AP Bio Unit 1: Chemistry of Life (Old)
1/39
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Electronegative
Oxygen is slightly ______
Hydrogen Bond
A weak bond between two molecules resulting from an attraction between differently charged molecules.
Valence Electrons
The outer electrons of an atom
Cohesion
Attraction between a molecule and molecules of the same type
Adhesion
Attraction between a molecule and different molecules
Greater
In water molecules, cohesion is [Greater/Weaker] than adhesion
Surface Tension
Water has this property due to it having more adhesion than cohesion
Solvent
Water is a good _____ due to its polarity
It is able to dissolve other substances
Polar
Molecules like water that have slight charges on different areas depending on the atom
Nonpolar
Molecules like ethane that do not have a charge
Hydrophobic
No attraction to water
Hydrophylic
“Water loving”— attraction to water
Macromolecules
Very large molecules essential for biological processes
CHO
Elements that compose carbohydrates
Carbohydrate
Represented as long chains or ring structures, this macromolecule is a major fuel and building material
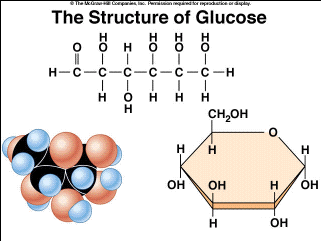
Monossacharide
The smallest form of a carbohydrate
CHONS
Elements that compose proteins
Protein
This macromolecule is composed of amino acid linkages called peptides
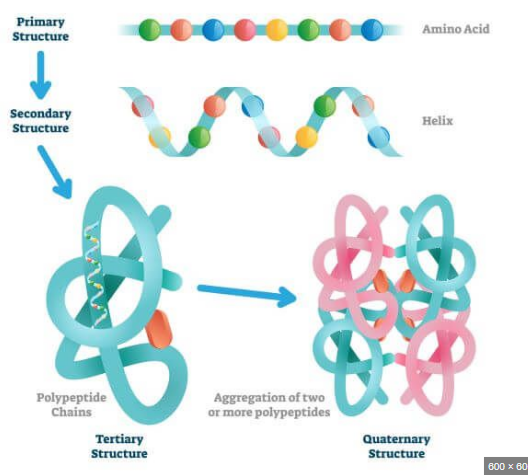
Primary Structure
Sequence of a chain of amino acids
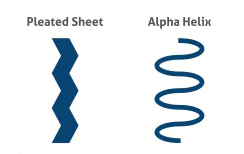
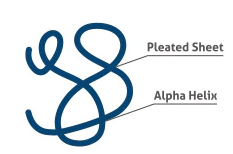
Secondary Structure
Hydrogen bonding of the peptide backbone: fold into a repeating pattern (alpha helix or pleated sheets)
Tertiary Structure
Three-Dimensional folding pattern of a protein due to sidechain reactions
Quaternary Structure
Proteins of more than one amino acid chain

Lipid
This nonpolar macromolecule is a fat composed of long chains of hydrocarbons. It is energy rich
Covalent
This is the type of Bond lipids form when they join and release H2O
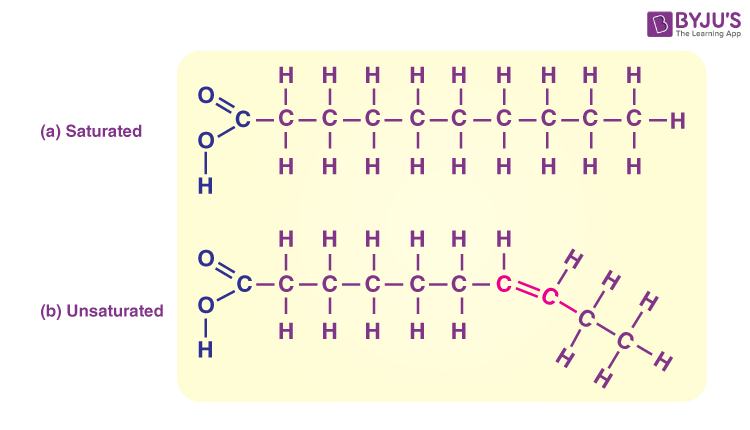
Saturated
When a fatty acid is [saturated/unsaturated], it only has single bonds so it can pack closer together
Unsaturated
When a fatty acid is [saturated/unsaturated], it has double bonds which change the direction of the molecule, preventing it from being able to pack closely together
Nucleotides
Thousands of linked monomers that make up a nucleic acid
CHO
Elements that compose lipids
CHONP
Elements that compose nucleic acids
Nucleic Acid
This type of macromolecule directs the formation of proteins and stores and transfers information. It is made of many linked nucleotides. DNA, RNA
Ribose
A type of simple sugar
Deoxyribose
Simple sugar w/out hydroxyl group
Enzyme
A biological catalyst → lowers the amount of energy needed for a reaction
Substrate
The thing that enters the enzyme
Active Site
The place on an enzyme that takes in a substrate
Product
When an enzyme completes its process on a substrate, this is the result
Catalysis
Acceleration of a chemical reaction (by an enzyme)
Competitive Inhibition
Another molecule competes with the substrate for the active site
Noncompetitive Inhibition
An inhibitor binds to another site and closes the active site
Allosteric Enzymes
Enzymes that change shape in response to another molecule