RADS 3043 Basic Procedures Final
1/309
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
310 Terms
B. Toward the elbow
According to Bontrager, which way do you angle the central ray (CR) for the Stetcher (PA Axial) when the patient's wrist and image receptor are flat?
A. Away from the elbow
B. Toward the elbow
C. Pronation
Which of the following terms is defined as a rotation of the forearm so that the palm is down?
A. Abduction
B. Eversion
C. Pronation
D. Suponation
E. Rotation
D. Open metacarpophalangeal and IP joints
Which of the following is part of the evaluation criteria for a PA oblique 2nd - 5th digits?
A. No collimation
B. Entire digit rotated 40 degrees
C. Open IP and MCP joints that are perpendicular to IR
D. Open metacarpophalangeal and IP joints
False
True or False. The correct anatomical position refers to the body standing erect, face and eyes forward, arms extended by the side with palms facing forward, heels together, and toes pointing inferiorly.
Scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform
The wrist is comprised of 8 carpal bones. What is the correct order of the proximal row of the carpal bones from lateral to medial?
Appendicular skeletal
Which skeletal area consist of approximately 126 bones?
Olecranon process and coronoid process
Which bony processes are located on the proximal end of the ulna?
D. Date of birth
You have called Mr. Comello for his exam. What should you use to verify his identity?
A. Social Security Number
B. Exam being performed
C. Ordering physician
D. Date of birth
C. View
The term that is used to describe the body part as seen by the IR is?
A. Position
B. Projection
C. View
D Method
D. Flexed 90 degrees
According to the text, in which position do you place the elbow when positioning the patient for a lateral view of the wrist?
A. Extended
B. Flexed 45 degrees
C. Flexed 60 degrees
D. Flexed 90 degrees
E. Elbow placement is not a consideration when positioning the patient for a lateral view of the wrist
During the first 10 days of the menstrual cycle
When should the 10 day rule be applied to non-emergency radiographic examinations of the abdomen on women of child bearing age?
D
Which of the following is the PIP of the 2nd digit?
D. A (Soft tissue and bony trabeculation) and C (Scaphoid and adjacent articulations open)
Which of the following is evaluation criteria for ulnar deviation of the wrist?
A. Soft tissue and bony trabeculation
B. Mid-carpal area in the center of the film
C. Scaphoid and adjacent articulations open
D. A and C
E. A, B, and C
PIP joint
Where is the central ray directed on the PA projection of the right 3rd digit?
Trapezium and scaphoid
Which carpal bones are best demonstrated on the PA oblique (lateral rotation) of the wrist?
Posterior fat pad
Which fat pad in the elbow lies deep within the olecranon fossa?
Supinator fat pad
Which fat pad in the elbow lies parallel with the anterior proximal radius?
MCP joint space
Where is the central ray directed for a PA oblique projection of the 1st digit?
Saggital
The plane that divides the body into right and left sides is the ___________ plane.
B
Which of the following illustrations best represents the PA oblique of the hand?
45 degrees
How much rotation should be used for an AP oblique projection of the elbow, no matter which oblique is performed?
40-44 inches
What is the recommended SID for radiography of the elbow?
B
Which of the following represents the 2nd metacarophalangeal joint?
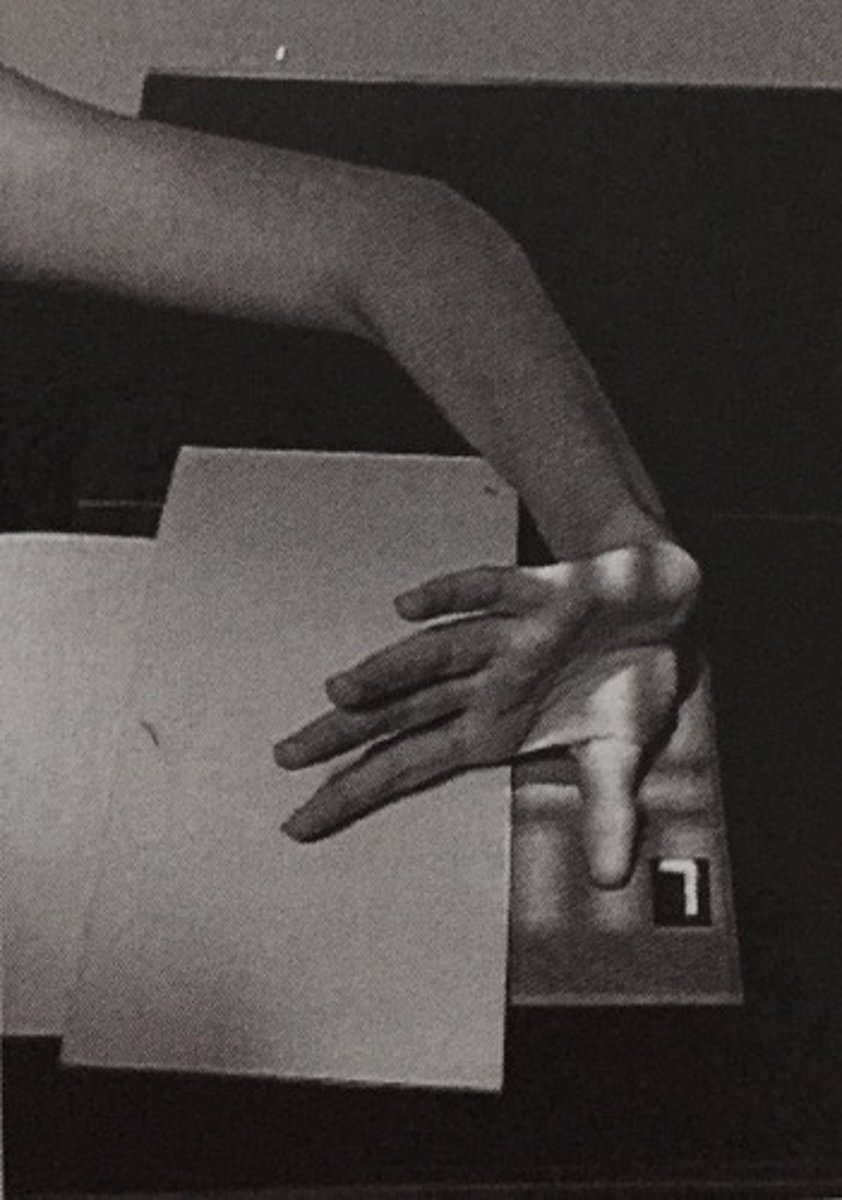
AP 1st digit
What does the following positioning picture represent?

D. They convex slightly anteriorly
Which of the following is not identify a characteristic of metacarpals?
A. They are long bones
B. Cylindrical in shape
C. The neck is easily fractured
D. They convex slightly anteriorly
E. The first metacarpal contains two sesamoid bones
B. Head of the 3rd proximal phalynx
Which is more distal?
A. Base of the 3rd proximal phalynx
B. Head of the 3rd proximal phalynx
C. Head of the 4th proximal phalynx
D. Base of the 2nd proximal phalynx
Long bone
Phalanges are classified as what type of bone?
Projection
The direction of the x-ray beam as it enters the body, passes through, and finally exits the body, is known as:
Trapezium
On page 129 of the textbook, there is a radiograph of a PA wrist. The letter "E" corresponds to the carpal bone that articulates with the 1st metacarpal. This would be the __________.
Capitate
The carpal bone that articulates with the 3rd metacarpal
Oblique
Flexing the fingers with the hand in the PA position places the thumb in the __________ position?
27 in each
How many bones are found in both hands/ wrists?
Hamate
Which carpal bone is wedge-shaped and has its prominent density on its anterior surface?
Lunate
What carpal bones articulate with the radius proximally?
Trapezoid
Which carpal bone has a smaller surface anteriorly than posteriorly and is four sided?
Saddle
If the intercarpal joints of the wrist are gliding type joints, the the 1st carpometacarpal joint is a synovial, __________ type joint.
Room 3 only
In lab, which room(s) has automatic tracking on the collimator?
B. Coranoid process
An AP oblique, medial rotation, of the elbow, will result in what anatomic feature being projected free from superimposition?
A. Radial head and radial tuberosity
B. Coranoid process
Radial head and radial tuberosity
An AP oblique, lateral rotation, of the elbow, will result in what anatomic feature being projected free from superimposition?
True
True or False? The largest bone in the proximal row of the carpal bones is the scaphoid
C. The incorrect bucky is selected
In lab, when room three or four does not detent, the most probable cause would be __________.
A. The AEC is engaged
B. The incorrect tube is selected
C. The incorrect bucky is selected
D. The incorrect IR location is selected
Small focal spot
In lab, in rooms 3 and 4, when the light is on for the focal spot; is the large or the small focal spot selected?
(1) Radial
(2) Lateral
The proximal head of the radius articulates with the __________ notch of the ulna on the __________ side.
Fingers are flexed for the ball catcher and not for the Norgaard
The Norgaard and the Ball Catcher positions are roughly the same. What is the difference
B. Synovial
A thick, yellow, viscous, lubricating fluid found in some joints is termed?
A. Cartilage
B. Synovial
C. Visceral
D. Hyaline
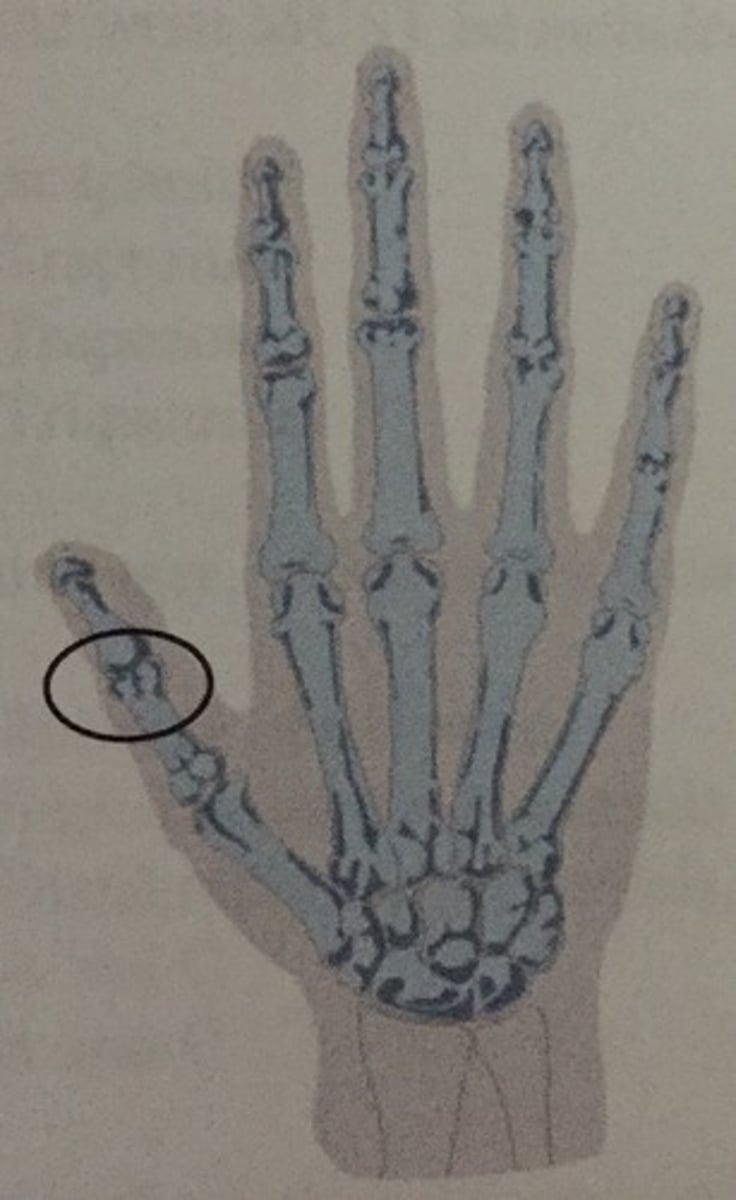
IP joint
What does the circle identify?
A. Humerus and forearm 90 degrees, in the same plane
What best describes the correct patient position for a lateral forearm?
A. Humerus and forearm 90 degrees, in the same plane
B. Humerus and forearm 45 degrees, in the same plane
C. Humerus and forearm 90 degrees, but it does not matter if they are in the same plane
D. Humerus and forearm 45 degrees, but it does not matter if they are in the same plane
False
True or False? Real people can be x-rayed in our lab.
C. Built into the control panel
Technique charts are generally found:
A. On the reader/processor
B. In each individual room
C. Built into the control panel
D. Just outside of each room
Rooms 1 and 2
Rooms 3 and 4
Which control panels in the x-ray rooms are the same?
Trapezium
Which bone of the wrist must be included on any view of the 1st digit?
E. B (Superimposed metacarpals) and C (Distal radius, ulna, carpals, proximal half of metacarpals)
According to Bontrager, which of the following must be seen on a lateral wrist?
A. Rotation of the wrist
B. Superimposed metacarpals
C. Distal radius, ulna, carpals, proximal half of metacarpals
D. A and C
E. B and C
B
Which of the radiographs is the best representation of a PA wrist?
Because you want the part to be close to the IR
Why should you perform a AP radiograph of the 1st digit instead of a PA radiograph of the 1st digit?
D. All of the above
According to Bontrager, which of the following evaluation criteria indicate you have a diagnostic view of a lateral forearm?
A. Soft tissue and bony trebeculae are visible
B. Both joints are seen on the radiograph
C. The elbow is flexed 90 degrees
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
IR angled 20 degrees and perpendicular CR
or
IR flat and CR angled 20 degrees toward the elbow
What is the correct IR and CR position for the stecher?
B. Concave anterior surfaces, no obstruction of proximal phalanx or MCP joint by adjacent digits
According to Bontrager, what indicates a true lateral of the 2-5 digits?
A. Entire digit rotated 45, including the distal portion of the adjoining metacarpal, no obstruction of proximal phalanx or MCP joint by adjacent digits
B. Concave anterior surfaces, no obstruction of proximal phalanx or MCP joint by adjacent digits
C. Neither of the above statements are correct
A
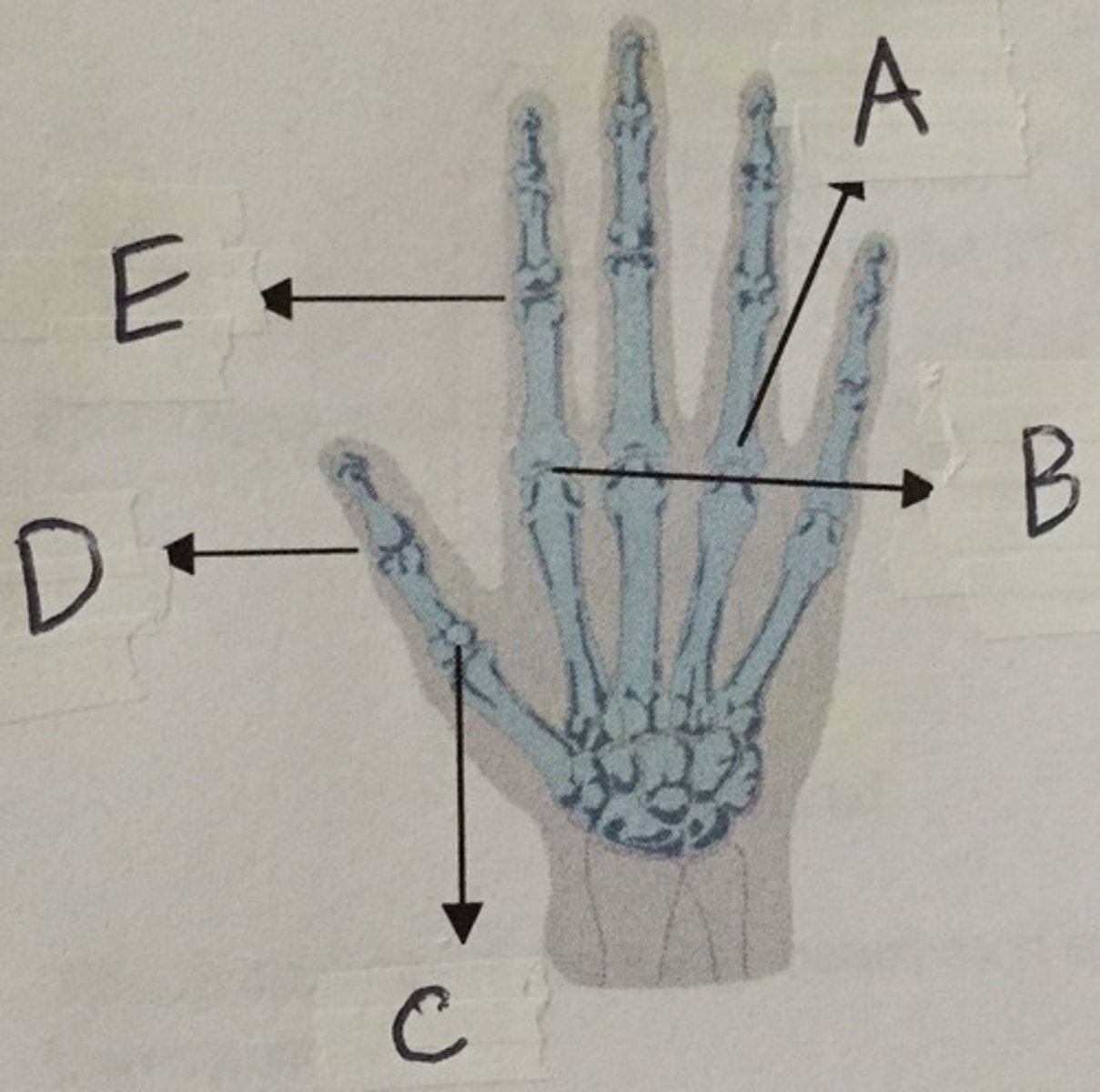
Identify the ulna
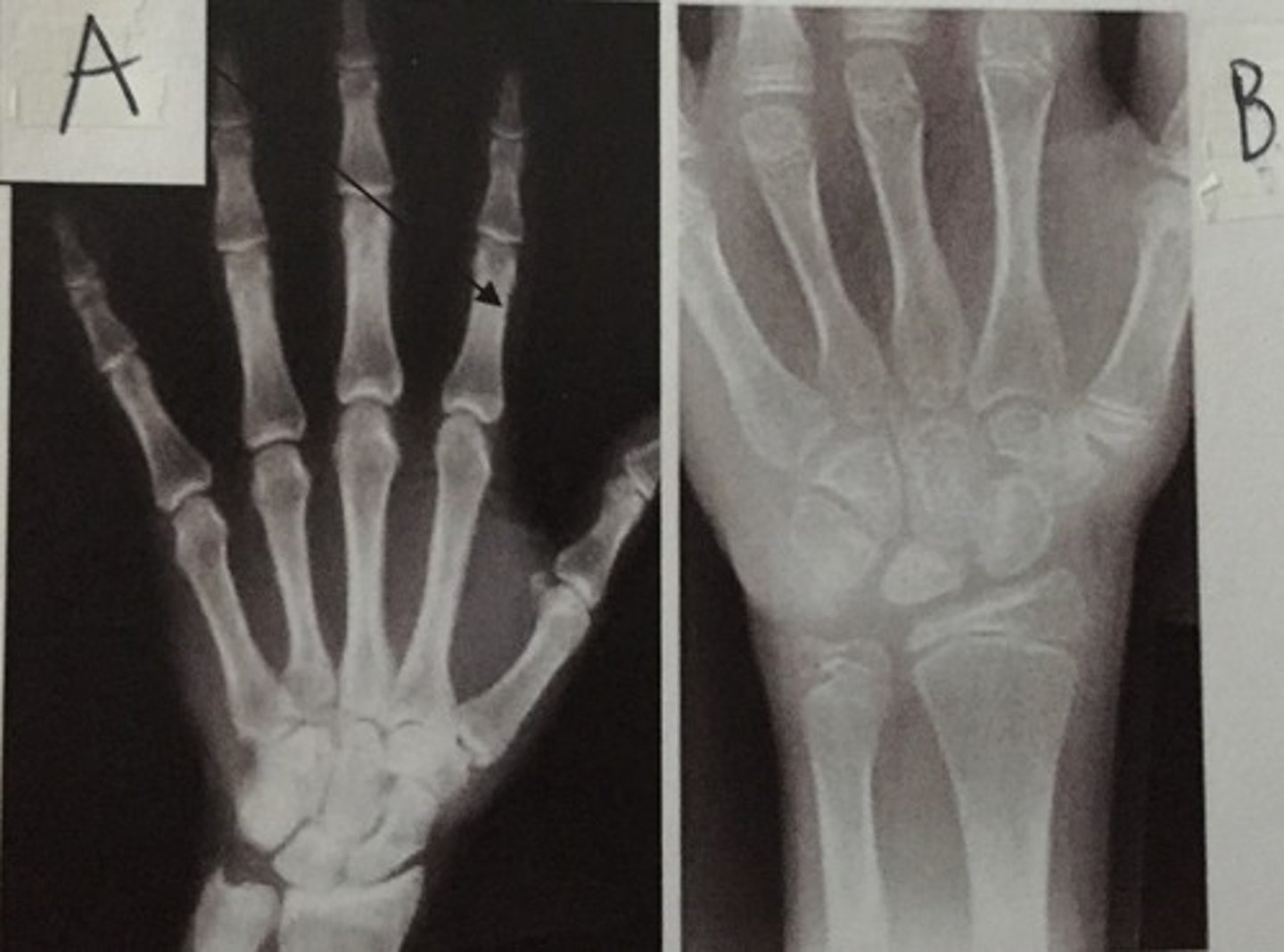
E
Identify the radial styloid process
B
Identify the coronoid process
D
Identify the radial body
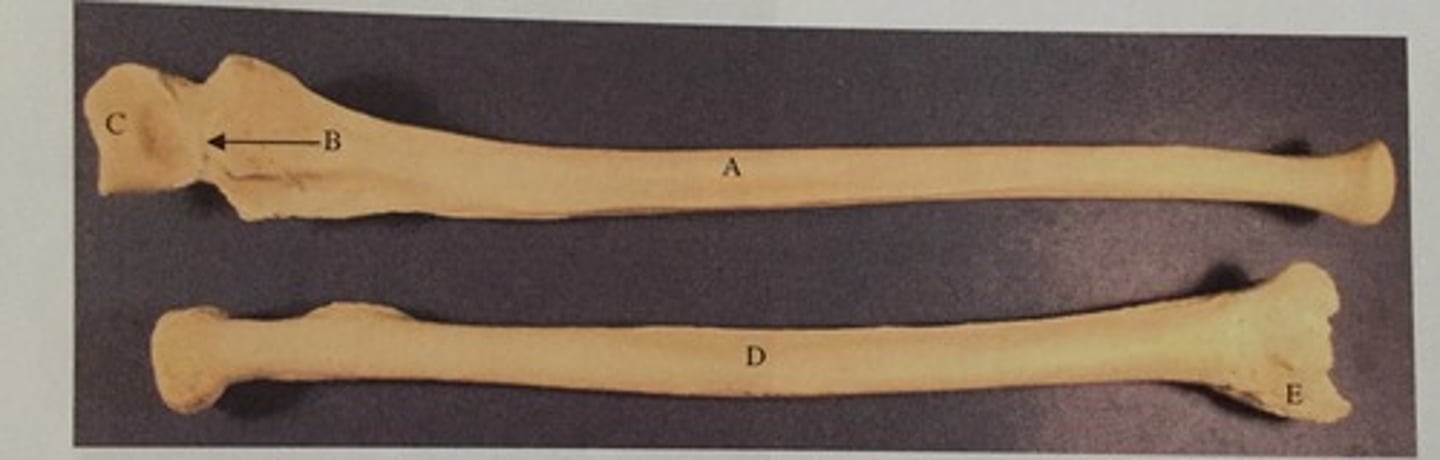
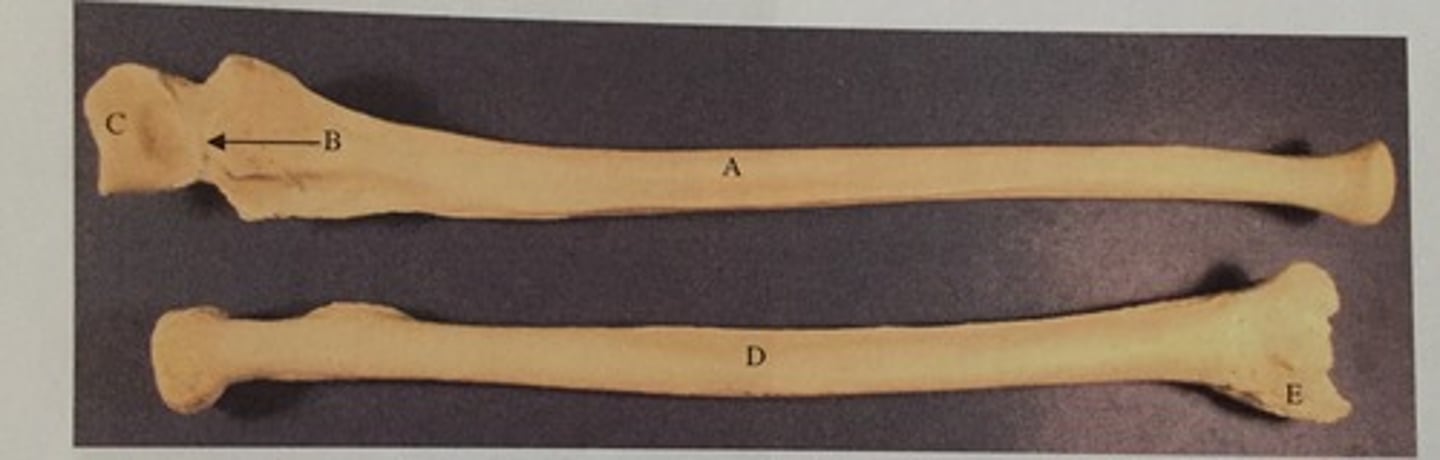
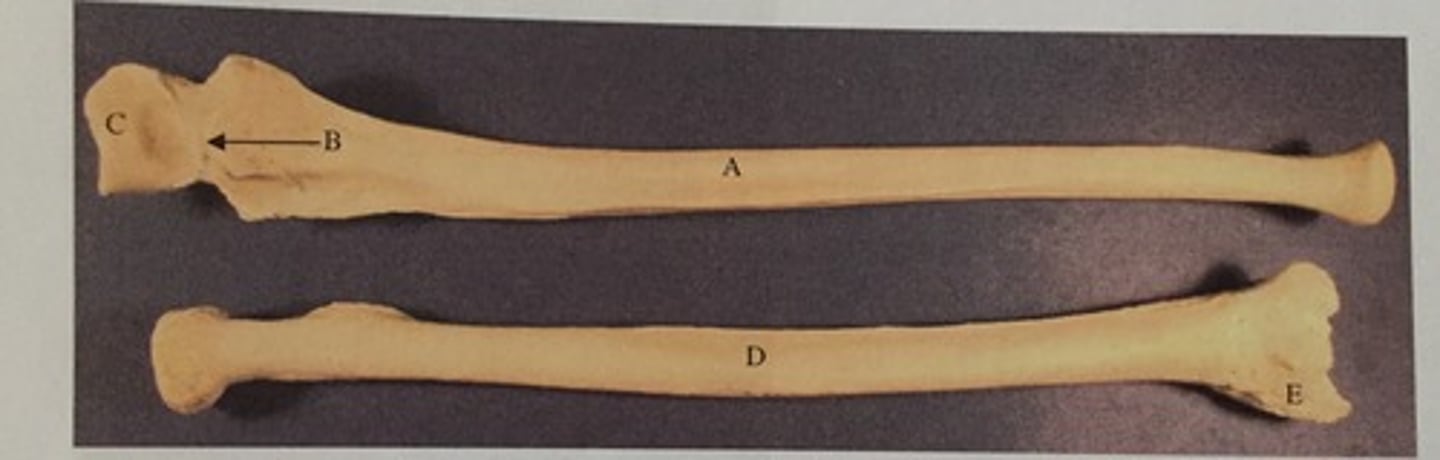
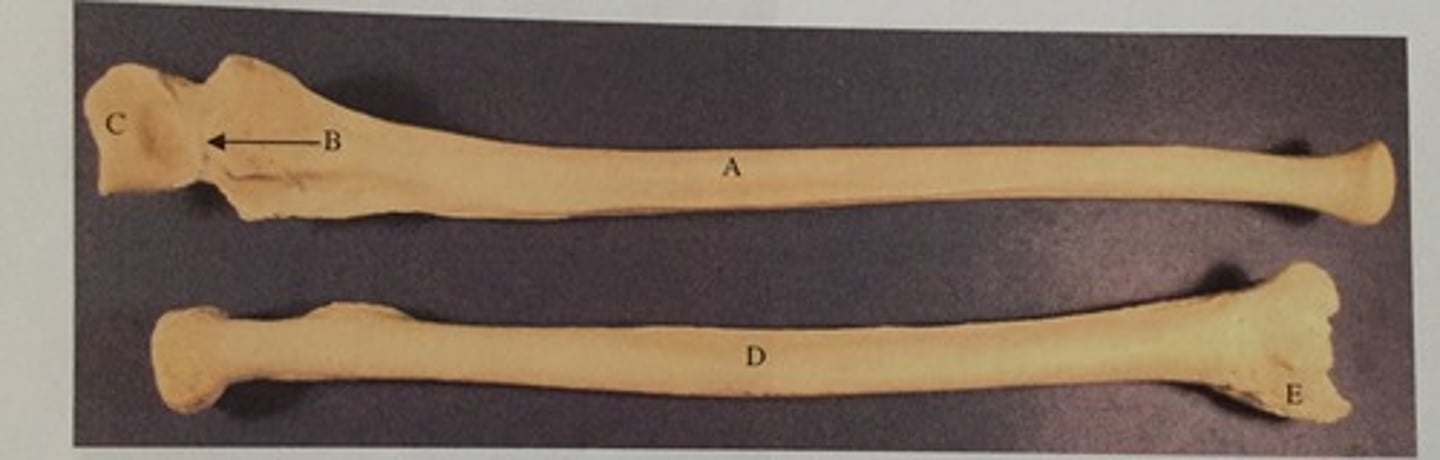
C
Identify the olecranon process
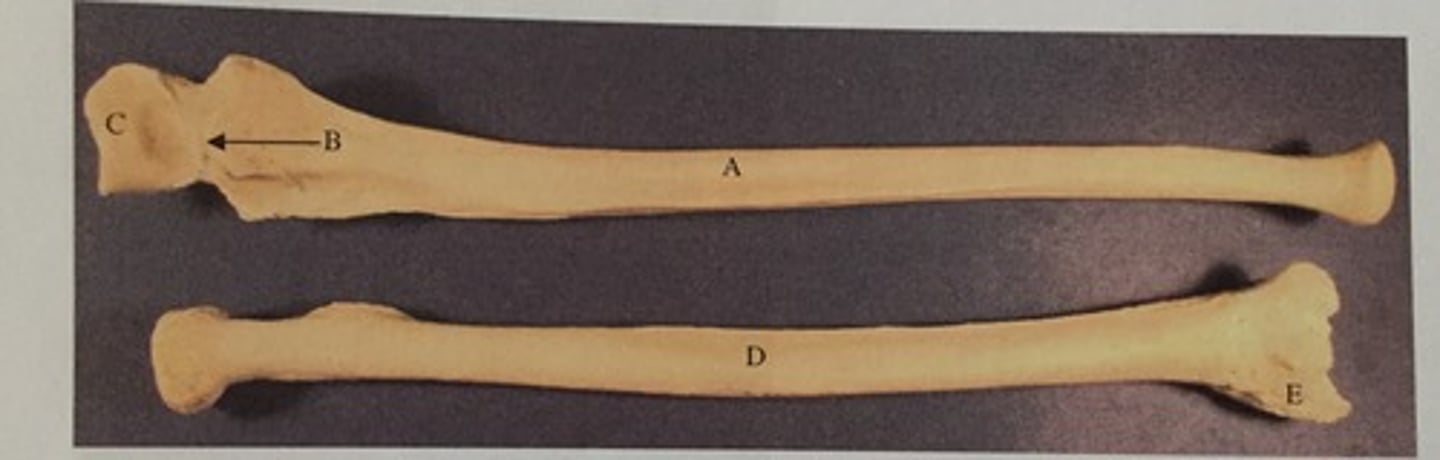
D
Identify the coronoid process
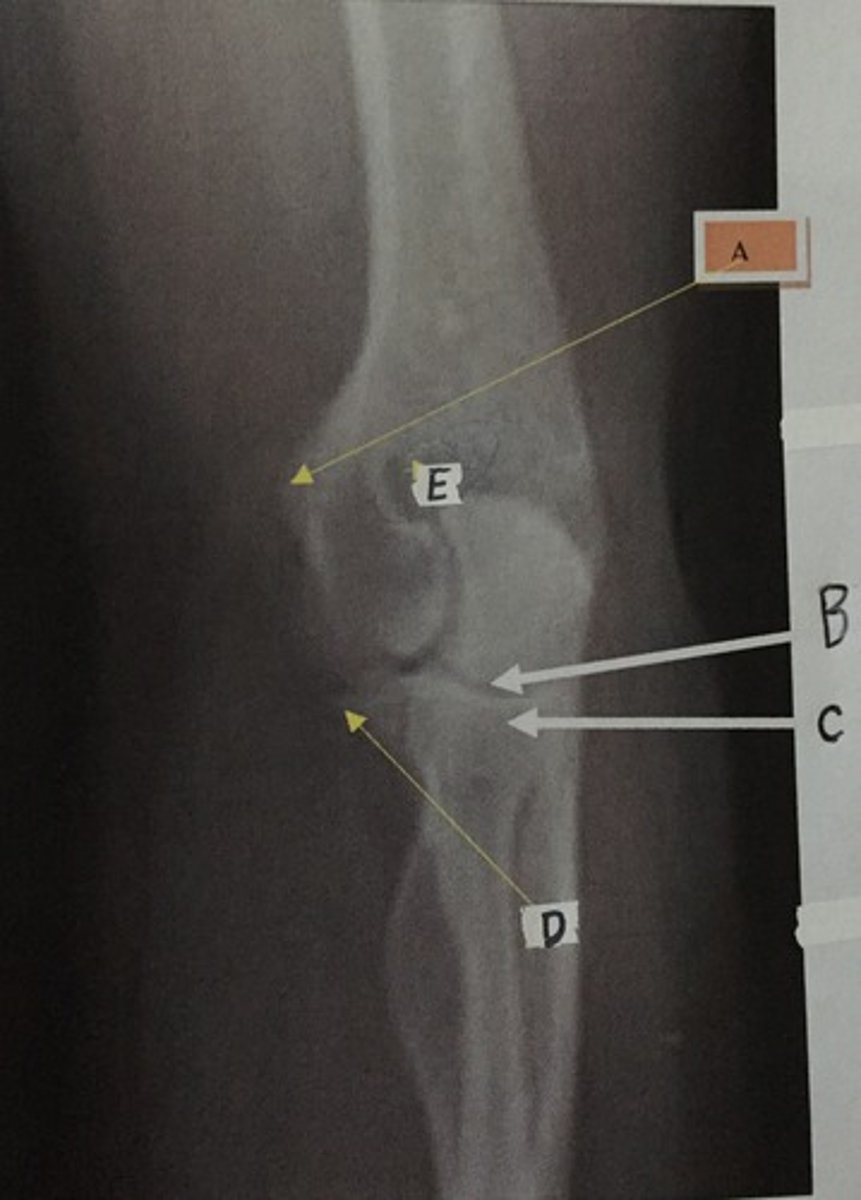
B
Identify the capitulum
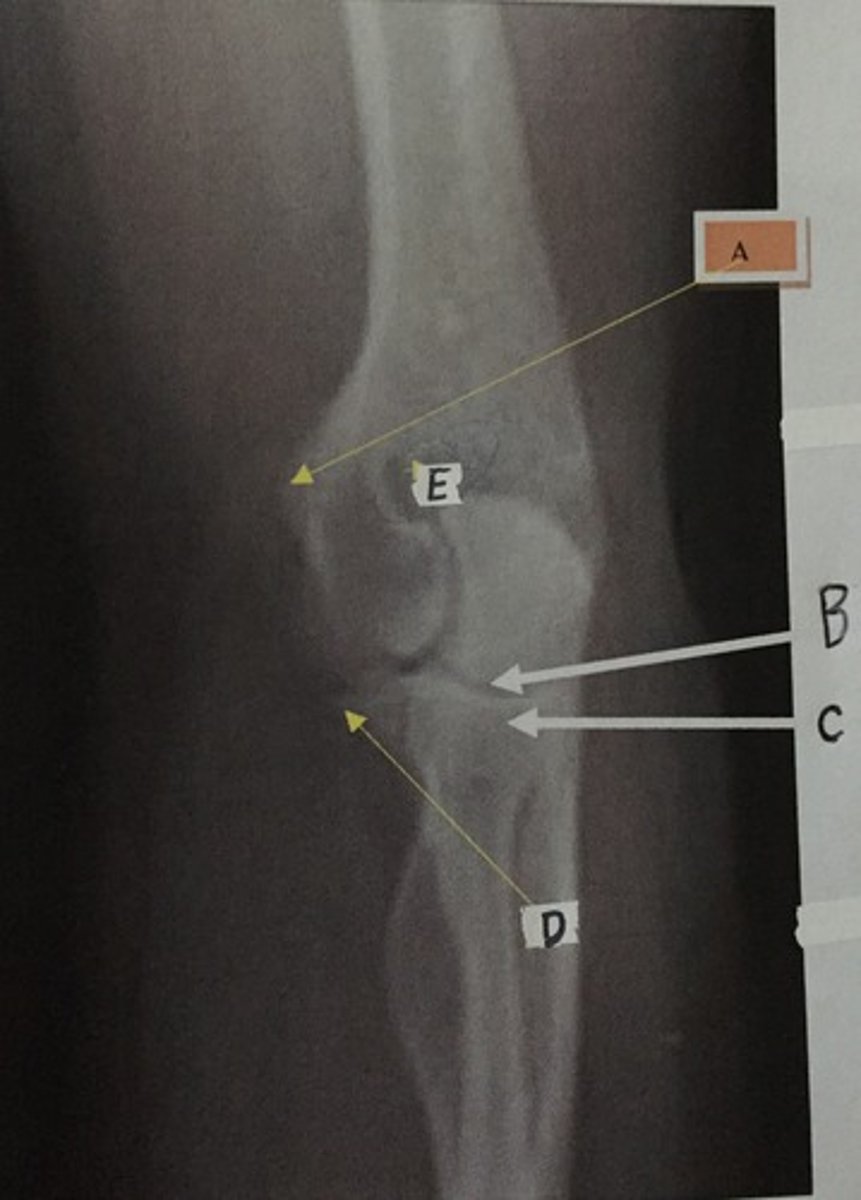
E
Identify the olecranon fossa
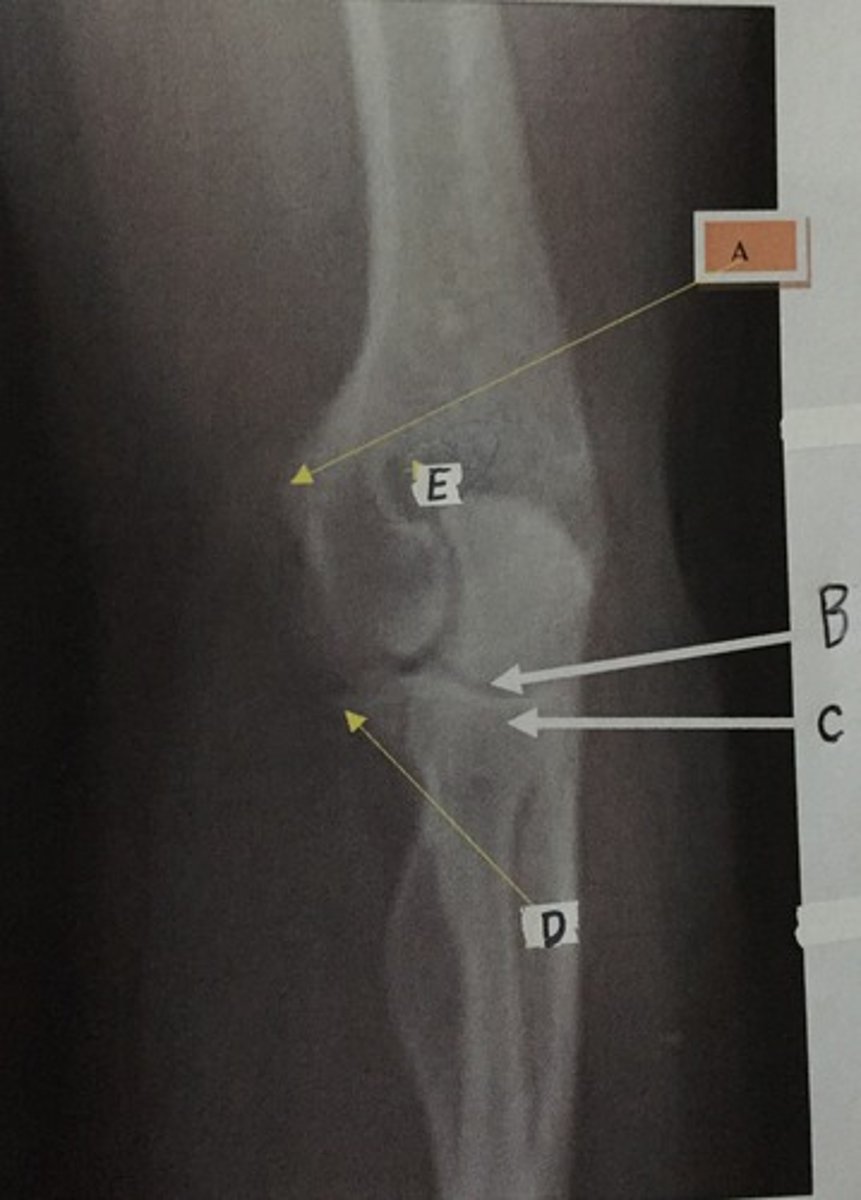
C
Identify the radial head
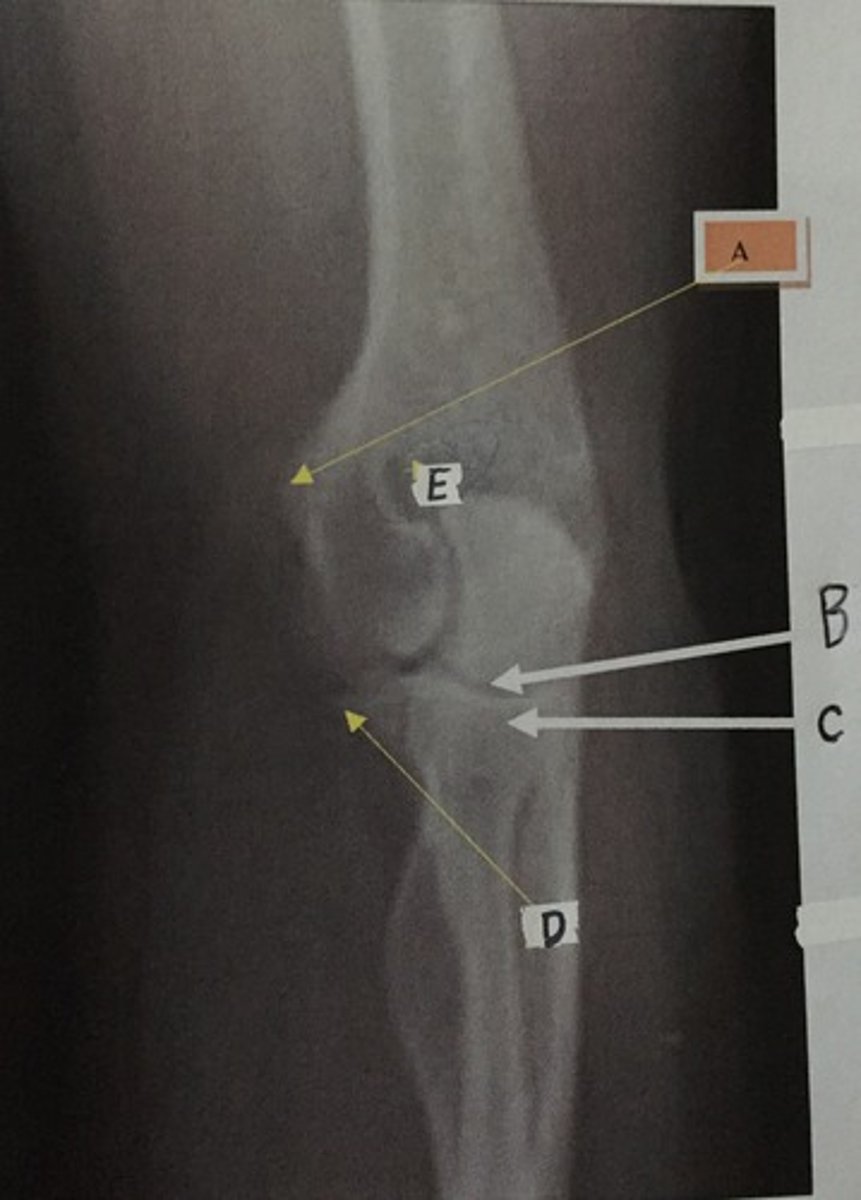
A
Identify the medial epicondyle
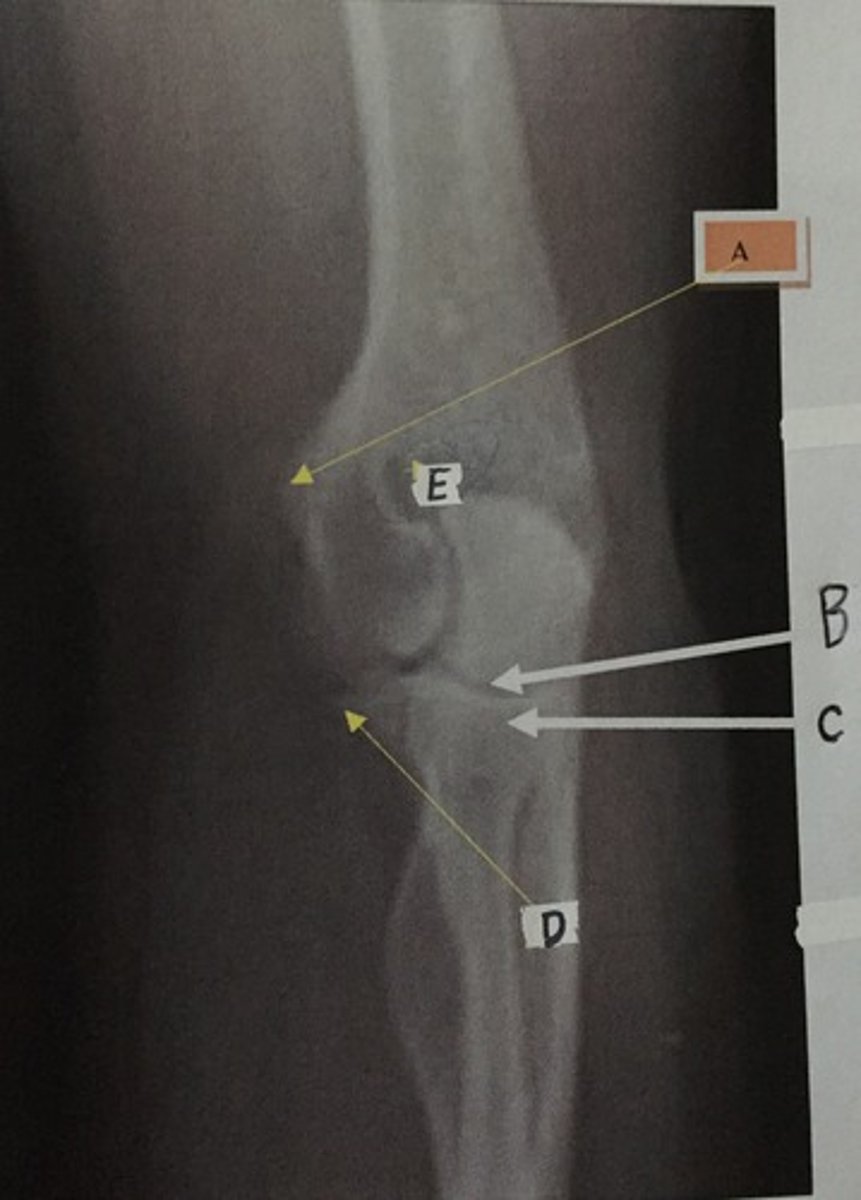
B
Identify the lunate
A
Identify the trapezoid
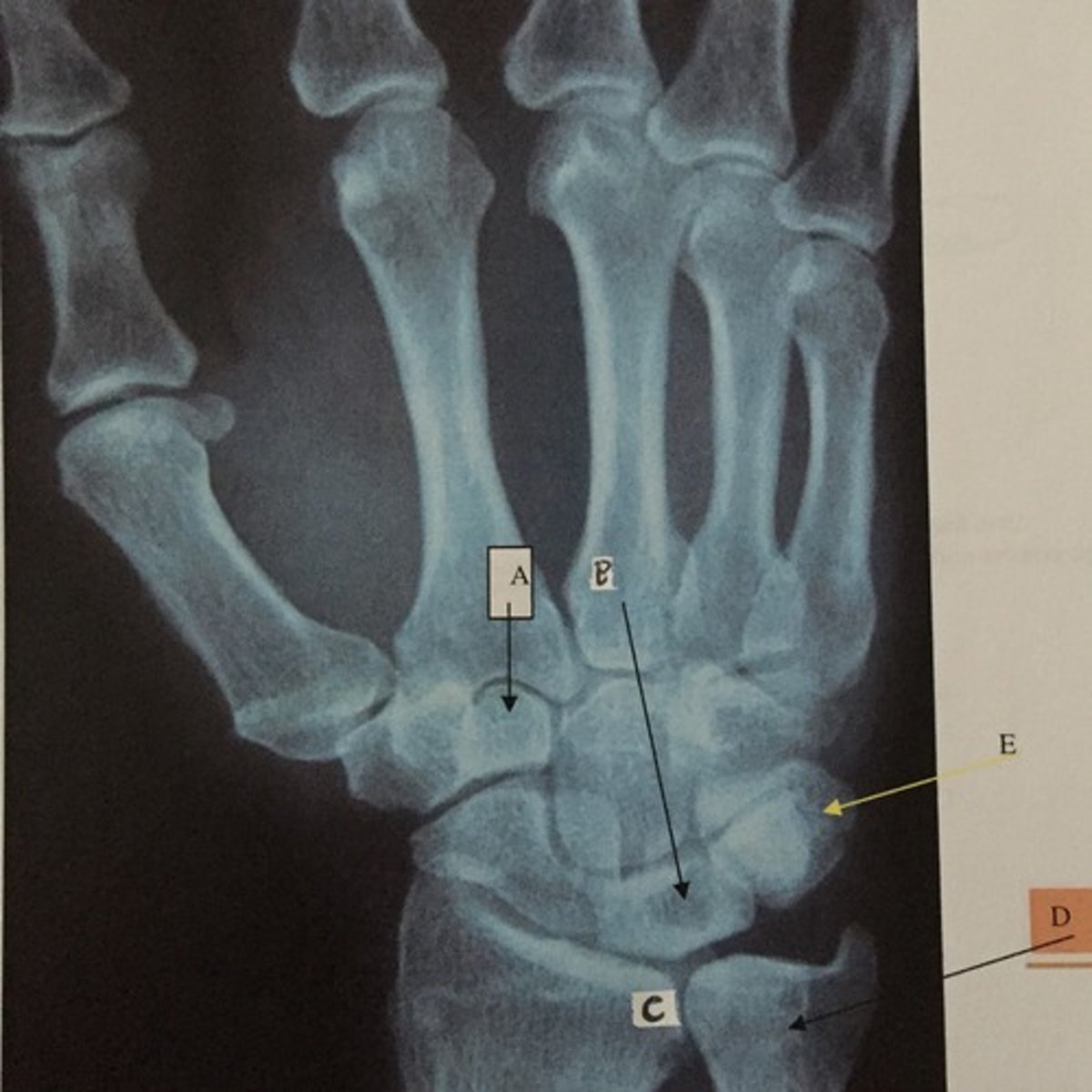
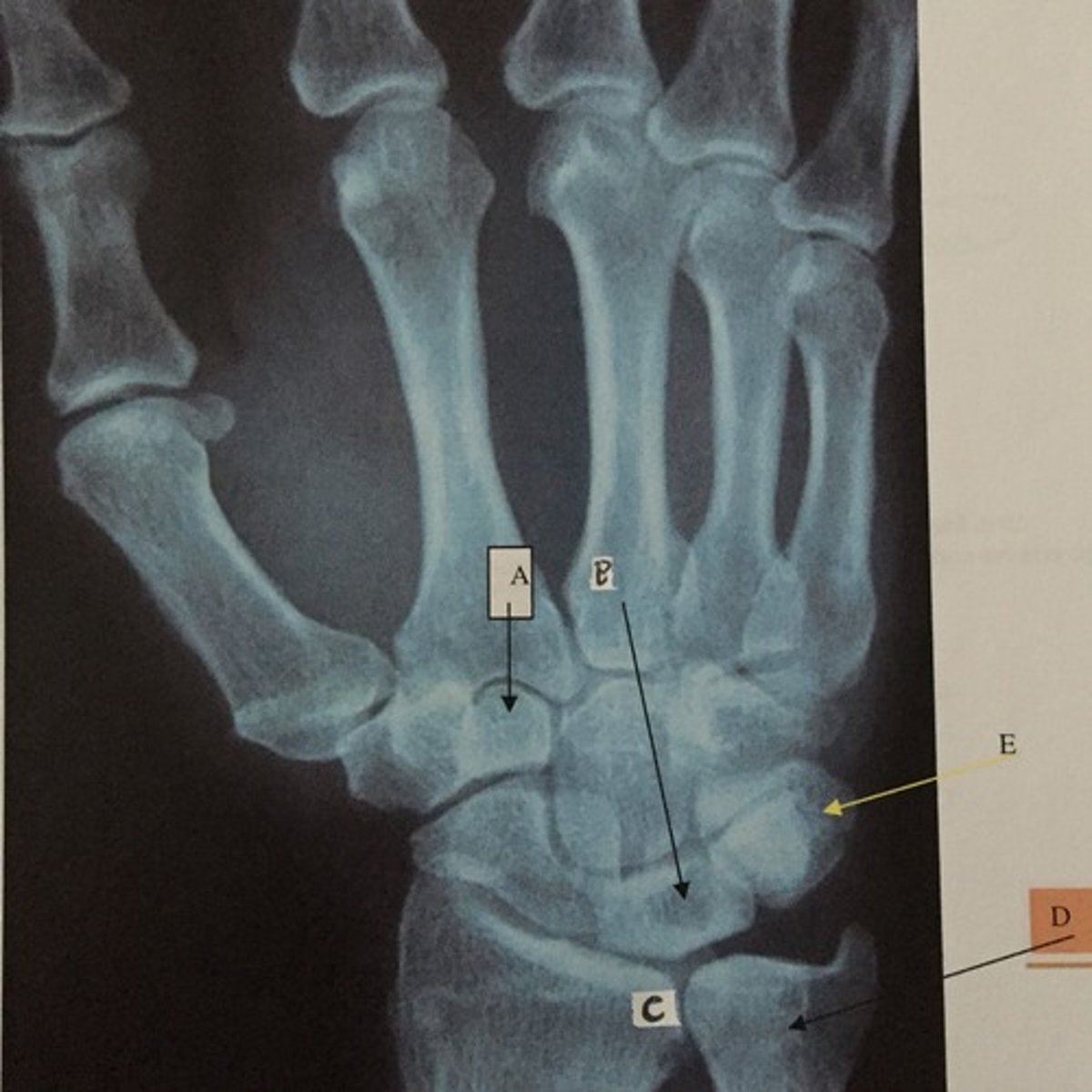
D
Identify the ulna
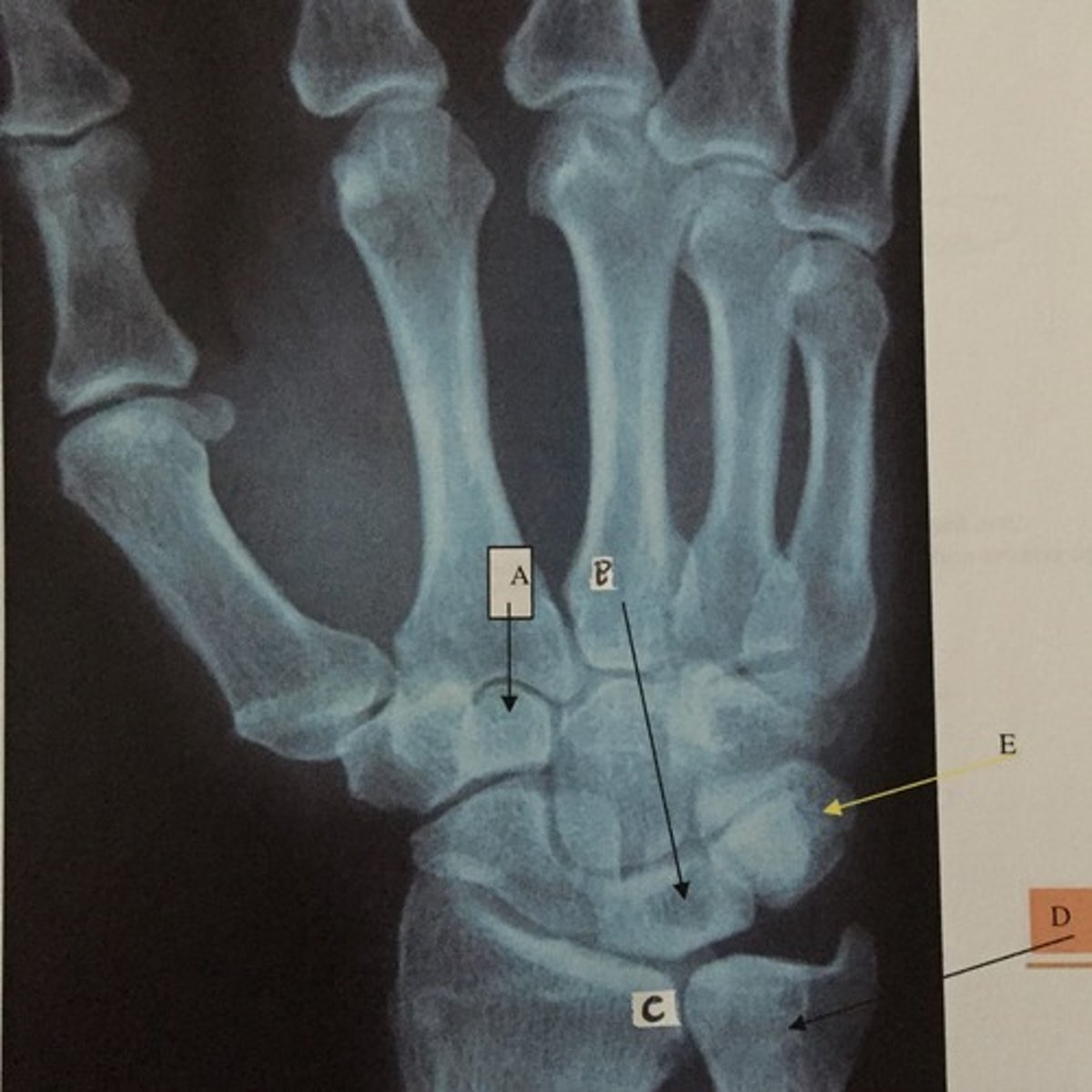
E
Identify the triquetrium
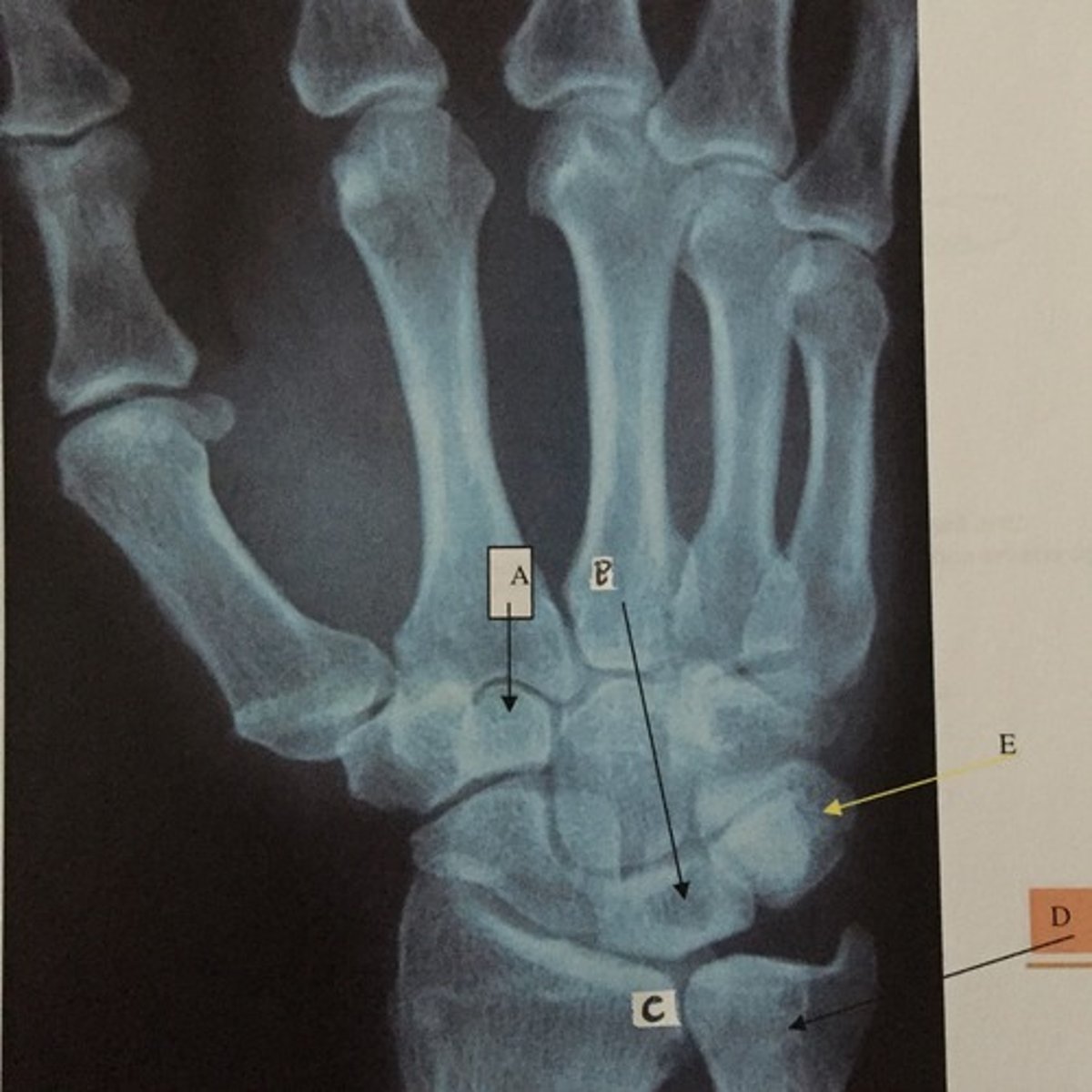
C
Identify the radius
Synarthroses
What is the term used to describe immovable joints?
Diarthroses
What is the term used to describe freely moveable joints?
Amphiarthroses
What is the term used to describe slightly moveable joints?
Diaphysis
What is the term used to describe the shaft of a bone?
Epiphysis
What is the term used to describe growth plates in bones?
Lateral elbow
Superimposed humeral epicondyles; radial tuberosity facing anteriorly; olecranon process seen in profile; radial head partially superimposing the coronoid process. This evaluation criteria describes which of the following positions?
Trauma, flexion distal humerus
Distal humerus without rotation or distortion; proximal radius superimposed over the ulna; closed elbow joint; foreshortened proximal forearm. This evaluation criteria describes which of the following positions?
Perform flexion of the distal humerus and flexion of the proximal forearm
When a patient cannot fully extend the forearm for an AP elbow due to trauma, you have to:
False
True or False. Visualization of fat pads on a AP elbow may be the only evidence of injury.
Extension and flexion
The humerus and ulna articulation and the humerus and radius articulation allow for what type of movement?
Sesamoid bone
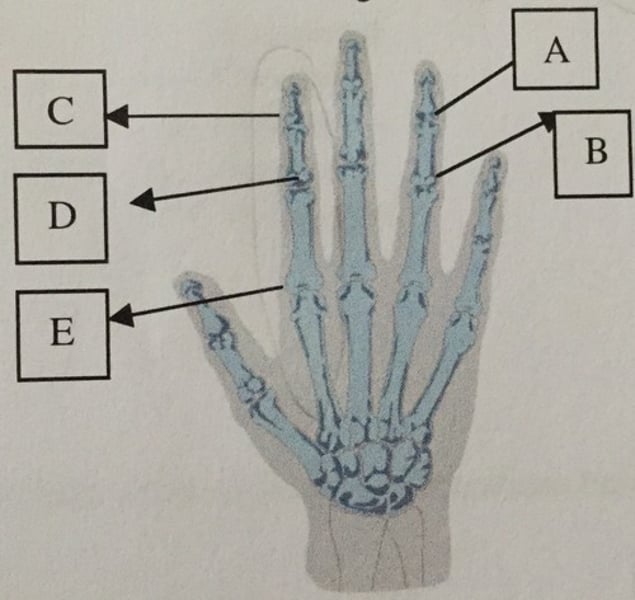
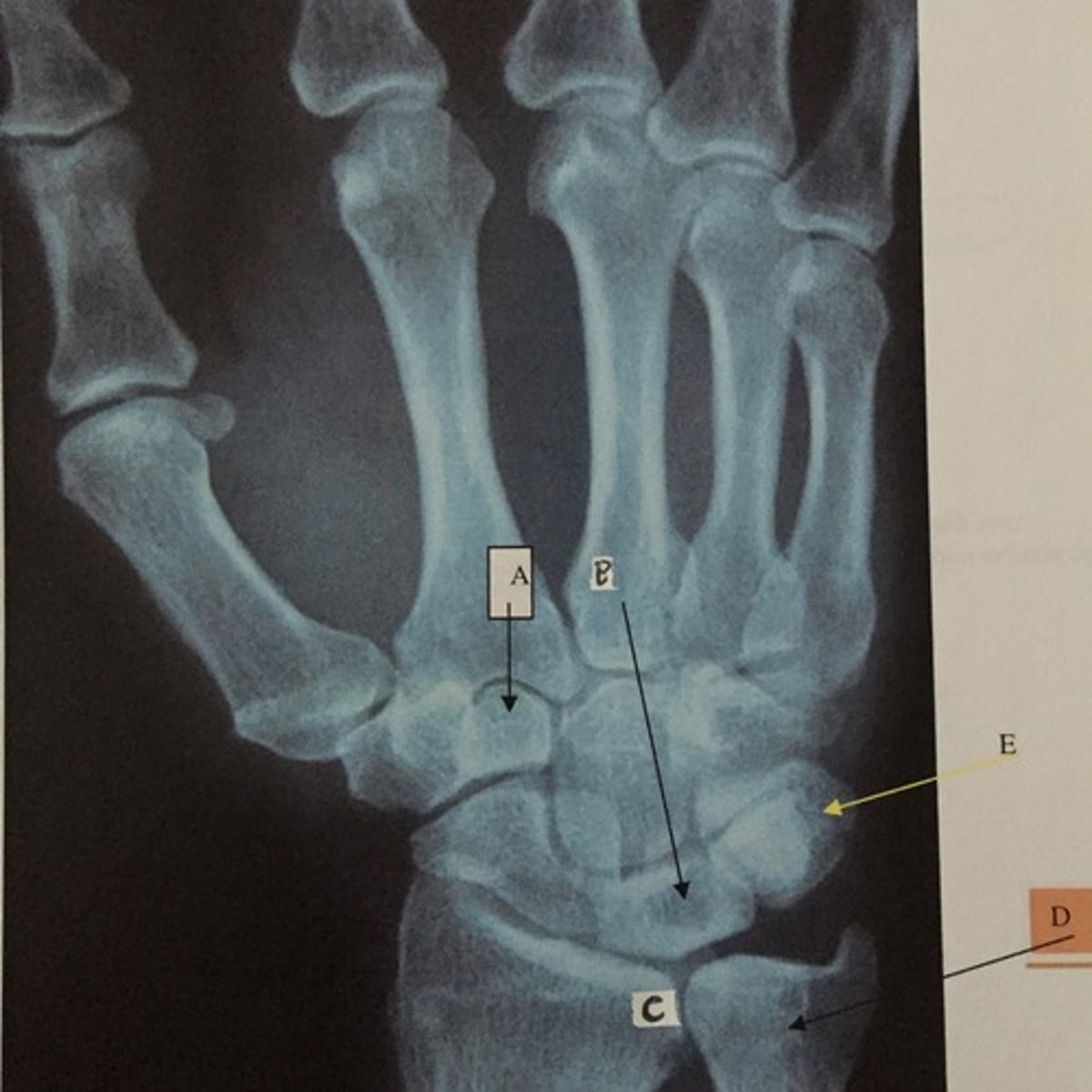
What is A?
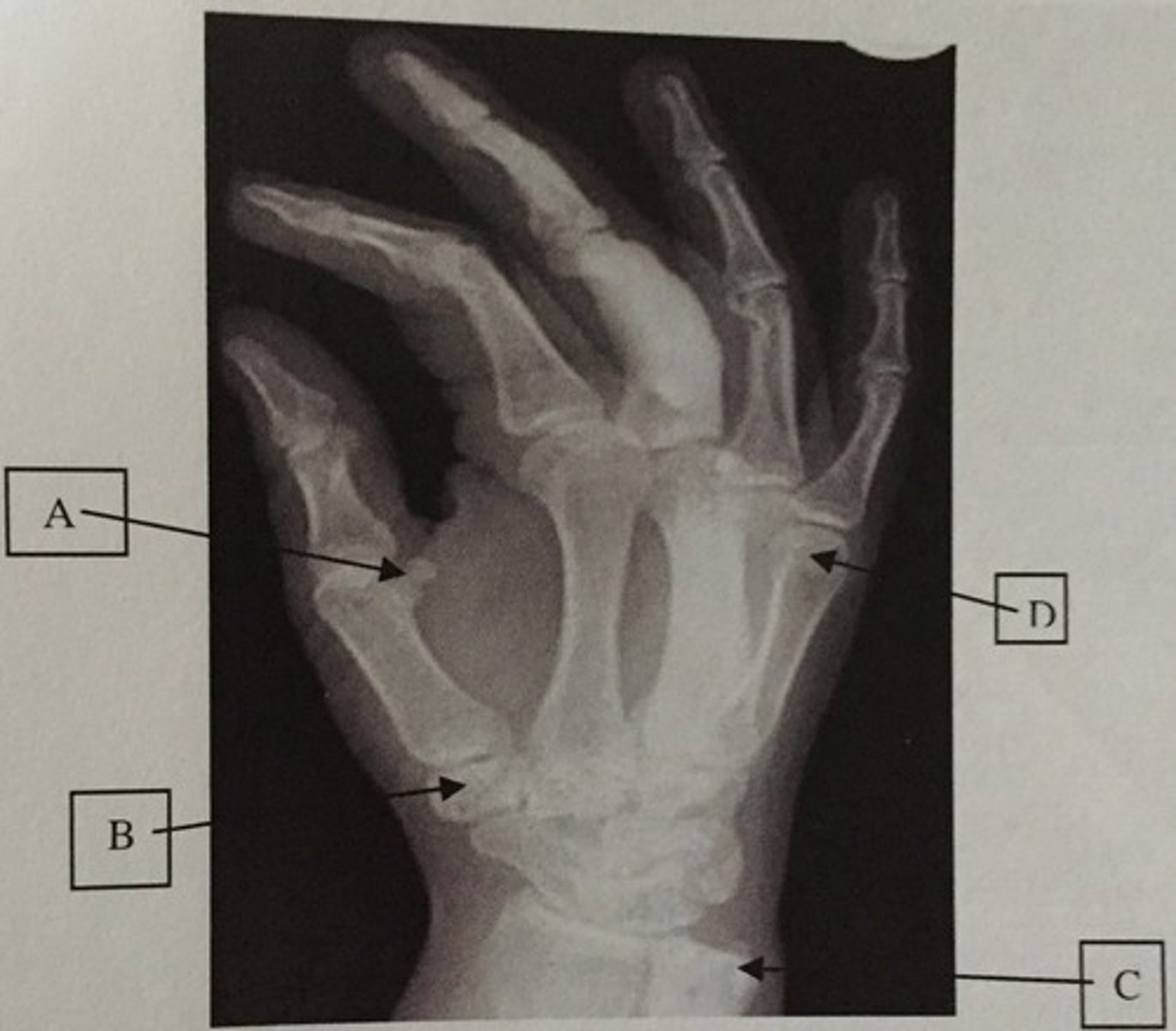
Ulnar styloid process
What is C?
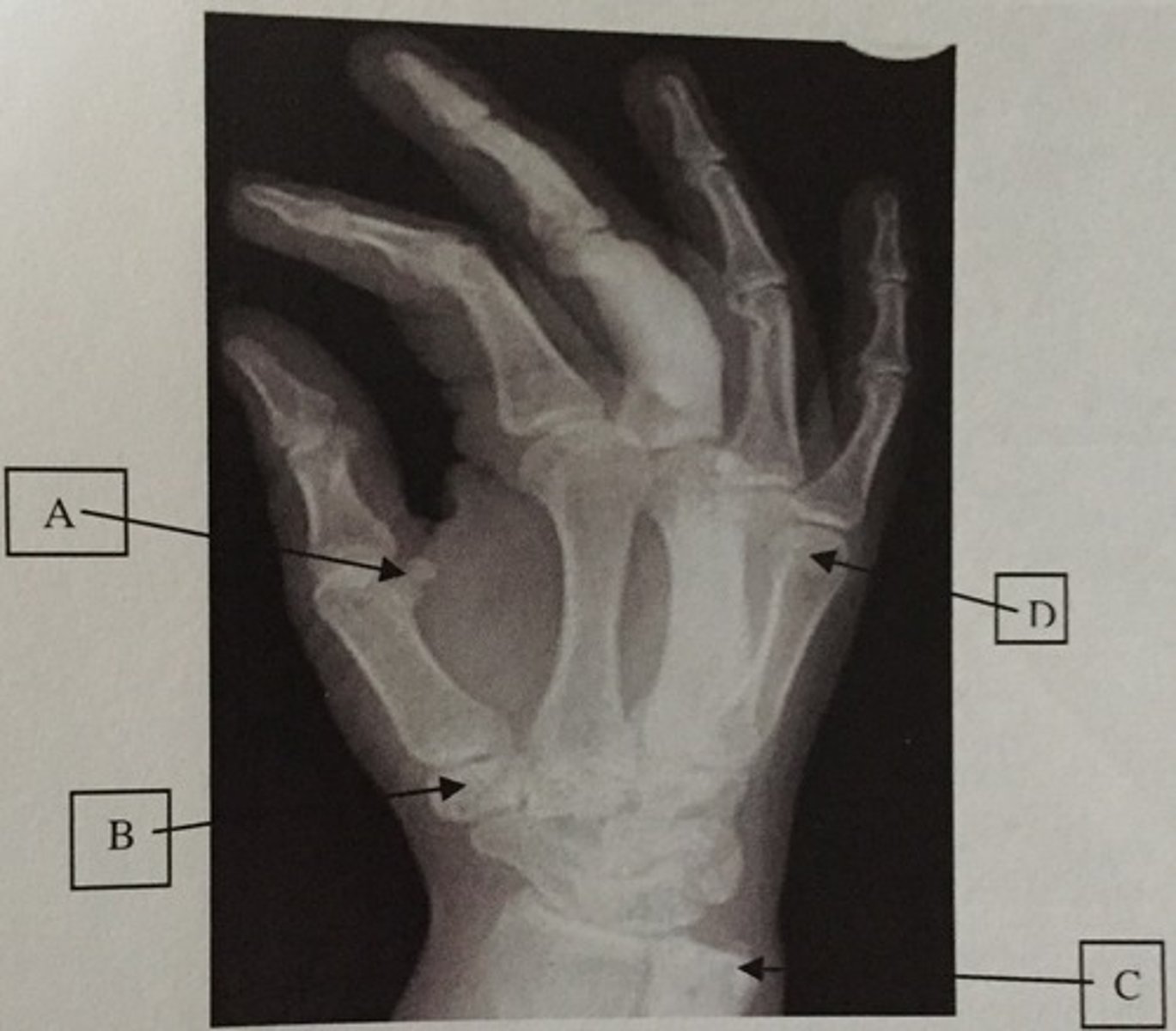
Head of the 5th metacarpal
What is D?
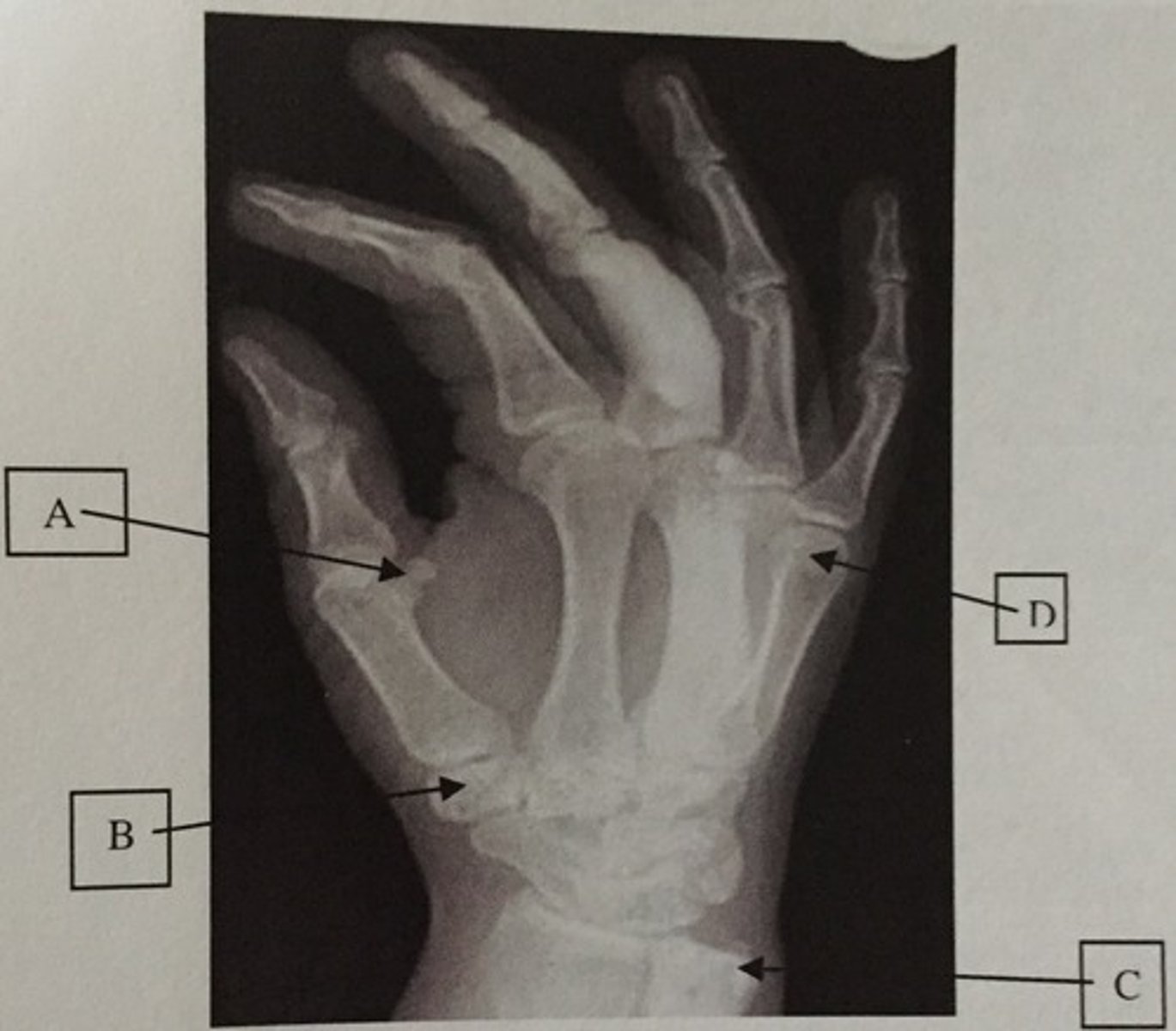
Trapezium or Greater multangular
What is B?
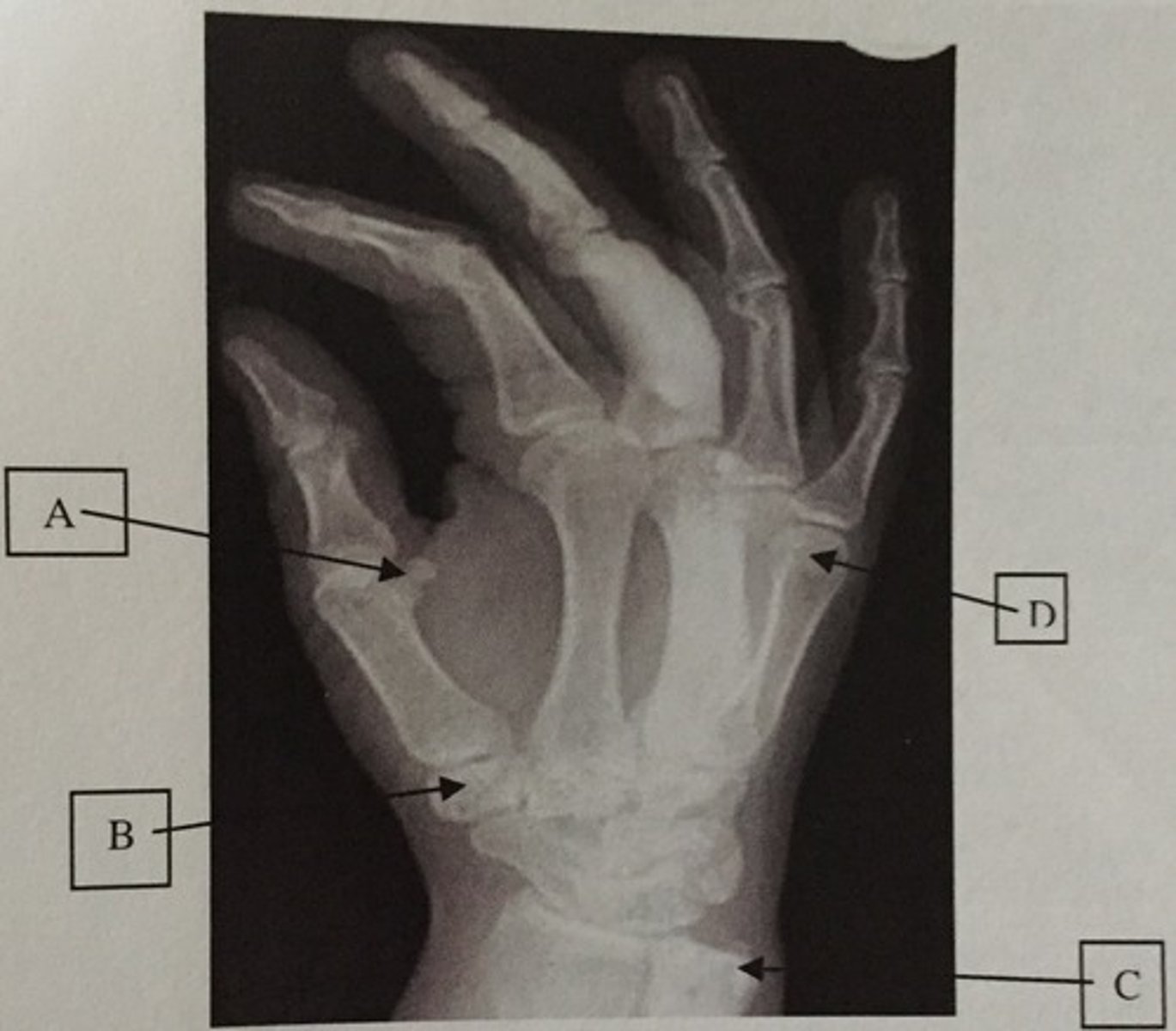
Distal humerus
What is number 84?
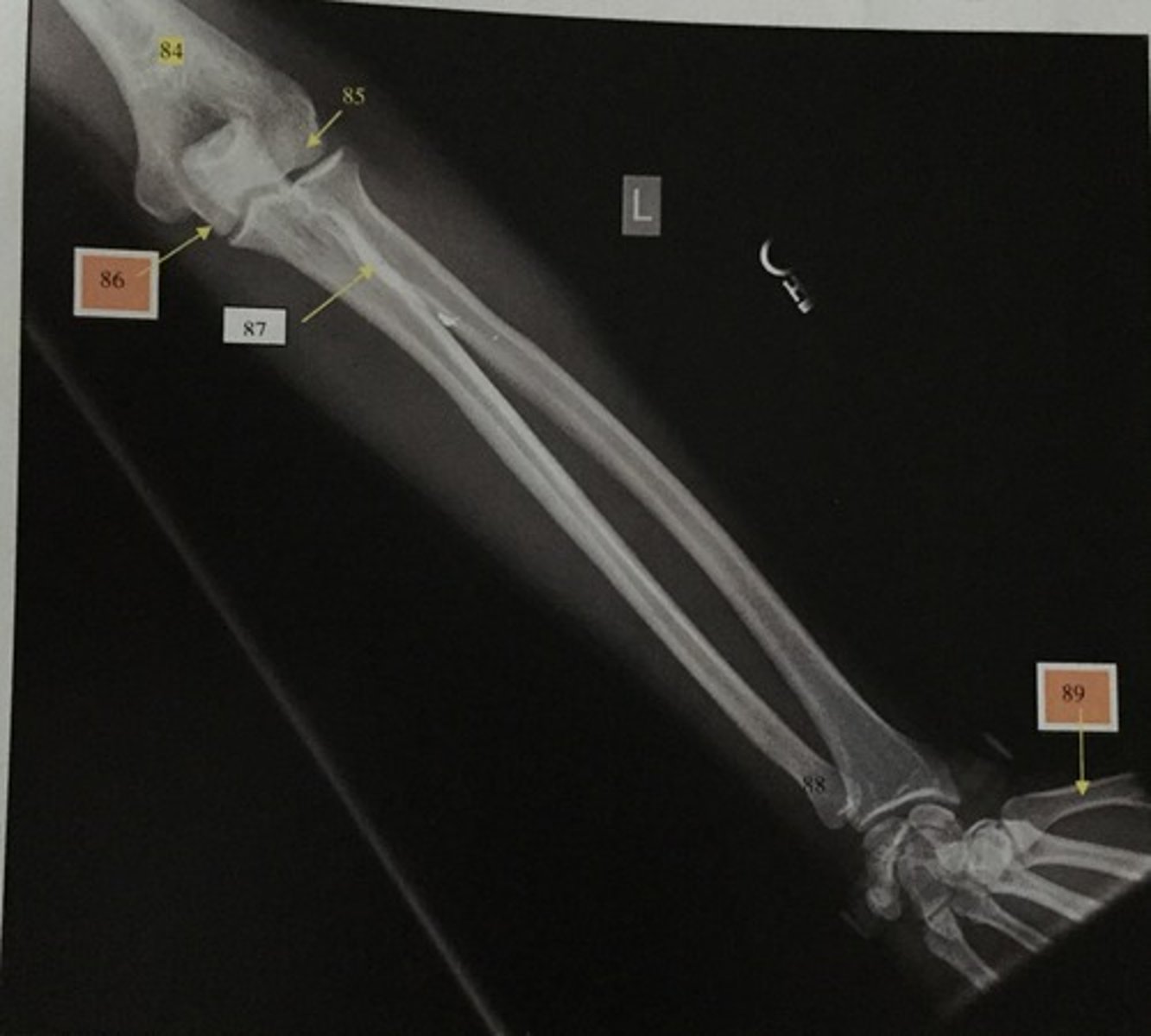
Capitulum
What is number 85?
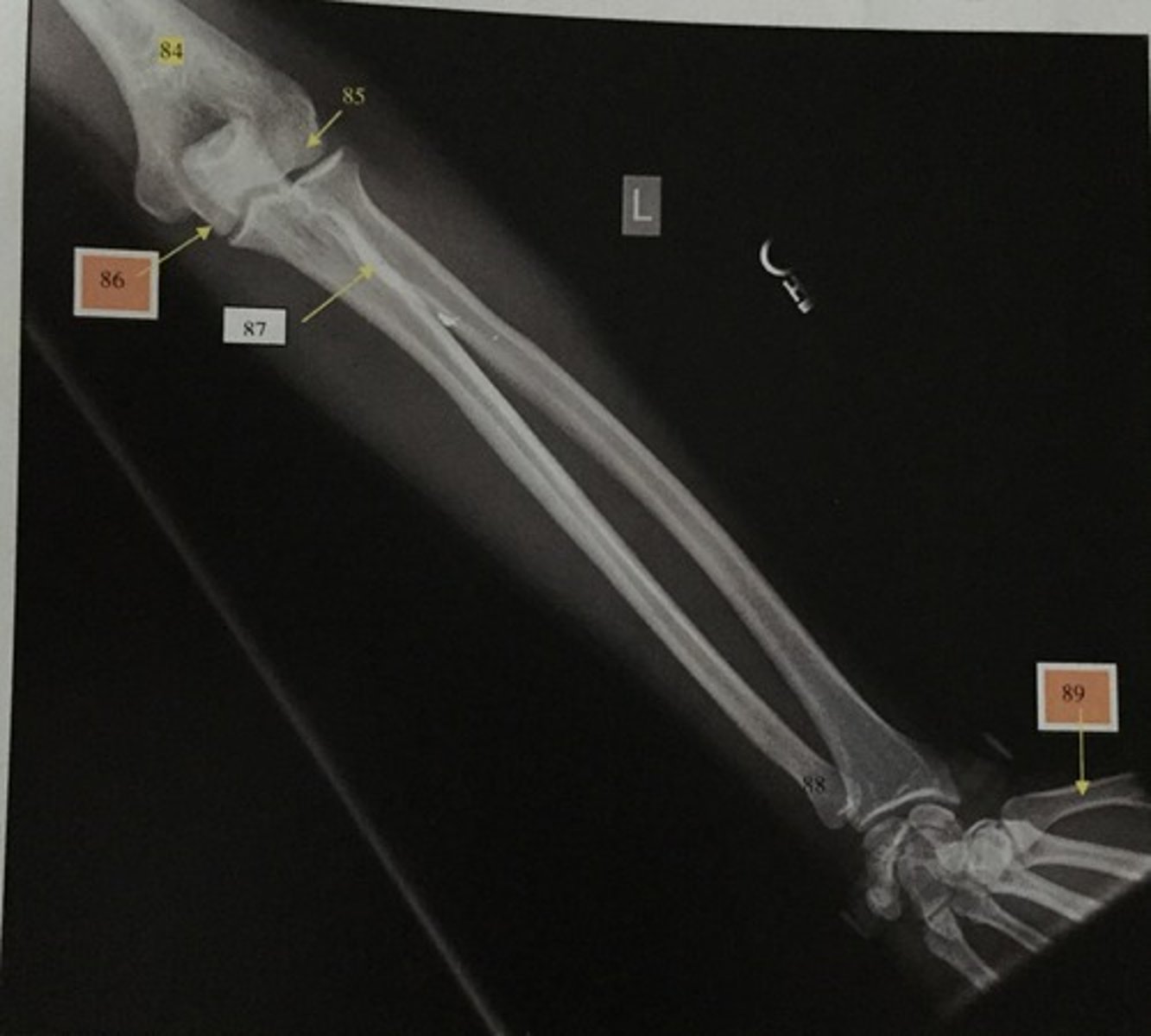
Trochlear
What is number 86?
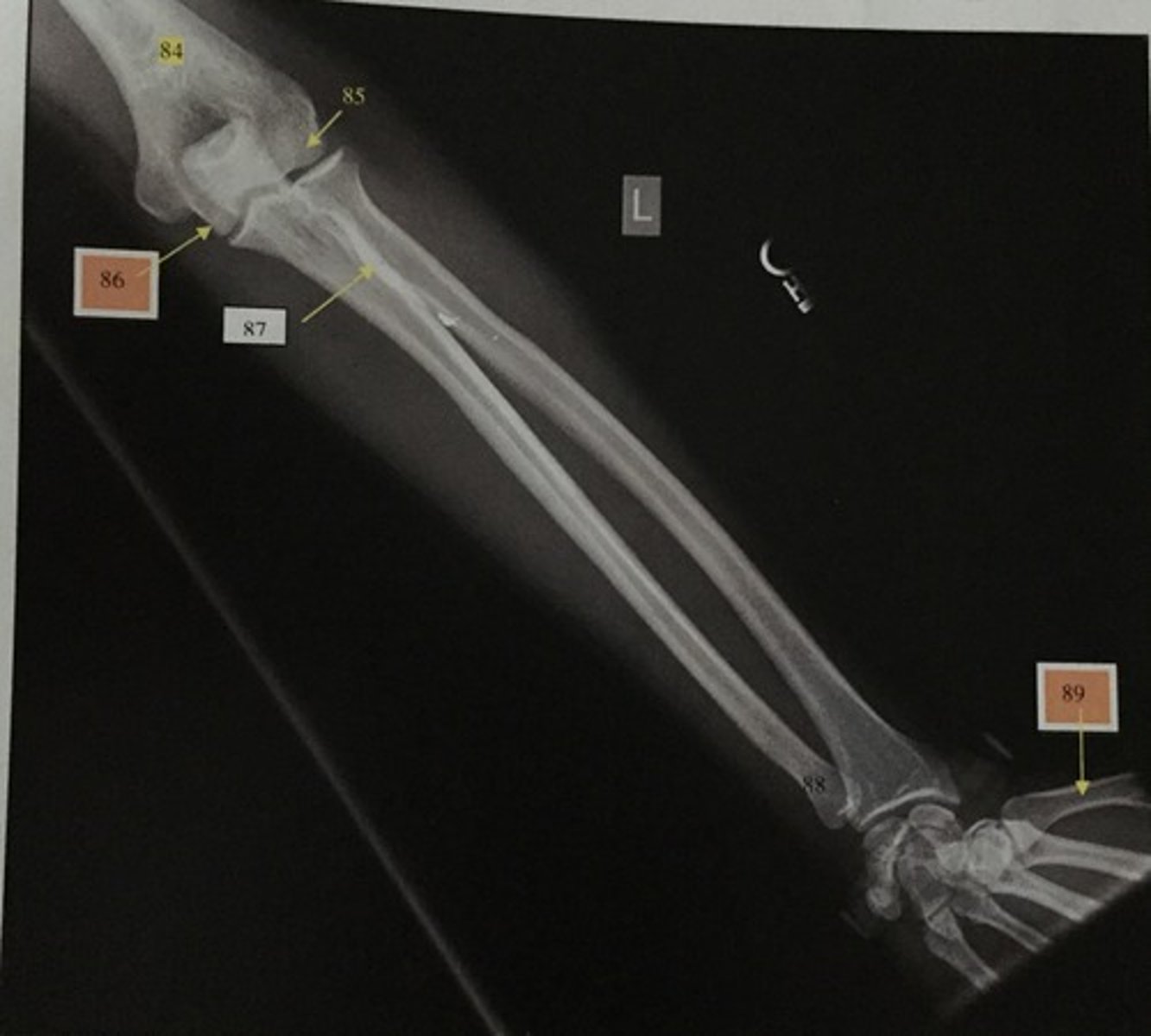
Radial tuberosity
What is number 87?
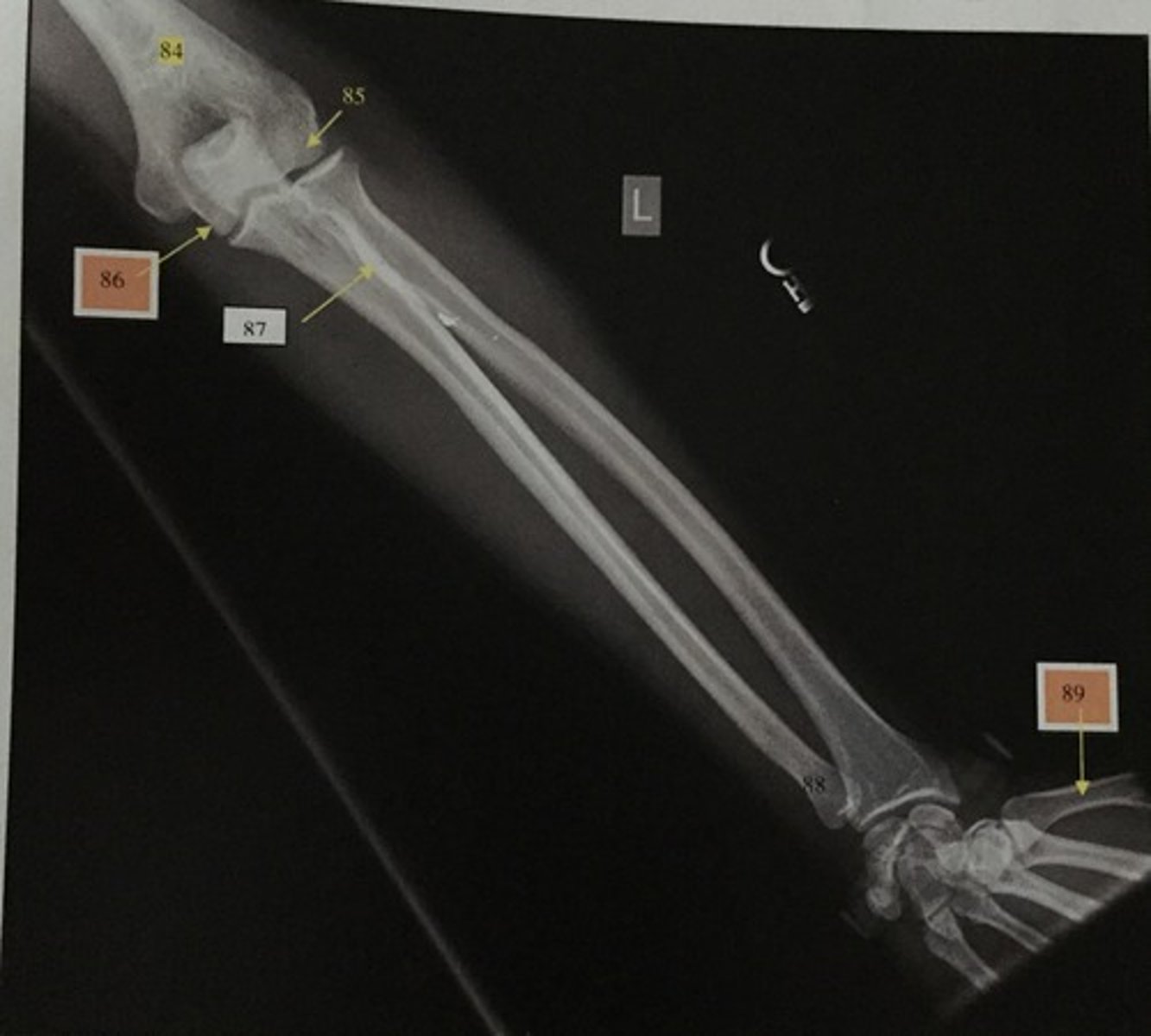
Ulnar head
What is number 88?
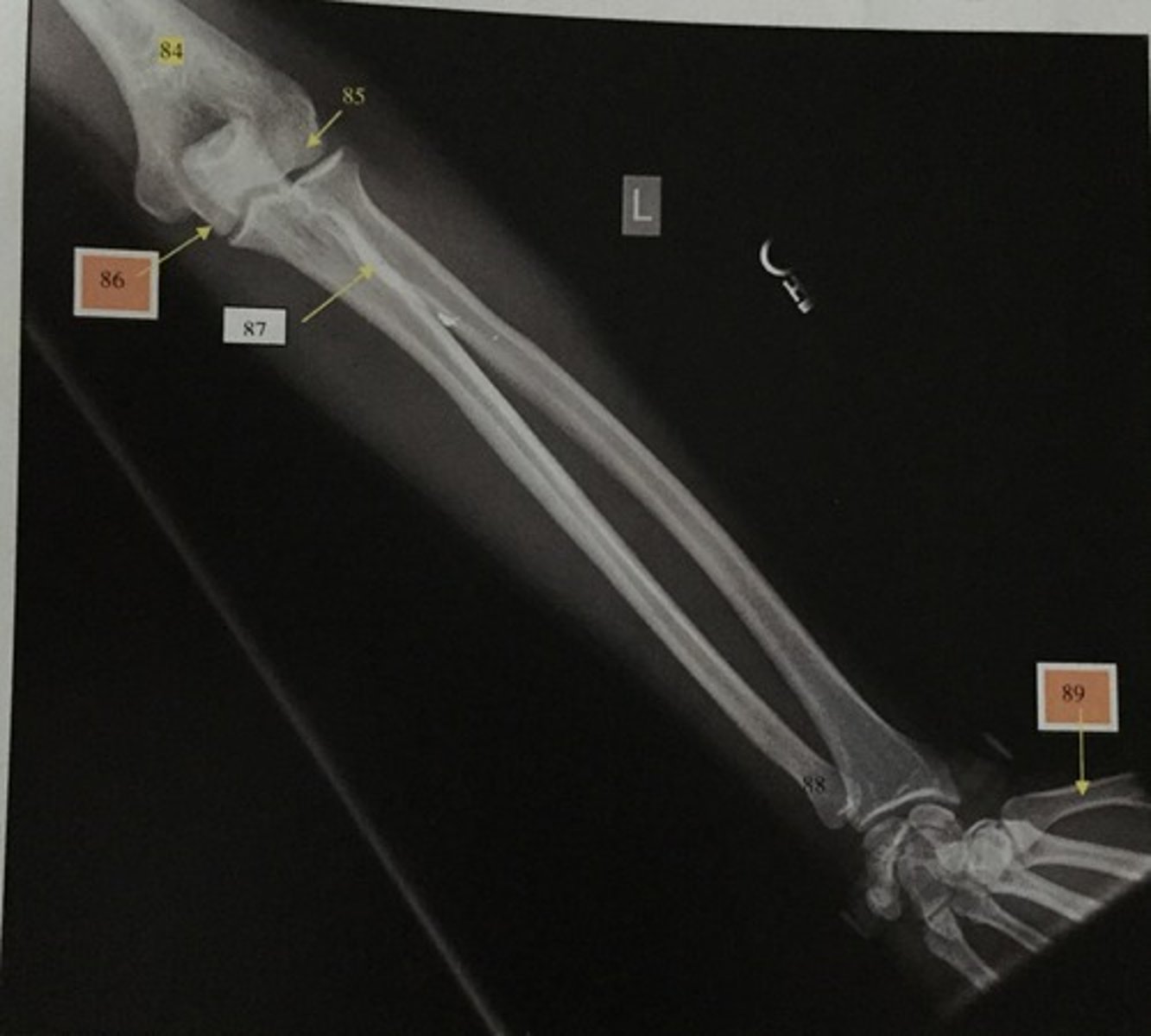
1st metacarpal
What is number 89?
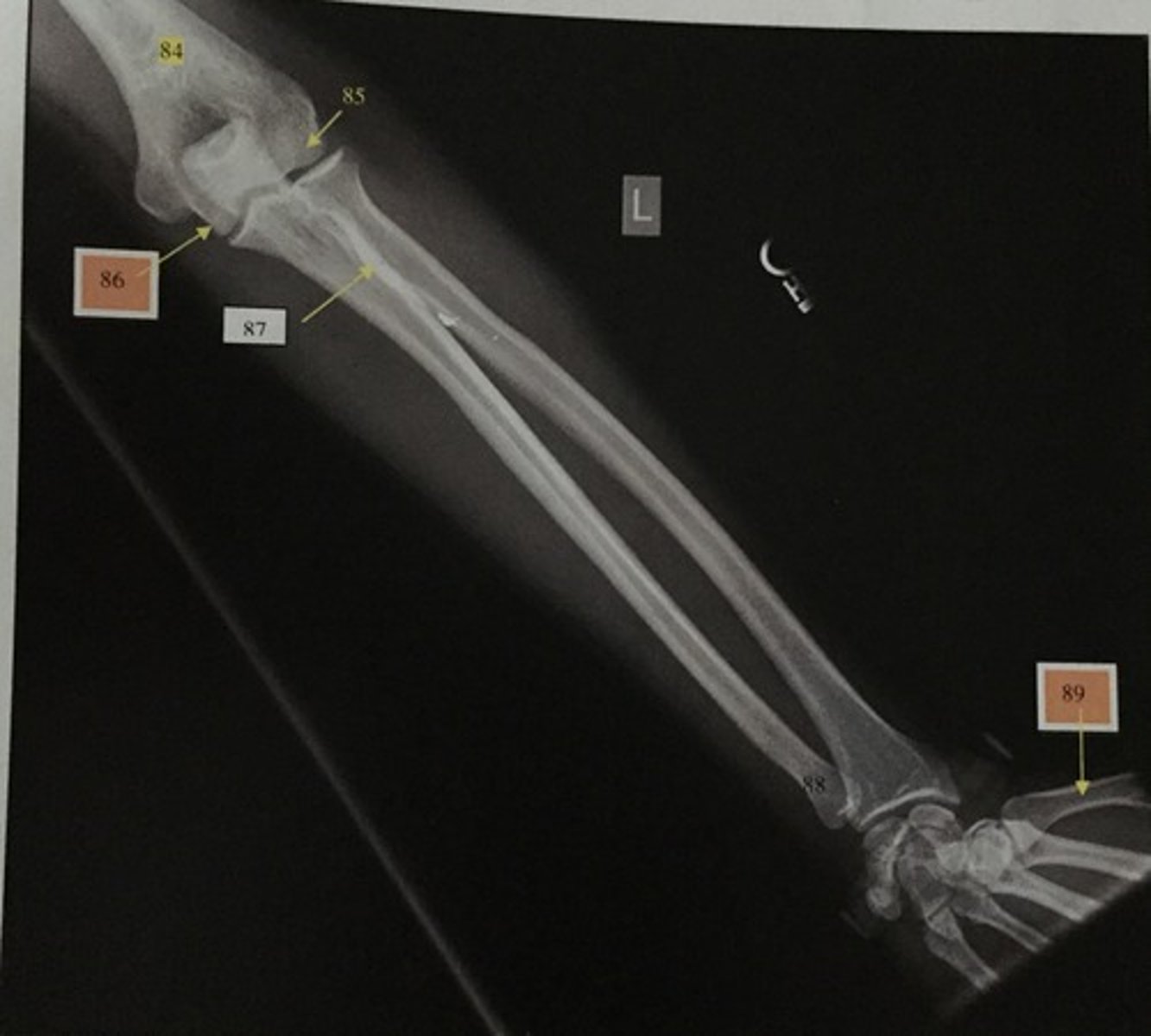
Wrist
Short bones are located in the feet, ankle, and the __________.
Diarthrodial
A joint that is said to be freely moveable is termed __________.
Abduction
Movement of an extremity away from the midline of the body is termed __________.
Olecranon process
The most proximal part of the ulna is the __________.
True
True or False. The radiocarpal joint is a synovial, ellipsoidal freely joint.
False
True or False. The interphalangeal joints are hinge joints that are freely moveable but are not considered synovial.
2nd MCP
To obtain a radiograph of a lateral extended hand, the CR should enter the __________.
True
True or False. For an AP radiograph of the forearm, the hand is supinated.