ap psych - unit 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
1
New cards
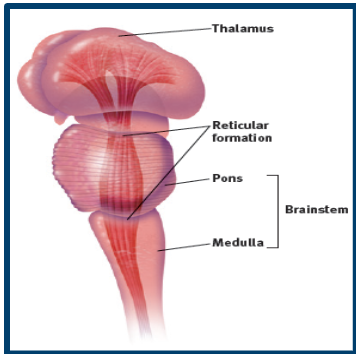
brain stem
medulla, pons, reticular formation, cerebelllum, thalamus
2
New cards
medulla
functions: breathing + beating heart + other autonomic functions
3
New cards
pons
has nerves that help with voluntary movements and speech
4
New cards
reticular formation
nerve network that travels through the brainstem into thalamus + involved with arousal, alertness, and sleep-wake cycles
5
New cards
what is the function of the reticular formation?
controls arousal + filters incoming sensory stimuli
6
New cards
thalamus
relay station for incoming + outgoing sensory information
sends sensory signals to the correct part of the brain
sends sensory signals to the correct part of the brain
7
New cards
cerebellum
processing sensory input, coordination/movement, and balance
8
New cards
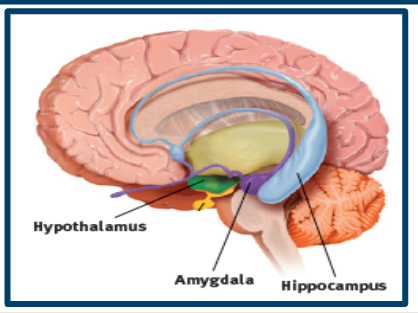
limbic system
regulates emotion, learning, and memory
9
New cards
amydala
linked to emotion, fear, aggression
starts the flight-or-fight response in SNS
starts the flight-or-fight response in SNS
10
New cards
hypothalamus
controls hunger, thirst, sex, linked to emotion/reward, and governs the endocrine system via the pituitary gland
11
New cards
hippocampus
turns short-term memories into long-term ones
12
New cards
frontal lobes
decision making, analysis, judgment, planning, and processing of new memories
13
New cards
parietal lobes
spatial reasoning + processes sense of touch and assembles input from other senses into a form you can use
14
New cards
temporal lobes
processing auditory information and the encoding of memory
15
New cards
occipital lobes
processing vision
16
New cards
motor cortex
controls voluntary movements
17
New cards
somatosensory cortex
registers information from the skin's senses and body movements
18
New cards
broca's area
language center in left frontal lobes
involved in speaking + writing
involved in speaking + writing
19
New cards
wernicke's area
language center in left temporal lobe
involved in hearing + reading
involved in hearing + reading
20
New cards
left hemisphere
- focused on logic + language
- controls right side of the body
- receives sensory input from body's right side
- controls right side of the body
- receives sensory input from body's right side
21
New cards
right hemisphere
- focused on creativity + arts + imagination
- controls left side of the body
- receives sensory input from body's left side
- controls left side of the body
- receives sensory input from body's left side
22
New cards
split-brain
operations in which the corpus callosum must be cut
the two hemisphere cannot communicate with each other anymore
the two hemisphere cannot communicate with each other anymore
23
New cards
wernicke’s aphasia
inability to understand sounds or create meaningful speech after damage to Wernicke’s area
24
New cards
cerebellum
manages coordination and balance + things that require practicing to improve (helps body to remember those actions)
25
New cards
prefontal lobe
specializes in foresight, judgement, and memory
26
New cards
motor cortex
area of the frontal lobe that controls voluntary movement
27
New cards
visual cortex
area of the occipital lobe that receives visual input and sends it to other visual areas in the cortex
28
New cards
angular gyrus
allows people to read words on paper and transfers that information as an auditory form
29
New cards
auditory cortex
area of the temporal lobe that processes hearing
30
New cards
amygdala
emotional regulation + fear
31
New cards
nucleus accumbens
forebrain area that functions in the pleasure/reward circuit
32
New cards
basal ganglia
neurons cells that are involved w/ voluntary movements
33
New cards
brain lateralization
some functions are controlled or more influenced by one hemisphere of the brain than the other
34
New cards
neuroimaging technique
tools that help researchers and doctors understand different aspects of the human brain
35
New cards
eeg (electroencephalogy)
studying brain waves by recording the brain’s electrical activity by placing electrodes on the scalp
36
New cards
ct (computed tomography)
a series of x-rays that produces detailed images of the body
37
New cards
pet (positron emission tomography)
imaging technique that uses radioactive glucose to evaluate the brains activity and blood flow
38
New cards
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
an imaging technique that uses magnetic impulses to create detailed images of the body
39
New cards
FMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging)
a method to image brain activity using an MRI machine - brain activity is measured by the blood flow and oxygen flow that is imaged in different parts of the brain
40
New cards
lesion studies
studies of the brain where specific parts of the brain are destroyed and the results are interpreted to understand brain activity
41
New cards
pituitary gland
regulates growth and controls other glands via hormones
42
New cards
pineal gland
controls production of melatonin (what makes you sleep)
43
New cards
thyroid gland
regulates metabolism; produces hormone that controls levels of calcium +
44
New cards
mirror neurons
type of neuron that makes people mirror the actions of others or themselves
45
New cards
explain a neuron’s ions
a neuron has a positively charged inside and a negatively charged outside at rest
46
New cards
explain polarization
neurons when at rest are polarized; the outside of the neuron is more positive than the inside of the neuron
47
New cards
explain depolarization
when the threshold is met, depolarization occurs and positive ions are able to enter the neuron which causes for action potential to occur
48
New cards
threshold
the minimum amount of stimulus needed for an action potential to occur
49
New cards
repolarization
the movement of positive ions which leave the neuron so that the cell can return to its resting state
50
New cards
refractory period
a short time when no other action potentials can occur until the axon is back in its resting state
51
New cards
electrical synapses
sends messages quickly and immediately; there is no space between the neurons
52
New cards
chemical synapses
messages take longer to send as neurons use neurotransmitters to send neural signals
53
New cards
acetylcholine (ach)
enables muscle action, learning, and memory
54
New cards
dopamine
influences learning, attention, and emotion
55
New cards
serotonin
impacts hunger, sleep, arousal, and mood
56
New cards
too much serotonin can cause…?
OCD, anxiety, and headaches
57
New cards
endorphins
influences the amount of pain/pleasure the body feels
58
New cards
epinephrine/adrenaline
helps w/ the fight-or-fight response
59
New cards
norepinepherine/noradrenaline
helps w/ the fight-or-flight response, alertness, + arousal
60
New cards
glutamate
involves w/ excitatory messages and helps w/ long-term memory and learning
61
New cards
GABA
helps w/ sleep and movement; slows down nervous system
62
New cards
excitatory neurotransmitter
depolarizes neurons; increases chance of action potential
63
New cards
inhibitory neurotransmitter
decreases the chance of action potential
64
New cards
hyperpolarization
inside of the neuron becomes more negative which prevents threshold from being reached
65
New cards
agonists
molecules that mimic neurotransmitters and increase their effectiveness (either by increasing the production or preventing reuptake from happening)
66
New cards
antagonists
molecules that decreases or block the effects of a neurotransmitter
67
New cards
neuroplasticity
neuron’s ability to adapt to damage + environmental changes
68
New cards
neurogenesis
the process that causes for new neurons to be formed
69
New cards
psychoactive drugs
chemical substances that alter perceptions and emotions
70
New cards
depressants
drugs that depress/reduce neural activity and slow reaction times
71
New cards
opioids
depressant drugs that are pain relievers
72
New cards
stimulants
drugs that promote neural activity
73
New cards
hallucinogens
drugs that affect a person’s sensations w/o the use of stimuli
74
New cards
restoration theory
sleep restores people’s energy that is depleted during the day
75
New cards
psychodynamic theory
dreams fulfill unconscious wishes
76
New cards
informative processing theory
sleeping allows individuals to build and restore memories
77
New cards
describe stage 1 of the sleep cycle
non-rapid eye movement; mind starts to relax + easy to wake up from
78
New cards
hypnagogic sensations
people think they are experiencing things in real-life when they are not, they are drowsy
79
New cards
beta waves
low amplitude brain waves hat show that someone is awake/alert
80
New cards
activation-synthesis theory
dreams are the body’s way of making sense of random neural activity
81
New cards
cognitive theory
dreaming can help with problem solving and creativity
82
New cards
pineal gland
products melatonin + regulates circadian rhythm
83
New cards
hypothalamus
controls pituitary gland and releases hormones
84
New cards
parathyroids
regulates levels of calcium in the blood
85
New cards
adrenal glands
related to the fight-or-flight response; releases epinephrine and norepinephrine
86
New cards
pancreas
regulates level of blood sugar via insulin and helps with digestion
87
New cards
testes + ovaries
releases sex hormones to promote growth
88
New cards
central nervous system (brain + spinal cord)
brain’s neurons work in neural networks that sends messages quickly
89
New cards
peripheral nervous system
connects sensory and motor neurons to cns
90
New cards
somatic nervous system
controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles
91
New cards
autonomic nervous system
controls automatic functions of internal organs
92
New cards
sympathetic nervous system
body’s arousal system and causes fight-or-flight
93
New cards
parasympathetic nervous system
returns body to calm, relaxed state after fight-or-flight response
94
New cards
priming
the effect in which a stimulus facilitates/inhibits the problem processing of the same/similar stimuli
95
New cards
describe stage 2 of the sleep cycle
individual is no longer easily awakened and experiences sleep spindles (bursts of neural activity)
96
New cards
describe stage 3 of the sleep cycle
body is very relaxed + usually when sleepwalking, sleeptalking, and night terrors happen
97
New cards
REM
dreams happen, rapid eye movement, brain shows activity, muscles are relaxed but other body systems are active
98
New cards
sleep terrors/night terrors
* people randomly wake up in the middle of the night feeling intense pain/fear
* they have an increased heart rate and sweat
* they have an increased heart rate and sweat
99
New cards
sleep apnea
when people randomly stop breathing in the middle of their sleep