Topic 14- Development 1
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is development in biology?
Development includes all changes that occur during an organism’s lifetime.
What are the key features of deuterostome development?
In deuterostomes, the blastopore becomes the anus during embryonic development.
What functions do the egg's outer coverings serve?
They protect the egg from environmental factors and aid in nutrient/waste exchange during early development.
What mechanisms help prevent polyspermy?
Gametic isolation and blocks to polyspermy, including the fast and slow block mechanisms.
What is fertilization?
The fusion of two haploid gametes (n + n) to form a diploid zygote (2n).
What are the major outcomes of fertilization?
Restores diploid ploidy, triggers egg activation, initiates embryonic development, sometimes determines the sex of the offspring.
What is the acrosome reaction?
The release of enzymes from the sperm's acrosome to penetrate the egg’s zona pellucida.
What is the cortical reaction?
A calcium-triggered release of enzymes from cortical granules that modifies the zona pellucida to block polyspermy.
What is karyogamy?
The fusion of egg and sperm nuclei to form the diploid zygote.
When is fertilization considered complete?
After the first cleavage division, when the embryo officially forms.
What are the structures surrounding a mammalian egg?
Plasma membrane, zona pellucida, and follicle cells.
What is the role of cortical granules?
They release enzymes that prevent additional sperm from entering the egg.
Describe the process from sperm binding to egg fusion.
Sperm binds to the zona pellucida, acrosomal enzymes are released to dissolve egg layers, sperm reaches and fuses with the egg's plasma membrane (plasmogamy), calcium is released → triggers cortical reaction → enzymes block other sperm.
What is polyspermy, and how is it prevented?
Polyspermy is when multiple sperm fertilize the egg; it’s prevented by fast and slow blocks (cortical reaction).
What triggers egg activation?
A rise in calcium ion concentration within the egg cytoplasm.
What changes occur during egg activation?
Increased respiration, activation of maternal enzymes, initiation of protein synthesis from maternal mRNA, completion of meiosis II, fusion of nuclei (karyogamy).
What guides the sperm nucleus to the egg nucleus?
Microtubules.
What type of cell is formed after fertilization?
A diploid, totipotent zygote (capable of developing into any cell type).
What is cleavage in embryonic development?
A rapid series of mitotic divisions that convert a zygote into a multicellular embryo.
What is unique about the cell cycle during cleavage?
There are no G1 or G2 phases, and no growth or protein synthesis occurs.
What are the main stages of cleavage?
Zygote (single diploid cell), Embryo (2+ cells), Blastula (128+ blastomeres; hollow ball of cells).
What is a cleavage furrow?
An indentation on the cell surface that eventually divides the cell during cytokinesis.
What are the animal and vegetal poles?
Animal pole becomes the actual embryo; Vegetal pole contains yolk and nutrients.
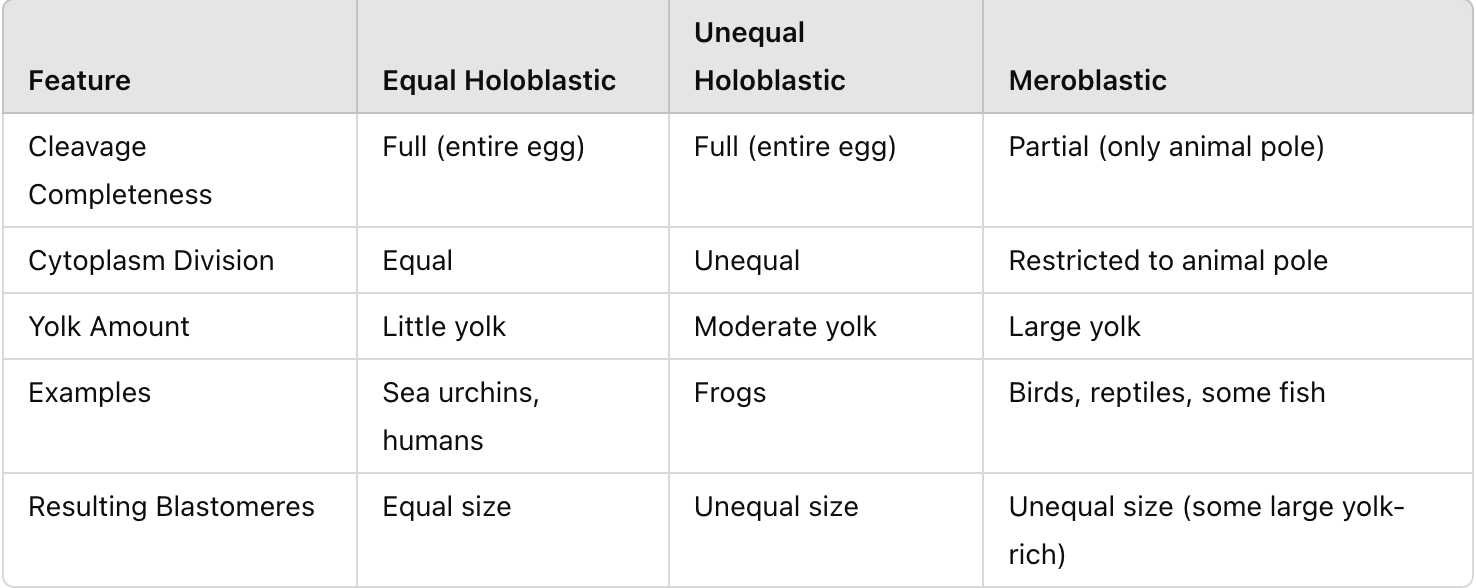
What is equal holoblastic cleavage?
Cleavage furrow fully divides the egg; equal division of cytoplasm → equal blastomeres; occurs in low-yolk eggs (e.g., humans, sea urchins).
What is unequal holoblastic cleavage?
Full cleavage furrow, but unequal division of cytoplasm; unequal blastomeres; occurs in moderate yolk eggs (e.g., frogs).
What is meroblastic cleavage?
Cleavage furrow does not completely divide the egg; occurs only in animal pole; found in eggs with large yolk (e.g., birds, reptiles, fish).
Sequence Animal Development in 6 steps:

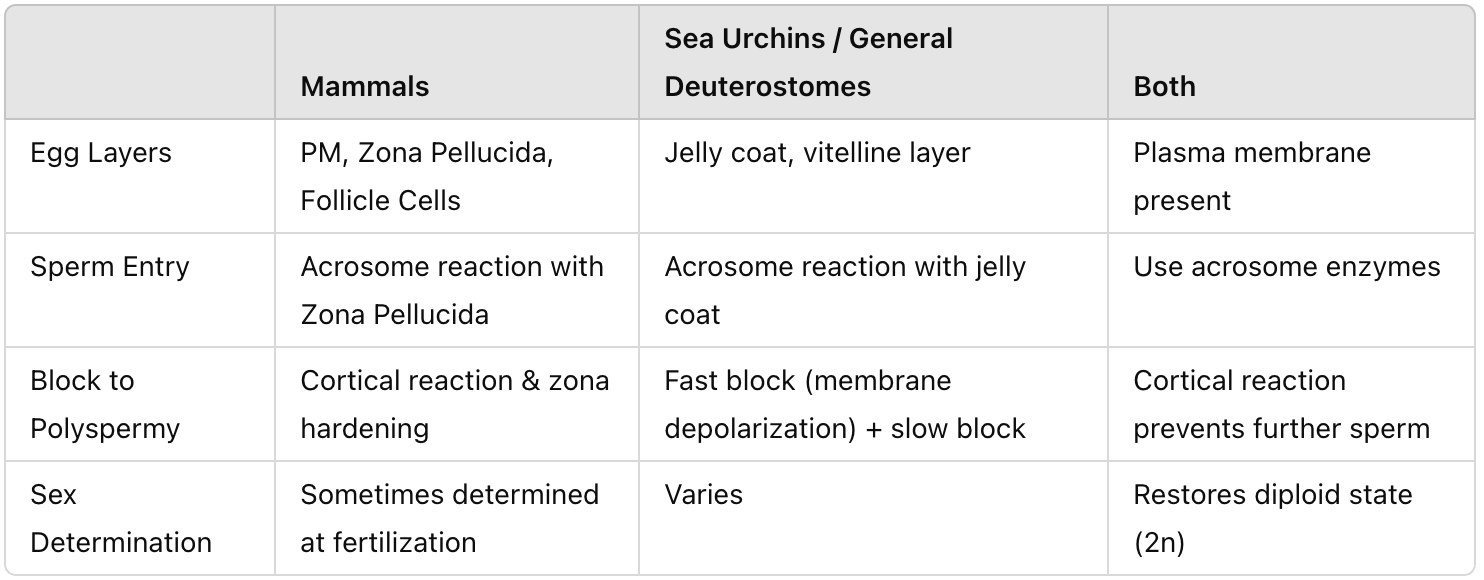
Compare and contrast fertilization in mammals and general deuterostomes such as sea urchins in terms of egg layers, sperm entry, lock to polyspermy, and sex determination.
Sequence the process of fertilization in 10 steps

Sequence the process of cleavage

Compare and contrast cleavage patterns (equal holoblastic, unequal holoblastic, and meroblastic) regarding cleavage completeness, cytoplasm division, yolk amount, examples, and the resulting blastomeres.
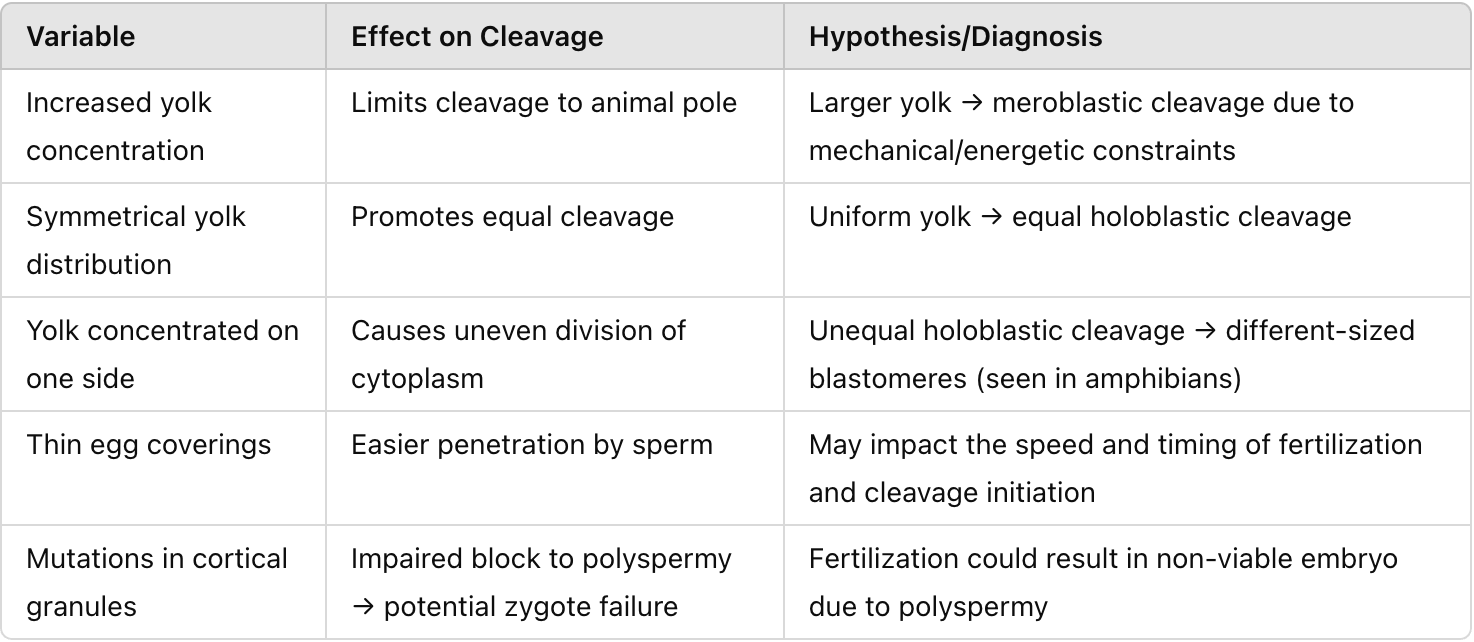
Hypothesize and diagnose the impact of variability on cleavage patterns with variables such as increased yolk concentration, symmetrical yolk distribution, yolk concentrated on one side, thin egg coverings, and mutation in cortical granules.