CALCULATIONS
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
What is a mole?
the amount of substance in grams that has the same number of particles as an atom in 12g of carbon-12
What is the relative atomic mass?
average mass of one atom compared to one twelfth of an atom of carbon-12
What is the relative molecular mass?
the average mass of a molecule compared to one twelfth of the mass of one atom of carbon-12
How do you calculate moles for pure solids, liquids and gases?
moles = mass/Mr
How do you calculate moles for gases?
PV=nRT
How do you calculate moles for solutions?
concentration = moles/volume
How do you convert mg to g?
divide by 1000
How do you convert kg to g?
multiple by 1000
How do you convert a tonne into gs?
multiple by 1000000
What is avogradros constant
one mole contains 6.022×10²³ atoms
What is the calculation to find the number of particles?
moles of substance x avogradros constant
How do you find the density?
mass/volume
What is the empirical formula?
simpest ratio of atoms of each element in the compound
How would you find the empirical formula of a compound?
divide each mass by the atomic mass of the element
divide the answers by the smallest one of those numbers
multiply to give whole numbers
the whole numbers are the empirical formula
What is the molecular formula?
the actual number of atoms of each element in the compound
What is a hydrated salt?
contains water of crystalisation
How would you dehydrate using a crucible?
weigh an empty clean dry crucible and lid
add 2g of hydrated calcium sulfate to the crucible and weigh again
heat strongly with a bunsen for a couple of minutes
allow to cool
weigh the crucible and contents again
heat crucible again and reweigh until you reach a constant mass (ensures the reaction is complete)
Why should large amounts of calcium sulfate not be used in the decomposition experiment?
as decomposition is likely to be incomplete
Why would a wet crucible give inaccurate results?
mass loss would be too large as the water would be lost when heating
Why should small amounts of the solid not be used?
as the percentage uncertainties in weighing will be too high
What is a solution?
a mixture formed when a solute dissolves in a solvent
How do you change cm³ into dm³?
divide by 1000
How do you change cm³ into m³?
divide by 1000000
How do you change dm³ into m³?
divide by 1000
What occurs if ions dissociate?
when soluble ionic solids dissolve in water they will dissociate into separate ions, leading to the concentration of ions differing from the concentration of the solute
How would you make a solution?
weigh the sample bottle containing the required mass of solid on a balance
transfer to beaker and reweigh sample bottle
record the difference in mass
add 100cm³ of distilled water to the beaker, using a glass rod to stir
heat gently to ensure all the solid has dissolved
pour the solution into a 250cm³ graduated flask via a funnel
rinse beaker and funnel and add washings from the beaker and glass rod to the volumetric flask
make up to the mark with distilled water using a dropping pipette for the last few drops
invert flask several times to ensure uniform solution
Where should the miniscus sit?
the bottom of the miniscus should sit on the line on the neck of the flask
How do you dilute a solution?
pipette 25cm³ of original solution into a 250cm³ volumetric flask
make up to the mark with distilled water using a dropping pipette for the last few drops
invert the flask several times to ensure uniform solution
Why is a volumetric pipette more accurate than a measuring cylinder?
it has a smaller uncertainty
Why should you use a teat pipette to make up to the mark in the volumetric flask?
ensures the volume of the solution is accurately measured so it doesn’t go over the line
How does diluting a solution affect the solution?
doesn’t affect the moles present
increases the volume of solution so the concentration would be lower
How would you calculate the new diluted concentration?
original concentration x original volume/new diluted volume
What is the new diluted volume equal to?
the original volume of solution added + the volume of water added
What’re some common hazards in chemistry?
irritants (dilute acids and alkalis), wear goggles
corrosive (stronger acids and alkalis), wear goggles
flammable, keep away from naked flames
toxic, wear gloves, wash hands after use
oxidising, keep away from flammable materials
What is the ideal gas equation?
PV= nRT
What’re the units for the ideal gas equation?
P - Pa
V- m³
T- K
n- moles
R- 8.31JK^-1 mol^-1
How do you convert degrees celcius into kelvin?
add 273
What occurs in an experiment involving a gas syringe?
volume of gas depends on pressure and temperature so these need to be noted
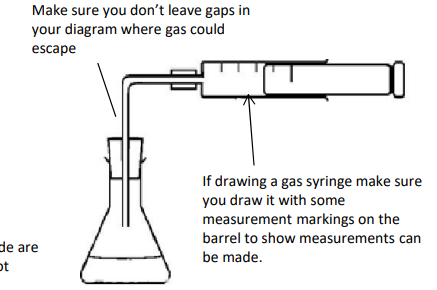
What’re some potential errors when using a gas syringe?
gas escapes before bung is inserted
syringe sticks
some gases like carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide are soluble in water so the true amount of gas is not measured
What equation relates 2 of the same amount of gas under different conditions together?
P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2
What is the property of equal volumes of any gases measured under the same conditions of temperature and pressure?
they contain the same number of moleculesd
What is the equation for the percentage yield?
actual yield/ theoretical yield x 100
What is the equation for the percentage atom economy?
mass of useful products/ mass of all reactants x 100
Why do chemists want a high percentage yield?
there has been an efficient conversion of reactants and products
Why do chemists want a high percentage atom economy?
the maximum mass of reactants ends up in the desired product
What is the method for titrations?
rinse equipment (burette with acid, pipette with alkali, conical flask with distilled water)
pipette 25cm³ of alkali into a conical flask
touch surface of alkali with pipette
add acid solution from burette
make sure the jet space in the burette is filled with acid
add a few drops of indicator
use a white tile underneath to help observe the colour change
add acid to alkali while swirling the mixture and add acid dropwise at end point
note burette reading before and after addition of acid
repeat titrations until atleast 2 concordant results
What is the colour change with phenolphthalein?
pink (alkali) to colourless (acid)
What is the colour change with methyl orange?
yellow (alkali) to red (acid)
What is a concordant result?
readings within 0.1 of each other
What’re safety precautions for titrations?
acids and alkalis are corrosive so wear eye protection and wipe up spillages
wear gloves
What will the jet space not being filled properly prior to commencing the titration lead to?
errors as it will lead to a larger than expected titre reading
Why is the conical flask used instead of a beaker?
as it is easier to swirl the mixture in the conical flask without spilling the contents
How could indicators affect the titration?
they’re weak acids so lots of drops will affect the titration result
What can you assume if there are 2 or 3 concordant results?
that the results are accurate and repeatable and that the titration technique is good and consistent
How should you record results?
results should be recorded in a table
results should be recorded in full (initial and final)
record titre volumes to 2dp
Why is distilled water added to the conical flask during a titration?
washes the sides of the flask so all the acid on the side is washed into the reaction mixture to react with the alkali
Why can distilled water be added to the titration?
as water does not react with the reagents or change the number of moles of acid added
How do you deal with excess acid?
sodium hydrogen carbonate and calcium carbonate are good for neutralising excess acid as they’re not corrosive and will not cause a hazard if used in excess
What is a reading?
the values found from a single judgement when using a piece of equipment
What is a measurement?
the values taken as the difference between the judgements of 2 values
How do you calculate the percentage uncertainty?
uncertainty/ measurement made on apparatus x100
How can you decrease apparatus uncertainties?
decrease the sensitivity uncertainty by using an apparatus with a greater resolution
increase the size of the measurement made
How do you find the percentage uncertainty of a burette?
use 2 readings, as the uncertainty should be taken account at the start and end readings
How can you reduce uncertainties in a titration?
replace measuring cylinders with pipettes or burettes which have a lower apparatus uncertainty
use a larger volume titre in the burette
How do you reduce uncertainty in measuring mass?
use a balance which measures to more decimal places
use a larger mass
weigh by difference