Flatworms and Bilaterians
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Movement > Cephalization
Bilateral symmetry, head vs. tail.
Bilateria =
triploblasts
What phylums are important to us?
Xenacoelomorpha and Platyhelminthes
What are the subphylums of phylum Xenacoelomorpha?
Acoelomorpha
Xenoturbellida
Phylum Xenacoelomorpha; Subphylum Acoelomorpha
Small, flat, marine worms.
350 spp.
Ciliated epidermis
Ventral mouth opens into gut cavity, no anus.
Muscles present: longitudinal, circular, diagonal
Phylum Xenacoelomorpha; Subphylum Xenoturbellida
Deep sea worms
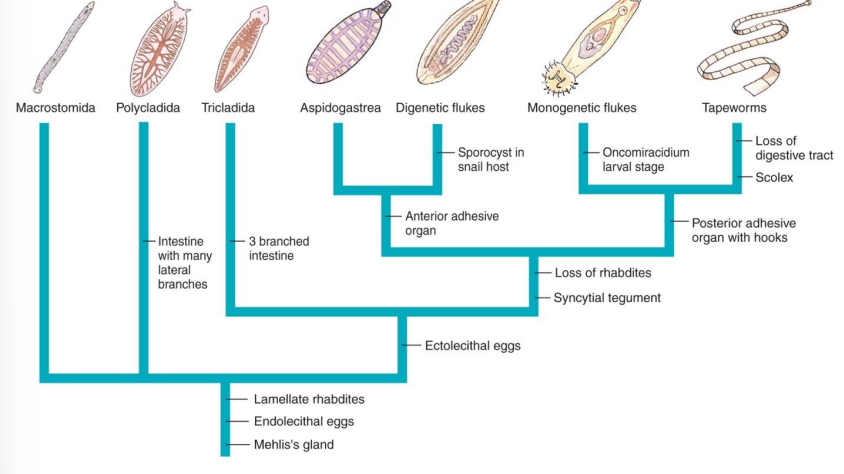
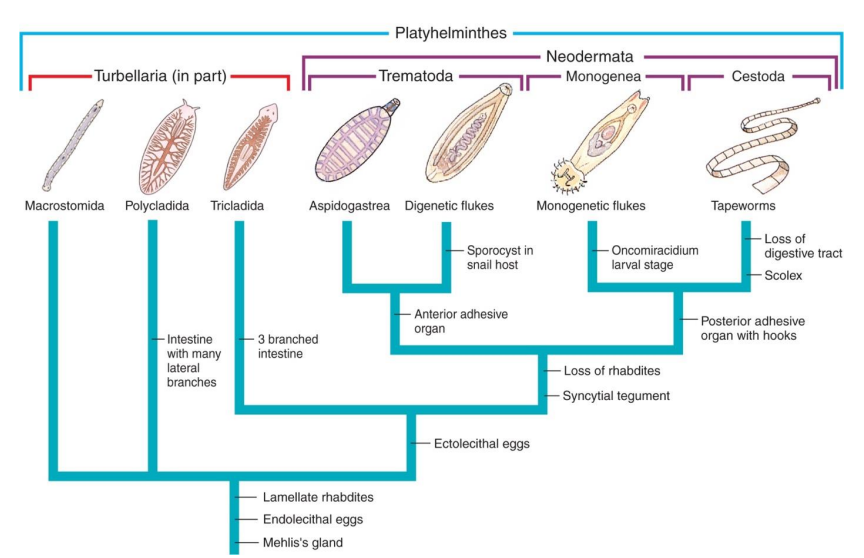
Phylum Platyholminthes: Classes
Lophotrochozoan protosome
Class Turbellaria
Class Trematoda
Class Monogenea
Class Cestoda
Class Turbellaria
Paraphyletic group; free-living
3500 spp.
Marine, freshwater, terrestrial
triclad vs. polyclad gut
penis fencing. Feeding
Class Trematoda
Parasites, generally of vertebrates; digenetic flukes.
11,000 spp.
struct. sim to turbellarians, with mods for parasitism (eg. suckers)
Class Monogenea
parasites, typically ectoparasites of fish gills; monogenetic flukes
1100 spp.
Simple Life Cycle, single host
egg > oncomiracidium > adult parasite
Class Cestoda
parasites (in gut of vertebrates); tapeworms
3400 spp.
Class Cestoda: Body Plan
Composed of posterior scolex, repeating segments (proglottids), making the strobila
No gut, absorb nutrients through skin
Each proglottid contains both male and female organs
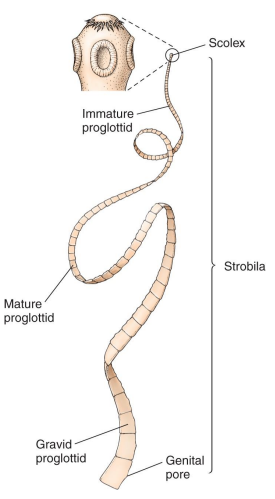
Class Cestoda: Beef tapeworm
Taenia saginata
Life Cycle
Adult (in human) > zygote > shelled larva (in grass) > cysticercus juvenile (in cow) > human
Phylum Platyhelminthes: Basic Bodyplan
Bilateral symmetry
Triploblastic
Acoelomate
Dorsoventrally Flattened
Cephalized
Flatworm Structure
“Planarian” - freshwater turbellarian
ciliated epidermis with rhabdites
body wall muscles, also muscles around pharynx
Planarian
extendable pharynx
branched gut or gastrovascular cavity
CNS
Sense organs
Excretory system of protonephiridia
Well developed reproductive system
No respiratory or circulatory systems
Planarian Regeneration
Important model organism for developmental biology
Class Trematoda: Chinese Liver Fluke
Clonorchis sinensis
Complex life cycle
adult > egg > miracidium > sporocyst > redia > cercaria > metacercaria
snails (and fish) are intermediate hosts, vertebrates are definitive hosts
Class Trematoda: Blood Flukes
Schistosoma spp.
responsible for schistosomiasis
affects 200 million people worldwide
Life Cycle:
adult > egg > miracidium > sporocyst > cercaria