Evolution and Genetics
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Natural Selection
indirect at gene level, direct at individual
individuals over reproduce but #s stay constant due to environmental limitations
environment dictating natural selection at 3 levels
genetic (developmental) structure
structural (stimuli) behavior
behavioral (selection) reproduction of genes
VP formula
VP = VG + VE + VGE
adaptation
genetically based features favored by selection
adaptive traits
traits that enhance survival of their bearer relative to others
difference between adaptations and adaptive traits
adaptations are adaptive traits but not all adaptive traits are adaptations
indirect competition
each individuals independently deals w/ the selection
direct competition
interaction among individuals IS the selection
2 ways to determine adaptive value of behaviors
cost benefit analysis and comparative approach
cost benefit analysis
cost = decreased reproduction or # alleles
benefit = increase reproductive fitness
ex: optimal quail group size
comparative
convergent and divergent species
divergent species
closely related species, but possess different behaviors in their differing environments (ex. mobbing behavior of gulls-- cliff vs. ground)
convergent species
different species in similar environments have similar behaviors (
ex. ground squirrels and ground gulls
evidence for links between genetics and behavior
twin studies, drosophilia genetics, hybridization, transgenic, artificial selection, AVP/OT in moles, BDNF, Kallman syndrome
AVP/OT in moles
extra 460 nucleotides in middle of promoter for OT and AVP receptor genes = monogamy
BDNF
mutation causes issues
kallman syndrome
small gonads, no sense of smell, sexually indifferent
gene turned on in olfactory bulb, produces anosmin
Anosmin connects olfactory axons w/ olfactory bulb, causing smell
GnRH neurons that trigger sexual development begin in nose
If no anosmin, no olfactory tracks to brain, so no GnRH released
pleiotropy
1 gene controls many traits
artificial selection
dog breeds, etc
transgenics
inserting and/or transferring a gene from one species to another; the molecular transfer of species-specific behavior
ex. Drosophila per gene, controls several “rhythms”
knockout:
fosB knockout mice and nuturing
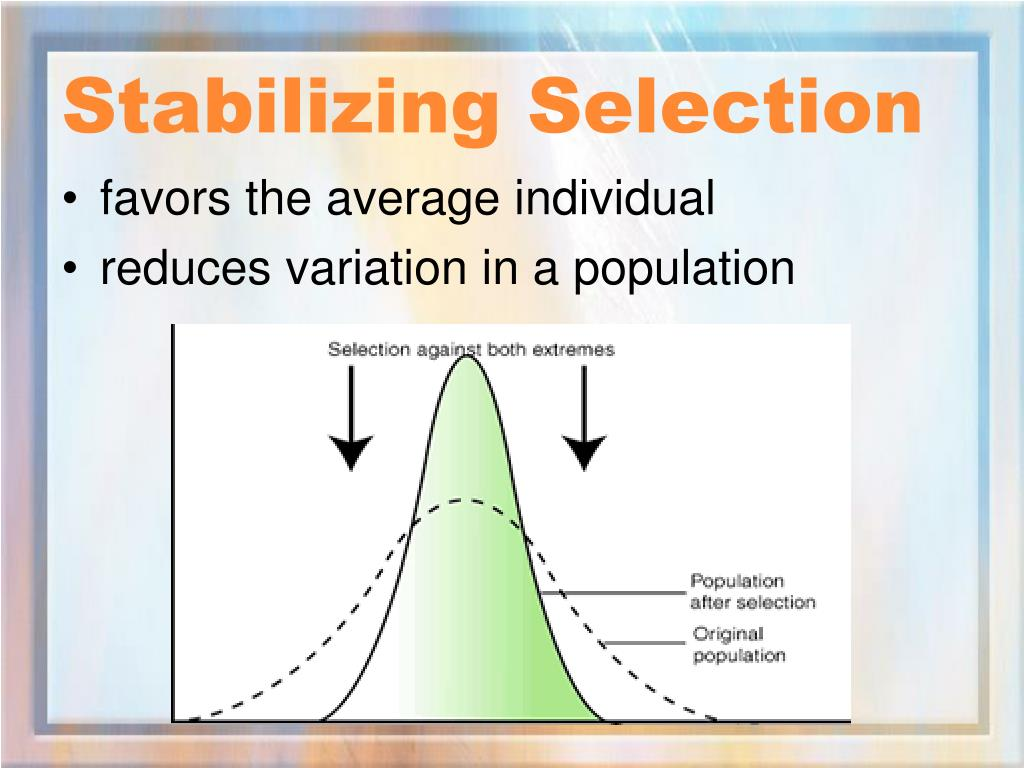
stabilizing selection
directional selection

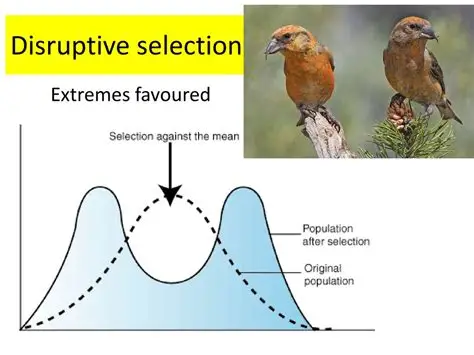
disruptive selection