Gymnosperms
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
conifers
The most familiar gymnosperms are the ___________, the cone-bearing plants such as pines.
sporophylls
The ovules and seeds of gymnosperms (“naked seeds”) develop on the surfaces of specialized leaves called ________
ovaries
In contrast, ovules and seeds of angiosperms develop in enclosed chambers called ________.
Gymnosperms
_________ appears in the fossil record much earlier than angiosperms
Mesozoic era
The ________________ was the age of gymnosperms
progymnosperms
The gymnosperms probably descended from _________, a group of Devonian plants.
seeds
While the earliest progymnosperms lacked __________, by the end of the Devonian, some species had evolved them.
Adaptive radiation
__________ during the Carboniferous and early Permian produced the various phyla of gymnosperms.
ginko, cycads, gnetophytes, and conifers
The four phyla of extant gymnosperms are ______________________
Phylum Ginkgophyta
consists of only a single extant species, Ginkgo biloba.
Ginkgo biloba
This popular ornamental species has fanlike leaves that turn gold before they fall off in the autumn.
seed coats on female plants decay producing a repulsive odor to humans
Landscapers usually only plant male trees of gingko biloba, why is that?
Cycads
__________ (phylum Cycadophyta) superficially resemble palms.
Palms
_________ are actually flowering plants.
Circinate vernation
young leaves curved inward
dimorphic
Leaves usually __________ (two types of leaves in one plant)
prescence of permanent leaf scar
first Morphological Characteristics of Phylum Gnetophyta
Weltwitschia plants
from deserts in southwestern Africa, have straplike leaves.
Gnetum
species are tropical trees or vines
Ephedra
___________ (Mormon tea) is a shrub of the American deserts.
Morphological Characteristics of gymnosperms
• Prescence of permanent leaf scar
• Leaves usually dimorphic (two types of leaves in one plant)
• Foliage leaves
• Scale leaves
• Circinate vernation (young leaves curved inward)
Megasporangia
____________ are produced on megasporophylls
Microsporangia
______________ are produced on microsporophylls
Heterosporous
different types of spores that are different in structure, size and function
cones or strobili
Sporophylls aggregated to form
monosporangiage
Cones/strobili are ______ (having only one sporangium (or a single type of sporangium), a structure that produces spores)
ovule
Female cone, megasporophyll and ovule • Megasporangium aka the __________
short-lived
Male cone, microsporophylls and microspores. Males core are ______________; female cones live for many years
Cycas female cone
No definite female cone or strobilus in Cycad
Female strobilus
is an aggregation of spirally arranged megasporophylls
Megasporophylls
resemble foliage leaves
Megasporophylls
Similar to seed-bearing leaves
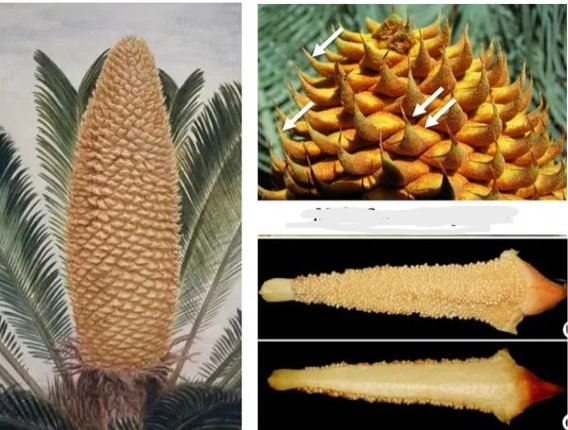
Cycas male cone
Male strobili (cone) are produced at the apex of the stem
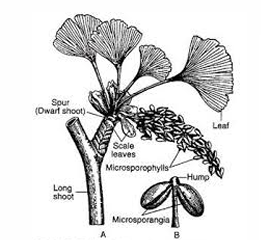
gingko biloba
identify

Cycads
idenitfy

Weltwitschia
identify

Gnetum
identify

Ephedra
identify

circinate vernation
identify

dimorphic leaves
identify

female cone
identify

male cone
identify

cycas megasporophyll with ovules
identify

male cone

gingko biloba