monomers and polymers
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is a monomer?
A small basic molecule
What is a polymer?
Long chains of repeating monomers chemically bonded
What is the monomer of carbohydrates?
Glucose
What is the monomer of proteins?
Amino acids
What is the monomer of DNA/RNA?
Nucleotides
What is the monomer of lipids?
Fatty acids (x3) + glycerol
Saccharides
Sugar
Mono
One
Poly
Many
Mer
Part
How many amino acids are there?
20
How do monomers form polymers?
Addition reactions (no by-products) or
Condensation reactions (with small molecule by-products like water).
What is the chemical formula for monosaccharides (sugar/glucose)?
C₆H₁₂O₆
What is the chemical formula of amino acids?
R-CH(NH₂)-COOH
What is the chemical formula for glycerol?
C₃H₈O₃
What is the chemical formula for fatty acids?
R-COOH
carbohydrate
Polysaccharides and are polymers made from repeating units of monosaccharides. The monosaccharides are joined together via a condensation reaction which forms a glycosidic bond between the adjacent monosaccharides.
Polysaccharides
Large, insoluble carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
Simplest form of carbohydrates, consisting of single sugar units
Glycosidic bond
a covalent bond formed between two monosaccharide molecules during a condensation reaction, with the elimination of a molecule of water
Protein
Proteins are large, complex polymers made from amino acid monomers, which are joined together by peptide bonds formed in condensation reactions.
Polypeptide
a polymer of amino acids linked together by peptide bond
amino acid
Monomer of proteins
Peptide bond
Covalent bond between amino acids
DNA
double-stranded, helical molecule that carries the genetic code for the synthesis of proteins. It is a polymer of nucleotides, each consisting of a deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
Polynucleotide
a polymer made up of many nucleotide monomers linked together by phosphodiester bonds to form a long chain.
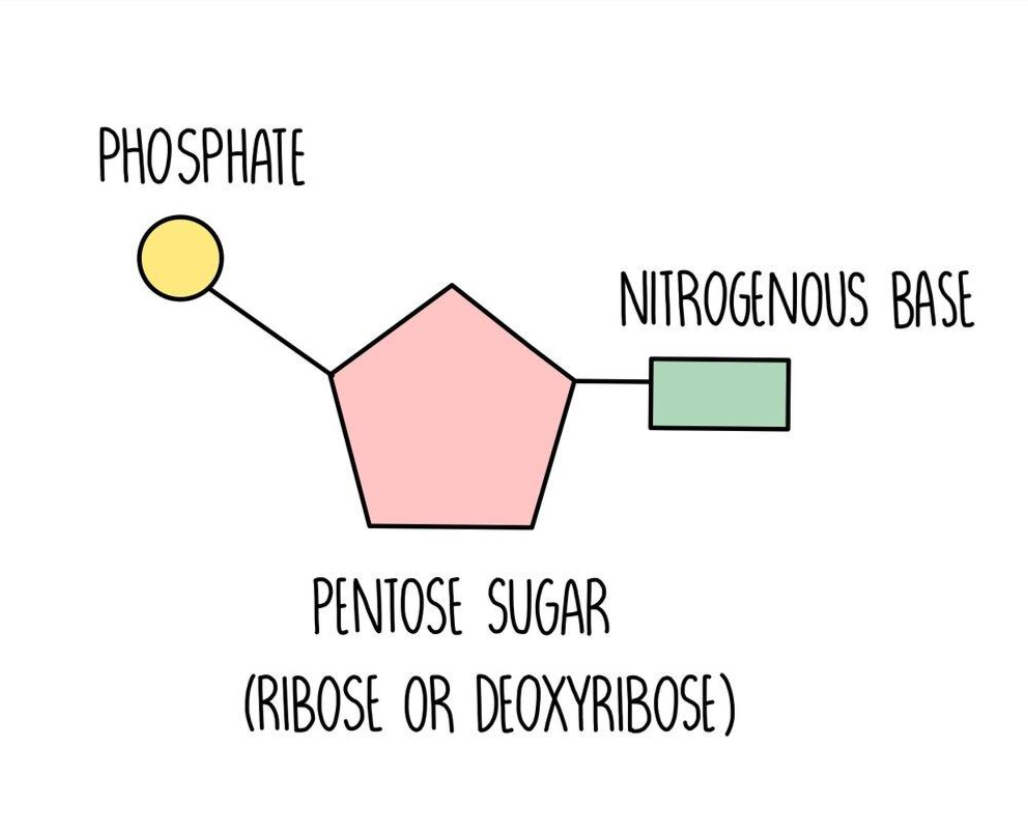
Nucleotides
monomer of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). it contains a pentose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base
phosphodiester bond
a covalent bond that forms between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the hydroxyl
Lipid
Insoluble biological molecules formed from smaller molecules like glycerol and fatty acids in condensation reactions.
Fatty acids
a molecule consisting of a hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group (–COOH) at one end
Glycerol
a three-carbon alcohol that acts as the backbone of triglycerides and phospholipids. Each carbon atom in glycerol has a hydroxyl group (–OH), which allows it to form ester bonds with fatty acids in condensation reactions.
Condensation reaction
a chemical reaction in which two molecules are joined together with the removal of a water molecule (H₂O). This reaction is responsible for forming important biological polymers such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
Hydrolysis reaction
a chemical reaction in which a molecule is split into two smaller molecules by the addition of a molecule of water (H₂O). It is the reverse of a condensation reaction.
Ester
Production of the reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol, water is also produced