Respiratory System [Chapter 22]
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
1
New cards
What is respiration?
Processes that provide tissues with O2 and rid them of CO2
2
New cards
What is pulmonary ventilation?
movement of air into and out of the lungs
3
New cards
What is external respiration?
gas exchange between lungs and blood
4
New cards
What is gas transport
Blood carries hasses to and from tissues
5
New cards
What is internal respiration
exchange of gases between blood and body cells
6
New cards
What is the upper respiratory tract?
Nares, Nasal cavity, Paranasal sinuses, Pharynx [naso, oro, larygo]
7
New cards
What is the purpose of the upper respiratory tract
warms, humidifies, filters, and transports air
8
New cards
What is the nares
nostrils
9
New cards
Nares (Picture)
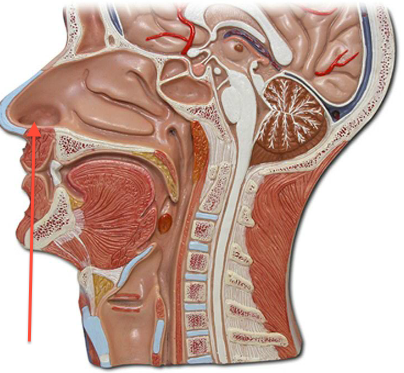
10
New cards
What important structures and processes are within the nasal cavities
Olfactory mucosa for smell
Conchae provide large surface area
Ciliated cells move mucus posteriorly
Conchae provide large surface area
Ciliated cells move mucus posteriorly
11
New cards
What is the function of paranasal sinuses
weight reduction and sound resonance
12
New cards
Nasal cavity (Picture)
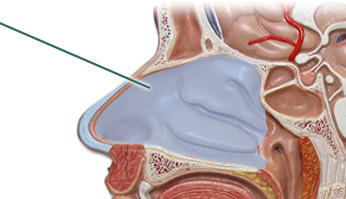
13
New cards
What is the pharynx
throat
14
New cards
What is the importance structures and functions of the Nasopharynx
Air passageway
Pharyngeal and tubal tonsils
Pharyngotympanic tubes, Middle war pressure equalization
Pharyngeal and tubal tonsils
Pharyngotympanic tubes, Middle war pressure equalization
15
New cards
What is the important structures and functions of the Oropharynx
Food and air passageway
Oral cavity meets nasopharynx
Palatine and lingual tonsils
Oral cavity meets nasopharynx
Palatine and lingual tonsils
16
New cards
What is the important structures and functions of the Laryngopharynx
Food and air
extends down esophagus a little
extends down esophagus a little
17
New cards
Nasopharynx (Picture)
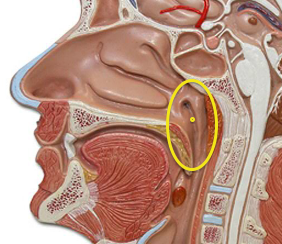
18
New cards
Oropharynx (Picture)
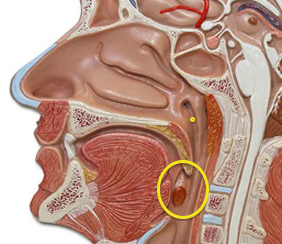
19
New cards
Laryngopharynx (Picture)
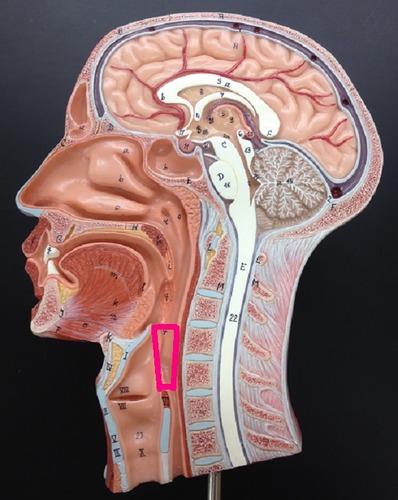
20
New cards
What is the Lower Respiratory System
Conducting and Respiratory zone
Larynx, Trachea, Bronchioles
Larynx, Trachea, Bronchioles
21
New cards
What is the conducting zone
no gas exchange, from nares to terminal bronchioles
22
New cards
What is the respiratory zone
gas exchange occurrence, Respiratory bronchioles, Alveolar ducts, Alveoli
23
New cards
What is the larynx
Voice box and air passageway
Made of eight hyaline cartilages
Made of eight hyaline cartilages
24
New cards
Larynx (Picture)
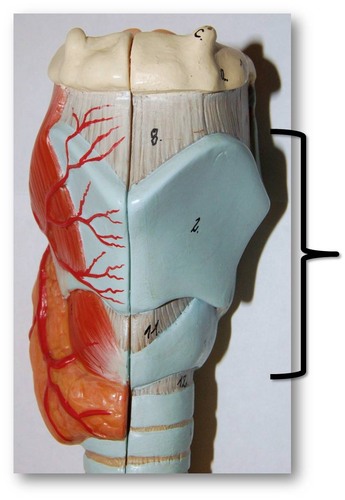
25
New cards
epiglottis (Picture)
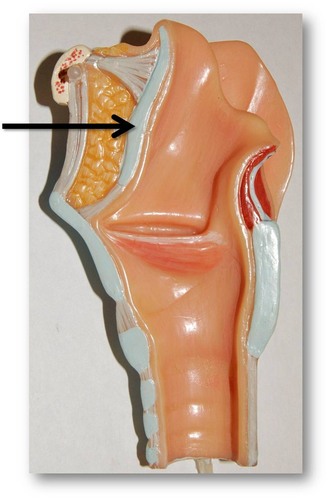
26
New cards
What is the epiglottis
Made of elastic cartilage
Covers glottis when swallowing, directs food into the esophagus
Covers glottis when swallowing, directs food into the esophagus
27
New cards
What is the trachea
Windpipe, extends from larynx to bronchi
Has hyaline cartilage rings, ciliated epithelium which move mucus superiorly
Has hyaline cartilage rings, ciliated epithelium which move mucus superiorly
28
New cards
trachea (Picture)
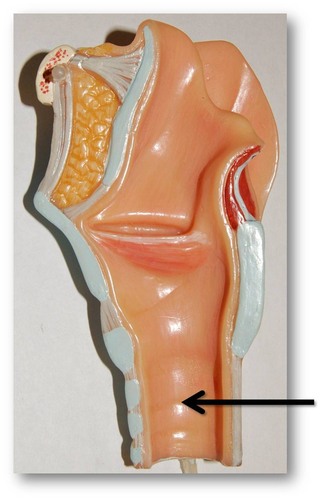
29
New cards
What is the bronchial tree
a branching system of air tubes in each lung, bronchioles and subdivisions
30
New cards
What are the bronchi
The two tubes which split from the trachea and carry air into the lungs
31
New cards
What are the bronchioles
Below 1 mm diameter
Airways in the lungs that lead from the bronchi to the alveoli.
Airways in the lungs that lead from the bronchi to the alveoli.
32
New cards
What are the Terminal Bronchioles
Below 0.5 mm diameter
end of conducting zone, smallest of the bronchi
end of conducting zone, smallest of the bronchi
33
New cards
What happens as you decrease down the bronchioles
Cartilage decreases, Smooth muscle increases, Ciliated cells decrease
34
New cards
What is the respiratory membrane
The thin membrane of alveoli where gas exchange takes place
0.5 micrometers thick, Simple Squamous epithelium
0.5 micrometers thick, Simple Squamous epithelium
35
New cards
What are Alveolar cells
Type I, Type II, and macrophages
36
New cards
What are Type 1 Alveolar cells
simple squamous cells where gas exchange occurs
37
New cards
What are Type II Alveolar cells
secrete surfactant
38
New cards
What is pulmonary circulation?
circulation between heart and lungs
39
New cards
What is Bronchial circulation
bronchial arteries provide oxygenated blood to lung tissue
40
New cards
What is the pulmonary plexus
at the root of each lung- both efferent and afferent autonomic fibers- formed by sympathetic trunks and vagus nerves
41
New cards
What does the sympathetic system do within the lungs
Dilation of bronchi
42
New cards
What does parasympathetic system do within the lungs
constriction
43
New cards
What is the visceral pleura?
serous membrane that covers lungs
44
New cards
What is the parietal pleura?
lines the walls of the thoracic cavity
45
New cards
What is Atmospheric pressure
760 mmHg
46
New cards
What is intrpulmonary pressure?
760 mmHg when airway is open
47
New cards
What is intrapleural pressure
4 mmHg or less
48
New cards
What is transpulmonary pressure?
Difference between the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures
P pul - P pip =4 mmHg
P pul - P pip =4 mmHg
49
New cards
What is Boyle's Law?
P1V1=P2V2
50
New cards
Is inspiration active or passive?
active
51
New cards
Is expiration active or paassive?
passive
52
New cards
What muscles facilitate inspiration
Diaphragm and External intercostals
53
New cards
What is negative pressure inspiration
lower pressure inside lungs providing the power needed
54
New cards
What muscles facilitate expiration
internal intercostals, and abdominal muscles
55
New cards
What is airway resistance
F=DeltaP/R
Delta P is the most important factor
Delta P is the most important factor
56
New cards
What is Alveolar surface tension
liquid molecules lining lungs attract each other, surfactant counters it
57
New cards
What is lung compliance?
It is the stretchability of our lungs. The more the lungs can expand the more the compliance.
58
New cards
What physical factors affect pulmonary ventilation
Airway resistance, Alveolar surface tension, Lung compliance
59
New cards
What is anatomical dead space?
The amount of gas that stays in the pipes, the conduction zone.
60
New cards
What is alveolar dead space?
non-functional alveoli due to collapse or obstruction
61
New cards
What is total dead space
sum of anatomical and alveolar dead space
62
New cards
What is alveolar ventilation?
6 L/min at rest
up to 200 L/min with exercise
up to 200 L/min with exercise
63
New cards
What is Dalton's Law?
The total pressure of a mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of gasses
64
New cards
What is Henry's Law?
gases will dissolve into a liquid in proportion to their partial pressures
65
New cards
What is ventilation-perfusion coupling?
matching of alveolar ventilation with pulmonary blood perfusion
66
New cards
How much of oxygen is carried by hemoglobin
98.5%
67
New cards
How much O2 can hemoglobin carry?
4 O2 molecules
68
New cards
What is the Bohr effect?
conditions in the body tissues enhance o2 unloading
69
New cards
How much COs in released by cells
200 ml/min
70
New cards
How much CO2 is dissolved in plasma?
7-10%
71
New cards
How much CO2 is bound to hemoglobin?
20%
72
New cards
How much CO2 is a bicarbonate
70%
73
New cards
What is the Haldane effect?
The lower the PO2 and hemoglobin saturation with O2, the more CO2 can be carried in the blood.
74
New cards
What is ischemic
impaired circulation
75
New cards
What is histotoxic hypoxia?
Cells cant absorb O2, as in from some poisons
76
New cards
What is Hypoxemic hypoxia
Inadequate O2 reaching blood from lungs
77
New cards
What part of the brain affects breathing
Medullary respiratory centers, which stimulate phrenic/intercostal nerves
78
New cards
What is eupnea?
normal quiet breathing of 12 breather/min
79
New cards
What chemical factors influence breathing rate
PCO2, PO2, And arterial pH
80
New cards
What is PO2
partial pressure of oxygen
81
New cards
What is hypercapnia
excess carbon dioxide in the blood
82
New cards
What is hypocapnia?
low CO2 in blood
83
New cards
What Are Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases (COPD)
Emphysema and Chronic Bronchitis
84
New cards
What is Emphysema
Blown out Alveoli and reduced surface area
85
New cards
What is chronic bronchitis?
Excessive mucus production
86
New cards
What is Asthma
chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways
87
New cards
What are Tubercles
lung nodules that can bust and spread bacteria