Atomic structure and the periodic table
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What is a element?
A pure substance where all the atoms are the same
What is a compound? What are features of compounds?
Compounds contain two or more different elements chemically combined in fixed proportions
Compounds usually have different properties from the elements they are made from
Have to use a chemical reaction to seperate compounds
What is a fixed proportion?
For every one atom of a element, we have one atom of another element
What is a mixture?
A mixture has different elements or compounds that are not chemicaly combined
Have to use a physical seperation technique to seperate a mixture
What is a molecule?
Has any elements chemically combined even if its the same element (has a little number next to it)
What does insoluable mean?
The solid will not dissolve in liquids
What does soluable mean?
The solid will dissolve in liquids
What are the state symbols?
Tells us the physical state of a chemical
(s) = solid
(l) = liquid
(g) = gas
(aq) = dissolved in water
Filtration
Used to seperate a insoluable solid from a liquid
A physical seperation technique
Use a filter funnel and filter paper in a conical flask
Pour the mixture into the funnel paper
The liquid will passes through the pores in the filter paper
The solid material can not pass through the filter paper
The liquid that passes through is called the ‘filtrate’
Crystallisation
Used to seperate soluable solids from a liquid
A physical seperation technique
Leave the mixture out for a few days so the liquid evaporates, leaving behind the solid
This process can be sped up by gently heating the liquid so evaporation occurs faster
However, certain chemicals can be broken down if heated so you have to be careful
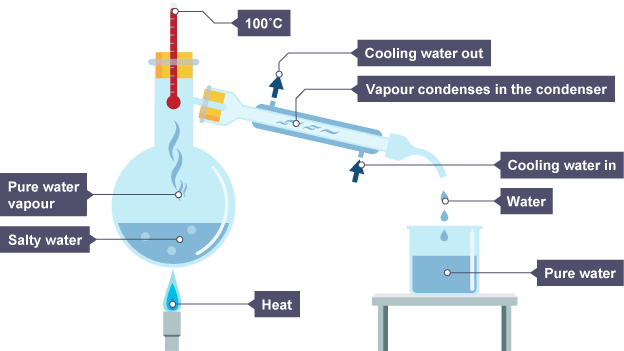
Simple distillation
Used to seperate a dissolved solid from a liquid while keeping the liquid
A physical seperation technique
Evaporate the liquid by heating which turns the liquid into a vapour
Then condense the vapour back to a liquid by cooling
Steps to carry this out:
Place our mixture into the flask and allow evaporation to occur by heating
vapour runs up the tube into the condenser, which has cold water running in and out of it keeping the tube cold
The vapour forms back ino the liquid due to the cooling
At the end the original flask contains the solid and the liquid in the beaker
Can be used to convert sea water into drinking water
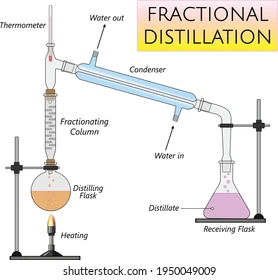
Fractional distillation
Used to seperate a liquids
Must have different boiling points
A physical seperation technique
Contains a fractionating column which contains hundreds of glass beads
When the liquids begin to evaporate, the vapours begin to mix together
When they reach the fractionating column which is cool at the top, the vapours condense and drip back into the flask where the liquids evaporate again
This repeated evaporation and condensation increases the amount of the lower boiling point chemical in the fractionating column
This means that a mixture of the vapours which contains more of the mixture of the lower boiling point goes to the condenser and turns back into a liquid
REVISE OVER SEPERATELY!!!
Paper chromatography
Allows us to seperate based on their different solubilities
A physical seperation technique
Take a piece of chromatography paper and draw a pencil line (pen would dissolve) near the bottom of the paper
Put a dot of the first mixture on the colour line
Place the bottom of the paper into a solvent (a liquid that will disolve substances)
The solvent makes its way up the paper and the mixture is dissolved
The mixture is carried up the paper by the solvent
A pure compound will leave a single spot
A mixture will seperate into different spots
What is the stationary phase in paper chromatography?
The paper as it does not move
A less soluble substance is more attracted to the stationary phase
What is the mobile phase in paper chromatography?
The solvent as it moves
A more soluble substance is more attracted to the mobile phase
What are the features of physical seperation techniques?
No new substances made
Does not involve chemical reactions
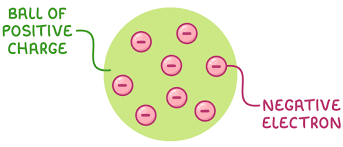
What was the plum pudding model?
An atom is a ball of positive charge with negative electrons embedded in it
How was the alpha scattering experiment carried out?
A experiment to test if the plum pudding model was accurate
Scientist used a piece of thin, gold foil and fired alpha particles (positive charge) at it
What were the results of the alpha scattering experiment?
Some alpha particles passed straight through the gold foil without changing direction
Told scientist atoms are mainly empty space
Some alpha particles deflected as it passed through the gold foil
The centre of the atom must have a positive charge as they positive alpha particles and centre of the atom repelled
Some alpha particles bounced off the foil
The centre of the atom contains a lot of mass
What was the nuclear model?
A new model of atoms
Has a positive nucleus which contains most of the mass
Empty space
Negative electrons surrounding it
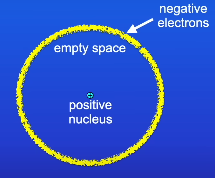
What are the features of the nuclear model after modifiaction?
Mainly empty space
Has a positive nucleus due to containing postive protons and neutral neutrons
Around the edge of the atom, there are shells/energy levels contains electrons (2,8,8)
Name the sizes of the parts of the nuclues
Radius of an atom = 1×10-14m
Radius of the nucleus = 1×10-14m
What are the relative charges of protons, neutrons and electrons?
Protons = +1
Neutron = 0
Electron = -1
This means there is no overall charge in atoms as 1+0+-1=0
What are the relative mass of protons, neutrons and electrons?
Protons = 1
Neutrons = 1
Electrons = very small
What is the atomic number and mass number?
7 → mass number → 7 protons and neutrons
To work out the number of neutrons = 7-3=4 neutrons 0
Li
3 → atomic number → 3 protons and 3 electrons (same number of each on atoms)
What is a isotope?
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
What are ions?
Atoms which have an overall charge
This is because ions have lost or gained ions
What do positive or negative ions gain?
Electrons are negative
Positive ions have gained electrons
Negative ions have lost electrons
Examples of negative and positive ions
23 = 23-11 = 12 neutrons
Na+ - lost one electron
11 = 11 protons and 11-1=10 electrons
19 = 19-9=10 neutrons
F- - gained one electron
9 = 9 protons and 9+1=10 electrons
How do we decide what mass number for elements are put into the periodic table when their are isotopes?
We take the average of the mass numbers of each isotope but the average is weighted for abundant (how common) each isotope are
How to calculate the relative atomic mass
Relative atomic mass=
(mass number of isotope 1 x percent abundance of isotope 1) +
(mass number of isotope 2 x percent abundance of isotope 2)
/100
How do electron energy levels work?
Look at the atomic number to see the number of electrons
This shows the number of shells and elctrons in each
Up to 2 in the first shell, up to 8 in the next shells after
What does the number of electrons on the outer shell tell us?
This tells us the group the element is
Boron has 3 in the outer shell so is in group 3
A full shell of electrons means its in group 0 (the noble gasses)
What did Mendeleev do?
Developed the first modern periodic table
He arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic weight as the atomic number hadnt been discovered yet
He then switched the orders of specific elements so they fitted the paterns of other elements in the same group and left gaps in the periodic table where he thought an element was missing
What differences were made to Mendeleevs periodic table?
Elements are arranged in order of the atomic number meaning every element is in the correct group
Ordering them by atomic mass didnt work due to isotopes
Has group 0 added as these had not been fully discovered during mendeleevs time
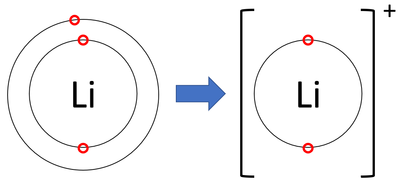
What impacts the atoms overall charge?
Electrons and protons have the same number of each in atoms
If we take away electrons, they no longer cancel eachother out, changing the overall charge
Metals always from positive ions
Eg Li37 original atoms canceled eachother out +3-3=0 but after taking away a electron it becomes +3-2=+1 which make its overall charge change to +1
What are the features of the noble gasses (group 0)?
The noble gasses are very unreactive elements
They are unreactive as the atoms are stable due to full outer shells and will not react
As we move down group 0, the boiling point increases as the atomic mass also increases
What are features of metals?
Found on the left (the highly reactive metals) and centre (the transition metals) of the periodic table
When metals react, they lose electrons in their outer shell to achieve a full outer energy level which gives them a stable electronic structure
Eg aluminium loses three to become stable
What are the features of group 1 metals (alkali metals)?
Always have one electron in their outer shell which is lost during a reaction to become stable
Group 1 metals are soft
Group 1 metals react rapidly with oxygen and create metal oxide
Group 1 metals also react rapidly with chlorine
As we move down group 1, the react more rapidly
What happens when group 1 metals react with oxygen?
Group 1 metals react rapidly with oxygen and create metal oxide
When a group 1 metal reacts with oxygen, the metals has one electron in its outer shell which transfers to the oxygens outer shell which has 6 electrons, making the metals atom stable
The oxygen atom still requires a electron to stable out its outer shell, so another lithium atom also transfers its electrons to the oxygen atom, stabilising all three elements
This changes the overall charges for each element
What happens when group 1 metals react with water?
Reacts rapidly with water and creates alkaline solutions
This creates metal hydroxide + hydrogen
Why do the group one metals get more reactive going down the group?
When certian elements react, they can loose their outer electrons more easily making them more reactive
This is because as the radius of the atoms increase, that means there is a greater distance between the positive nuclues and negative outer electrons which means the electron is less attracted to the nucleus
The outer electron is also repelled by electrons in the internal energy levels as negative + negative repel which decreases the attraction between the electron and nucleus is called shielding
What happens when group 7 non-metals react with eachother (the halogens)?
Have 7 electrons in the outer shell
When two group 7 elements react with eachother, they form together to make a covalent bond as they over lap and share a pair of electrons
This creates F2 and F-F
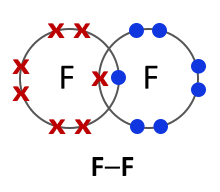
What is a covalent bond?
A chemical bond formed when two non-metal atoms share a pair of electrons
This can be represented with a stick between two atoms eg Cl-Cl
How do we use the boiling point and melting points in group 7 to find the physical state of the elements at room temperature?
Fluorine and chlorine are both gases at room temperature as their boiling points are lower the 20’c
Bromine is a liquid as it has a meling point lower then 20’c and the boiling point is higher then 20’c
Iodine is a solid at room temperature because both the melting point and boiling point is higher then 20’c
What is the relative molecular mass? How does it change going down group 7?
The relative molecular mass gives us the idea of the size of the molecule
The relative molecular mass increases (molecules get bigger)
What happens when halogens react with metals?
They form ionic compounds
The halogen gains one electron from the metal atom and froms a ion with -1 charge
This means the metals now have ‘ide’ at the end of the each element name eg bromide when it becomes a ion
The reactivity of the halogens
The halogens get less reactive moving down the group as it is harder to gain electrons
This is because going down the group there is a greater distance between the outer energy level and nuclues which means the electrons are less attracted to the nuclues
There are also more internal energy levels going down the group meaing they repel the outer electron
Describe the displacement in halogens
A more reactive halogen can displace a less reactive halogen from an aqueous solution of its salt
Eg
Sodium bromide dissolved in water (aqueous solution) + fluorine
bromide is less reactive so fluroien displaces it
→ sodium fluoride + bromine