Thermal Physics
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms

Explain how the energy is transferred from a solid to a liquid (melting stage) changes the arrangment of atoms
The energy transferred reduces the number of nearest atomic neighbours
State what happens to the potential energy of the atoms and to the kinetic energy of a atom when changing from a solid to liquid (melting stage)
The total kinetic energy remains constant.
The total potential energy increases.
the motion of the atoms changes when a liquid compared to a solid
The mean kinetic energy increases
The sample has a mass of 0.25 kg.
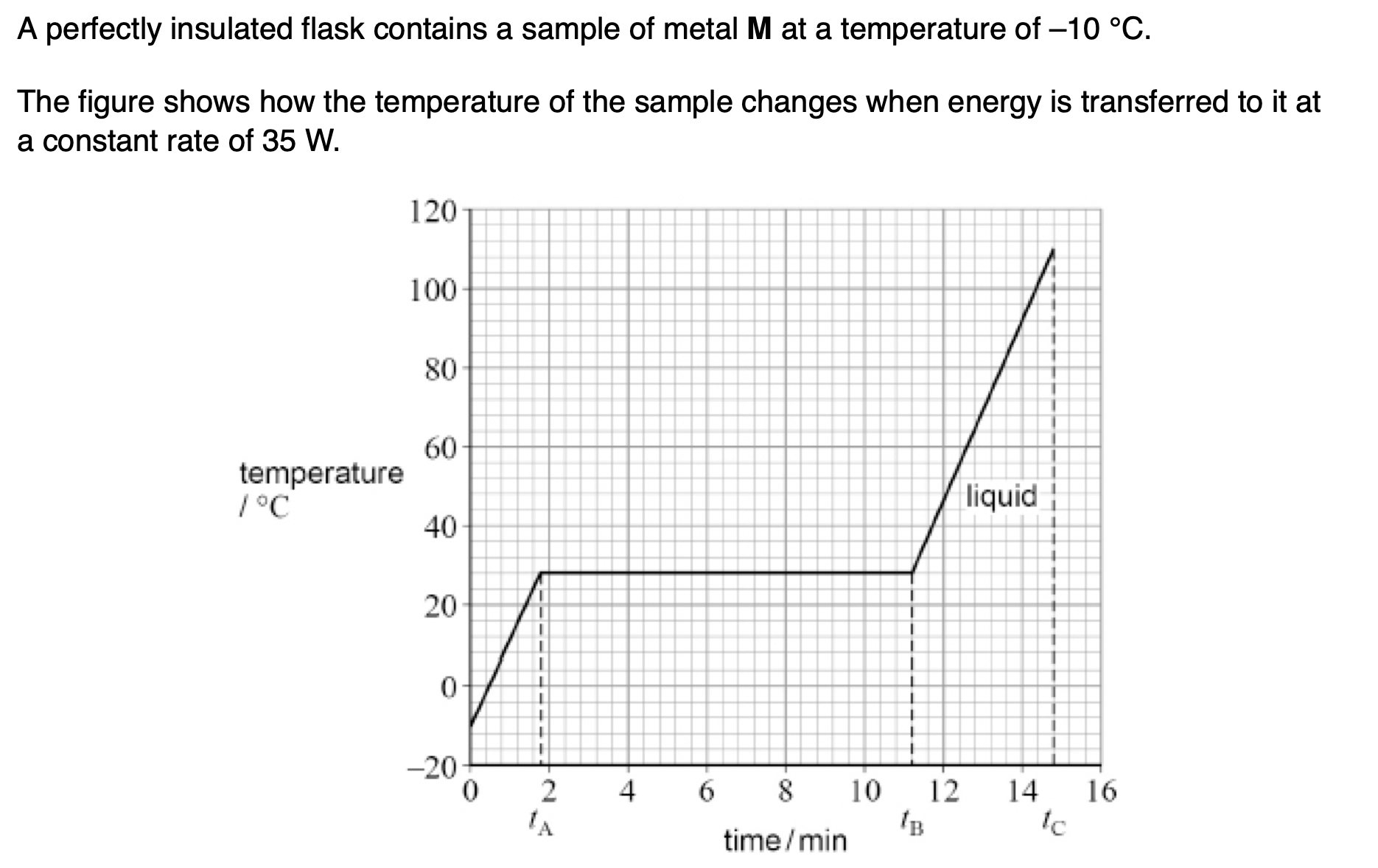
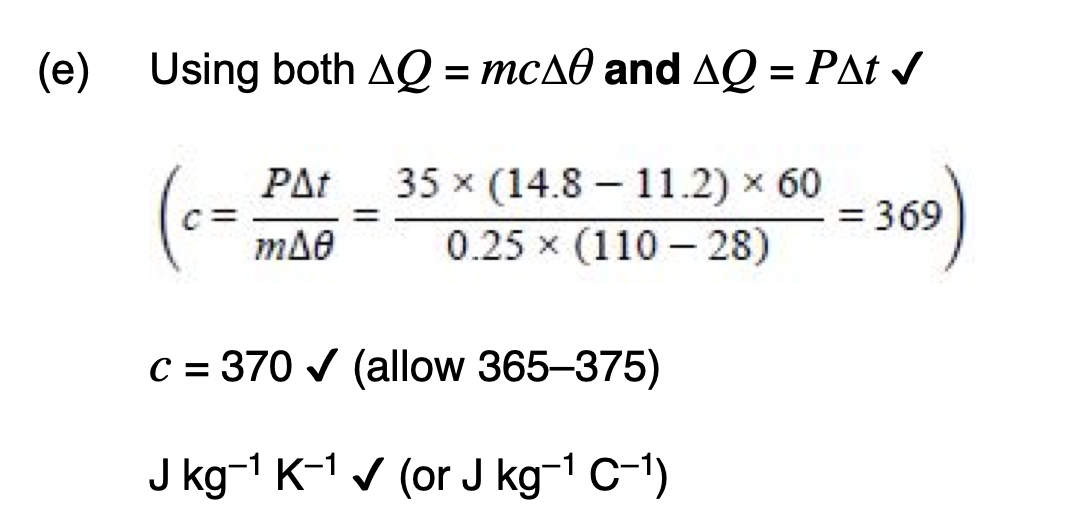


Explain what is meant by specific latent heat of fusion.
Specific latent heat of fusion is the energy required to change 1 kg of material from the solid state to the liquid state without a change of temperature or at the freezing/melting point
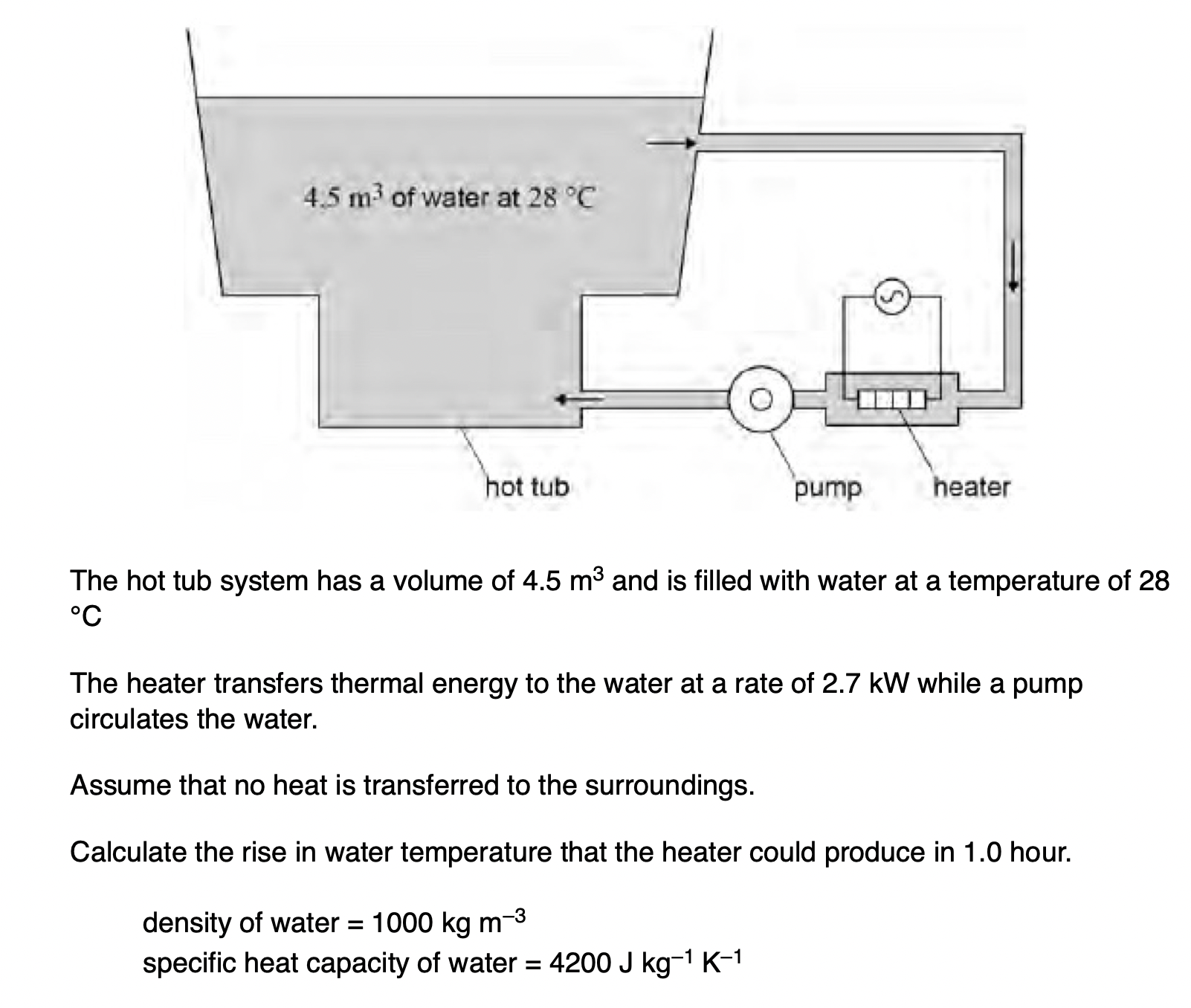

The pump can circulate the water at different speeds. When working at higher speeds the rise in temperature is greater. Explain why.
the pump is doing work on the water
Work can raise the temperature of a body
Lead has a specific heat capacity of 130 J kg−1 K−1
Explain what is meant by this statement.
it takes 130 J to raise the temperature of a mass of 1 kg of lead by 1 K

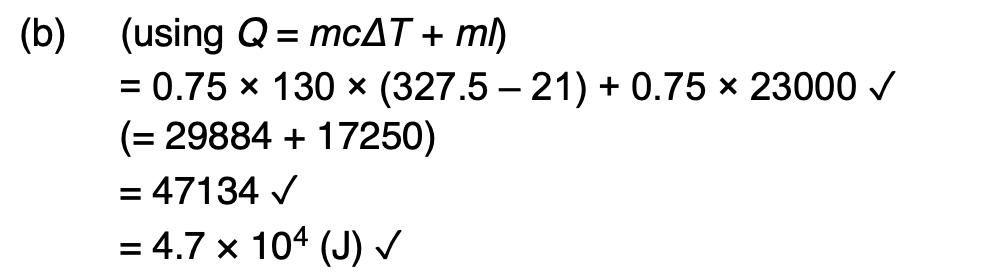

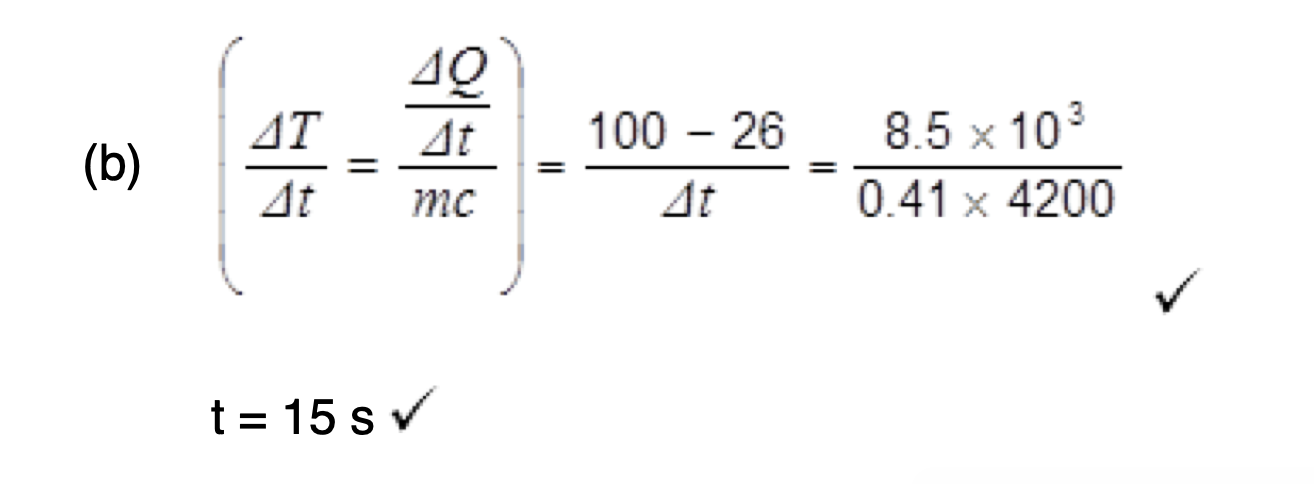



assumptions made about the motion of the molecules in a gas in the derivation of the kinetic theory of gases equation.
The molecules (continually) move about in random motion✓
Collisions of molecules with each other and with the walls are elastic✓
Time in contact is small compared with time between collisions✓
The molecules move in straight lines between collisions✓
Use the kinetic theory of gases to explain why the pressure inside a football increases when the temperature of the air inside it rises.
Ideas of pressure = F / A and F = rate of change of momentum
Mean KE of air molecules increases
More collisions with the inside surface of the football each second




Explain how the value of the ratio supports two of the assumptions made in the kinetic theory of ideal gases.
the volume of molecule is negligible compared to volume occupied by gas
• the particles are far apart Therefore Time during collisions is negligible compared to time between collisions
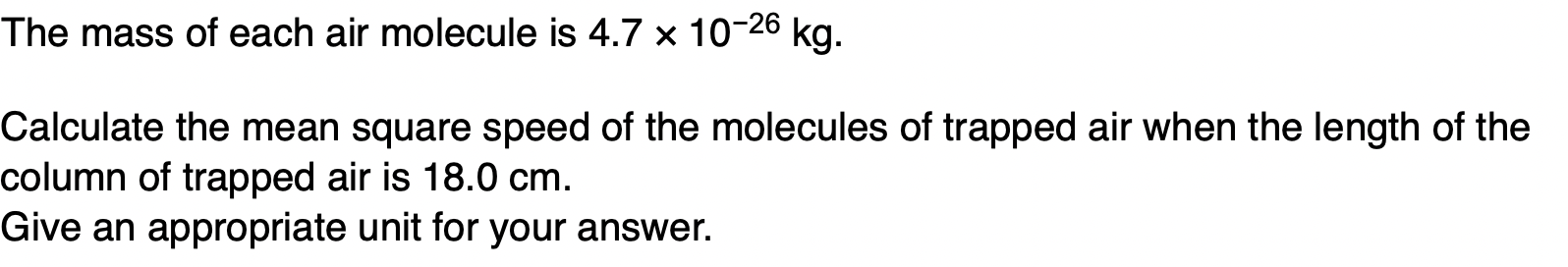



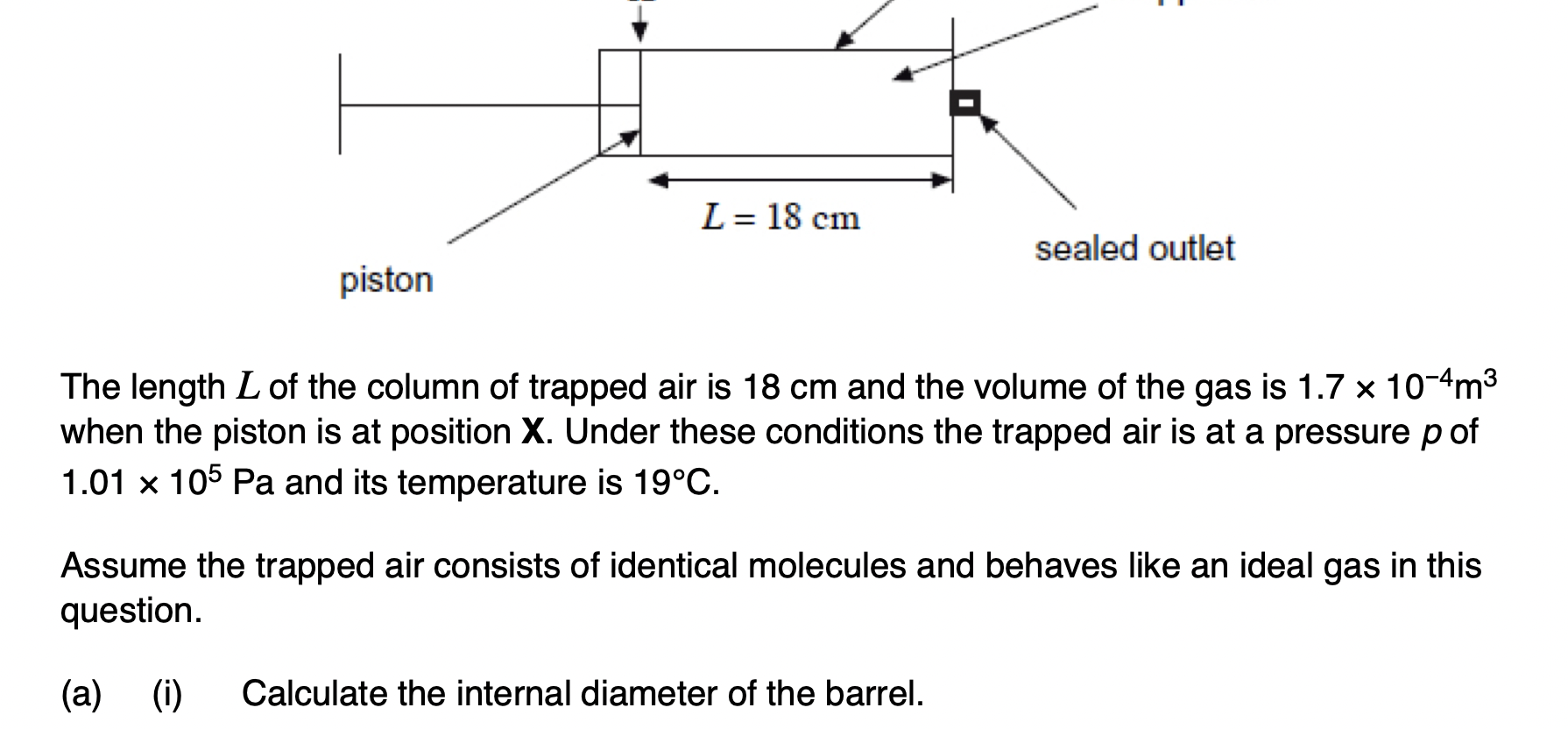
Explain how the relationship between p and L shown in Figure 2 can be predicted using the kinetic theory for an ideal gas.
L decreases then volume decreases
V = πr2 L / V is proportional to L
Decreased volume Increases number of collisions
Decreased volume causes Rate of change of momentum to increase
Increased rate of change of momentum causes force to increase causing an increase in pressure







Describe one way in which the motion of the molecules of air inside the bicycle tyre is similar and one way in which it is different at the two temperatures.
similar
-( rapid) random motion
- range of speeds
different
- mean kinetic energy
- root mean square speed
- frequency of collisions

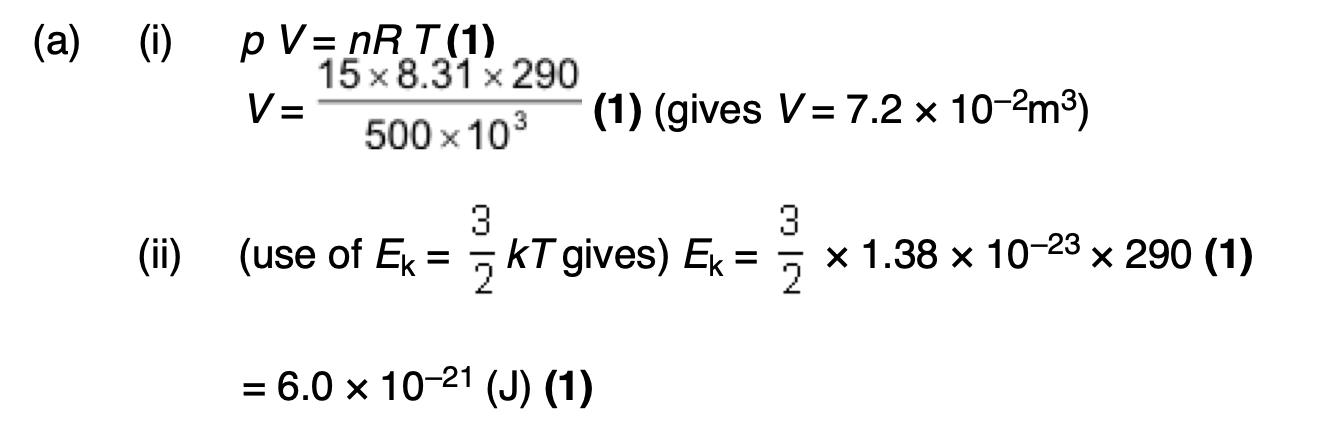

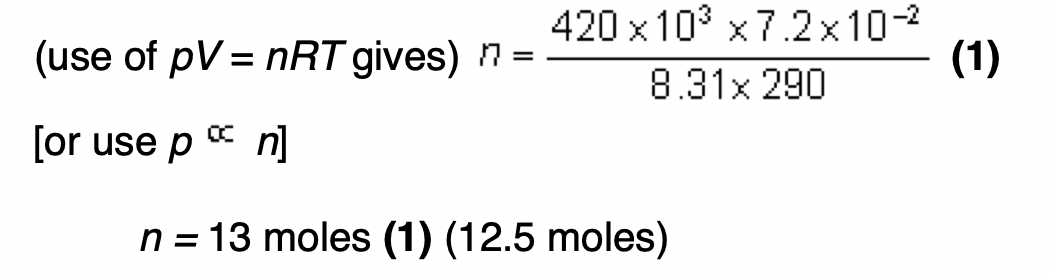
in terms of the kinetic theory why the pressure of the gas in the cylinder falls when gas is removed from the cylinder.
pressure is due to moving molecules (1)
when gas is removed there are fewer molecules in the cylinder (1)
rate of bombardment decreases (1)
molecules exert forces on wall
c² bar is constant
Explain why molecules of a gas exert a force on the walls of a container. Refer to Newton’s laws of motion in your answer.
molecules do not maintain a constant velocity when hitting the walls so they must experience a force.
Molecules have a rate of change of momentum when bouncing off the walls and force is related to rate of change of momentum.
A force is exerted by the wall on the molecules so themolecules exert a force on the wall.

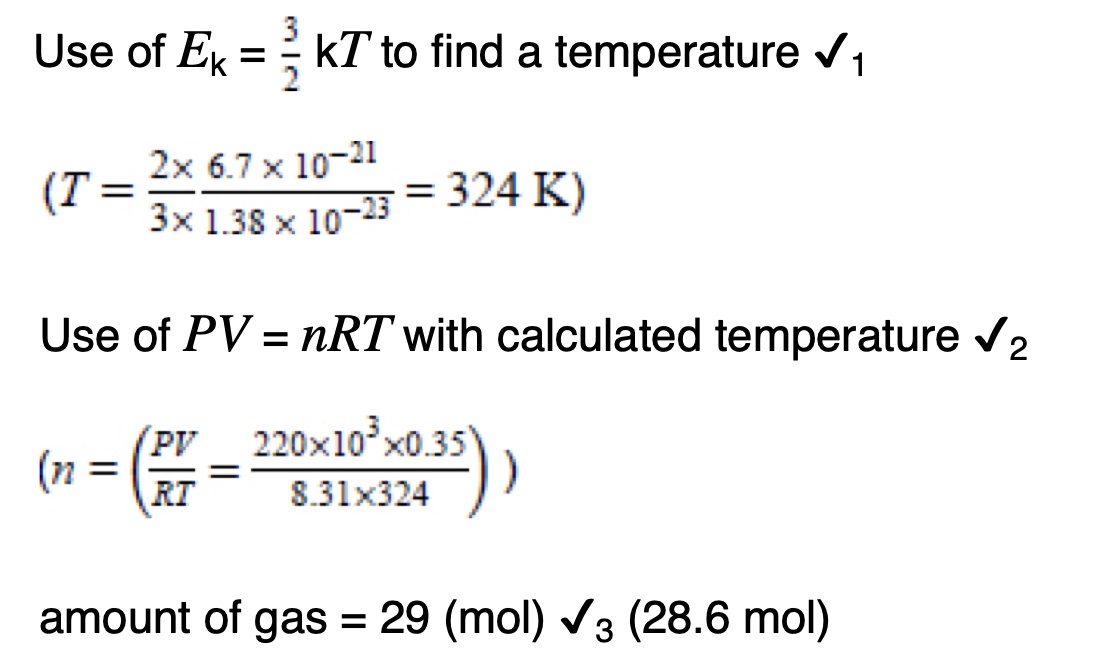
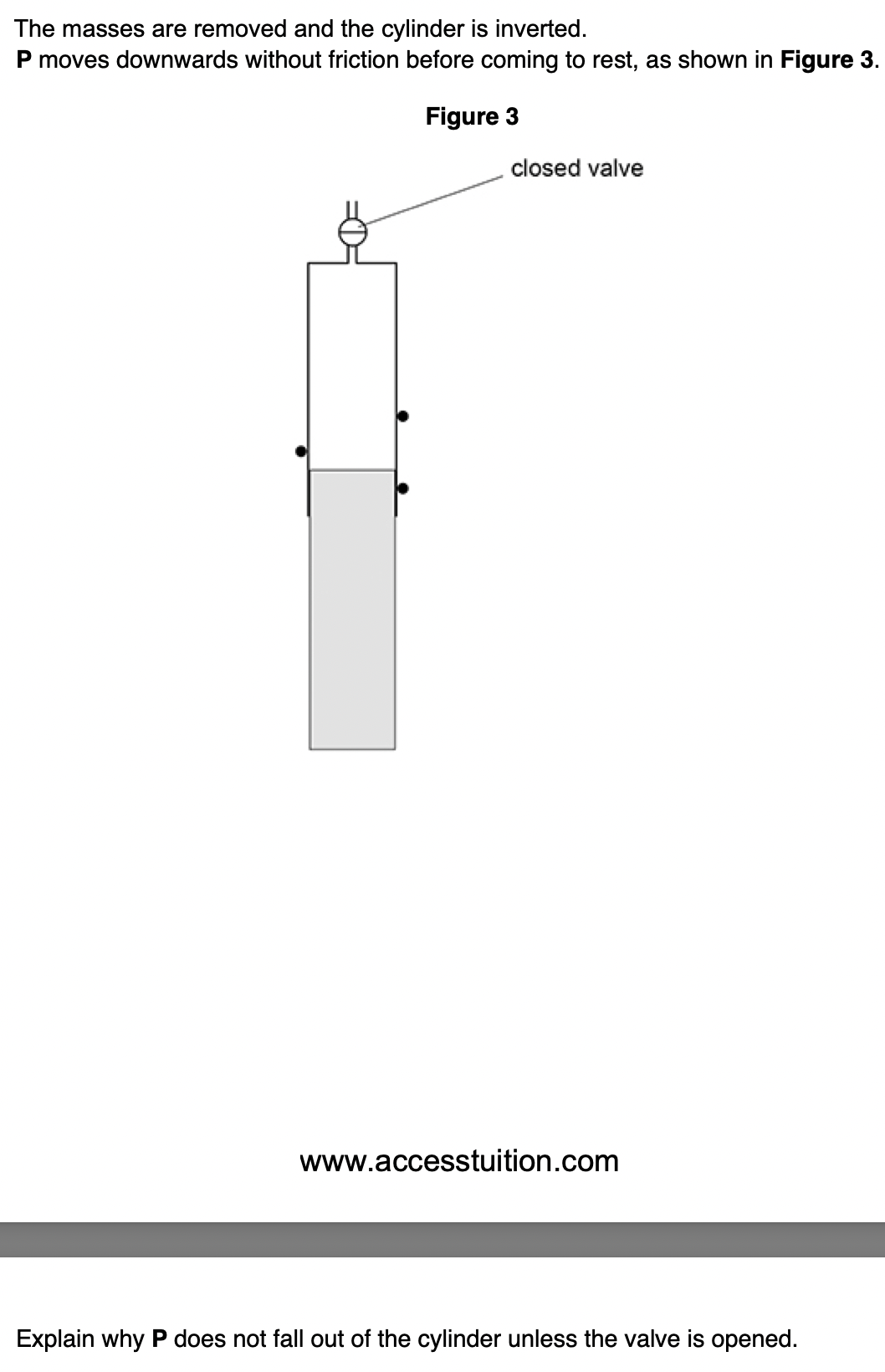
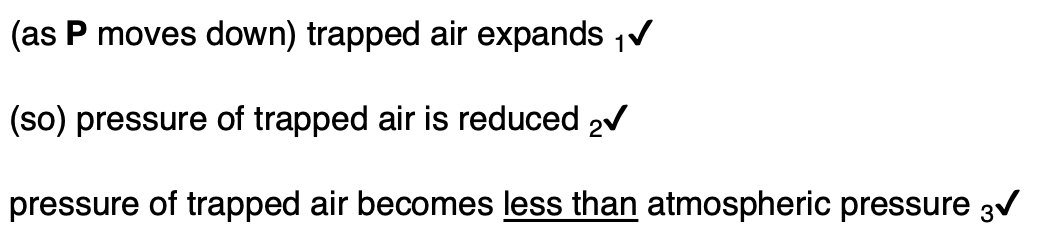







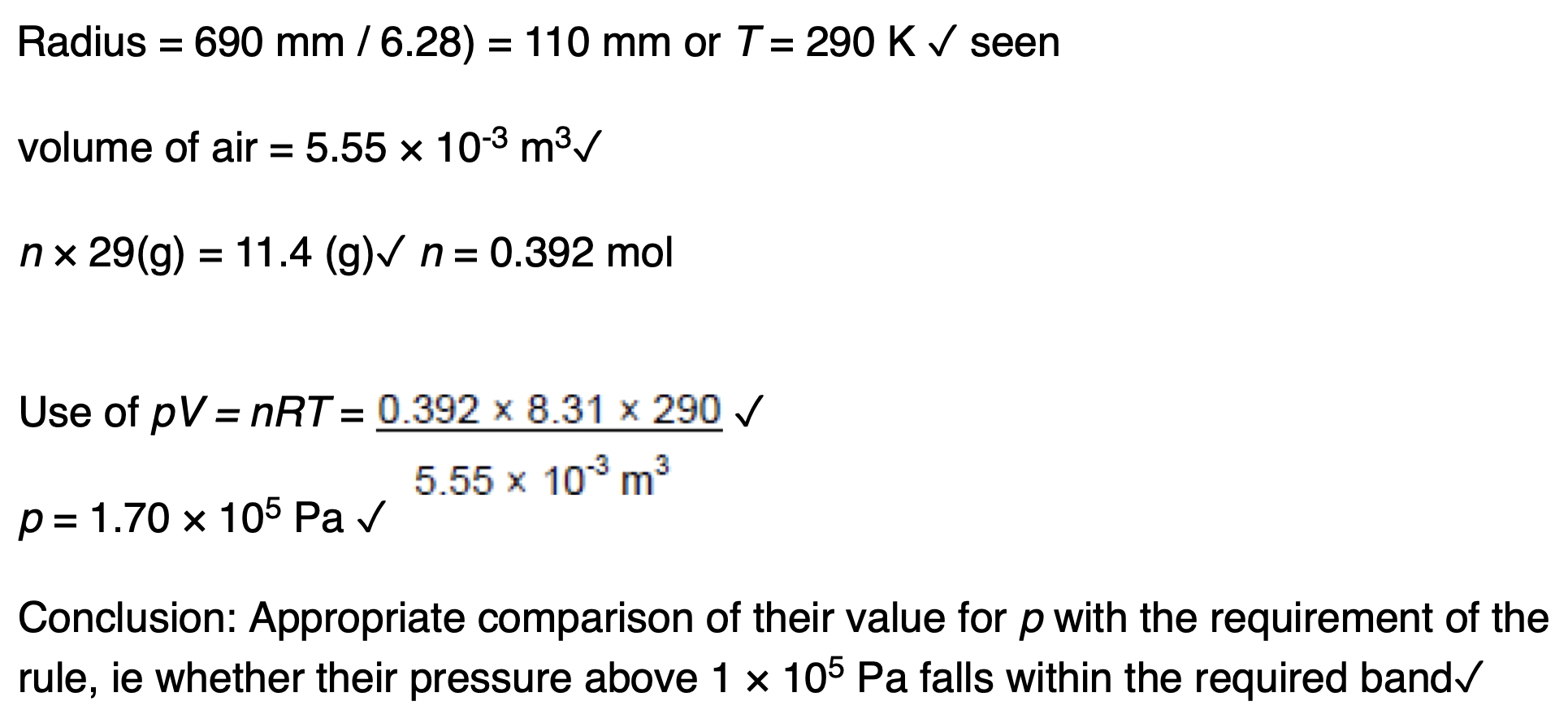
State one property of the air that must not change during the experiment.
temperature of air to achieve this change the pressure of the gas slowly
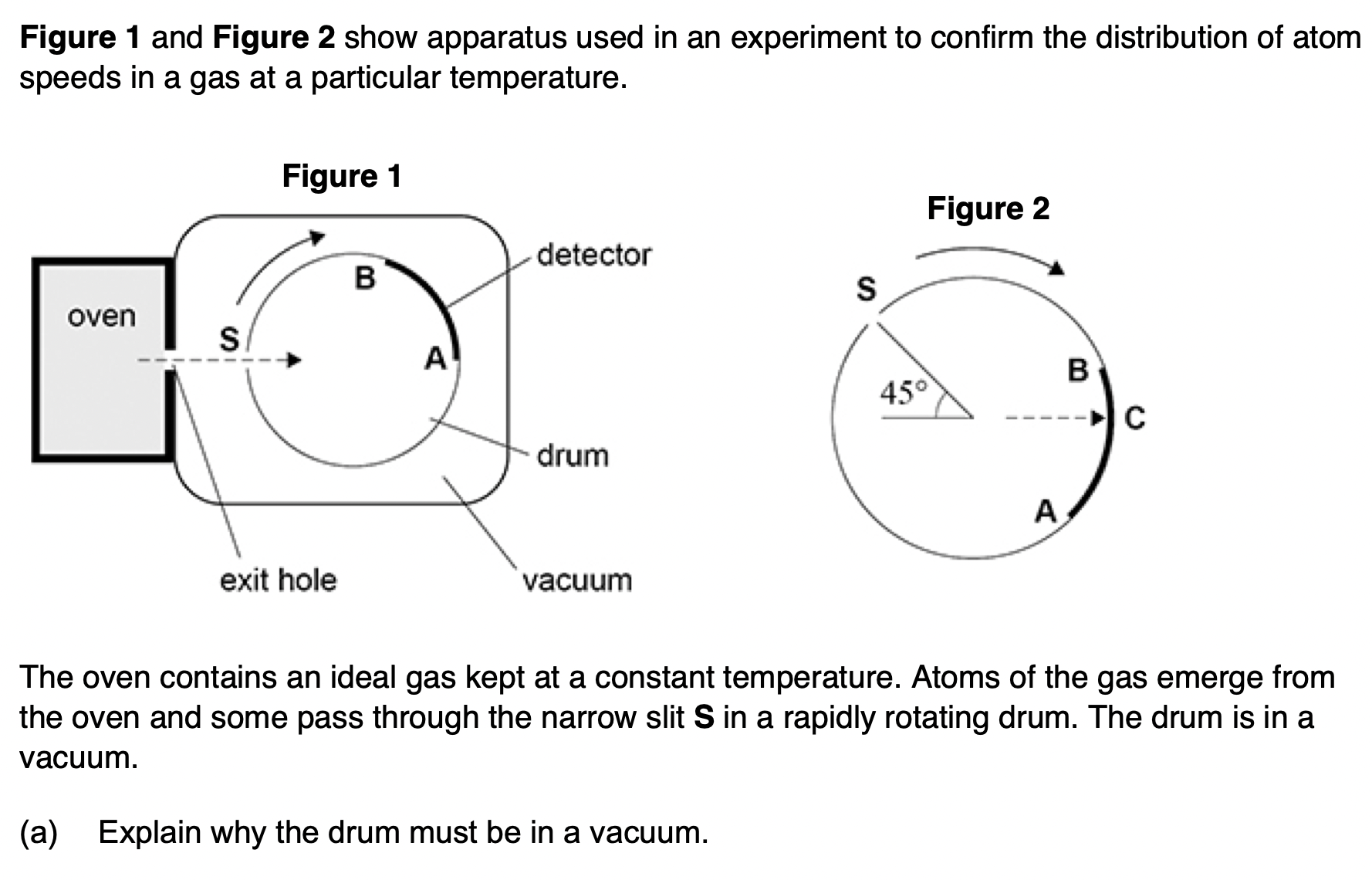
gas atoms will collide with air atoms, changing their direction or speed distribution.

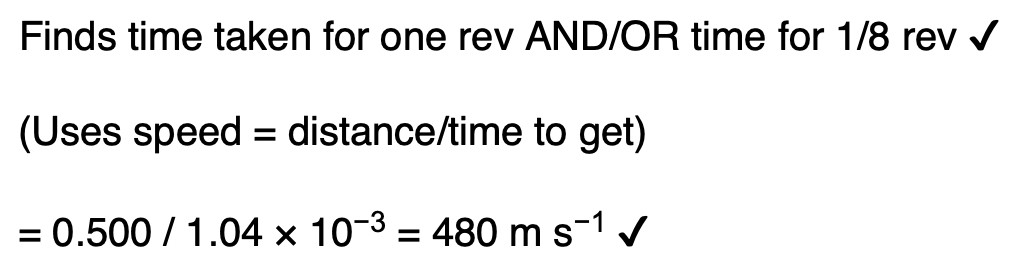


The oven temperature is kept constant during the experiment but the pressure in the oven decreases as atoms leave through the exit hole.
Explain, using the kinetic theory, why the pressure decreases.



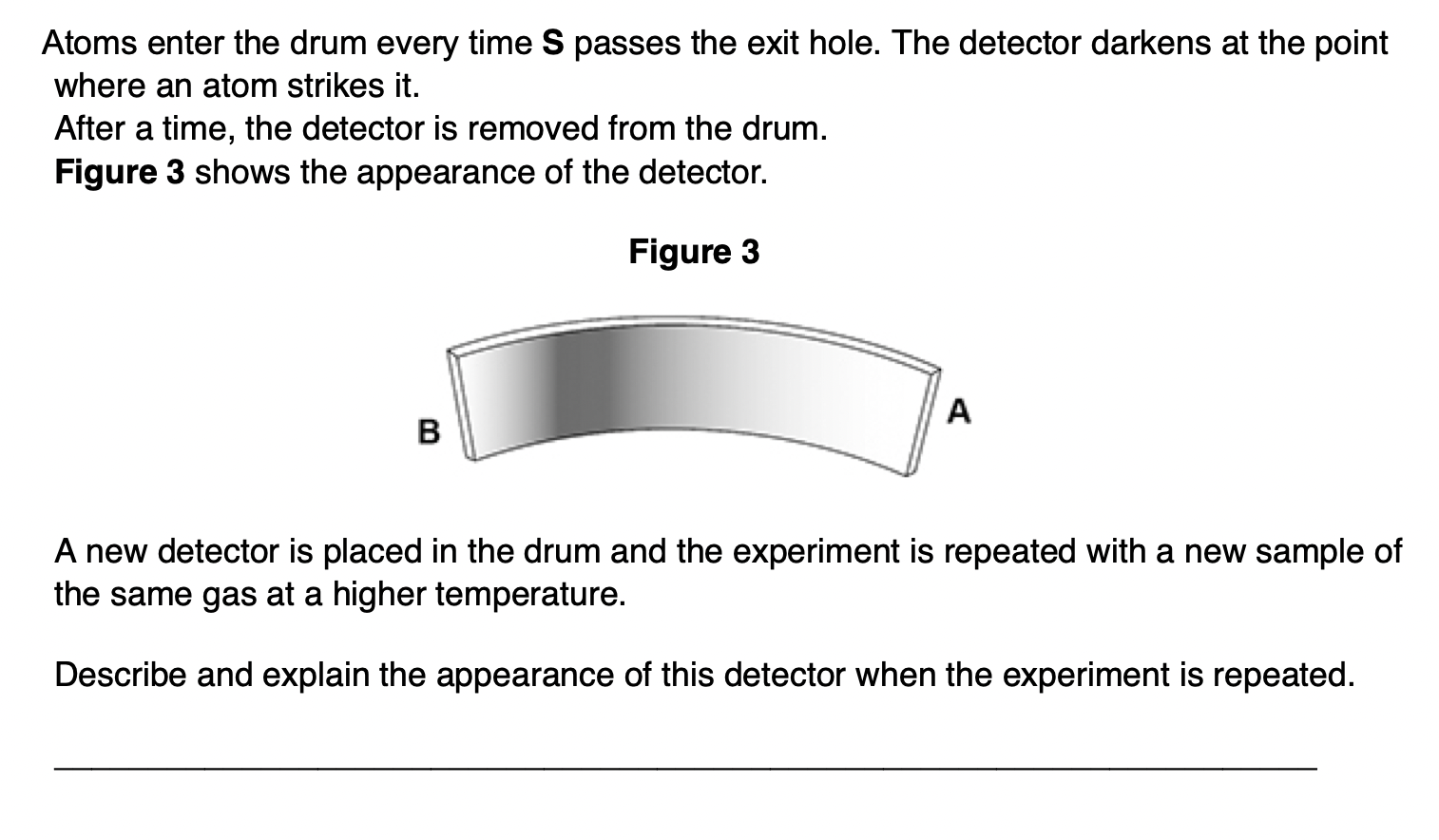
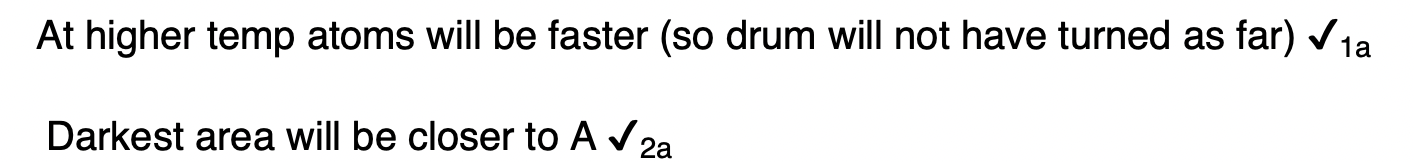
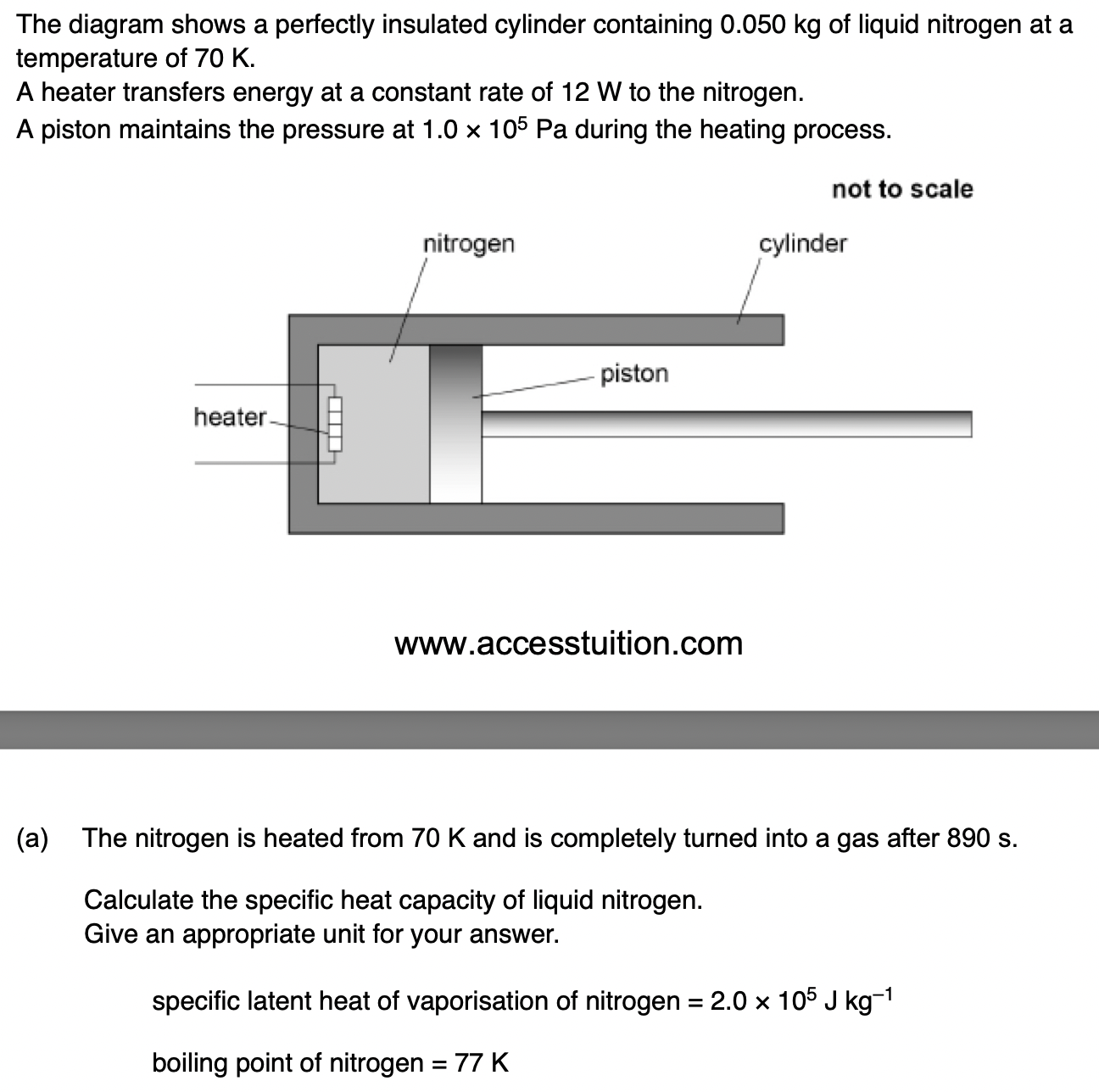
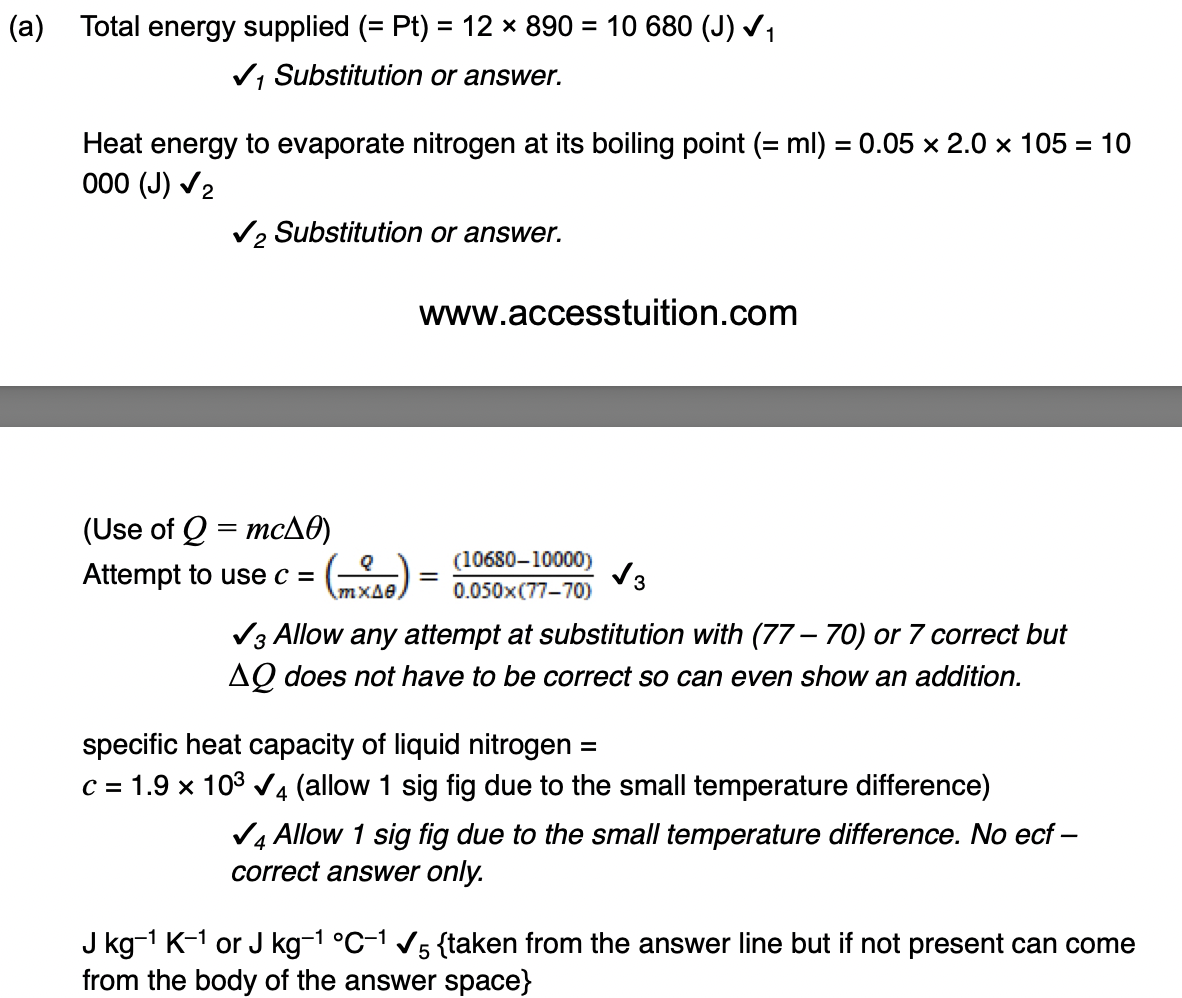


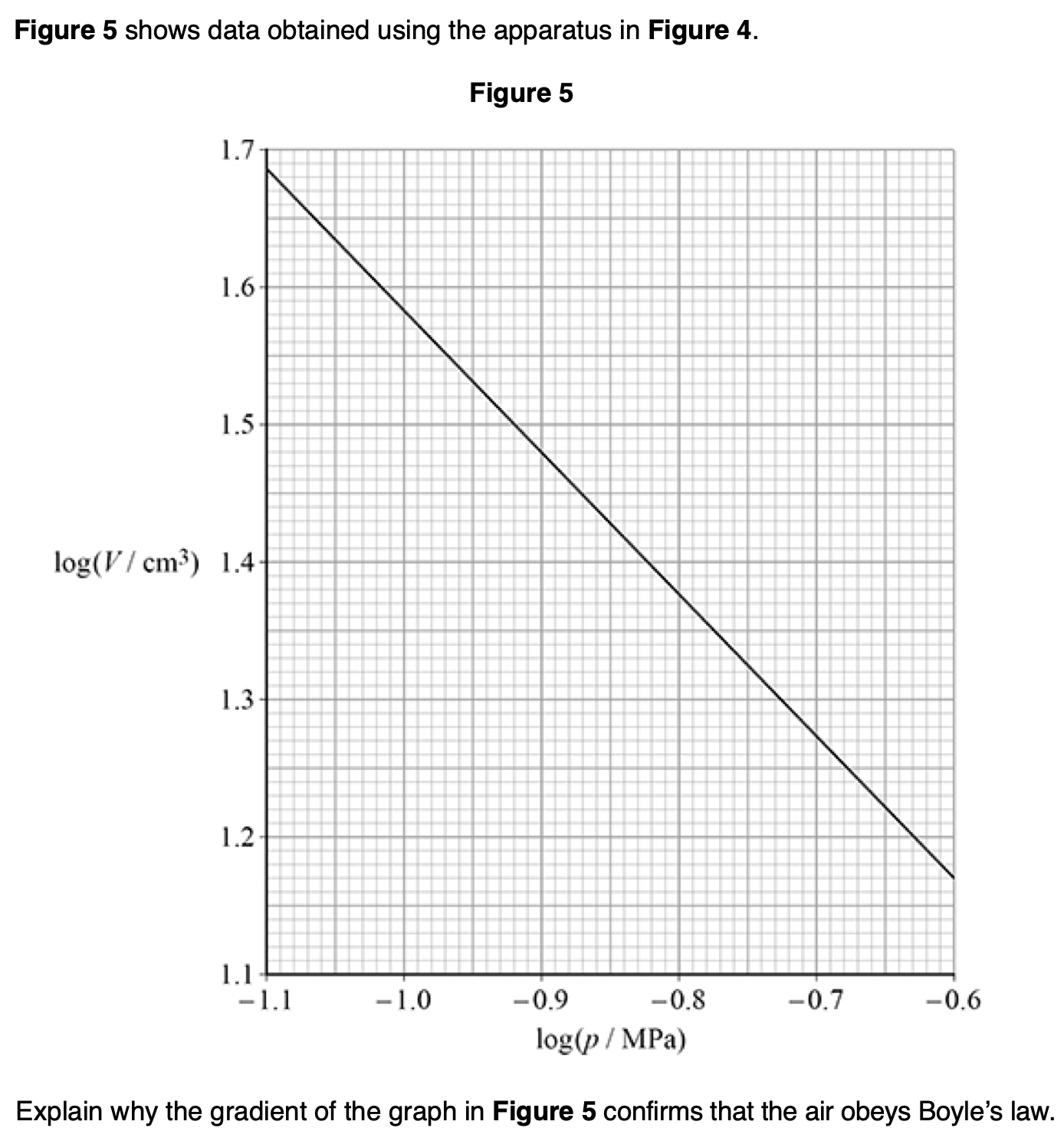
‘The pressure of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to its volume’, is an incomplete statement of Boyle’s law.
State two conditions necessary to complete the statement.
1. fixed mass or number of moles
2. constant temperature
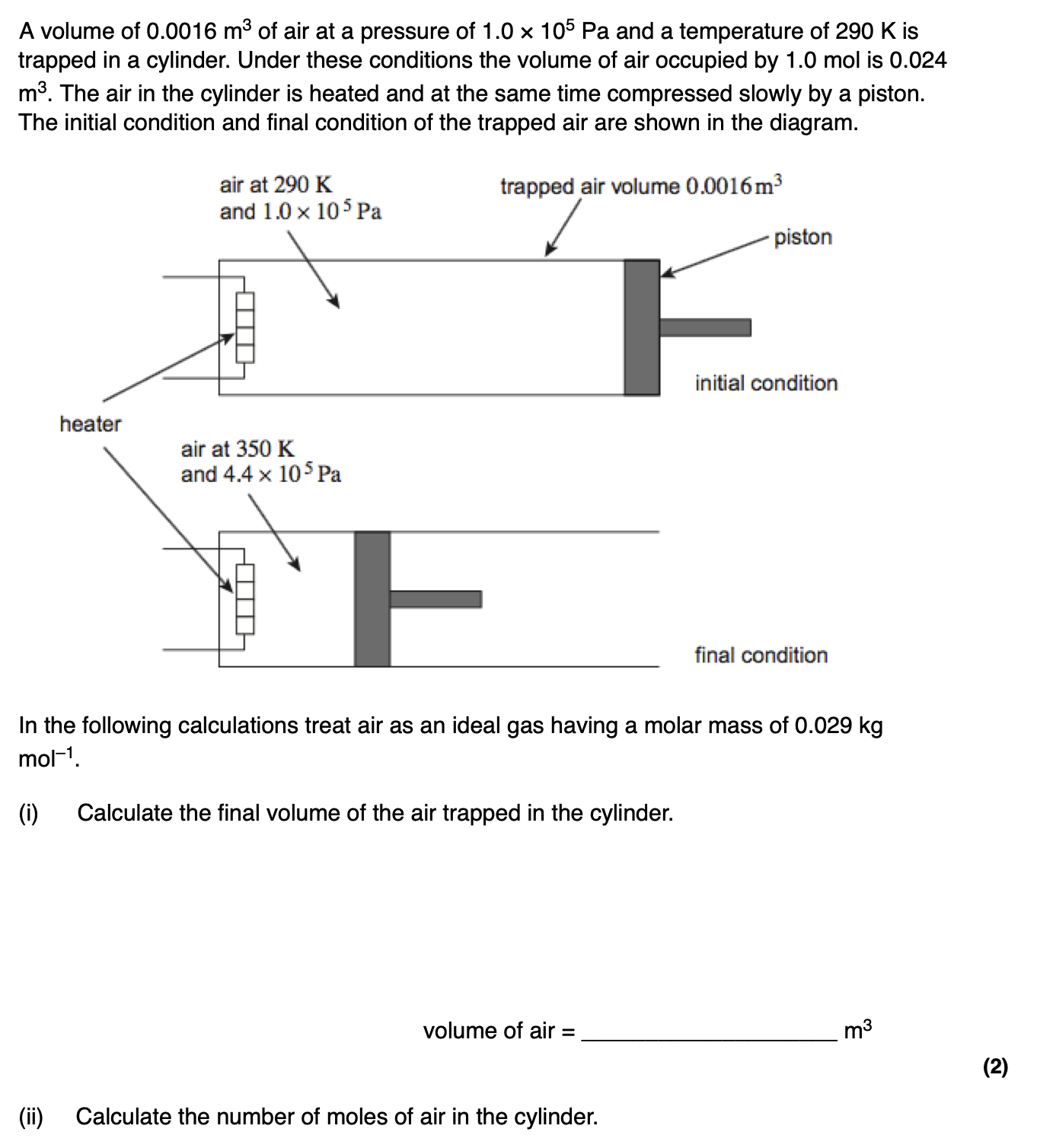
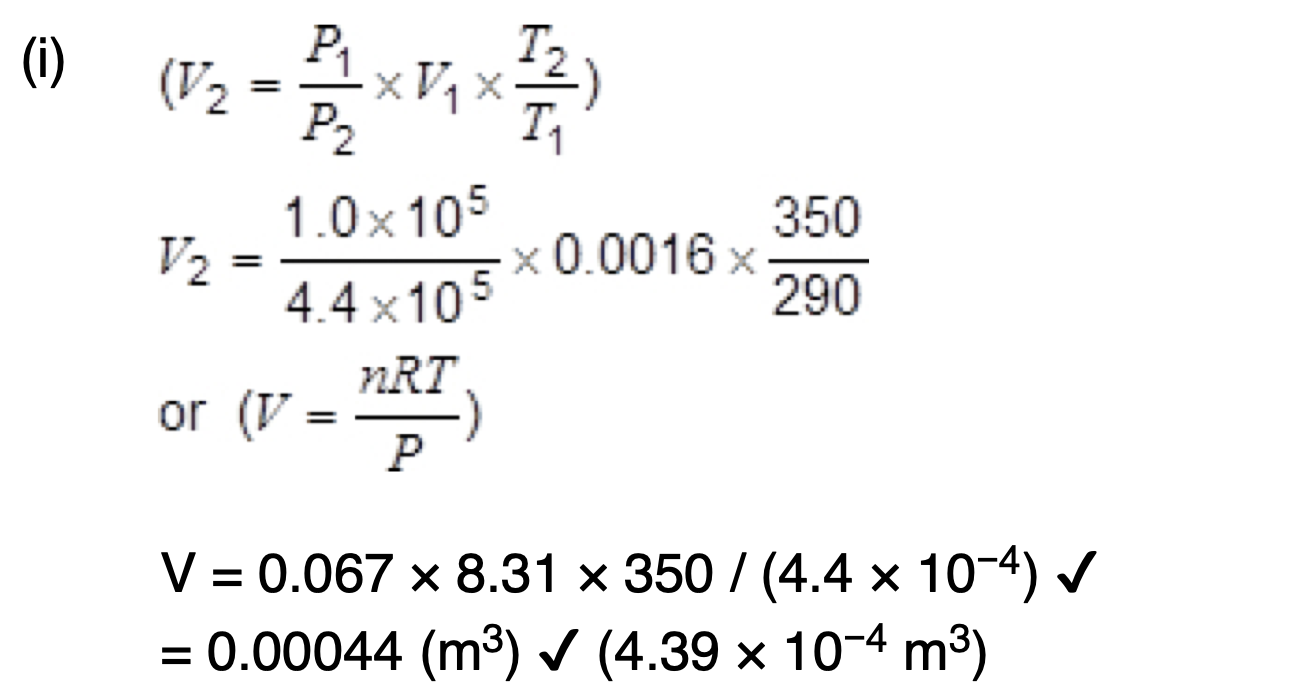
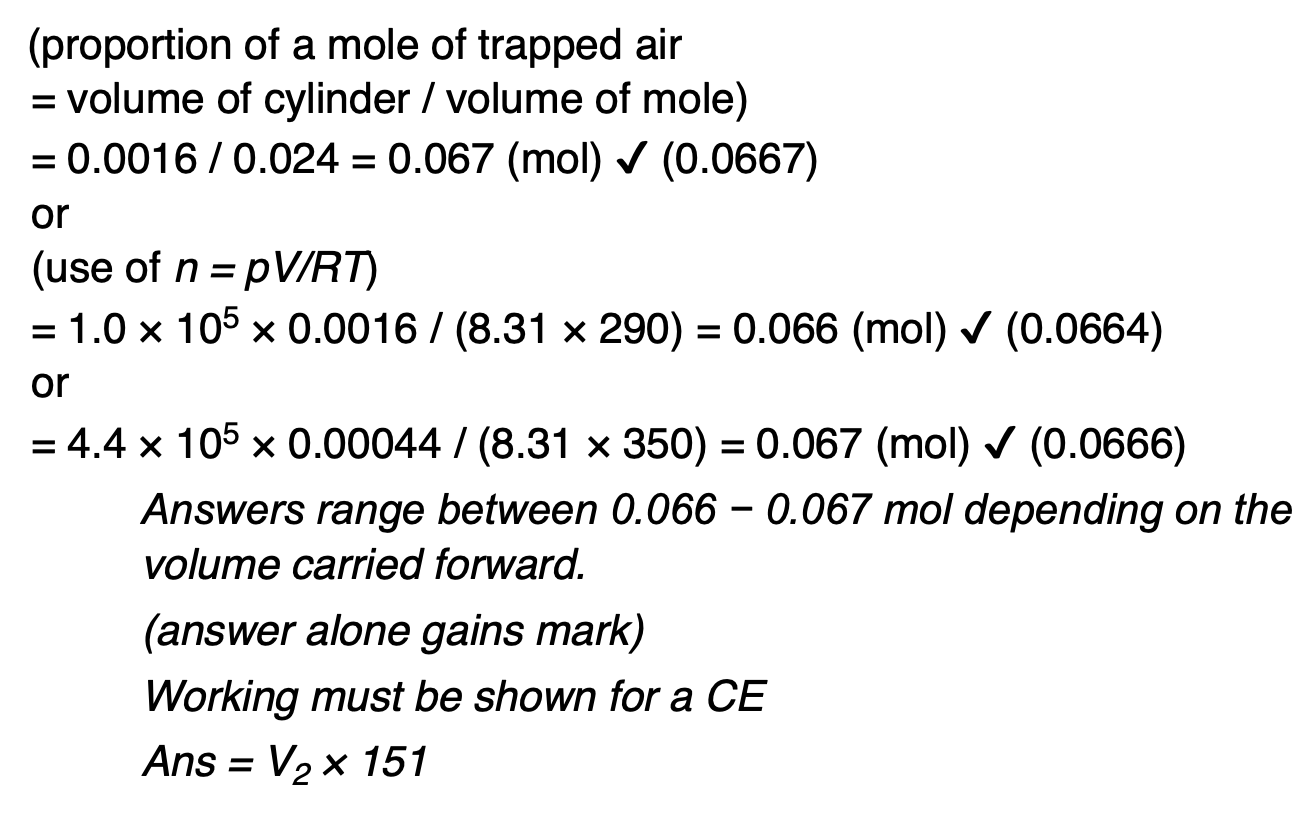

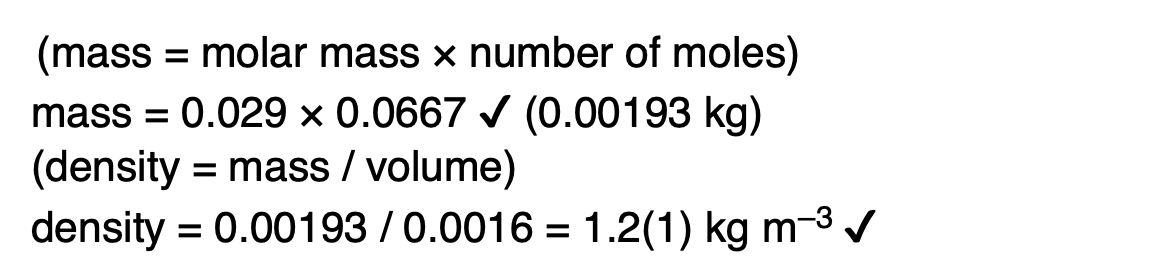
State and explain what happens to the speed of molecules in a gas as the temperature increases.
the average speed of molecules increases as the mean kinetic energy is proportional to the temperature

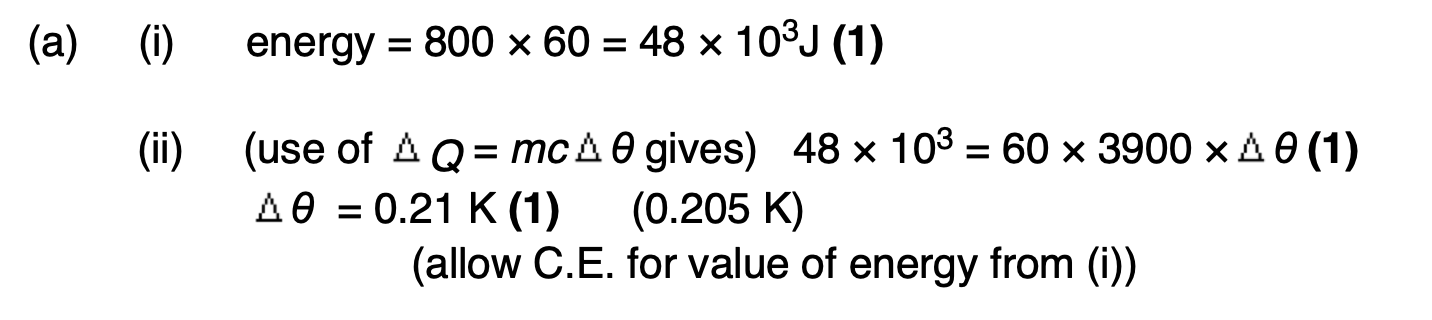
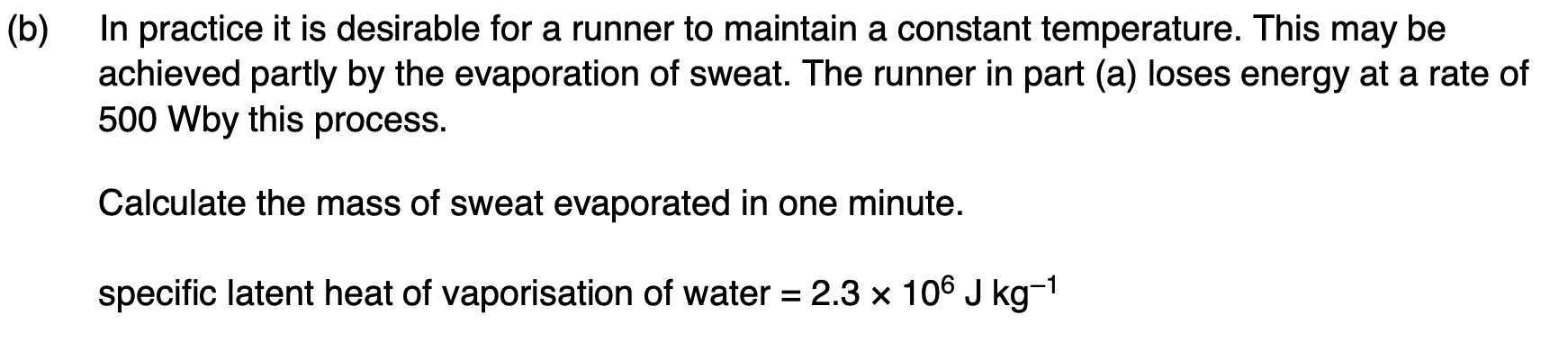
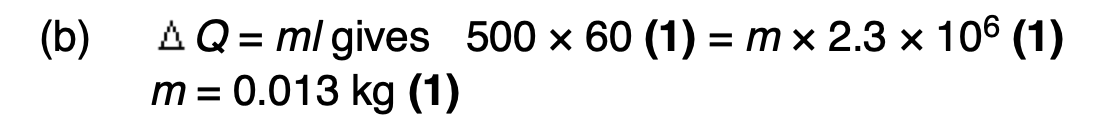
Explain why, when she stops running, her temperature is likely to fall.
not generating as much heat internally, still losing heat at the same rate, hence temperature will drop.
Explain why the driver would be less seriously injured in a collision if the air bag inflates than he would be if unrestrained.
moving driver has momentum in sudden impact momentum must be lost in v. short time
F = ma
air bag increases stopping contact time hence reduces force (or reduces force by decreasing the deceleration
Why is the driver of a car fitted only with seat belts more likely to be injured than if an air bag was fitted?
seat belt applies force to smaller area than air bag
causing greater pressure on parts of body
With reference to pressure, volume and temperature, discuss what happens to the air as the bag inflates.
air initially at v. high pressure occupies small volume
on expansion volume increases and pressure decreases
temperature of gas decreases as it expands
pressure caused by momentum change in molecular collisions
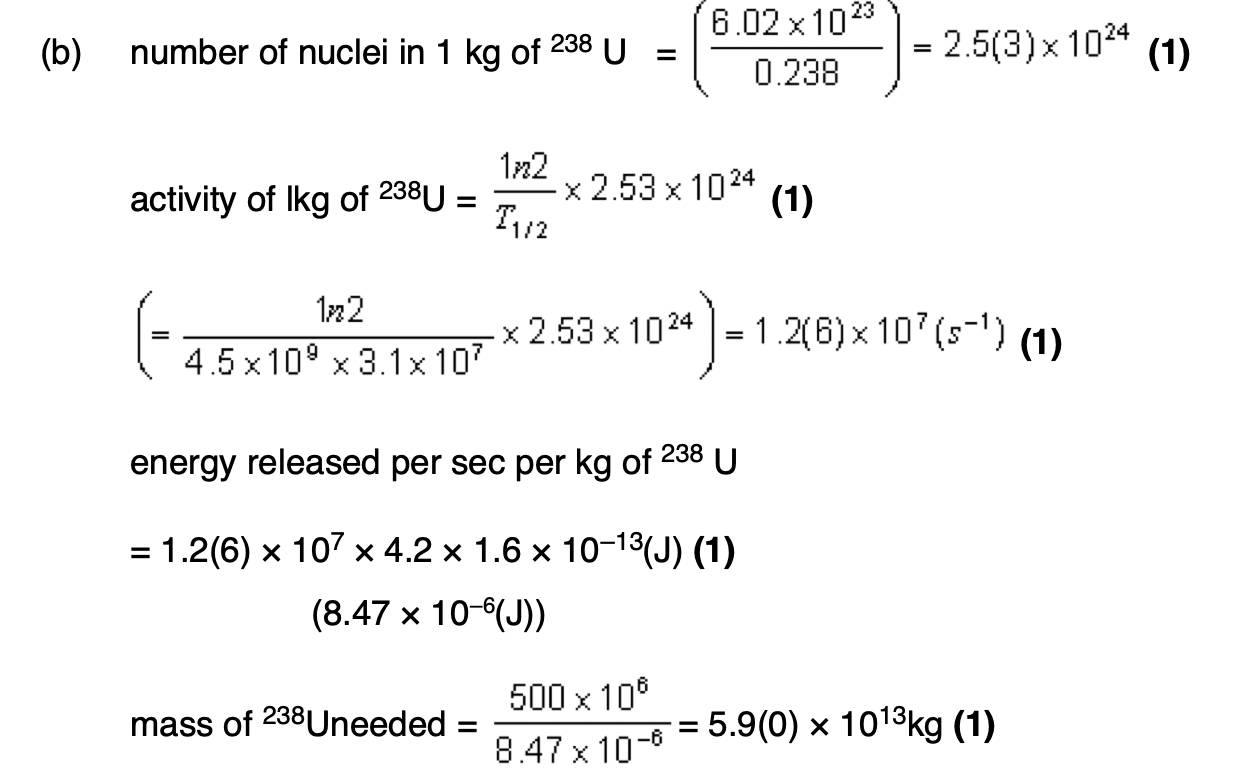
Define the Avogadro constant.
the number of atoms in 12g of carbon-12
or the number of particles / atoms / molecules in one mole of substance




Define the specific latent heat of vaporisation of water.
the energy required to change the state of a unit mass of water to steam
when at its boiling point temperature
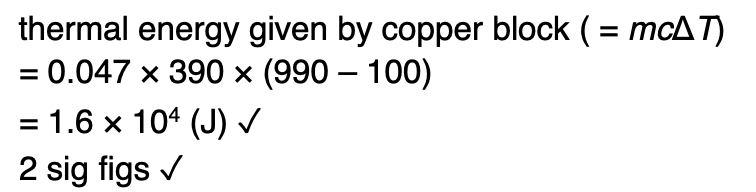


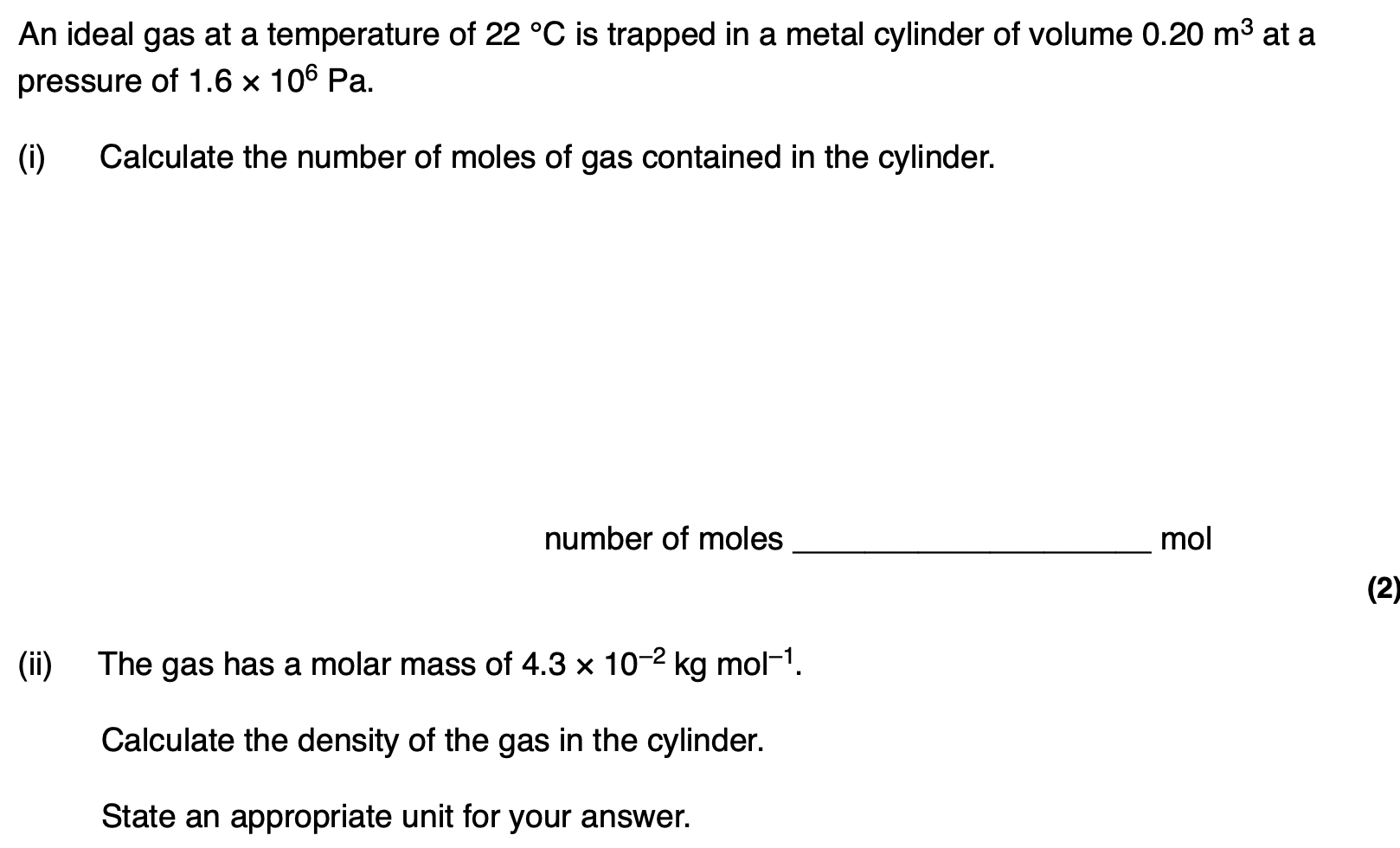
Outline what is meant by an ideal gas.
molecules have negligible volume
collisions are elastic
the gas cannot be liquified
there are no interactions between molecules





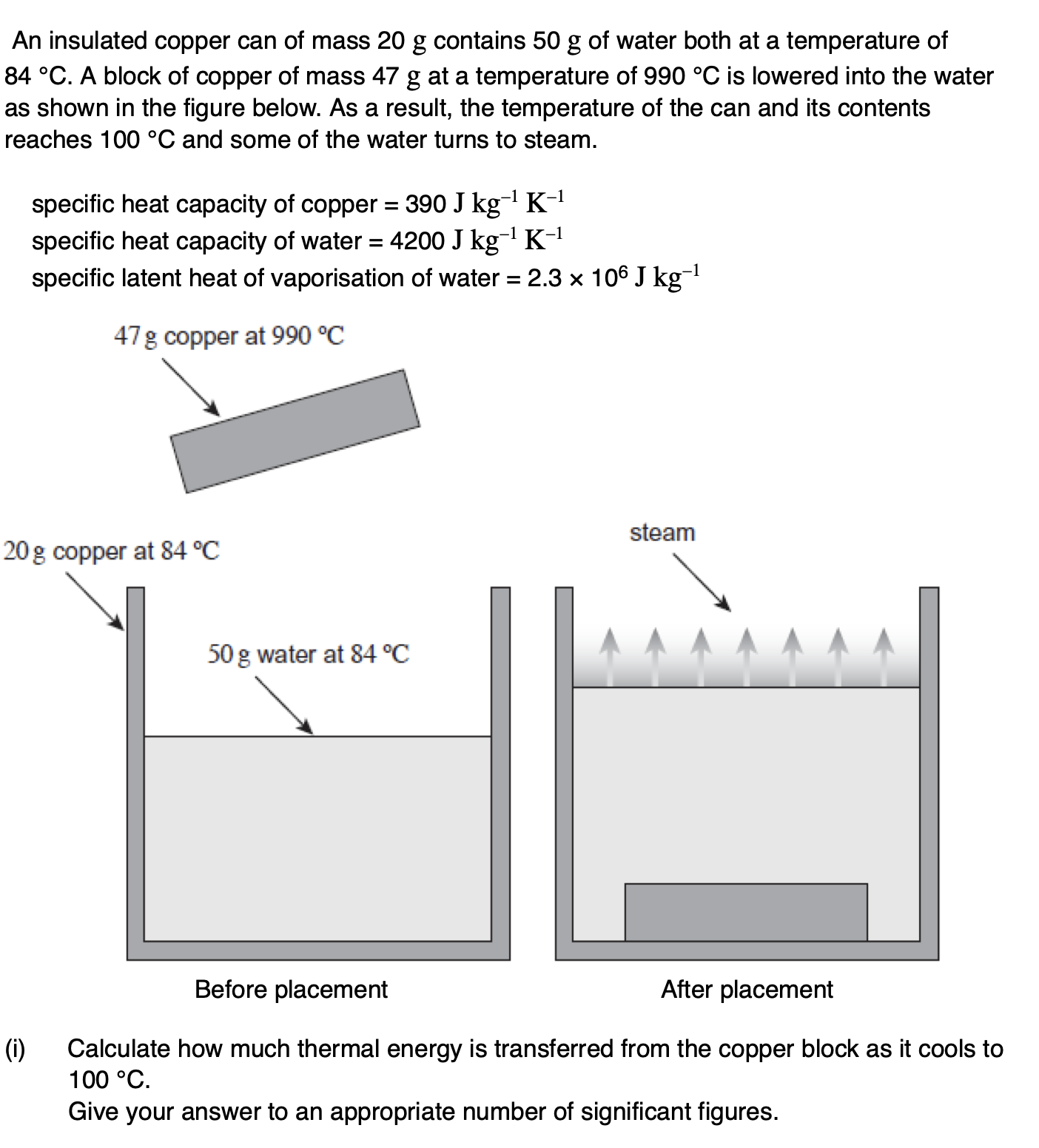
The whole procedure is repeated in an uninsulated container in a room at a temperature of 25 °C.
State and explain whether the final temperature of the water formed would be higher or lower than that calculated in part (b).
the temperature would be higher
as the ice/water spends more time below 25°C
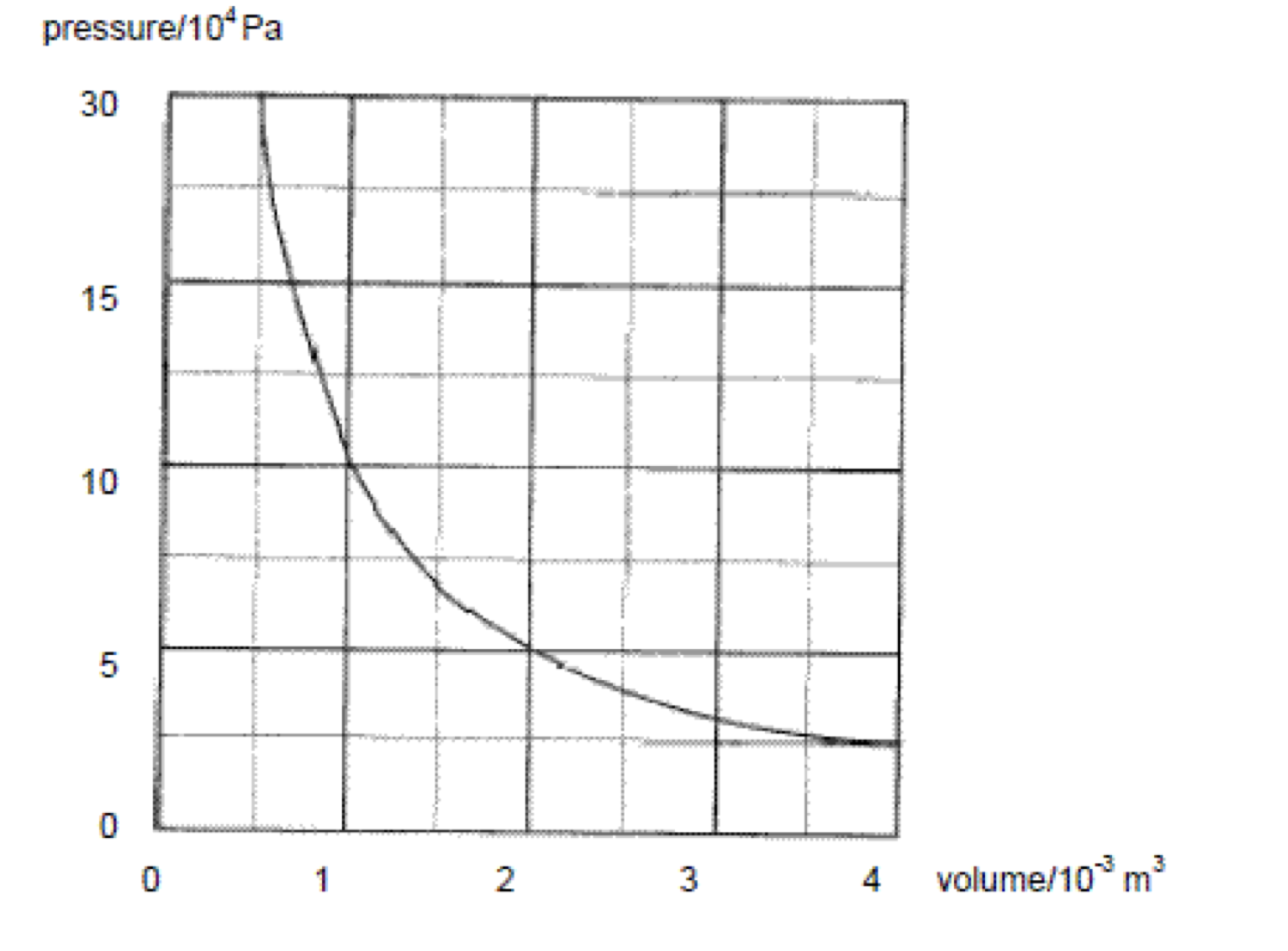


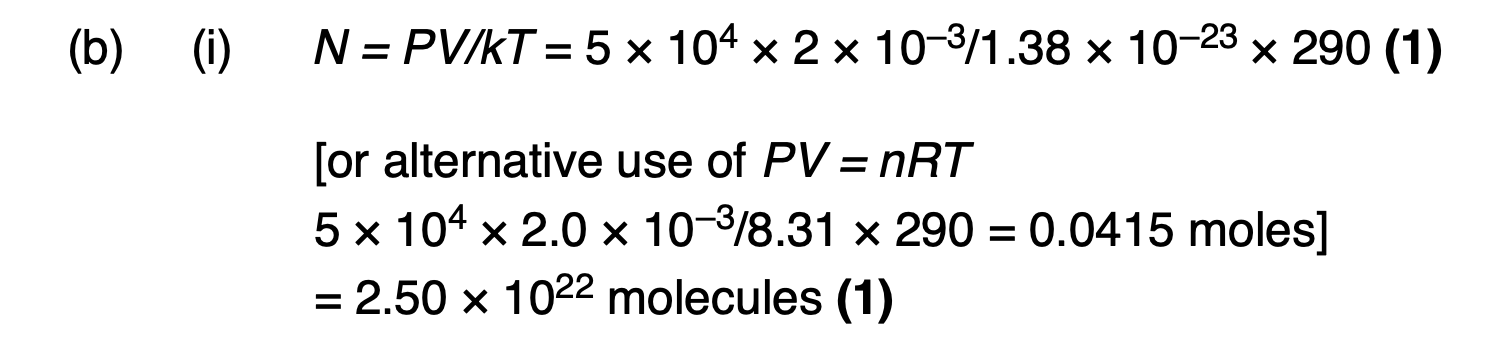
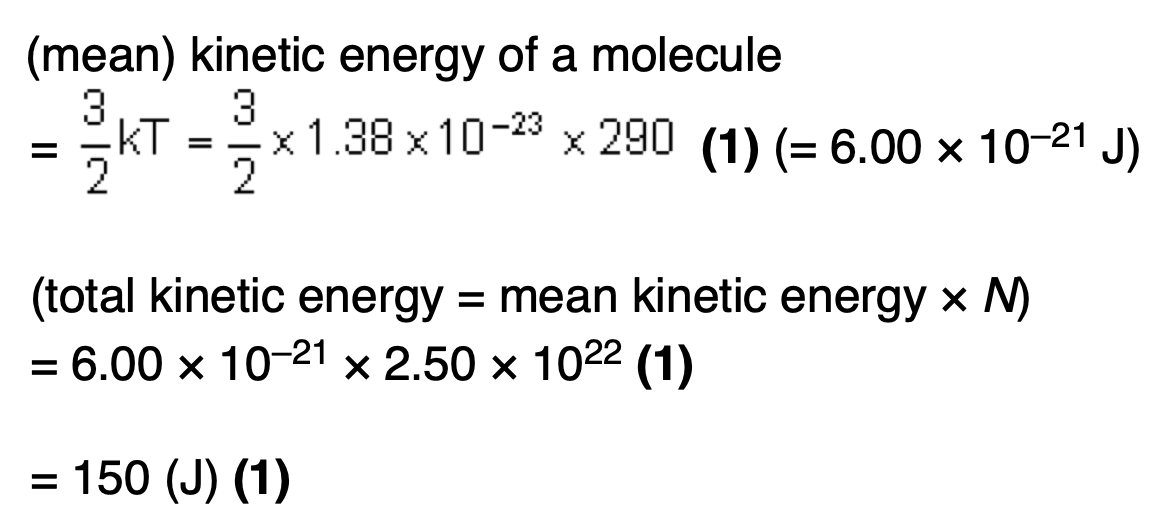



Explain, in terms of the first law of thermodynamics, how the temperature of the gas in the system can be the same at the beginning and the end of the process.
internal energy stays the same (1)
gas does work in expanding so W is negative (1)
gas must be heated to make U positive (1)
U and W equal and opposite (1)