P8: Forces in balance
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Scalar quantity
Only have magnitude (size)
6 examples of scalar quantities
Mass
Temperature
Speed
Energy
Distance
Time
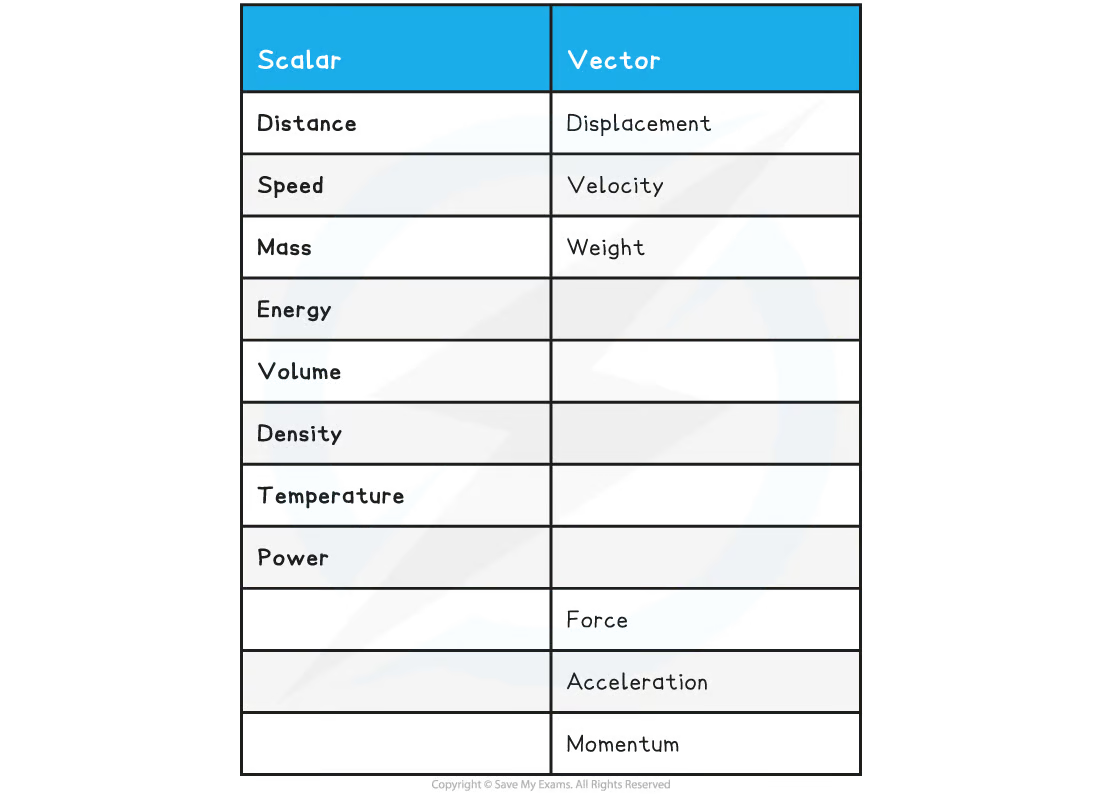
Vector quantity
Have magnitude and direction
6 vector quantity examples
Displacement
Weight
Force
Velocity
Acceleration
Momentum
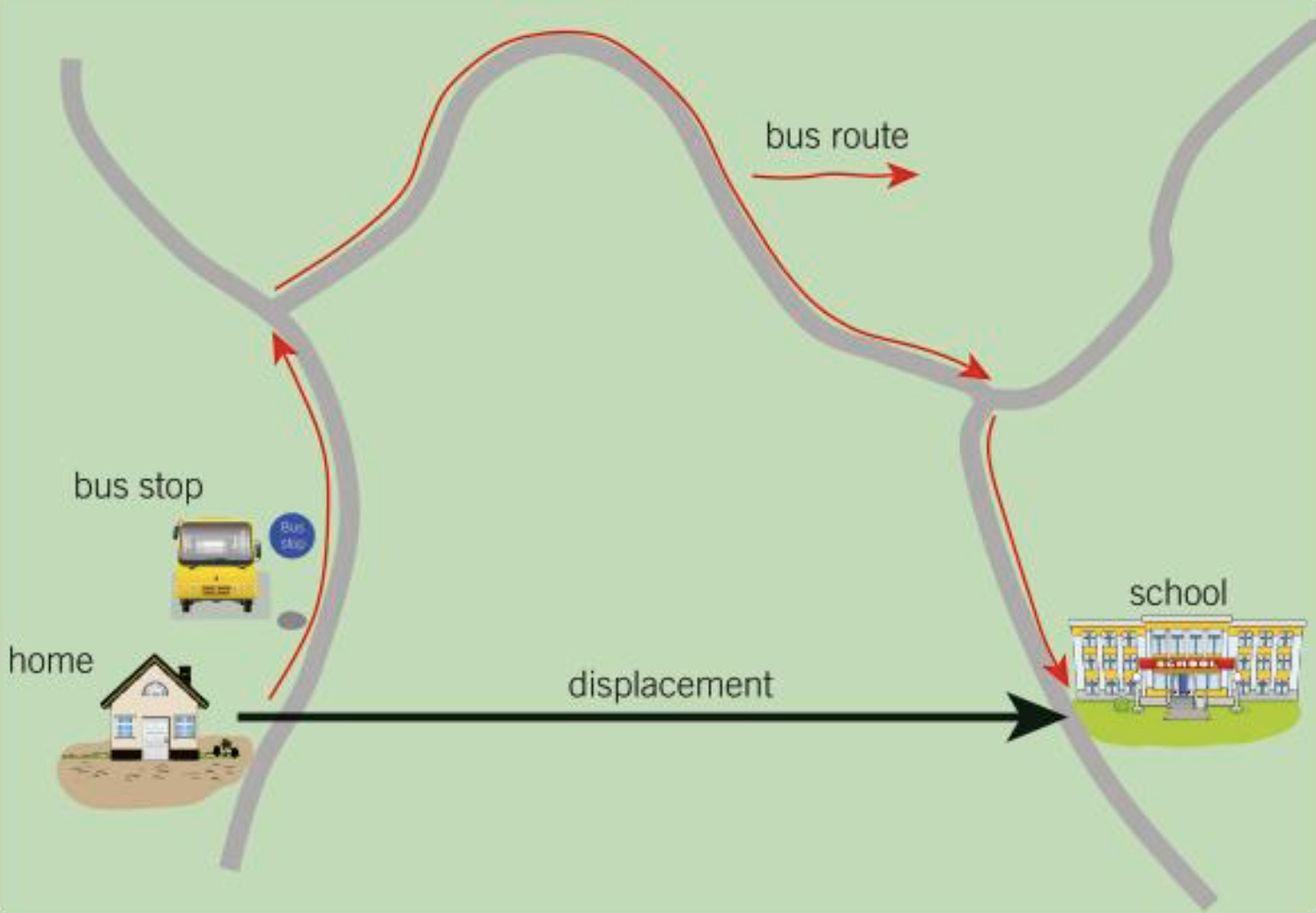
Is displacement vector or scalar?
Vector
Distance given direction
Eg 500 m (magnitude) due west (direction)
How do you represent vectors?
Arrows
Length of arrow = magnitude of vector
Direction of arrow = direction of vector
Is force a vector or scalar quantity?
Vector
F = m x a
Size + direction
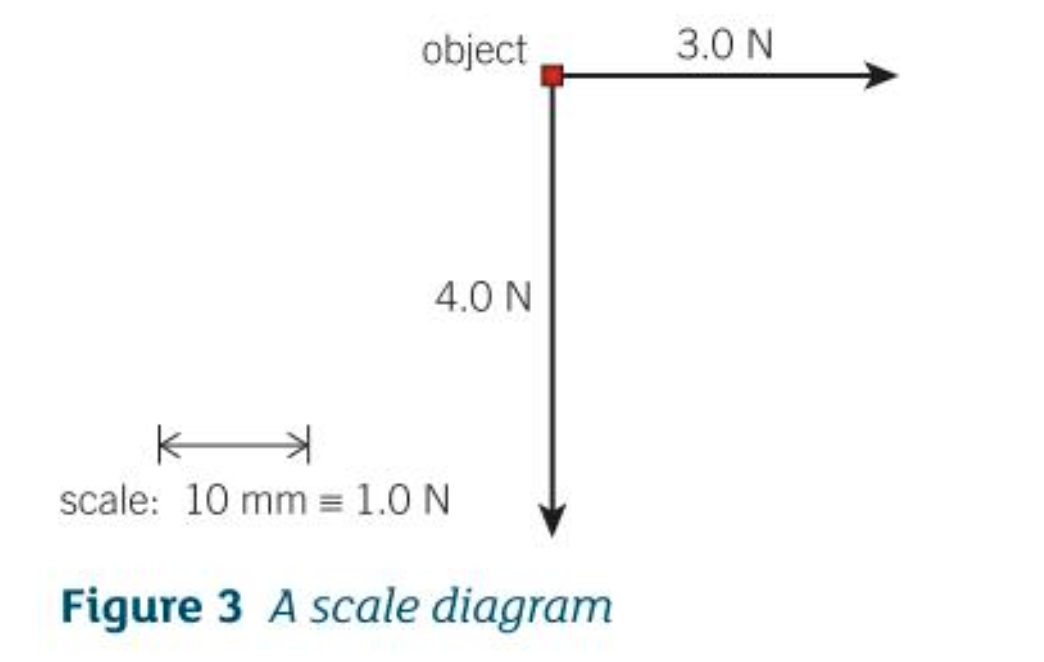
How do you represent forces on an object when more than 1 force acts on the object?
Scale diagram
1 unit of distance represents a force of 1N
30 mm arrow and 40 mm arrow
Vector quantities of distance, speed and mass
Distance, displacement
Speed, velocity
Mass, weight
Force
A push or pull that acts on an object due to the interaction with another object
Vector, N
Contact forces
Force that acts between objects that are physically touching
Example of contact forces
Friction
Air resistance
Tension
Normal contact force
Example of how air resistance is a contact force- use example of a skydiver
As they fall through the air, air particles collide with the parachute
Causes force of AR to act upwards
Normal contact force/reaction force
An object at rest on a surface exerts a force on the surface
Reaction force acts at right angles to the surface
Non-contact forces
A force that acts at a distance when objects are physically separated
Examples of non-contact forces
Gravitational force- attracts all objects to other objects
Electrostatic force- betw 2 charged objects (attraction/repulsion)
Magnetic force- experienced by certain objects in a magnetic field
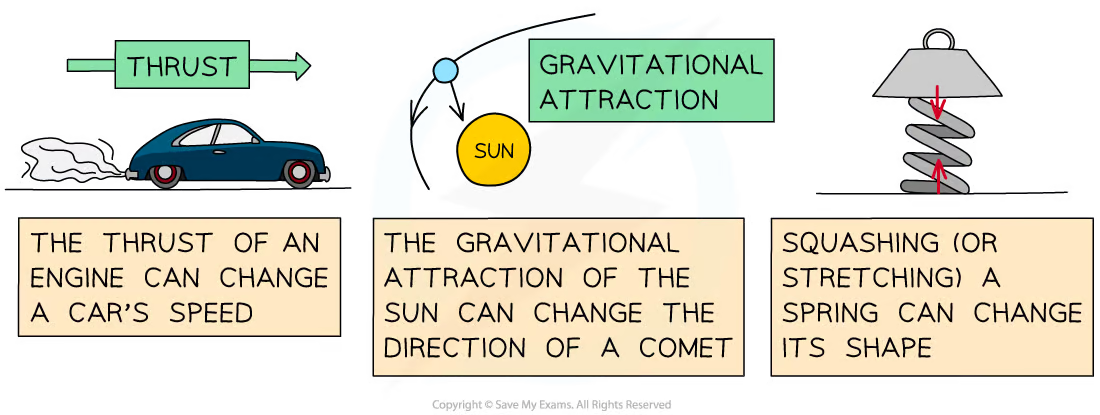
Effects a force can have on a body
Can change their:
Speed
Direction
Shape
Newton’s 3rd law of motion
When 2 objects interact with each other, they exert equal + opposite forces on each other
When a car moves forward:
The force of friction of the…
Road on the tyre = in the forward direction
Tyre on the road = in the reverse direction
Force equation
force (N) = mass (kg) × acceleration (m/s²)
Resultant force
A single force that has the same effect as all forces acting on the object
Altitude
Height above ground
Newton’s first law of motion
When forces acting on an object are balanced….
Resultant force on object = 0
If the object is:
At rest → it stays stationary
Moving → keeps moving w same speed + direction
Free body scale diagram of an aeroplane flying at a constant altitude at a constant velocity
Up + down arrows same length = balanced = constant altitude
Front + back arrows same length = balanced = constant velocity
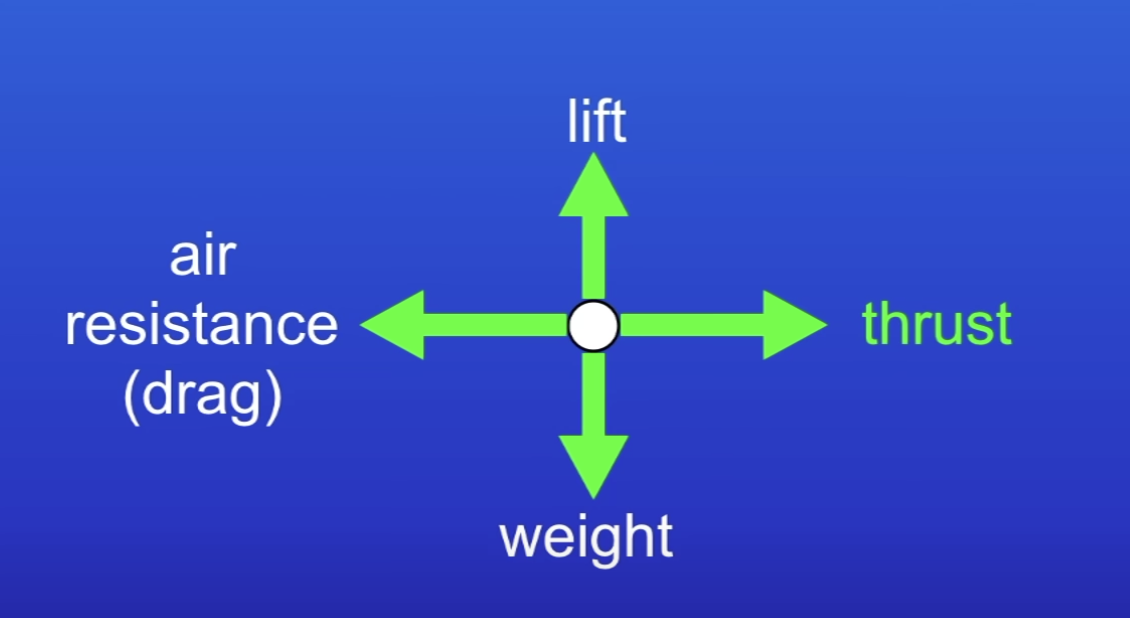
If 2 forces acting on an object have a 0 resultant force then the forces must be…
Equal + act in opposite directions to each other
What happens when forces acting on an object are unbalanced?
(resultant force isn’t 0)
An object will
change speed (accelerate or decelerate)
or change direction
When an object is acted on by 2 unequal forces acting in opposite directions, the resultant force is…
Equal to the difference between the 2 forces
In the direction of the larger force
Free-body force diagram of an object
Shows all the forces acting on 1 object
Object = dot
Forces = arrow
Moment of a force
The turning effect of a force about a pivot
What does the moment of a force measure
The turning effect of a force on an object
Moment (Nm) of a force equation
Force (N) x distance (d) = Moment (Nm)
M=fd
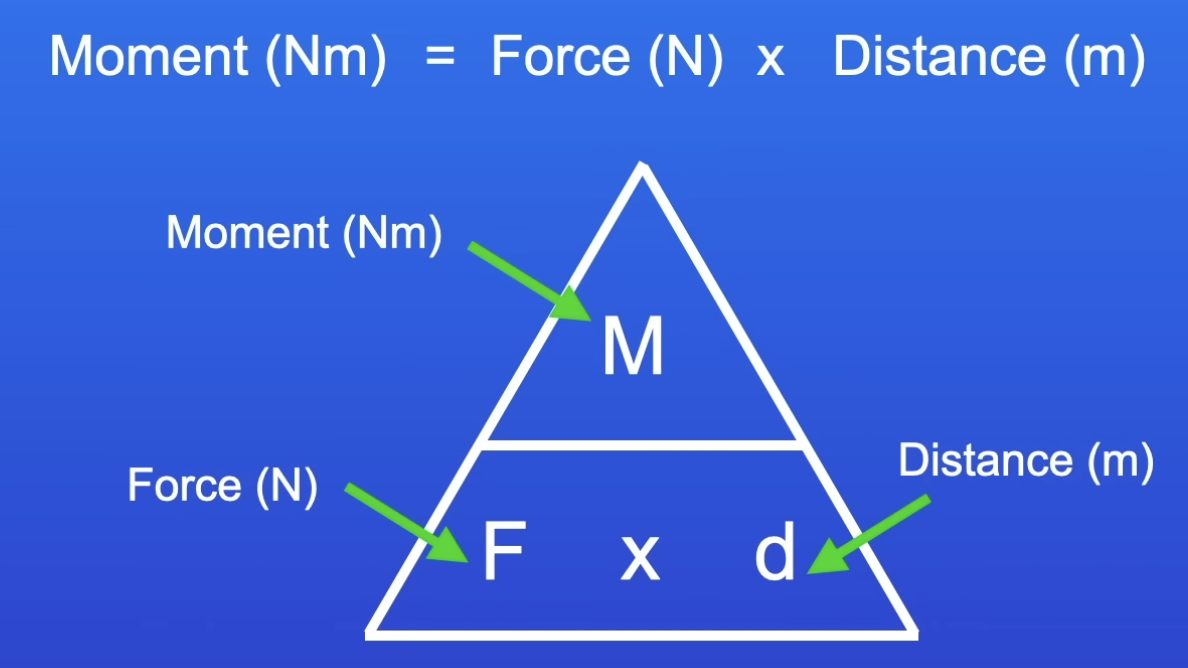
Distance when calculating the moment of a force
d must be perpendicular from the line of action of the force to the pivot
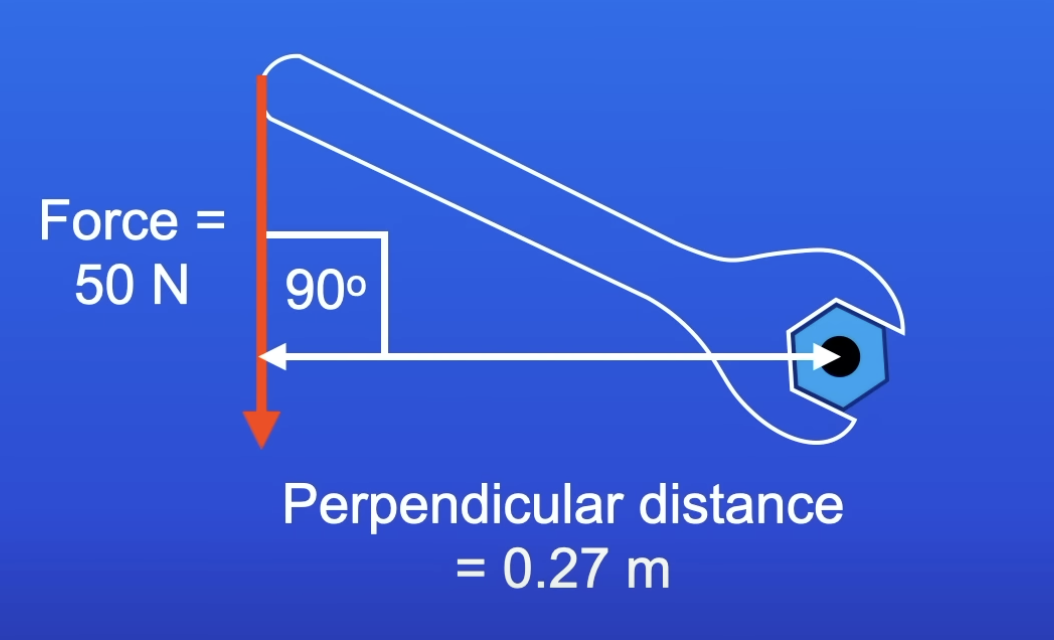
How can you increase the turning effect (moment) of a force?
Increase size of the force (F)
Increase d- use a spanner with a longer handle
Load
Weight of the object
Effort
Force the person applies to the crobar
Line that a force acts along
Line of action
Why levers are force multipliers?
Can exert a force greater than the effort
Effort can move a greater load
Pivot
Point of rotation
Examples of levers
Hammer- to remove a nail
Crowbar- to lift a plank of wood
What does a lever allow us to do?
Lift a heavy object by applying a small amount of force
What can levers and gears do?
Transmit the turning effects of forces
What do gears do if:
gear A is connected to the turning force of the engine
+ gear B is connected to the wheels?
Transmits the turning force from the engine to the wheels
Describe the turning effect of these 2 gears and why
gB = 2x the radius of gA
TE of gB = 2x as large as gA
gA rotates 2x everytime gB rotates 1
So WD by 2 gears = same
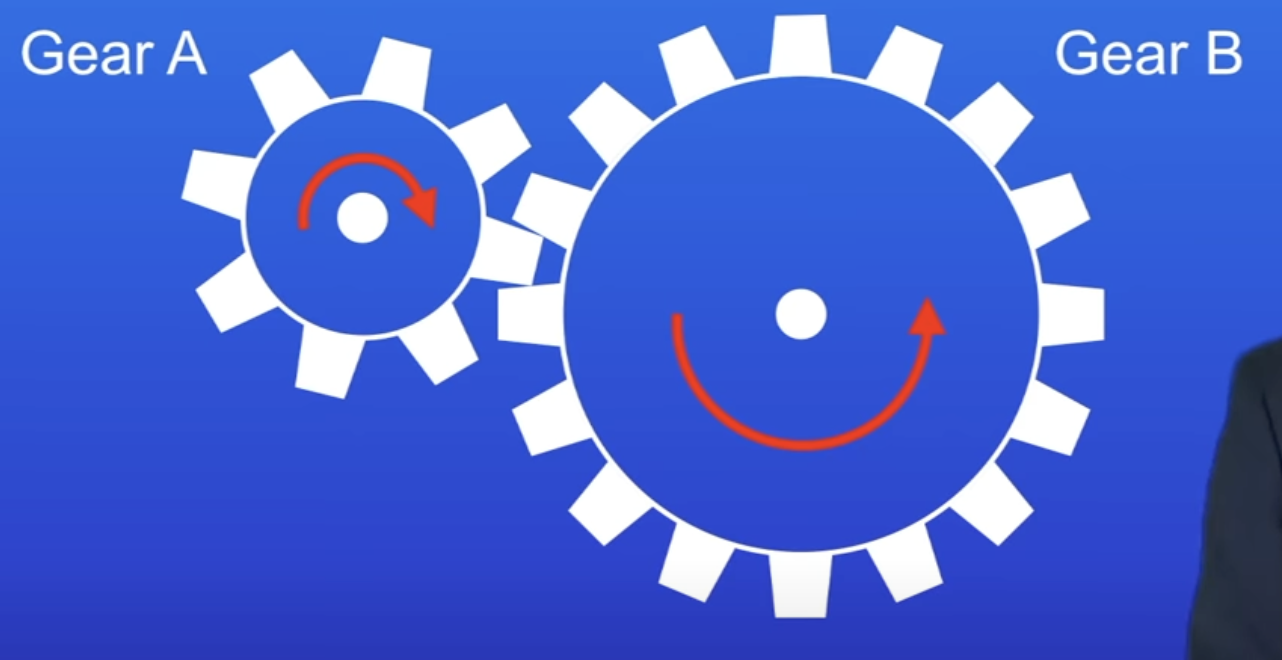
How do gears work?
1 gear turns → the other must also turn
Gears meet → teeth will move in the same direction (e.g. downwards)
Then 1 gear will move move clockwise, + the other anticlockwise (in opposite directions)
What does the moment (TE) produced by a gear depend on if the force applied to both is the same?
Size of the gear
radius of the gear (from pivot)
Why does the moment produced by a gear depend on its size?
TF on the larger gear acts further from its pivot than the TF of the smaller gear wheel acting on its pivot
M = Fd
What happens when a low gear is chosen?
Small gear turns large gear
Large gear turns slower
TE of large gear > small
What happens when a high gear is chosen?
Large gear turns small gear
Small gear turns faster
TE of small gear < large
Low gear vs high gear
L- Low speed, high TE
H- High speed, low TE
When an object is balanced…
Total clockwise moment about a pivot = total AC moment about that pivot
AC x m = C x m
What do gears do?
Change the moment of a turning effect
How can gears increase the moment of a turning effect (give a bigger TE)
Small gear must drive a large gear wheel
Gravity
Force of attraction between objects
Non-contact force
Vector
Mass
How much matter is in an object
Scalar
kg
Doesn’t depend where an object is
Weight
Force acting on an object due to gravity
Newton
Gravitational field strength (g)
A measure of the force of gravity in a particular location
Weight equation
Mass (kg) x g (N/kg) = Weight (N)
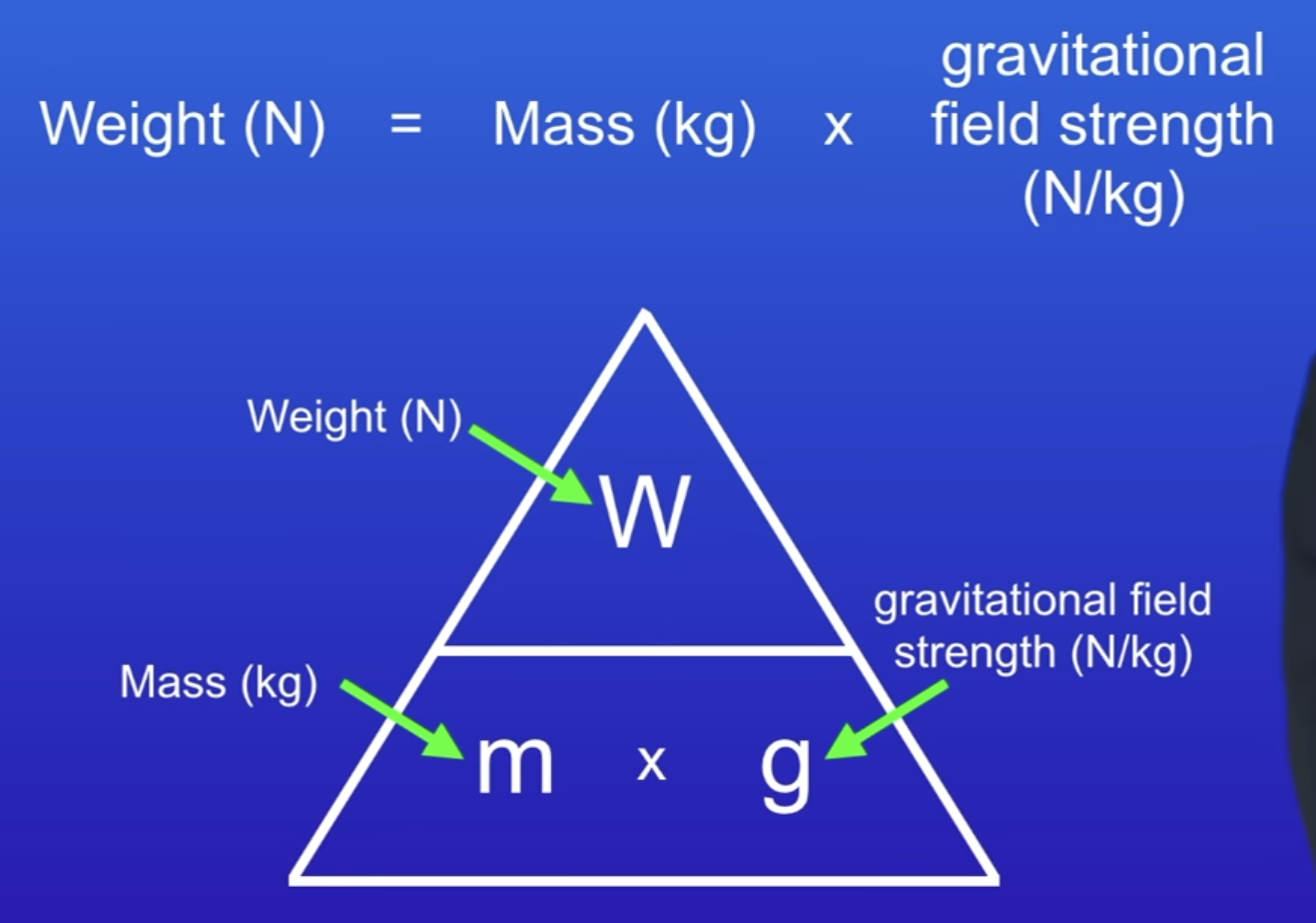
Relationship between weight and mass of an object
Weight of an object directly proportional to its mass
Weight ∝ Mass
Double mass = double weight
How can you measure an objects weight?
Newton meter or calibrated spring balance
Centre of mass
The single point through which the weight of an object acts
Where is the centre of mass of a uniform ruler?
Its midpoint
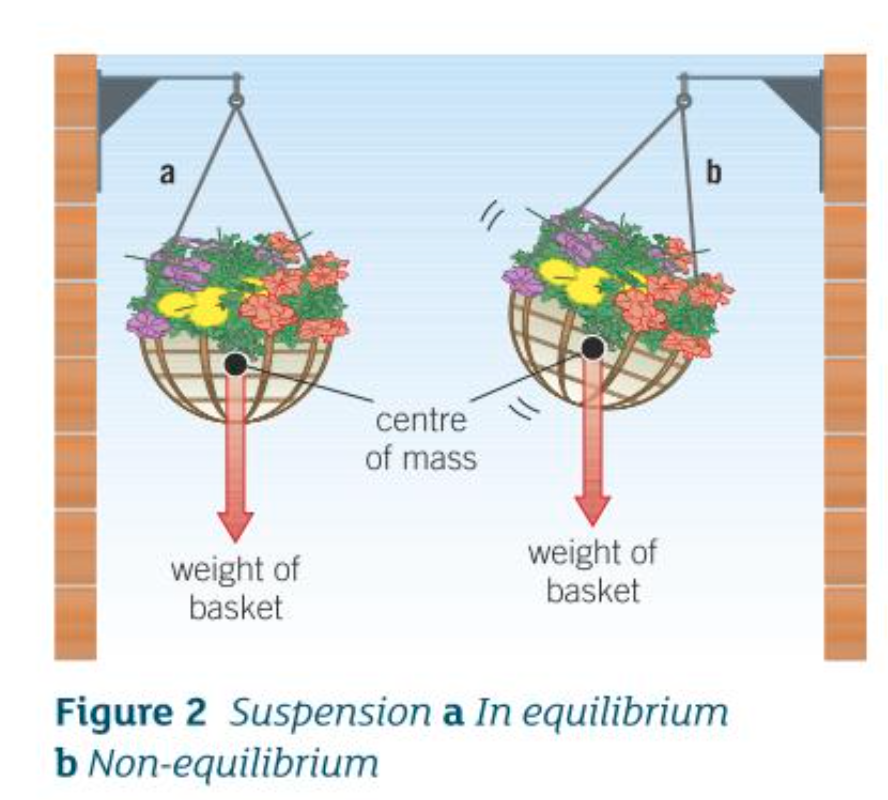
Suspension in equilibrium:
What happens when you suspend an object and then release it?
Comes to rest (equilibrium) with its CoM directly below the point of suspension
Its weight doesn’t exert a TE on the object → as its CoM is directly below the point of suspension
Suspension in non-equilibrium:
What happens when you turn an object from its equilibrium position?
Returns back to its equilibrium position
As its weight has a TE that returns an object to equilibrium
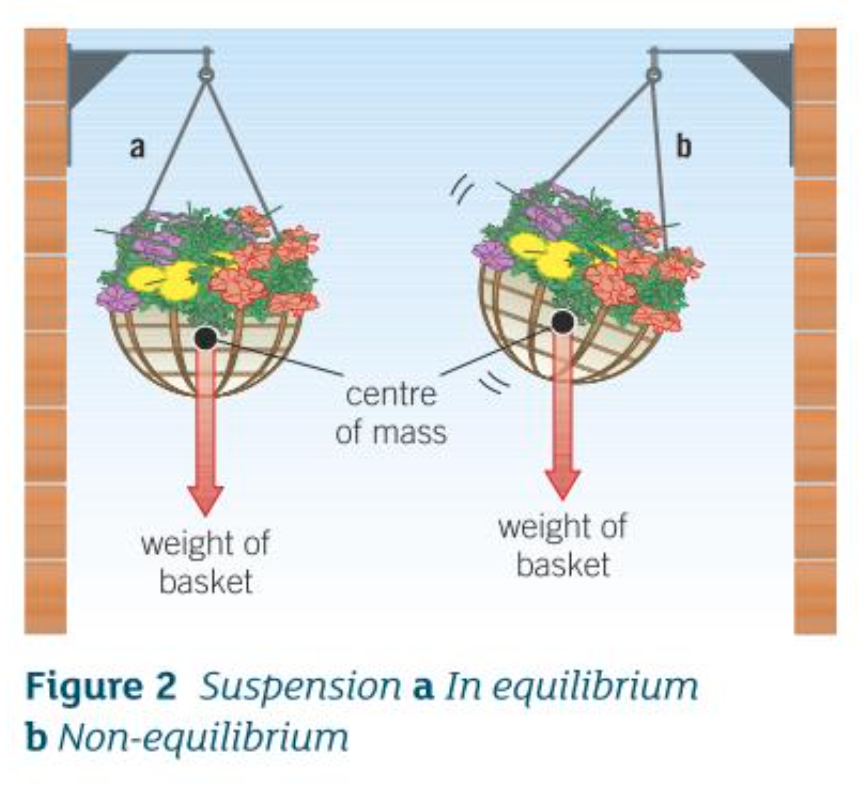
What does it mean if an object is freely suspended?
It returns to its equilibrium position after the turning force is taken away
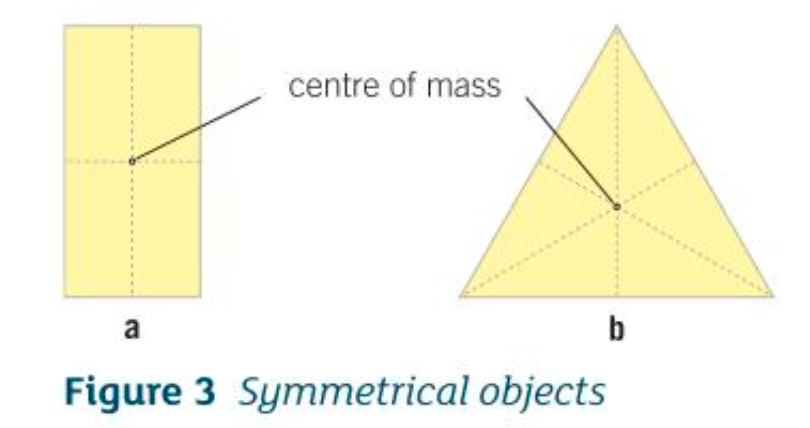
Where is the centre of mass of a symmetrical object?
Along the axis of symmetry
More than 1 axis of symmetry → where they meet
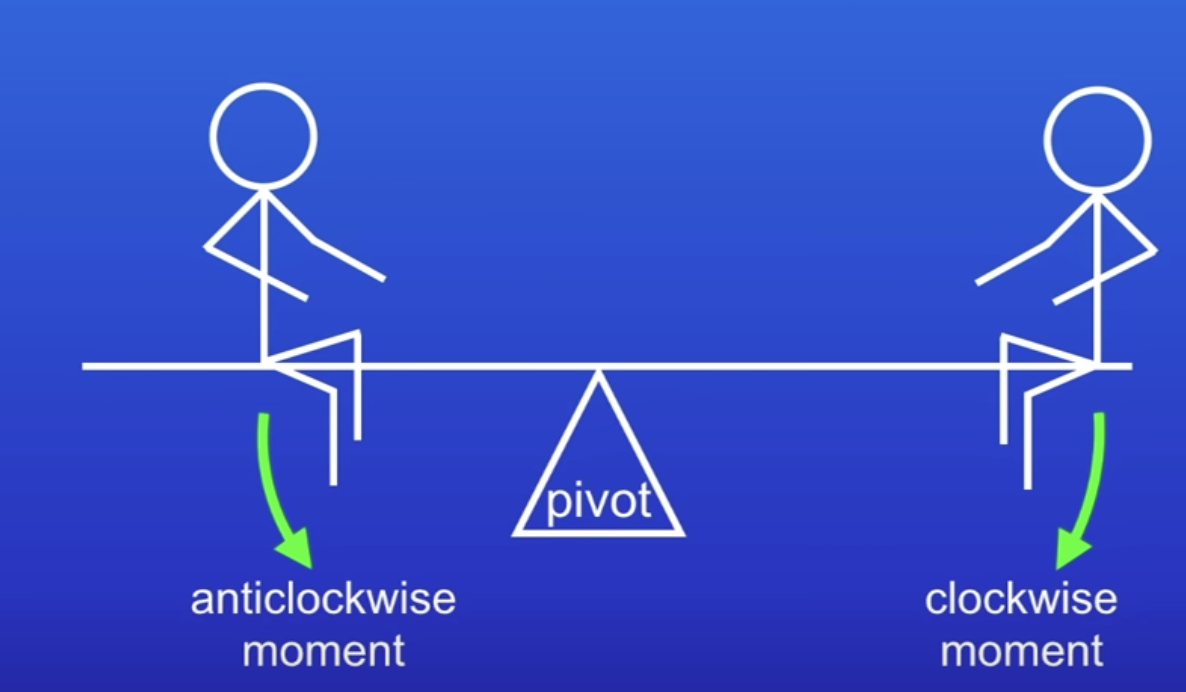
Balanced moments
Clockwise moment = anticlockwise moment
W1d1=W2d2
What happens when moments are balanced
Resultant moment is 0
Object does not move or turn
Principle of moments
If an object is balanced:
Total C moment about a pivot = total AC moment about that pivot
Forces that can turn an object at a fixed point
All forces acting on an object that don’t pass through a fixed point
How do you know if a turning force will turn an object clockwise or anticlockwise
Depends on the
Direction of the force
Position of the fixed point
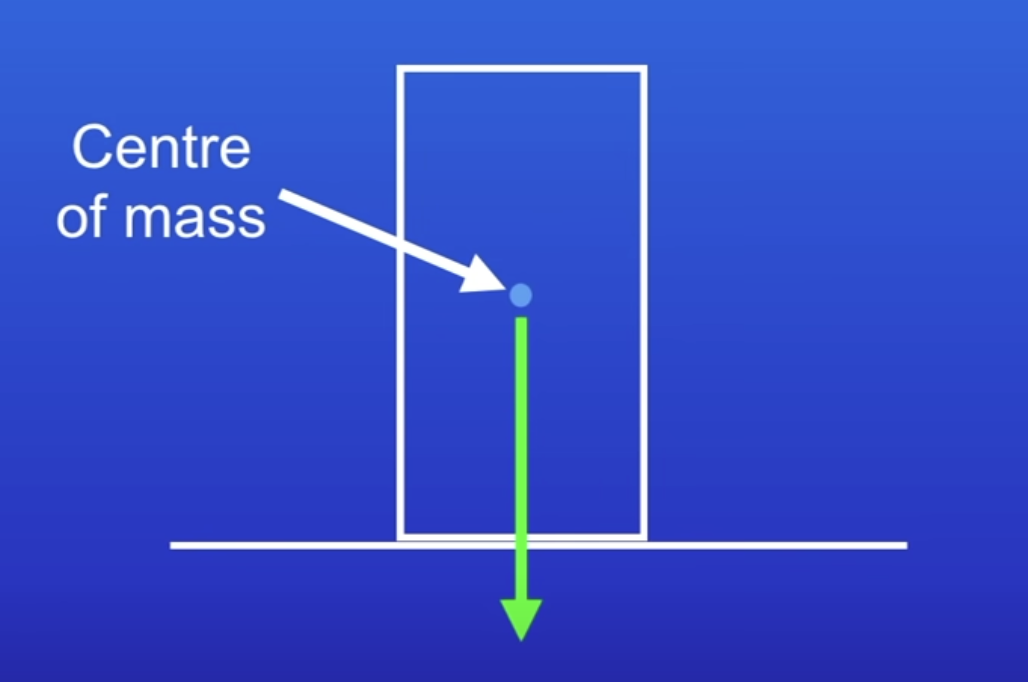
Why do objects remain stationary?
Use the example of a block on a flat surface
Weight of the block acts directly down from the CoM
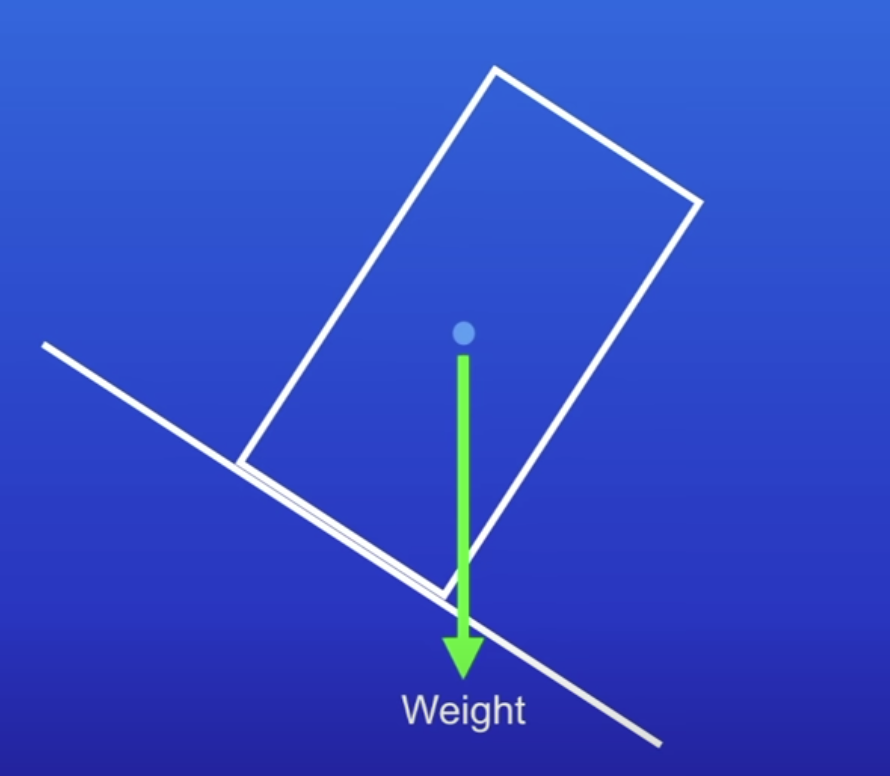
Why do objects topple?
Tilt the block → line of action of the weight is outside the base of the object
→ resultant unbalanced moment acting on the block
Conditions for an object to be in equilibrium
Resultant force on it is 0
Forces acting on the object have no overall turning effect
What does the weight of an object depend on?
The GFS at the point where the object is
What can a single force be resolved into?
2 forces acting at right angles to eachother
The 2 component forces tog have the same effect as the single force
If the resultant force is 0, what happens if an object is
At rest
Moving
Remains stationary
Keeps moving in the same direction + speed
If 2 forces act on an object along the same line, the resultant force is:
Sum- if Fs act in same direction
Difference- if Fs act in opposite direction
When is work done on an object?
When a force causes an object to move thru a distance
A force does work on an object when…
The force causes a displacement of the object
1 J of work done =
1 N force causes displacement of 1m
How do frictional forces lead to an increase in temp?
WD against FF acting on an object cause a rise in the temp of the object
What can cause an object to rotate?
Force / system of forces
If an object is balanced (in relation to moments)
Total C moment about a pivot = total AC moment about the pivot
A lever used as a force multiplier…
Exerts a greater force than the force applied to the lever by the effort
What are gears used to do?
Change the moment of a turning effect
How is a lever a force multiplier
Force applied to lever is further away from pivot + smaller in size than the force the lever applies on the object
If someone sits at the centre of a seesaw, why is the moment about the pivot 0?
Weight of the person acts downwards thru the pivot