Normal N' Wack Pregnancy
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
14 weeks
Each trimester is how long?
Spontaneous abortion (1st), Quickening (feeling the baby move) and heart sounds (2nd), Neonatal viability (3rd), Preeclampsia (3rd)
What can happen during a pregnancy?
LMP (Obstetricians - must confirm), Ovulation, fertilization
What can be used to determine estimated delivery date?
Add 7 days to LMP then Subtract 3 months
Naegle’s rule for Estimated Delivery Date (EDD)
Establish EDD (1st visit) and confirm it
How can we make an accurate assessment of gestational age - critical for decision making (preterm labor or complications)?
Every 4 weeks until 28, 2 weeks 28-36 weeks, Every week after 36 weeks
How often should we assess fetal and maternal wellbeing?
Weight, BP, edema, urine dipstick, fundal height, fetal heart tones, fetal position
What do we need to do EVERY prenatal visits?
Fetal cardiac activity on U/S
Key milestone at 6 weeks of pregnancy
Fetal heart tones by doppler, Nuchal translucency (might be 13), NIP (trisomy 18, 13, 21 and gender - might be 13)
Key milestone at 12 weeks of pregnancy
Quad screen (14-22 weeks)
Key milestone at 15 weeks of pregnancy
Quickening, Fetal heart tones by fetoscope (20)
Key milestone at 18-20 weeks of pregnancy
Glucose tolerance test (50 g → 100 g)
Key milestone at 24-28 weeks of pregnancy?
CBC, Ab screen, Rhogam, TDAP
Orders for week 28 of pregnancy?
RPR, HIV, GBS culture (36)
Orders for week 32-36 of pregnancy?
Antepartum testing
Orders for week 41 of pregnancy
Tenderness/paresthesia (early), breast growth, nipple growth and increased pigmentation, colostrum expression
Normal Breast changes in pregnancy
reddish, slightly depressed streaks (striae gravidarum - 70%)
Normal skin changes in pregnancy - mid preg
Increased by 40-45% (1500-2500 average cc - mostly plasma)
What happens to the blood volume in pregnancy (most rapidly in the second trimester)
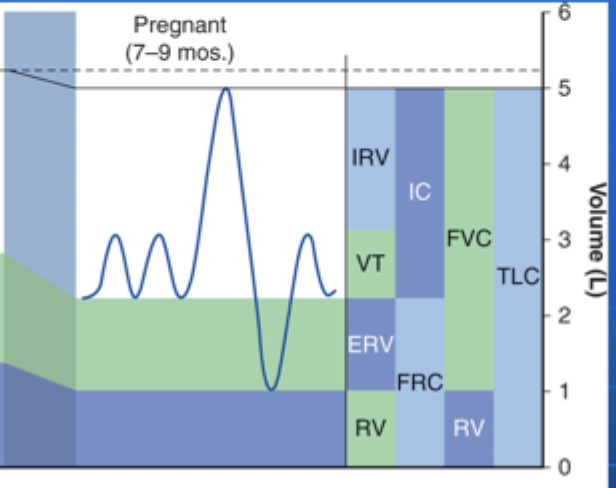
Reduction in Functional residual capacity (FRC), expiratory reserve volume (ERV), Residual Volume (RV); Increase in Inspiratory capacity and tidal volume
What are the most significant changes in the lung volumes in pregnancy?
Avulsion of the spiral arteries during placental separation (hemostasis is achieved by myometrial contraction, clotting, and obliteration)
What are the physiological changes in delivery?
Miscarriage/Spontaneous abortion, ectopic, gestational DM, hypertensive disorder, preterm labor, vaginal bleeding, postpartum mental health disorders
What is considered a complicated Pregnancy?
Abortion
The spontaneous termination of pregnancy before fetal viability that is accompanied by hemorrhage into the decidua basalis

2 weeks
After a miscarriage how quickly can ovulation re-occur?
Lack of embryonic or fetal development without cardiac motion on U/S
Diagnostics for a spontaneous abortion
Control bleeding, infection control
Management of a spontaneous abortion
1st trimester (55% - 2nd is 35%, 5% for 3rd)
Fetal loss is most common in the
infection (chlamydia), DM (glucose is a teratogen), thyroid disease, radiation exposure, nutritional extremes (deficiency or obesity), EtOH (regular or heavy usage), Excessive caffeine (500+ mg/day), Arsenic, lead, formaldehyde, uterine/cervical defects
Causes of a spontaneous abortion

Missed
Which type of abortion is characterized by a lack of embryonic/fetal development without cardiac motion on U/S WITH NO CERVICAL DILATION
Observation (wait for spontaneous evacuation), Misoprostol vs. Dilation and Curettage
Treatment plan for missed abortion
Incomplete
Which type of abortion is characterized by a lack of embryonic/fetal development without cardiac motion on U/S WITH INCOMPLETE UTERINE EMPTYING
Misoprostol vs. Dilation and Curettage
Treatment plan for incomplete abortion
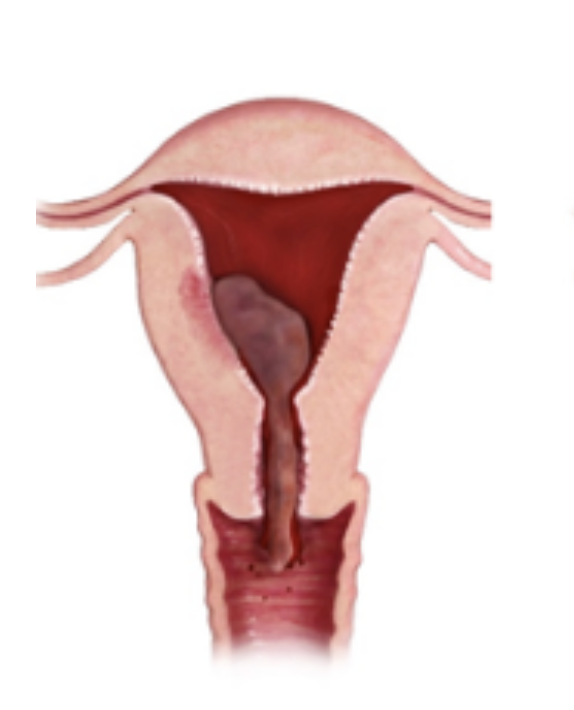
Complete
Which type of abortion is characterized by a lack of embryonic/fetal development without cardiac motion on U/S with complete evacuation of the uterus
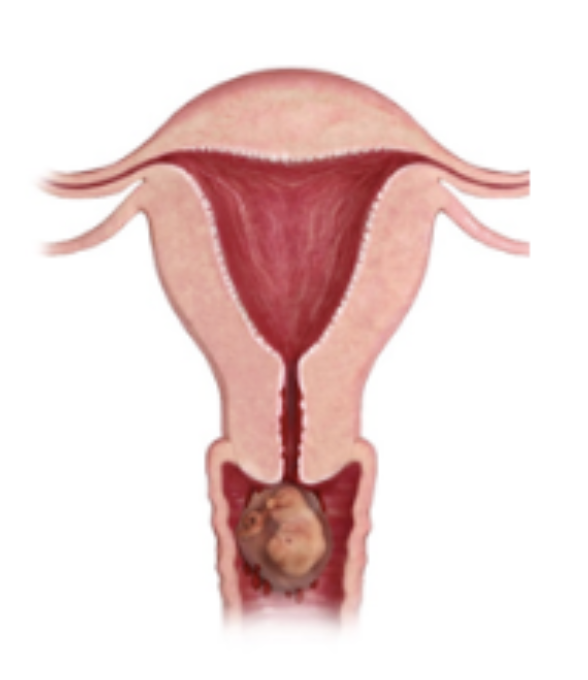
Tissue testing, reassurance
Treatment plan for complete abortion
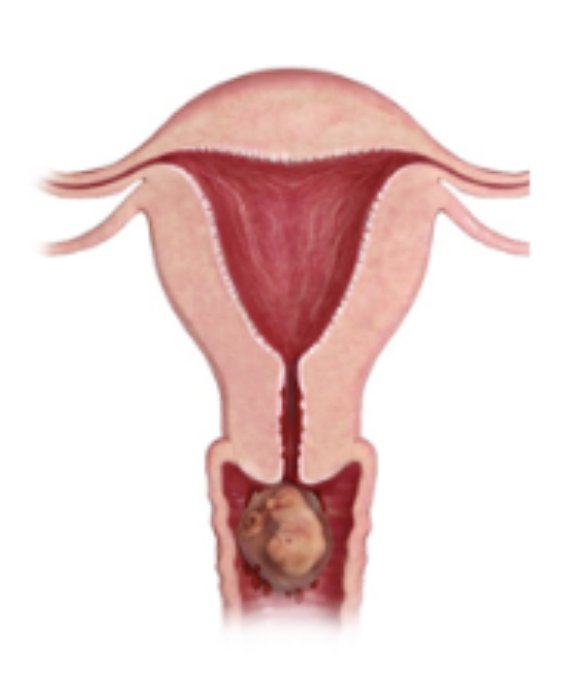
Ectopic Pregnancy (2% of all pregnancy)
The implantation of the fertilized egg in a location that is NOT the uterine cavity (like the fallopian tubes, cervix, ovary, cornual region of the uterus, abdominal cavity)
Maternal death due to hemorrhage in the 1st trimester (account for 25% of pregnancy related deaths)
Ectopic pregnancy is the leading cause of
Gestational Diabetes (GDM)
Any degree of glucose intolerance with onset or 1st recognition during pregnancies - affects 2-5%
Increased insulin resistance, decreased suppression of hepatic gluconeogenesis (due to hPL, prolactin, cortisol), insulin release fails to match demands
Etiology for gestational diabetes
24-28 weeks gestation (low to high risk women) - 1 hour OGT (screen), 3 hours to diagnose; Earlier with high risk, strong fam hx, morbid obesity, prior GDM
Screening for GDM
Fasting plasma glucose 126+; Random plasma glucose over 200; 130 1 hour OGT
Diagnostic criteria for GDM
A1-GBM (diet alone can control), A2-GBM (medications are required)
How is GDM classified?
2 hour GTT (75 g - above 140 is abnormal) 🏆 performed 6-12 weeks postpartum; fasting glucose annually
Postpartum management of GDM
Chronic HTN, gestational HTN, preeclampsia/eclampsia, Chronic HTN with superimposed preeclampsia
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy
Chronic HTN
Which form of HTN has an onset before 20 weeks gestation OR persists longer than postpartum
Gestational HTN
Which form of HTN has NO proteinuria, is onset beyond 20 weeks gestation or within 48-72 hours postpartum - should resolve 12 weeks postpartum
HTN, edema, Proteinuria
Triad of Preeclampsia - specific to pregnancy (usually the 1st one)
Nulliparity, Maternal age over 35, obesity, African American, multifetal gestation, Hx of preeclampsia in previous, chronic HTN, DM, vascular/connective tissue disease, nephropathy, antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
Risk factors for preeclampsia
Incomplete trophoblastic invasion, placental ischemia/oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, perturbation of angiogenesis
Patho for Preeclampsia - theories
BP 140/90+ twice at least 4 hours apart after 20 weeks gestation; 160/110 within short intervals; 300+ protein in a 24 hour urine, Protein/Creat ratio over 0.3+, Urine dipstick of 2+
Diagnostic criteria for Preeclampsia
Platelets under 100,000, BP 160/110+ twice at least 4 hours apart after 20 weeks gestation, elevated LFTs (2x), Severe persistent RUQ/epigastric pain, Serum Cr over 1.1 or doubling without renal disease pulmonary edema, cerebral/visual symptoms
Severe preeclampsia features
Hemolysis, Elevate liver enzymes, Low platelets
HELLP Syndrome for Preeclampsia - variant of severe (20%)
Delivery (if preterm only deliver if severe criteria)
Management of Preeclampsia
Eclampsia
Tonic-clonic seizures as a manifestation of preeclampsia, Headache occurs in 80%
Mg Sulfate (treat the seizure), deliver
Management of Eclampsia
prevent eclampsia, control HTN, expedite delivery
Mainstays of Preeclampsia management
Chronic HTN with superimposed preeclampsia
Chronic HTN with development of new onset proteinuria after 20 weeks
Abruptio placentae, preterm birth, intrauterine fetal growth restriction, stillbirth, maternal stroke/death, renal failure, hepatic rupture, cortical blindness
Complications of hypertension in pregnancy
Preterm delivery
A delivery under 37 weeks gestation or a birth weight under 2500g
Hx, multifetal pregnancies, smoking, short interpregnancy interval, poor nutrition, poor weight gain, over/under weight pre-pregnancy, infections, stress, trauma
Risk factors for pre-term birth
SEX, cervicovaginal infection, pre-term labor/labor, abruption (symptomatic), placenta previa, cancer, other
Causes of Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy
Postpartum Blues
A postpartum mental health disorder that occurs in 70% and is characterized by a transient state of tearfulness, anxiety, irritation, and restlessness
No therapy indicated - should resolve by day 10
Management of postpartum blues
life situation, stresses, hx of depressions
Risk factors for postpartum depression
Antidepressants and supportive care - self-limiting in 1 year
Treatment plan for postpartum depression
Schizophrenia, bipolar reaction (watch for feticide, homicide, suicide)
What are common reactions postpartum?
Hospitalization and treatment, usually last 2-3 months
Treatment plan for Postpartum Psychosis