Evidence for Evolution
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
tung tung tung sahur
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Biological diversity
The variety of living things
Evolutionary theory
Scientific explaination that is a collection of scientific facts, observations, and hypotheses that account for the diversity of life.
Evolution
( or change over time)
the process by which modern organism have descended from ancient organisms.
Theory
A well-supported testable explanation of phenomena that have occurred in the natural world.
The Big Bang theory
states that the universe began about 15 billion years ago as a dense tiny concentration of matter. That exploded violently. Energy and new forms of matter created by this explosion spread into space, gravitational attraction drew the matter together, forming stars and planets
Origin of Earth
Earth and other planets in this solar system develop 4.5 billion years ago.
From gases and dust orbiting the Sun gravity caused local accumulations of dust to form planets.
Solid matter was layered …
according to density. Heavy elements (iron) in the core, lighter elements formed a solid crust at Earth’s surface.
Radioactive decay …
deep in Earth heated the core
Magma
Molten rock inside Earth core that rose to the Earth’s surface (now lava)
Volcanic eruptions …
forced gases like nitrogen and water vapor out of the magma, that formed the atmosphere (no oxygen)
Earth condition 4.5 billion years ago
Surface covered with hot seas, kept by the molten Earth. Steam from sea formed huge clouds. Clouds precipitated to Earth in violent rainstorms, with lighting. On land active volcanoes spouted gas, steam and lava.

The early atmosphere and oceans contained … (Oparin model)
ammonia, water vapor, methane, and hydrogen.
What provided the energy to split molecules into atoms? (Oparin model)
Lighting, Earth’s heat, and Sun’s UV radition
The atoms bonded together to form … (Oparin model)
small organic compounds, carbon-containing molecules, characteristics of living things.
These molecules accumulated … (Oparin model)
in the ocean and formed a "primodial soup”, that after a long time formed globules of molecules that can reproduce and were the first life on Earth.
What did Miller and Urey do (hint: test)?
tested Oparin’s hypothesis.
Miller & Urey experiment
Filled a apparatus with water vapor, methane, hydrogen, and ammonia, passed an electric spark (lighting) through the mixture, and heated the mixture (earth’s heat). A liquid trap collected molecules formed in the apparatus.
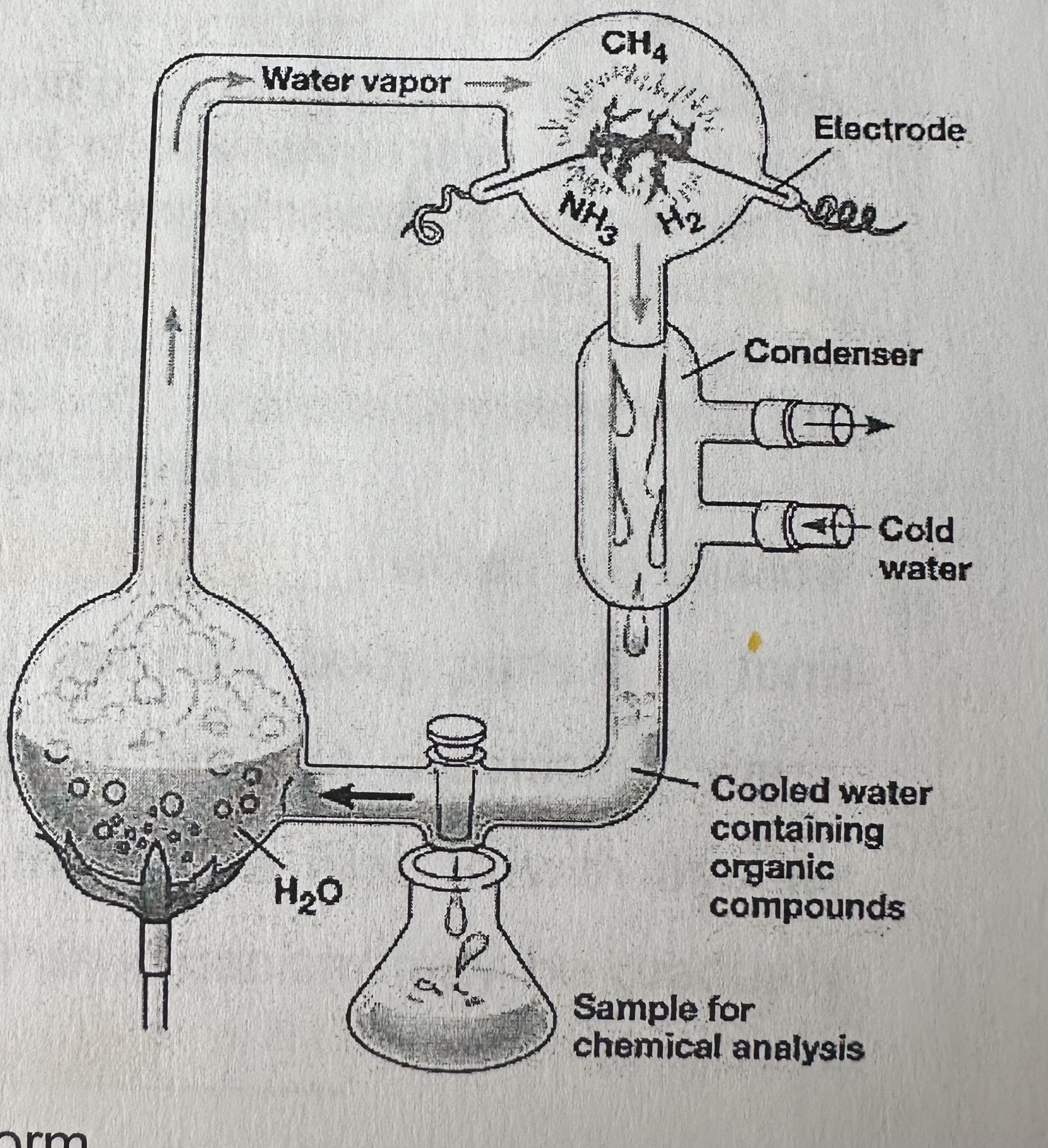
After seven days …
they analyzed the liquid and found amino acids (building blocks of proteins) and other organic compounds.
The first cells
“protocells”
Probably resembled anaerobic bacteria cuz no oxygen in atmosphere. Probably lived off organic compounds from environment.
Cells capable of …
photosynthesis like cyanobacteria and other bacteria developed later about 3 billion year ago.
These organisms …
made their own food and gave off oxygen that gradually accumulated in the atmosphere and allowed for complex aerobic life (capable of using oxygen to obtain energy)
Fossil
Any preserved part or trace of an organism that once lived.
A fossil is formed when …
all or part an organism is buried before it can be eaten or decompose.
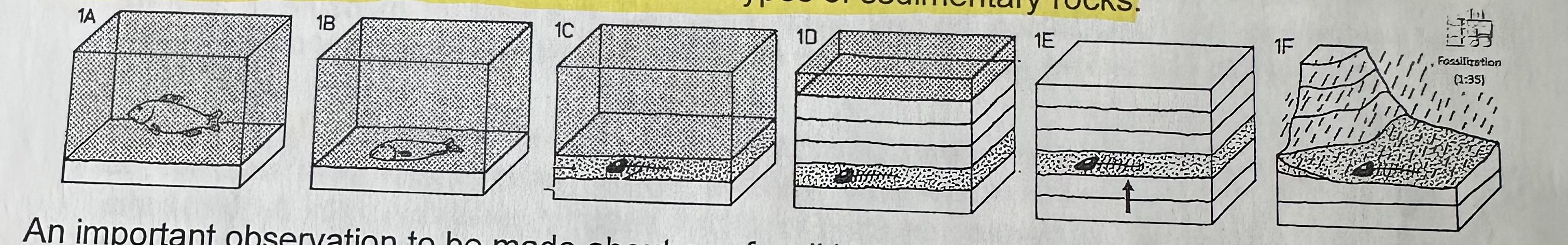
Most fossils are found in … (KNOW)
sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rock
forms from sediment (mud, silt, sand, and clay) that deposit in layers. High pressure on particles deep in sediment that become cemented together to form sandstone, limestone, shale and others.
Important requirements for fossilization …
are quick burial and presence of some hard parts. If not bacteria and other animals or processes that cause erosion can destroy it.
Meaning that not every organism …
becomes fossilized.
Imprints
Shallow, impressions in developing rock from soft body structures like feathers or leaves.

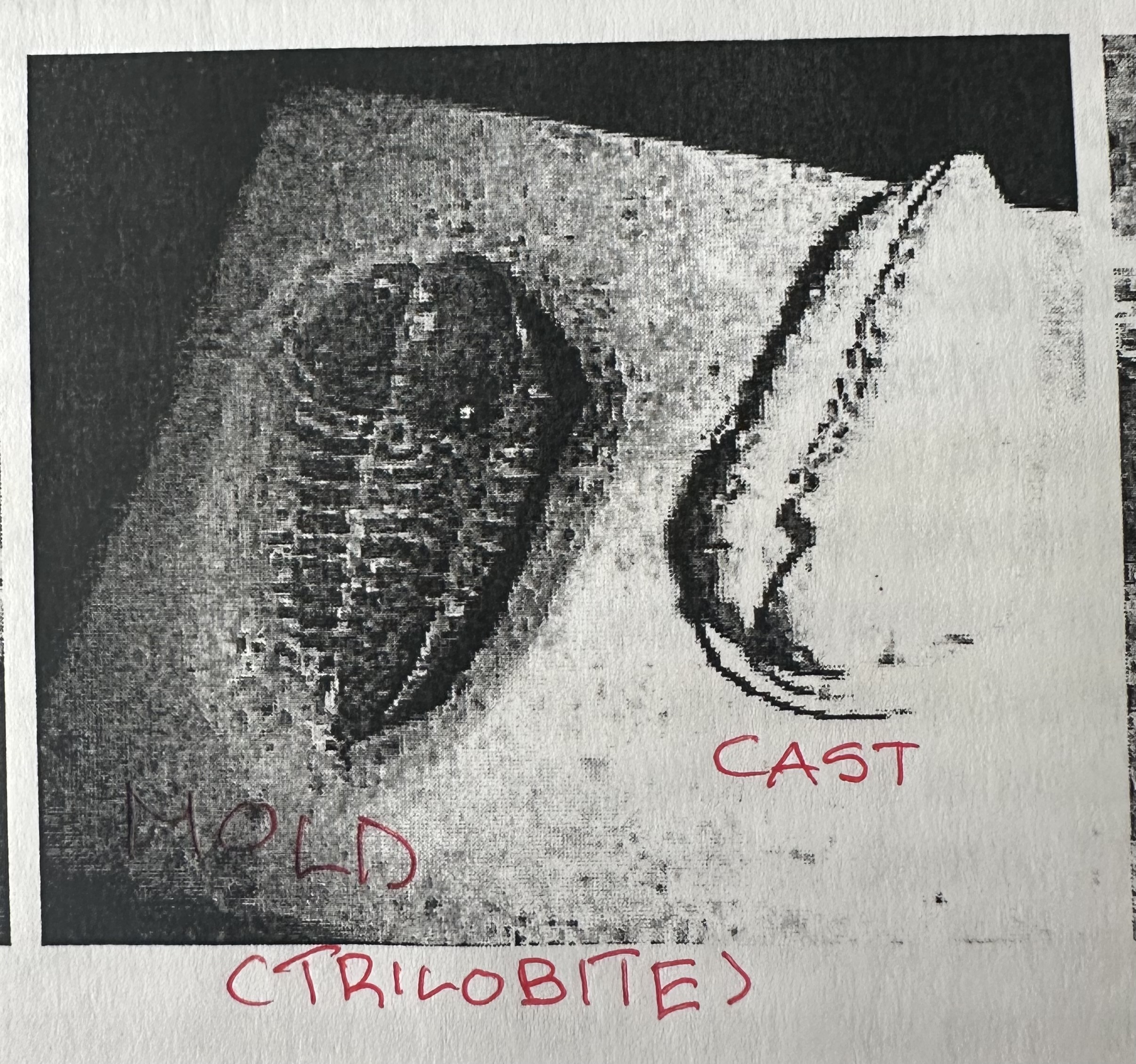
Molds (KNOW)
Deeper depressions in rock shaped like organism’s parts from teeth, shells, bones and other hard body parts.
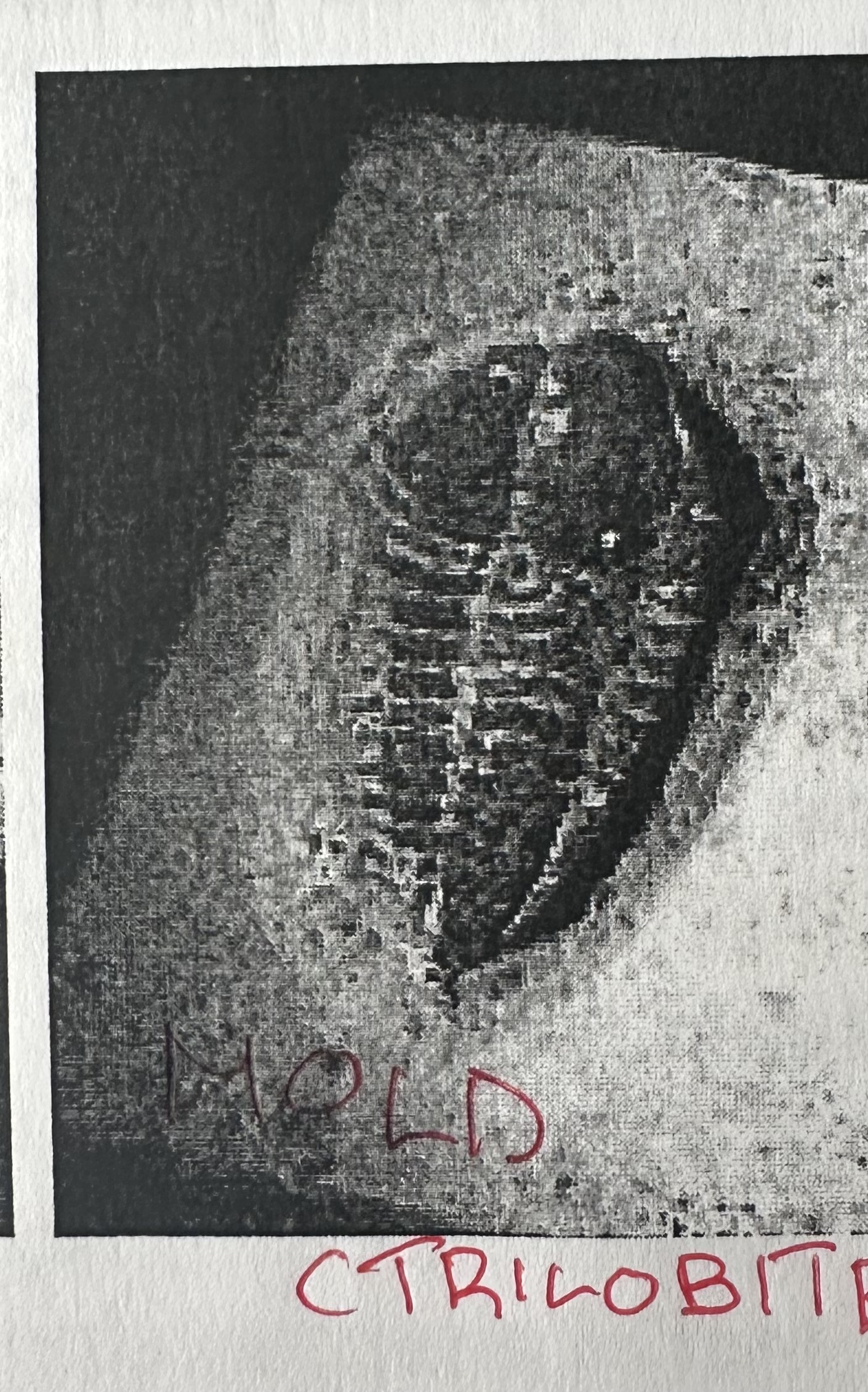
Casts
formed from the mold being filled with another material due to the organism decomposing
Petrified wood
fossils that are the hard parts of an organism being gradually replaced by minerals.

Original Skeletal Material
hard parts of organisms that are preserved as the original material. Invertebrate shells (calcium carbonate, silica, chitin) or vertebrate bones (calcium phosphate).

Amber Entombment
Certain trees have a stick resin that small insects and other small organisms may be trapped in, which after burial may harden into amber.

Peat Bogs
Sphagnum moss forms thick “peat” in bogs called Peat Bogs that are very acidic prevents decomposition of organisms.
Tar Impregnation
Tar pits are excellent sites for fossilization.
Rancho La Brea in southern California yielded rich collections of vertebrate bone, wood, etc.
Small pits yield perfectly preserved insects and insect larvae.
Refrigeration
During the ice age animals (eg. mammoths) fell into crevasses in frozen terrain or became trapped in permanently frozen soil. Some have been discovered perfectly preserved.
Fewer then … of the animal species …
10%, are likely to be preserved as fossils.
Why are fossils so rare? KNOW
Very hard to find
No quick burial → broken down
Soft-bodied & lack hard parts
Very hard to find
Most fossils are buried under tons of rock and can only be discovered by chance when they are uncovered (usually by the natural forces of weathering and erosion). Plus they’re only found in sedimentary rock
No quick burial → broken down
If not rapidly buried after death, quickly broken down by scavengers (body parts spread apart) and bacterial decay.
Vast majority of living species are insects (1.5 million species 1 million are insects). Rarely preserved as fossils live on dry land and unlikely to be buried by sediment after death.
Soft-bodied & lack hard parts
Many organisms are soft-bodied and lack hard parts. Only preserved if isolated from oxygen immediately aft. death occurs when rapidly buried in fine-grained sediment in water. Only happens in rare, isolated environements
Relative dating
age of fossil determined by position in sedimentary rock. In undisturbed sedimentary rock, most recent fossils found in upper layers and older fossils in lower layers. Can determine relative age.
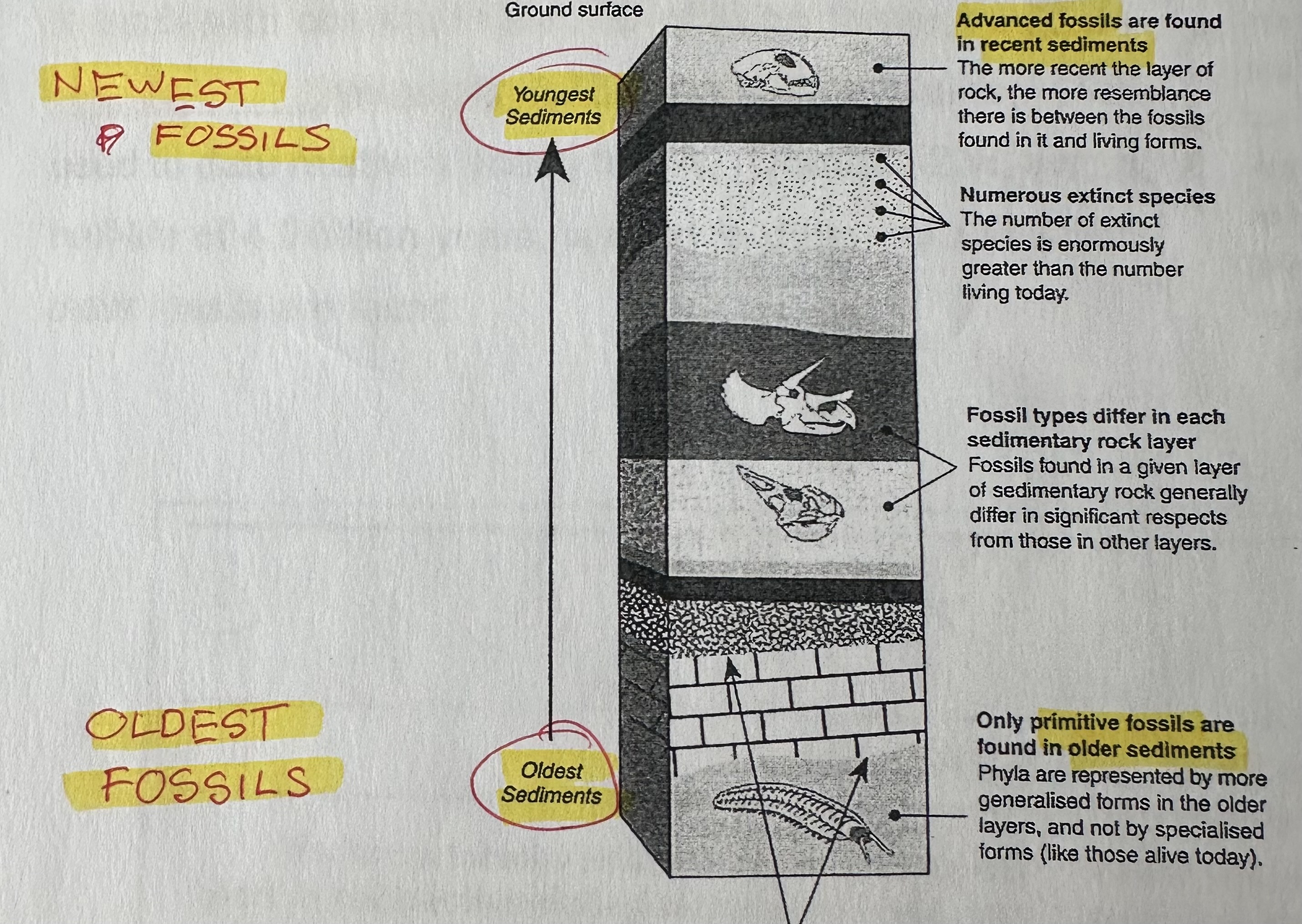
Flaw with relative dating
New surfaced fossils can go down deeper down with erosion. Possibly found with olders fossils and confuse the age of both fossils.
Absolute dating
Determaine exact age of fossils using radioactive isotopes (carbon-14) that decay into stable elements (nitrogen-14) at a constant rate (half-life)
Half life
Amount of time for specific radioisotope to decay half of its original mass (before half life). Carbon-14 half life is 5,730 years, uranium-238 = 4.5 billion yeras.
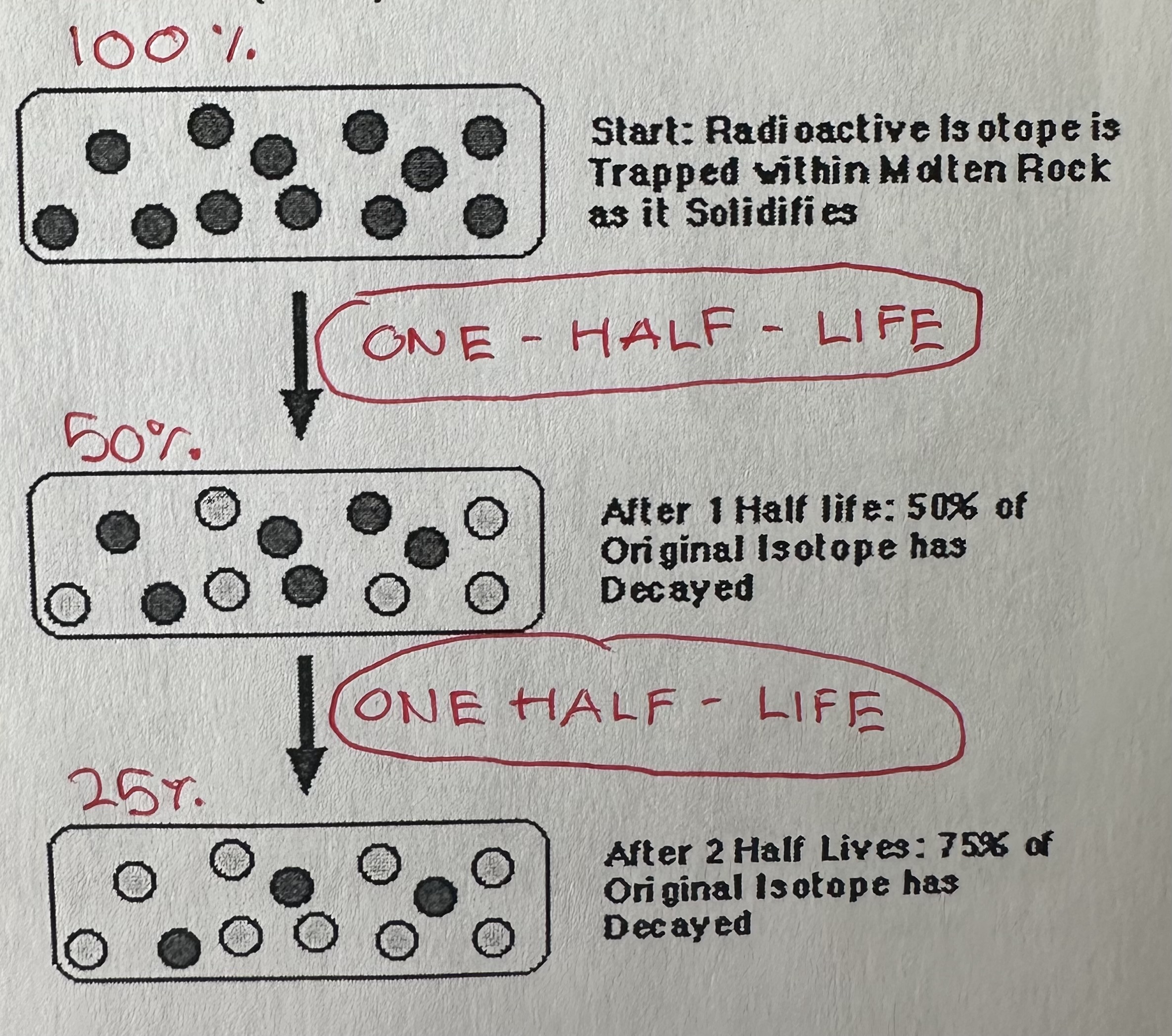
Carbon-14 is used to date fossils because …
it is replenished when alive but stop when die, 14C decays but 12C remain stable. Can determine age by comparing 14C and 12C (assuming 14C:12C living tissue today same as back then)
A fossil containing half 14C of living tissue would be …
5730 years old
A fossil with one-fourth 14C of living tissue would be
5370 × 2 = 11640 years old
Era KNOW
4 large units that is Earth’s 4.5 billion years.
Precambrian → Palezoic → Mesozoic → Cenozoic
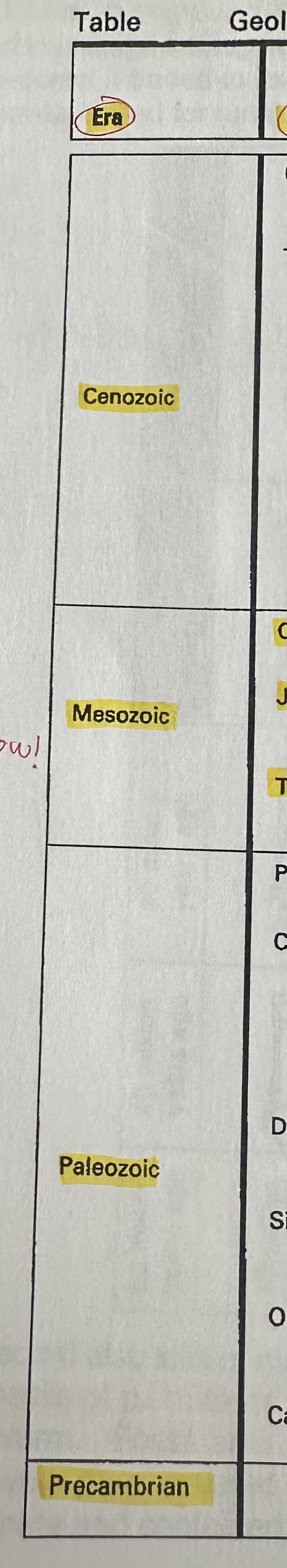
Period KNOW
Era further subdived, Mesozoic periods are: Triassic → Jurassic → Cretaceuos

Epoch
Period further divided in smaller time spans
Paleontologist
Scientists who study fossils
Fossil record
Millions of fossils collect by paleontologist through many years, represents the collective history of Earth’s organisms.
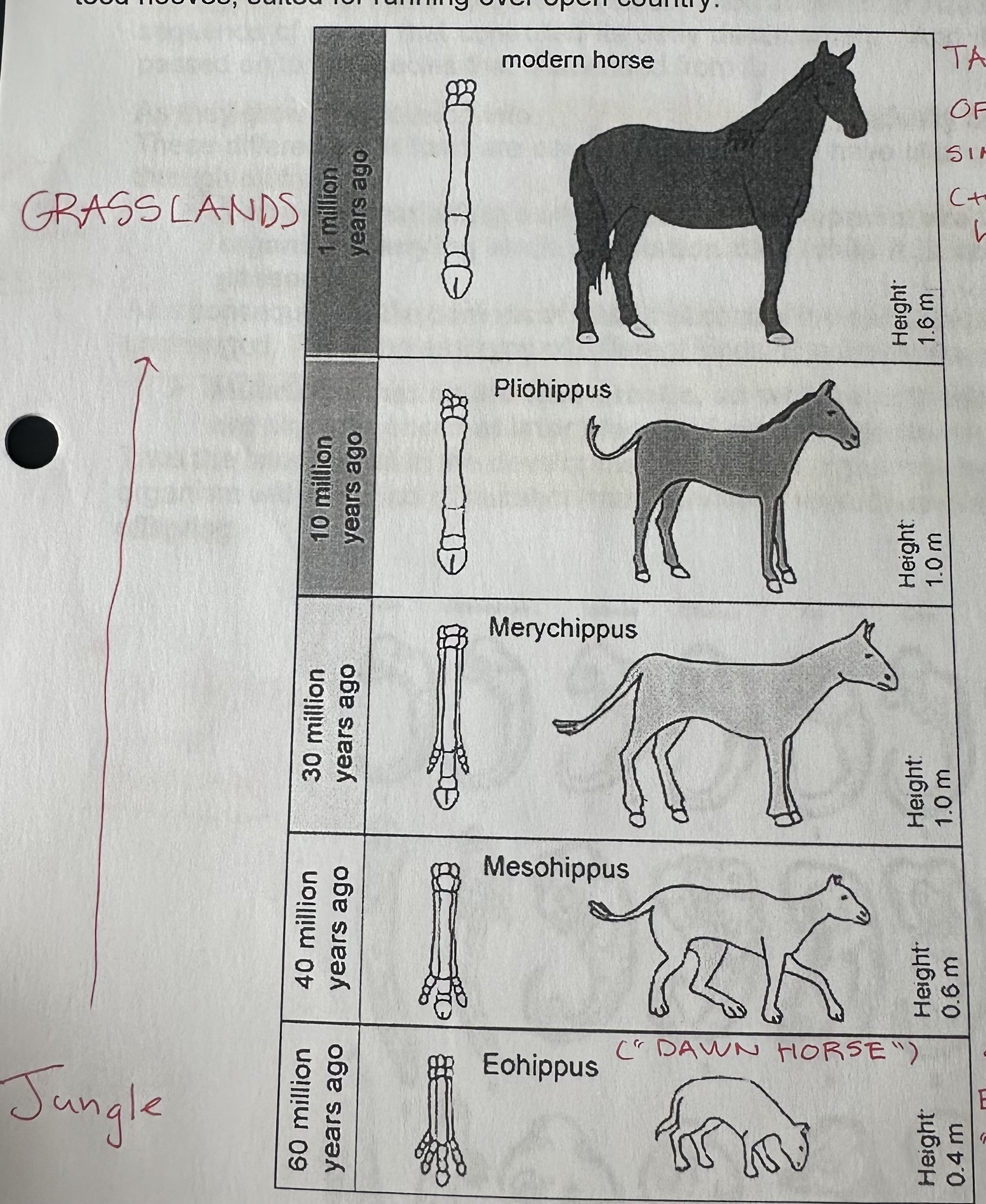
Horse evolutionary history
60 millions years the horse evolved from “dawn horse” a dog-like, small, eyes forward, with a “dog paw” (4 toes), that lived in jungles to tall (2m), eyes on side, single toe with hoof, that are adapted to hard tall grass plains.
Fossil records also tells …
major changes in Earth’s climate and geography. Fossils of palm trees found in the Antarctic (climate was once warm). Fossil shark teeth found in Arizona (desserts of American Southwest once covered by ancient seas.
Embryos
Organisms in the early stages of development
Comparative embryology
The study that compares embryos of different species, found similarities that support the theory of evolution.
Species with embryo similarites share …
common genetic instructions for embryo development, and therefore share a common ancestor.
Example of comparative embryology
Vertebrates (animals with backbones) have genes active during early embryological development that are the shared heritage from a common ancestor.
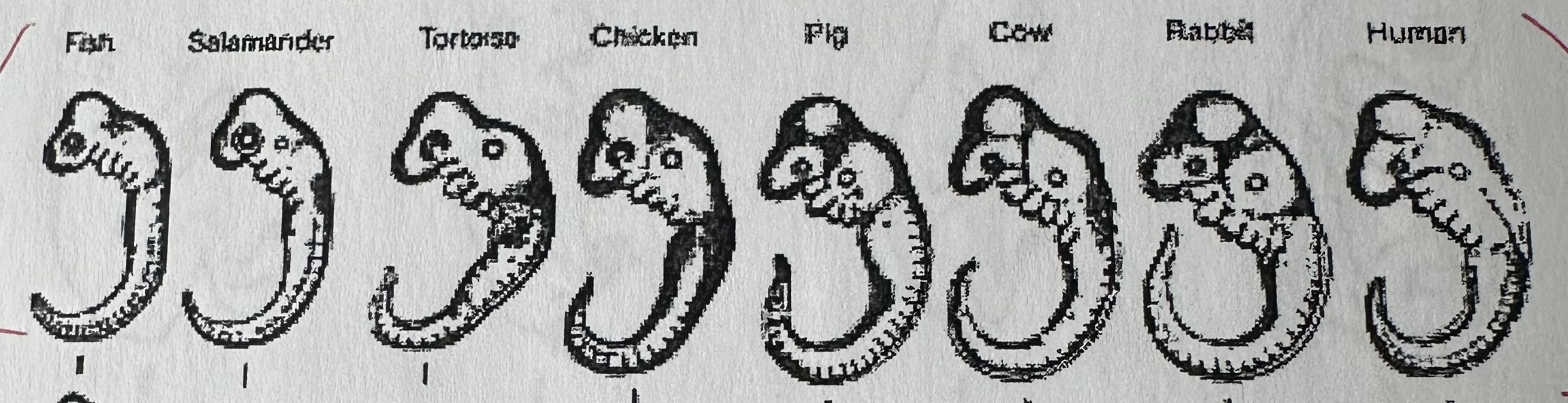
The common ancestor of …
these diff. species had a particular sequence of genes (controlled early development) and has been been passed on to species that descended from it.
Fetus
Developed embryos, become more and more dissimilar caused by genes that have changed during evolution through mutations.
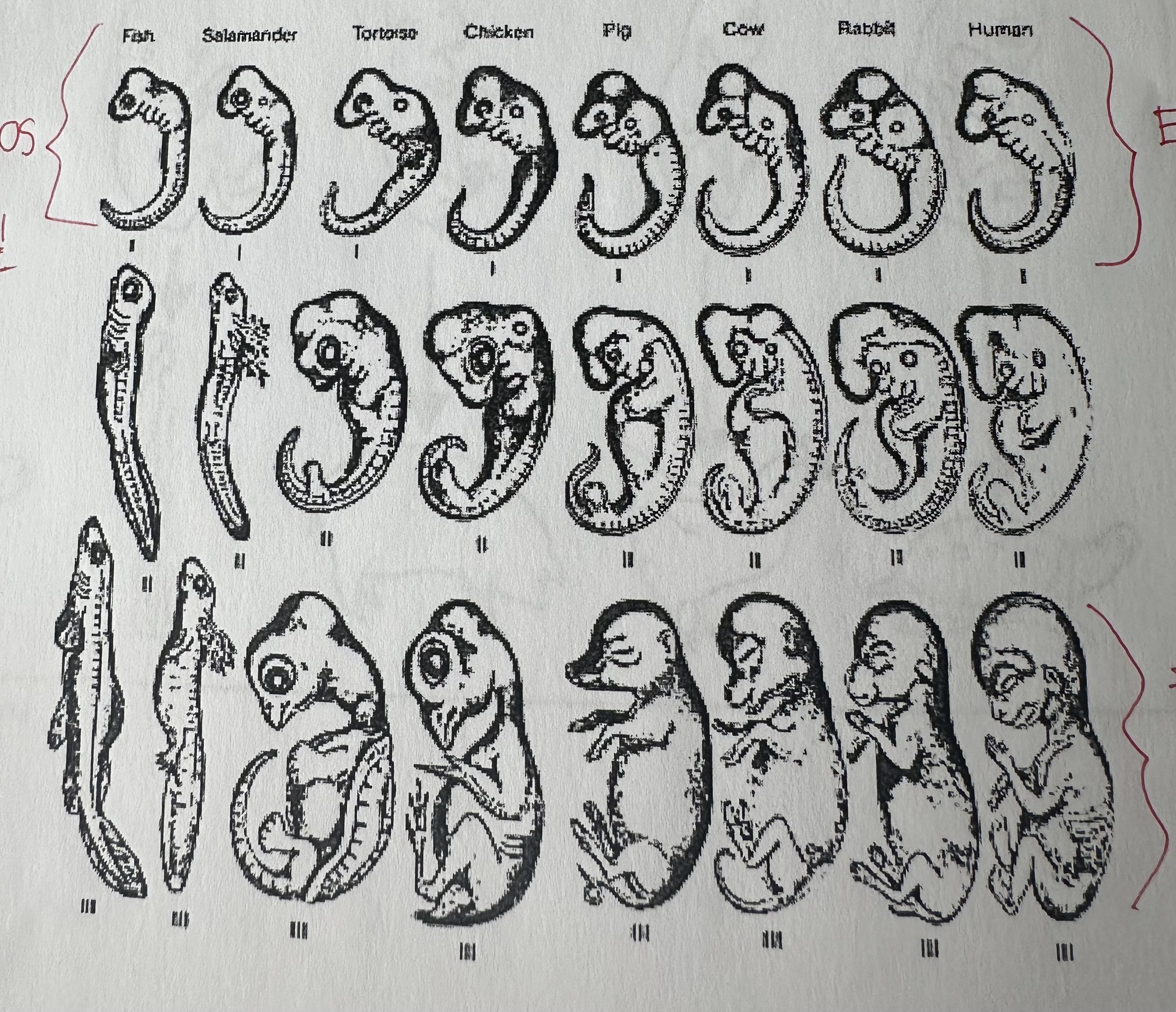
Why do embryos look similar? KNOW
Mutations that affect embryos are likely to be lethal. Organism with mutation dies as an embryo and genes are not passed on.
The genes that control embryo development …
remain relatively unchanged (is why embryos of diff. animals look alike).
Fetus are …
tougher so mutations that occur (useful or harmful) survive and reproduce and pass the changes to offsprings ( is why later development of related organisms begin to differentiate)
Homologous structures
Body parts with same basic structure, whether function is diff. or not.
Examples: Bat wing, human arm, and whale flipper
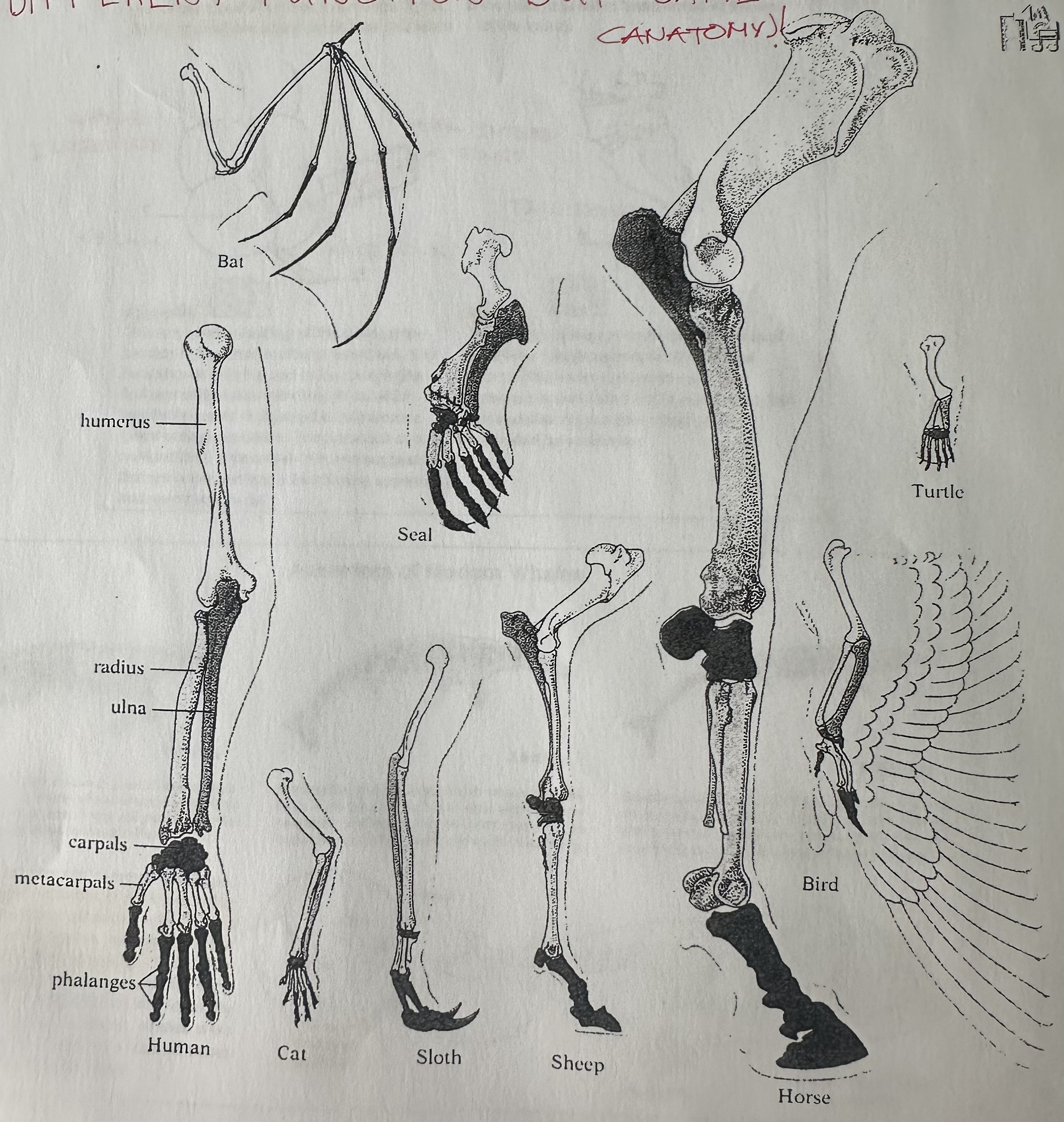
Homologous structures found in diff. organisms suggest …
that these organisms have a common ancestry.
Clumps of cells on diff. animal embryos that develop into limbs look …
quite similar, but embryo mature limbs grow into arms, wings, legs and flippers (different “form” and function)
Different forelimbs came from a …
series of evolutionary changes that altered the structure and appearance of the arm and leg bones of ancient animals.
Final structure of limbs of diff. species are …
adaptations that enable each species to be successful in their (different) environments.
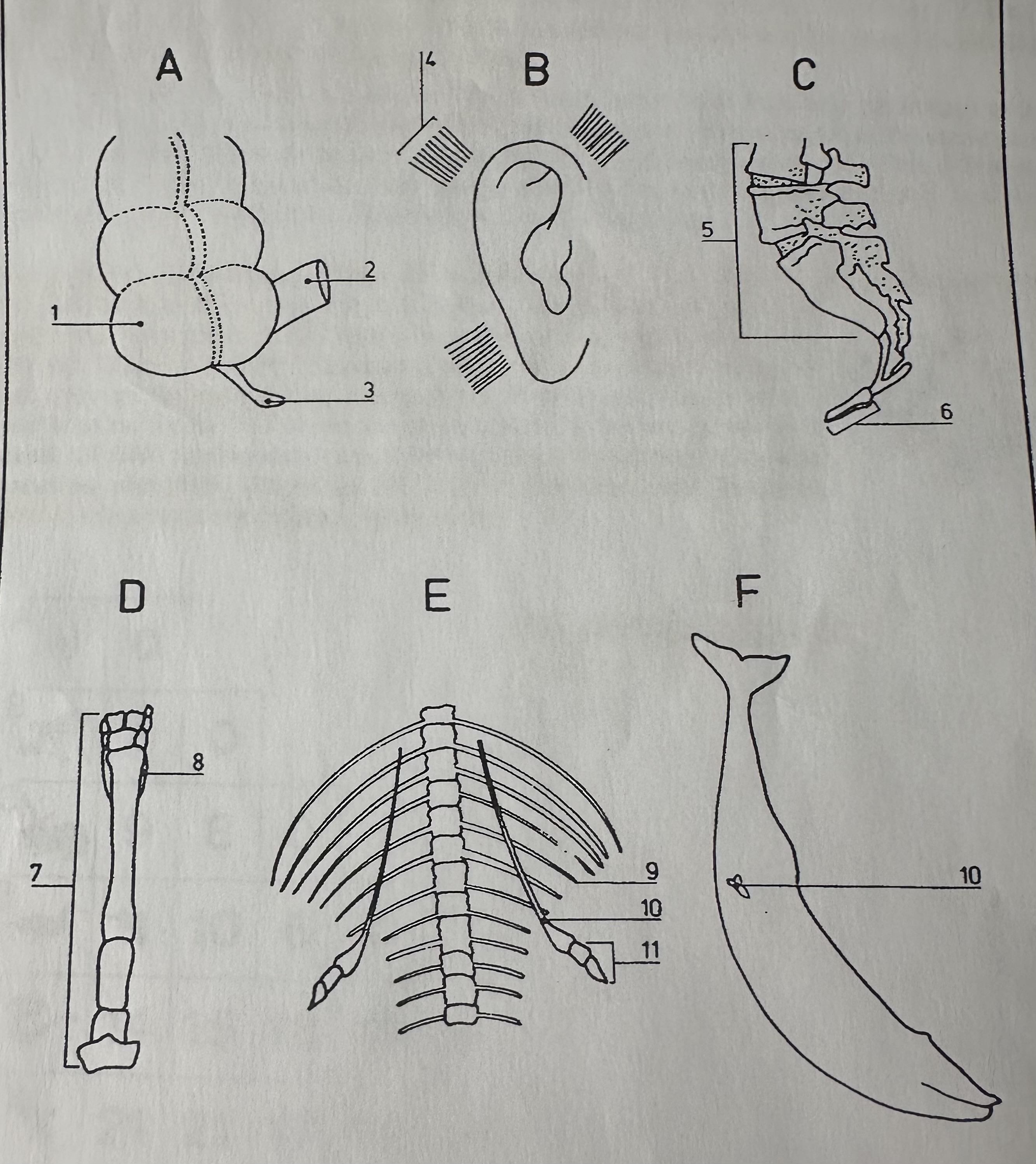
Vestigial structures
body structures that have been reduced in size and seem to serve little or no purpose (once performed a useful function in ancestral forms). Homologous with larger useful structures found in other living organims.
Vestigial structures provide evidence for evolution because evolution involves …
the loss or reduction of structures who main function is no longer valuable often becoming smaller but never disappearing completely.
Examples of vestigial structures
Appendix (humans) = suggests ancestors had a functioning appendix and were herbivores.
Coccyx / tail bone (humans) = evolutionary ancestors had a tail supported by vertebrae
Hindlimbs (modern whales) = Evidence for evolution from four footed terrestrial ancestor.
Leg bones in snake, Ear muscles (human), horse splint bone in leg
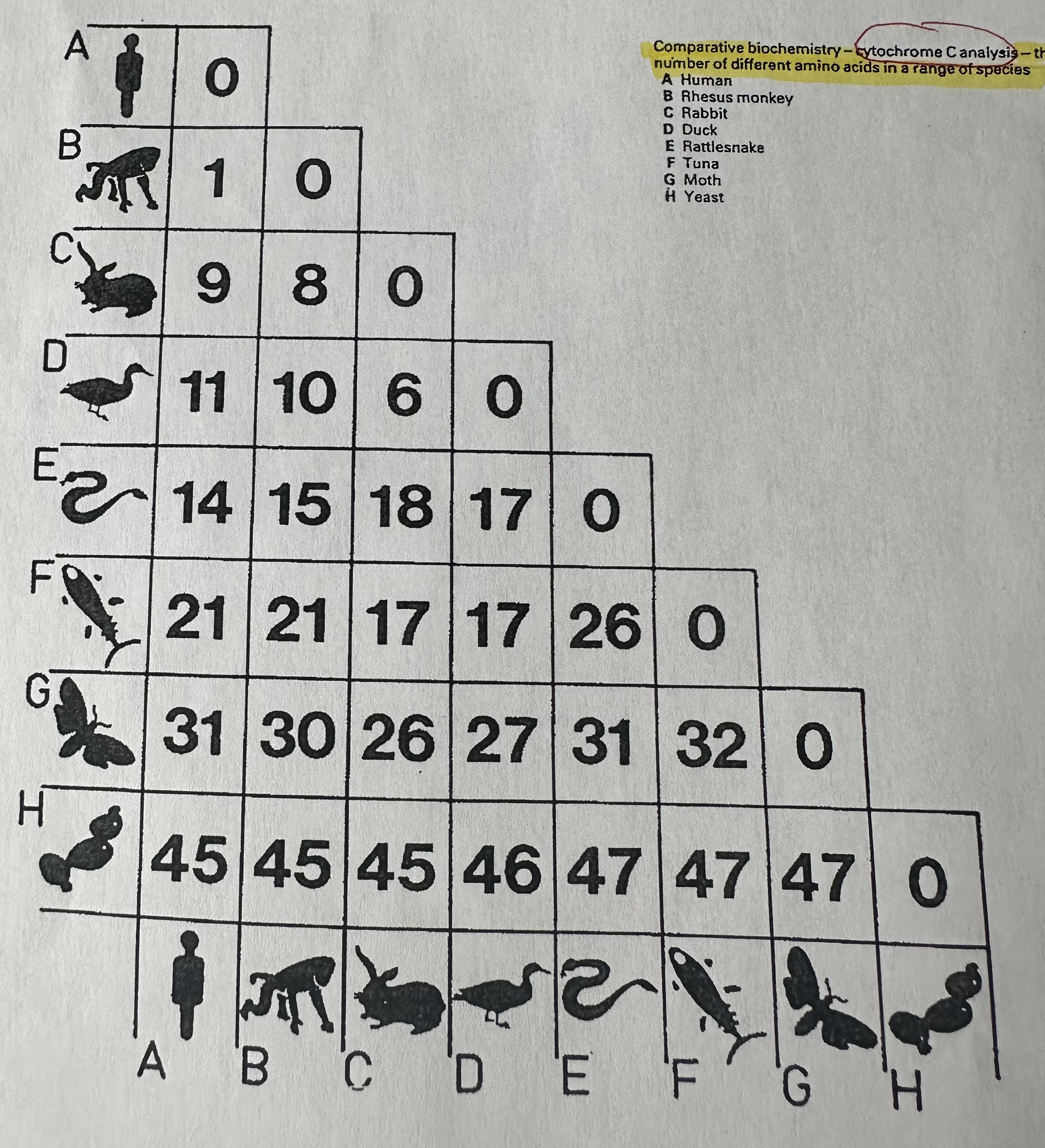
Comparative biochemistry
Study of molecules that make up different living things.
Evidence from comparative biochemistry shows that …
All organisms, from bacteria to humans share biochemical details. More closely related = more closely related important chemical compounds resemble each other.
Example of comparative biochemistry 1
All organisms use DNA and/or RNA. Eukaryotes DNA same structure and replicates same way. RNAs of various species may act a little diff. but all have similar structure. Also ATP found in all living things
Example of comparative biochemistry 2
Cytochrome C = protein (4 aerobic cellular respiration).
Diff. A.A seq. 4 diff. species.
But # of DNA nucleotide (in gene 4 cytochrome c) diff. less btwn more closely related species compared to distantly related species
(humans & monkeys 1 N difference, humans & snake 14 N difference)