Ap human unit 2
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
demography/demographic
The study of people
Ecumene
The portion of Earth's surface occupied by permanent human settlement.
Population distribution factors
Physical: climate, landforms, bodies of water, soil
Social: culture, economics, history, politics
Population density
Number of individuals per unit area
Arithmetic Density
Number of people per unit of land
Physiological Density
The number of people per unit of area of arable land, which is land suitable for agriculture.
Agricultural density
The ratio of the number of farmers to the amount of arable land
carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
Political distribution factors
Can favor areas that are more populated because they can have More government influence.
Economic distribution factors
Jobs are crucial places with more jobs will have a higher population density
Social process distribution factors
People have needs the more people the higher amount of places that provide those needs
Population distribution and density affect the environment and natural resources
The planet has a limited carrying capacity and we need to pay attention to the amount of resources we have otherwise we might run out
Demographic momentum
this is the tendency for growing population to continue growing after a fertility decline because of their young age distribution. This is important because once this happens a country moves to a different stage in the demographic transition model.
Consequences of over population
Not enough room, or enough resources for everyone. Everyone has too high of an ecological footprint.
Consequences of under population
-Labor Shortage, not enough workers
-loss of heritage, traditions die off
Fertility Indicators
The ability to produce offspring. Concerns the ability of people to have children
Total fertility rate
The average number of children born to a woman during her childbearing years.
Replacement birth rate
the number of children a couple must have in order to replace themselves in a population.
Crude birth rate
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
rate of natural increase
derived by subtracting the crude death rate from the crude birth rate; increases or decreases due to migration are not included (growth rate)
Distribution of highest Rate of natural increases
Sub Saharan Africa
Zero population growth
when the birth rate equals the death rate
Doubling time
The number of years needed to double a population, assuming a constant rate of natural increase.
Mortality indicators
Concerns when/how people in a society approach death
Crude death rate
The number of deaths per year per 1,000 people.
Life expectancy
A figure indicating how long, on average, a person may be expected to live
Migration rates
People leaving (outward migration) or entering (inward migration) will affect the population of a country, city, etc.
Factors of fertility
social, political, economic
Social fertility factors
If woman are valued based on number of kids, if male head is valued based on number of kids, sons are more likely to make a lot of money, if the religion supports birth control, the age structure.
Economic fertility factors
higher level of economic development=lower birth rate(kids can work)
Malthusian Theory(Thomas Malthus)
focuses on how the exponential growth of a population can outpace growth of the food supply and lead to social degradation and disorder
Criticisms of Thomas Malthus
Didn't foresee technological advances such as the Green Revolution that could increase food production. Didn’t consider migration that could redistribute population
Arguments of Neo-Malthusians
The growth of less developed countries are outstripping resources.
World population is not just stripping food but other resources as well. ie oil and water
Demand anti-natal policies such as birth control and family planning
Cornucopians
resources are not finite due to the advancement of technology
Ester Boserup(cornucopians)
Principal critic of Malthusian theory who argued that overpopulation could be solved by increasing the number of subsistence farmers.
Declining fertility rates changing social values
If societal norms place heavy emphasis on the value of a woman based the number of children woman may have, then birth rates will be higher
Declining fertility rates (education)
The longer a woman attends school, the lower the birth rate
Declining fertility rates ( health care)
Better pre-natal and post-natal care leads to fewer deaths of infants and mothers and lowers the fertility rate. With less fear of death, families generally choose to have fewer children.
Declining fertility rates (employment)
Woman having access to employment is key to lowering fertility rates because it shows society that they are more than just child bearer's
Contraception
prevention of pregnancy
Declining fertility rates (contraception)
Different religions and cultures allow or discourage or forbid contraception. Depending on the society a woman is a part of, contraception may or may not be taboo. If it's allowed fertility rates will be lower
Fertility trends and the shifting role of woman in society
As a woman's value (social politically and economically) improves woman will feel less need to have kids to prove them self.
Rapid Growth Population Pyramid
Piriphery high birth rate and death rate high rate of natural increase based on significantly wider
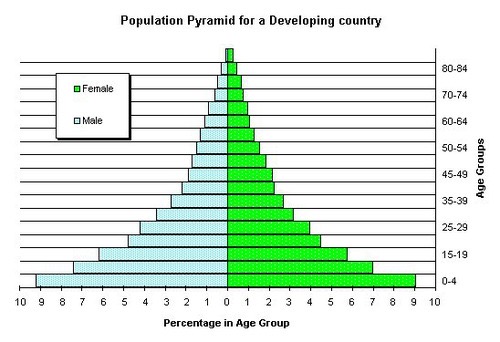
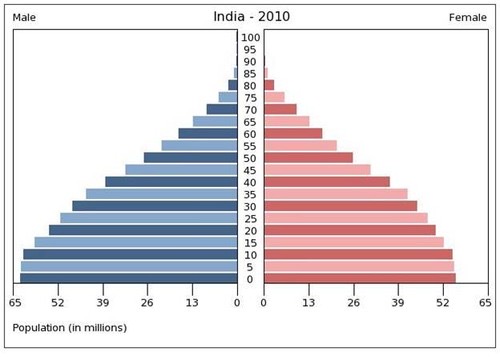
Medium Growth Pyramid
Level of development: Newly Industrialized, Semi-Periphery
In between developing an developed dependency transitioning
BRICS (Brazil, russia, India, china, south Africa) bee hive
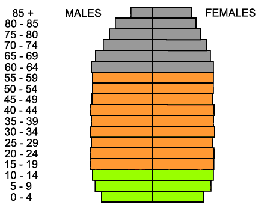
slow growth pyramid
Level of development: Developed, Core
Cohorts approximately equal, more older females cylinder/coke bottle/cylinder hourglass even/low dependency, low birth/death rate slow RNI
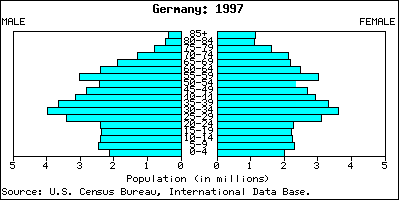
Negative growth rate
a population size gets smaller, reducing the number of people inhabiting that country. Higher death rate than birth rate, Japan, Italy, South Korea
War Population Pyramid
Many men in battle
Anti natal policies population pyramid
Less kids due to limits
Guest Worker Population Pyramid
Often a huge spike in males ages 20-54
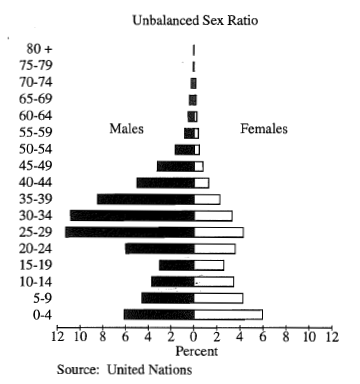
College Towns Population Pyramid
Large number of 18-24 year olds
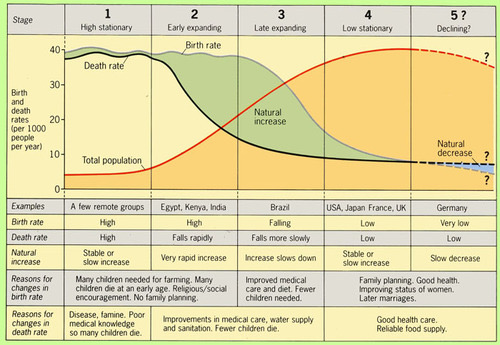
The demographic transition model
a model of how the size of a population changes as a country develops its economy
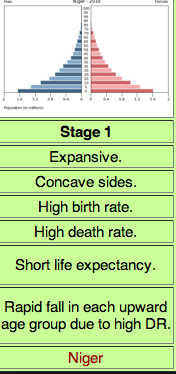
The demographic transition model Stage 1
Low growth; high birth and death rates with a natural increase close to 0, associated with preindustrial societies
NO COUNRIES
The demographic transition model Stage 2
High birth rate and rapidly falling death rates, very high natural increase, North America and Europe enter in the 1750s-advancements of Industrial Revolution increase standard of living, latin America and Asia enter in the 1950s-medical revolution increased healthcare EX: Egypt, Kenya, India, periphery triangle
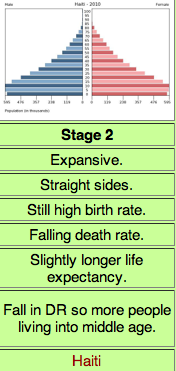
The demographic transition model Stage 3
Moderate growth; fertility rates begin to fall, associated with a mature industrial society BRICS AND MINT beehive
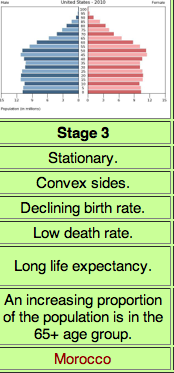
The demographic transition model Stage 4
Low Growth; birth rates continue to fall, accompanied by steady death rates, associated with postindustrial societies, core countries rectangle
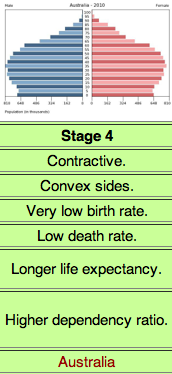
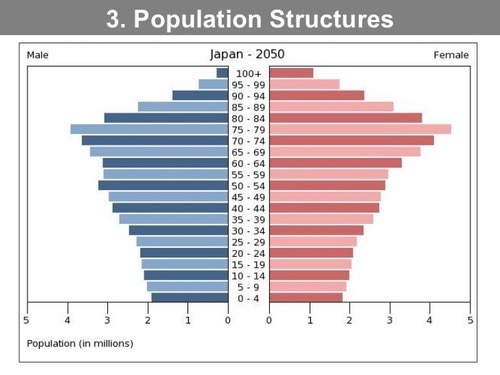
The demographic transition model stage 5
Very low birth rates, low death rates, slow decrease in Natural Increase, Germany, have few women in child bearing years Problems: few young people to support the elderly population, not enough workers to stimulate the economy negative RNI
Change in birth rate
Advancements in technology along with value of woman and family planing
Change in death rate
Change in food medical care sanitation
The demographic transition model Assumptions
Countries must follow the same path of devlopment of Europe
movement from rural to urban is the only path to economic development
The demographic transition model faults
it ONLY considers ECONOMIC factors
dtm exceptions
Russia= necitive factors that cause a drop in BR such as economic uncertainty poor health conditions and environmental issues
Epidemiological Transition Model
The theory that says that there is a distinct cause of death in each stage of the demographic transition model. It can help explain how a country's population changes so dramatically. communicable diseases to chronic usually around stage 2 or 3
Pro-Natal Policies
Policies that encourage pregnancy and birth
Anti-Natalist Policies
programs to decrease the number of births
Baby Bonus
government policy that awards money to parents of young children
affordable child care provisions
allows mothers and fathers cheaper child care or decrease in taxes
maternity/paternity leave
a period of time a mother or a father can take off work after the birth of a child; also: parental leave
Tax breaks
provisions of the tax code that reduce the amount of tax that is owed
India successes
Education for woman in the workforce access to birth control
China's One Child Policy
Law created in 1979 to slow down population growth and to prevent overpopulation
Intended effect: reduce population size by limiting family size
Unintended consequences: sex ratio imbalance , shortage of workers
Dependency ratio
The number of people under age 15 and over age 64 compared to the number of people active in the labor force
Consequences of aging population
Shortage of workers, costs of caring for the elderly
Consequences of to many young people
Future job shortage, more housing needed, stress on prenatal care/ health care, more education needed
emigrant
A person who leaves a country or region to live elsewhere.
Immigrant
a person who comes to a country where they were not born in order to settle there
Catalyst of migration
Digital infrastructure allows people to move and work in more places
Cultural push factors
Changes or lack thereof of societal norms regarding gender roles, religious practices, or attitudes on societal roles of groups of people
Economic Push Factors
lack of economic opportunity
Environmental push factors
Natural Disasters and famines
Political push factors
Armed conflict, civil wars, oppressive governments/laws, persecution
Cultural pull factors
Religious freedom, similar ethnic groups, language, education, entertainment
Economic pull factors
job opportunities, higher wages, lower cost of living
Environmental pull factors
Favorable climate
Political pull factors
Laws, fewer restrictions, political freedom, stable government
Migration
Form of relocation diffusion involving permanent move to a new location.(choice)
Internal migration
Migration within a country
Gravity Model
A mathematical formula that describes the level of interaction between two places, based on the size of their populations and their distance from each other. ex: someone migrating from London to the USA is most likely to settle in places like New York
Step migration
Migration to a distant destination that occurs in stages, for example, from farm to nearby village and later to a town and city
Intervening Opportunities
The idea that one place has a demand for some good or service and two places have a supply of equal price and quality, then the closer of the two suppliers to the buyer will represent an intervening opportunity, thereby blocking the third from being able to share its supply of goods or services. Intervening opportunities are frequently utilized because transportation costs usually decrease with proximity. Good things that help you continue step migration
intervening obstacle
An environmental or cultural feature of the landscape that hinders migration. Bad things that make it harder to migrate
Counter migration
the return of migrants to the regions from which they earlier emigrated
Cyclical movement
A regular journey that begins at a home base and returns to the exact same place. Commute to school and back
Voluntary Migration
movement in which people relocate in response to perceived opportunity; not forced.
Periodic movement
Movement - for example, college attendance or military service - that involves temporary, recurrent relocation(longer time away)
Chain migration/ kinship links
migration of people to a specific location because relatives or members of the same nationality previously migrated there
Guest Workers
legal immigrant who has work visa, usually for a certain period of time
Remittances
Money migrants send back to family and friends in their home countries, often in cash, forming an important part of the economy in many poorer countries
Rural-urban migration
Permanent movement from suburbs and rural area to the urban city area.
Forced Migration
Human migration flows in which the movers have no choice but to relocate.