OCR B Geography GCSE Distinctive Landscapes
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
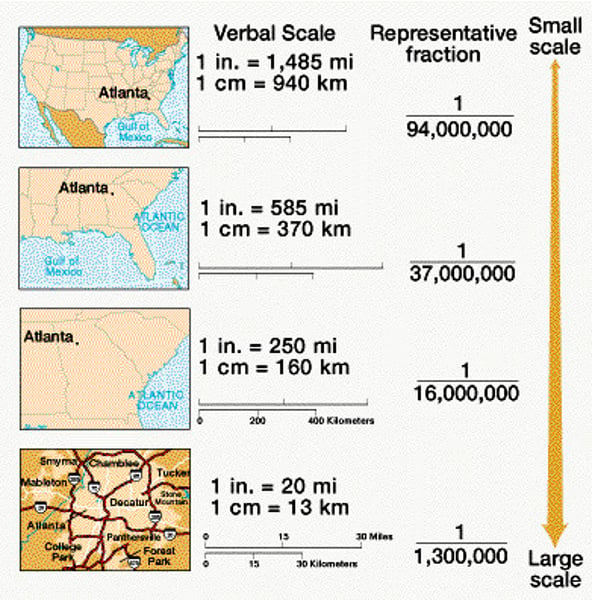
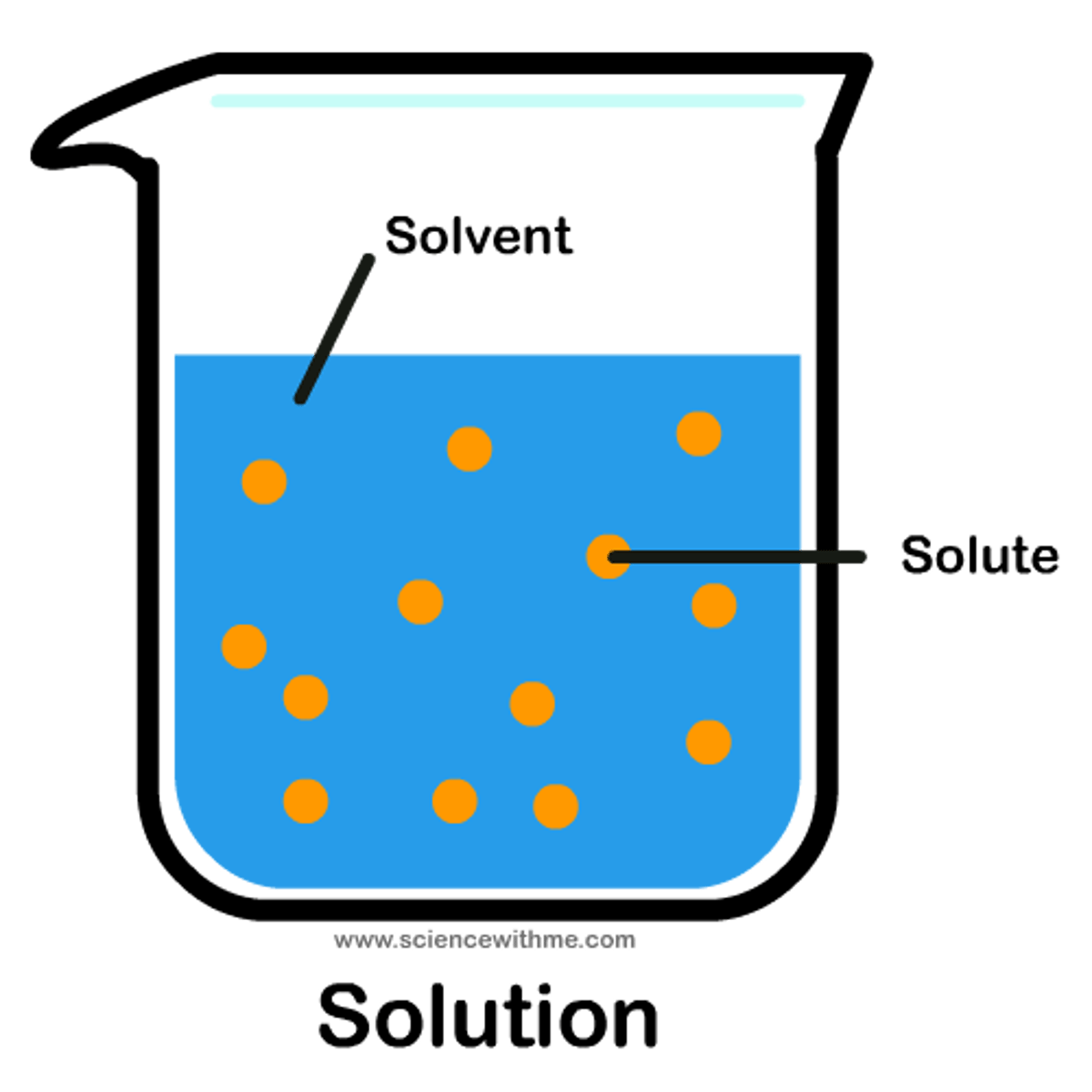
scale
can refer to maps that are drawn at particular levels of detail; in geography this often refers to whether something is looked at from the local, regional, national or global scale
local
tends to refer to a small area or region when considering the scale of a study but can alos be used to refer to one's own neighbourhood or an area known to a person; can be in relation to the learner or another small scale location
regional
used to refer to the characteristics of a defined area within a larger area; the scale can vary but within geography, could include East Anglia or a district within a country; An area of land that has common features, which may be artificial, such as dialect, language, religion, industry or administrative boundaries, or natural such as climate and landscape
national
referring to a nation or country; a scale of looking at things where particular countries are the subject of study.
built landscape
the human-made surroundings that provide the environment for human activity; may also refer to towns, cities and other urban environments

natural
existing in, or derived from, processes that do not involve humans
natural landscape
a landscape that is the result of natural processes and has not been shaped or changed by human activity
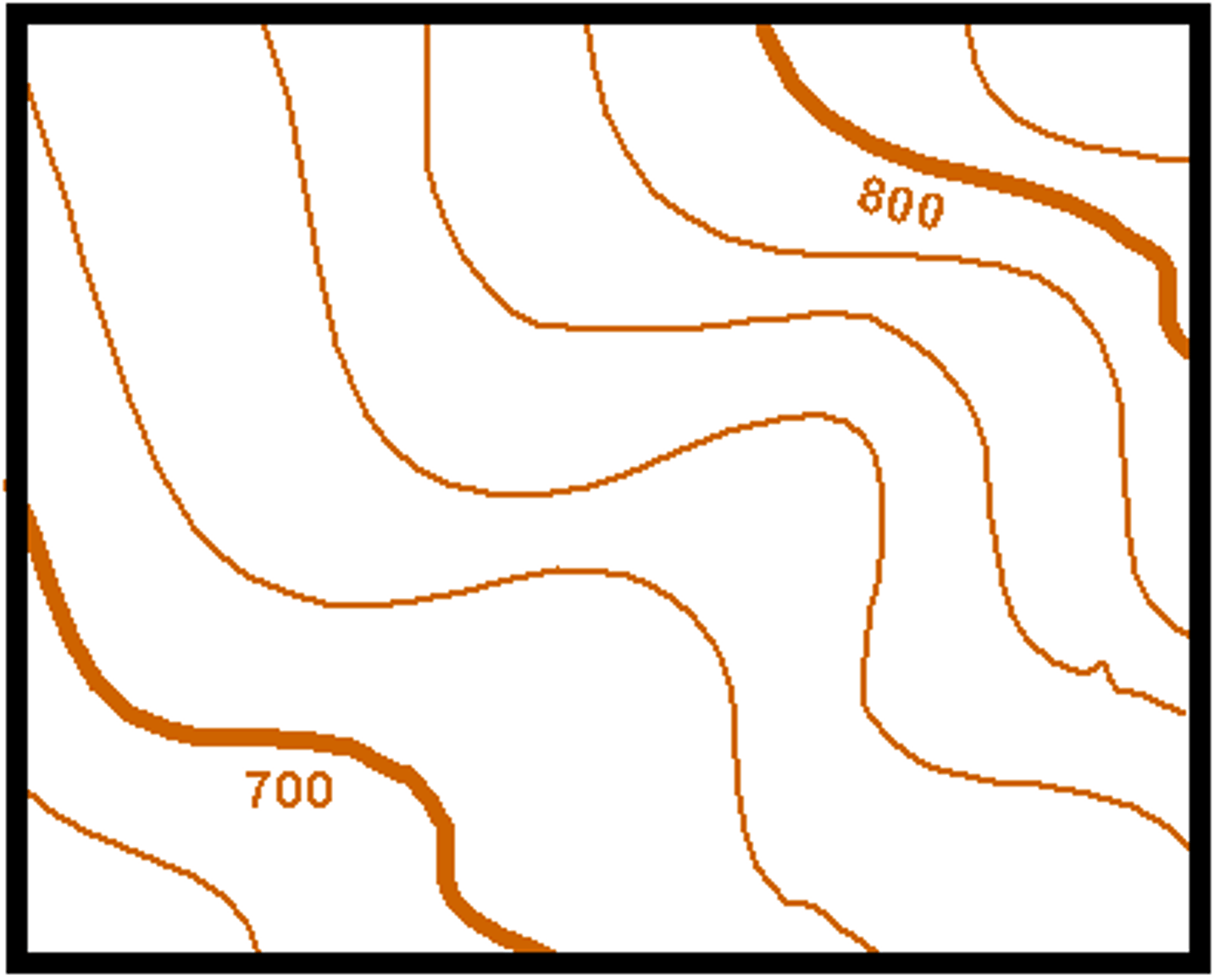
contour lines
a line on a map joining places of equal height
spot heights
the height of a specific point on the land, which is added to an Ordinance Survey map
landform
a natural, recognisable feature of the Earth's surface
lowland
low lying land, usually flat or gently undulating
upland
higher land, including hills and mountains, usually more rugged with dramatic peaks and valleys
ice age
a glacial episode characterised by lower than average global temperatures and during which ice covers more of the Earth's surface
glacial processes
processes resulting from the action of ice, often in the form of glaciers or other landforms but can also involve the cold temperatures associated with glacial periods
Geomorphic processes
processes which result in a change in the shape of the Earth; from 'geo' meaning the earth and 'morph' meaning to change shape
mechanical processes
physical processes which act mechanically on a substance
chemical processes
processes that result from chemical reactions and interactions
biological processes
processes that result from the action of living organisms, whether plant or animal, in nature
geology
the study of rocks and their formation, structure and composition
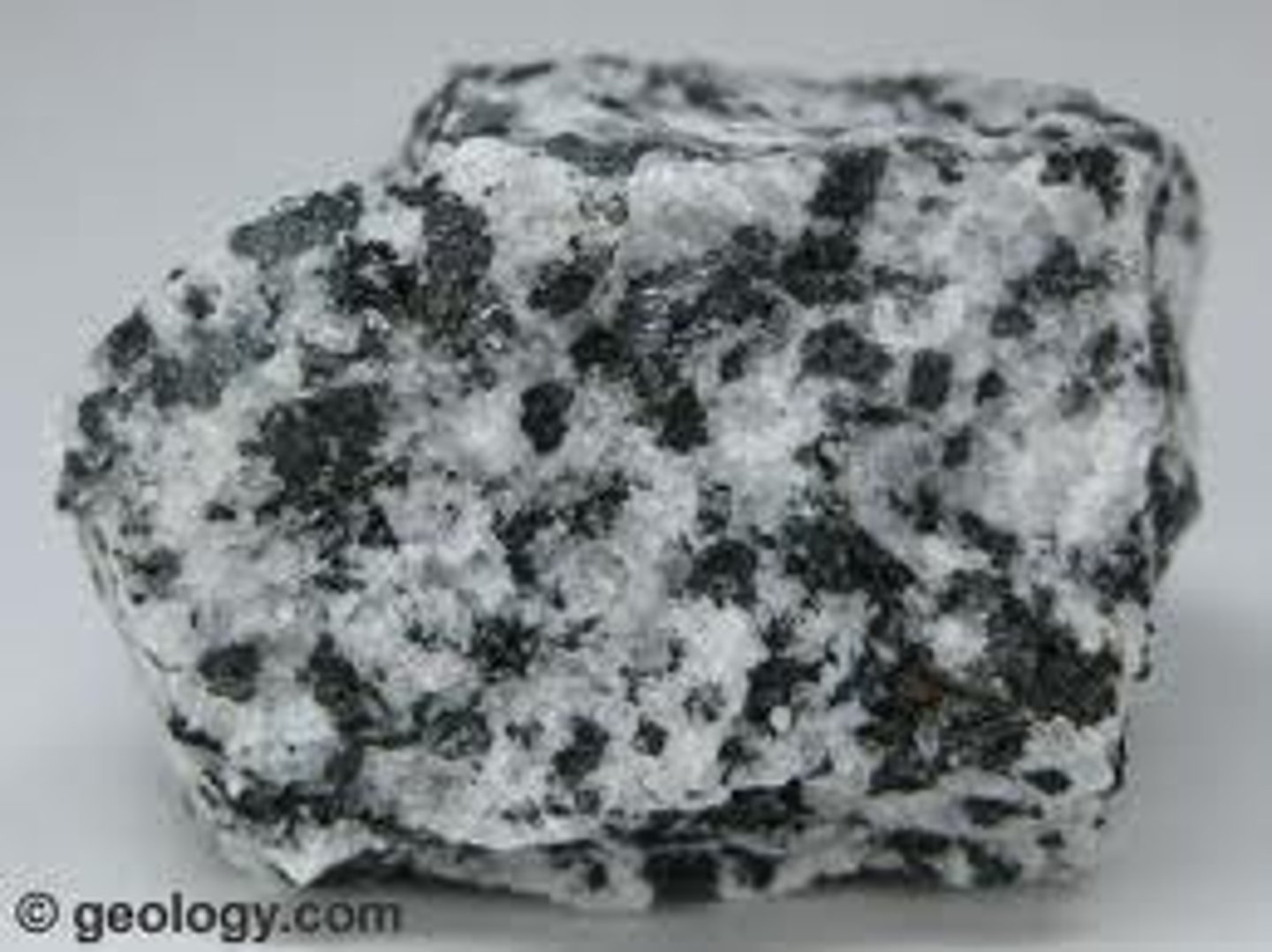
igneous
when referring to rocks, this means rocks formed within the interior of the earth, and shaped by heat

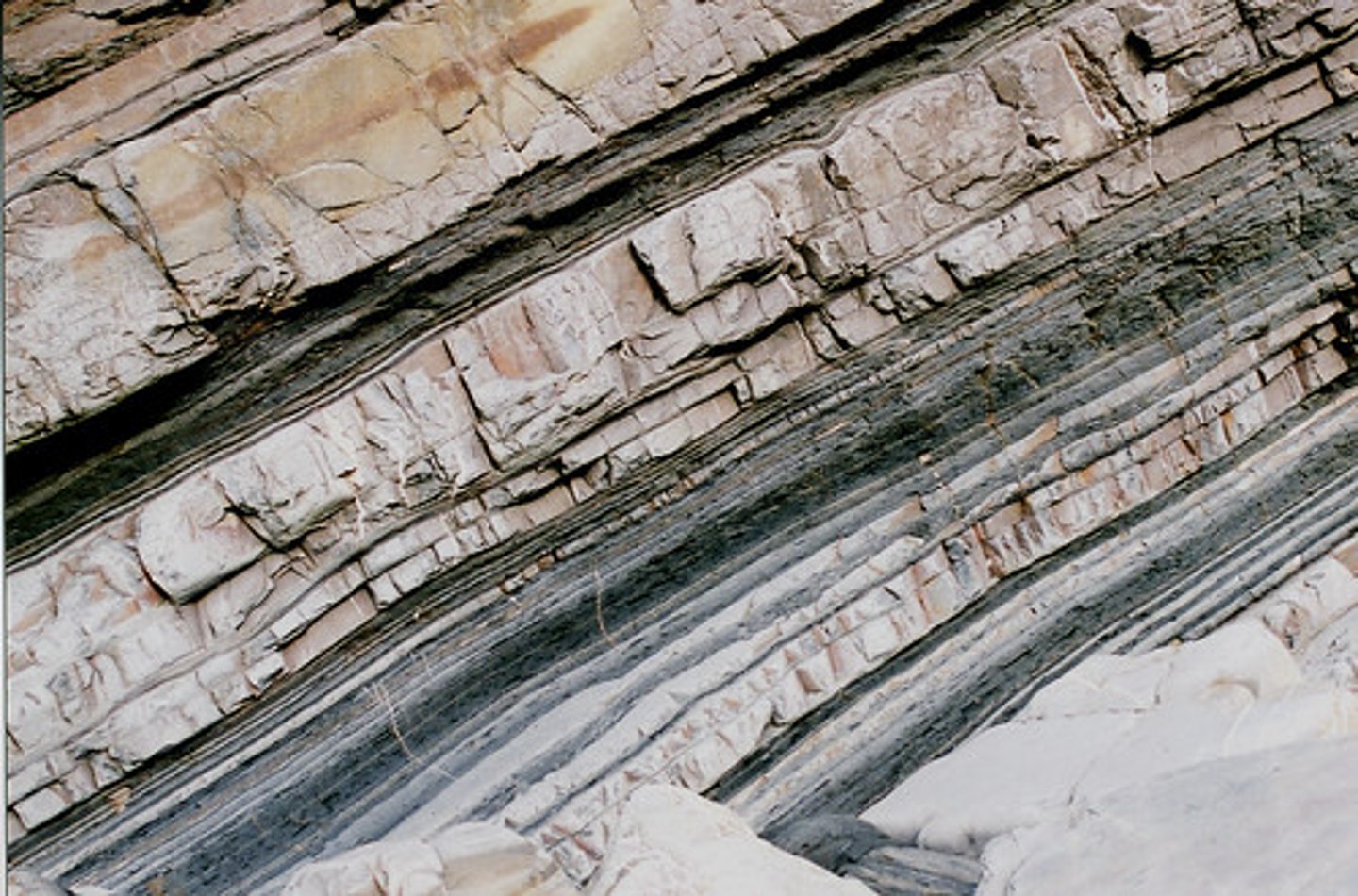
sedimentary
rocks that have been produced from layers of sediment, usually at the bottom of the sea

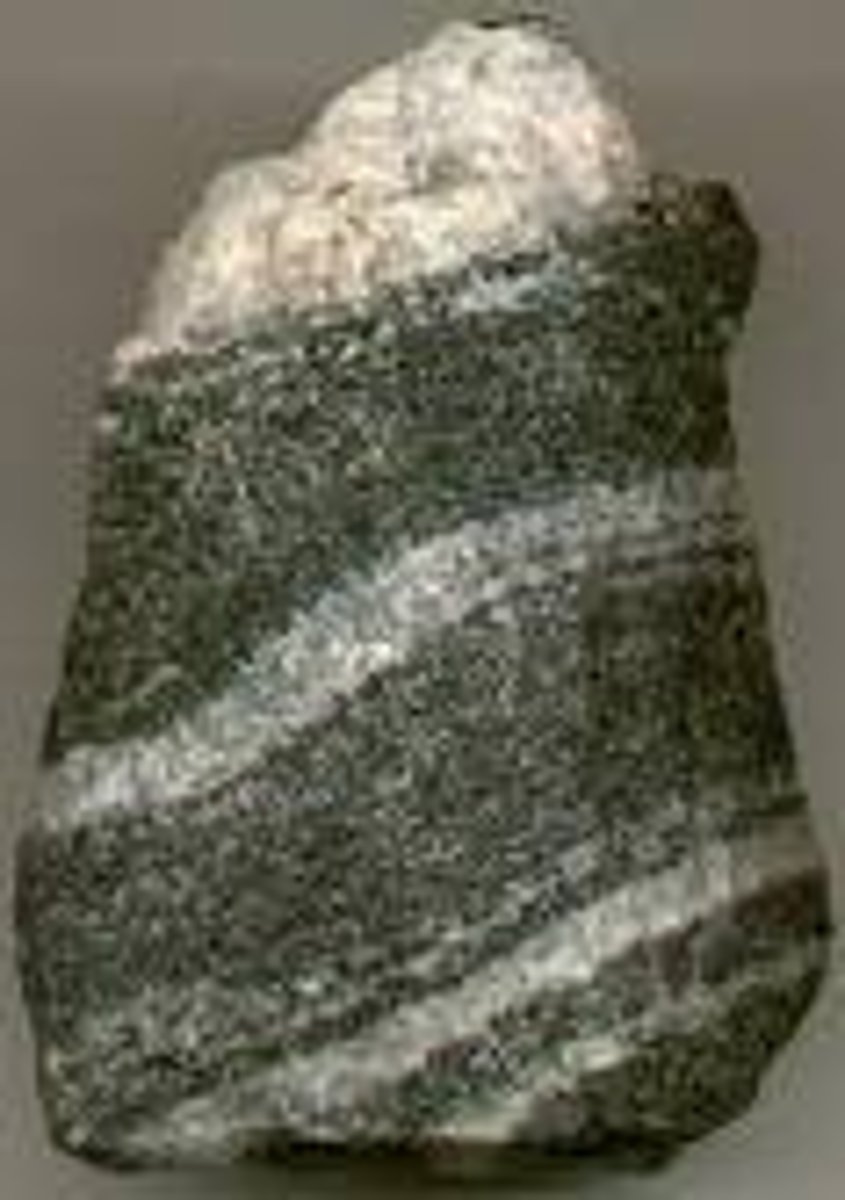
metamorphic
rocks that have been changed as a result of heat and pressure being applied to them over long periods of time

impermeable
a surface or substance that doesnt allow water to pass through it

permeable
a surface or substance that does allow water to pass through it
coniferous
trees that are evergreen and have needle shaped leaves

deciduous
trees that shed their leaves during winter to retain moisture, also known as broadleaved trees

climate
the expected condition of the atmosphere based on a long term average of 30 or more years
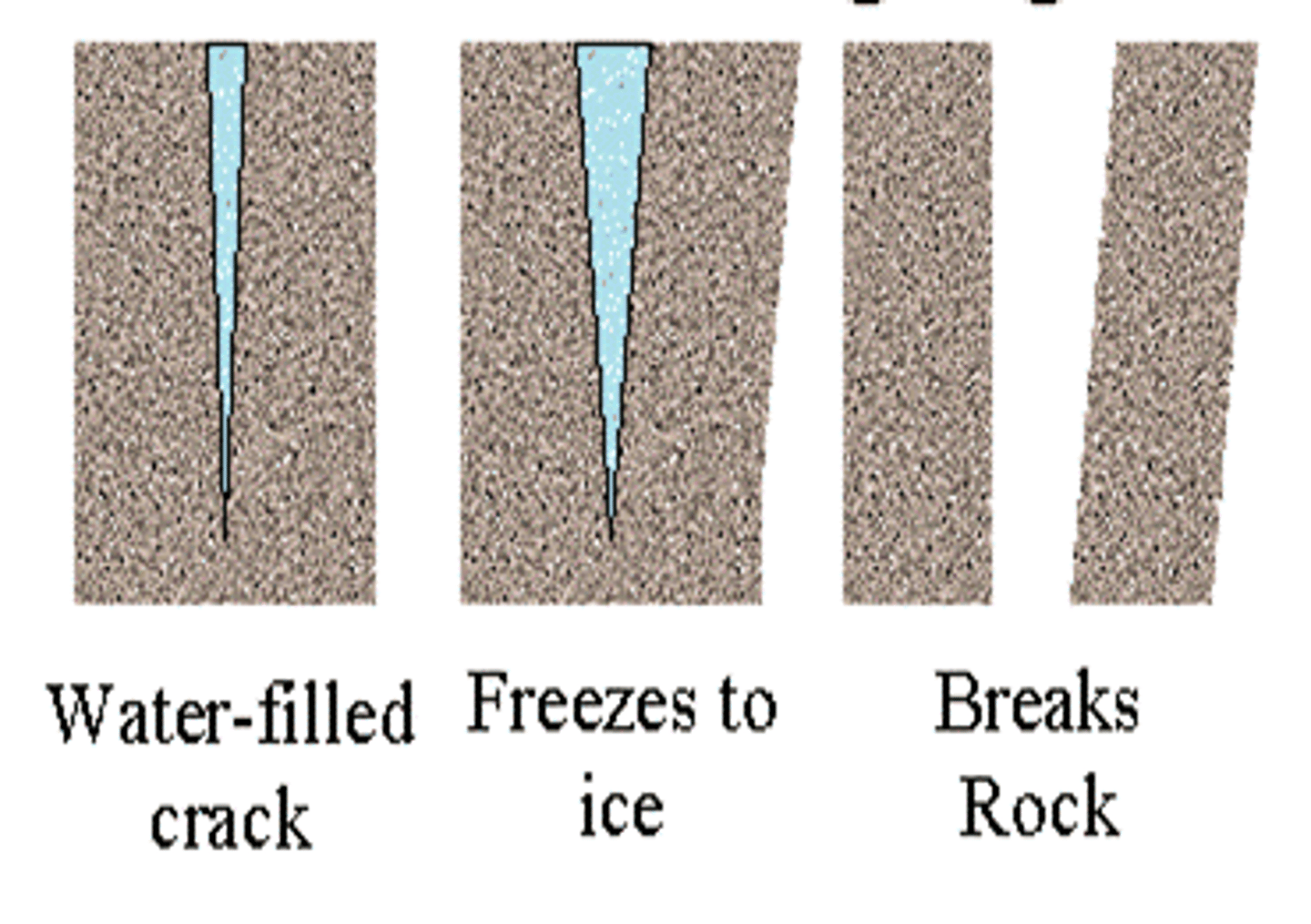
freeze-thaw cycle
the daily fluctuations of temperature either side of freezing point; when repeated they contribute to physical weathering
rural
areas which are not urban; characteristic of the countryside rather thyan towns or cities

urban
refers to areas which have been built by people; towns and cities

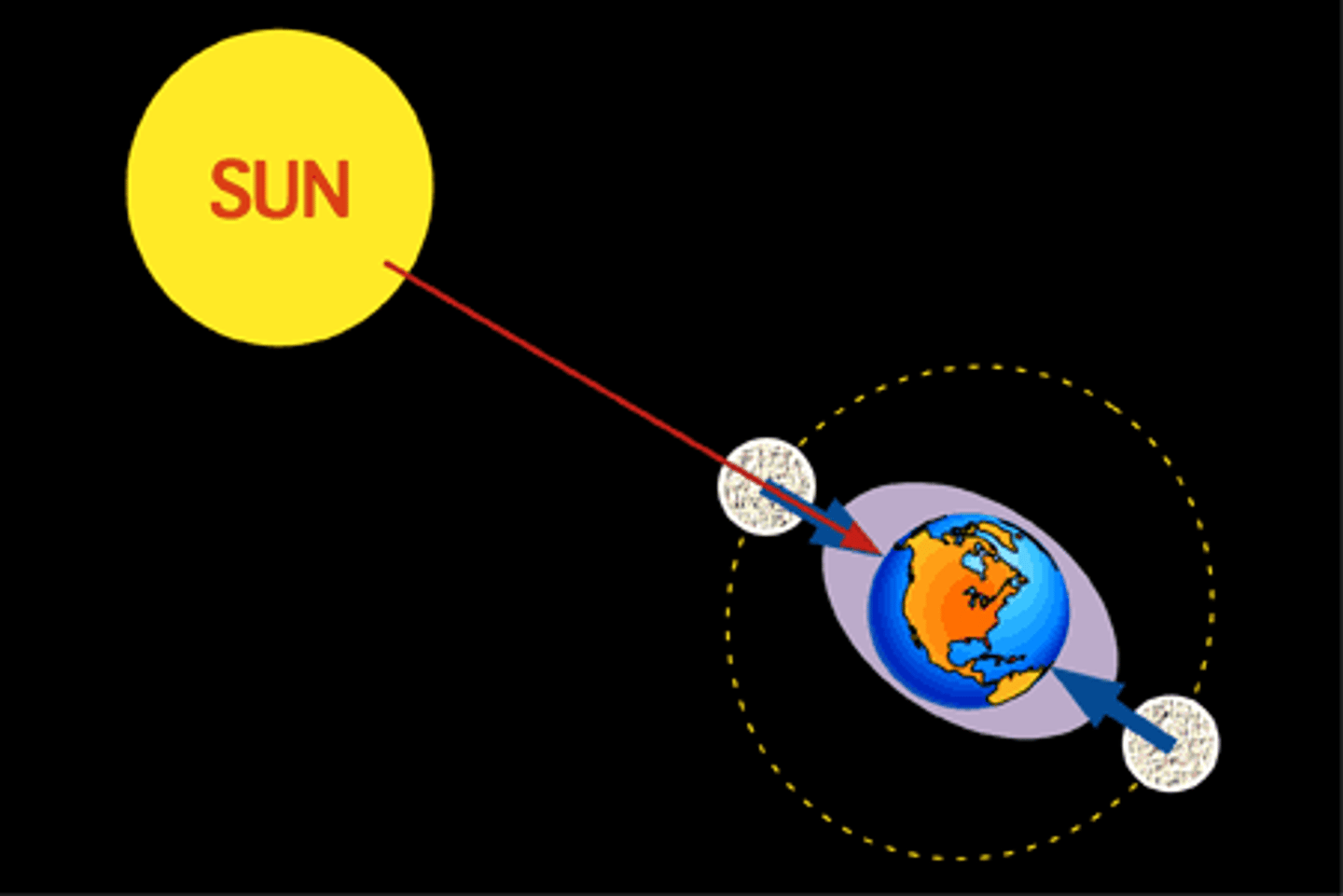
tides
changes in sea level as the result of the Moon; regular movements which occur every day
sub-aerial processes
processes which aid weathering and the mass movement of material; they include the action of the weather
oxidation
a chemical reaction between a substance (often iron) and oxygen in the air; it can change the appearance (reddish brown) and weaken it.
hydrolysis
some minerals are affected by water, when acidic rainfall reacts with minerals to form weaker materials which are more easily washed away
carbonation solution
carbon dioxide dissolves in rainwater to form weak carbonic acid, this reacts with calcium carbonate, leading to the formation of soluble calcium bicarbonate
weathering
the disintegration or decomposition of material in situ, by physical, chemical or biological processes
erosion
processes by which rock, sand, and soil are broken down and carried away
mass movement
the downslope movement of material due to gravity
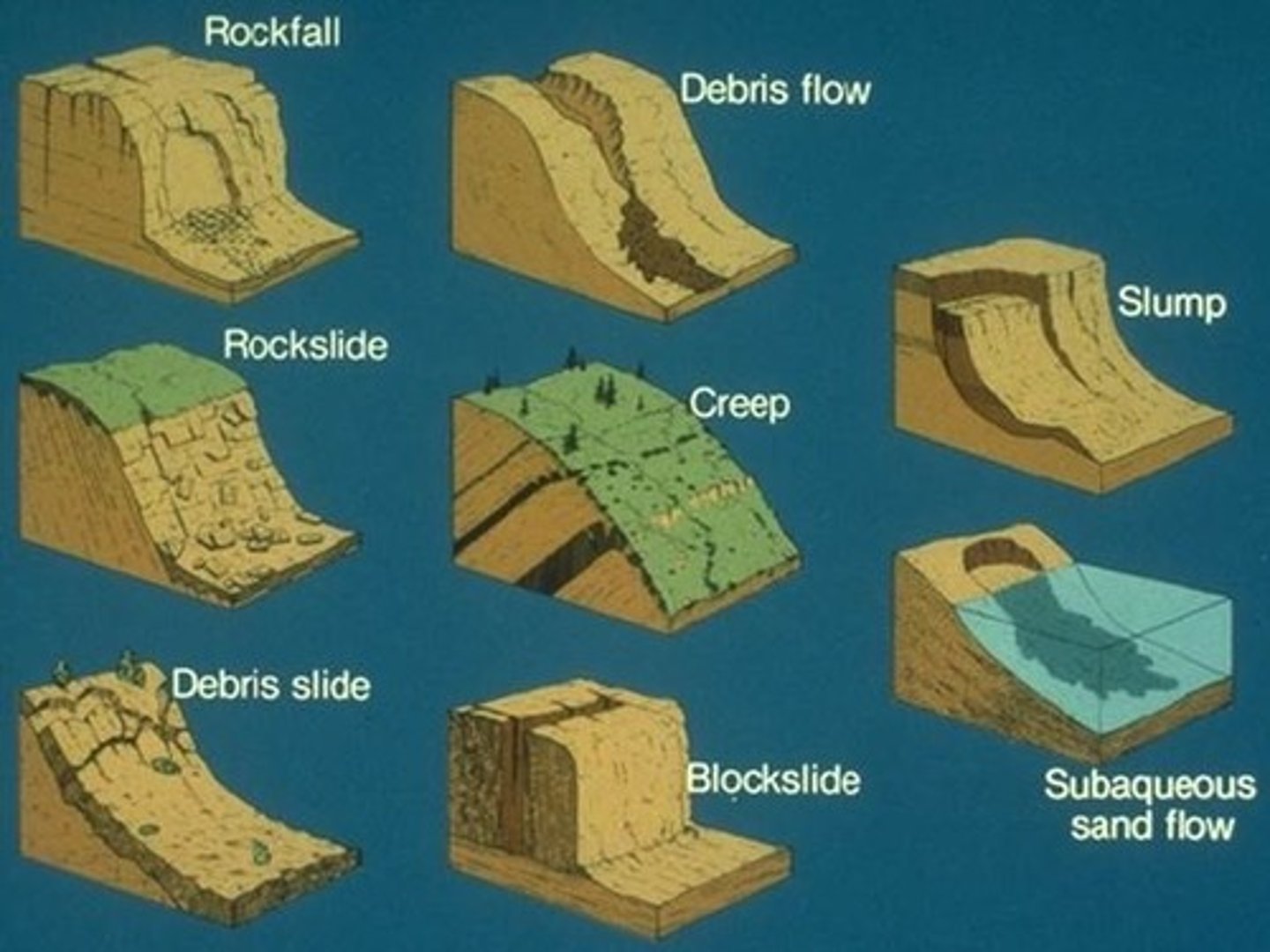

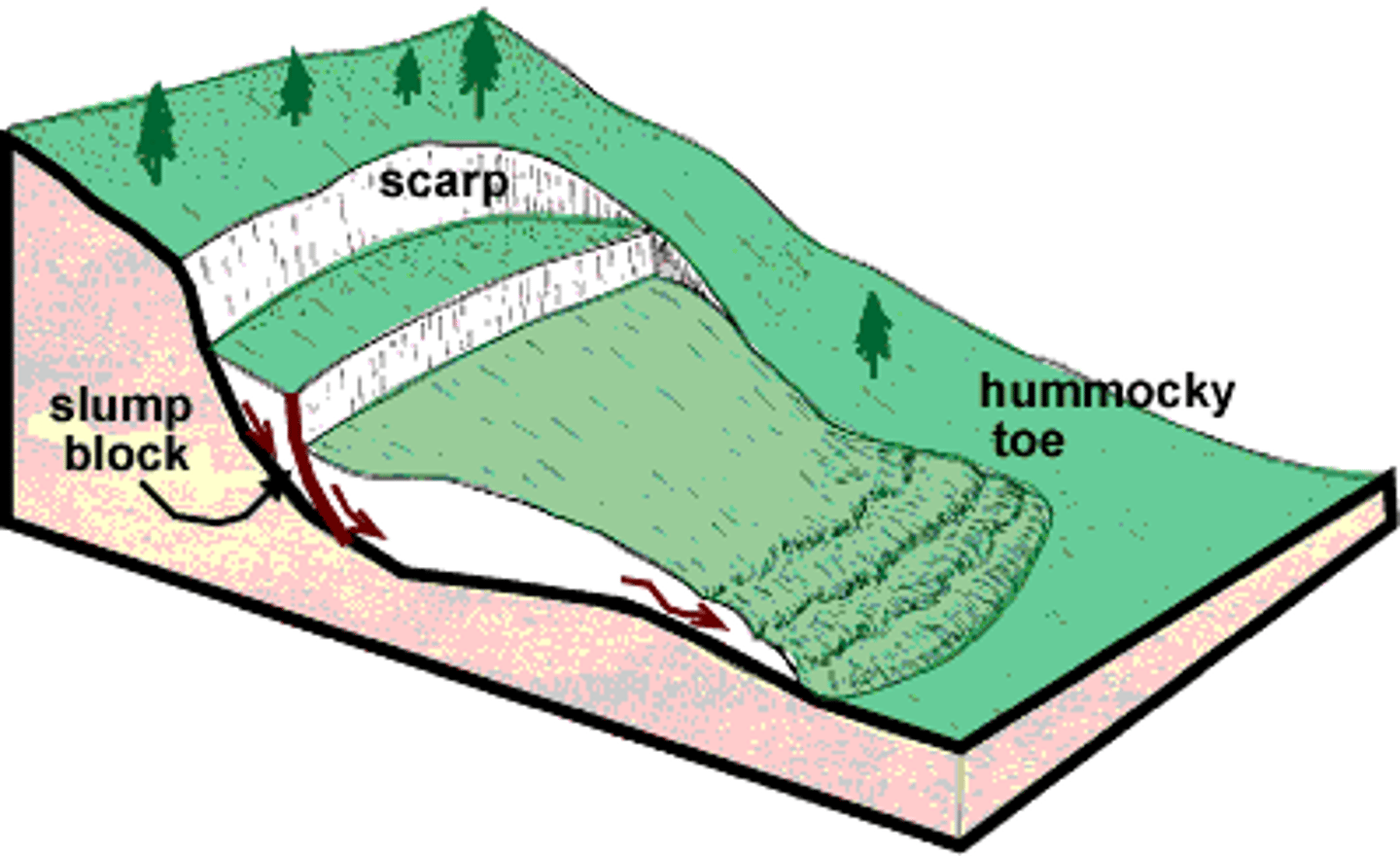
rotational slump
the downslope movement of material along a curved slip plane
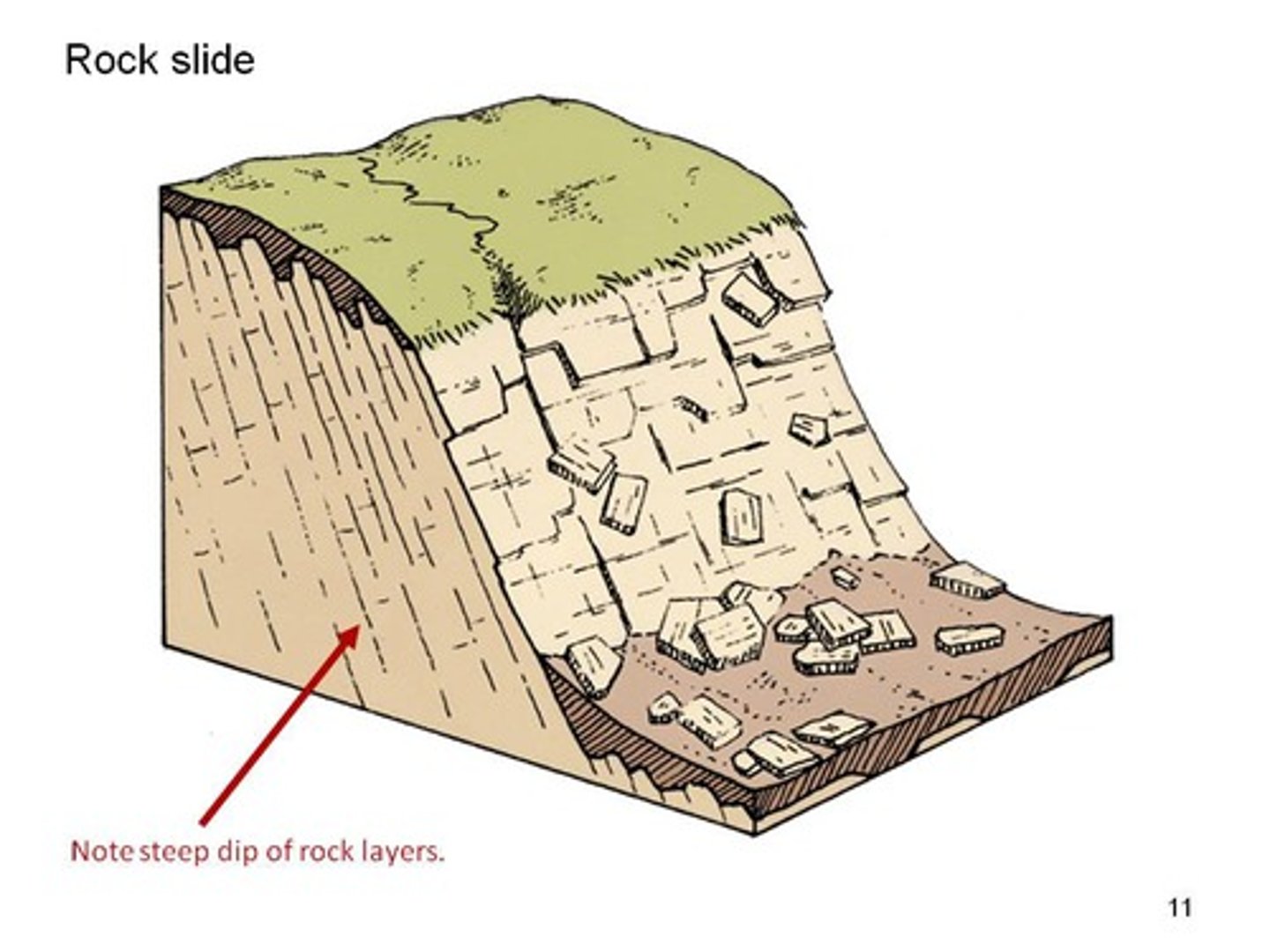
rock slide
the downslope movement of material along a straight slip plane
waves
elliptical or circular movement of the sea surface that are translated into a movement of water up the beach as they approach the coastline

abrasion
the scraping, scouring or rubbing action of materials being carried by a moving feature suchs as a river, glacier or wave, which erode rocks

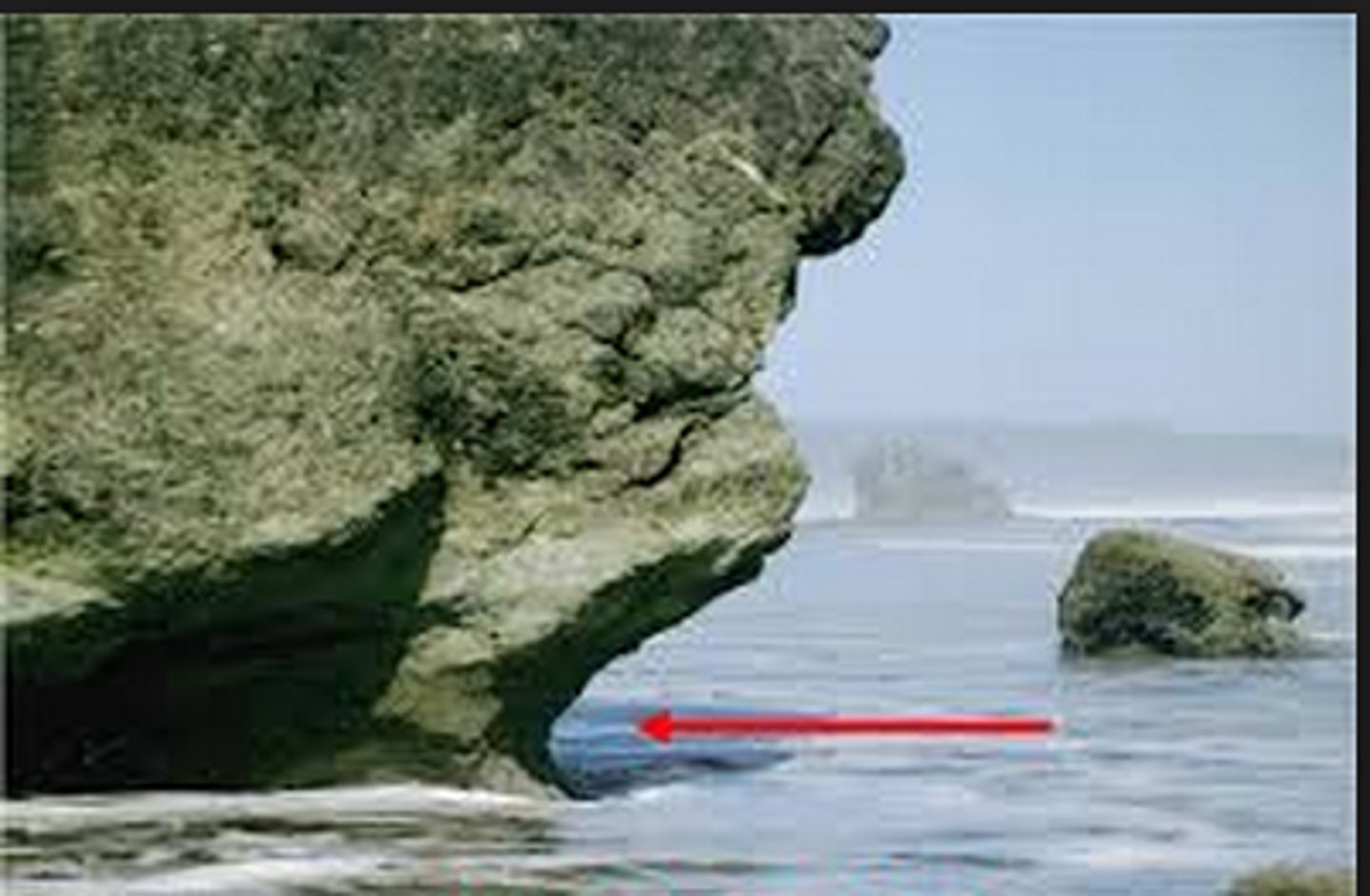
wave-cut notch
an erosional landform undercutting the base of a cliff between low and high water marks

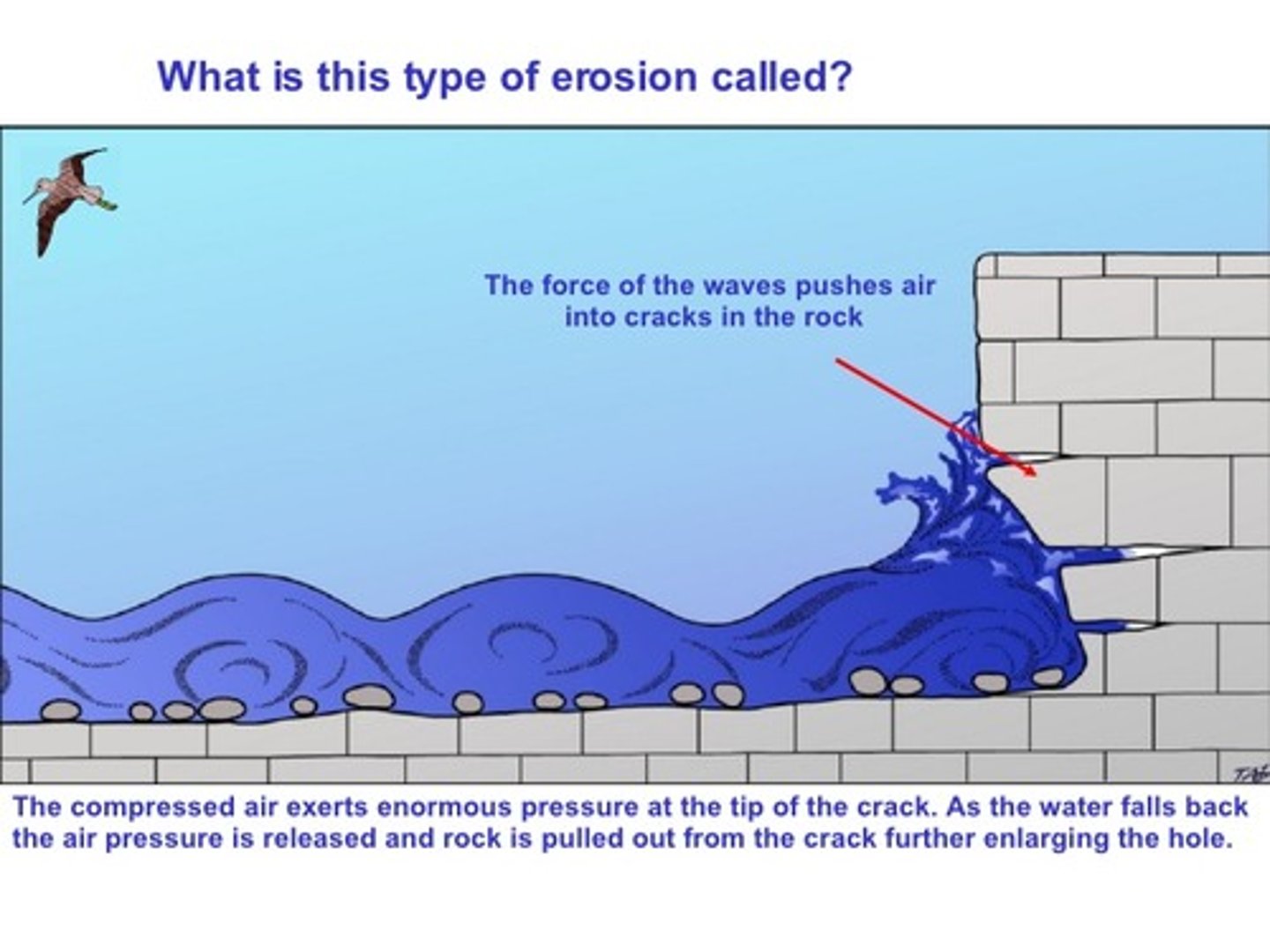
hydraulic action
an erosive process which involves the pressure of water hitting a surface, compressing air into any cavities which exist and resulting in the removal of rock fragments over time
solution
the dissolving of soluble materials by acidic water
attrition
a reduction in the size and angularity of material as it knocks together

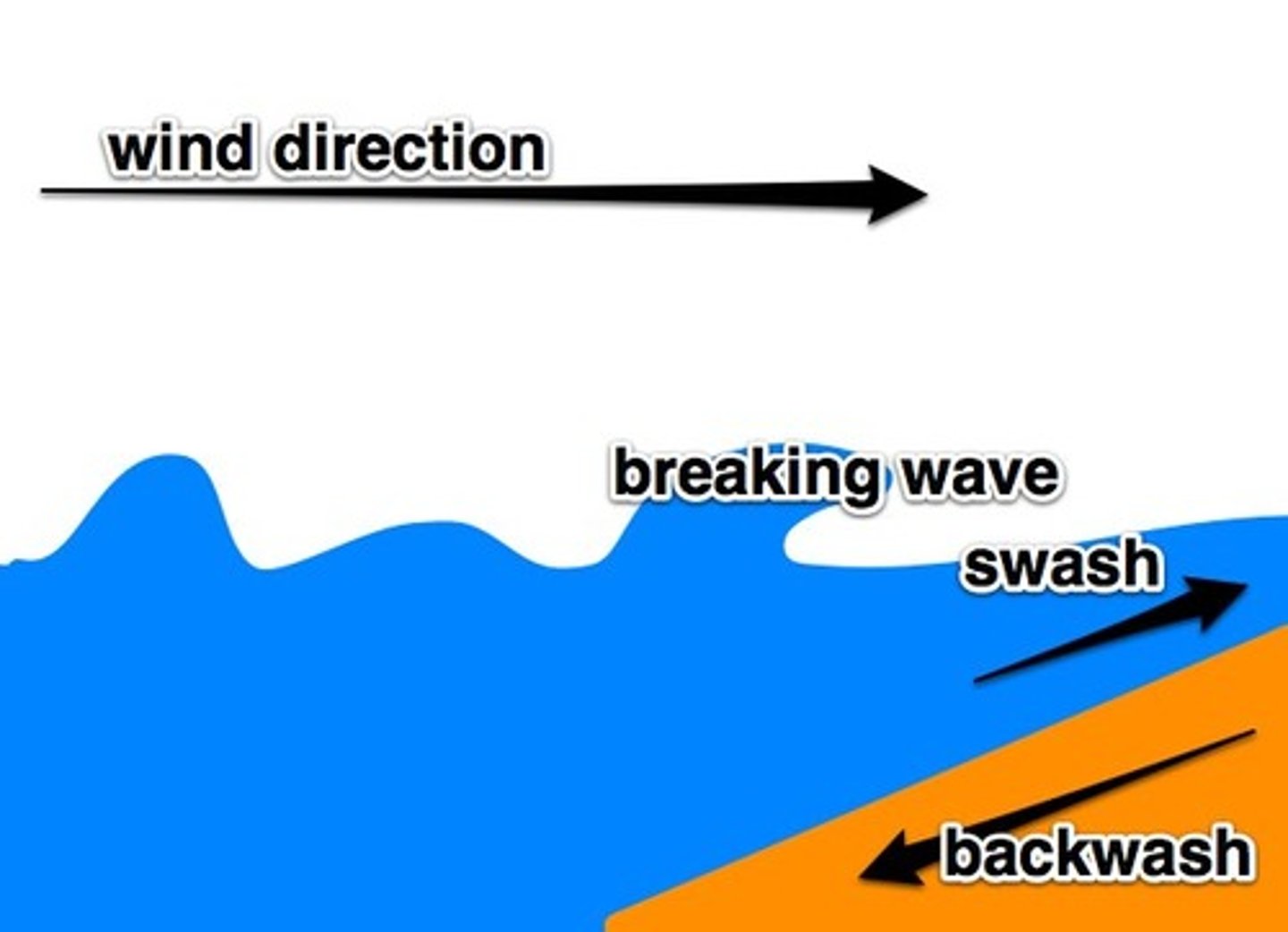
swash
The movement of water up the beach following the breaking of a wave on the coastline
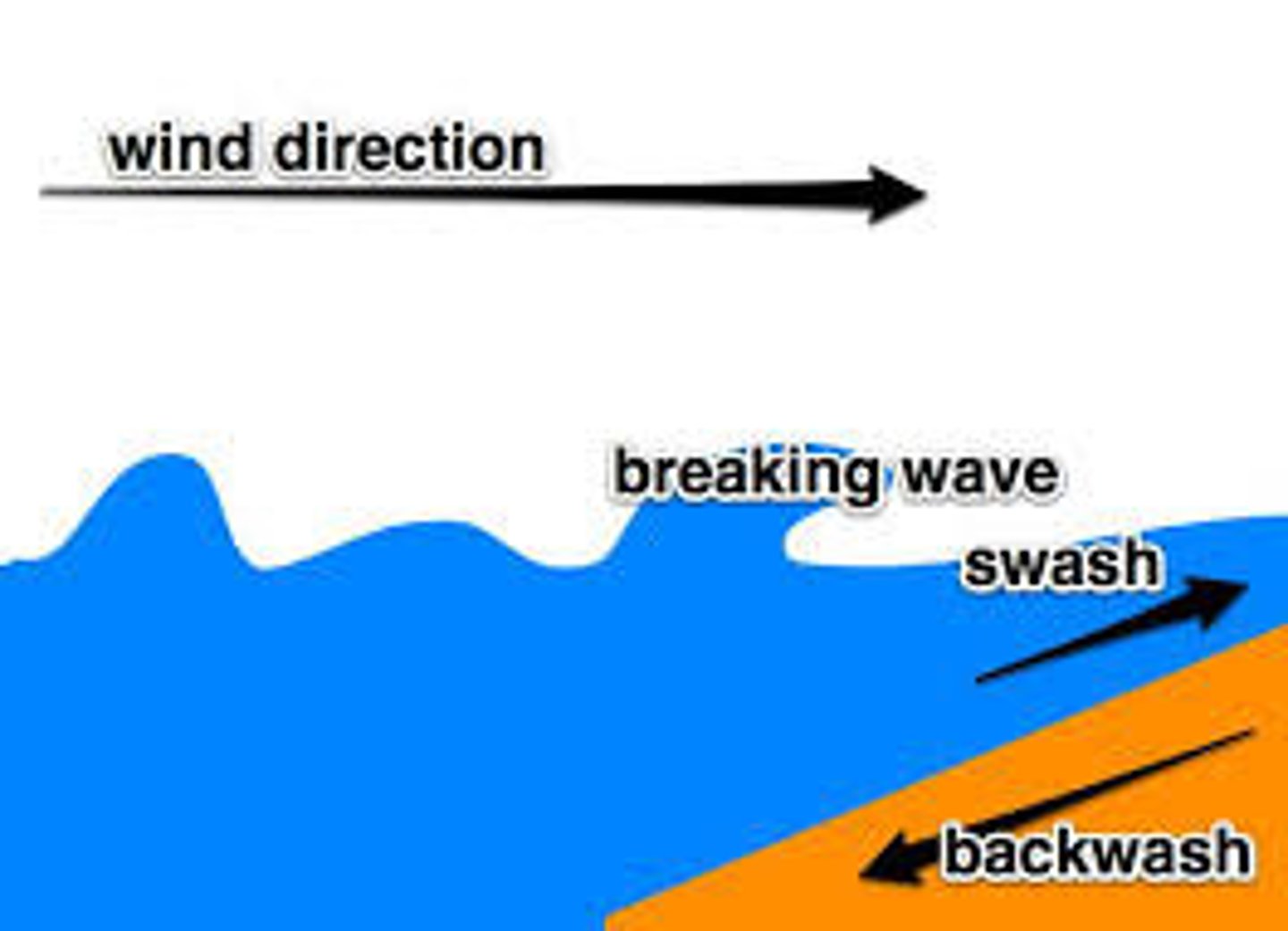
backwash
The movement of water from a broken wave as it moves down the beach
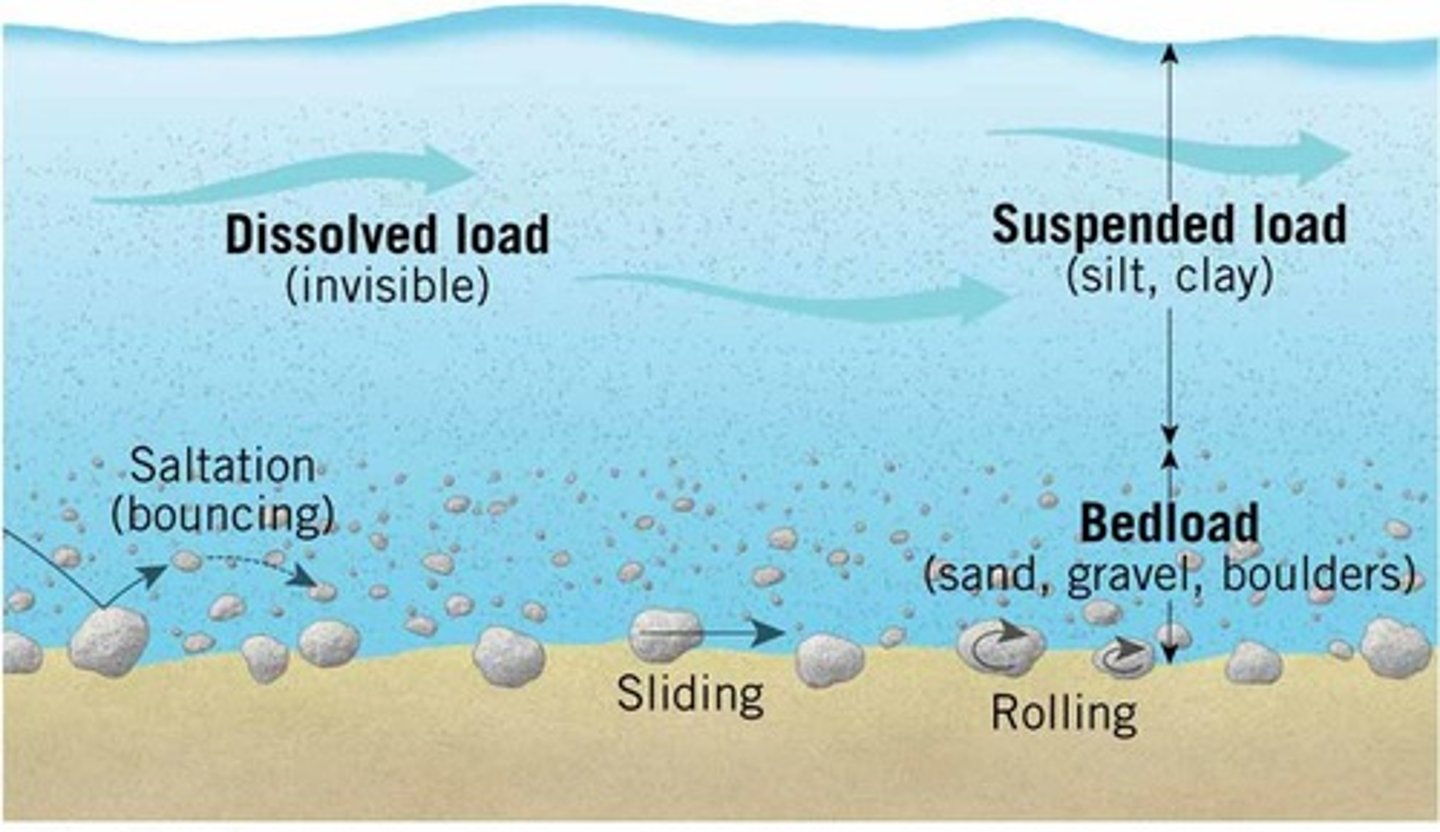
transport
the movement of material by a range of processes
longshore drift
The movement of sediments along a stretch of coastline as a result of the wind and swash approaching the beach at an angle
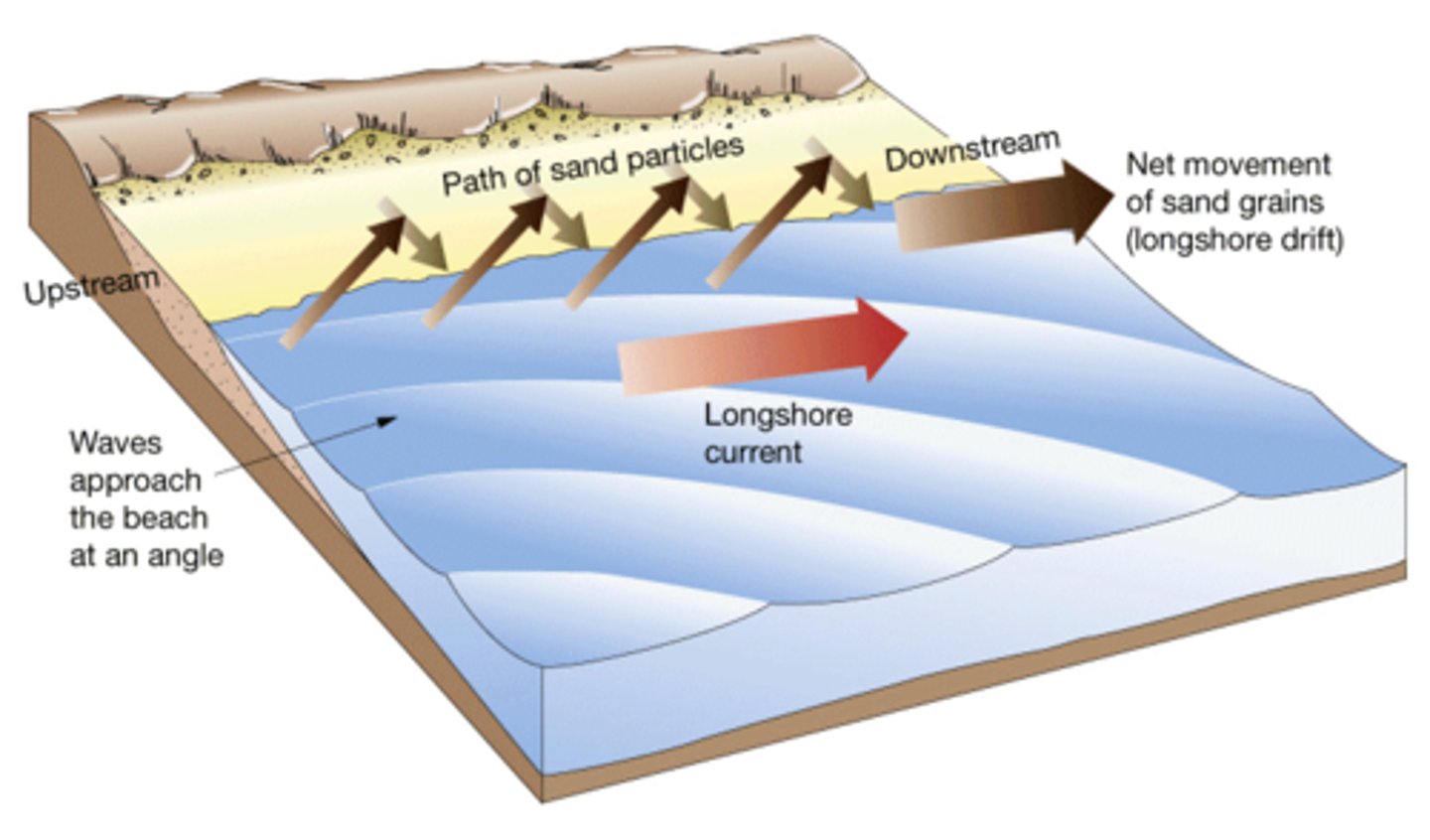
deposition
the process by which sediment being transported is laid down
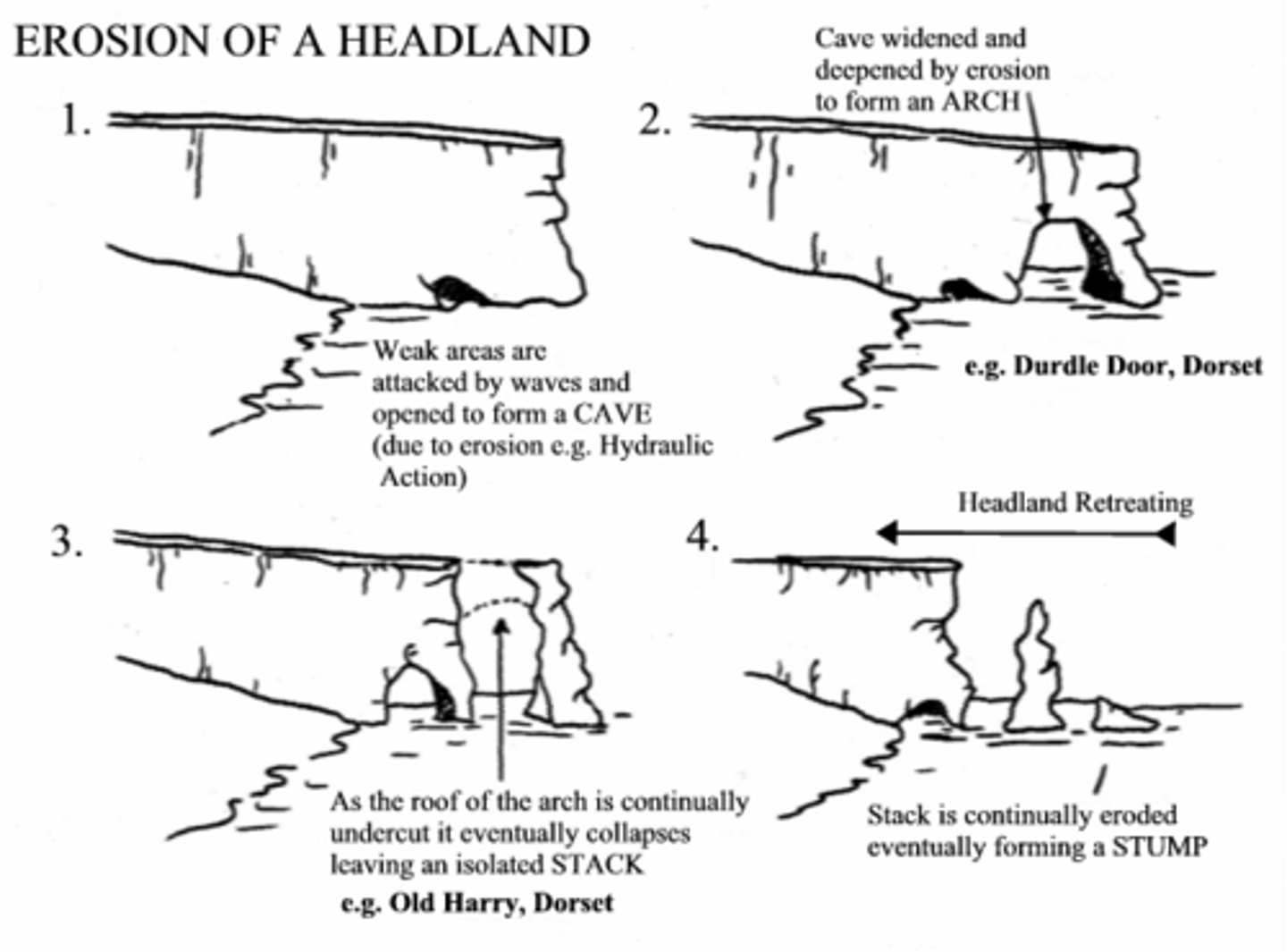
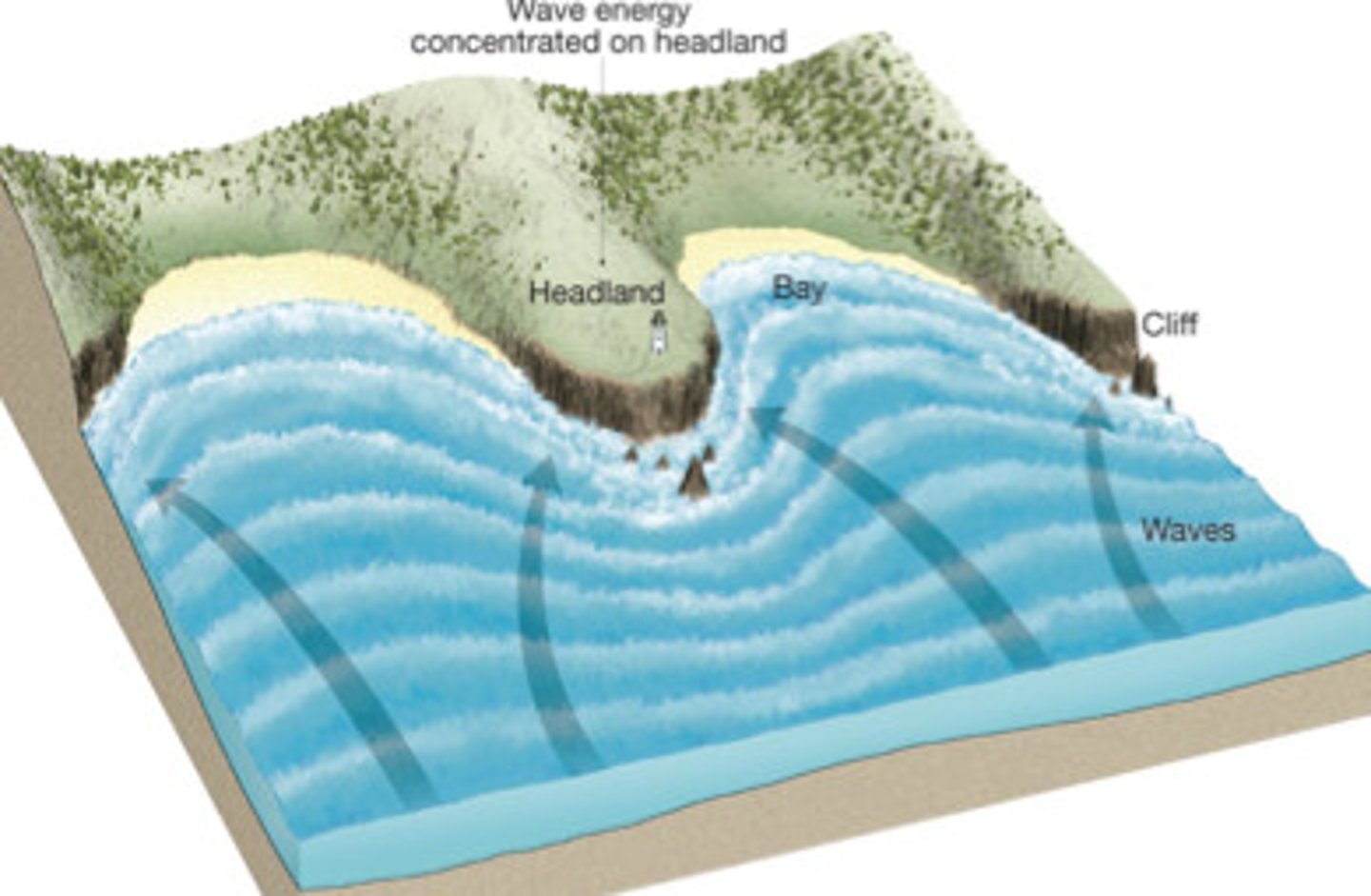
headland
an area of land that extends out into the sea, usually higher than the surrounding land; also called a point
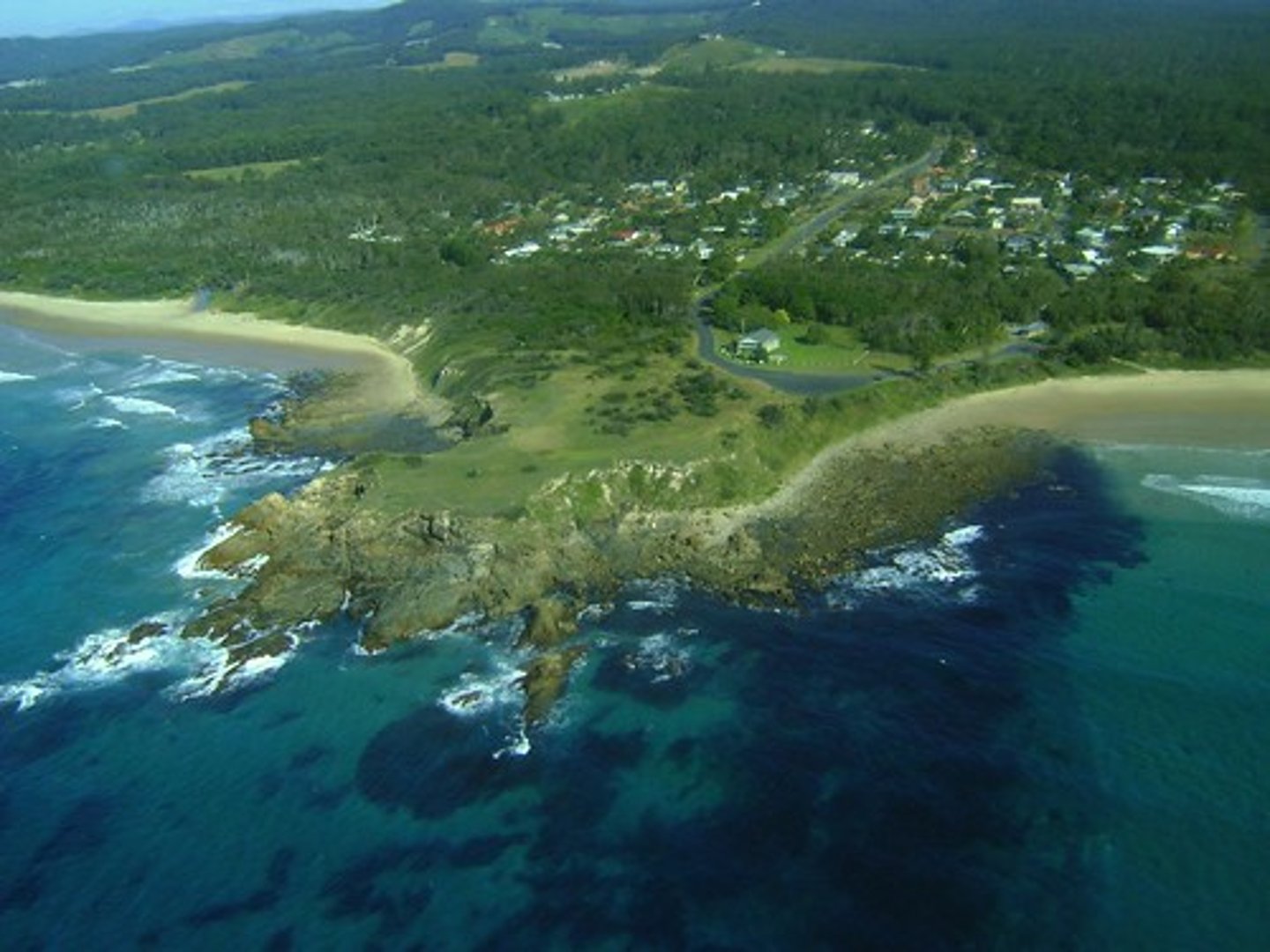

bay
the area between two headlands which has been eroded at a faster rate, usually lower and often contains a beach
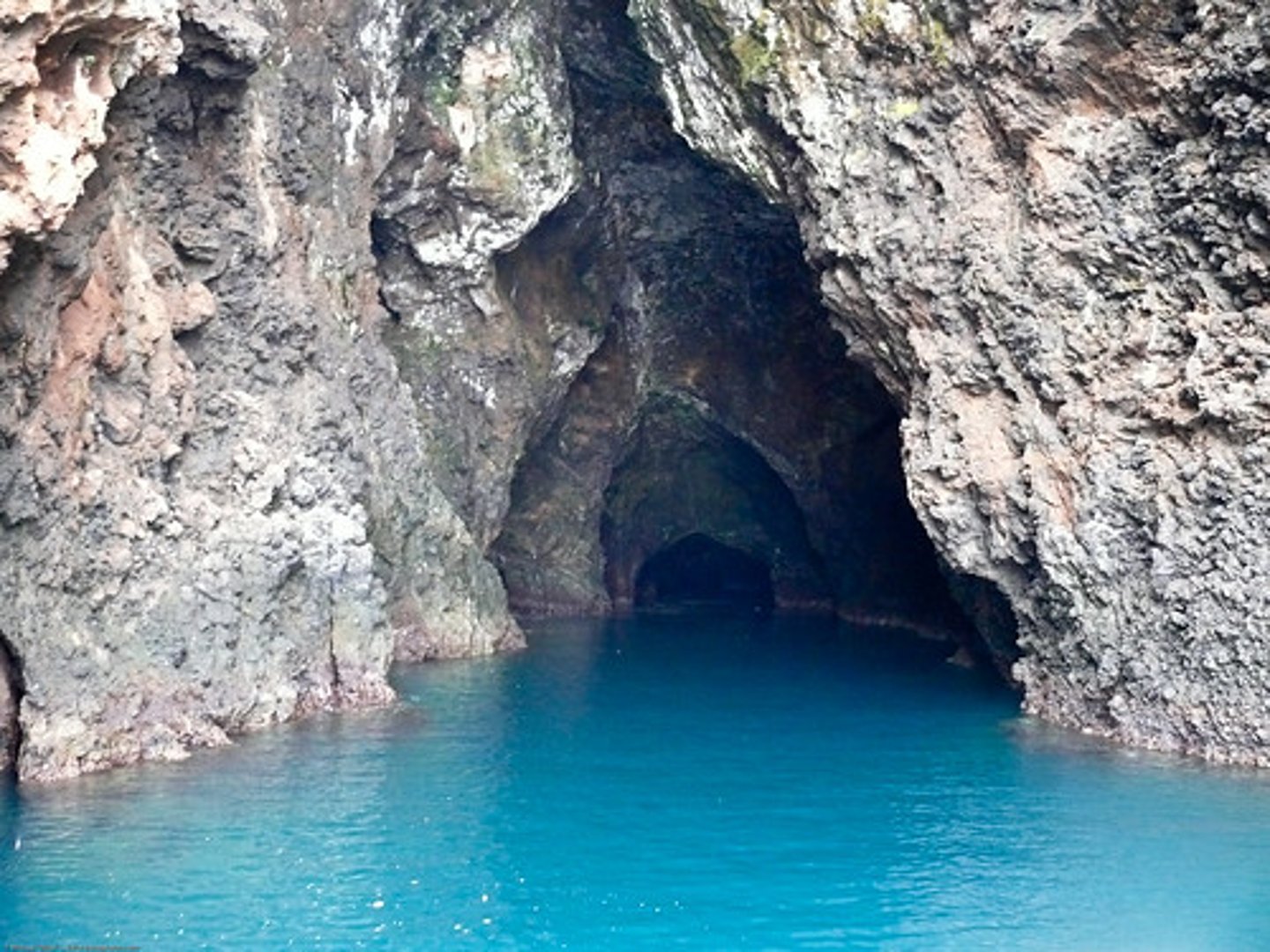
cave
the extended cracks and hollows at the base of a cliff

arch
an erosional landform where a cave has been eroded straight through a headland

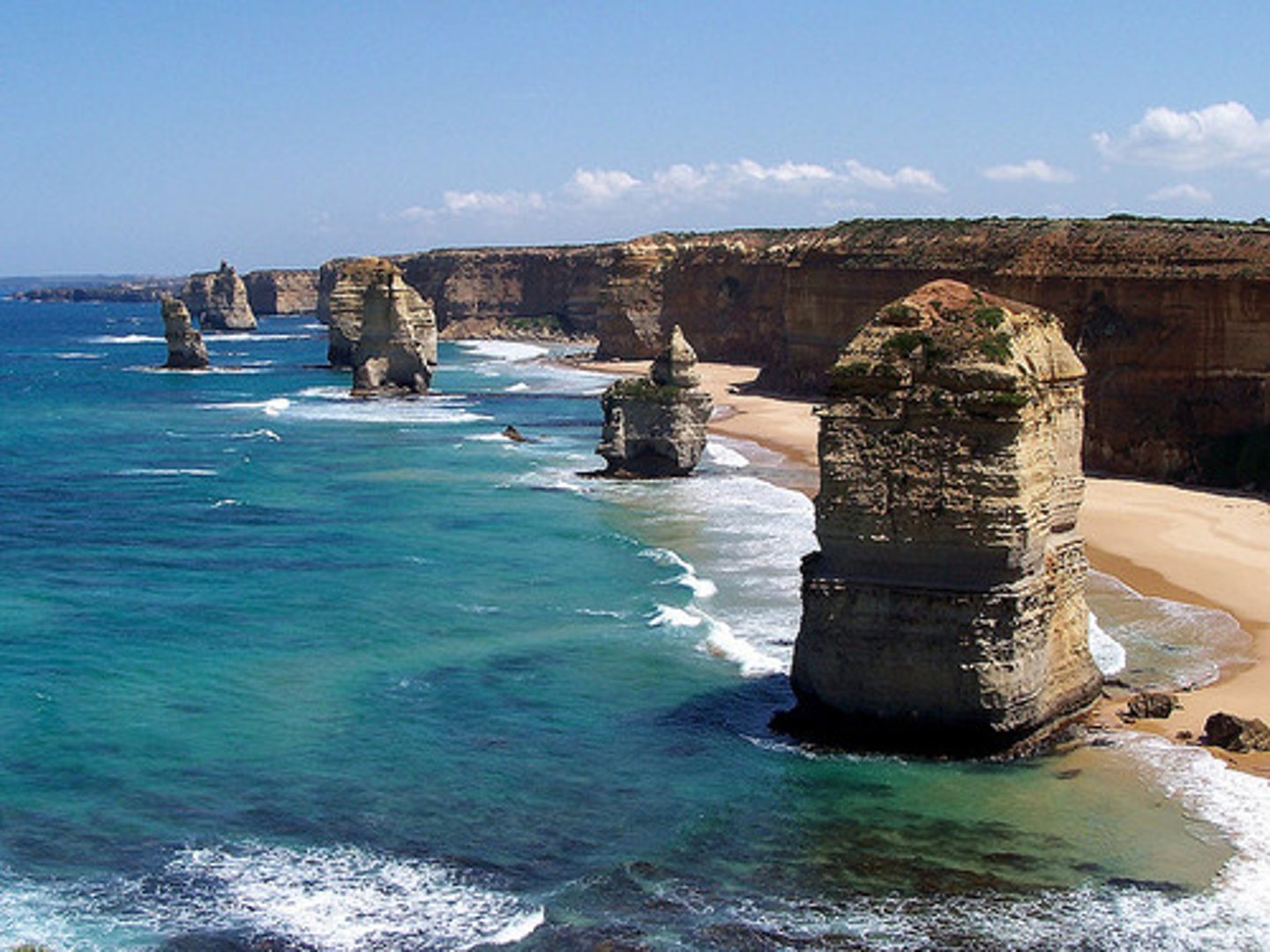
stack
a coastal feature that results from erosion; a section of the headland that has become separated from the mainland and stands as a pillar of rock

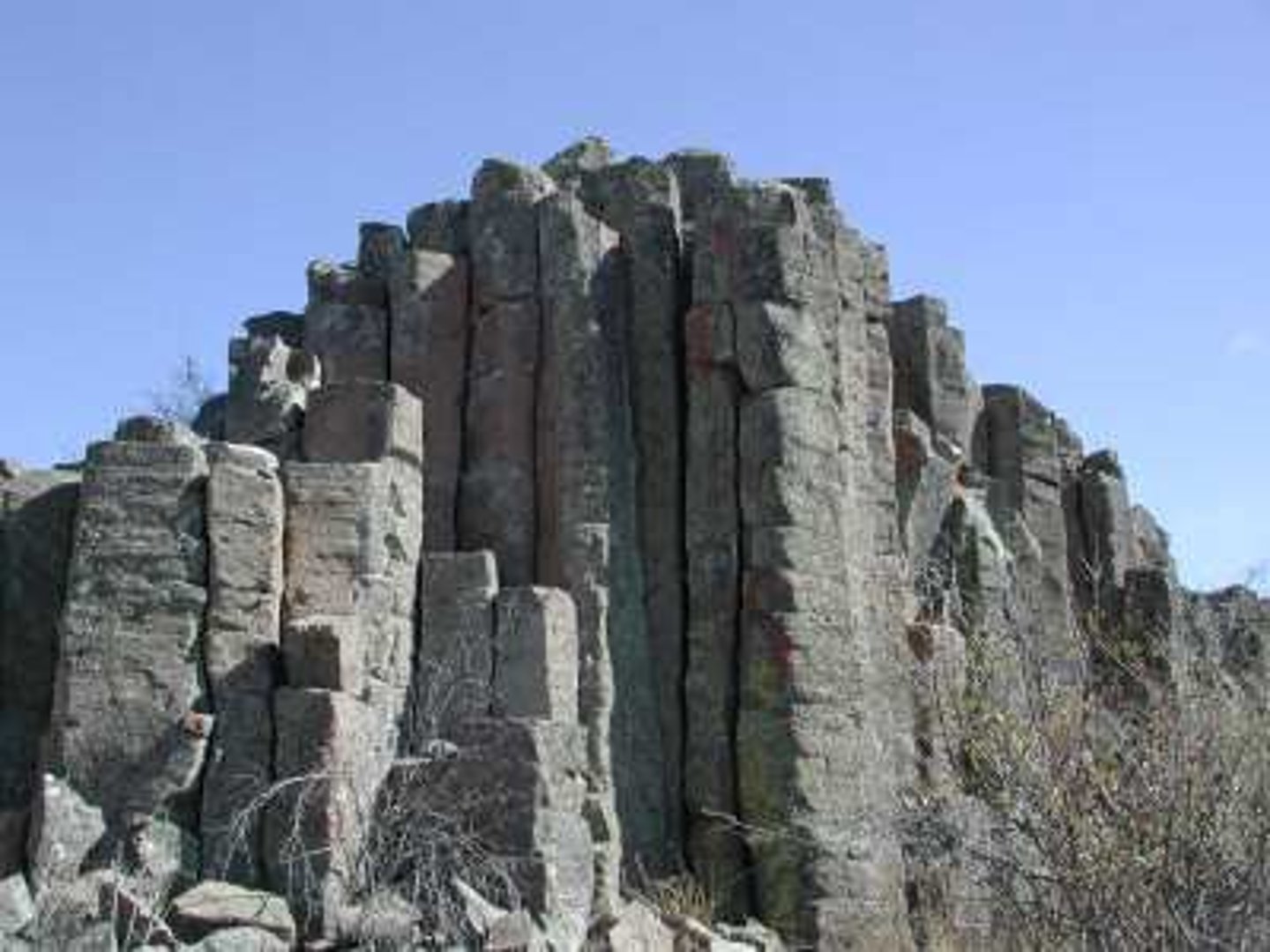
joint
a vertical crack within a rock, such as limestone, which result from the natural shrinking of the rock over time as it was formed; these may form weaknesses allowing water to penetrate the rock

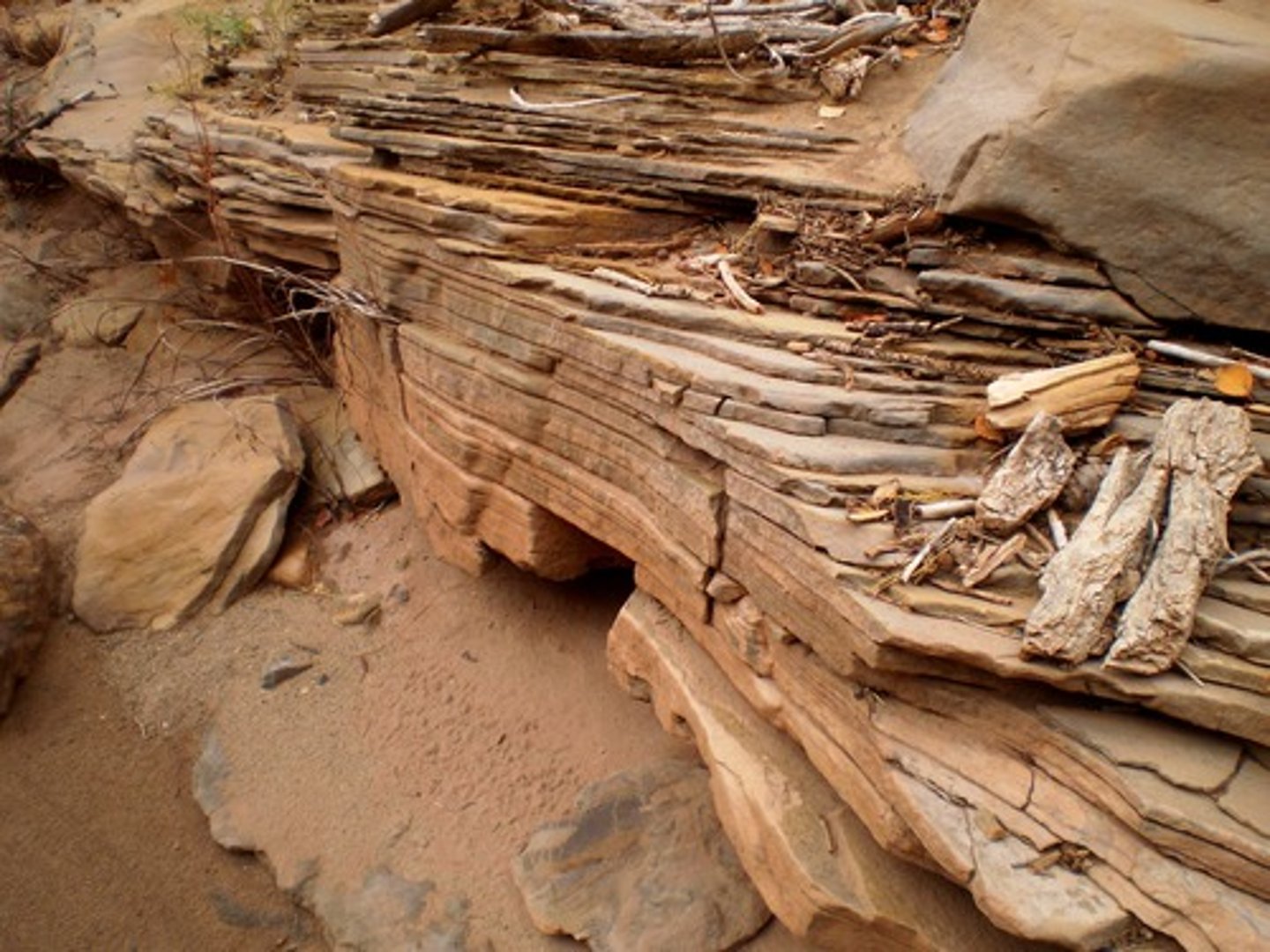
bedding plane
within a sedimentary rock, these represent the points where layers of sediment accumulates; they may later form horizontal weaknesses within the rock along which water may penetrate

natural arch
an arch-shaped structure formed as a result of natural processes within a rock feature such as a cliff
stump
a coastal feature that results from the collapse of a stack to form a protrusion of rock close to the sea surface
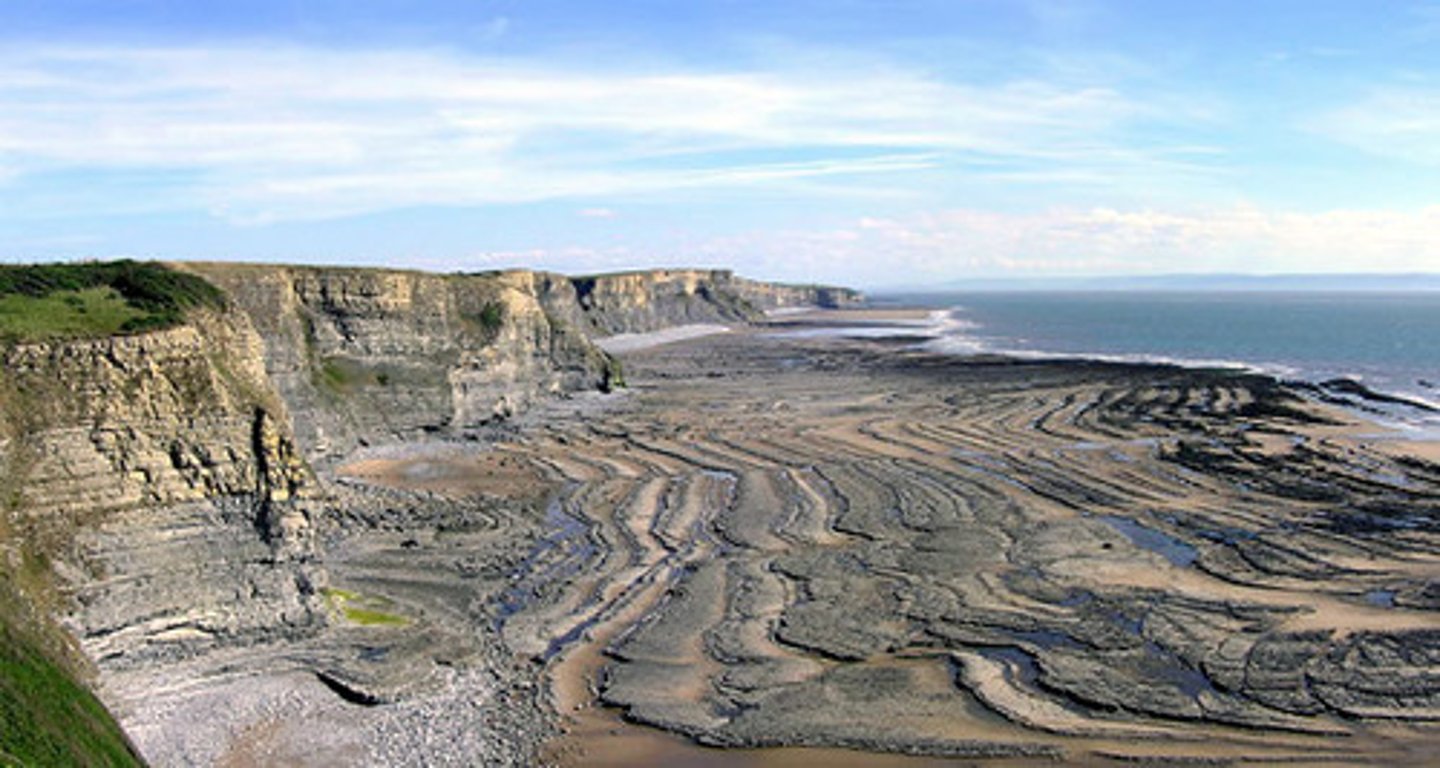
wave-cut platform
a flat area along the base of a cliff produced by the retreat of the cliff as a result of erosive processes.

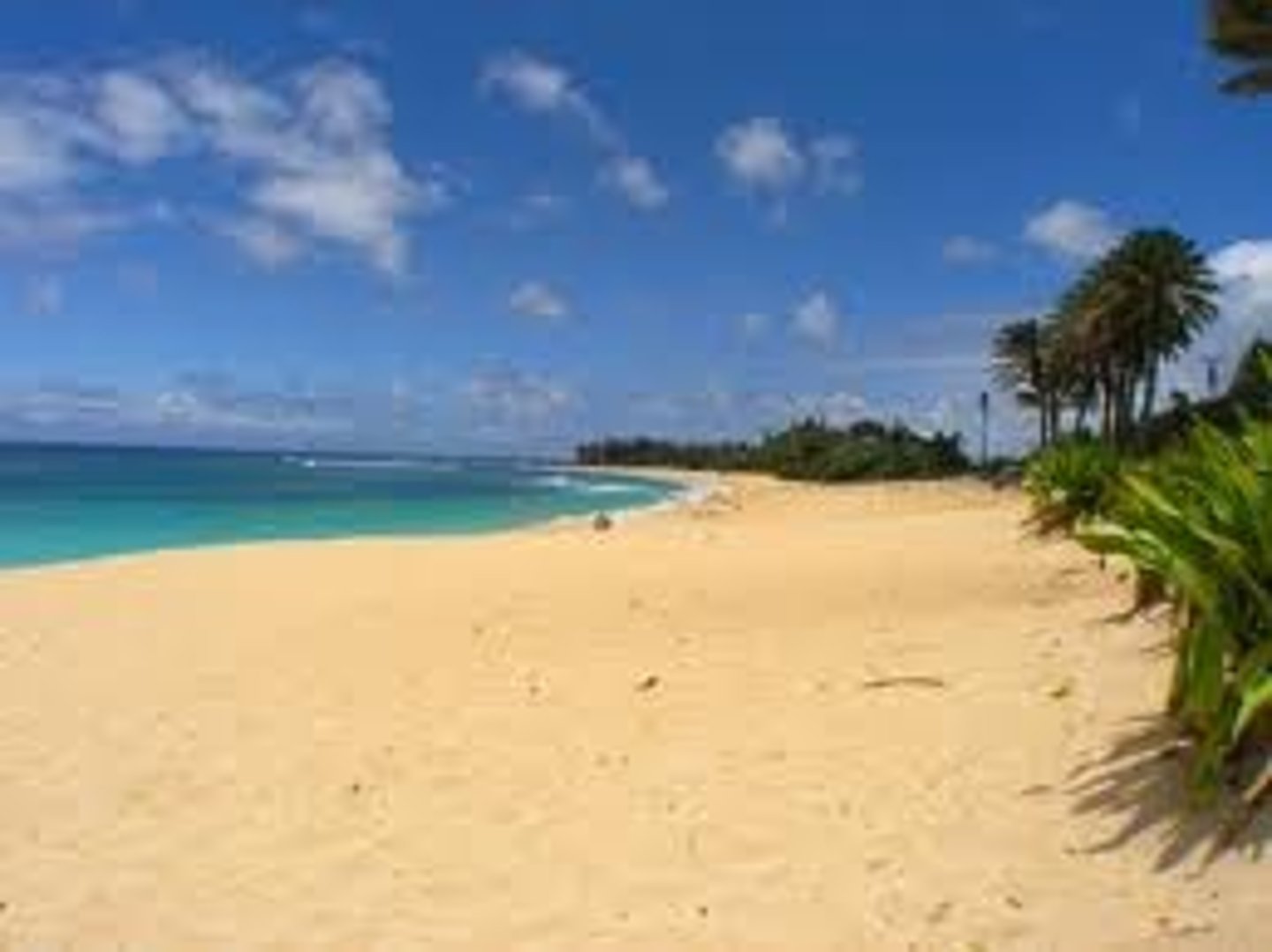
beach
an area of the shoreline that is made up of deposited sediment

wave refraction
bending of waves due to shallowing water slowing them down
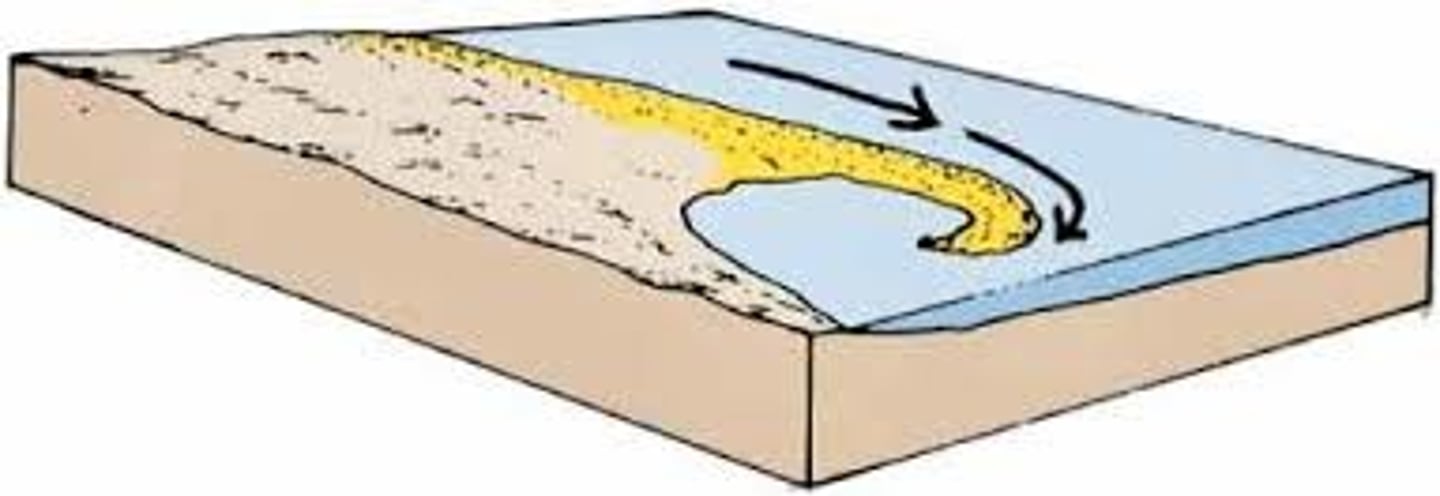
spit
a depositional landform formed at a change in direction of the coastline, due to longshore drift
corrasion
particles being carried by the river water or sea waves are thrown against the river banks or coastline
corrosion
the chemical decomposition of rocks; sometimes called solution
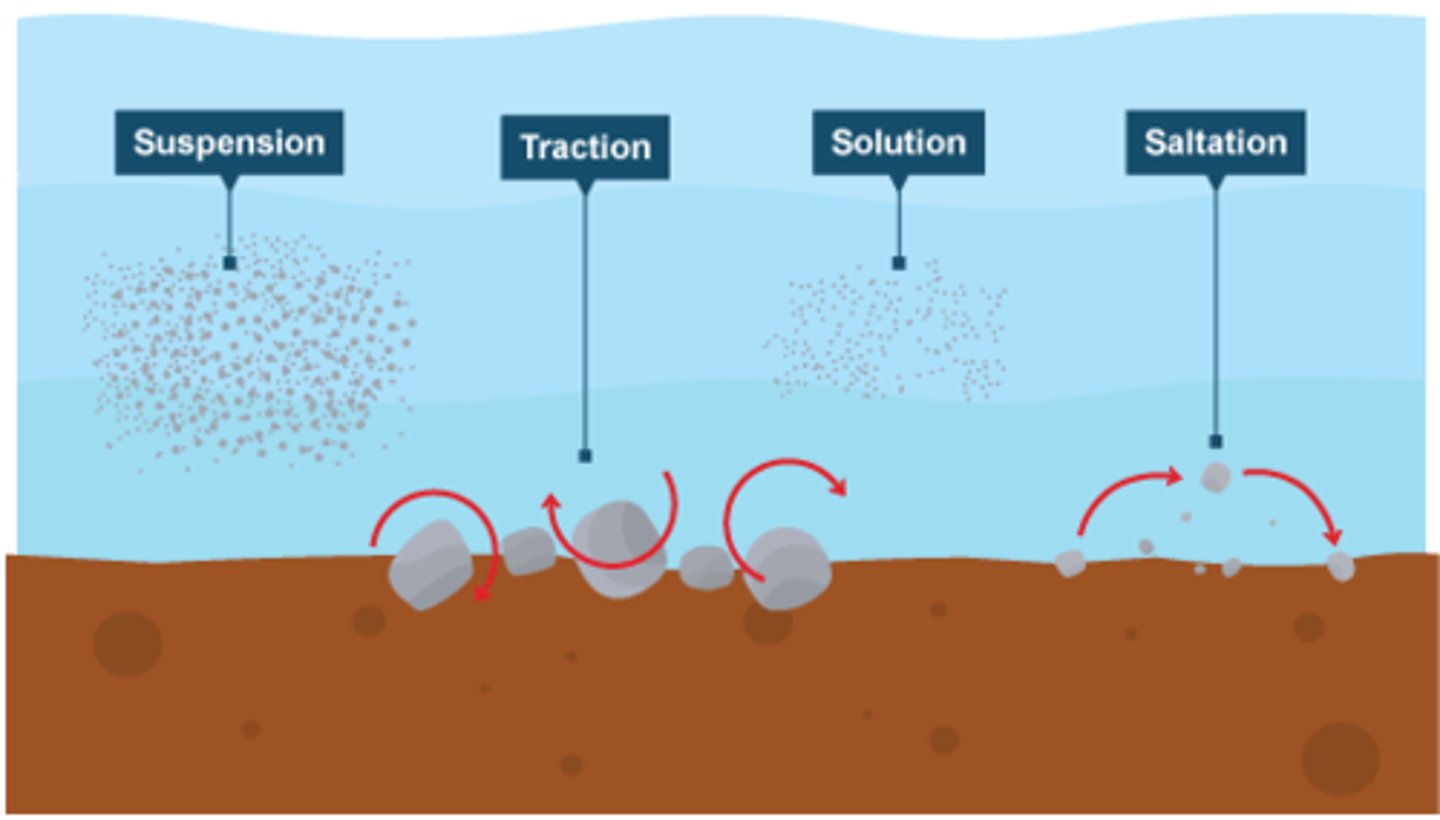
traction
The pushing or rolling of large sediment along a river or sea bed
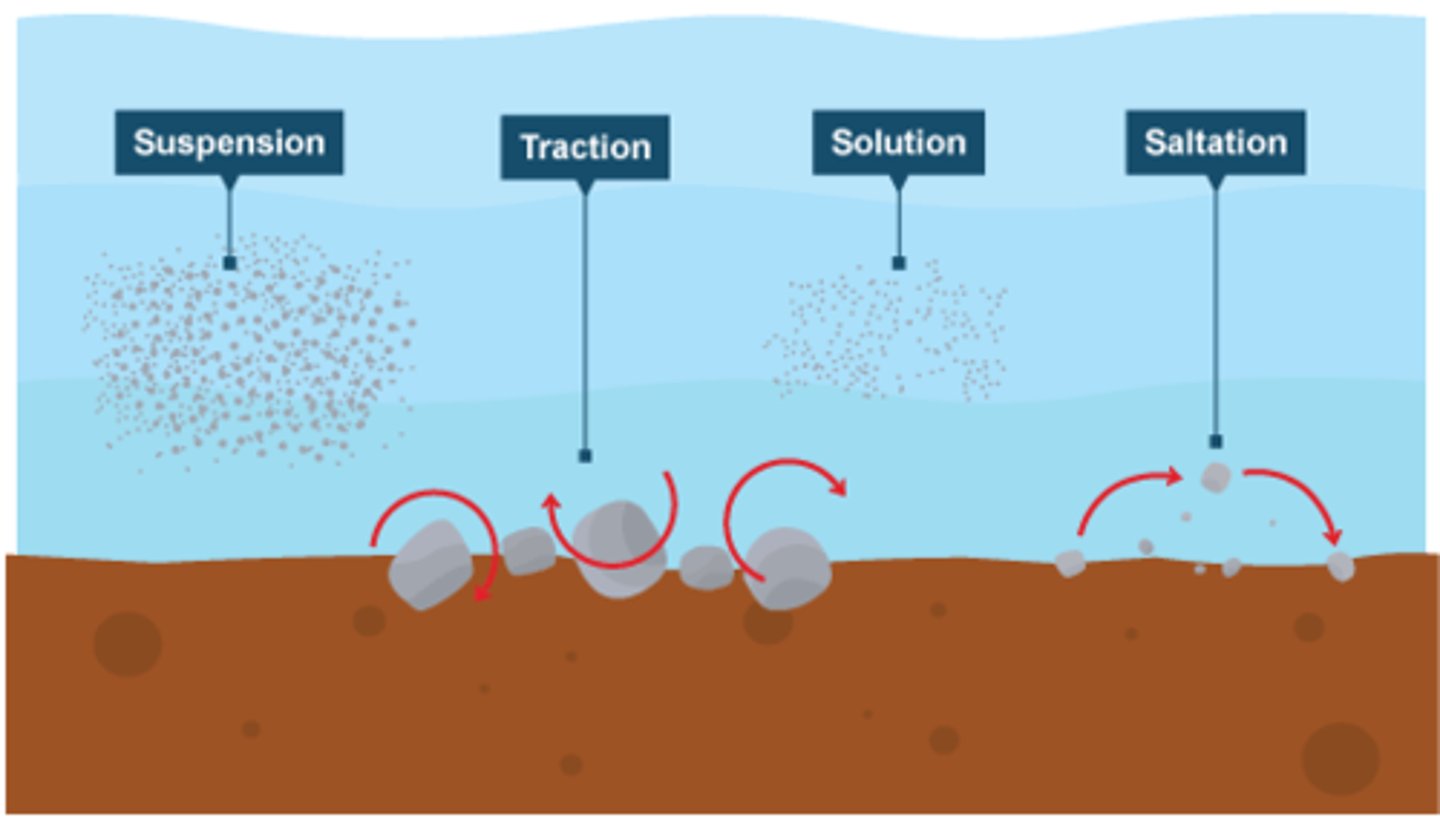
saltation
the hopping or bouncing of sediment along the river or sea bed
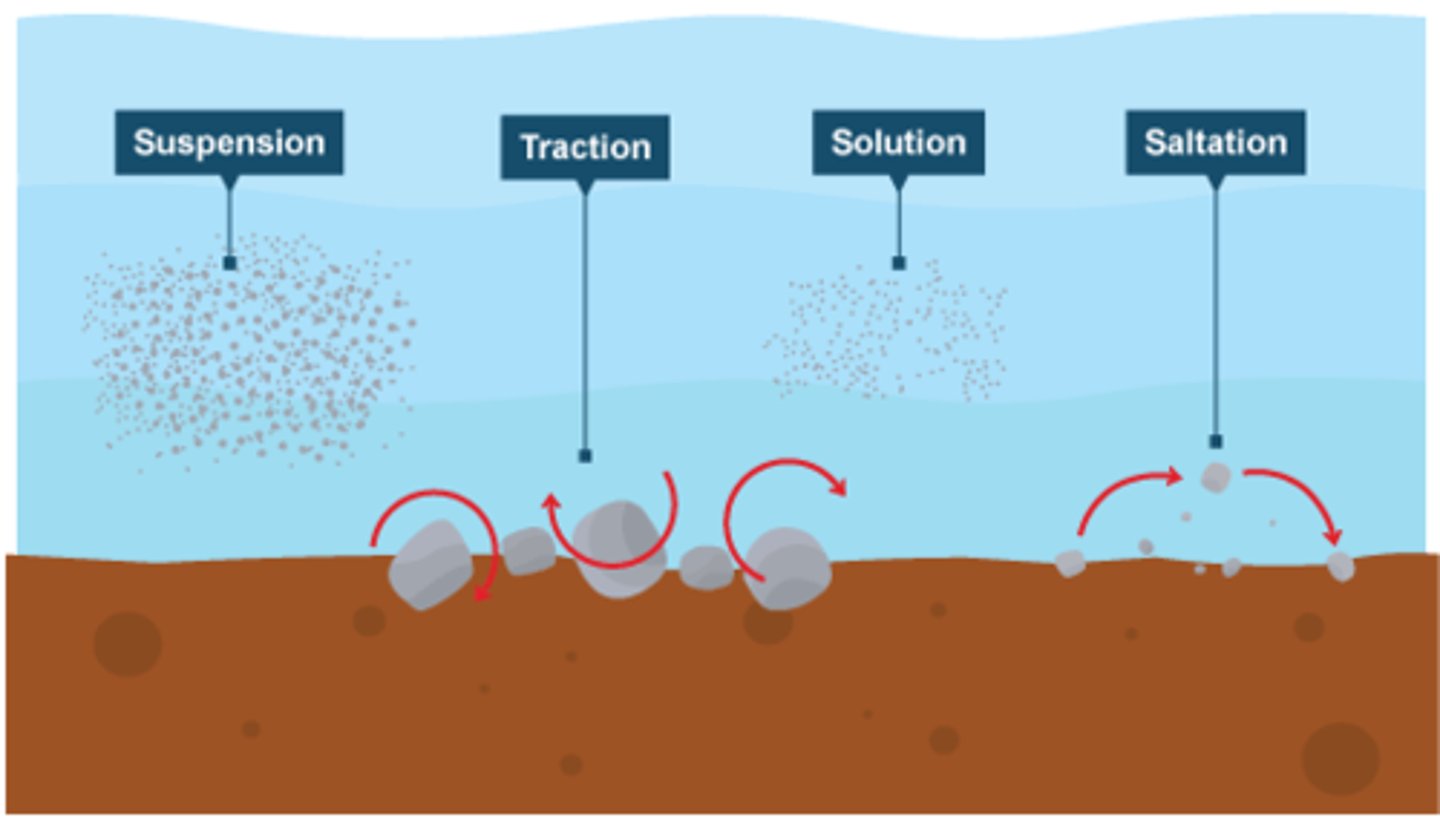
suspension
the process by which small sediment is carried along by river water or waves
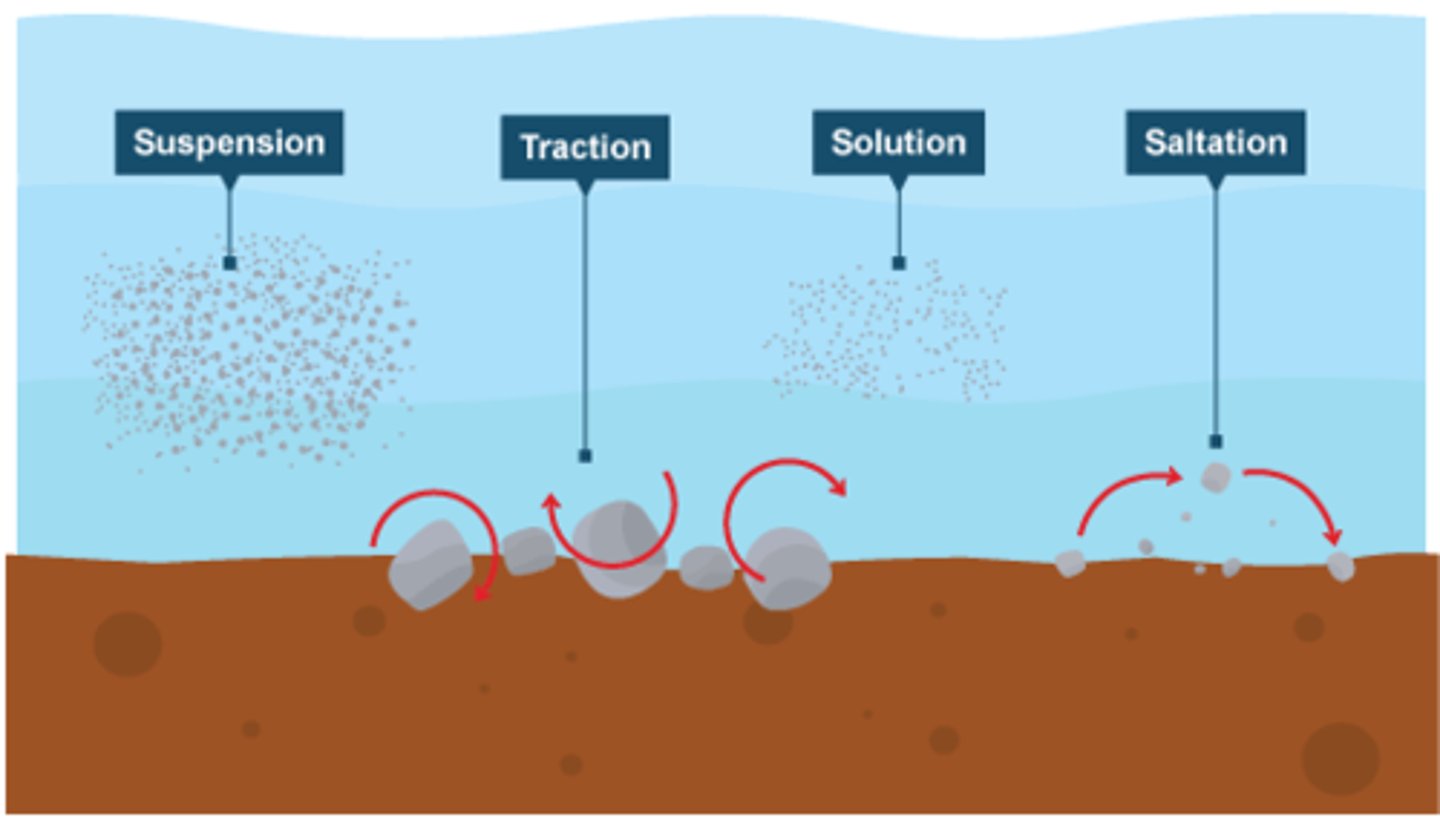
solution transport
the transport process by which material is dissolved in
discharge
The amount of water passing a given point in a river per unit of time; usually measured in cubic metres per second or CUMECS
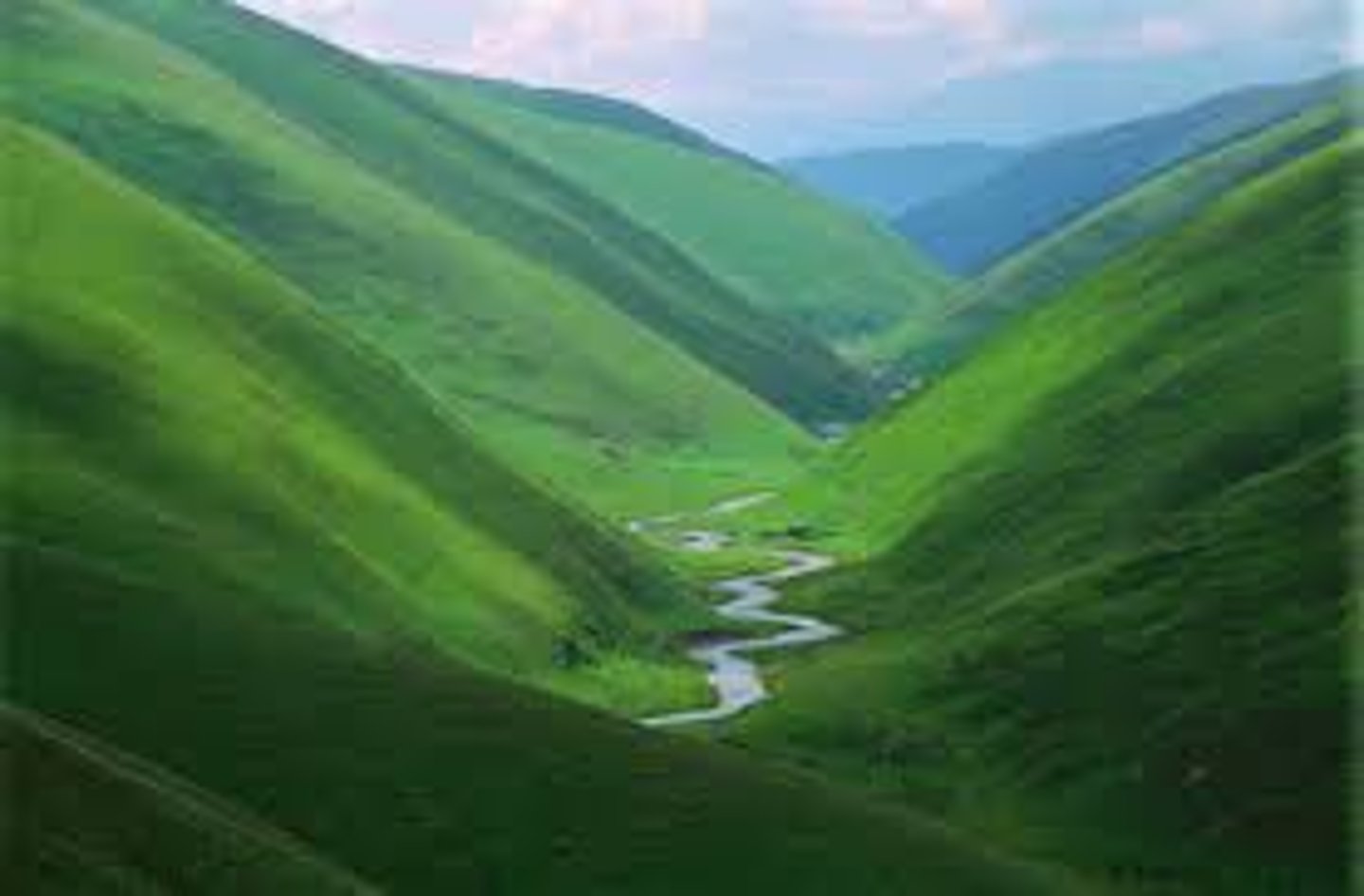
v-shaped valley
an erosional landform with steeply sloping straight sides usually found in the upper course of a river valley

waterfall
a steep fall of water where its course crosses between different rock types, resulting in different rates of erosion
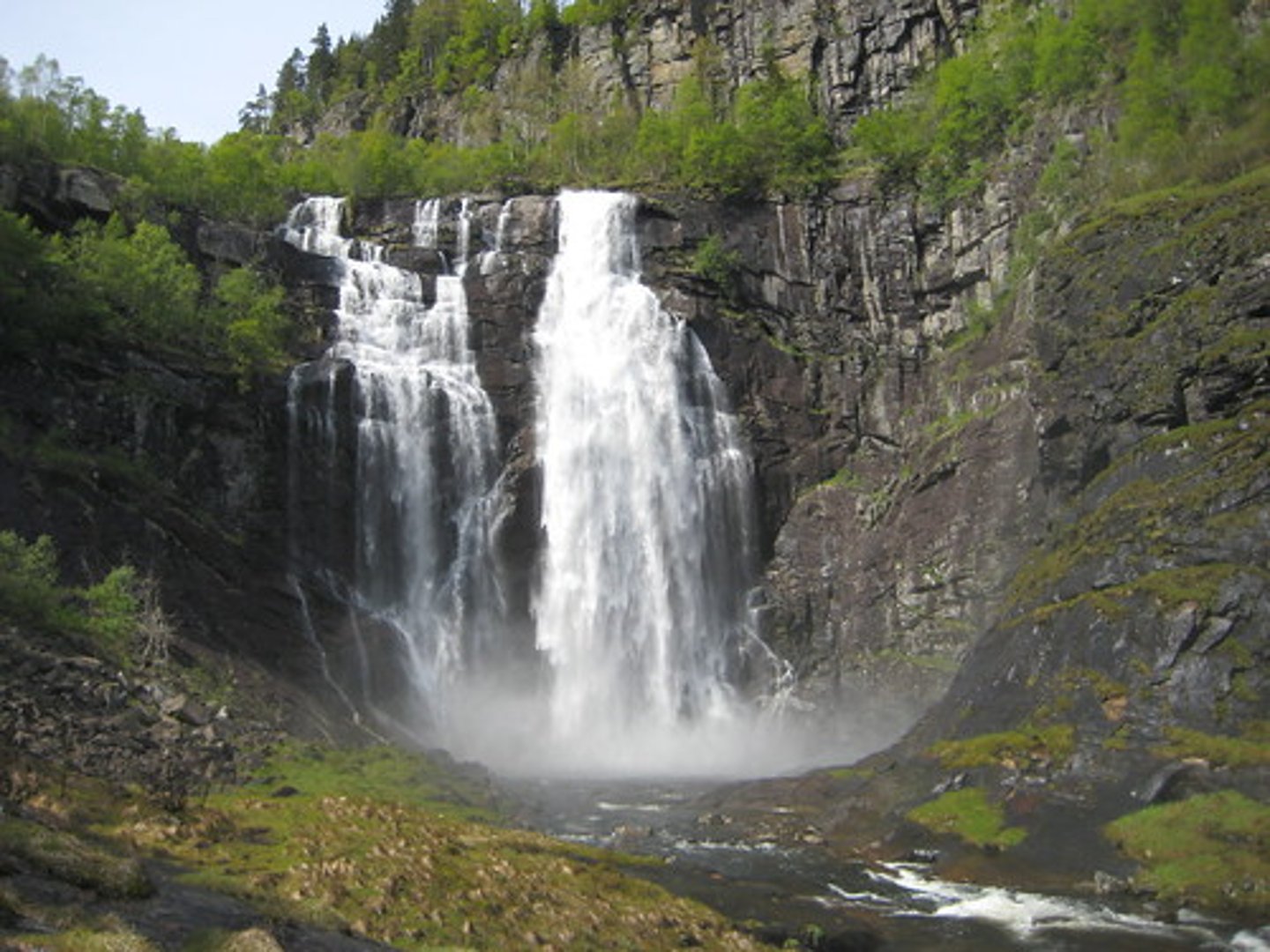

plunge pool
a pool formed at the base of a waterfall
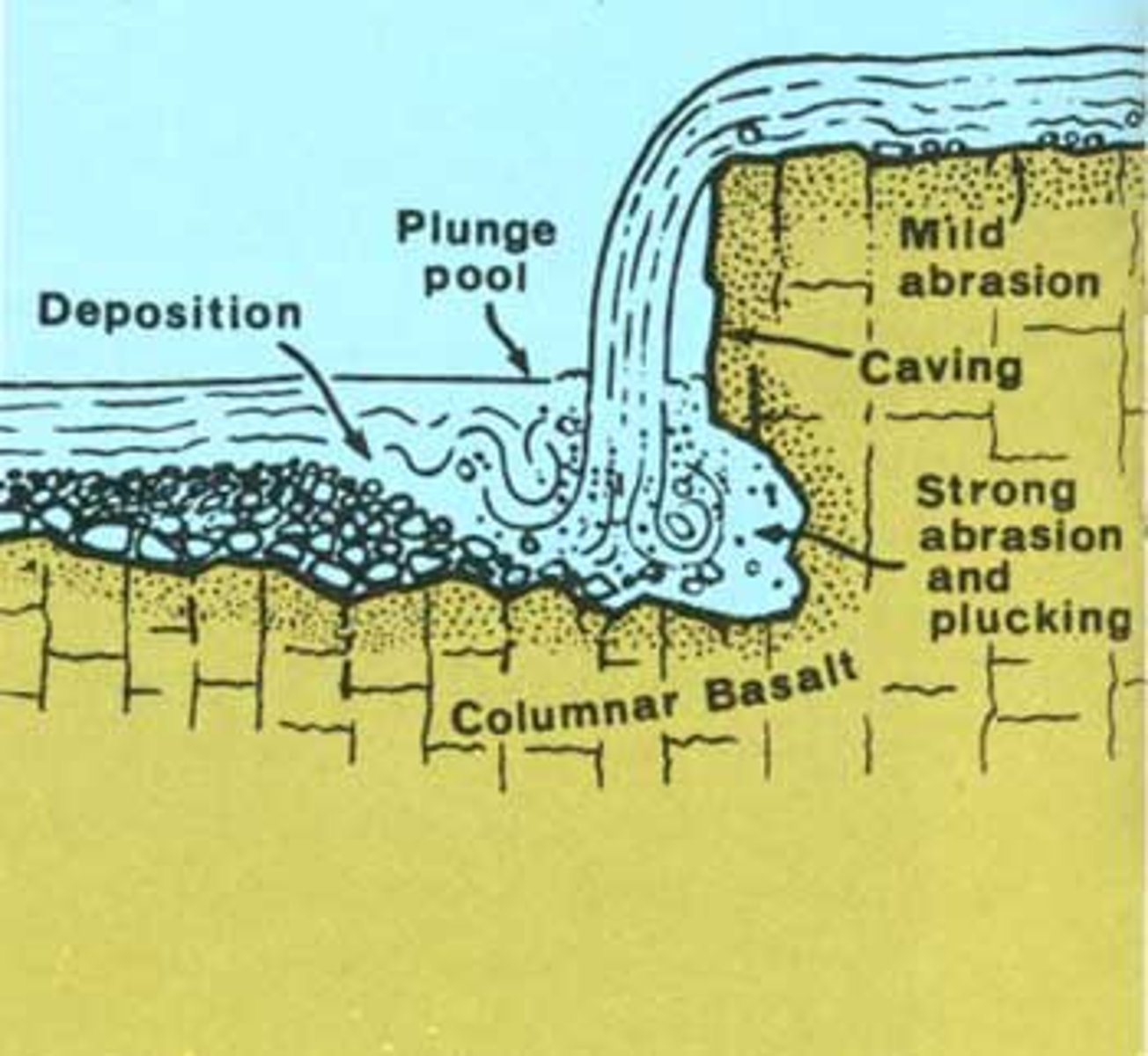
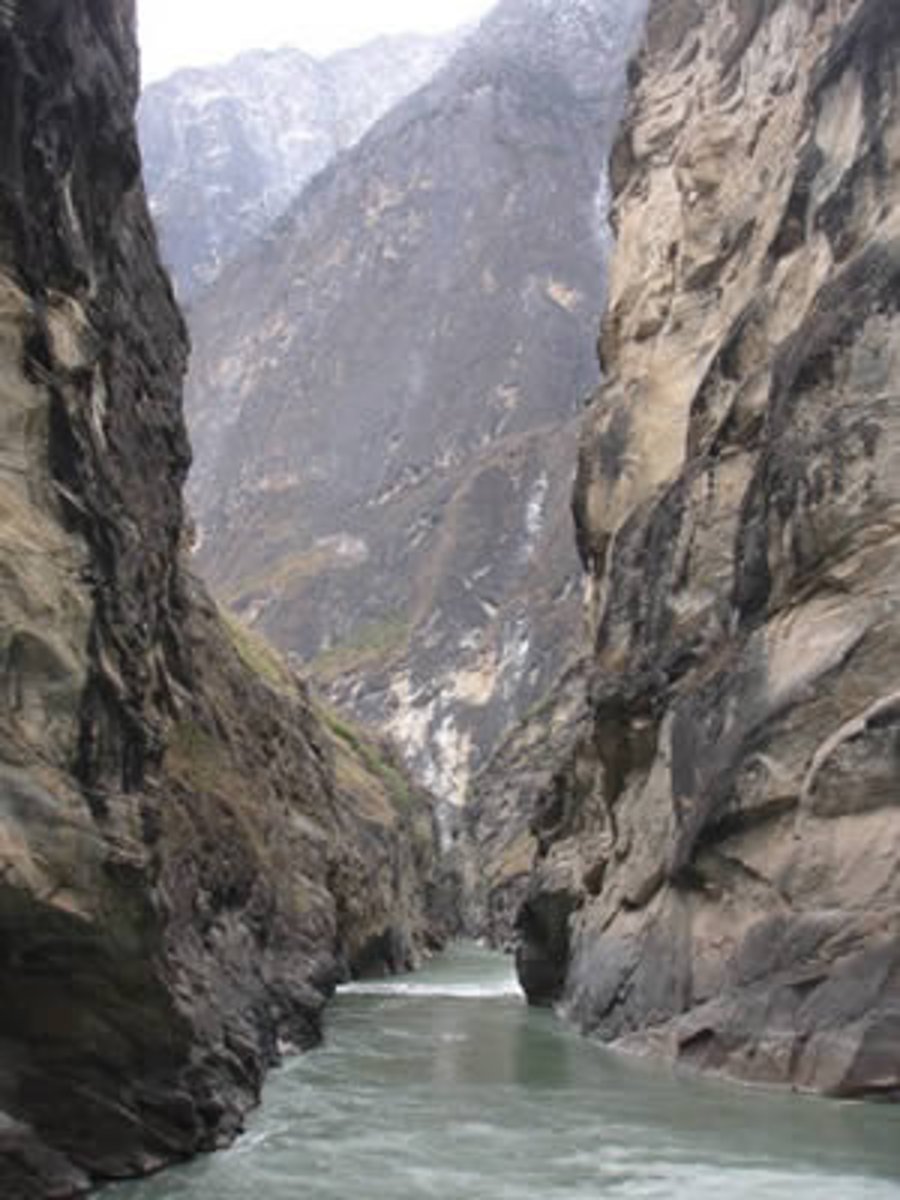
gorge
a narrow passage formed as a waterfall erodes backwards

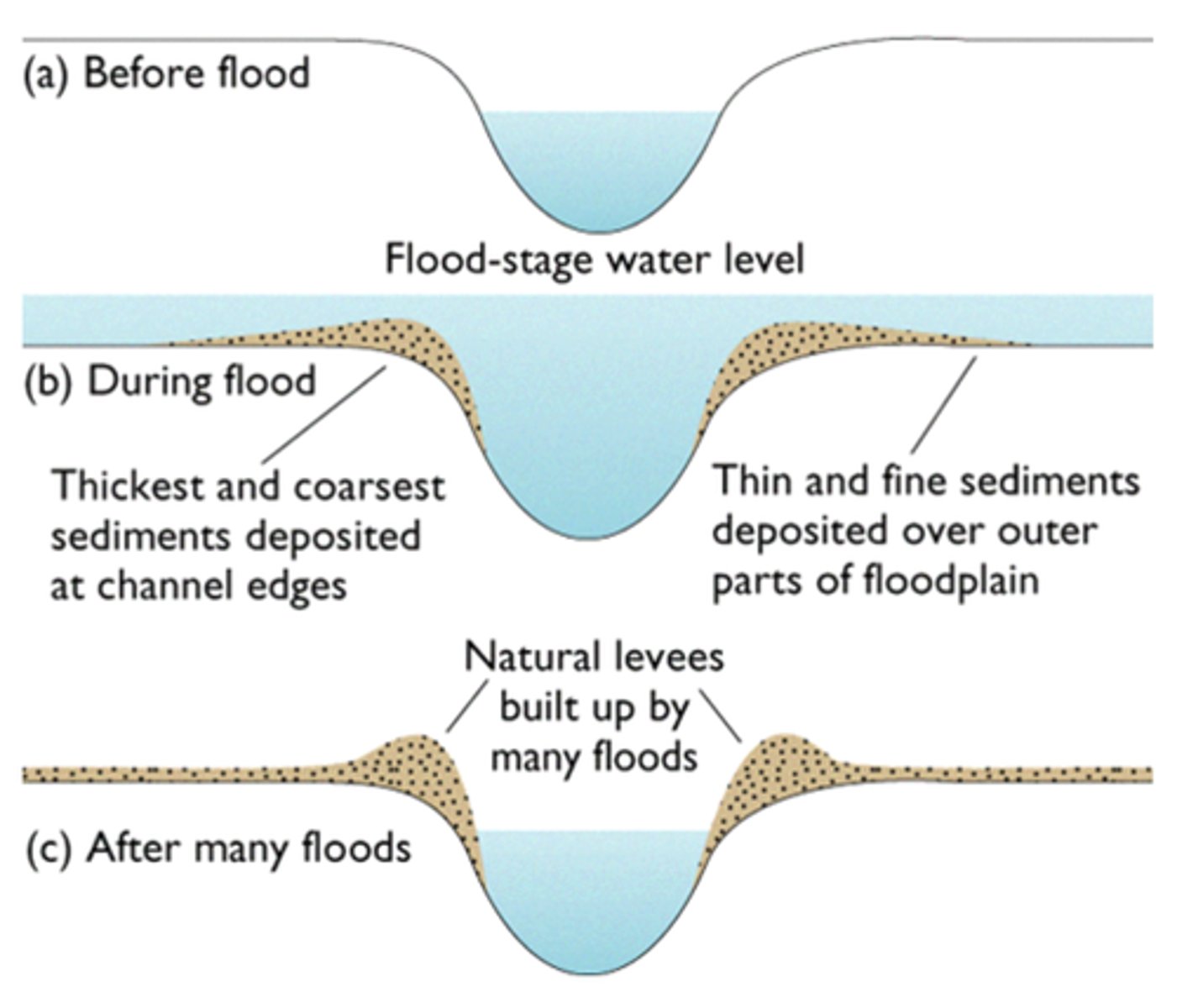
floodplain
the flat area of land either side of a river channel forming the valley floor, which may be flooded
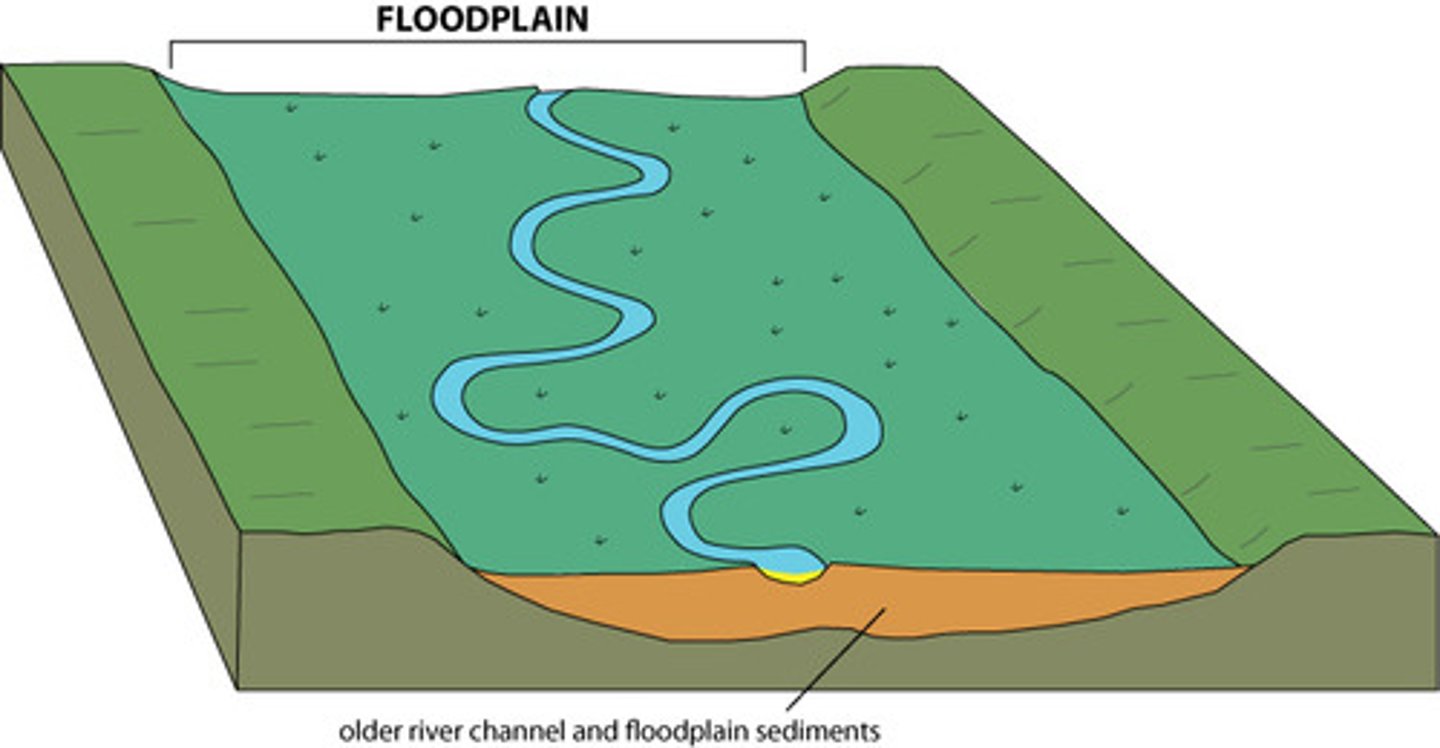
levee
raised banks along a river that help to reduce the risk of flooding
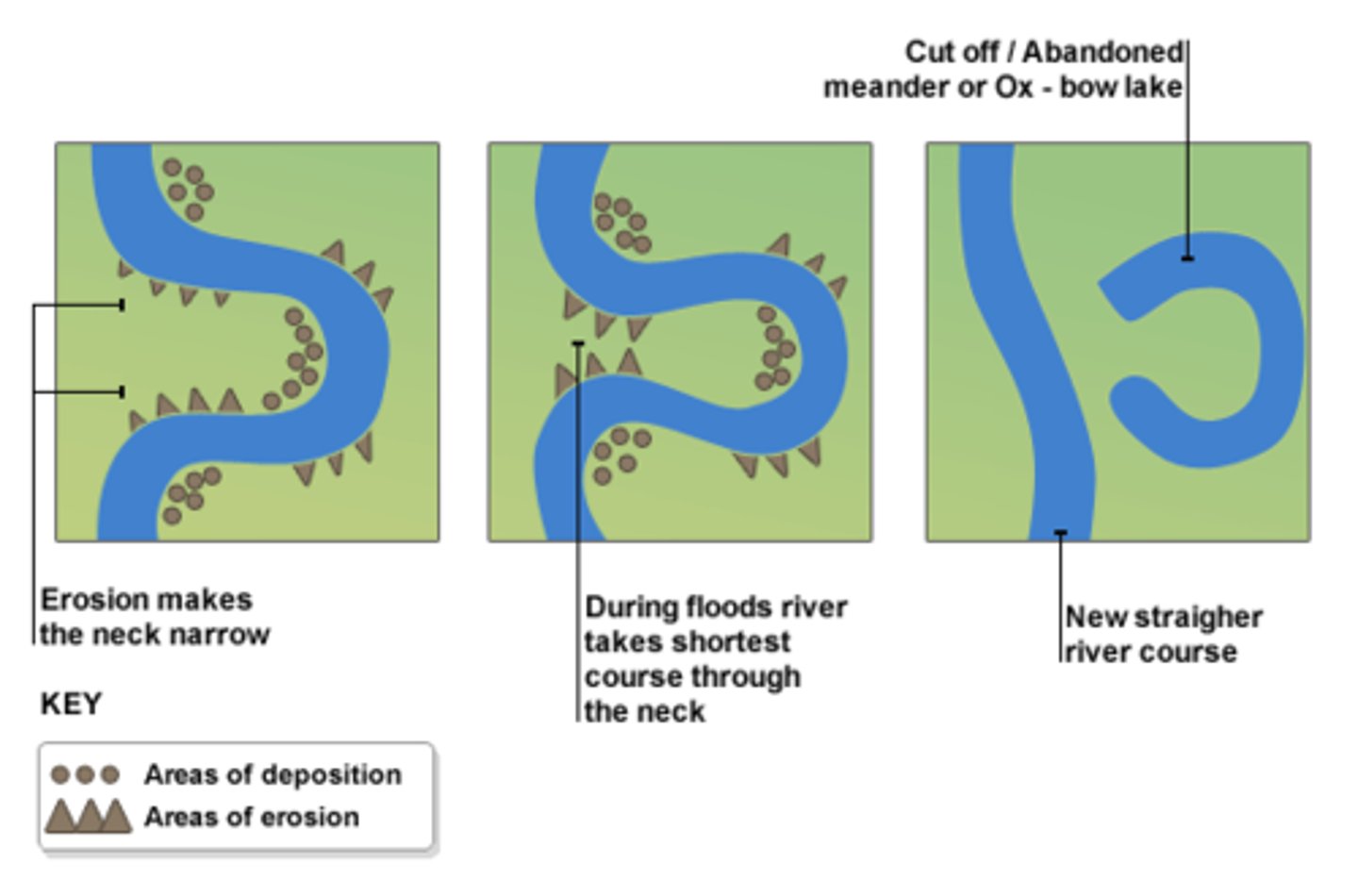
meander
a sinuous bend in a river that results from the flow of water along it
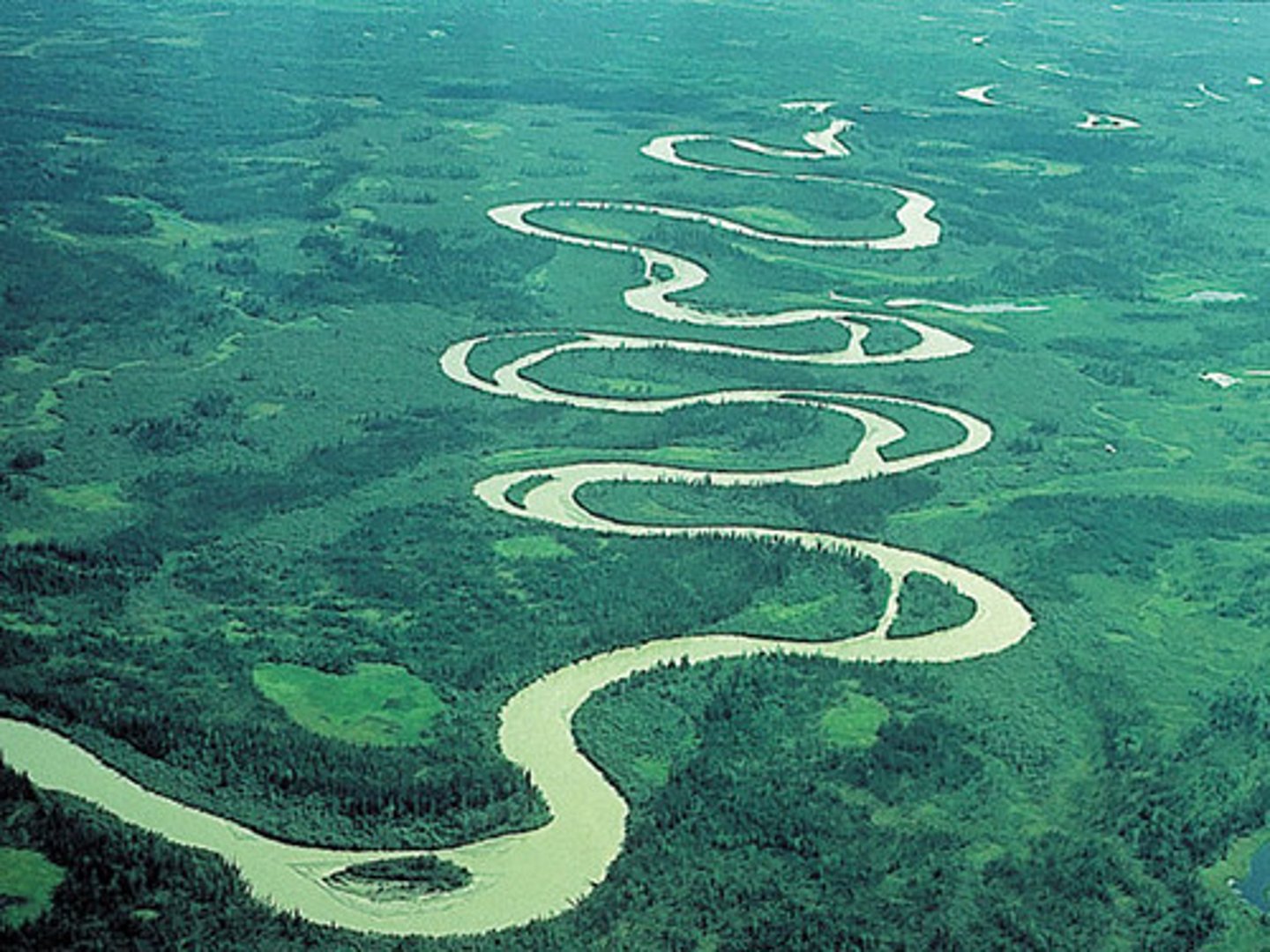

ox-bow lake
a horse shoe-shaped lake that forms when a meander is separated (cut off) from the main river channel as a result of erosion
urbanisation
the process of towns and cities developing and becoming bigger as as their population increases

agriculture
the use of land for growing crops (arable) or rearing livestock (pastoral)

Industry
the use of land for turning raw materials into processes goods

SSSI
Site of Special Scientific Interest
SAC
Special Area of Conservation
AONB
Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty