KIN 1200 Topic 1
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
the study of how exercise affects the functions of the body which can influence health and or performance. Students learn the impact of exercise at the whole body, system, and cellular level
exercise physiology
prepares students to pursue a variety of career opportunities in public health,
health care, population health and other health science related industries. Coursework focuses on evidence based public health strategies to prevent chronic disease and promote community population health. Graduates will be prepared with a solid undergraduate foundation to pursue further graduate study and/or professional degrees in pre-health, such as occupational therapy, physical therapy, physician assistant, dental hygiene, public health, and athletic training. Additionally, it provides students with the skills and competencies of the Certified Health Education Specialist.
health sciences degree
students completing the B.S. in Health and Physical Education Teacher
Education complete the requirements for Louisiana teacher certification in both
Health and Physical Education K-12. Students in this major may also pursue
add-on certification in Adapted Physical Education or other content areas
health and physical education K-12 degree
provides a strong science-based academic preparation for students who wish to pursue study in physical therapy or occupational therapy. This undergraduate program is also an appropriate choice for students who seek fitness-based careers, particularly those in clinical settings, such as cardiac rehabilitation
exercise science degree
designed to prepare students for careers in fitness and exercise specialties. Graduates seek employment in personal training, corporate fitness/wellness, and strength and conditioning coaching. It also provides entry requirements for most occupational therapy programs
fitness and human performance degree
prepares students both for graduate studies and employment in a variety of sport and recreational settings, playing a role in economic, sport, leisure, and fitness of the region. Southeastern Louisiana University students are in a geographical location that encourages practical experience. The University is roughly 45 miles away from New Orleans, the home of the New Orleans Saints, Voodoo, Pelicans, and the New Orleans Sport Foundation. Likewise, Baton Rouge is roughly 35 minutes from the campus and offers a variety of recreational and sport businesses where students can gain valuable experience. Baton Rouge offers the nationally recognized Baton Rouge Recreation Department, Youth and Adult Soccer Leagues, and the Baton Rouge Sports Foundation. Sport management professionals can be found working in a number of settings within the fields of sport and leisure/recreation. Some settings for employment include: Professional, Collegiate, and Amateur/Olympic Sport Organizations, YMCAs and Municipal Recreation Departments, Private clubs (i.e. tennis or golf), Entertainment industry
sport management degree
a discipline that studies movement and the associated functional responses and adaptations. The goal is to facilitate an understanding of the links between fitness, exercise, diet and health. Ultimately, the discipline provides a scientific approach to study how exercise and the human body interact in order to understand the physiology of exercise as well as its benefits and results.
what is exercise science?
There are various disciplines:
Muscular Anatomy and Kinesiology
▪ Exercise Physiology
▪ Exercise Testing and Prescription
▪ Biomechanics
▪ Motor Learning
▪ Sports Psychology
disciplines of exercise science
part of a multidisciplinary team whose work ranges from helping people recover from unhealthy effects of a sedentary lifestyle to assisting athletes to perform at their maximum capability
what do exercise science professionals do?
Teaches the following:
Skeletal muscle and major bone location and identification
▪ Origin
▪ Insertion
▪ Function/action
▪ Other kinesiological example concepts
▪ Agonist/antagonist, concentric/eccentric/isometric contractions,
muscle fiber types
anatomy and kinesiology (KIN 275)
the attachment site that doesn’t move during contraction, while the insertion is the attachment site that does move when the muscle contracts
origin
usually distal, or further away, while the origin is proximal, or closer to the body, relative to the insertion
insertion
movement, support, protection, heat generation, and blood circulation
five main functions of the muscular system
skeletal muscles pull the bones causing movement at the joints. skeletal muscles pull on the soft tissues of the face causing facial expressions. movement caused by the respiratory muscles enables breathing
movement
muscles of the body wall support the internal organs. as the muscles lose their tone, the internal organs of the abdominal-pelvic cavity may bulge outward as seen in some individuals as they age
support
skeletal muscles, particularly of the body wall, cushion the body’s internal
organs (abdominal cavity) from force applied to the exterior of the body
protection
heat is a waste product of muscle metabolism, which helps maintain an internal body temperature of 98.6 F. Shivering is a mechanism of the muscular system that generates heat to warm an overly cooled body
heat generation
cardiac muscles aid pumping action of the heart by aiding blood circulation
blood circulation
the muscle that is contracting (it’s in “agony”)
agonist
the muscle that is relaxing or lengthening (not in agony)
antagonist
one way to remember which muscle is the agonist-it’s the one that’s in “agony” when you are doing the movement as well as it is the one that is doing all the work
agonist vs antagonist
the muscle tension rises to meet the resistance then remains stable as the muscle shortens
concentric contraction
the muscle lengthens as the resistance becomes greater than the force the muscle is producing
eccentric contraction
when you hold a key position with little to no movement
isometric movements
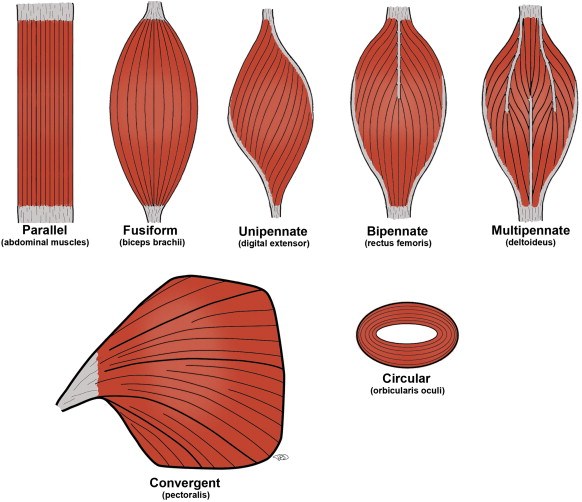
fusiform, unipennate, bipennate, triangular, spiral, strap
different shapes of muscles
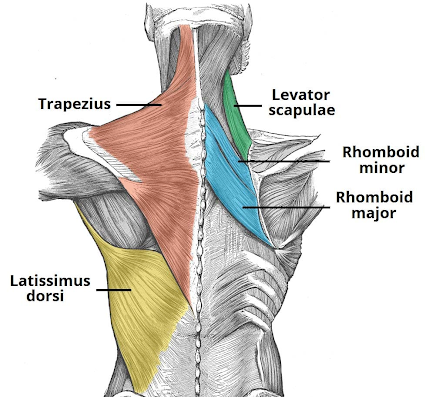
function to stabilize the medial border of the scapula. The rhomboids are very active in scapular adduction or retraction, which can be defined as backward rotation of the scapula toward the vertebral column.
rhomboids (major and minor) - retraction and scapula stabilization
The application of physics and mechanical systems to
the human body.
▪ Studies the effects of forces such as inertia, weight, and pressure
▪ Angular motion and force such as that found in joints (Torque)
biomechanics (KIN 372)
motion, force, momentum
three principles of biomechanics
how an object or body moves through space
motion
the pull or push that enables an object to change direction, slow or stop
force
the velocity and weight of an object as it moves
momentum
pushing someone in a wheelchair, gravity, wrestling, opening a door, lifting a weight, kicking something, pushing a shopping cart
examples of force
walking, jumping on a trampoline, running around on a track, driving
example of motion
Newton’s cradle, jumping high on a trampoline, basketball, baseball, bowling ball, ice skater, roller blader
example of momentum
you can associate many exercises with more than one pattern based on how you use them. A bench press is a PUSH movement pattern while a deadlift could be a PULL for the back or squat variation for the legs. Examples of a pull pattern include a dumbbell row or a pull-up
biomechanics in program design
the inherent property of a body that makes it oppose any force that would cause change in its motion. A body at rest and a body in motion both oppose forces that might cause acceleration. The inertia of a body can be measured by its mass, which governs its resistance to the action of a force, or by its moment of inertia about a specific axis, which measures its resistance to the action of a torque about the same axis
inertia
a tendency of a body to resist change in motion or at rest
inertia
this can be found using Newton’s second law– F=ma__which translates to, Force equals inertial mass times acceleration
how to calculate force of a mass
when a moving car suddenly stops, the person sitting in the car falls forward because the lower portion of the body contact with the vehicle comes to rest
example of calculating force of a mass
tendency of a body to remain in the state of rest
inertia of rest
tendency of a body to remain in a particular direction
inertia of direction
tendency of a body to remain in a state of uniform motion
inertia of motion
pen, tablet, etc resting on a table, getting moved by a car while you’re riding it
example of inertia of rest
running at the same pace, round abouts
example of inertia of direction
long jump, rolling a ball
example of inertia of motion
objects have a natural tendency to resist change. Heavier objects (objects with more mass) are more difficult to move and stop. Heavier objects (greater mass) resist change more than lighter objects
why do heavier objects have more inertia?
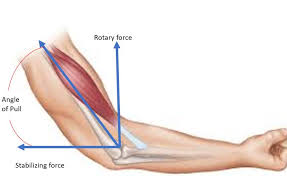
a measure of the force that can cause an object to rotate about an axis. it can either be static or dynamic. angular, rotational force applied to and by the human body. it’s due to the segmental levers rotating around joints
torque
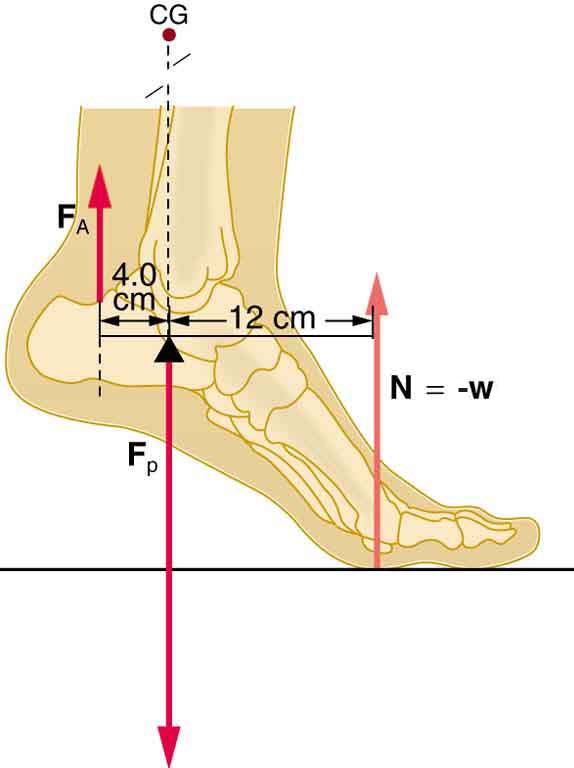
a person pushing a closed-door is applying static torque because the door isn’t rotating despite the force applied. Pedaling a cycle at a constant speed is an example of static torque as there is no acceleration.
examples of torque
T=Fd (T is for torque measured in Newton-meters, F is force measured in Newtons, d is the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the applied force in meters)
formula for torque
▪ Force distributed over a given area
▪ p = F/A
▪ The smaller that A (area) is, the greater that p becomes
▪ This means that a given force exerts more pressure over a small
area than a large one
▪ Expressed as Pascals (or newtons per square centimeter)
example kinetic variable: pressure
What are the pressures exerted by a 556 N woman with a flat soled shoe or
spiked heel?
▪ Area of flat sole = 175 cm²
* Area of spiked heal = 4 cm²
For flat soled shoe - p = 556/175 ; p = 3.18 pascals
For the spiked heel - p = 556/4 ; p = 139 pascals
(The spiked heel exerts about 43 times more pressure than the flat soled shoe)
Lecture portion covers
many topics:
▪ Metabolism
▪ Exercise responses
▪ Muscular function
▪ Cardiovascular function
* Lab experiments range from cycle tests to underwater weighing to handgrip strength
exercise physiology class (KIN 392/393)
the study of how exercise affects the functions of the body which can influence health and or performance. Students learn the impact of exercise at the whole body, system, and cellular level
exercise physiology
develop fitness and exercise programs that help patients prevent or recover from chronic diseases (e.g., hypertension, diabetes, obesity, heart disease, cancer) and improve cardiovascular function, body composition, strength, and flexibility
exercise physiologists
The study of physiological responses and adaptations to
exercise
▪ Muscle contraction
▪ ATP synthesis (Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport Chain)
▪ Actin and Myosin interactions
▪ Fiber differences and adaptations
exercise physiology
the muscle tension rises to meet the resistance then remains stable as the muscle shortens
concentric contraction
when you hold a key position with little to no movement
isometric movements
the muscle lengthens as the resistance becomes greater than the force the muscle is producing
eccentric contraction
the function of ATP synthase is to produce ATP. ATP is necessary to power all cellular processes, so it is constantly being used by cells and constantly needs to be produced. Each ATP synthase can produce about 100 molecules of ATP every second. in general, the main energy source for cellular metabolism is glucose, which is catabolized in the three subsequent processes—glycolysis, tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA or Krebs cycle), and finally oxidative phosphorylation—to produce ATP
what is ATP synthesis used for?
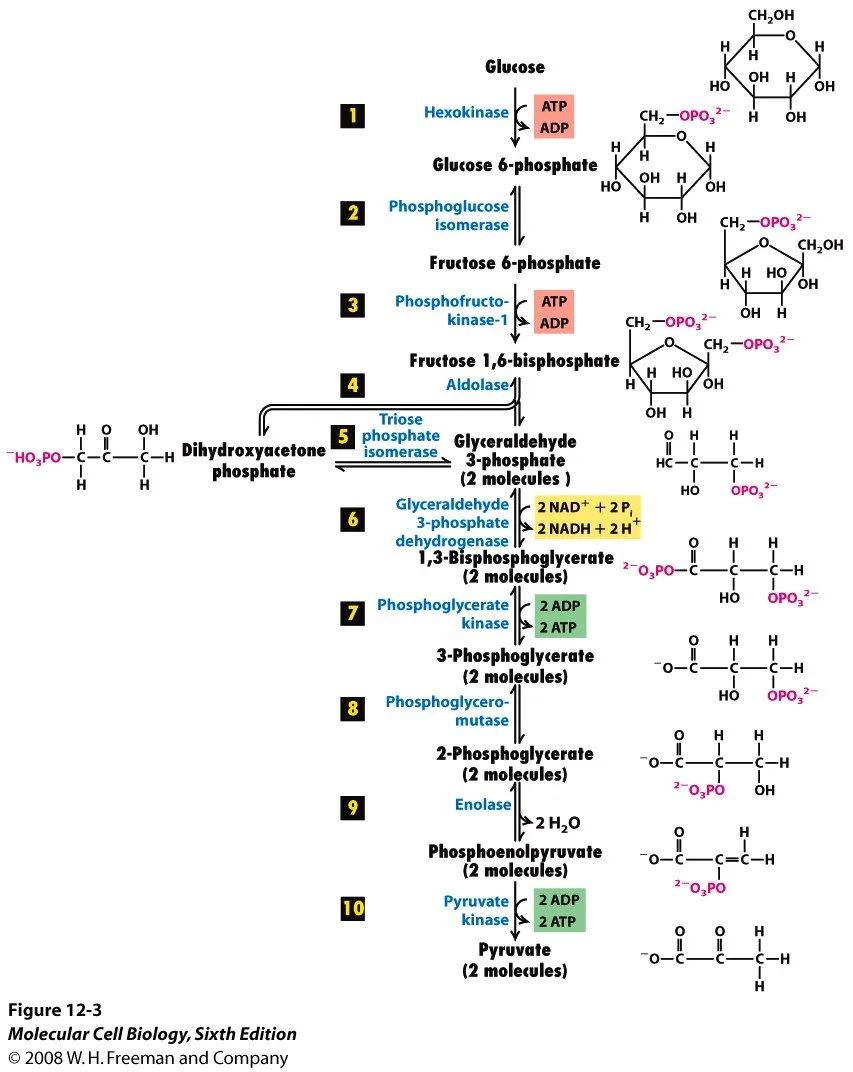
the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism. Glycolysis consists of an energy-requiring phase followed by an energy-releasing phase
glycolysis
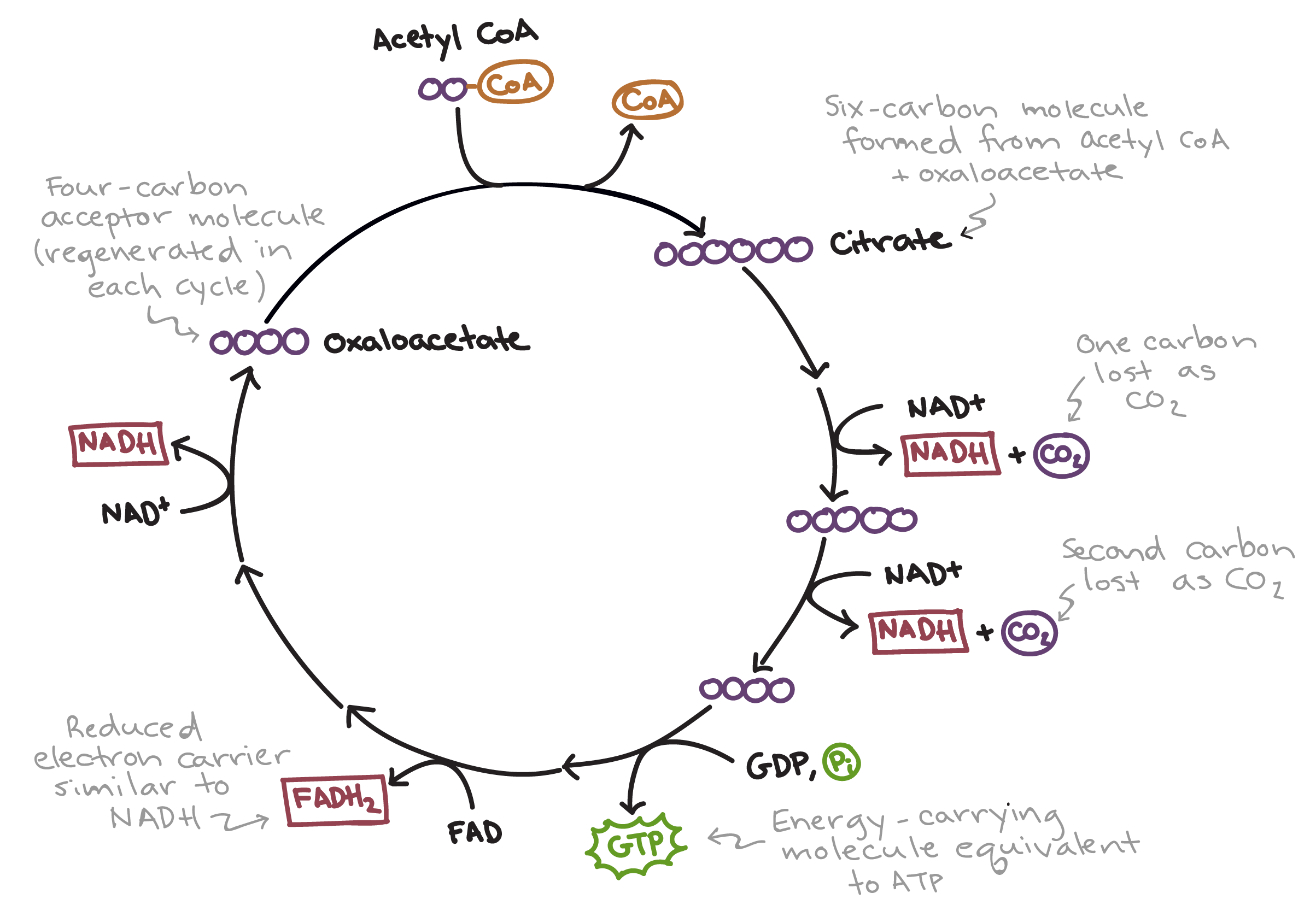
the sequence of reactions by which most living cells generate energy during the process of aerobic respiration. It takes place in the mitochondria, consuming oxygen, producing carbon dioxide and water as waste products, and converting ADP to energy-rich ATP
kreb cycle
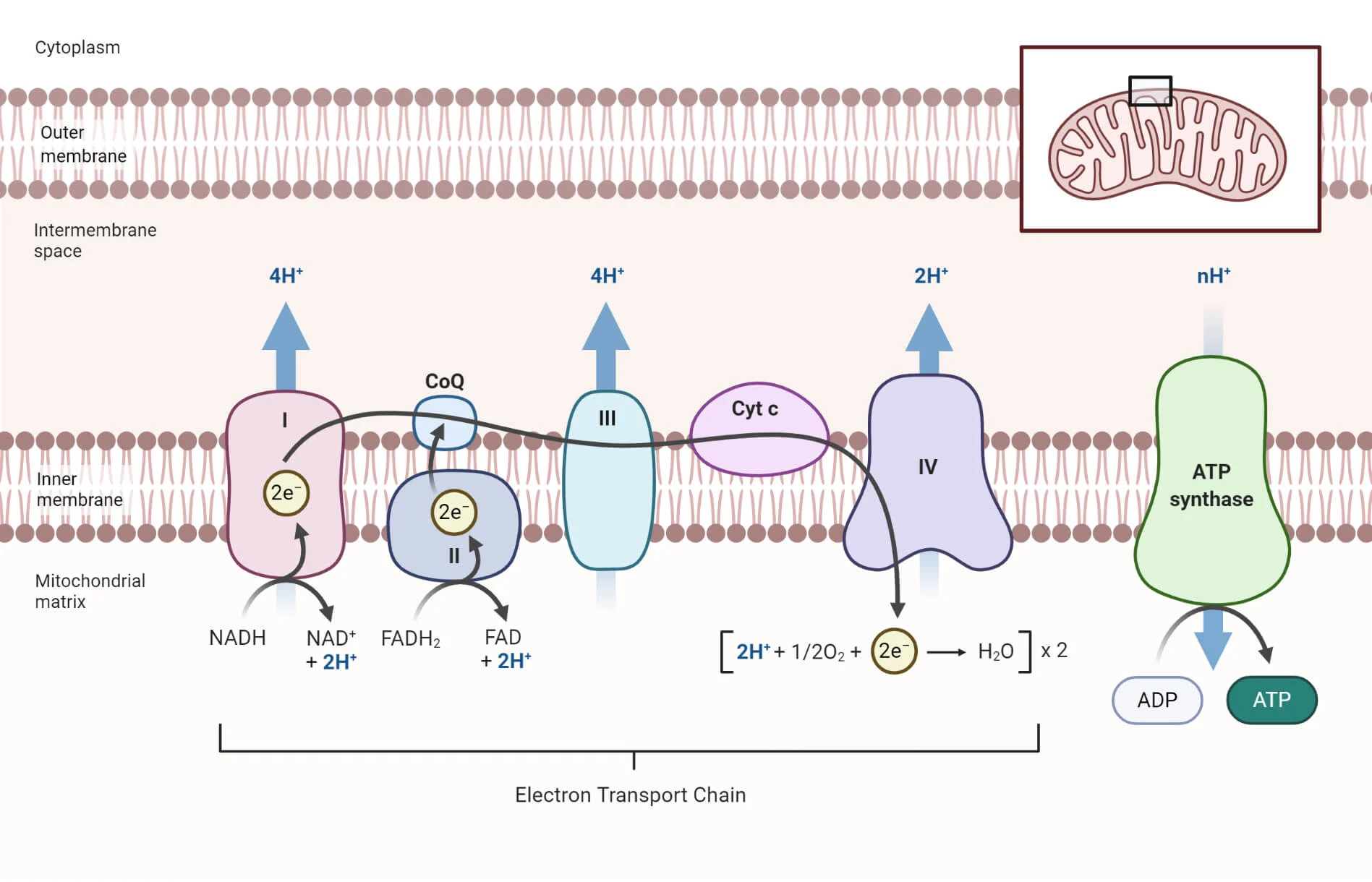
the ETC is a collection of proteins bound to the inner mitochondrial membrane and organic molecules, which electrons pass through in a series of redox reactions, and release energy. The energy released forms a proton gradient, which is used in chemiosmosis to make a large amount of ATP by the protein ATP-synthase
electron transport chain
a protein that creates fine contractile filaments within muscle cells
actin
a protein that causes muscle cells to generate dense contractile filaments
myosin
additionally, they are in charge of both cellular and non-cellular motions. Actin is a protein that creates fine contractile filaments within muscle cells, which is the main distinction between actin and myosin. Myosin, on the other hand, is a protein that causes muscle cells to generate dense contractile filaments
what is the difference between actin and myosin? How are they involved in muscle contraction
power-building exercise, by contrast, causes muscle cells to manufacture more filaments of actin and myosin and to install them next to the existing ones within each cell. This is why weight-training makes muscles thicker. This buildup happens if the muscles are worked at more than 40 percent of capacity
what happens to actin and myosin during exercise?
Adaptations: persistent functional changes that occur due to many
bouts of exercise (training)
▪ Muscle strength
▪ Muscle size (hypertrophy)
▪ Cardiac function
▪ VO2 changes
▪ Muscle adapts to aerobic exercise training to become a more efficient
energy provider. An improved capacity for oxygen extraction from the
blood supply and an altered cellular control of energy metabolism likely
contribute to the improved muscle performance evident with training.
exercise physiology
examples of exercises that develop muscular strength and power include resistance training, such as weightlifting, bodyweight exercises, and resistance band exercises. Running, cycling, and climbing hills are also options
what are 5 example of muscle-strengthening?
a test that records the electrical activity of the heart. The ECG reflects what's happening in different areas of the heart and helps identify any problems with the rhythm or rate of your heart. The ECG is painless and takes around 5-10 minutes to perform
electrocardiogram
ejection fraction in a healthy heart is 50% to 70%. With each heartbeat, 50% to 70% of the blood in your left ventricle gets pumped out to your body
what is the normal range for cardiac function test?
Various aspects of testing and prescription of exercise:
▪ Body composition
▪ VO2 testing
▪ EKG analysis
▪ Blood pressure changes
exercise testing class (KIN 424 and 434)
Family History + CV disease
▪ Cigarette Smoking + Current or last 6 months
▪ Hypertension + 140+/90+ or meds
▪ Hypercholesterol + Total > 200 or LDL > 30 or
HDL < 35 or meds
▪ Impaired glucose + Fasting glucose 110+
▪ Sedentary lifestyle + Not regularly active
▪ Obesity + BMI 30+ or girth > 100 cm
▪ High HDL - HDL >60
risk stratification: risk factors
sometimes called “good” cholesterol, absorbs cholesterol in the blood and carries it back to the liver. The liver then flushes it from the body. High levels of HDL cholesterol can lower your risk for heart disease and stroke
HDL (high-density lipoprotein cholesterol)
▪ Pain/discomfort in the chest, neck, jaw, arms, or other areas indicative
of ischemia ( Inadequate blood supply to an organ or part of the body,
especially the heart muscle).
▪ Shortness of breath at rest or with mild exertion
▪ Unusual fatigue or shortness of breath with normal activities
▪ Dizziness, Syncope, Orthopnea, Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea, Ankle
Edema, Known Heart Murmur, Palpitations/Tachycardia, Intermittent
Claudication
risk stratification: symptoms of disease
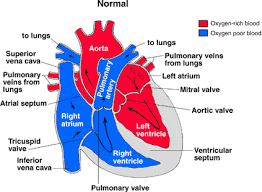
blood comes into the right atrium from the body, moves into the right ventricle and is pushed into the pulmonary arteries in the lungs. After picking up oxygen, the blood travels back to the heart through the pulmonary veins into the left atrium, to the left ventricle and out to the body's tissues through the aorta. Enters the heart from the lungs and goes out to the body
oxygen-rich blood
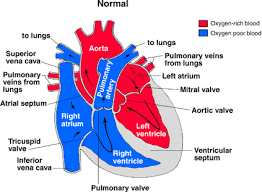
enters the heart from the body and goes out to the lungs
oxygen-poor blood
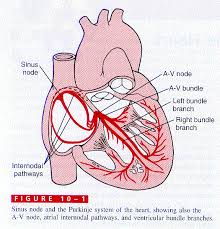
Cardiac Conduction System - Normal
Function of the Heart ...
This pathway is made up of 5 elements:
The sino-atrial (SA) node. ( The pacemaker
of the Heart)
The atrio-ventricular (AV) node.
The bundle of His.
The left and right bundle branches.
The Purkinje fibres.
what are the 5 steps of the electrical pathway of the heart?
Equipment:
▪ Parvomedics Metabolic System
▪ Used in conjunction with treadmill or cycle
▪ Measures percentage of gases exhaled and oxygen consumption
▪ Electrocardiography (ECG)
▪ Monitors electrical events of the heart
▪ Can be used to diagnose cardiac problems
exercise physiology lab
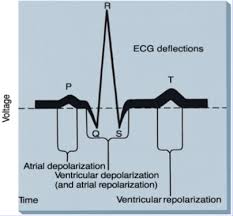
▪ P Wave
▪ PR Interval
▪ QRS Complex
▪ ST Segment
▪ T Wave
ECG waveforms
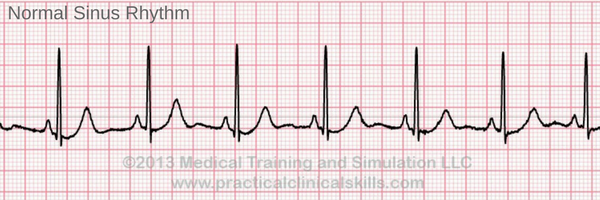
refers to the cardiac rhythm that is presented by a normal, healthy heart. It has a rate between 60 to 100 beats per minute and typically shows beats at equal intervals from one another
normal sinus rhythm (NSR)
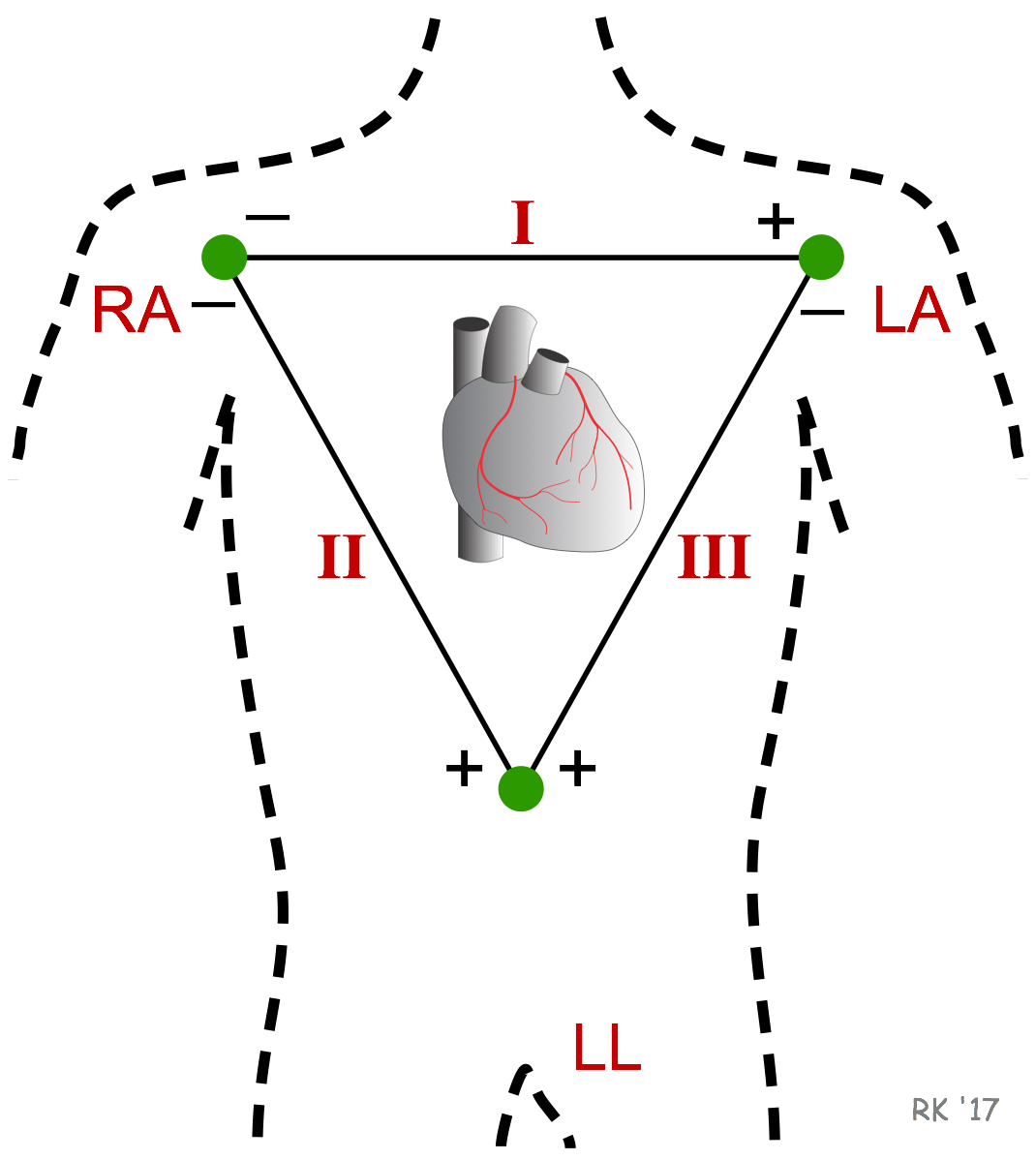
used primarily for basic heart monitoring
ekg lead 1
provides the best and most direct view of the heart’s electrical pathways
ekg lead 2
has a positive electrode on the left leg and a negative electrode on the left arm. These three bipolar leads roughly form an equilateral triangle (with the heart at the center) that is called Einthoven's triangle in honor of Willem Einthoven, who developed the electrocardiogram in the early 1900s
ekg lead 3
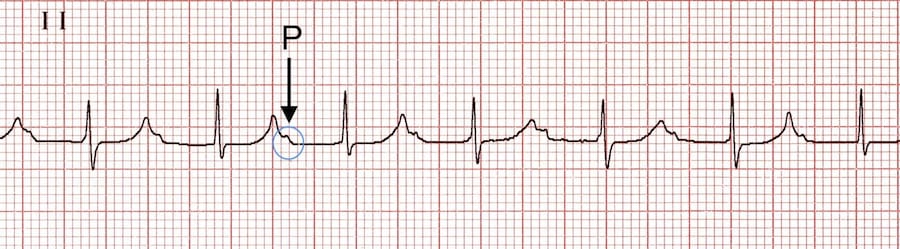
rhythm
may be normal variant or indicator of disease
usually occurs without any symptoms and may require no treatment
example ekg abnormality: first degree av block

what is this?
Lab equipment: Cycle Ergometer and VO2 Metabolic System