial artery should be at the _______ level
cardiac
Where should the arm position be in a seated patient?
arm rest of chair
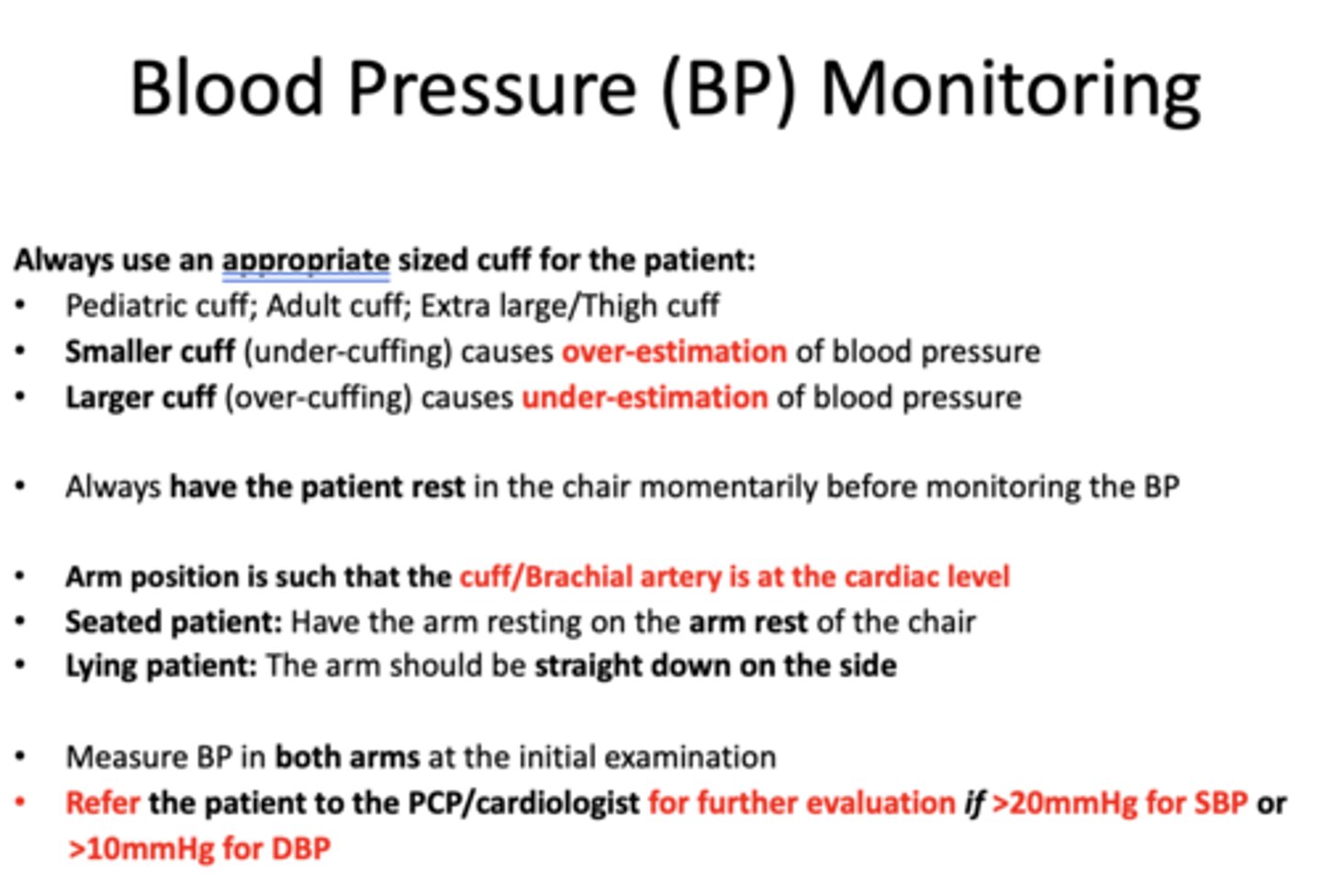
Where should the arm position be in a lying down patient?
straight down on sides
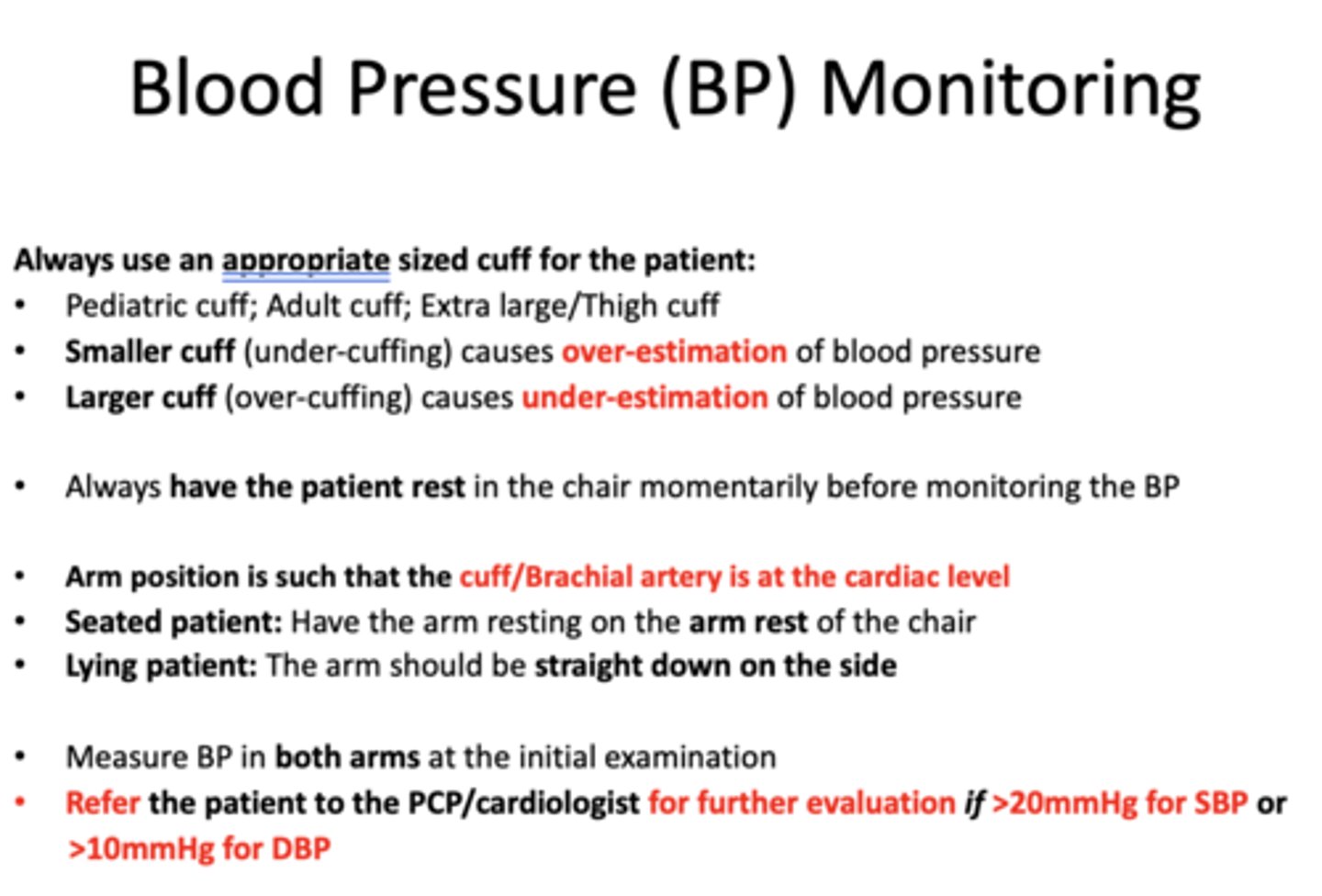
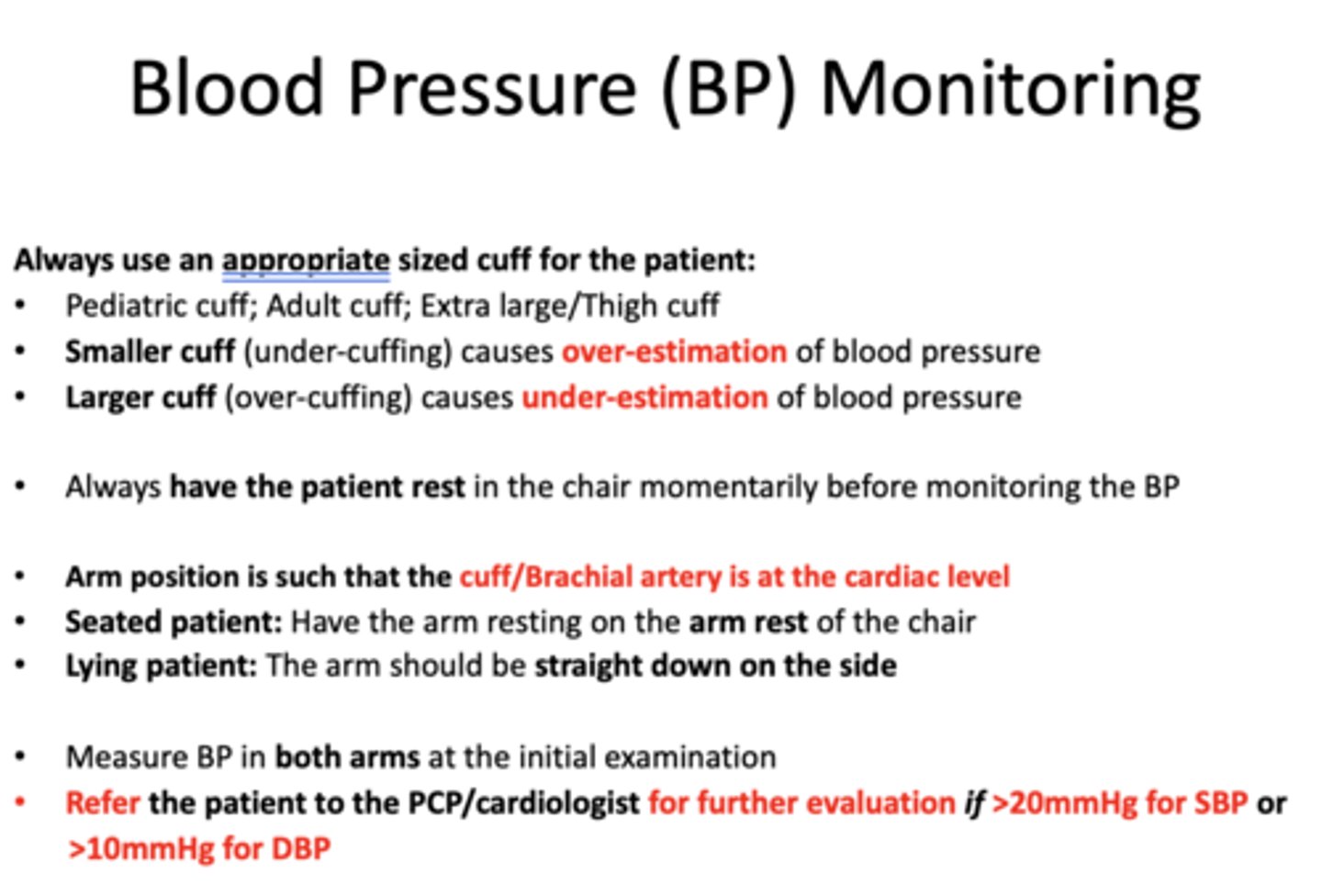
When should you refer patients to PCP/Cardiologists for further evalation in terms of SBP and DBP?
>20mmHg for SBP
>10 mmHg for DBP
Lowering the arm below heart level leads to an ___________ of SBP & DBP
over-estimation

Raising the arm above heart level leads to _________ of BP readings
under-estimation
stress affect on BP:
increase

caffeine affect on BP
increase

meal consumption affect on BP:
decrease

smoking affect on BP:
increase

An average of 2-4 readings are needed for diagnosis of _________ in the presence of high/elevated readings
hypertension

If initial readings of BP are elevated, should you tell the patient?
NO! (This will cause anxiety and alter other BP readings)

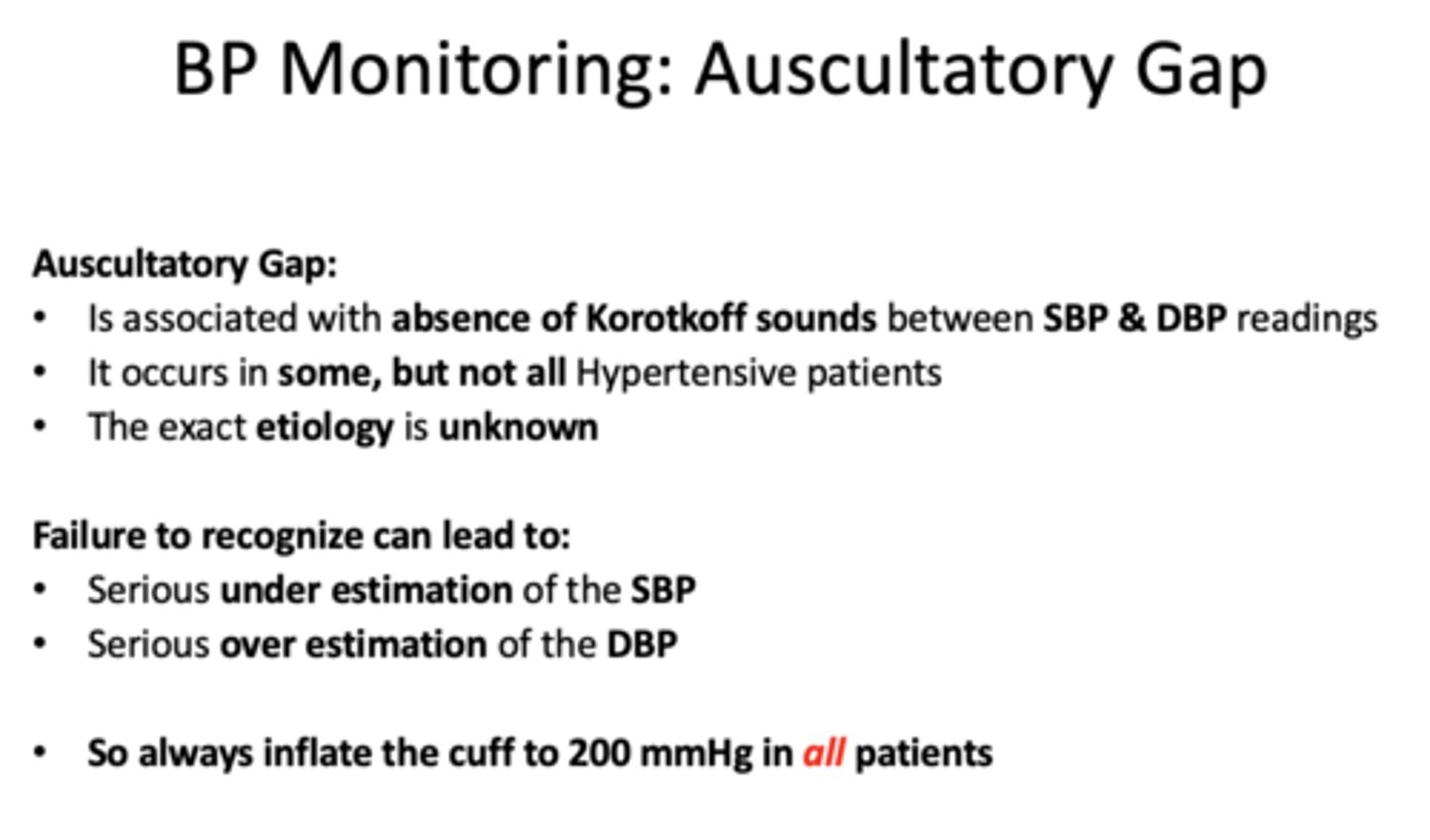
______________ is associated with absence of Korotkoff sounds between SBP & DBP readings
auscultatory gap
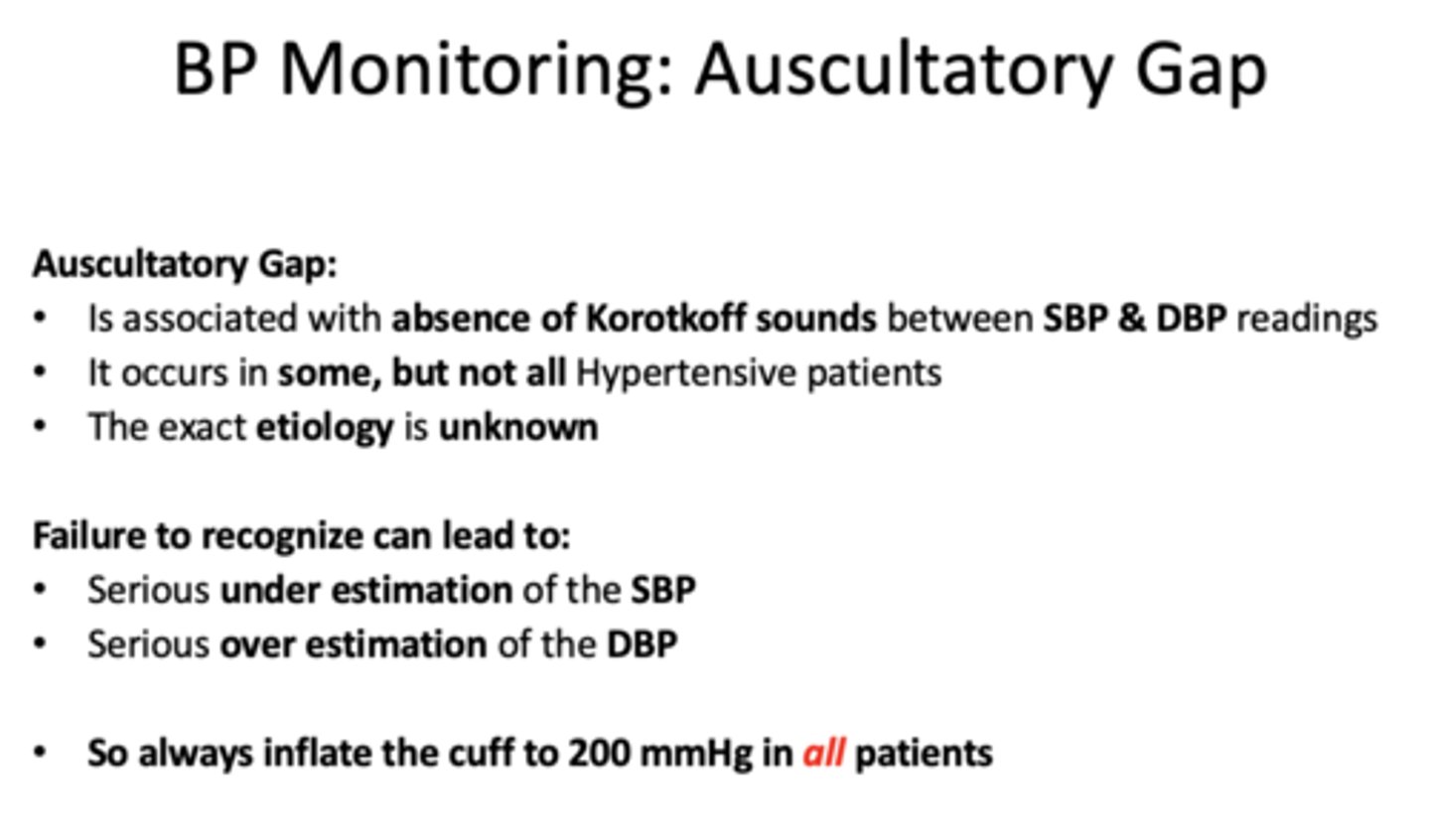
Asculatatory gaps occur in...
some but not all hypertensive pts
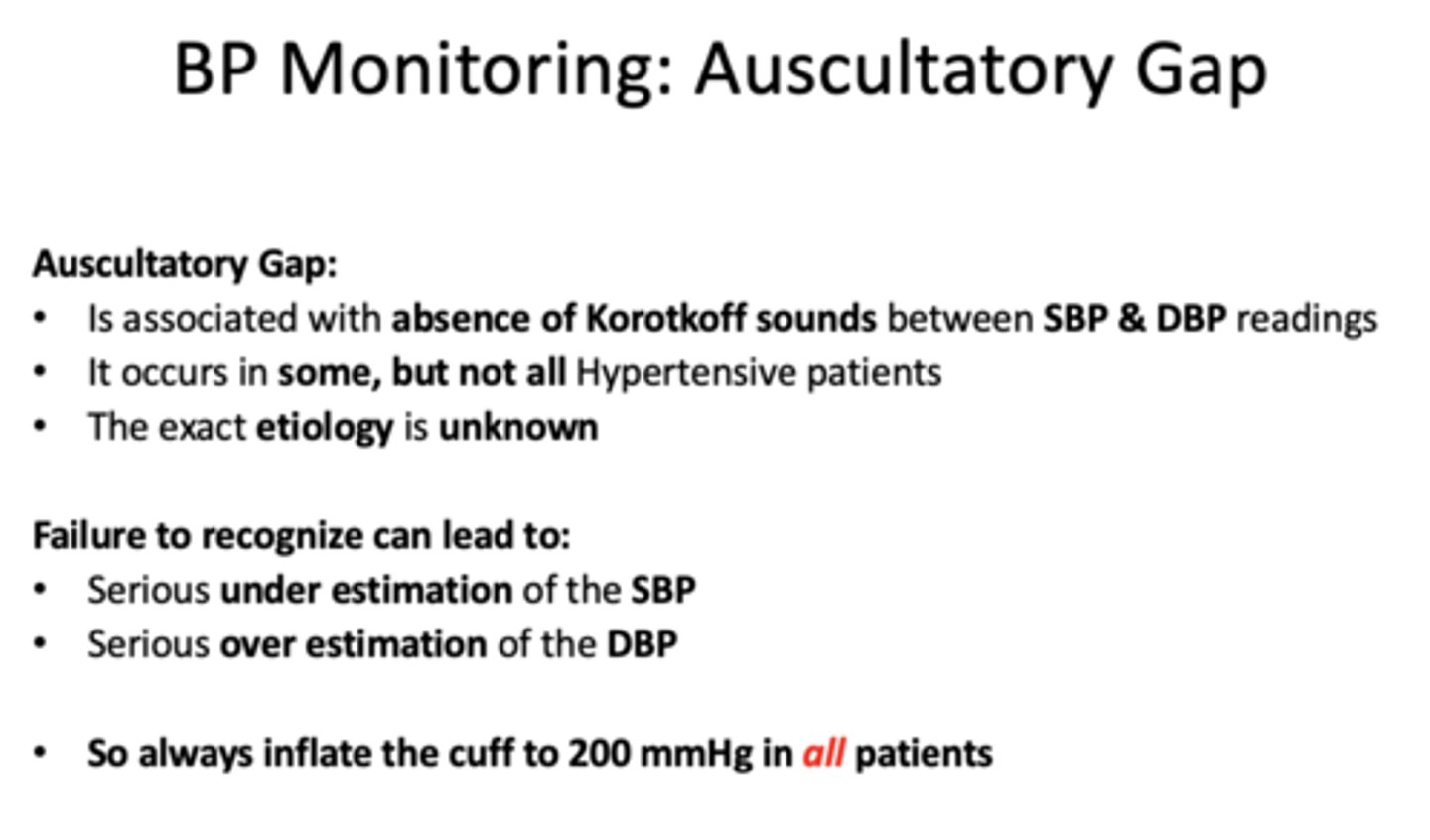
the exact etiology of asculatatory gaps are _____________
unknown
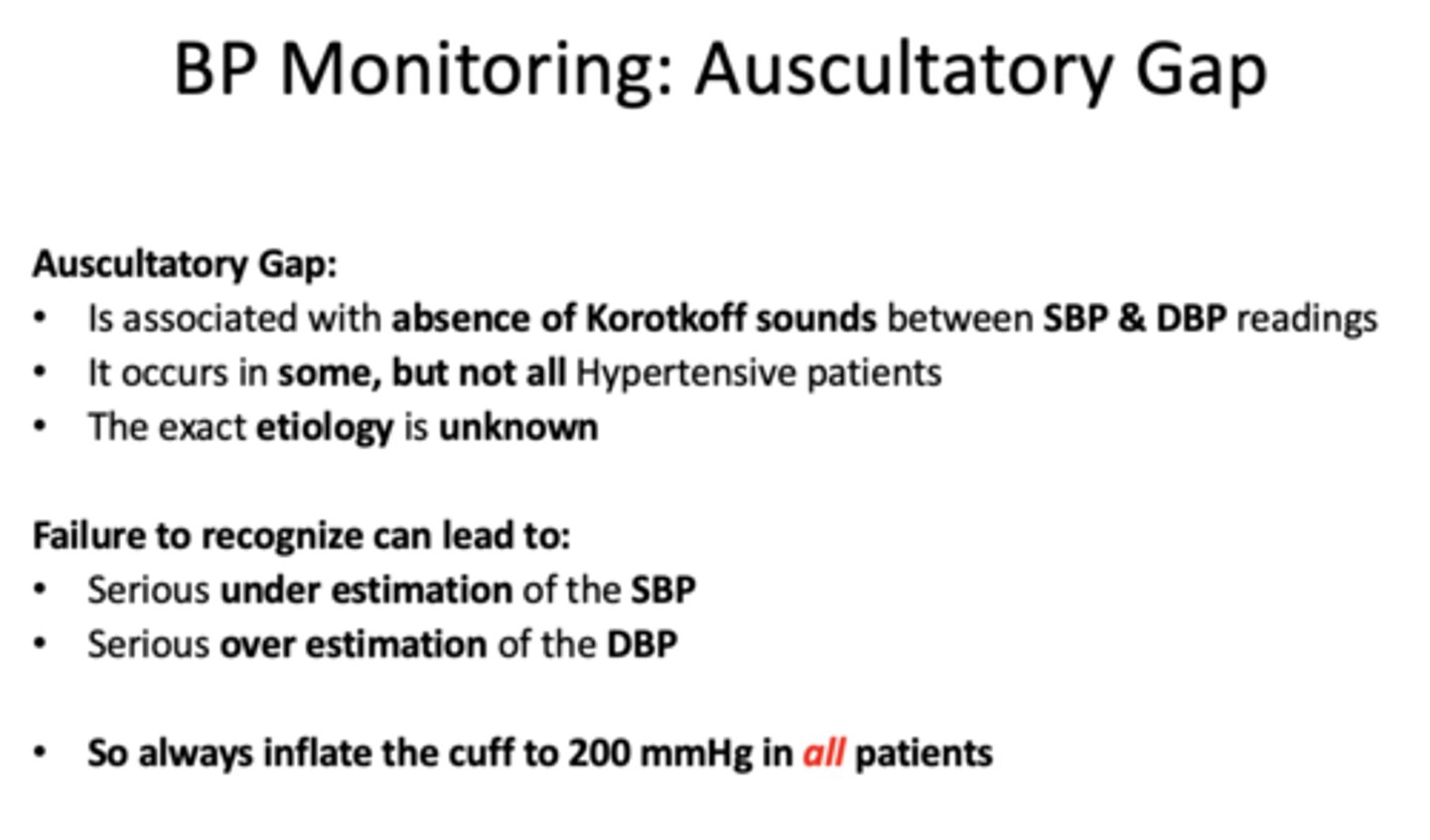
failure to recognize auscultatory gaps can lead to (2)
-underestimation of SBP
-overestimation of DBP
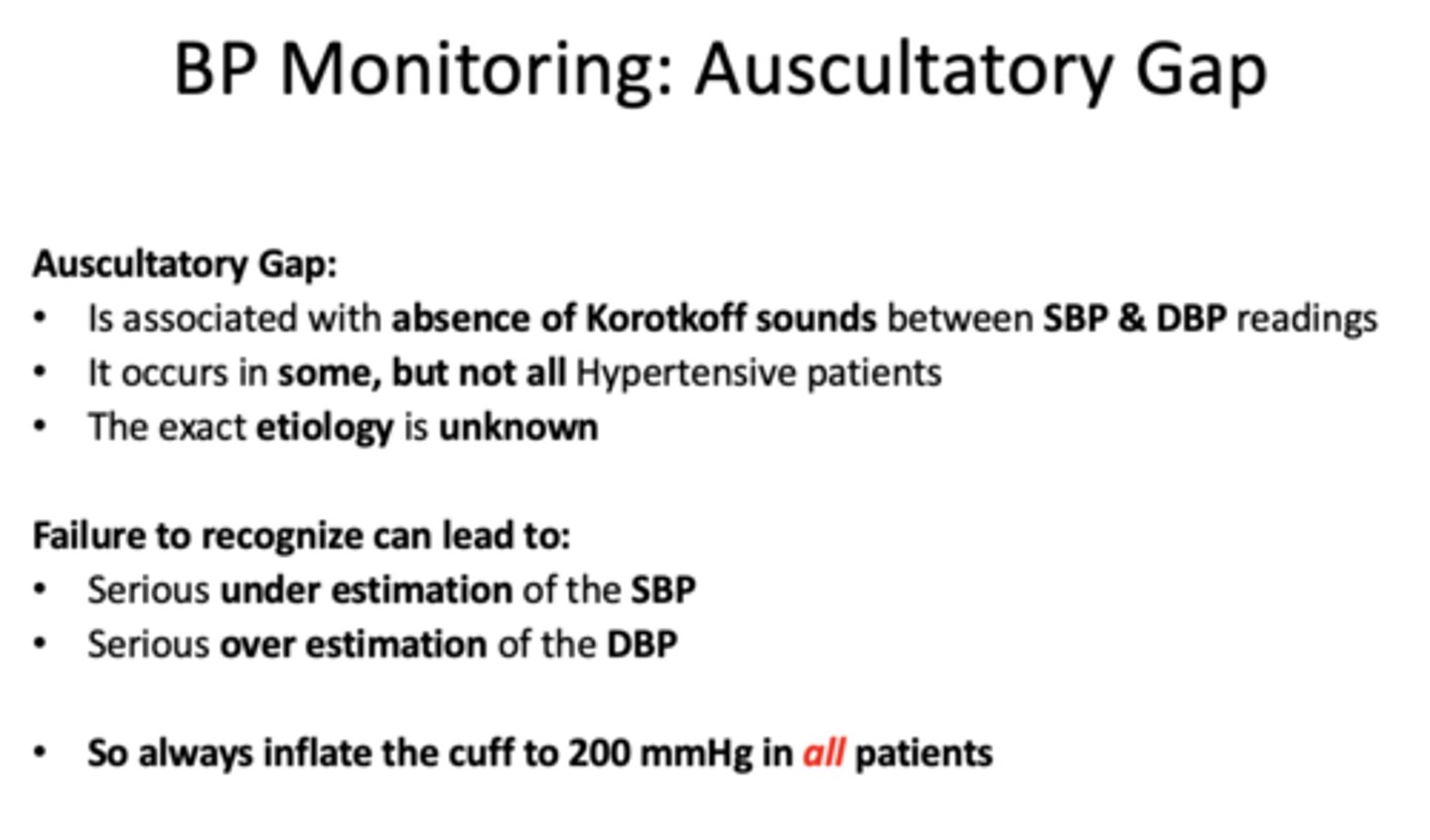
always inflate the cuff to _____ mmHg in all patients
200
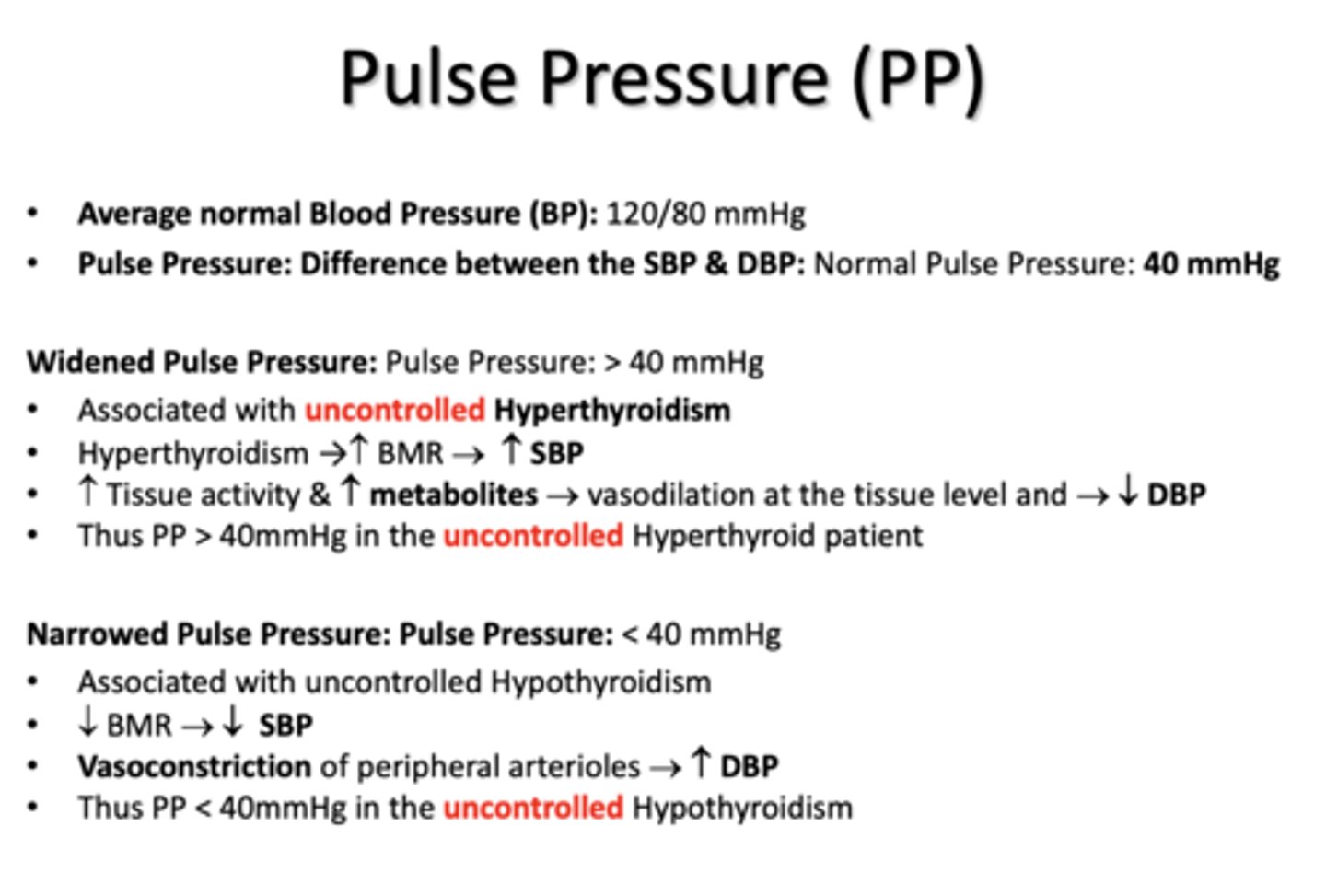
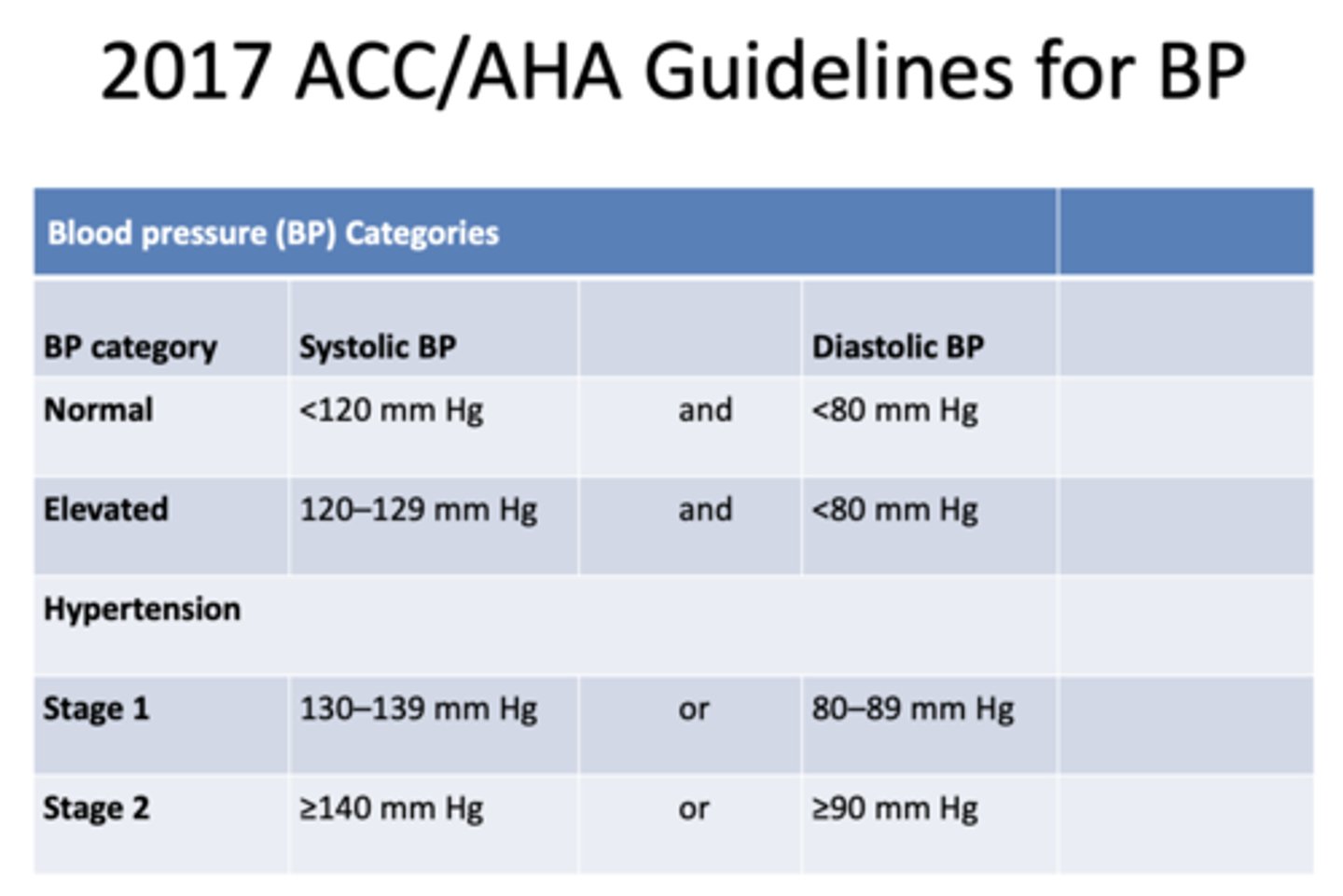
Average normal Blood Pressure (BP):
120/80 mmHg
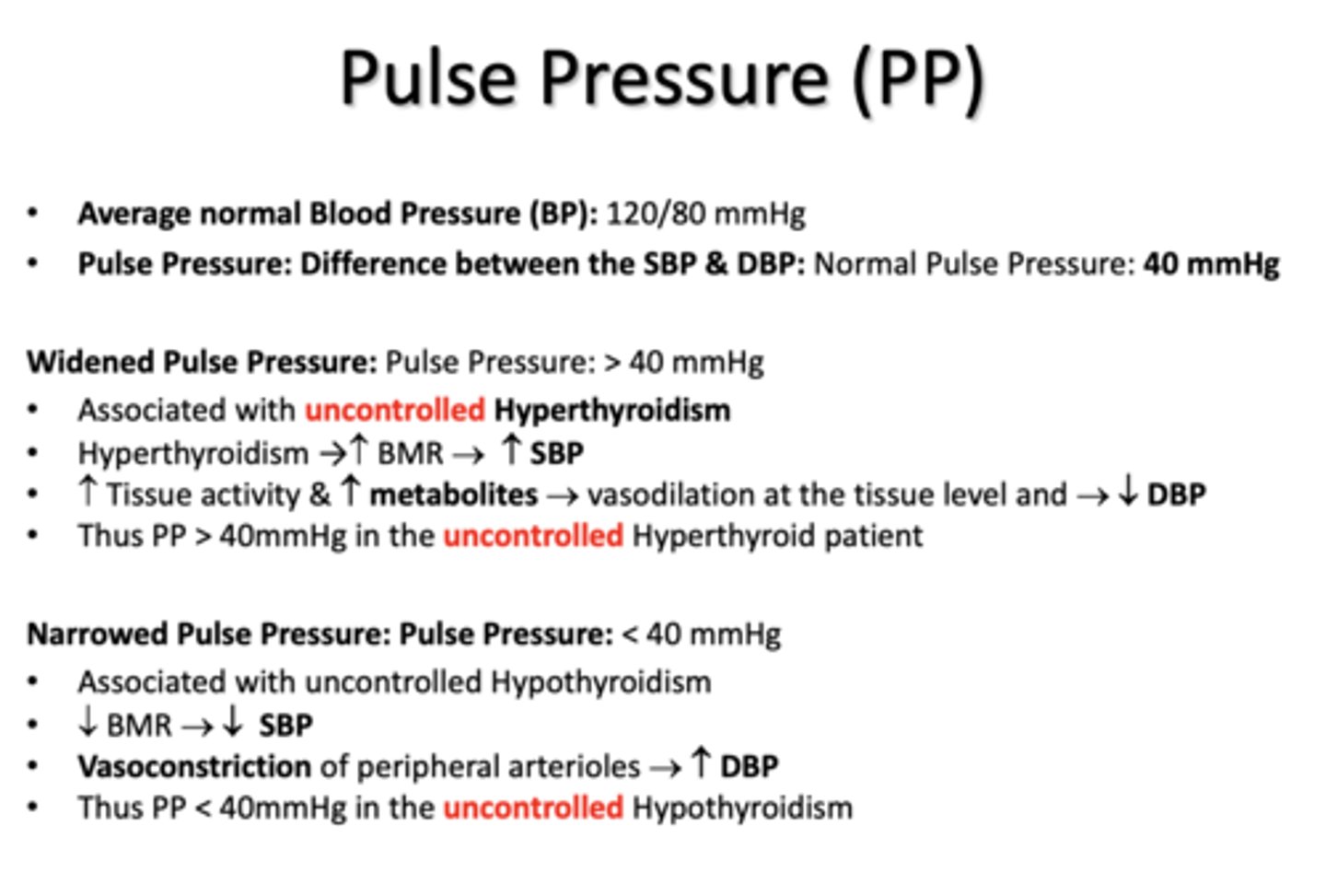
normal Pulse Pressure (Difference between the SBP & DBP)
40 mmHg
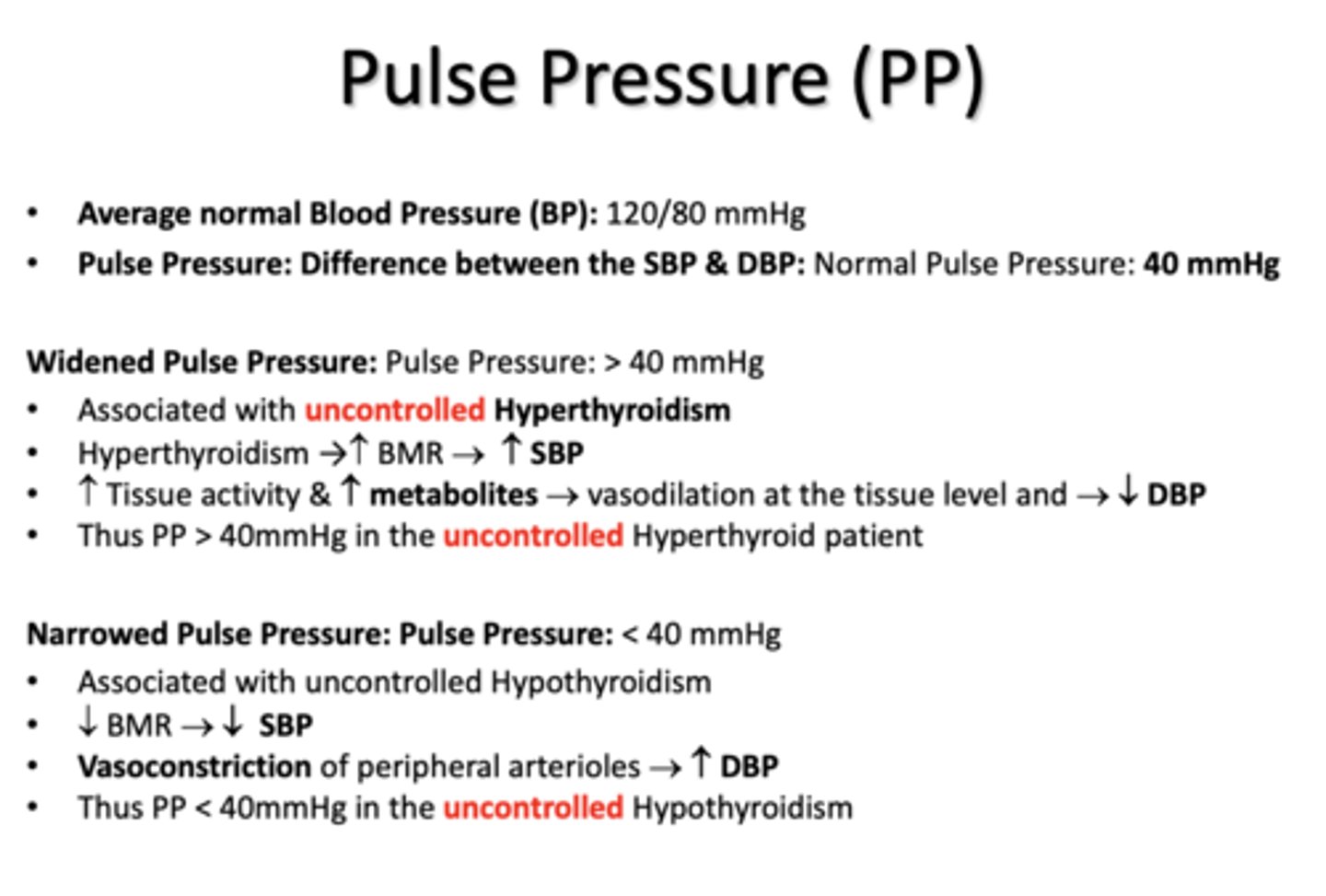
a Widened Pulse Pressure is associated with ________
uncontrolled hyperthyroidism
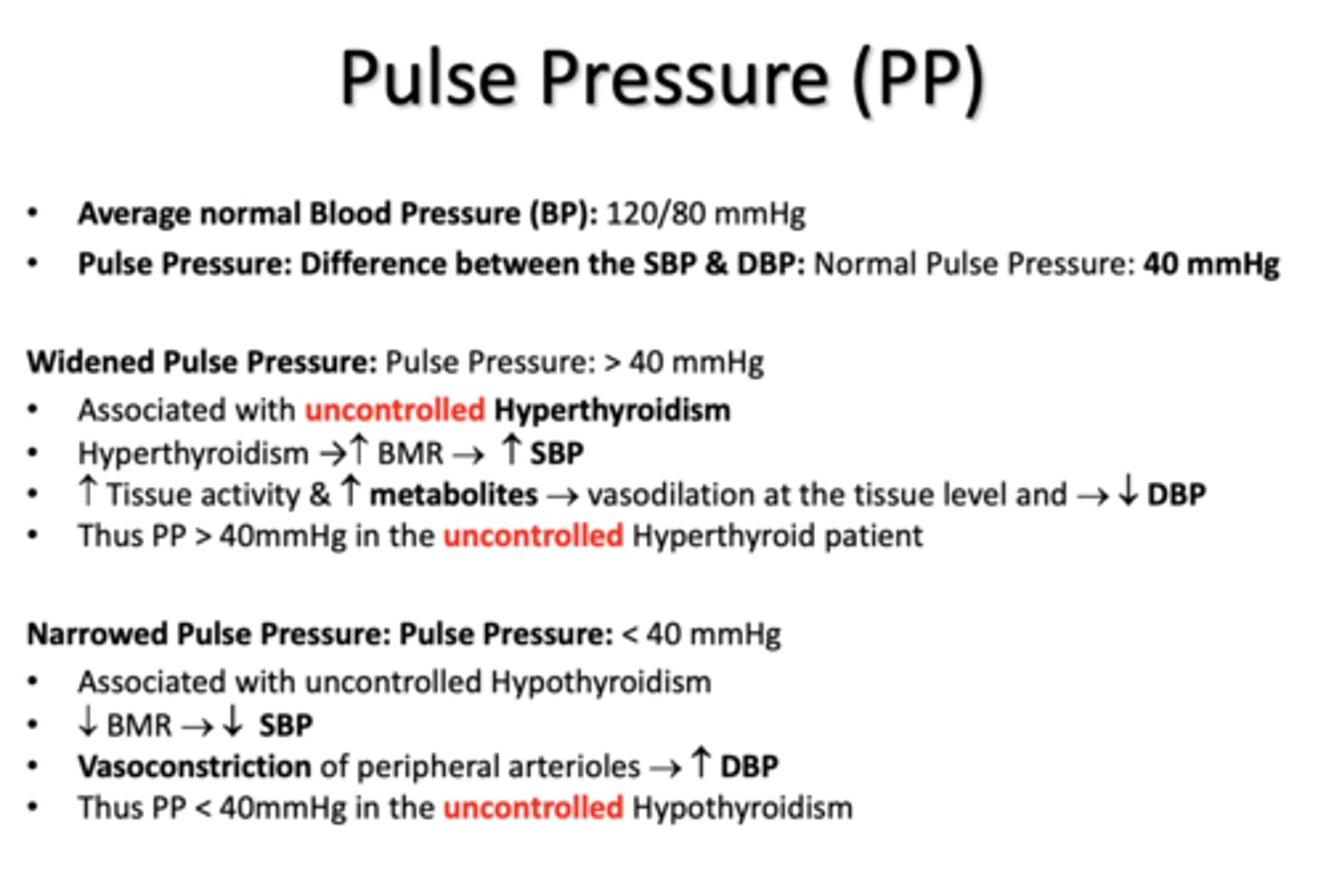
a Narrow Pulse Pressure is associated with ________
uncontrolled hypothyroidism
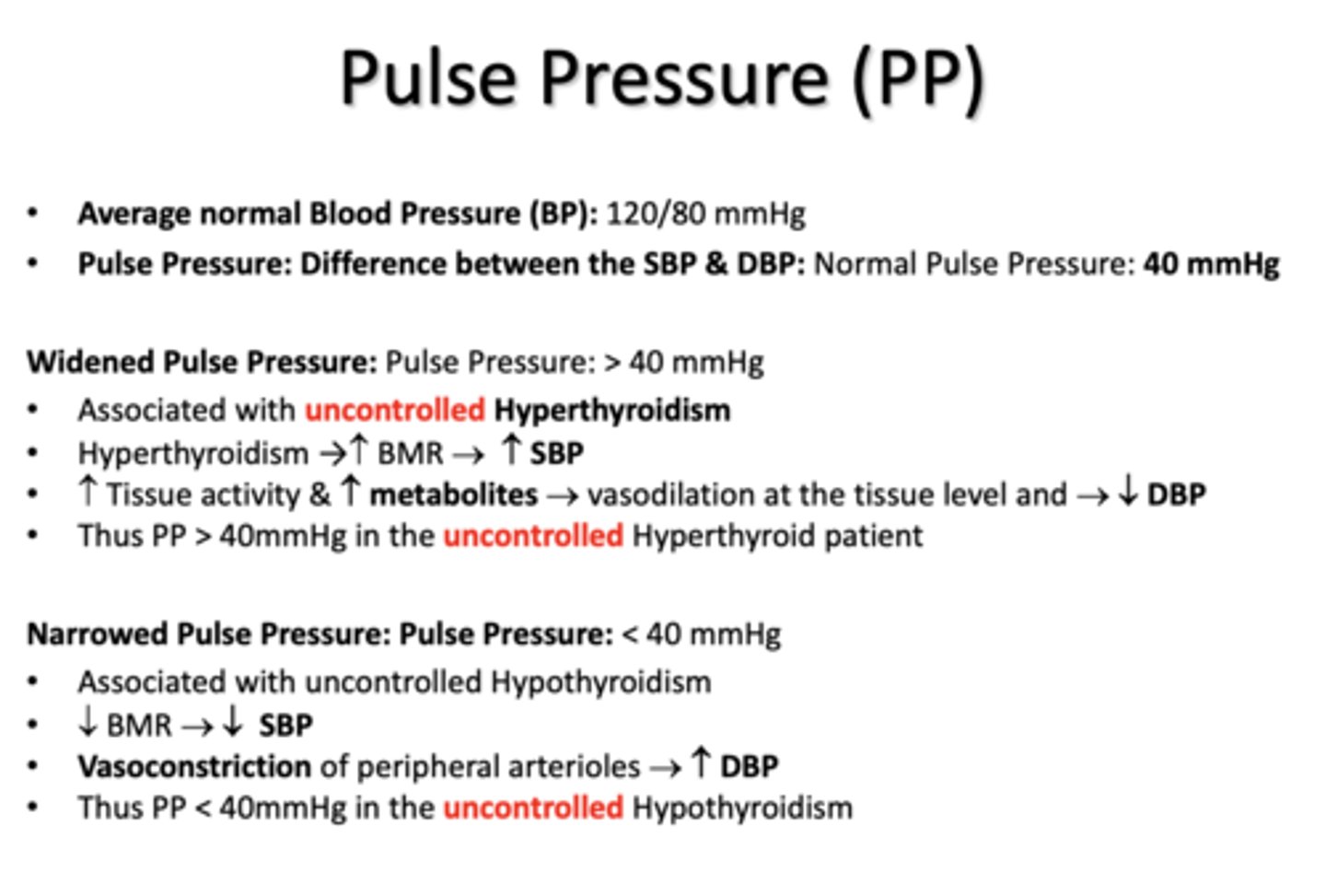
uncontrolled hyperthyroidism due to a widened pulse pressure is associated with a ____ in SBP and ____ in DBP
increased, decreased
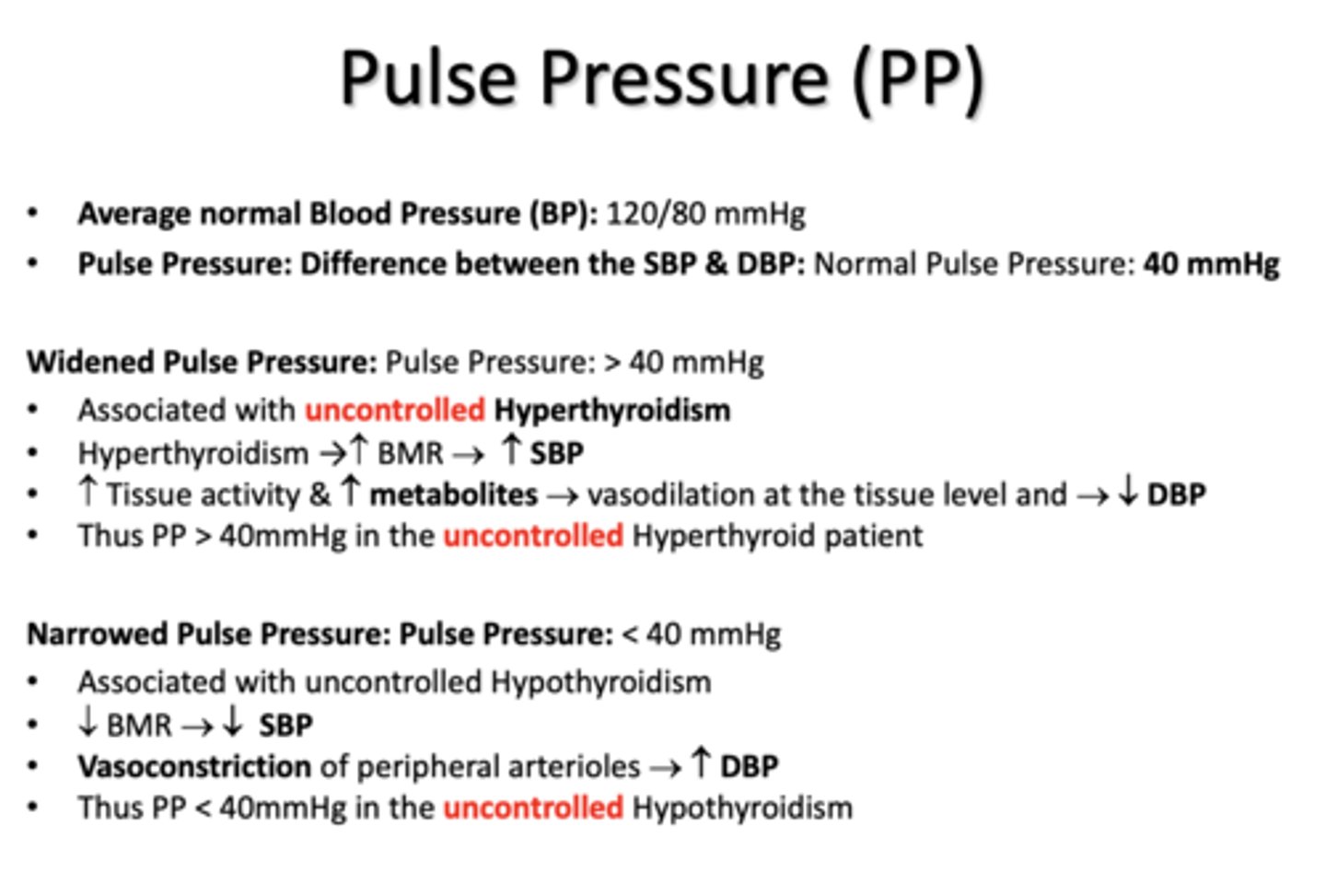
uncontrolled hypothyroidism due to a narrowed pulse pressure is associated with a ____ in SBP and ____ in DBP
decreased, increased
stage 1 hypertensive patients will have a SBP range of:
130-139 mmHg
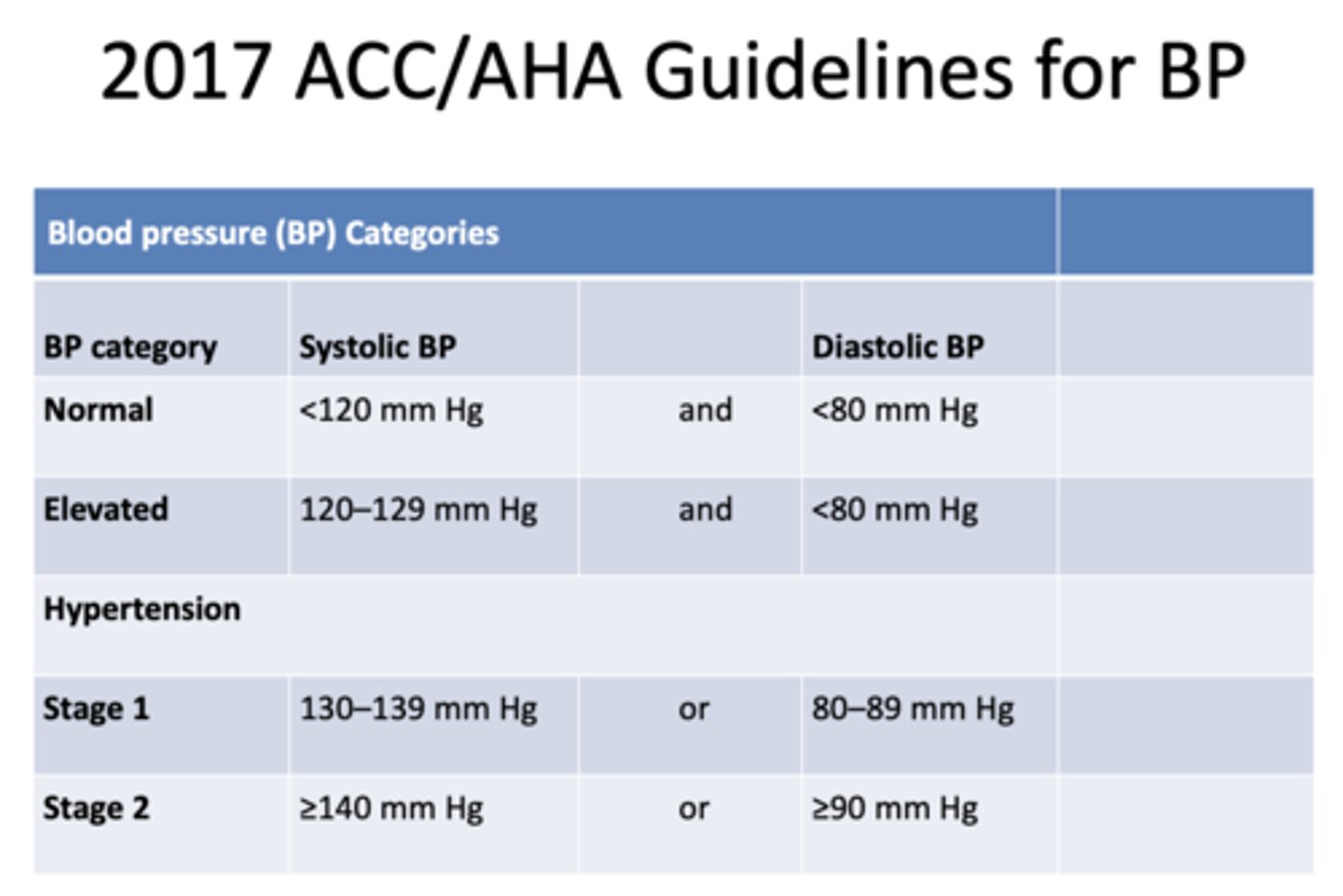
stage 2 hypertensive patients will have a SBP range of:
≥140 mmHg
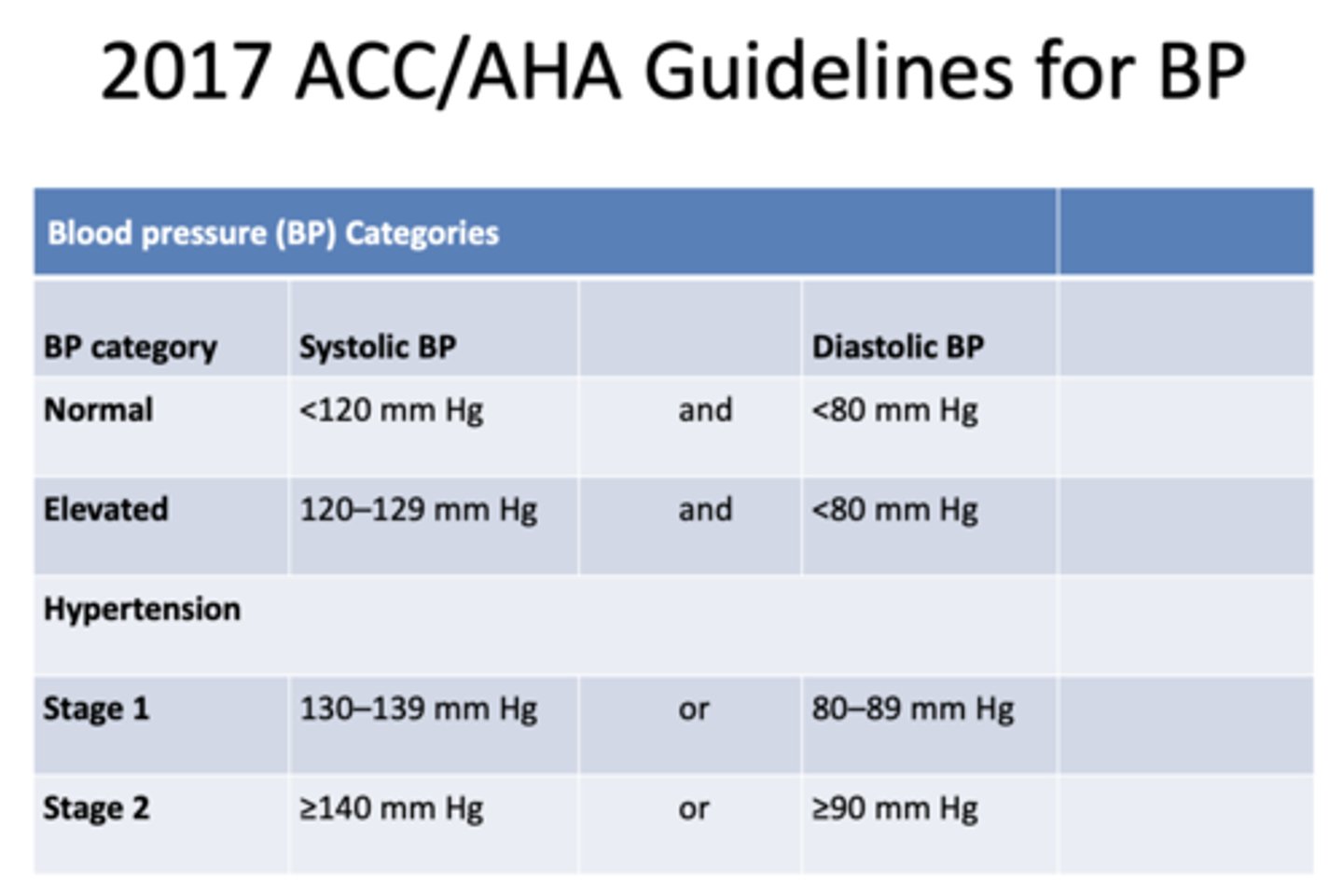
stage 1 hypertensive patients will have a DBP range of:
80-89 mmHg
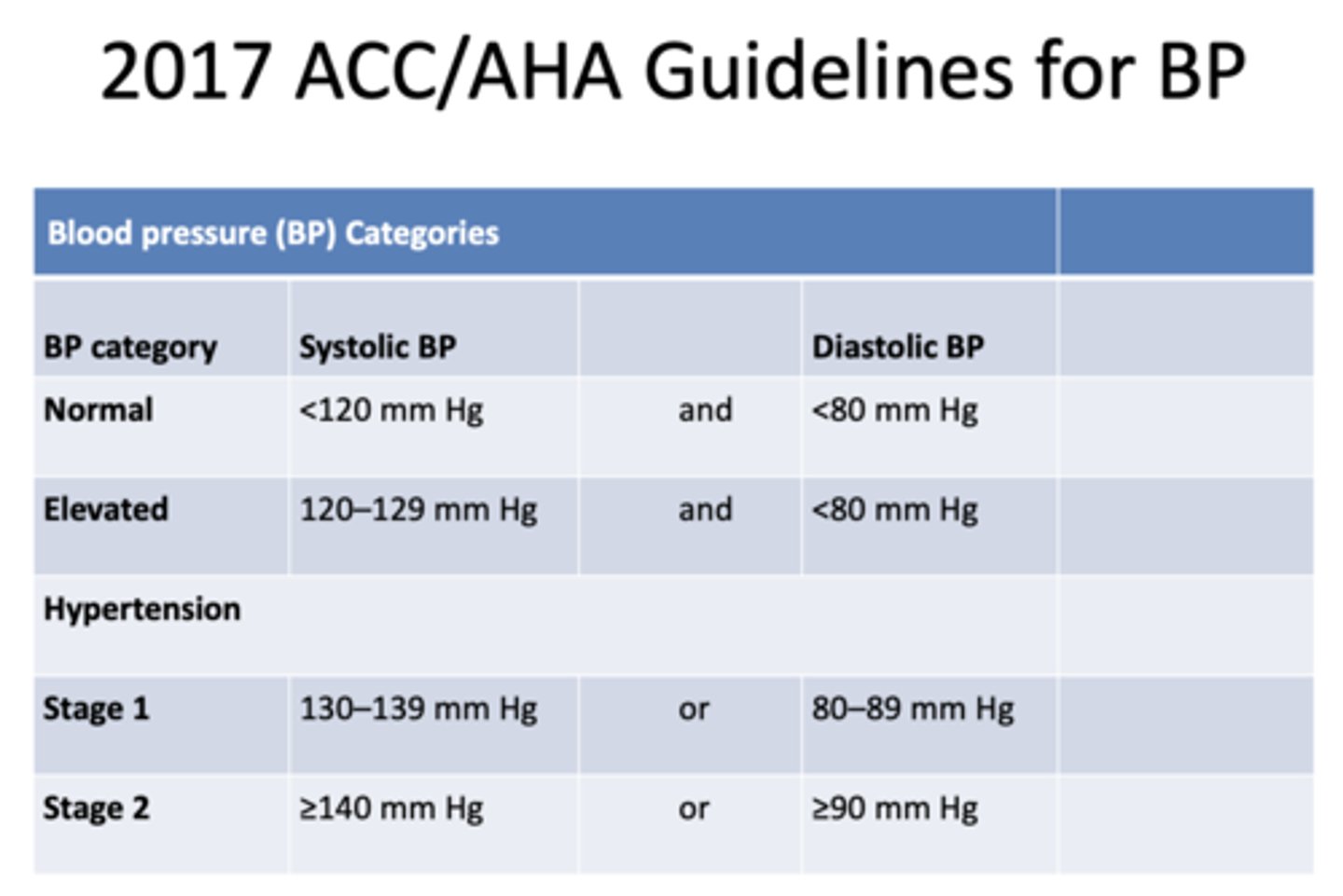
stage 2 hypertensive patients will have a DBP range of:
≥90 mmHg
SBP estimation by palpation is only used as a guide as it generally gives an ________ of the patient’s true SBP
over-estimation
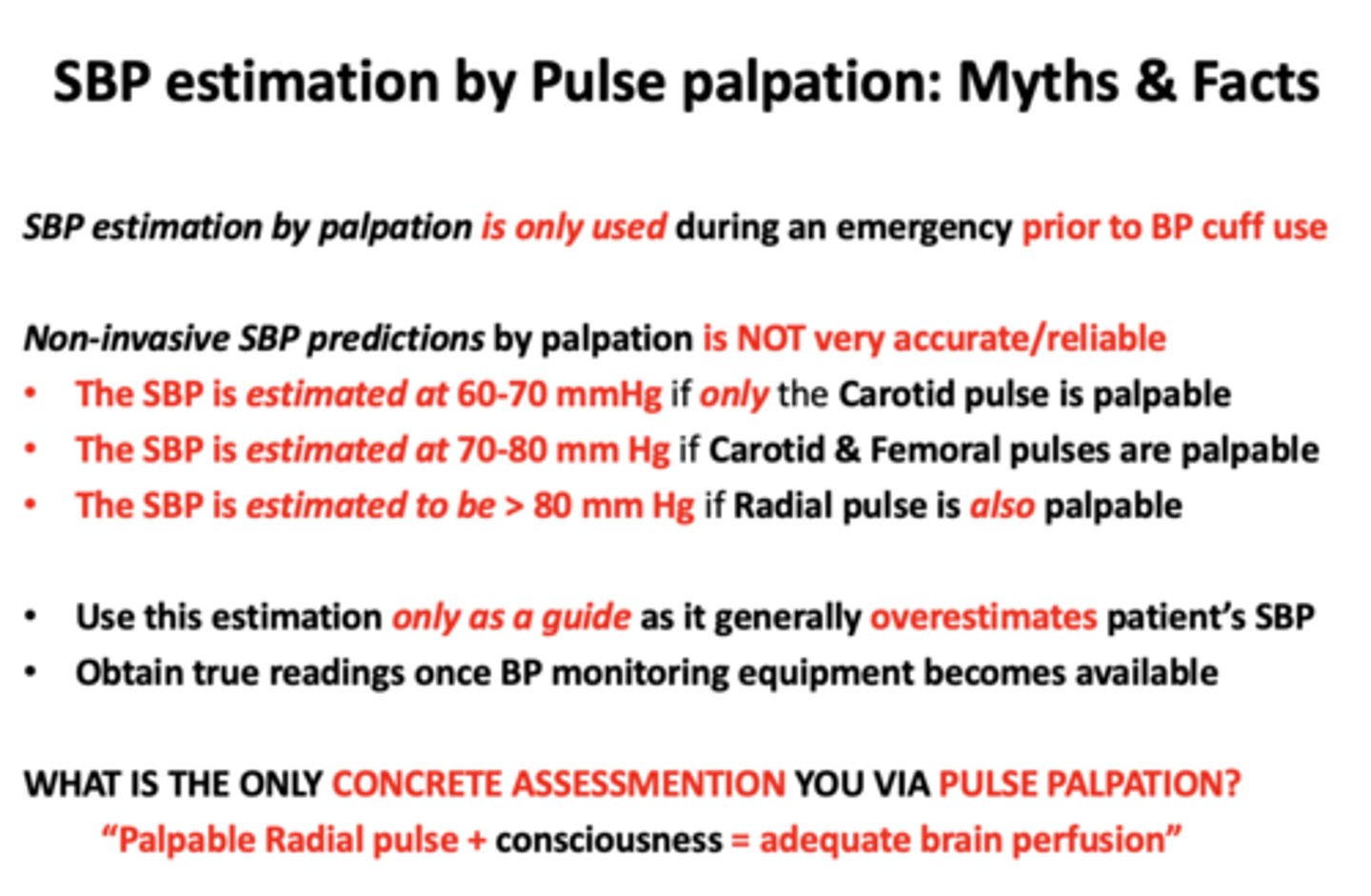
The SBP is estimated at 60-70 mmHg if only the ______ is palpable
Carotid pulse
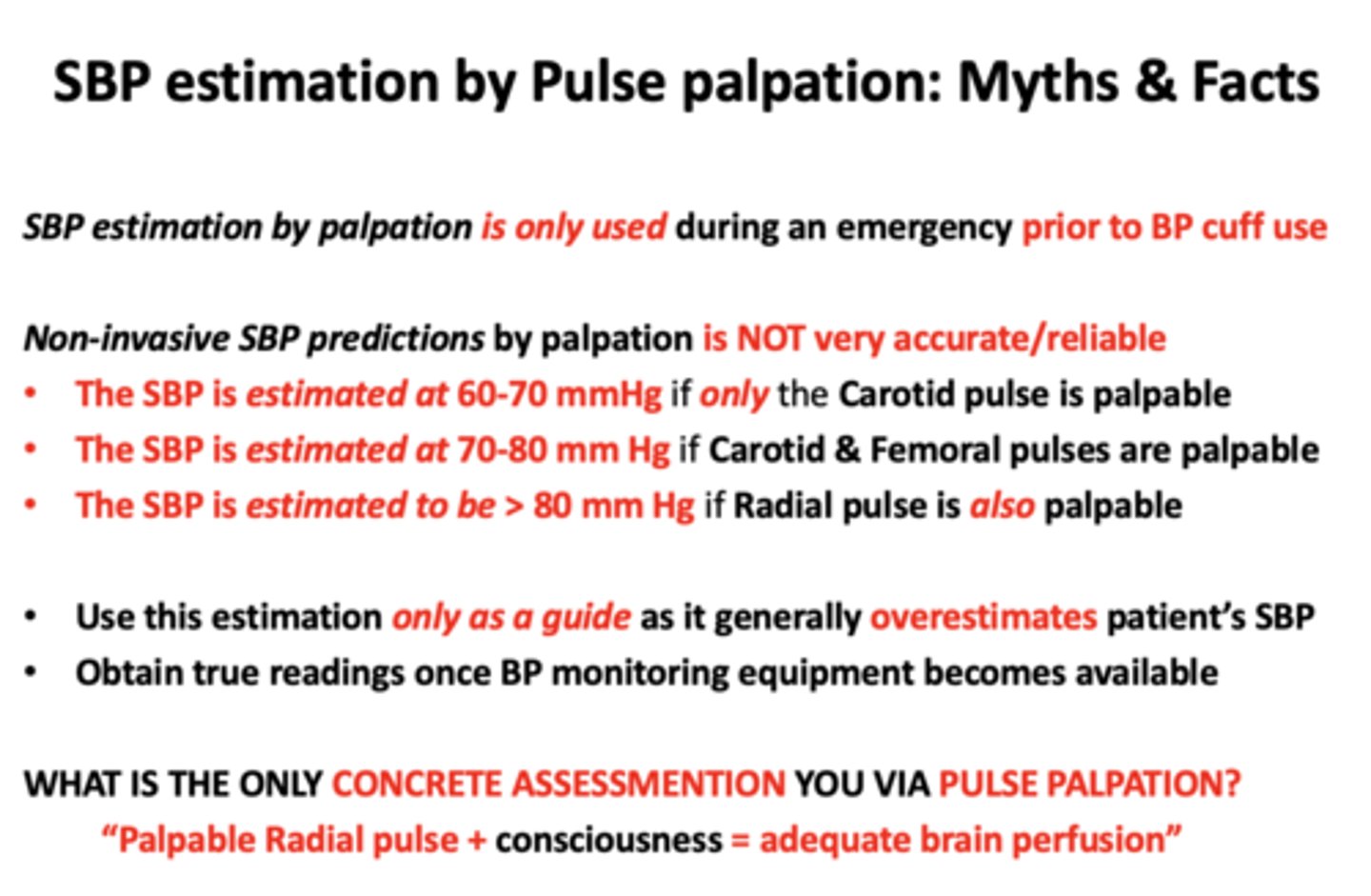
The SBP is estimated at 70-80 mm Hg if _____ are palpable
Carotid & Femoral pulses
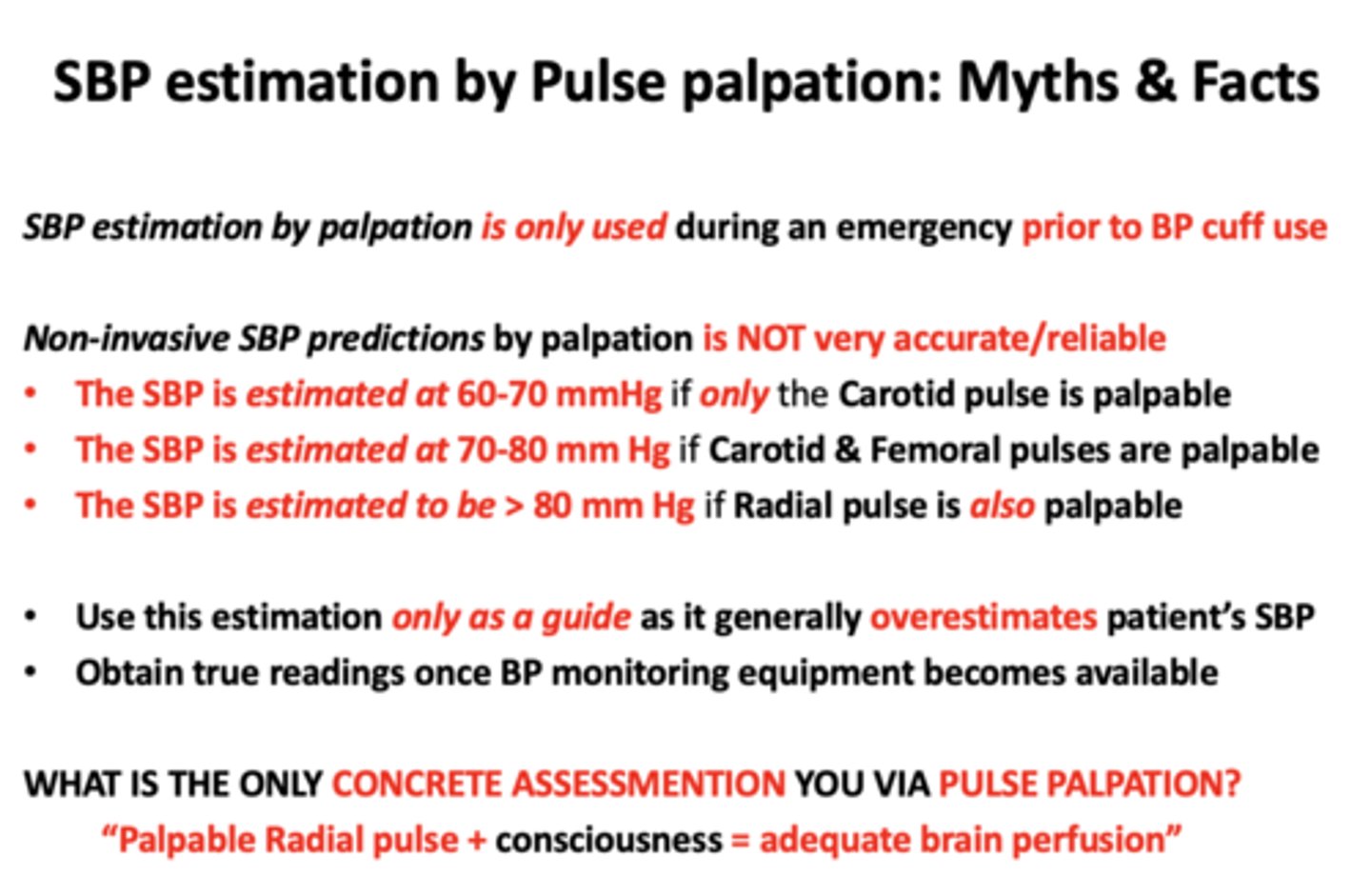
The SBP is estimated to be > 80 mm Hg if _____ is also palpable
Radial pulse
SBP estimation by palpation is only used during an emergency prior to
BP cuff use
What is the ONLY CONCRETE ASSESSMENTION via pulse palpation
Palpable Radial Pulse + consciousness = adequate brain perfusion
A patient presents with flattened appearance of distal phalynx with loss of angle between proximal edge of nail and skin. What are four things commonly associated with clubbing of the nails?
cyanotic heart disease
lung cancer
COPD
cystic fibrosis
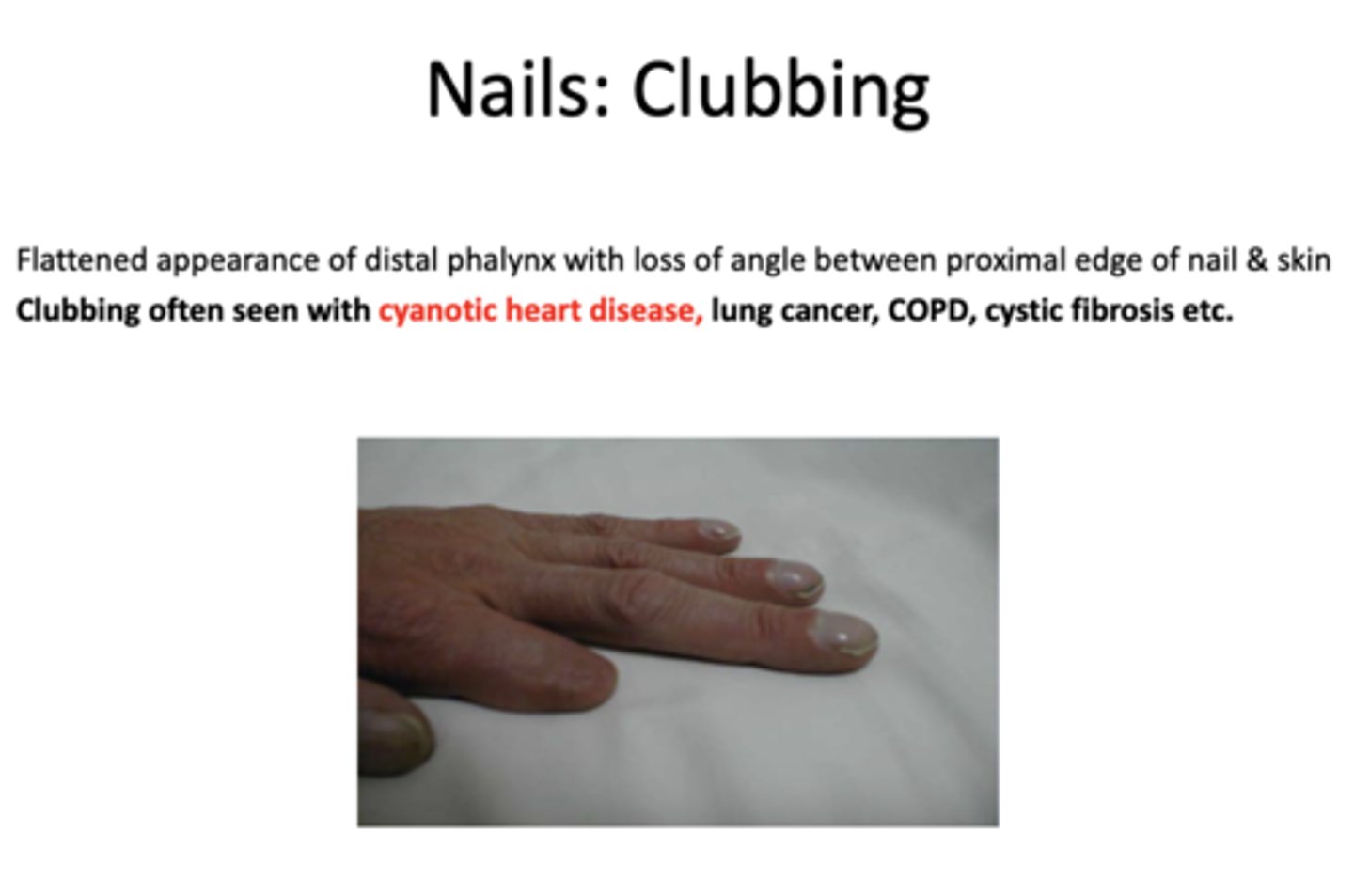
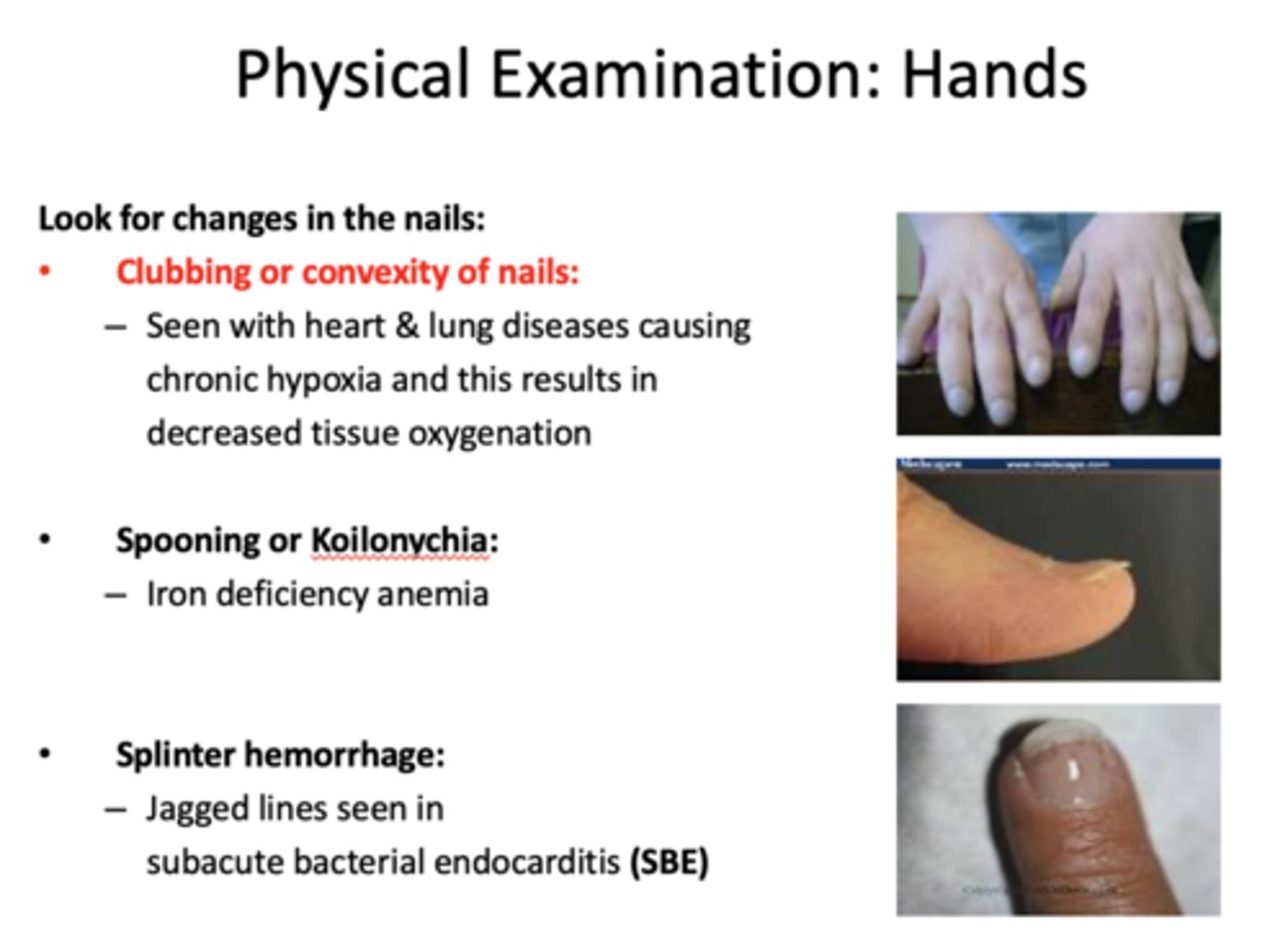
What presents with the following characteristics:
- Extremity changes
- Seen with heart & lung diseases causing chronic hypoxia and this results in decreased tissue oxygenation
clubbing or convexity of nails
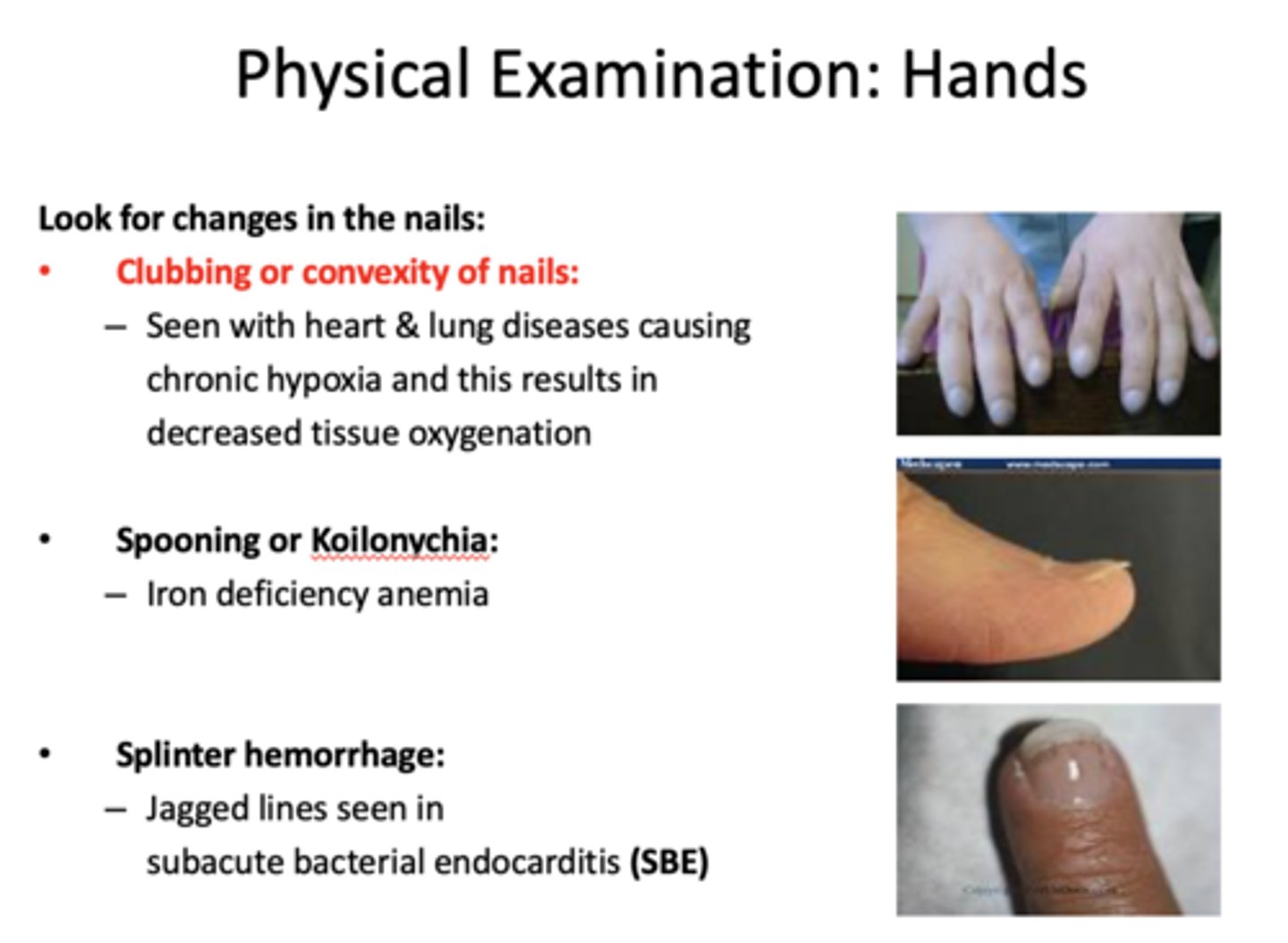
What presents with the following characteristics:
- Extremity changes in nails
- Iron deficiency anemia
Spooning or Koilonychia
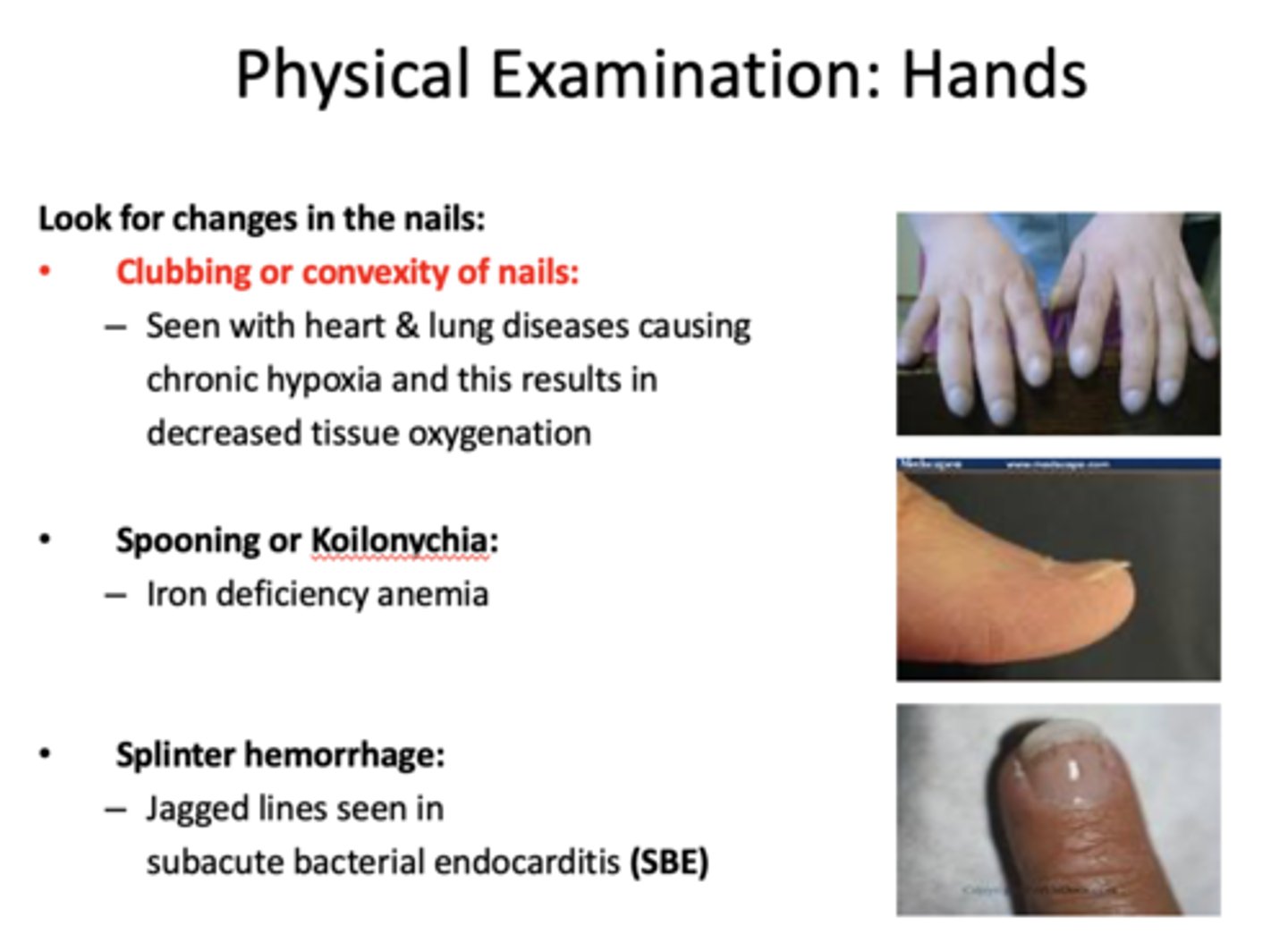
What presents with the following characteristics:
- Extremity changes in nails:
- Jagged lines seen in subacute bacterial endocarditis
Splinter hemorrhage
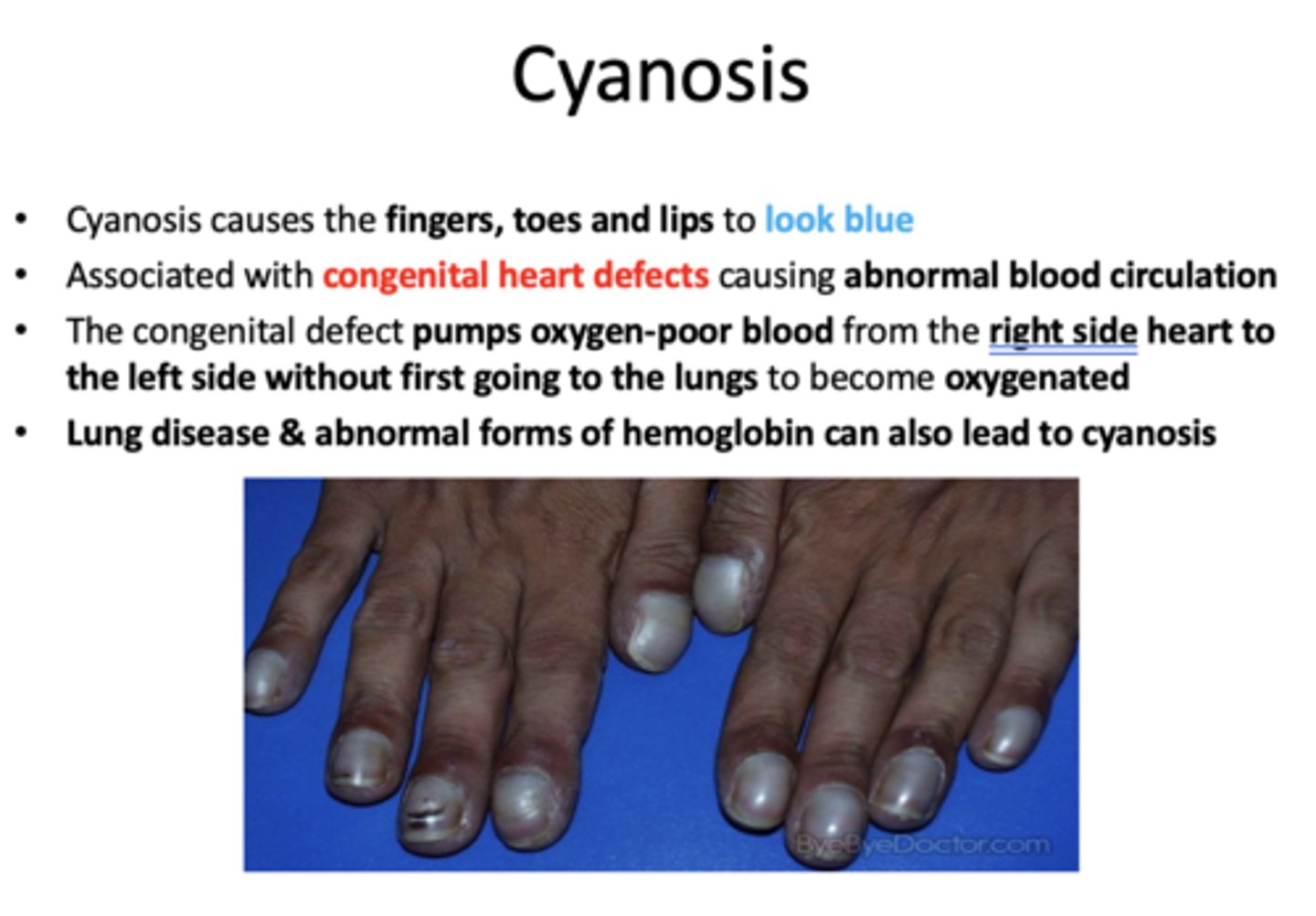
cyanosis in extremities, causing abnormal blood circulation is associated with:
congenital heart defects
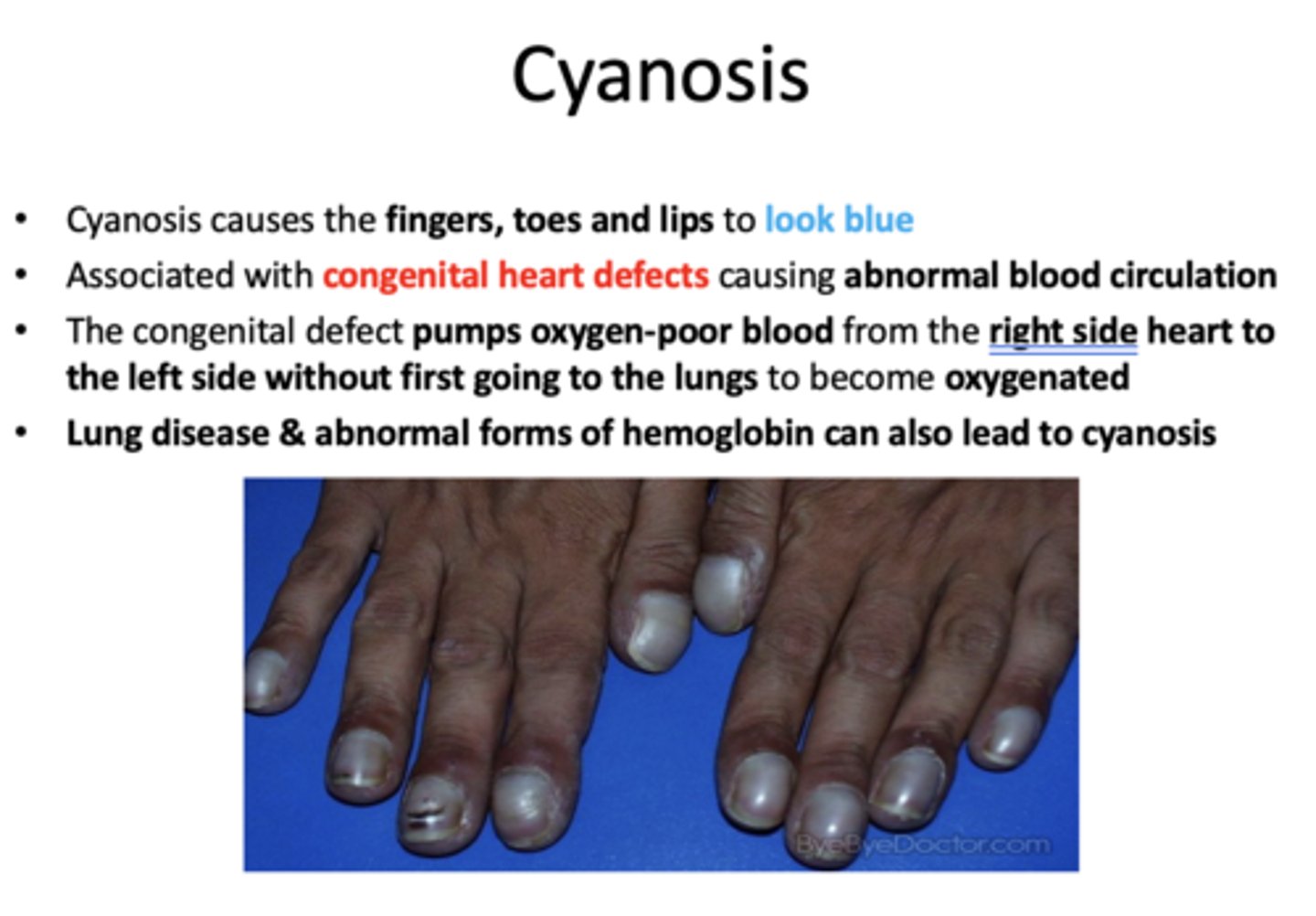
t/f: lung disease and abnormal forms of hemoglobin can also lead to cyanosis
true