Control and Coordination
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Control and coordination are provided by ____
Nervous and Muscular tissue
Receptors
All information from our environmentis detected by the specialised tip of nerve cells
Located : Sense organs
Gustatory receptors
Taste
Olfactory receptors
Nose
Nerve impulse
An electrical signal that passes along the neuron.
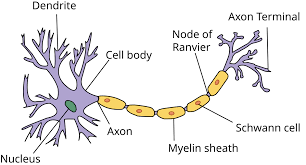
Structure of Neuron
Dendrite Tip:
The information acquired at the end of the dendrite tip of a nerve cell, sets off a chemical reaction that creates an electrical impulse,
Axon:
The impulse travels from the dendrite to the cell body and then along the axon to its end.
Nerve ending:
At the end of the axon, the electrical impulses releases some chemicals.
Synapse ( Neuromuscular junction) :
The chemicals cross the synapse And start a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron.
Sensory Neuron
Carry nerve impulse from receptors or sense organs to brain or spinal cord
Motor Neuron
Carry nerve impulse from Central nervous system ( brain and spinal cord ) to the effector organs like muscles or glands.
Relay Neuron
Connect Sensory to motor neuron. They are located in the brain and spinal cord.
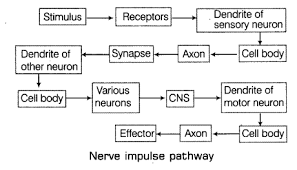
How do nerveous impulses travel throughout the body?
All information from our environmentis detected by the receptors present in the body which transfer it to the sensory neuron.
The information is acquired at the end of the dendrite tip of a neuron causes a chemical reaction that produces an electrical impulse
This impulse travels from the dendrite of sensory neuron to its cell body ( cyton ) and then along the axon to its end
At the end of axon, the electrical impulse causes the release of some chemicals aka neurotransmitters
These chemicals cross the synapse and start a similar electrical impulse in dendrite of next neuron
A similar synapse allows the delivery of such impulses from neuron to other cells such as muscles cells or glands ( effectors )
Neuromuscular Junction
The point where muscle fiber comes in contact with a motor neuron carrying a nerve impulse from the Central Nervous system
AKA Synapse.
Limitations to the Use of Electrial Impulse
The electrical impulse will reach only those cells that are connected by a nervous tissue, not each and every cell in the body
Once an electrical impulse is generated in a cell and transmitted the cell will take some time to reset its mechanism before it can generate and transmit a new impulse.
Reflex Action
Its is an automatic and rapid response to a stimulus, It protects the body from damage and does not invlove conscious thought.
Reflex actions are controlled by ___ and why not the brain.
Reflex actions are controlled by Spinal cord and not the brain as it takes more time to instruct the muscles too move.
Which neruron transports the reflex action?
It is passed straight to the Motor neuron through a relay neuron.
Spinal Cord
Nerves from all over the body meet in a form of a bundle on their way to the brain. Hence the process of detecting signals is quick.
Reflex arc
The pathway taken by the nerve impulses in a reflex action.
Stimulus / Danger→ Receptor ( Sense organs ) → Sensory neuron → Spinal Cord (Relay neuron) → Motor neuron → Effector (muscle)
Effector : Executes the effect by neuromuscular movement
Importance of reflex action
It enables an immediate response to an harmful stimulus.
It reduces the overloading of the brain
it increases the chances of survival
PNS ( Peripheral Nervous System )
It facilitated the communication between the Central Nervous system and other parts of the body.
Types: Cranial Nerves and Spinal Nerves
Cranial Nerves
Nerves which emerge from the brain and spread throughout the head
Spinal Nerves
Nerves which emerge from the Spinal Cord and spread through the body.
CNS
Central Nervous system : It is the centre of control and coordination of the body activities.
Types : Brain and Spinal Cord.
Recieves information from all parts of the body and integrates it.
Human Brain
The main coordinating centre of the body which enables organism to think and take decisions.
The human brain recieves information from the sense organs, inteprets it and sends instructions to the muscles or other organs.
Functions of the Human brain
It coordinates activites of the body so the mechanisms and hormonal reactions of the body work together.
It recieves the informations carrying nerve impules from all sensory organs of the body
It correlates the various stimulus from different sense organs and produces appropriate reaction
Forebrain
The forebrain is the Most Important part and the largest part of the brain.
It does all the main thinking. It recieves sensory impulse from various receptors in the body.
Cerebrum: It is responsible for the main thinking part of the brain. It is responsible for reasoning, speech, hearing and intelligent sights.
Sensory Areas : It recieves various sensory impulses from various receptors like ears and nose.
Association Areas: It recieves sensory information and inteprets it by relataing it to past experiances and other receptors
Hypothalamus : Controls the temperature, urge to eat and drinking.
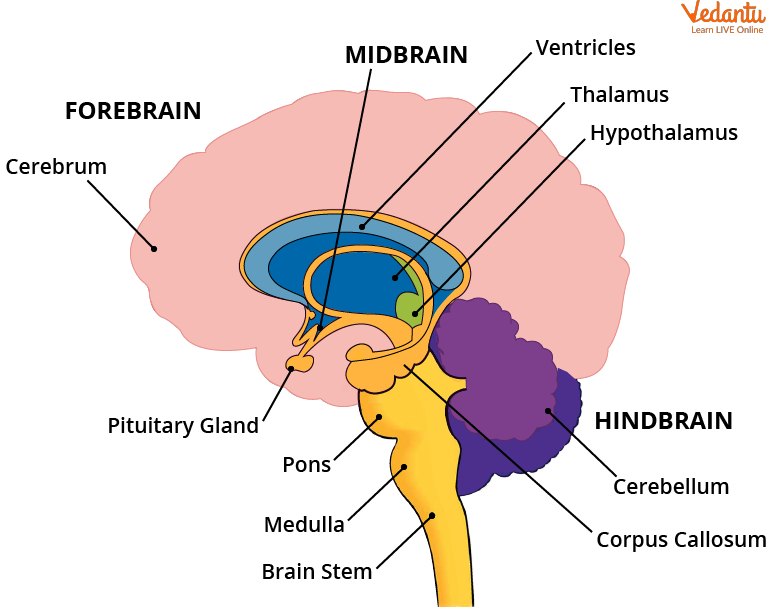
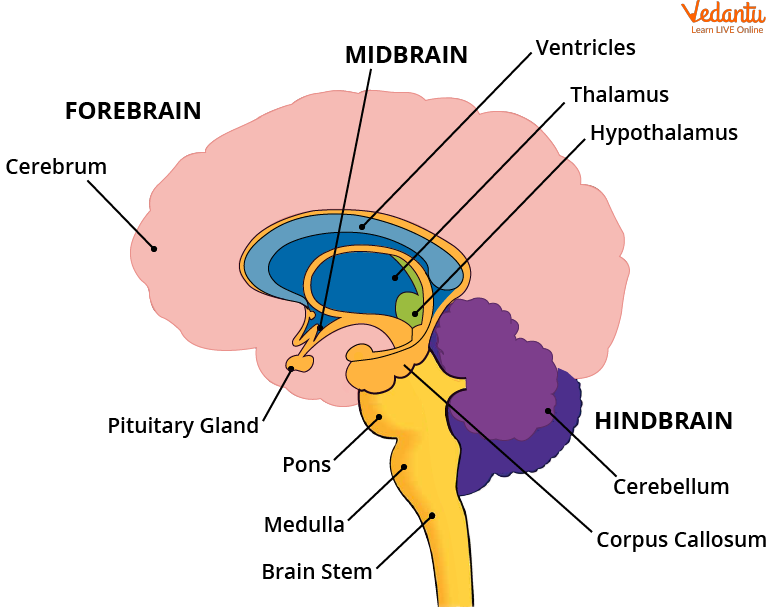
Midbrain
It connects the forebarin to the hindbrain. It controls the head, neck and trunk movement. It controls the reflex movement of the eye muscles, pupil. To locate the sounds and visual reflex that involved in focusing of the objects.
Hindbrain.
Provides the connections between spinal cord and rest of the brain.
Cerebellum: It controls and coordinates different musculary actions.
Its is responsible for percision of voluntary actions.
It maintains posture and equilibrium of the body.
Medulla: Controls Involuntary actions such as breathing, blood preassure, salvation and vomitting.
Pons: It takes part in respiration. It relays impulses between different parts of the brain.
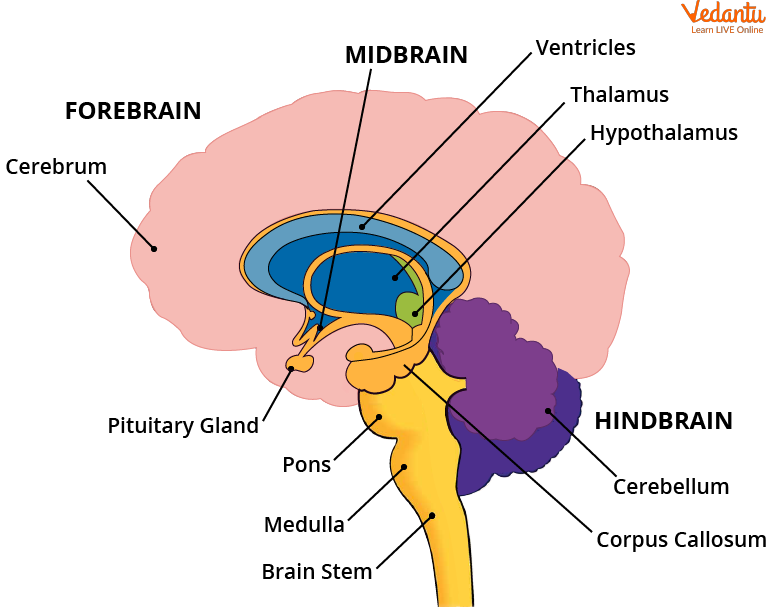
Protection of the Brain
The body is designed in such a way that the brain sits inside a bbony boc called cranium and contained in a fluid filled ballon which provides as an shock absorption.
Protection of the Spinal Cord
A hard bumpy structure called vertebral column or backbone present at the back protects the spinal cord
Immediate response to Stimulus
Plants use electrochemicals to convey information from cell too cell. Plants do not have specialised tissue for conduction of information
Plants cell change their shape by changing the amount of water. Shrinking or swelling.
Tropic Movement
Movement due to growth, these are directional movements in plants due to which the plants appears to move.
Phototropic Movement
Stimulus: Light
Movement of plant part in response to light.
Shoots : Towards lights
Roots : Away lights
Geotropic Movement
Stimulus: Gravity
Movement of plant part in response to Gravity
Shoots: Towards / Upwards Gravity
Roots: Away / Downwards Gravity
Hydrotropic Movement
Stimulus: Water
Movement of plant part in response to water.
Roots: Towards water
Chemotropic
Stimulus: Chemical
Movement of plant part in response to chemical.
Ex: Growth of pollen tube towards ovules during fertilisation
Hormones
A chemical compound, which diffuse all around the original cells and is detected by the other cells using special molecules.
Why chemical communications and not electrical impulse?
Cells cannot continously create and transmit electricaal impulses. Thus, most organism use chemical communications since it reaches all the cells.
Plant hormones : Auxins
Synthesised at the tip of the shoots.
Helps the cells grown longer.
They diffuses towards the shady side of the shoot simulating the cells.
Plant hormones : Gibberellins
Help in the growth of the stem and flowers
Plant hormones : Cytokinins
Promote Cell division.
Highest concentrations: Occur in seeds and flowers
Plant hormones : Abscisic Acid
Responsible for wilting of leaves.
Endocrine Glands
Other name: Ductless gland
Secrete hormone that act on distant sites known as Target organs or cells
Hypothalamus
Plays an important role in the release of many hormones.
Ex: When growth hormone is low, it releases growth hormone.
Controls urine, temperature and hormone production control.
Pituitary gland
Secretes: Growth hormone
Regulates overall growth and development.
The pituitary gland's main function is to produce and release hormones that regulate many bodily functions. It's often called the "master gland" because of this.
Pineal Gland
Secretes: Melatonin
Regulates: elevated levels at night (during dark hours) and low levels during the day (during light hours).
Function : to receive information about the daily light-dark (day-night) cycle from the retinas in your eyes
Adrenal Gland
Secretes: Adrenaline
Its secreted directly into the blood and carried to different parts of the body.
Involves preparation of fight and flight response.
It works in stress situations, it targets hearts, which makes it beat more.
Thyroid Gland
Secretes: Thyroxin
It helps in regulating carbohydrates, proteins, and fat metabolism.
Iodine is necessary for synthesis of thyroxine.
Parathyroid Gland
Secretes: parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Function: regulates the amount of calcium in the blood.
This hormone is essential for healthy bones, muscles, and nerves.
Thymus
Function : to produce and mature T lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell that helps the body fight infection.
Location : in the chest, between the lungs, and in front of the heart.
Testes Gland
Secrete: Testosterone
Changes associated with puberty and Development of Male Organs
Ovaries
Secretes: Oestrogen
Development of Female Sex organs and Regulates menstrual cycle.
Pancrease
Secretes: Insulin
Regulates blood sugar level
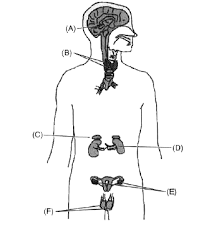
A - Pituitary
B - Thyroid
C -Adrenal
D - Pancreas
E - Ovary
F - Testis.
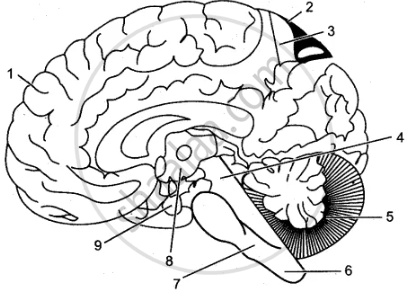
Cerebrum
Gray matter
White matter
Mid brain
Cerebellum
Spinal Cord
Medulla Oblongata
Hypothalamus
Pituitary body
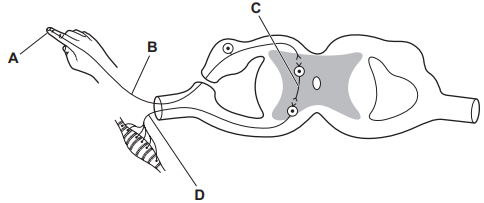
A is the receptor,
B is sensory neuron
C is a Synapse
D is an effector muscle connected to a motor neuron.