Unit 1 section B -- bio chem
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Origins of Life. Carbohydrates. Proteins. Amino acids. Protein structure and function.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Isomer
a collection of compounds that have the same chemical formula but have different bonds in place that allow for various physical and chemical properties
SI units
International System of Units
Carbohydrates
the starches and sugars present in foods
Lipids
fats, oils, and waxes, made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
covalent bond
sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
Polar covalent bond
Unequal sharing of electrons
Macromolecules
A very large organic molecule composed of polymers
Monomers
small units that join together with other small units to form polymers
Polymers
large compound formed from combinations of many monomers
Antigens
foreign substances that trigger the attack of antibodies in the immune response
Peptide bond
covalent bond formed between amino acids through a condensation reaction
Nucleic acid
macromolecule containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus
Condensation reaction
when two molecules become covalently bonded to each other through the loss of H- and OH-, to create H2O
Monosaccharides
The most basic, fundamental unit of a carbohydrate. Simple sugars
Polysacchrides
long chains of carbohydrate molecules, composed of monosaccharides
Pentose sugar
Deoxyribose and ribose; a building block of nucleic acids
Hexose sugar
a sugar that contains 6 carbon atoms in every molecule
Starch
A polysaccharide storage in plants consisting entirely of glucose
Amylose
unbranched starch
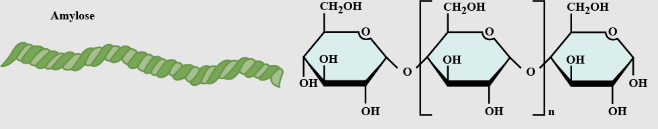
Describe the difference of Amylose and Amylopectin
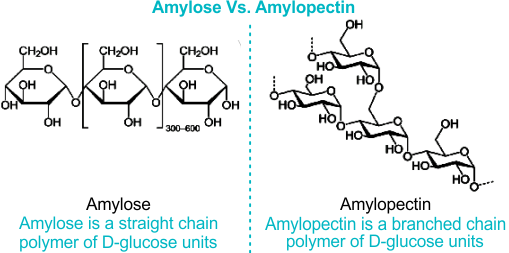
Amylopectin
Branched starch
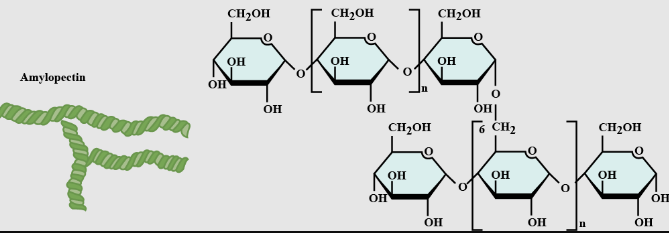
Glycogen
An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide; the animal equivalent of starch.
how many bonds can carbon form?
four covalent bonds
Hydrolysis reaction
A chemical reaction that breaks apart a larger molecule by adding a molecule of water
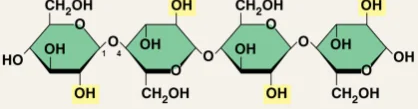
Alpha bonds
Chemical bonds between hexose sugars where the OH- groups are at 4' and 1'
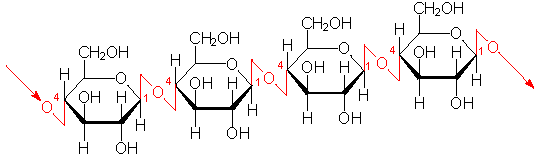
Beta bond
Chemical bond between hexose sugars where the OH- groups alternate at 1' and 4' with an H
Amino acid
compound with an amino group on one end and a carboxyl group on the other end
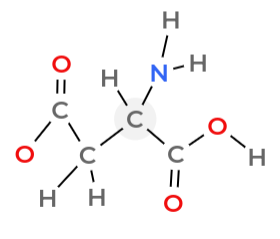
Identify the carboxyl group
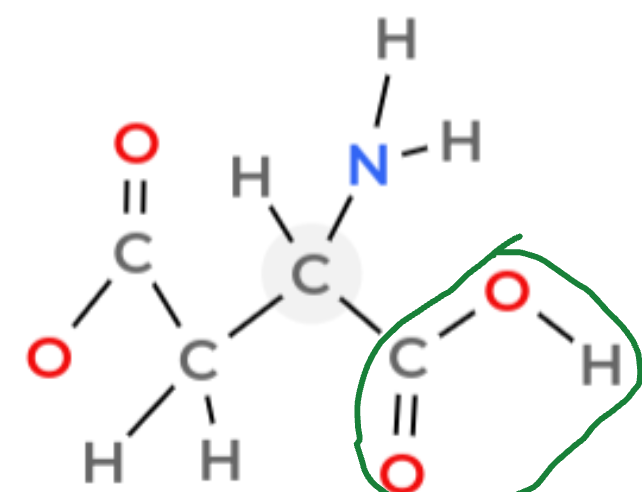
How do you identify a carboxyl group
Look for a carbon double bonded to an O and an bonded to an OH. The formula is -COOH
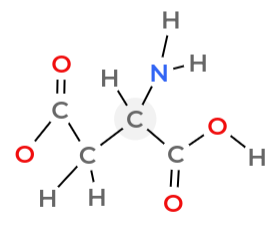
Identify the amine group
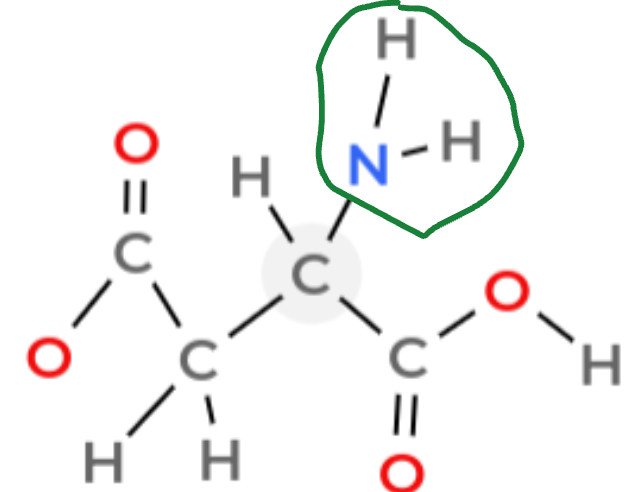
How do you identify an amine group
NH2.
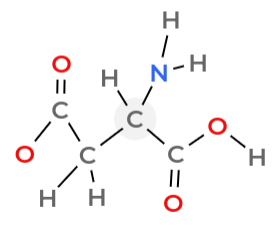
Identify the side chain/R group
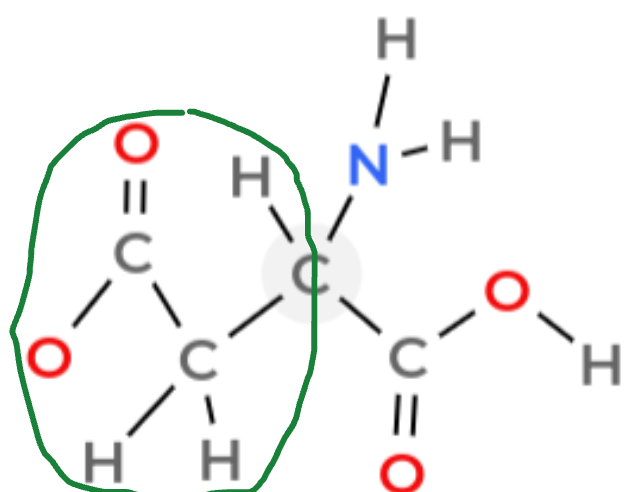
Amine group
NH2 in an amino acid
Carboxylic acid group
-COOH
Side chain / R group
the distinguishing group of atoms of a particular amino acid
Dipeptide
Two amino acids bonded together
Essential amino acids
Amino acids that are needed, but cannot be made by the body; they must be eatin in foods
Non-essential amino acids
amino acids that the body can synthesize on its own; does not need to get from dietary sources
Genetic code
the ordering of nucleotides in DNA molecules that carries the genetic information in living cells
Denaturation
loss of normal shape of a protein due to heat or other factor
Primary Structure
made of Polypeptide chain
Secondary structure
hydrogen bonds between amino and carboxylic group
Tertiary structure
Bonds between R-groups
Quatenary structure
multiple polypeptide chains
Conjugated protein
a protein with another chemical group (e.g., carbohydrate) is attached by covalent bonding or other bond types
Prosthetic group
non-peptide (non-protein) compounds that attach to proteins and assist them in various ways
Globular structure
globular proteins are compact and spherical. The hydrophobic amino acid side chains are berried within
fibrous structure
fibrous proteins are composed of long, narrow strands