B6: CM Repro Exam 1 (1-10, currently updated to 1/2)
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
polymastia
What disorder is classified as supernumerary breasts?
-Hint: they occur superior/inferior to normal pair, occasionally developing in axillary fossa or abdominal wall & may appear anywhere along a line extending from axilla to the groin
polythelia
What disorder is classified as accessory nipples?
-Hint: they occur superior/inferior to normal pair, occasionally developing in axillary fossa or abdominal wall.
rudimentary
Supernumerary breasts usually consist of only a _________ nipple and areola, which may be mistaken for a mole/nevus until they change pigmentation with the normal nipples during pregnancy. Glandular tissue may also be present and further develop into lactation
breast
arterial supply of the ________ derives from the:
-medial mammary branches of perforating branches and anterior intercostal branches of internal thoracic a.
-lateral thoracic and thoraco-acromial aa., which are branches of the axillary a.
-posterior intercostal aa. in 2nd-4th intercostal spaces
axillary v.
venous drainage of the breast is mainly to the __________, but there is some drainage to the internal thoracic v. The venous pattern is often visible, esp. during pregnancy
axilla, chest, and liver
Where does breast cancer end up?
RUQ
Where does most breast malignancy occur?
-Hint: area of the breast with the most tissue
radiation
What is a downside to mammogram?
-Hint: can CAUSE breast cancer if started when young
US
What is the 1st line modality in the workup of a palpable breast mass in a pregnant or lactating pt?
I will evaluate the patient in my office. Will likely refer for an ultrasound examination.
A 36 year old woman, recently post partum, chose to breast feed her infant baby boy. She soon thereafter identified a lump in her left breast. She calls your office to report this new finding.
Which of the following is likely your advice?
breast
___________ complaints include:
-breast pain
-mass
-nipple discharge, crusting, or retraction
-inflammation or dimpling
breast pain
most common breast complaint
non-cyclic and unilateral
Which types of breast pain are more suspicious for malignancy?
cyclic
(cyclic/non-cyclic) breast pain:
-66% of pts
-hormonally mediated
-fibrocystic changes
-imaging NOT usually indicated for BL pain and no abnormalities on Hx or PE (make sure you ALWAYS do PE!)
non-cyclic
(cyclic/non-cyclic) breast pain:
-33% of pts
-post-menopausal hormone therapy
-some antidepressants
-caffeine/tobacco
-inflammatory
-cancer
-chest wall pain
fibrocystic changes
What disorder:
-often presents with cyclic breast pain
-diffuse symmetrical thickening and lumps in breast (most commonly in RUQ)
-dense breasts that contain higher proportion of stromal and glandular tissue
-usually pre-menopausal
benign breast pain
Tx for _______ _______ ____ involves:
-supportive garments
-analgesics like NSAIDs (oral or topical)
-low fat diet
-decreased caffeine
-inc. Vit E
-danazol (Synthetic steroid)
danazol
What is the only medication approved by US FDA for treatment of mastalgia?
Hint: synthetic steroid, ADR = androgen-like effects
costochondritis
What disorder:
-potential cause of breast pain
-upper costal cartilages at costchondral or costosternal junction most frequently involved
-based solely upon ability to reproduce pain by palpation of tender areas
-Tx = NSAIDs
simple cyst
What disorder:
-originate from lobules of breast
-often in pre-menopausal women
-typically contains a greenish-yellow or brown fluid that is sent to cytology
-hypoechoic/anechoic on US
excise
When to ______ a simple cyst:
-bloody aspirate
-remains palpable
-recurs
simple cyst
aspirate
When to _____ a simple cyst:
-larger cyst (>3 cm) that obscures breast tissue on mammogram
-symptomatic
simple breast cyst
ID
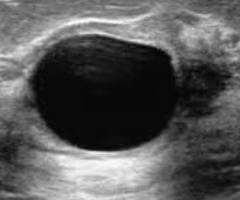
complex breast cyst
What disorder:
-more suspicious than simple breast cyst
-mixed echoes, irregular or ill-defined border on US
-BIOPSY!!!
complex breast cyst
ID
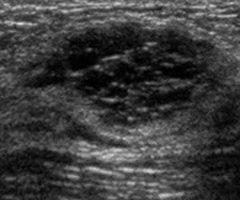
galactocele
What disorder:
-milk retention cyst from cystic collection of fluid caused by obstructed milk duct
PE: mass in lactating woman (post-partum, breast feeding)
Mammogram: indeterminate mass
US: complex mass
Dx: clinical Hx and ASPIRATION that yields a milky substance
Tx: excision not necessary and no increased risk for subsequent breast cancer
galactocele
ID
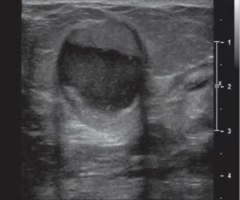
galactocele
ID
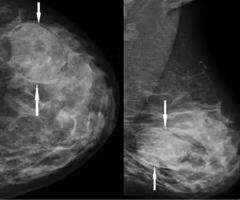
fibroadenoma
What disorder:
-most commonly diagnosed solid benign breast disease
-pre-menopausal women!!!! (goes away post-menopause)
-well-defined, mobile mass that seems unfixed to surrounding tissue
Dx = confirmatory biopsy
Mammogram: well-defined, smooth, oval-shaped hyperechoic lump
<35yo
Tx for fibroadenoma ____:
-observation (must confirm benign by biopsy) and sequential US --> if increases in size it requires excision
-cryoablation (must confirm benign by biopsy)
>35yo
Tx for fibroadenoma ____ or inc. risk:
-eval/mammography
fibroadenoma
ID
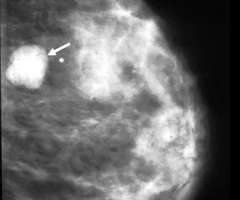
giant fibroadenoma
What disorder:
-often in adolescents
-lumpy and rubbery mass on PE
-often in children
->5 cm (essentially a fibroadenoma >5 cm)
-Tx = surgical excision
phyllodes tumor
What disorder:
-uncommon, 0.5% breast malignancies
-related to fibroadenoma (fibroepithelial)
-diverse range of biologic behavior: clearly benign to clearly malignant
-leak-life projections on pathologic examination
Mammogram: typically smooth, polylobate, resembles fibroadenoma
-suspicion rises based on large tumor size at presentation or rapid growth
Tx = excision
fat necrosis
What disorder:
-benign condition commonly occurs as a result of breast trauma
-adequate Hx essential for making differential diagnosis!
PE: palpable breast mass (may be confused with malignancy and may mimic malignancy on radiologic studied)
Dx: biopsy required!
-involvement of Cooper's Suspensory Ligaments (fibrous connections between inner breast skin and pectoral fascia) can cause shortening/retraction and dimpling of the breast
mastitis
What disorder:
-minute lacerations in skin allow bacteria to enter breast
-most common in lactating woman
-most commonly due to S. aureus
Tx:
-CONTINUE NURSING
-PO Abx for 14 days w/ dicloxacillin
on exam
inflammatory breast cancer
What disorder:
-malignant cells within dermal lymphatics
-often mimics mastitis
-rapid and diffuse involvement of entire breast w/ breast markedly increased in size within weeks
Dx = BIOPSY!!!!!!!!
-may see peau d'orange changes
breast abscess
What disorder:
-complication of lactational and non-lactational (Smokers and obesity) mastitis
-due to obstruction of duct
Tx = I & D w/ biopsy & do not stop breast feeding
intraductal papilloma
What disorder:
-papillary tumor growing from lining of breast duct
-can harbor areas of atypia or ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
-most common cause of pathologic nipple discharge (serous/bloody)
Tx = excision
intraductal papilloma
ID
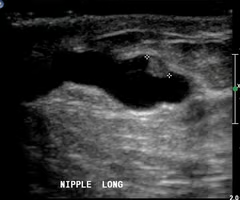
duct ectasia
What disorder:
-dilation of ducts in retroareola area
-cause not well understood -- likely inflammatory
-dilation of tubular structure
duct ectasia
ID
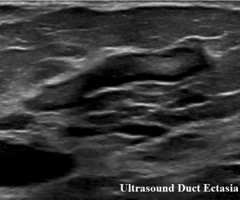
duct ectasia
ID
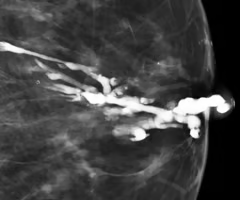
ductal excision w/ biopsy
Treatment of nipple discharge often involves ___________
ductal hyperplasia
What type of epithelial hyperplasia:
-# of epithelial cells increases to 3-4 cell layers in thickness (compared to double layer --1 myoepithelial and 1 columnar layer)
atypical ductal hyperplasia
What type of epithelial hyperplasia:
-occurs when hyperplasia shows some features of intraductal carcinoma
-definite RF for development of carcinoma
ductal carcinoma in situ
What type of epithelial hyperplasia:
-90% of epithelial hyperplasia
-pre-malignant state
-consists of cells that have a cytology characteristic of malignancy but no invasion outside ductal system (doesn't invade BM)
-tumor marker! increased risk (12X)
obesity, pharmacology, surgery
Risk reducing intervention for breast cancer involves what 3 things?
sporadic
Most (~90%) breast cancers are _______ (environmental causes rather than inherited or genetic mutation)
can
RFs you (can/cannot) control for breast cancer include:
-weight
-diet
-exercise
-alcohol
-smoking
-estrogen exposure (HRT, BCPs)
cannot
RFs you (can/cannot) control for breast cancer include:
-gender
-age
-FHx
-personal history
-race
-radiotherapy to breast (E.g., previous non-Hodgkin lymphoma)
-breast biopsy w/ atypia, hyperplasia
-exposure to estrogen (e.g., early menstruation, late menopause)
-DES exposure
protective
pregnancy and breast feeding are _____ factors for breast cancer
true
T/F: The older you are, the higher your absolute risk of breast cancer
BRCA1/2
Women with __________ (genes) have absolute higher risk of breast cancer
absolute
(absolute/relative) risk is used to describe the likelihood of certain Tx outcome or course of disease
relative
(absolute/relative) risk is used to describe the risk/benefit of certain lifestyle choices or treatments (development or recurrence of breast cancer)
high
______ risk pt for developing breast cancer includes:
• Genetic/Inherited Predisposition
• Prior Chest XRT
• Atypical Hyperplasia
• Lobular carcinoma in situ
• 5-year risk of 1.7% or greater (Gail Model)
breast cancer
recommendations for high risk pts for developing _________ include:
-early/more frequent clinical breast exams
-more frequent mammography
-MRI of breast
-ER modulators (e.g., Tamoxifen)
-Aromatase inhibitors
-risk reducing/prophylactic surgery --> BL mastectomy, salpingo-oophorectomy (BL)
tamoxifen
Which anti-estrogen medication:
-useful for risk reduction in high-risk pts for breast cancer
-prevents estrogen binding to ER
-for ER+ breast cancers
-for inherited AND non-inherited RFs
-increased risk of endometrial cancer and VTE
anastrozole
Which anti-estrogen medication:
-useful for risk reduction in high-risk pts for breast cancer
-aromatase in post-menopausal women converts androgens in peripheral tissues to estrogen --> inhibits this!
BL prophylactic mastectomy
What treatment as risk reduction for high-risk pts for breast cancer is for VERY high risk pts and decreases risk by 95% if BRCA1/2 (+) and 90% if strong FHx of breast cancer?
screening mammography
Survival is improved in pts whose breast cancer is diagnosed by ______________
mammography
What is the key for early detection of breast cancer?
prophylactic BL mastectomy
Which Tx for pts with BRCA1/2 mutations:
-simple (e.g., no axillary node dissection)
-90-95% risk reduction for breast cancer (not 100% because not all breast tissue removed)
-33% choose this
prophylactic salpingo-oophorectomy
Which Tx for pts with BRCA1/2 mutations:
-90% risk reduction for ovarian cancer (not 100% b/c some cells can be left behind)
tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitor (chemoprevention)
Which Tx for pts with BRCA1/2 mutations:
-38% risk reduction
ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
What disorder:
-malignant cells within lumen of breast duct
-5X increased risk for invasive breast cancer
-purpose of Tx = prevent progression to invasive disease via lumpectomy/partial mastectomy + radiation OR mastectomy
lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS)
What disorder:
-abnormal cells within lumen of lobule
-1 in 5 risk for invasive breast cancer
-not considered cancer but rather a marker for future cancer
-majority (80%) never develop invasive cancer
Tx: observation (BL) as surgery and rad not necessary, can do chemoprevention with tamoxifen
true
T/F: without an invasive component (e.g., just carcinoma in situ), lymph node eval not required
invasive breast carcinoma
What disorder:
-breast carcinoma that invades/infiltrates through BM of breast duct/lobule
-malignant cells can invade surrounding blood vessels and lymphatic channels allowing for metastatic spread to regional and distant sites
-80% arise from ductal system as invasive ductal carcinoma
Dx: palpable breast mass biopsied by FNA or core needle, non-palpable breast mass biopsied with stereotactic mammography using core needle or wire localization open excisional biopsy
breast cancer
Tx for ____________ involves:
-surgery
-radiotherapy
-chemo
-targeted drug therapy
-immunotherapy
-hormonal
-biologic
-combo of above
breast conservation therapy
Which surgical therapy for breast cancer:
-lumpectomy/partial mastectomy
-sentinel lymph node biopsy
-radiation therapy (XRT)
-reconstruction optional w/ many options
modified radical mastectomy
Which surgical therapy for breast cancer:
-mastectomy with axillary lymph node dissection
-optional breast reconstruction w/ many options
sentinel lymph nodes
What are the first nodes encountered along lymph drainage pathways of lesion?
radiotherapy/radiation therapy
What treatment for breast cancer:
-REQUIRED with breast conservation therapy
-local control of cancer within retained breast
-decreases recurrence and improves survival
Side Effects:
• Radiation changes to the heart and lungs
• Skin changes/hyperpigmentation
• Changes to breast contour (swelling/contracture)
• Fatigue
• Lymphedema
• Rib fracture
• Brachial Plexopathy
• Secondary Cancer (sarcoma of bone, muscle, lung)
bone, brain, lung, liver
What are common sites for breast cancer metastasis (hematogenous, lymphatic, or direct extension)?
tissue expansion
A common breast reconstruction technique is _______________, which involves expansion of the breast skin and muscle using an inflatable temporary tissue expander
TRAM flap
Which breast reconstruction surgery:
-avoid foreign body infection
-transfers muscle, subcutaneous, and skin
-bigger cut but results sure
-take blood supply with muscular flap since muscular flap provides blood to the tissue
DIEP flap
Which breast reconstruction surgery:
-skin and subcutaneous cut (no muscle)
-microsurgery to anastomose artery/vein
-less beneficial result
-more costly but better cosmetically
trastuzumab
What is a monoclonal antibody therapy against HER2 receptors?
Note: Overexpression of HER2 is associated with more aggressive breast cancer with increased metastasis and lower survival
triple negative
Which type of breast cancer:
-ER (-), PR(-), HER2(-) and HER2 neu proteins on myoepithelial and luminal epithelial cells in breast
-limits Tx options
-does not respond to Tx with hormonally targeted therapy or monoclonal Ab therapy (anti-HER2)
-more aggressive
-treatable with systemic chemo
neoadjuvant
(neoadjuvant/adjuvant) chemo:
-administered pre op
-indicted to shrink large tumors and improved operability
adjuvant
(neoadjuvant/adjuvant) chemo:
-administered post op
-indicated for pts with increased risk of cancer recurrence and with metastasis --> large tumor, (+) LN, (-) ER/PR, triple (-)
neoadjuvant
(neoadjuvant/adjuvant) radiation therapy:
-administered pre-op
-shrink large tumors to improve operability
-take inoperative tumors and make them operable
adjuvant
(neoadjuvant/adjuvant) radiation therapy:
-administered post-op
-used in addition to breast conserving surgery to provide local control of cancer within retained breast
-has dec. recurrence and improved survival rates
inflammatory breast carcinoma
What disorder:
-5% of breast malignancies
-invasion of dermal lymphatics with cancer cells
-rapid diffuse involvement of entire breast with erythema and edema (peau d'orange presentation)
-mimics mastitis and breast abscess --> reason you ALWAYS biopsy these
Mammogram: thick edematous skin
Dx: skin biopsy
Tx = chemo + rad + mastectomy
Prog: 30% long-term survival
paget's disease of breast
What disorder:
-3% of breast cancers
-malignancy of breast that is manifest clinically with eczematous changes with scales of nipple-areolar complex
-occasionally misdiagnosed as a dermatologic condition
Histo: neoplastic cells (paget cells) interspersed between keratinocytes of nipple epidermis
-90% associated with underlying DCIS or invasive breast carcinoma, thought that the underlying malignant cells migrate through duct system into epidermis
Tx = simple mastectomy or lumpectomy w/ rad
pregnant and lactating women
Breast cancer in ___________ involves:
-diagnosis may be delayed due to breast size and density changes
Mammogram is safe when used with shielding
Stage 1 and 2: do modified radical mastectomy instead of lumpectomy + axillary lymph node dissection and rad because you cannot expose pregnant female to rad
If there are involved LNs and chemo indicated --> delay until 2nd trimester
Termination of pregnancy is NOT part of Tx plan for breast cancer and does NOT IMPROVE SURVIVAL
males
Breast cancer in ___________ involves:
-RFs = trauma, estrogen therapy, endogenous estrogen, previous exposure to rad or Klinefelter's syndrome, FHx, Jewish ancestry
Most common = invasive ductal carcinoma
Dx = late, likely have direct extension of chest wall at this point
Tx for early-stage = modified radical mastectomy with post-op rad
cervical and breast
What are the 2 cancers most commonly diagnosed during pregnancy?
benign
80% of breast masses found during pregnancy are:
US
What should be the initial imaging modality in a pregnant patient with a breast mass?
hint: radiation concerns
Conservative management of breast cancer includes lumpectomy, sentinel lymph node bx, and post op XRT. XRT and chemotherapy during the first trimester can be harmful to the fetus and are not recommended due to teratogenic affects of fetus.
Why would a pregnant patient in her first trimester choose mastectomy over lumpectomy for treatment of her breast cancer?
Conservative management of breast cancer includes lumpectomy (anesthesia), sentinel lymph node bx (radionuclide) and post op XRT; all carry increased teratogenic risk to the fetus
Which breast cancer treatments will be harmful to the fetus?
multidisciplinary approach
Breast cancer is often treated with a(n) _________ _____ involving general surgeon/breast surgical oncologist, radiation oncologist, and medical oncologist, pathologist, which has been associated with a reduction in breast cancer mortality. Additional disciplines may include plastic surgeon, social worker, psychologist, genetic risk assessment.