Chpt18 SICECNE
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
A ___ is a group of individuals of the same species that mate and produce offspring
Population
A ___ ___ consists of all genes present in a population, including all alleles for each gene
Gene pool
Why do members of a population share a gene pool?
Because they interbreed with one another
The number of times an allele occurs in a gene pool, as a percentage of the total occurrence of all alleles for that gene in that gene pool, is called ___ ___
Allele frequency
When calculating allele frequency, dose it really matter whether the trait is recessive or dominant?
No

What is this circle graph showing us in the mice population?
Allele frequency
What can we say for sure is happening when there is a change in allele frequencies in a population over time?
Evolution
A change in allele frequency over time is caused by-
Natural selection
When an individuals genotype is combined with environmental conditions during its lifetime, what is produced?
Phenotype
A ____ includes all physical, physiological, and behavioral characteristics of an organism, such as eye color or height.
Phenotype
Natural selection dose not act on an individuals genotype, it instead acts on its-
Phenotype
Mutation, genetic recombination during sexual reproduction, and lateral gene transfer all produce-
Genetic variation
What type of genetic variation is a heritable change in genetic information?
Mutations
Different from a mutation, what type of genetic variation is the reason we differ so much from our parents?
Genetic recombination
What process during meiosis where paired chromosomes swap lengths of DNA at random is a mechanism to produce genetic recombination?
Crossing over
When genes are pass between two individuals without an offspring being produced, is a type of genetic variation called
Lateral gene transfer
A single gene that controls only two or three alleles can be categorized as?
A single-gene trait
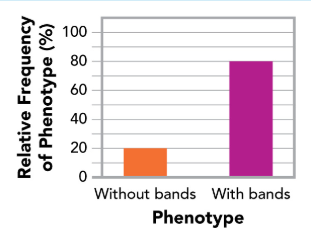
This graph is displaying what kind of trait?
A single-gene trait
Traits controlled by two or more genes, each gene having two or more alleles, is called?
Polygenic trait
Unlike single gene traits, what can produce a wider range of both genotypes and phenotypes?
Polygenic traits
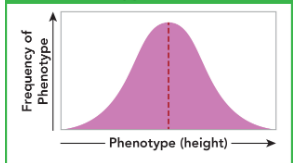
This is an example of which kind of trait?
Polygenic trait
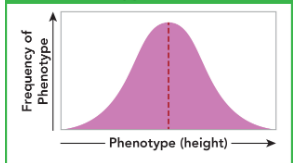
On another note, polygenic traits when graphed can also be known as?
Normal distribution
When natural selection produces a change in allele frequencies, what type of trait is it acting on?
Single-gene traits
When natural selection affects the relative fitness of phenotypes, what type of trait is it acting on?
Polygenic traits
What are the three types of selection for polygenic traits?
Directional selection, stabilizing selection, and disruptive selection
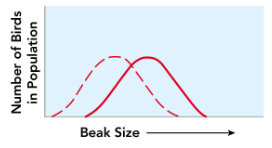
This is an example of?
Directional selection
This is an example of?
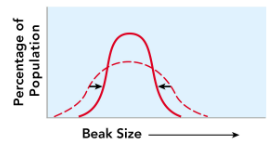
Stabilizing selection
This is an example of?
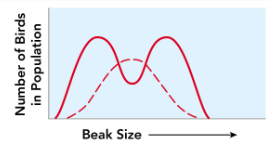
Disruptive selection
What type of selection results in the range of phenotypes shifting
Directional selection
Which type of selection results in the narrowing of the curve?
Stabilizing selection
What type of selection can result in one species breaking off into two separate species?
Disruptive selection
What type of selection is the most damaging to intermediate phenotypes?
Disruptive selection
When allele frequency is changed at random, it is referred to as
Genetic drift
Genetic drift is more likely to happen in a large or small population?
Small
What can cause a dangerous allele to be more frequently passed down, simply by chance?
Genetic drift
Say that a natural disaster were to cause a population to suddenly and unexpectedly reduce in size. What kind of genetic drift would this be?
Bottleneck effect
___ ___ (a type of genetic drift) is a change in allele frequency following a dramatic reduction in the size of a population.
Bottleneck effect
Migration of a small subgroup in a population which causes a change in allele frequencies is best known as?
Founder effect
What would you call a population that is not evolving and allele frequencies in its gene pool are not changing?
Genetic equilibrium
What is the principle that states allele frequencies in a population should remain constant unless one or more factors causes those frequencies to change?
Hardy-Weinberg principle
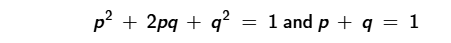
In an equation such as this, which variable represents the allele frequency of the dominant allele?
P
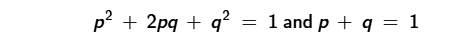
In an equation such as this, which variable represents the allele frequency of the recessive allele?
Q
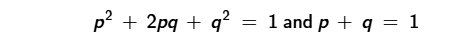
In an equation such as this, what dose 2pq represent?
The frequency of heterozygous individuals
When females of any animal species select mates based on size, strength, or coloration, it is simply known as what type of selection?
Sexual selection
A factor that can cause a change in allele frequency, where genes are moved in and out of the population due to immigration or emigration, is called?
Gene flow
Random mating, a large population, no gene flow, no mutations, and no natural selection are all the criteria for what?
Genetic equilibrium
When we refer to the origin of a new species, we simply use what term?
Speciation
What can reproductive isolation lead to?
Populations splitting into two different species
What are the types of reproductive isolation?
Behavioral, geographic, and temporal
What type of isolation is it when two populations are separated by geographic barriers like rivers, mountains or large bodies of water?
Geographic isolation
When two populations that were once able to interbreed evolve differences in courtship rituals or other behaviors, what type of isolation can ocuur?
Behavioral isolation
When two or more species reproduce at different times, like how pollination cant occur when two species of flowers bloom at different types of the year, is called what type of isolation?
Temporal isolation
What is the criteria for genetic equalibrium?
Large population, random mating, no gene flow, no mutations, and no natural selection
What does a molecular clock use to estimate the time two species have been evolving independently?
Mutation rates in DNA
When using a molecular clock, how will you know if a large amount of time has passed since two species shared a common ancestor?
There are major differences in DNA sequences
One way new genes can evolve is through ___, followed by modification, of existing genes.
Duplication
During meiosis, when paired chromosomes swap in a process called crossing over, what will result when an unequal swap gives one chromosome in the pair an extra copy of one or more genes?
The evolving duplicated genes may gain new functions over time
In other cases, gene ___ has allowed copies of genes to acquire completely new functions.
Duplication
Small change in ___ gene activity during embryological development can produce large changes in adult animals.
Hox
A small change in what type of gene can account for a major evolutionary difference between two important animal groups?
Hox genes
What repeating process does a molecular clock rely on to mark time?
Mutation
What does it mean if there are more differences between DNA sequences of two species?
More time has passed since they shared a common ancestor
Why must a population be large to maintain genetic equilibrium?
To avoid genetic drift
A ___ is a population of physically similar, interbreeding organisms that do not interbreed with such other groups.
Species
When does crossing over occur in meiosis?
Prophase I