Histology
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
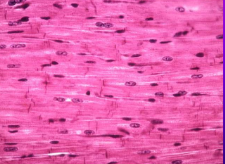
simple squamous
Flat, irregularly shaped, thin
Found in blood vessels and membranes
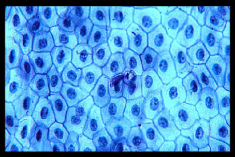
stratified squamous
Flat and irregular on free surface
Protect against abrasion
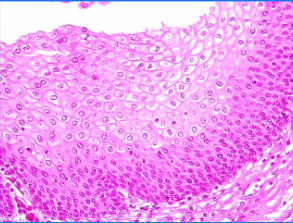
simple cubidal
Heavy and stout
Found in rings
Found in organs that play a secretory role
Glands
Kidneys
Ovaries
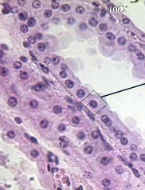
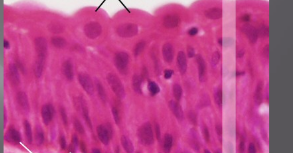
simple columnar
Protective layer on internal surface of organs (stomach, intestines, gallbladder)
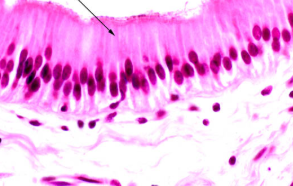
pseudostratified ciliated columnar
One layer but appear as more because so closely compacted together
Cilia on free surface
Nuclei found in different locations
Found in lungs, pharynx, trachea
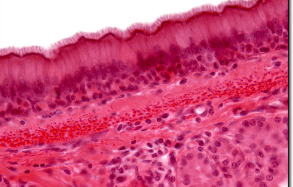
transitional
If filled with urine, stretched so squamous-like
If empty, cells appear columnar
Found in ureter, urethra, bladder
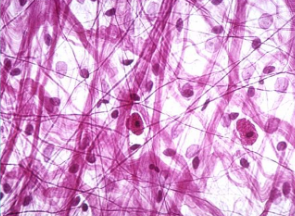
connective tissue
Most widely distributed tissue
Holds us together
Highly vascular
Matrix (intercellular space) may contain fibers
Three types of matrix
Connective tissue proper: amorphous
Cartilage (bristle): firm but flexible
Bone: hard and durable, made of salts
tendons
Dense connective tissue
Fibroblasts manufacture the fibers
Connect muscle to bone
ligaments
Dense connective tissue
Fibroblasts manufacture the fibers
Connect bone to bone
More elastic
areolar
Connective tissue proper
Found below the epidermis
Holds skin to muscle and holds organs in place
Cells are known as fibroblasts and produce fibers
Looks like a spider web
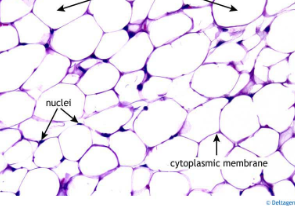
adipose
Fat tissue
Contains a large vacuole of oil
Functions
Energy
Absorb shock
Insulate and maintain temperature
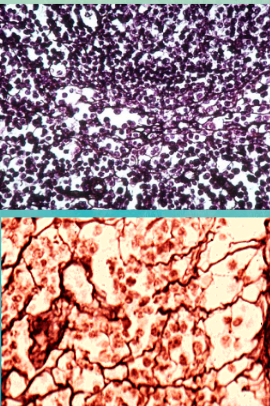
reticular connective tissue
Consists of a delicate network of reticular fibers
Forms the stroma or internal supporting network in lymph organs
blood
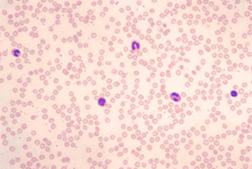
blood: erythrocytes (red blood cells)
Anucleated made in bone marrow
Hemoglobin carries oxygen
blood: leukocytes (white blood cells)
Larger and nucleated
5 types (3 made in bone marrow and 2 in lymph)
Phagocytize bacteria
blood: thrombocytes (platelets)
Smallest
Function in coagulation
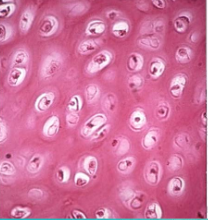
hyaline cartilage
Most common
Predominant model for the formation of our skeleton
Cell known as chondrocyte and sits in a lacunae
No fibers in the matrix
Found in nose and the trachea
elastic cartilage
Looks like hyaline but has elastic fibers in the matrix
Found in ear and epiglottis
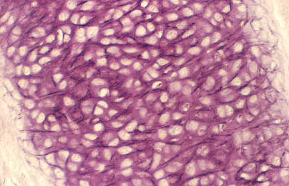
fibrocartilage
Contains collagen fibers
Found in pubis symphysis and intervertebral discs
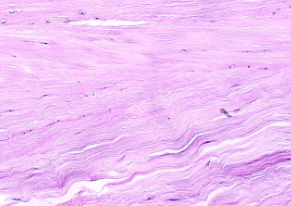
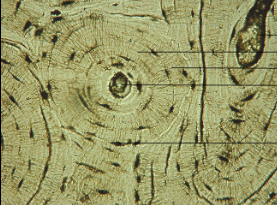
compact bones
Circular like tree rings
Cells sit in a lacuna
Central haversian canal
Matrix made of calcium and phosphorus salts
osteoblast
bone forming cell
osteocyte
maintains bone
osteoclast
break down bone
muscle
Functions in movement
Contractility: ability to shorten
Elasticity: ability to retain original shape
Irritability: ability to be excited
Proteins enable muscle to contract
Needs stimulus
skeletal muscle
Also called striated and voluntary
Attached to the skeleton
Part of the Somatic Nervous System
Under voluntary control (PNS)
Striations produced from actin and myosin proteins
Multinucleated

smooth muscle
Involuntary
Lacks striations
Controlled by autonomic nervous system (involuntary)
Oval shaped cells
One central nucleus
Found in GI tract and blood vessels
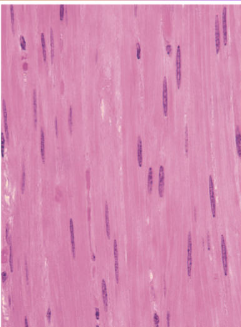
cardiac muscle
In heart ONLY
Autorhythmic cells -Autonomic Nervous System plays a role (sleep vs. exercise).
Striations not as distinct
Branched cells with 1 nucleus
Intercalated discs strengthen the connection between cells
Do not require nervous stimulation
Autonomic nervous system can change the pace