set 1: disturbances & ocean warming
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
how do corals begin their lifecycle
as polyps
what is the process by which corals grow a skeleton
metamorphosis
what do coral develop to aid survival
symbiotic algae that reproduces
why is nutrient recycling important
as corals love in nutrient poor waters
what are the two types of variation
spatial and temporal
define disturbances
an event that damages or kills residents at a given site
what are the two type of disturbance durations
acute and chronic
what happens when acute disturbances occur frequently without enough recovery time
it causes chronic disturbance
why are natural disturbances important for ecosystems
play a critical role in structuring ecosystems
how do disturbances affect biodiversity
immediate levels on disturbance may promote diversity but this depends on its frequency and intensity
what are the three equilibrium hypotheses
niche diversification hypothesis
circular network hypothesis
compensatory mortality hypothesis
what is the equilibrium hypothesis about community composition
communities are usually in a state of equilibrium and recover to that state after a disturbance
high diversity is maintained without continual species composition changes
what is the niche diversification hypothesis
at equilibrium, each species is competitively superior in exploiting a particular subdivision of the habitat
diversity is a function of the total range of habitats and the degree of specialisation of the species to parts of that range
what is the circular network hypothesis
at equilibrium, each species uses interference mechanisms which cause it to win over some competitors but lose to others (A>B>C but C>A)
what is the compensatory mortality hypothesis
mortality from causes unrelated to the competitive interaction falls heaviest on whichever species ranks highest in competitive ability
what is the non-equilibrium hypotheses
the species composition of communities is seldom in a state of equilibrium
high diversity is maintained only when the species composition is continually changing
what are the three non equilibrium hypothesis
equal chance hypothesis
gradual change hypothesis
intermediate disturbance hypothesis
what is the equal chance hypothesis
species are approximately equal in ability to colonise, exclude invaders, and resist environmental vicissitudes
local diversity depends only on the number of species available in the geographical area and the local population density
unlikely as it requires equal ability to resist physical extremes and recruitment to independent of local population
what is the gradual change hypothesis
gradual environmental changes, that alter the ranking of competitive abilities, occur at a rate high enough so that the process of competitive elimination is seldom if ever completed
not supported by organisms with long life expectancies
what is the intermediate disturbance hypothesis
diversity is higher when disturbances are intermediate on the scales of frequency and intensity
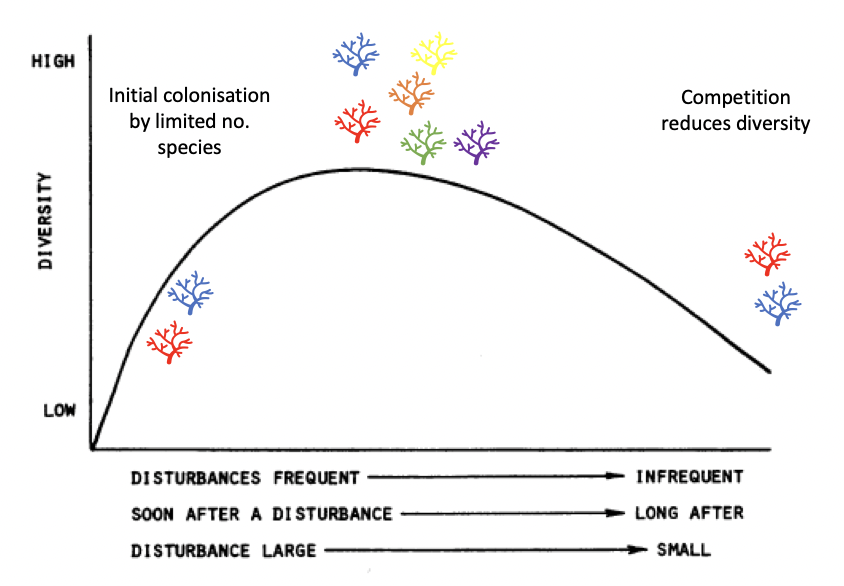
which hypothesis is most believed
intermediate disturbance hypothesis
what are the criticisms of IDH
empirical refutation: review of over 100 published studies find that predicted peak of diversity at intermediate diversity rarely occurs
what are the theoretical refutations of IDH
disturbance weakens competition
disturbances interrupt competitive exclusion
identity of the dominant competitor changes on an intermediate timescale