regression correlation and hypothesis testing(y2)
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
finding a linear relationship for y = ax^n
logy = loga + nlogx
finding a linear relationship for y = kb^x
logy = logk + xlogb
product moment correlation coefficient
a measure describing the strength of the linear correlation between two variables, denoted as r for a sample or p for a population
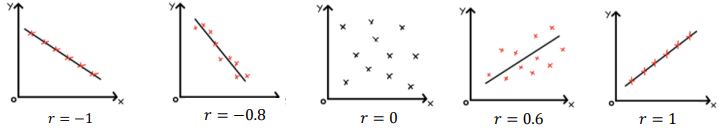
PMCC values
-1 (all points lie on a straight line with a negative gradient)
-1>r<0 (all points lie somewhat close to a straight line with a negative gradient, the lower the value the closer they are) 0 (no correlation whatsoever)
0 (all points lie randomly and have no inherent closeness to a straight line)
0>r<1 (all points lie somewhat close to a straight line with a positive gradient, the higher the value the closer they are)
1 (all points lie on a straight line with a positive gradient)
finding PMCC for bivariate data
method varies by calculator, but for the casio fx-991cw:
-press the home button and go to statistics mode
-select 2-variable mode
-input the x and y values for all of the points
-press ok and select reg results
-select y = a + bx
-the PMCC is given by r
hypothesis testing for zero correlation on a bivariate data sample
-the null hypothesis will be p = 0
-the alternate hypothesis depends on the question (but will usually be p > 0 or p < 0)
-find the critical value for the PMCC
-compare it to the real PMCC
-come up with a conclusion