Procedures - Positioning Terms and Movement
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
Sagittal Plane
vertical plane that passes through the body from front to back and divides the body into left and right portions
Coronal Plane
vertical plane dividing the body into anterior and posterior planes
Midsagittal Plane
divides the body into equal left and right parts, median plane
Mid-coronal Plane
divides the body into equal anterior and posterior parts
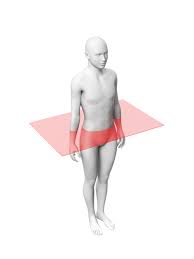
Horizontal (transverse)(axial) Plane
divides the body into superior/inferior parts; passes through the body at right angles to sagittal and/or coronal planes
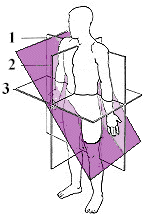
Oblique Plane
longitudinal or transverse plane that is at an angle or slant an not parallel/perpendicular to the other planes
sagittal
What Type of plane is this?
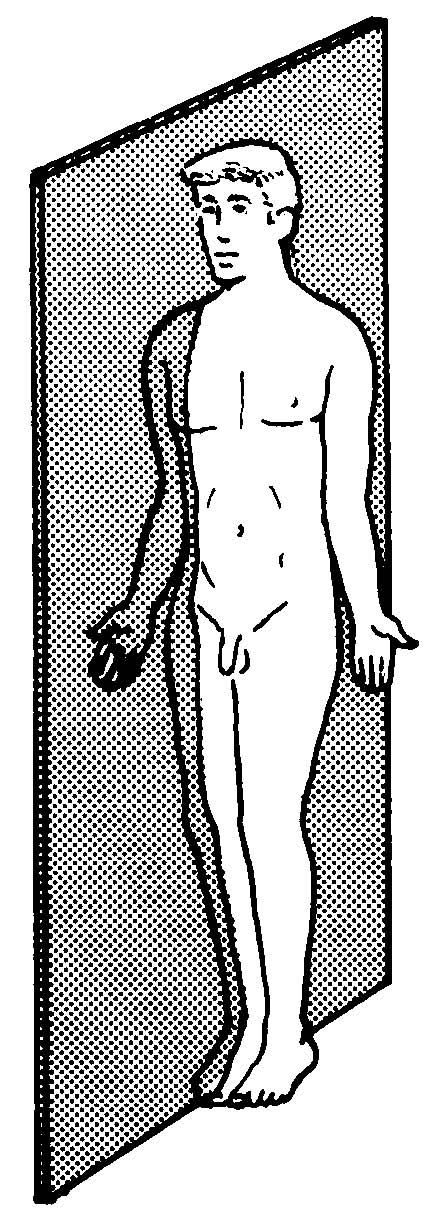

midsagittal
What type of plane is this?
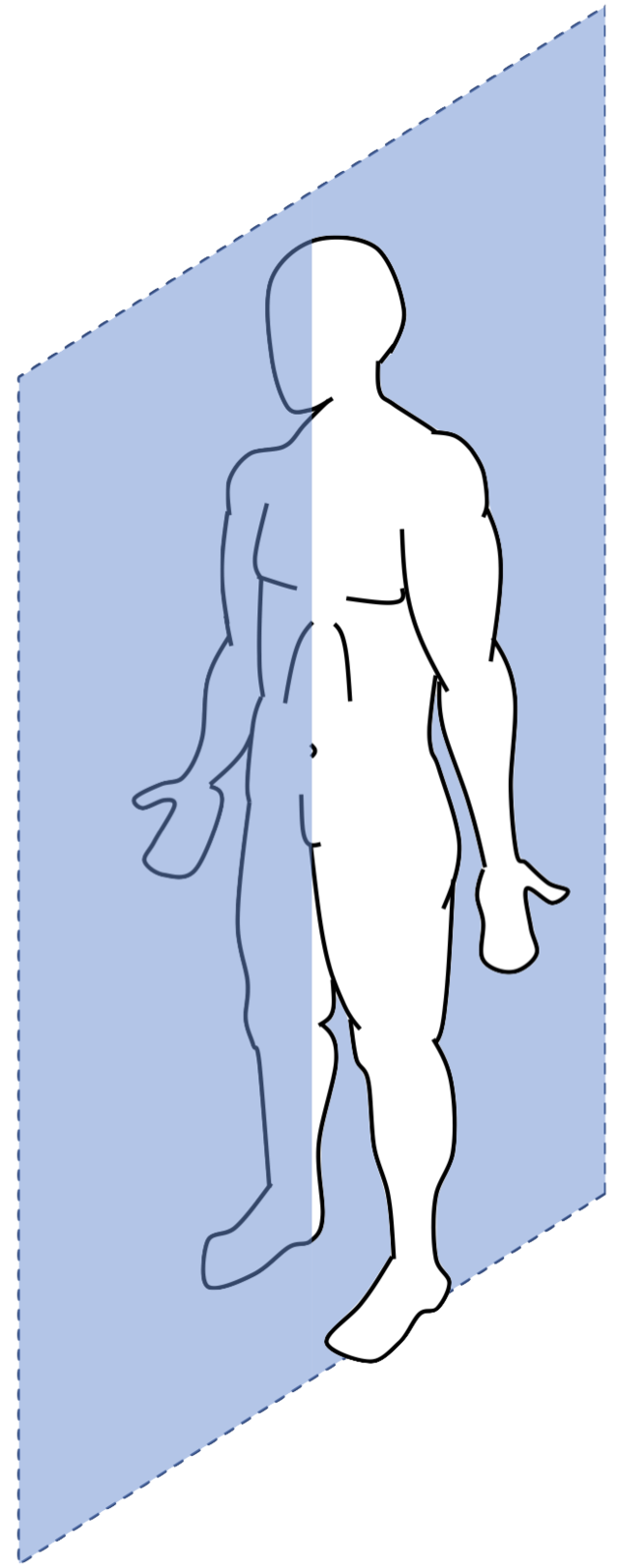
midcoronal
What type of plane is this? (pretend it is equally divided on both sides)
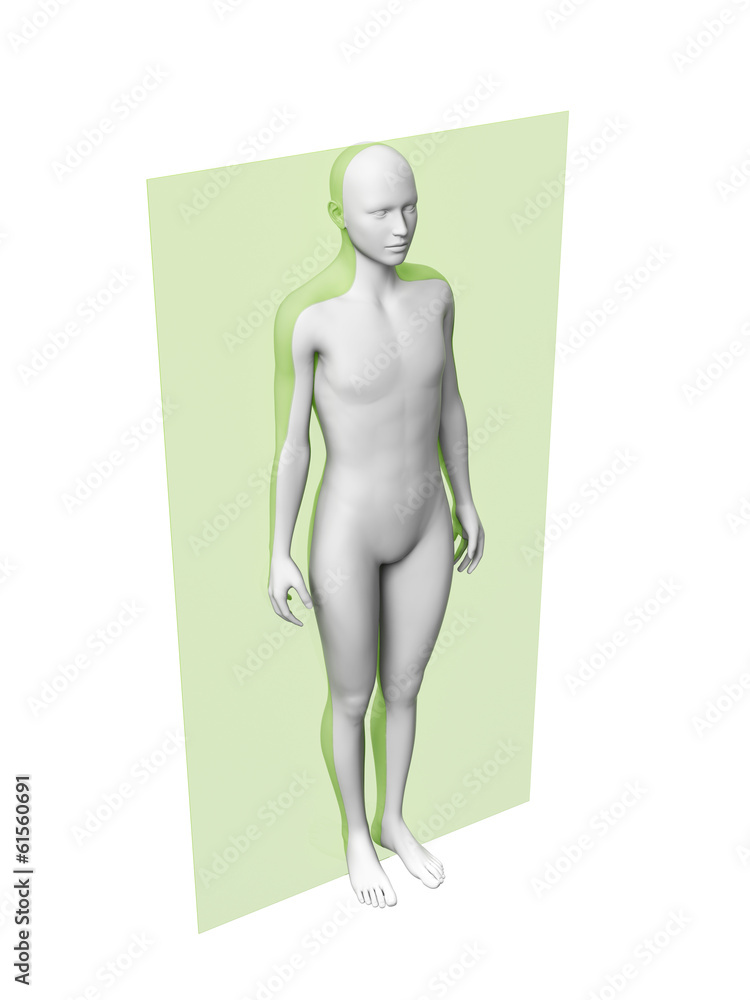

coronal
What type of plane is this? (pretend that it is NOT equally divided on both sides)

horizontal, transverse and/or axial
What type of plane is this?
oblique
What type of plane is this? (only look at the purple section)
Thoracic Cavity
divided into pericardial segment with two parts, pleural and pericardial cavity
Pleural cavity
houses the lungs
Pericardial cavity
houses the heart
pleural membranes, lungs, trachea, esophagus, heart, great vessels, and pericardium
List a few organs housed within the Thoracic Cavity
Abdominopelvic cavity
divides into an abdomen cavity and pelvic cavity
peritoneum, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, stomach, intestines, kidneys, proximal ureters, and major blood vessels
List a few organs housed within the Abdominal Cavity
rectum, urinary bladder, reproductive organs, distal, ureters
List a few organs housed within the Pelvic Cavity
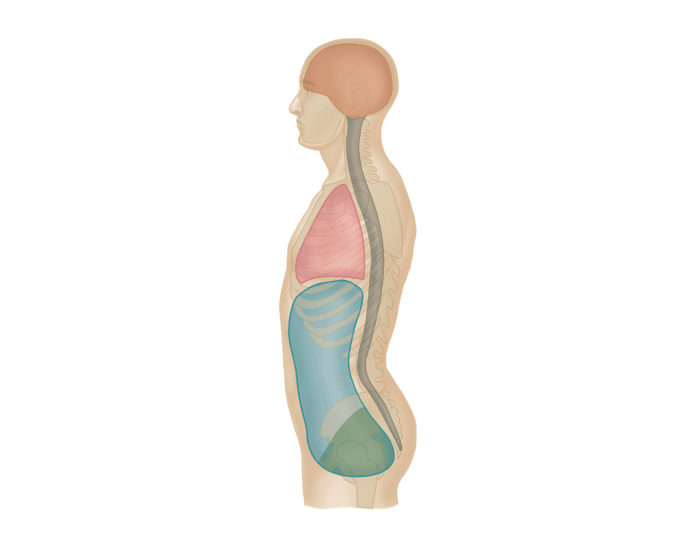
thoracic cavity
What cavity is listed in RED
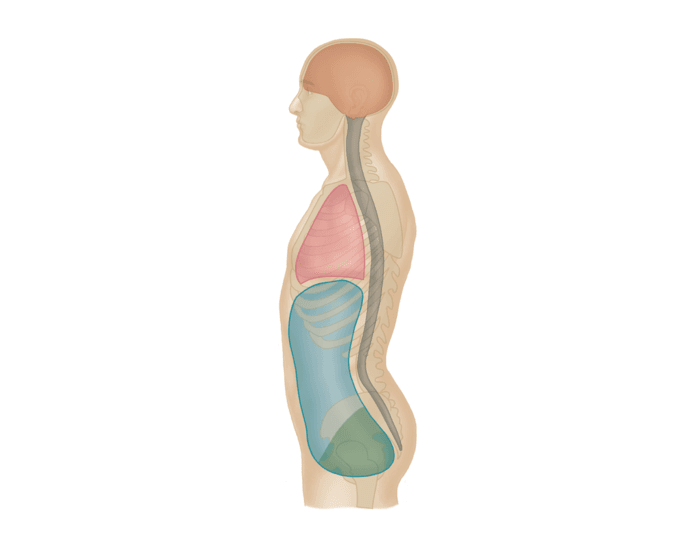
abdominopelvic cavity
What cavity would be considered the BLUE and GREEN
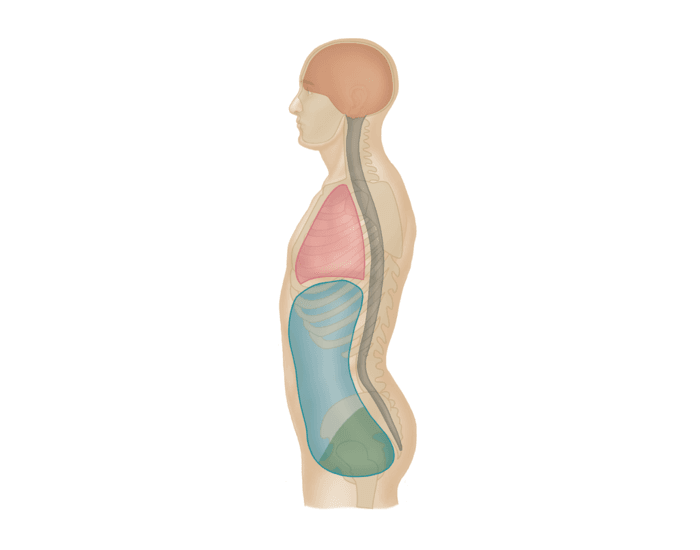
abdominal cavity
What cavity would be considered just in the BLUE
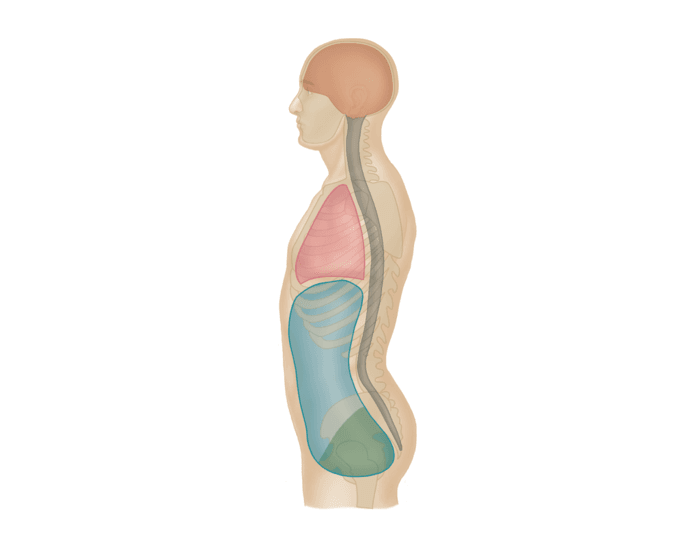
pelvic cavity
What cavity would be considered just in the GREEN
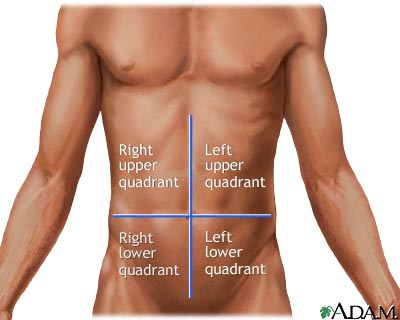
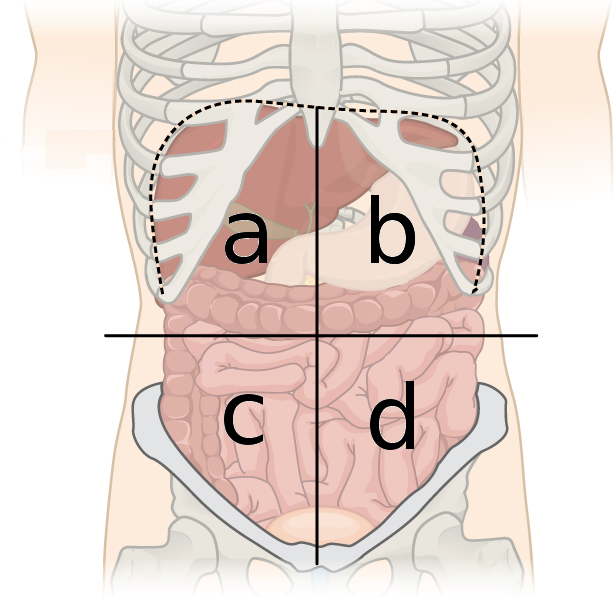
RUQ, RLQ, LUQ, LLQ
What are the four quadrants of the abdomen
right upper quadrant (RUQ)
What quadrant is A

left upper quadrant (LUQ)
What quadrant is B
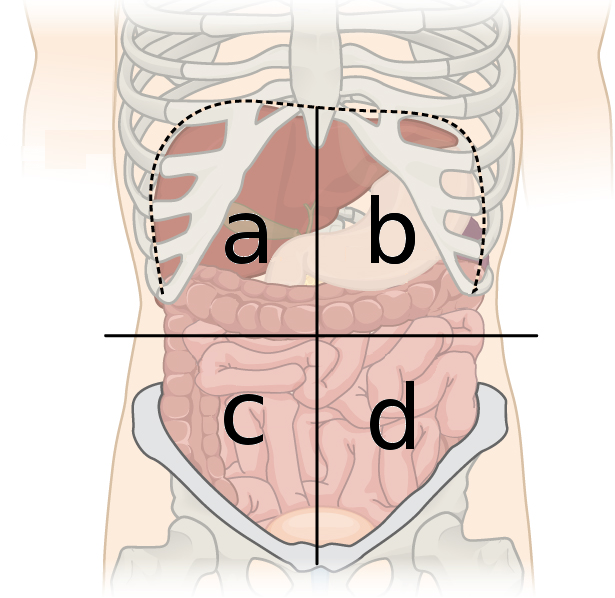
right lower quadrant (RLQ)
What quadrant is C
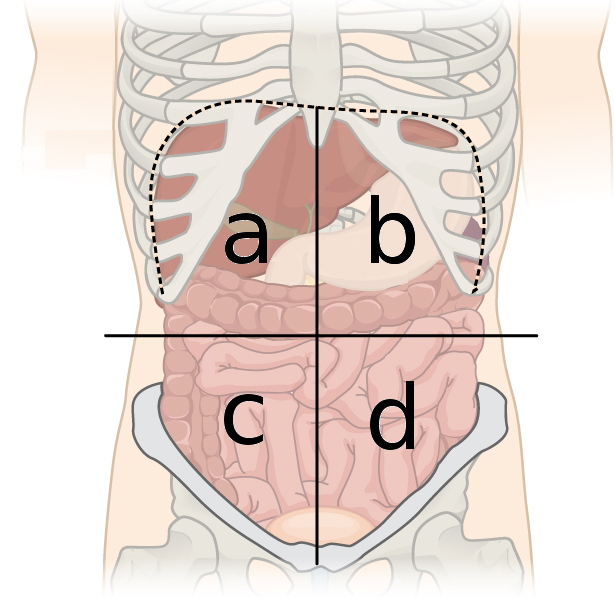
left lower quadrant (LLQ)
What quadrant is D
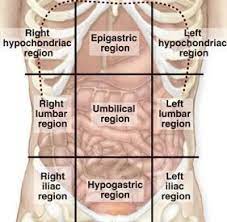
right hypochondriac, epigastric region, left hypochondriac, right lumbar, umbilical region, left lumbar, right iliac, hypogastric region, left iliac
What are the 9 regions of the abdomen
right hypochondriac region
What region is number 1
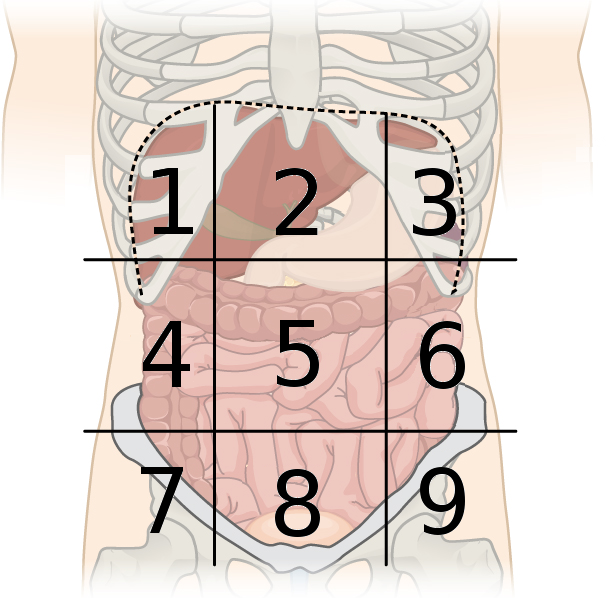
epigastric region
What region is number 2
left hypochondriac region
What region is number 3
right lumbar region
What region is number 4
umbilical region
What region is number 5
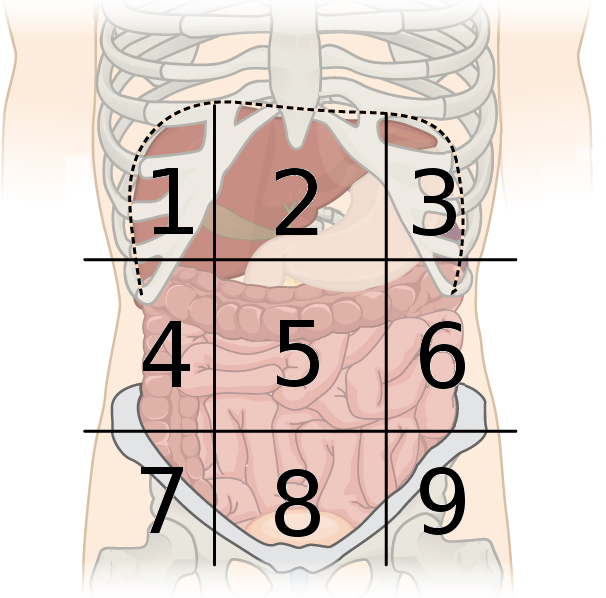
left lumbar region
what region is number 6
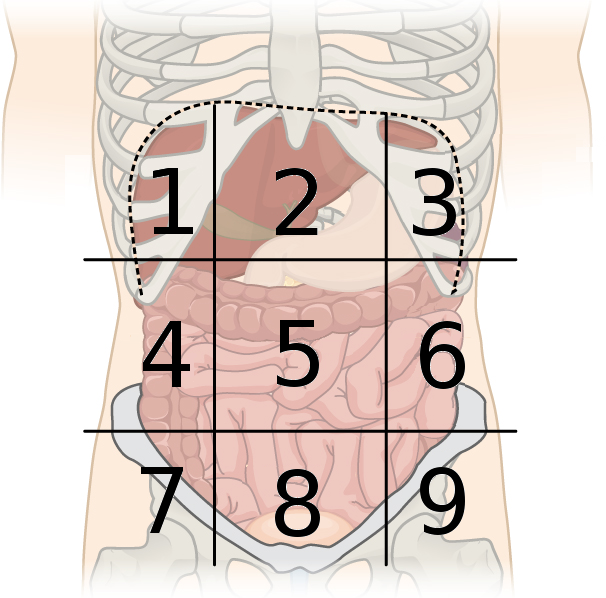
right iliac region
What region is number 7
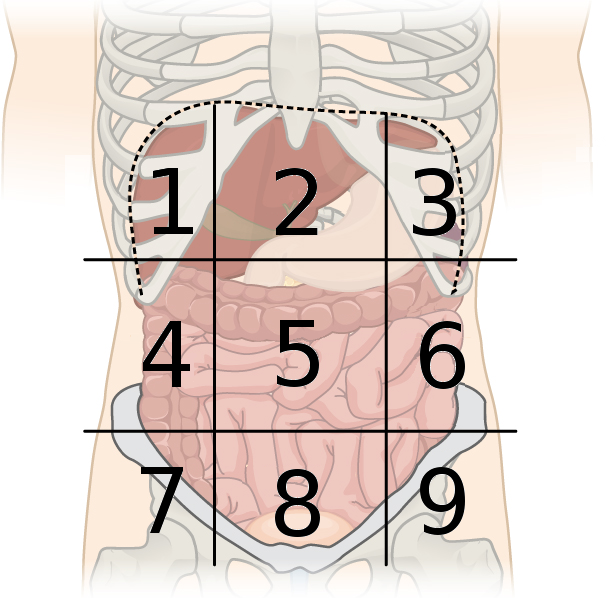
hypogastric region
What region is number 8
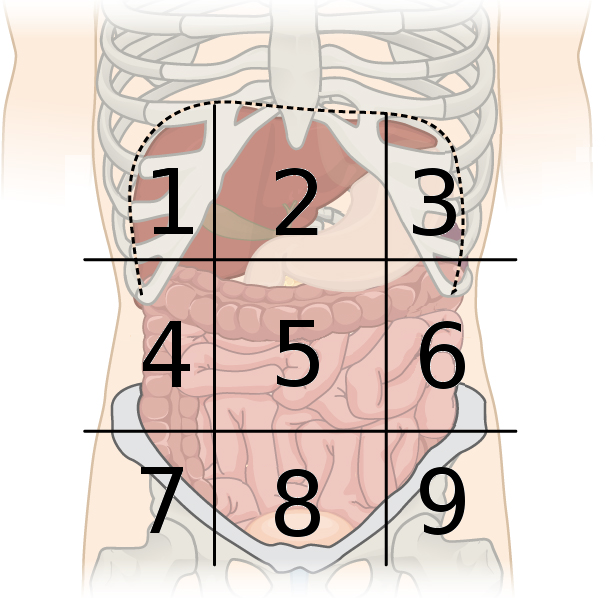
left iliac region
What region is number 9

Body Habitus
variations in the shape of human bodies, affects locations of organs
sthenic, hyposthenic, asthenic, hypersthenic
What are the 4 types of body habitus
sthenic
What body habitus is the 50% average type
hyposthenic
What body habitus is the 35% slightly below average type
asthenic
What body habitus is 10%, thin, and organs are low and near the middline
hypersthenic
What body habitus is 5% massive, and organs are high and transverse
hypersthenic
Identify which body habitus this is
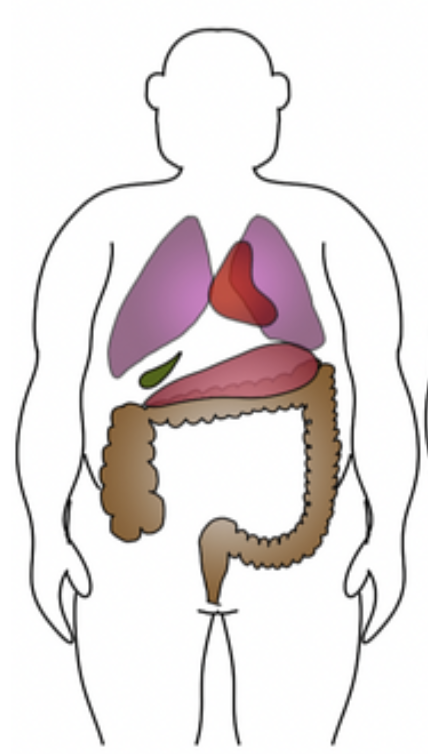
sthenic
Identify which body habitus this is
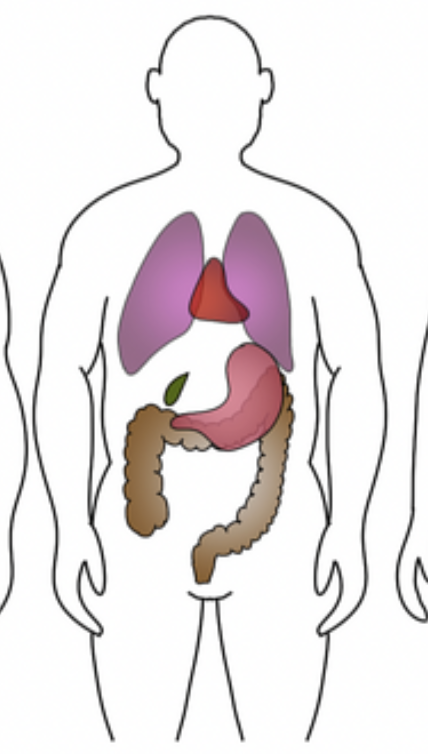
hyposthenic
Identify which body habitus this is
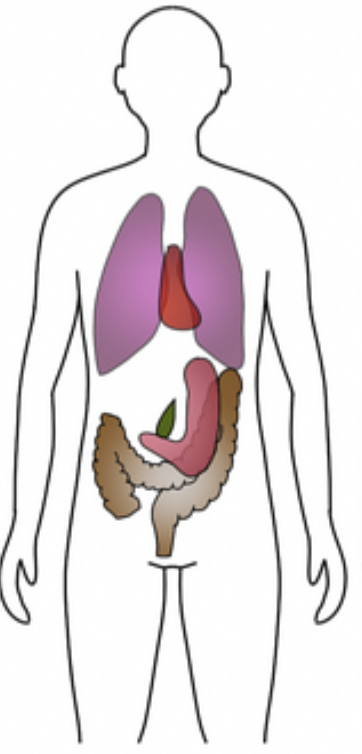
asthenic
Identify which body habitus this is
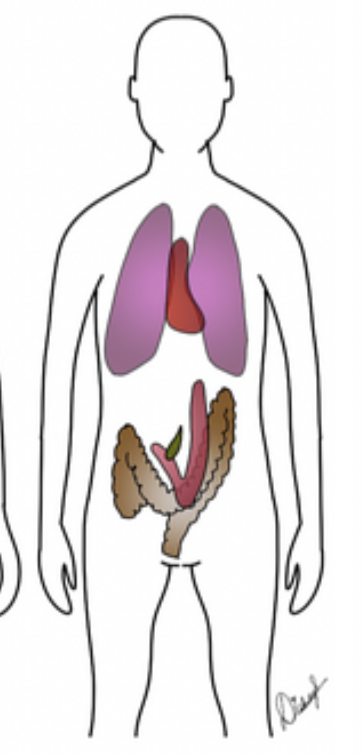
sthenic
Identify which body habitus this is
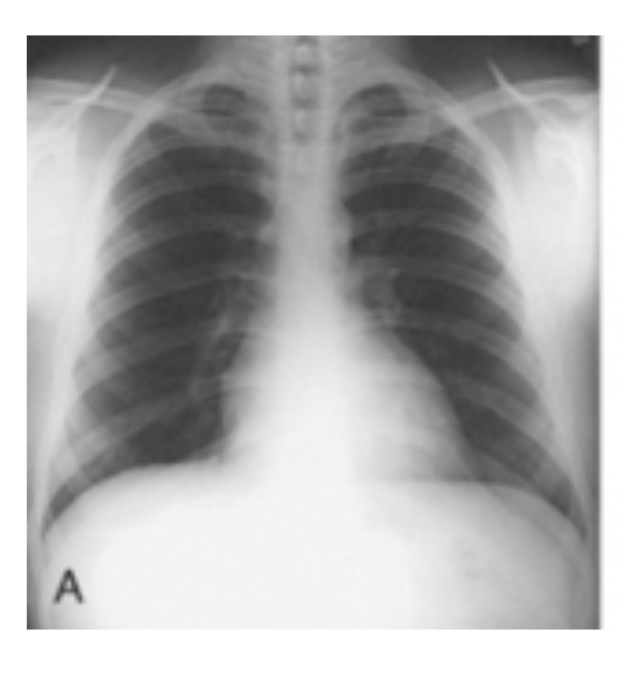
hyposthenic
Identify which body habitus this is
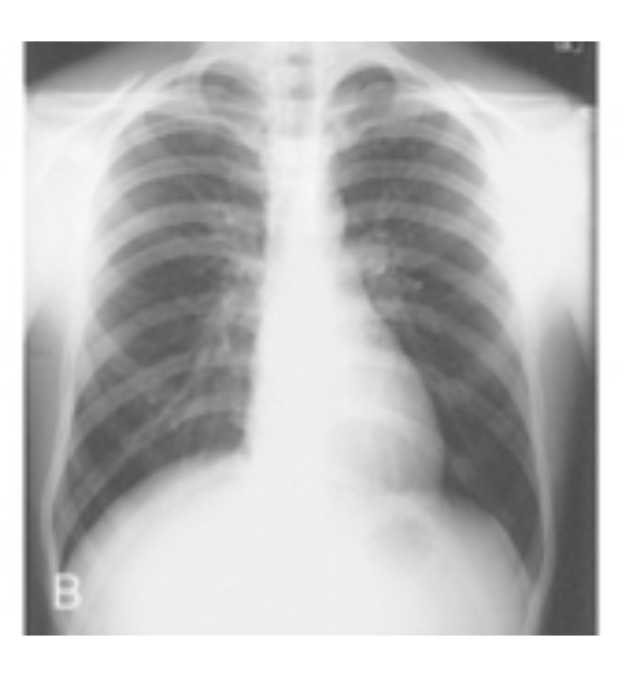
asthenic
Identify which body habitus this is
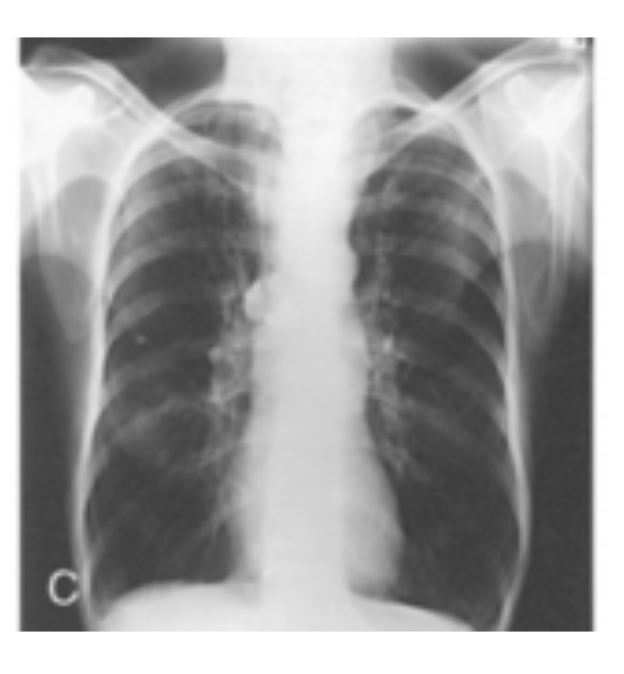
hypersthenic
Identify which body habitus this is
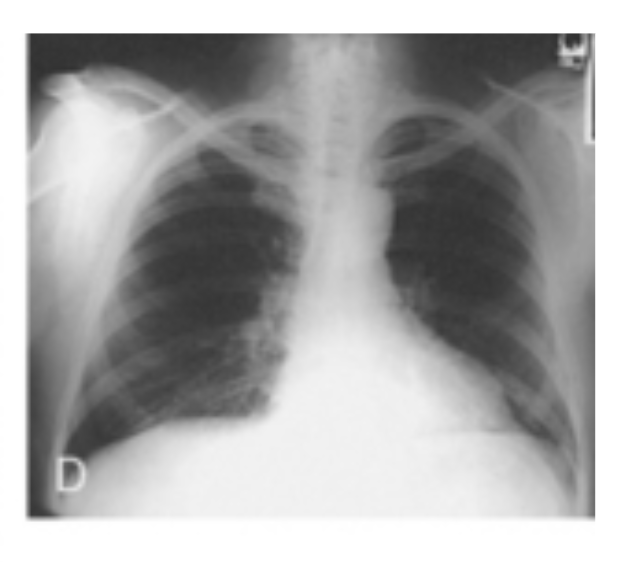
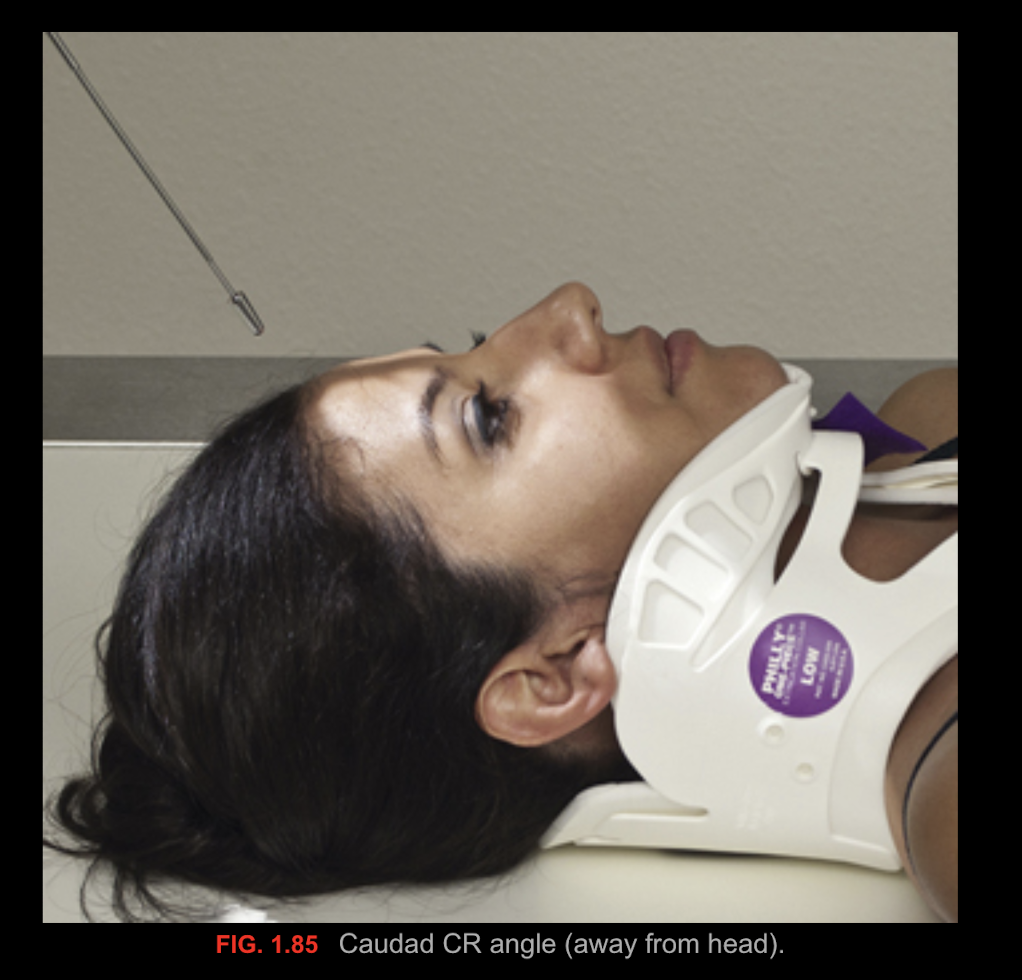
Caudad/Caudal
(tube angles)
parts away from the head of the body, to the feet, angulation toward the feet
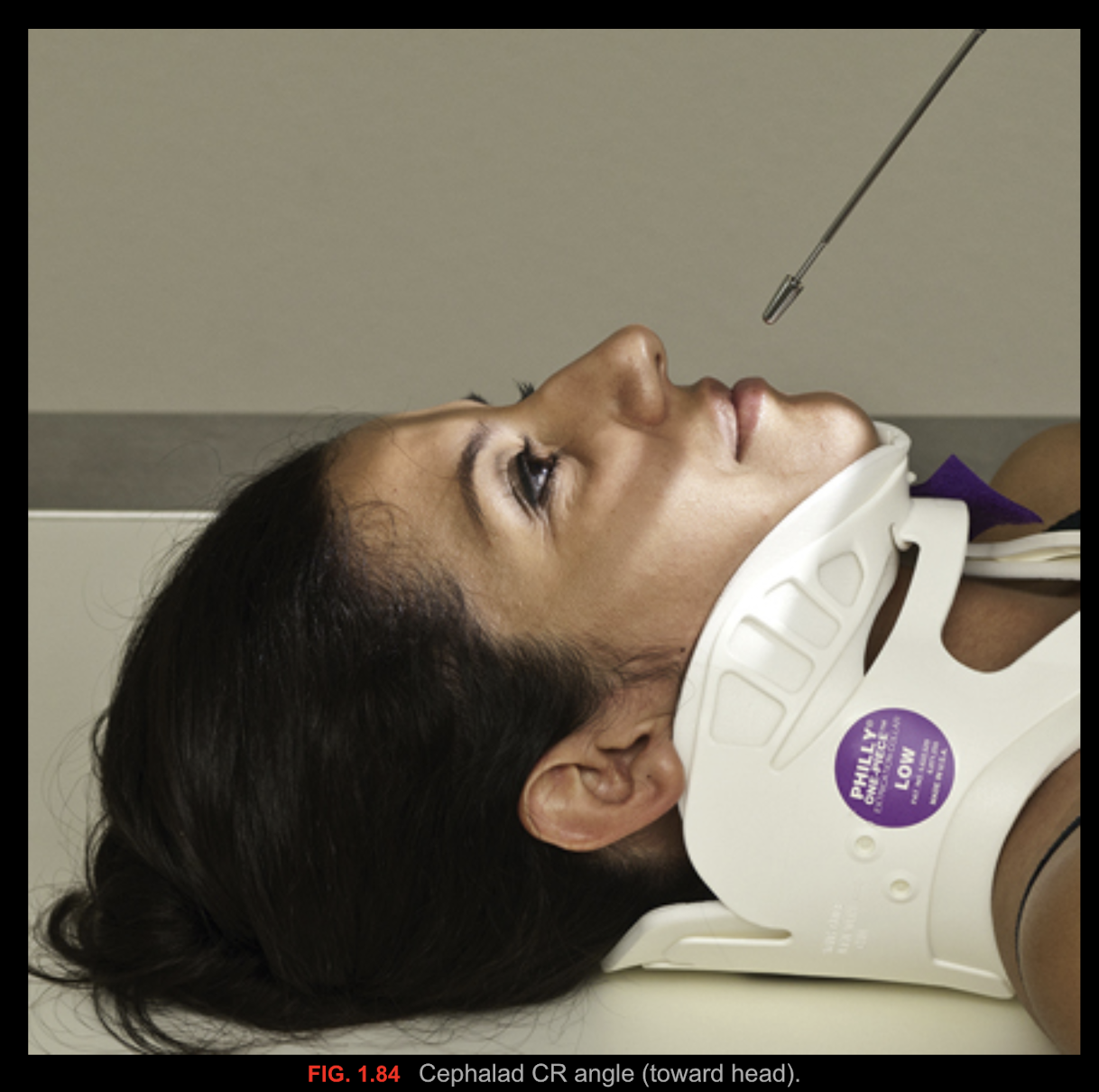
Cephalad/Cephalic
parts toward the head of the body, to the head, angulation toward the head
Medial
toward the center, toward the midline of the body
Lateral
away from the center, away from the midline of the body
Distal
parts farthest from the point of origin (use for extremities)
Proximal
parts nearer the point of origin (used for extremities)
Deviation
to turn aside or to turn away from the standaard course
Superior
up
Superolateral
up and away from the midline of the body
Superomedial
up and toward the midline of the body
Inferior
down
Inferolateral
down and away from the midline of the body
Inferomedial
down and toward the midline of the body
Anterior / Ventral
the front
Anterosuperior
located in front and above
Anteroinferior
located in the front and below
Posterior / Dorsal
the back
Posterosuperior
located in the back and above
Posteroinferior
located in the back and below
Interior
inside of something, nearer to the center
Exterior
situated on or near the outside
Superficial
nearer the skin’s surface
Deep
further away from the skins surface
Ipsilateral
on same side of the body or part
Example: the right thumb and the right great toe are ___________
Contralateral
on the opposite side
Example: the right knee and the left hand are ______________
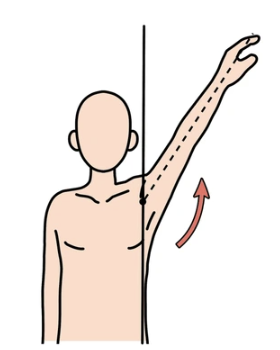
Abduction
movement of a part away from the central axis of the body, lateral movement
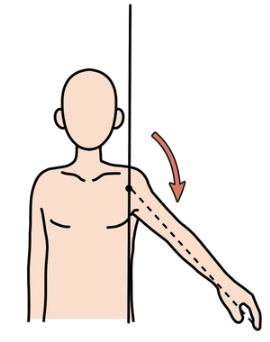
Adduction
movement of a part towards the central axis of the body, medial movement
Extension
straightening of a joint, increasing the angle of the joint
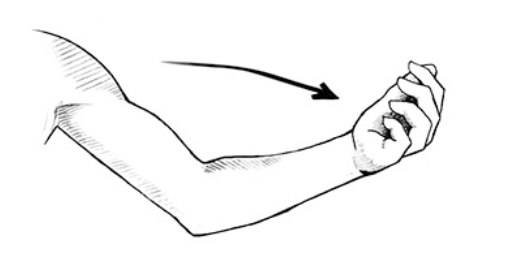
Hyperextension
excessive straightening of a joint
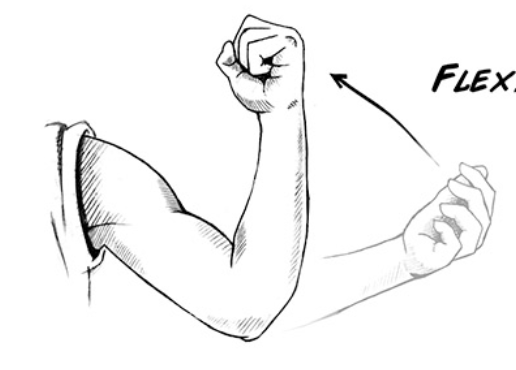
Flexion
act of bending of a joint, decreasing the angle of the joint
Hyperflexion
excessive flexion of a joint
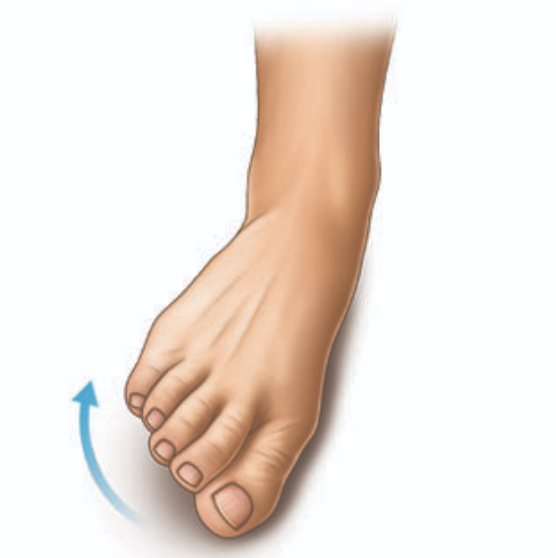
Evert
outward turning of the foot at the ankle
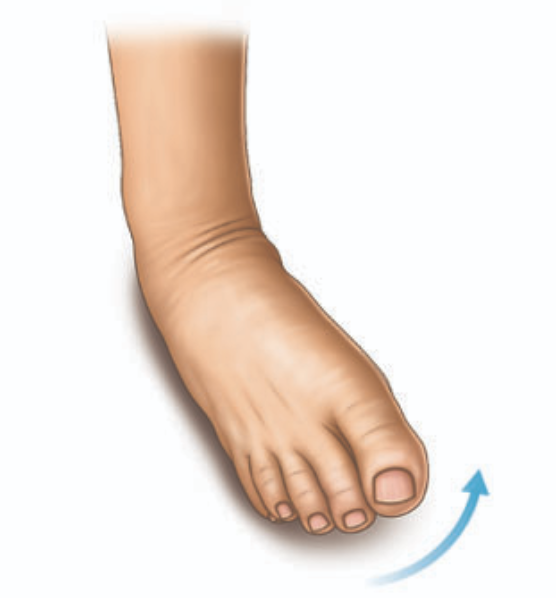
Invert
inward turning of the foot at the ankle
Pronate
rotation of the forearm so the palm is down
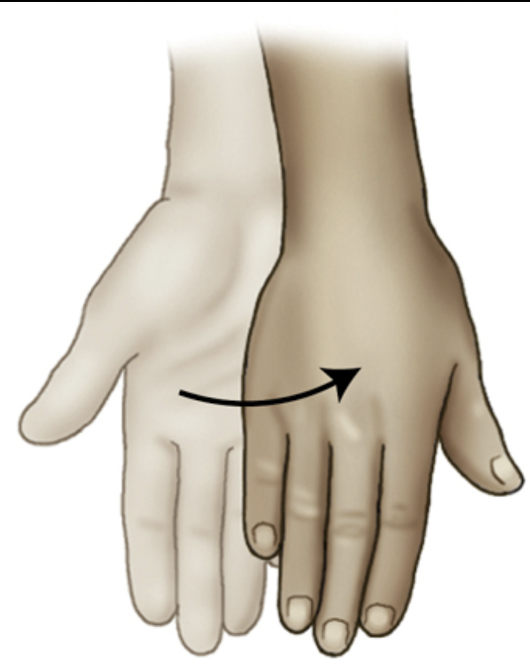
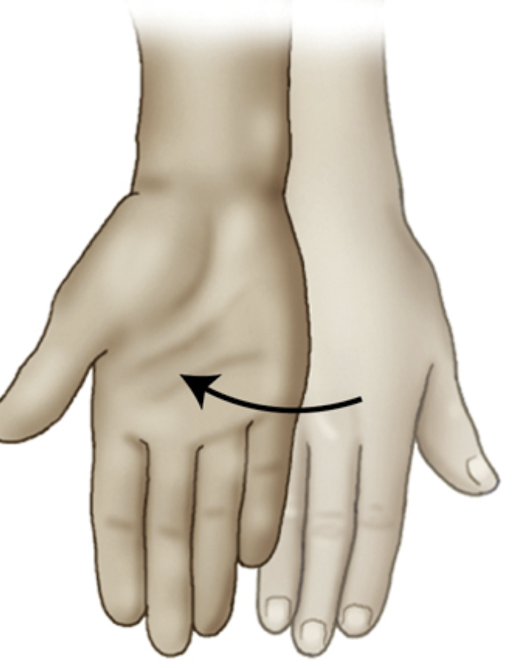
Supinate
rotation of the forearm so the palm is up
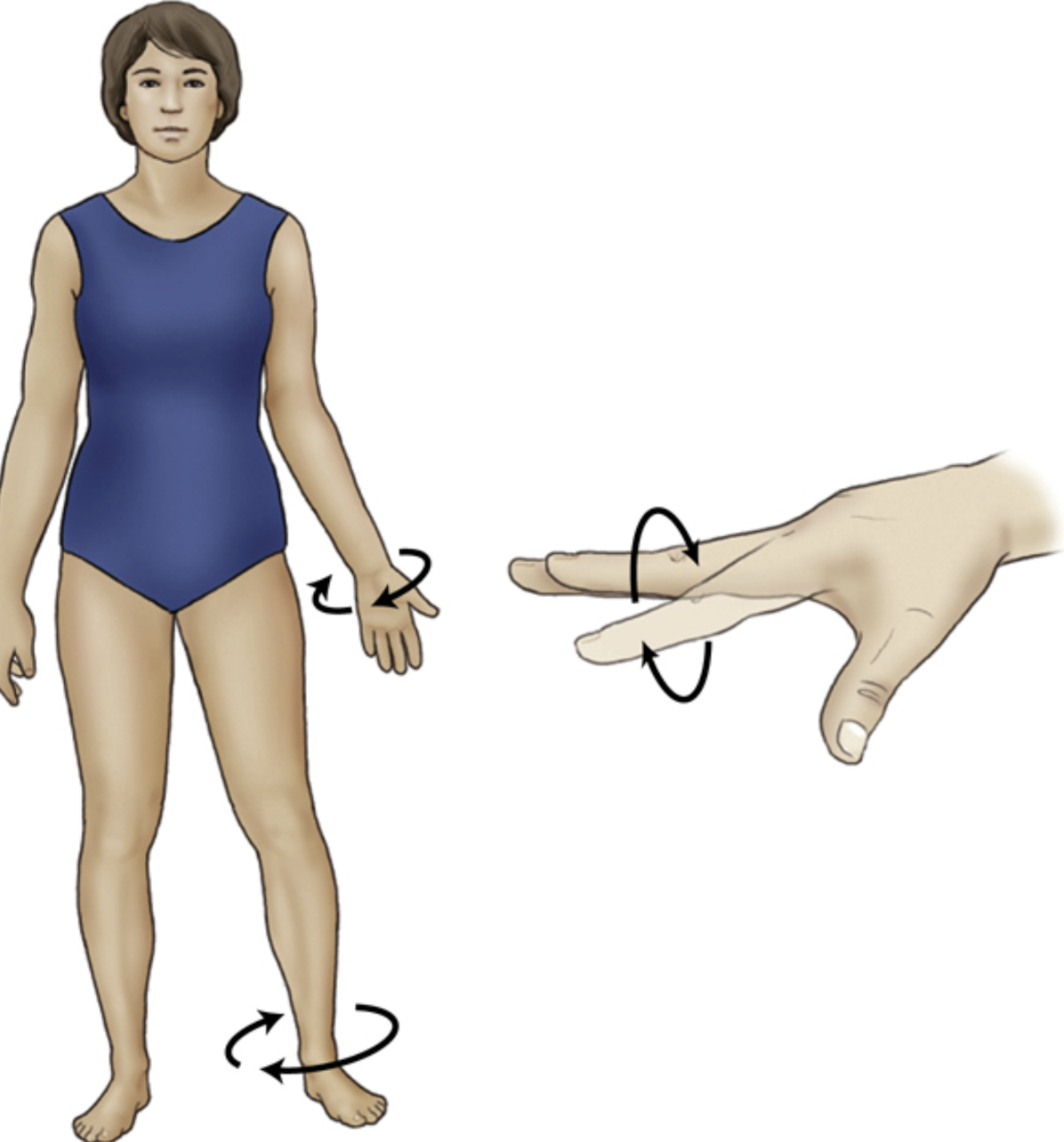
Rotation / Rotate
turning or rotating of the body or body part around it axis
Circumduction
circular movement of a limb
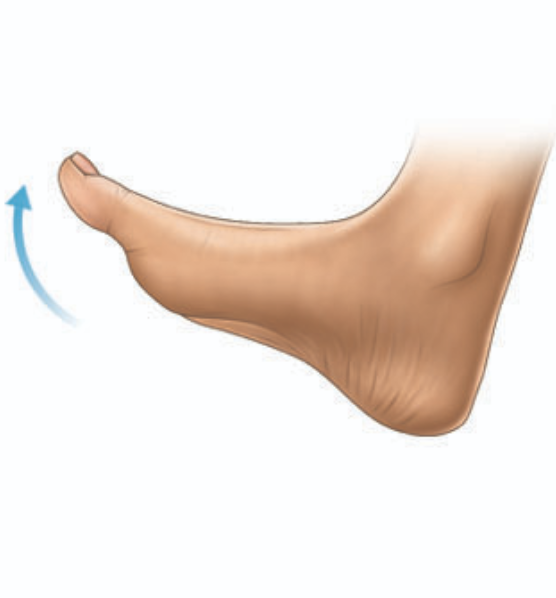
Dorsiflexion
flexion of the foot toward the leg
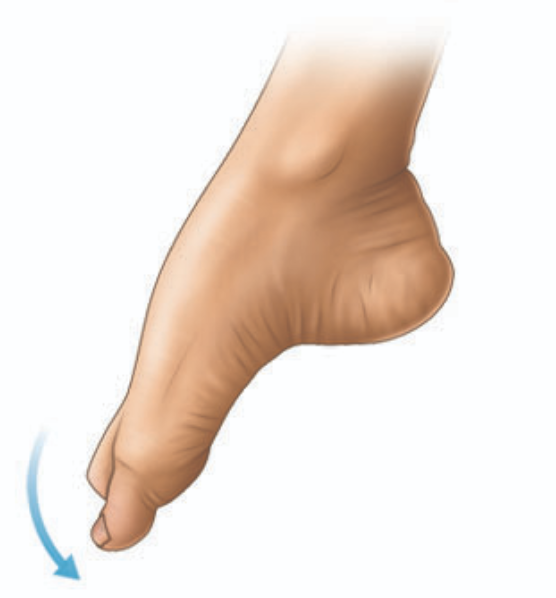
Plantar Flexion
extension of the foot toward the plantar surface
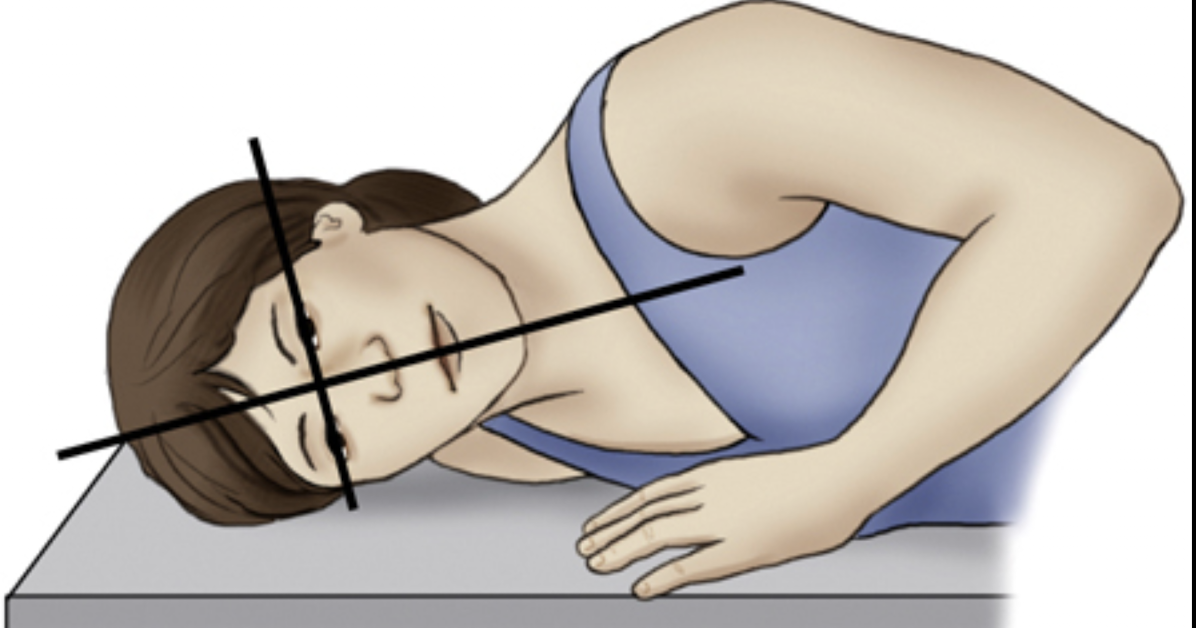
Tilt
tipping or slanting a body part slightly, is in relation to the long axis of the body
Peripheral
towards the edges
Central
in the middle
Visceral
covers organ
Parietal
lining outside of a cavity
Palmer
palm of hand
Plantar
bottom of foot
Body Positions
specific placement of the body part in relation to the x-ray table or IR
known as the radiographic position
Anatomic Position
upright position, arms extended by the sides with palms facing forward, head and feet directed straight ahead