Chapter 4: Tissues
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
simple squamous epithelium function
diffusion and filtration
simple squamous epithelium location
kidney glomeruli, air sacs of lungs, lining of heart, blood, lymphatic vessels, ventral body cavity (serosae)
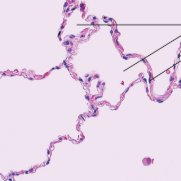
simple squamous epithelium
simple cuboidal epithelium function
secretion and absorption
simple cuboidal epithelium location
kidney tubules, secretory portions of small glands, ovary surface
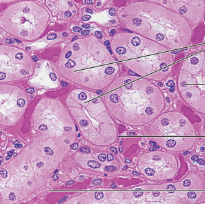
simple cuboidal epithelium
simple columnar epithelium function
absorption (secretion of mucus/enzymes)
may contain cilia/goblet cell
simple columnar/pseudostratified columnar
nonciliated simple columnar epithelium location
digestive tract, gallbladder, and ducts of some glands
ciliated simple columnar epithelium location
small bronchi, uterine tubes, and uterus
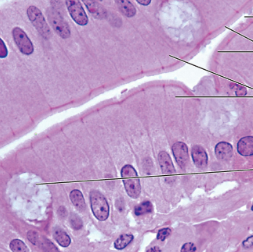
simple columnar epithelium
pseudostratified columnar epithelium all cells touch ___
basement membrane
pseudostratified columnar epithelium only tall cells reach ___
apical
pseudostratified columnar epithelium function
secretion of mucus; propulsion of mucus by cilia
non-ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium location
male reproductive tubes/large glands
ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium location
trachea/upper respiratory tract
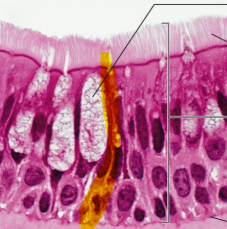
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
stratified epithelium are named according to
shape of cells at top (apical)
stratified epithelium regenerate from
below (basal)
stratified epithelium function
protection
stratified epithelium location
high friction areas (mouth, vaginal canal)
stratified squamous epithelium many layers are
squamous
stratified squamous epithelium deeper layers are
cuboidal/columnar
thickest epithelial tissue
stratified squamous epithelium
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium function
keratin waterproof
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium location
epidermis
nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium function
forms moist lining of body openings
nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium location
lining of mucous membranes (esophagus, mouth, anus, vagina)
stratified squamous epithelium function
protects underlying tissues in areas subject to abrasion
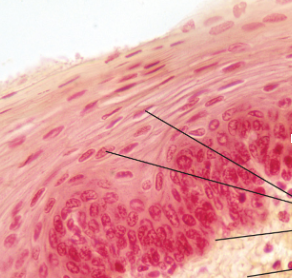
stratified squamous epithelium
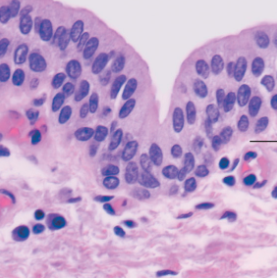
stratified cuboidal epithelium function
protection
stratified cuboidal epithelium location
ducts of glands
stratified cuboidal epithelium
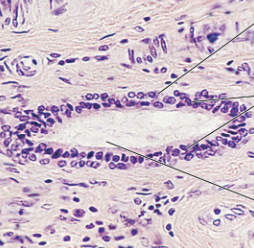
stratified columnar epithelium function
protection and secretion
stratified columnar epithelium location
rare; male urethra and large duct of some glands
stratified columnar epithelium
transitional epithelium relaxed
cuboidal
transitional epithelium stretched
squamous
transitional epithelium function
expands bladder when its full
transitional epithelium location
urinary bladder, ureters, proximal urethra
tight junction function
close off intercellular space/prevent molecules from passing
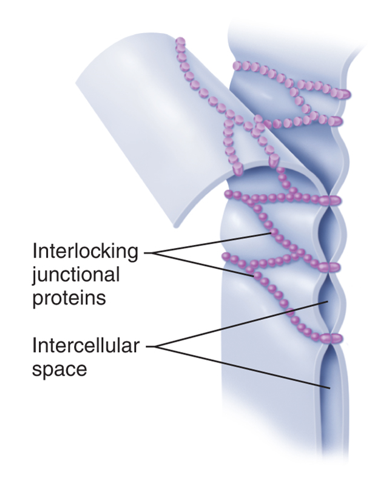
tight junction
adhesive belt junction function
anchoring
desmosomes function
bind cells together
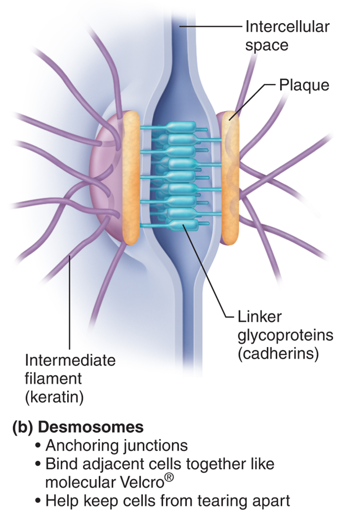
desmosomes
gap junctions
passageway for small molecules between two cells
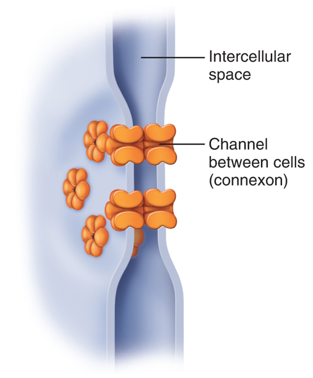
cell junctions
desmosome proteins
keratin and cadherins
gap junction proteins
connexon
four main types of body tissues
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
apical
top
basal
bottom
lateral
side wall
epithelial first name
number of cell layers
epithelial last name
shape of cells
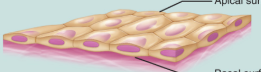
simple
one layer of cell touches basement membrane
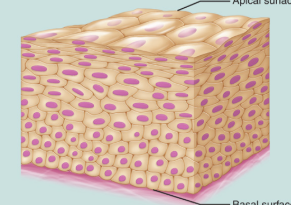
stratified
multiple layers but only basal layer touches basement membrane

squamous
disc

cuboidal
cube

columnar
column
endocrine glands
ductless glands that secrete directly into surrounding tissue fluid
gland that produces hormones
endocrine
exocrine glands
ducts carry products to epithelial surface
mucus-secreting, sweat and oil, salivary, liver and pancreas gland
exocrine
goblet cells product
mucin
goblet cells unicellular or multicellular
unicellular
mucin + water
mucus
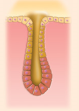
simple tubular
simple tubular example
intestinal glands
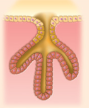
simple branched tubular
simple branched tubular example
stomach glands
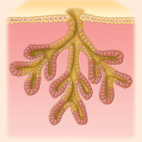
compound tubular
compound tubular example
duodenal glands of small intestine
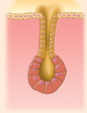
simple alveolar
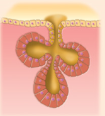
simple branched alveolar
simple branched alveolar example
sebaceous oil glands
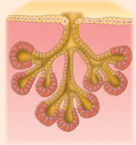
compound alveolar
compound alveolar example
mammary glands
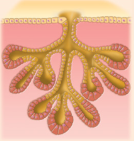
compound tubuloalveolar
compound tubuloalveolar example
salivary glands
end of second month of development tissues
primary tissue types and major organs in place
adulthood tissues
few tissues regenerate, many retain populations of stem cells
with increasing age epithelia
thins
with increasing age collagen
decreases
with increasing age bones, muscles, and nervous tissue
begin to atrophy
with increasing age poor nutrition/circulation
poor tissue health
lost cells are quickly regenerated by
cell division
main types of connective tissue
connective, cartilage, bone, blood
connective tissue origin
mesenchyme
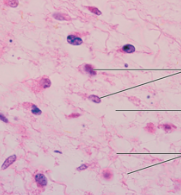
mesenchyme
areolar connective tissue cells include
fat, white blood, mast
areolar connective tissue function
hold water to help cushion organs and fight against infection
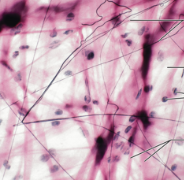
areolar connective tissue
loose connective tissue subclasses
areolar, adipose, reticular
dense connective tissue subclasses
regular, irregular, elastic
connective tissue matrix
gel-like with all fiber types (collagen, reticular, elastic)