Ch. 2 Electrostatics
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
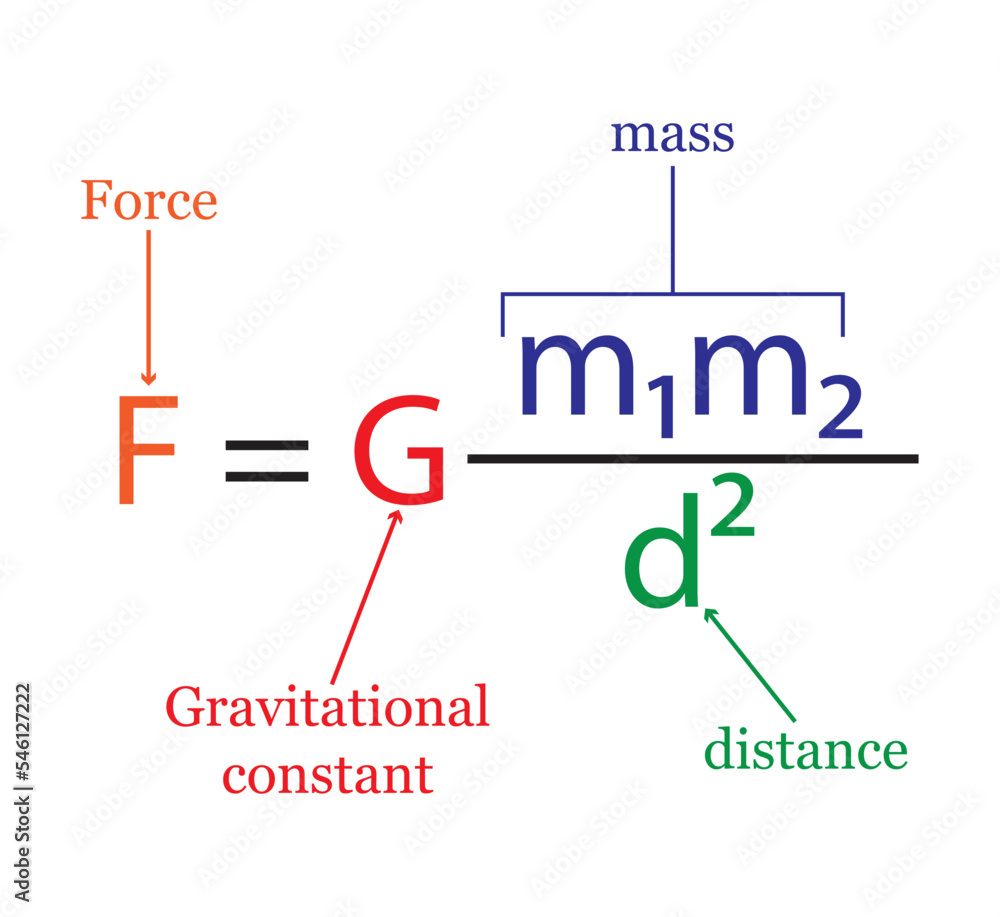
force of gravity formula
gravitational constant: 6.67 × 10^-11 Nm²/kg²
coulomb’s law
k=9.0 × 10^9 NR²/C²


r-r’
Electric Field of a Point Charge
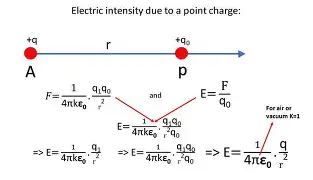
Force of a Charge
Fq=qE
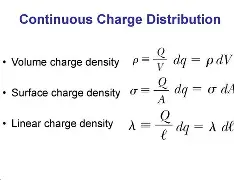
Electric Fields of Continuous Distributions
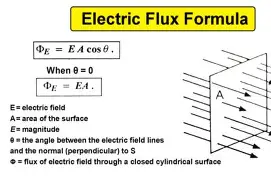
Electric Flux Formula
Gaussian Surface
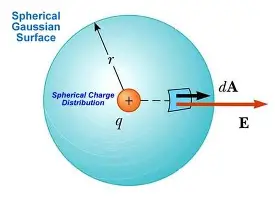
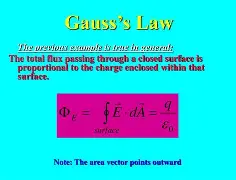
Gauss’s Law
∇⋅E=ρ/ε₀
Insulating & Conducting Surfaces
Qenc=σA
Insulating Surface: σ/2ε₀
Conducting Surface: σ/ε₀
Electric Potential
V(xo)-V(xa)=kQ/rb-kQ/ra)=-∫(xa→xb) E⋅dl
as long as xa/=xb, then this formula is path independent
if xa=xb, then E⋅dl = 0
∇x E =0, the curl of an electric field vanishes when it is a possible electric field
Electric Potential due to a Point Charge
V=kQ/r
Electric Field & Electric Potential Relation
E=-∇V
Volt → Energy Conversion
1 Volt = 1 Joule/Coulomb
Electric Potential due to Continuous Distribution
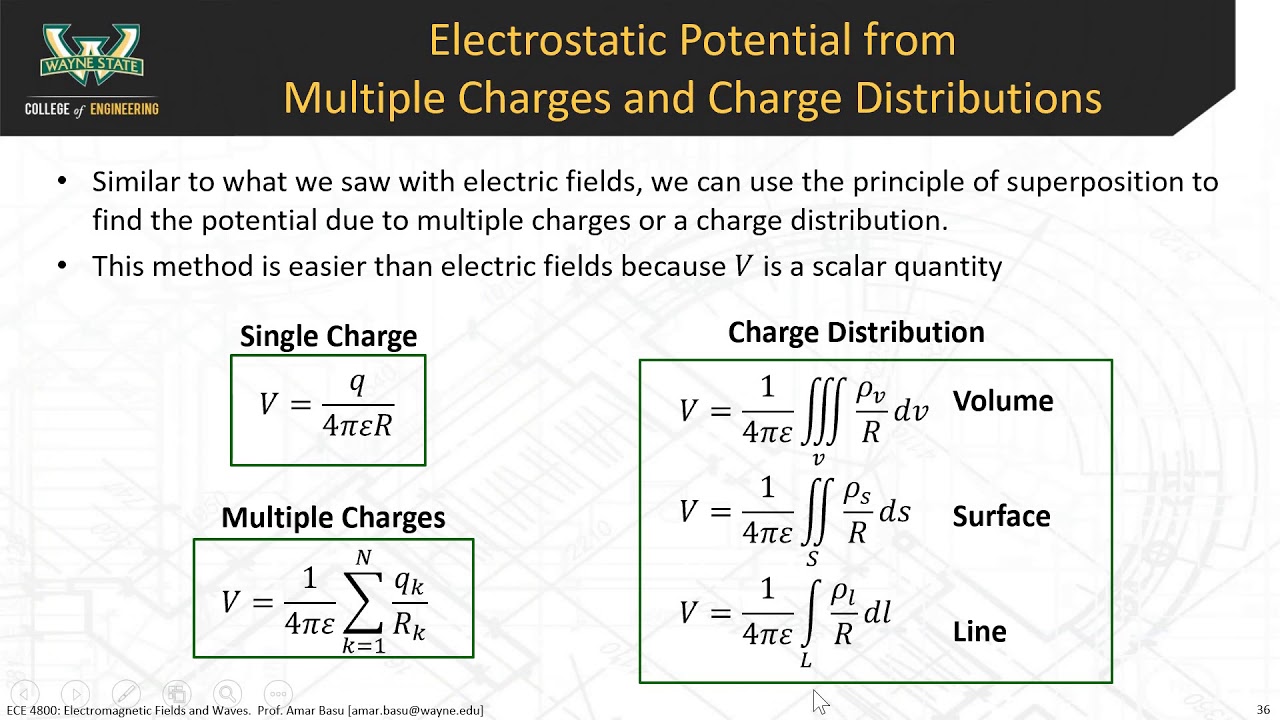
Work due to Electric Potential
W=qV
sum of charge distribution
W=Q²/8πε₀²R=1/2∫ρVdτ
U=(ε₀/2)E²
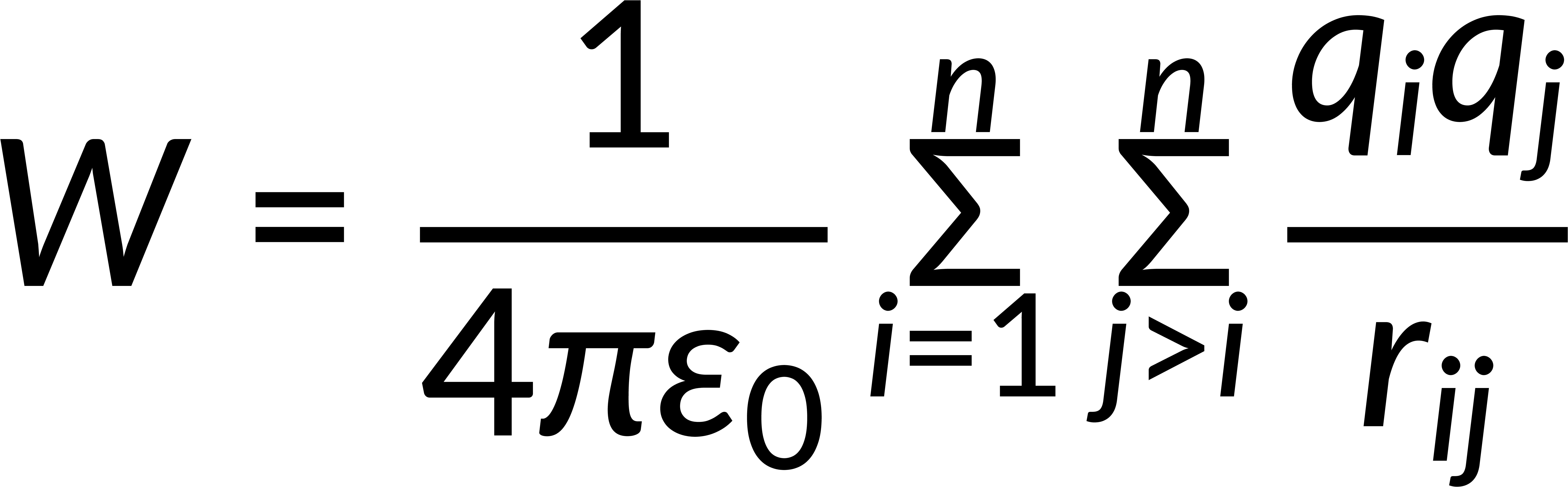
Laplacian of Electric Potential
∇²V=ρ/ε₀
Relationship between Electric Field, Electric Charge, and Electric Potential
E=-∇V=k∫ρ(r’)/(r-r’)dτ
V=-∫E⋅dl=k∫ρ(r’)/(r-r’)dτ
ρ=-ε₀∇²V=ε₀(∇⋅E)
Capacitors
Q=CV
C=ε₀A/d