CIE IGCSE Biology Unit 21: Human Influences on Ecosystems
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
How modern technology has resulted in increased food production?
- agricultural machinery to use larger areas of
land and improve efficiency
- chemical fertilisers to improve yields
- insecticides to improve quality and yield
- herbicides to reduce competition with
weeds
- selective breeding to improve production
by crop plants and livestock, e.g. cattle, fish
and poultry
social, environmental and economic implications of providing sufficient food for an increasing human global population
Economy:
-Higher energy prices as sources are depleted
-The gap between rich and poor becomes more evident.
Enviromental:
-Increased carbon emissions cause global warming
-Air pollution from factories as countries industrialise and exploit resources
Social:
-Unemployment due to reduced labour force in rural area

problems which contribute to famine
- unequal distribution of food,
- drought and flooding
- increasing population
- poverty

negative impacts to an ecosystem of large-scale mono-cultures of crop plants
-reduced diversity of plants and animals -increased difficulty in nutrient recycling -increased pesticide use and the use of unsustainable practices resulting in decreased yields

negative impacts to an ecosystem of intensive livestock production
-reduced diversity of plants and animals -increased difficulty in nutrient recycling
-increase in biomass production
-increase in methane and carbon dioxide production

reasons for habitat destruction
- increased area for food crop growth,
livestock production and housing
- extraction of natural resources
- marine pollution

undesirable effects of deforestation on habitat destruction
- extinction
- loss of soil
- flooding
- increase of
carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
undesirable effects of deforestation on the environment
-Loss of biodiversity
-Loss of habitat
-Loss of hiding place for prey from predators
-Soil erosion
-Global warming
sources and effects of pollution of land and water
insecticides, herbicides and nuclear fall-out

sources and effects of pollution of water
chemical waste, discarded rubbish, untreated sewage and fertilisers
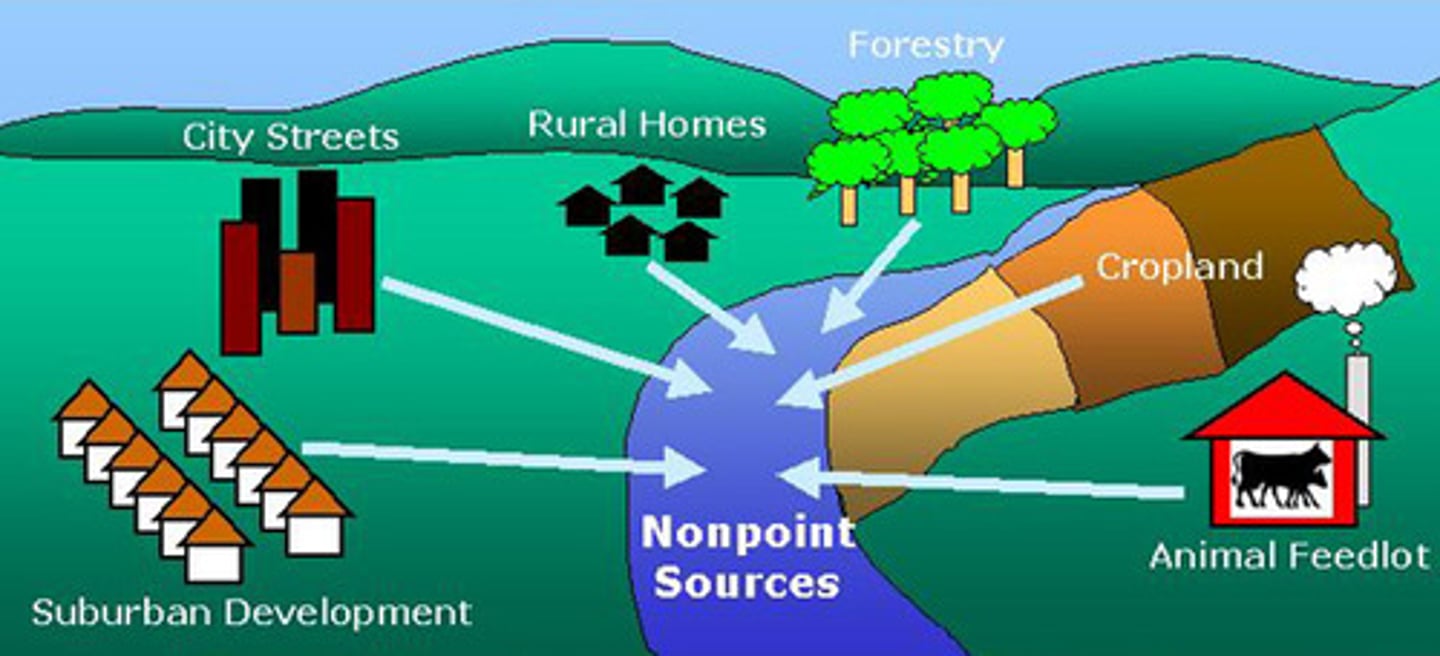
eutrophication
A process by which phosphorus and nitrogen, become highly concentrated in water, leading to increased growth of algae or cyanobacteria.
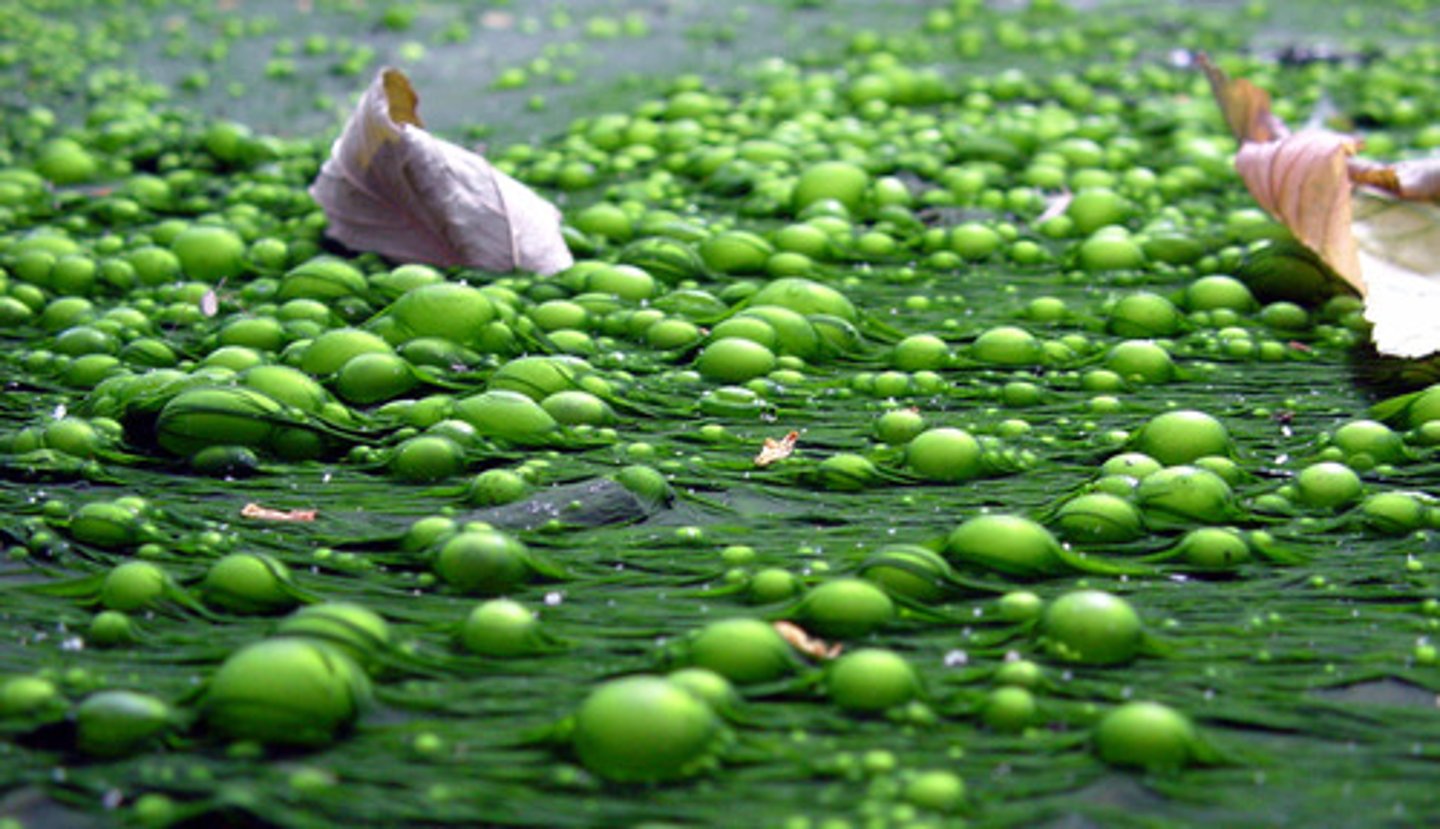

process of eutrophication of water
- increased availability of nitrate and other
ions
- increased growth of producers
- increased decomposition after death of
producers
- increased aerobic respiration by
decomposers
- reduction in dissolved oxygen
- death of organisms requiring dissolved
oxygen in water

effects of non-biodegradable plastics in the environment
-Animals that consume plastic will choke
-Burning of plastic releases toxic gases
-Fills up land fill sites and takes long time to degrade

sources and effects of pollution of the air by methane and carbon dioxide
- enhanced greenhouse effect
- climate change
greenhouse effect
the trapping of the sun's warmth in a planet's lower atmosphere due to the greater transparency of the atmosphere to visible radiation from the sun than to infrared radiation emitted from the planet's surface
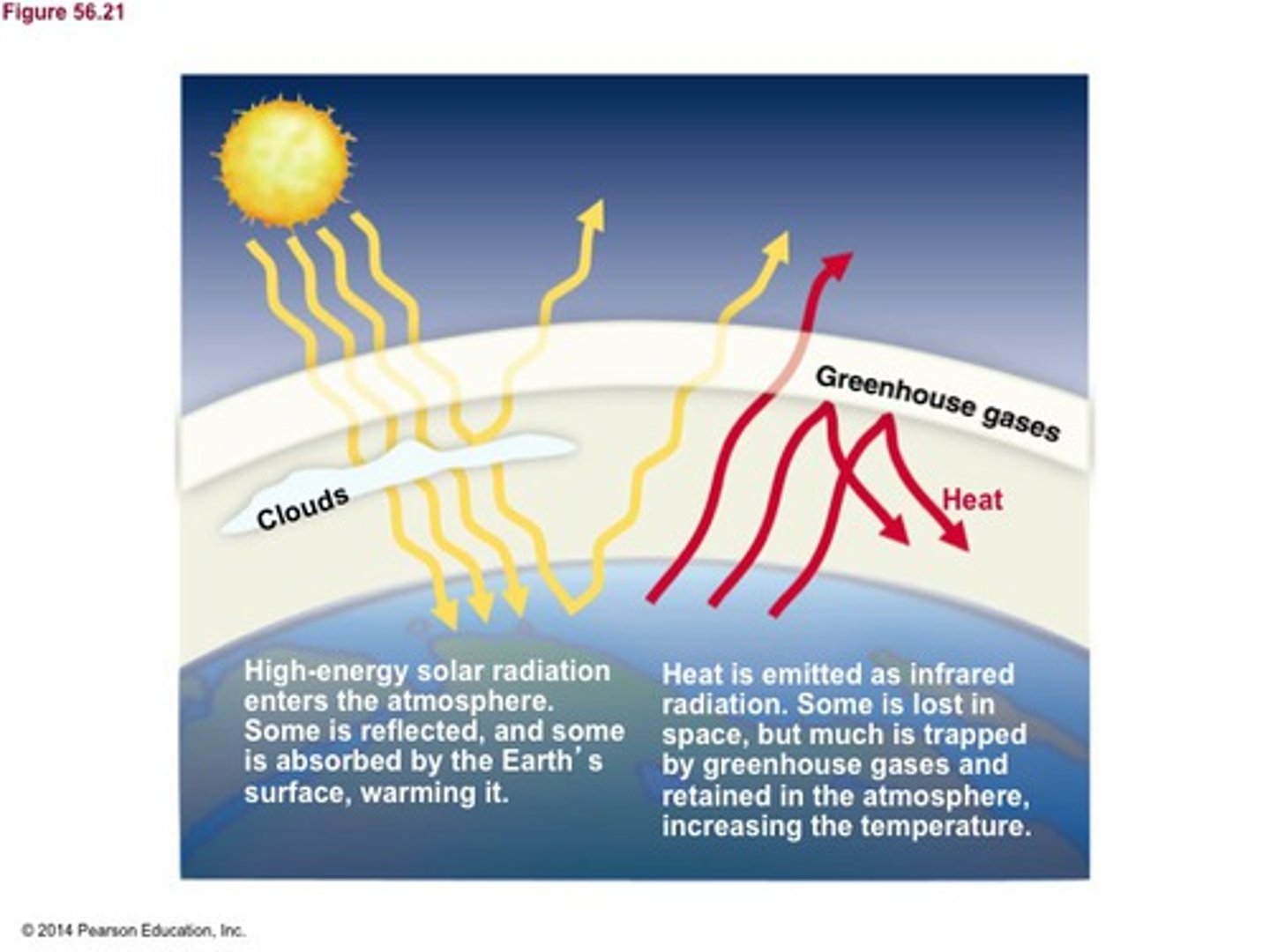
climate change
a change in global or regional climate patterns

causes and effects on the environment of acid rain
Burning of fossil fuels causes release of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide which mixes with water to form nitric and sulphuric acid
-Causes infertile soil
-Causes acidified water in lakes that kills aquatic life
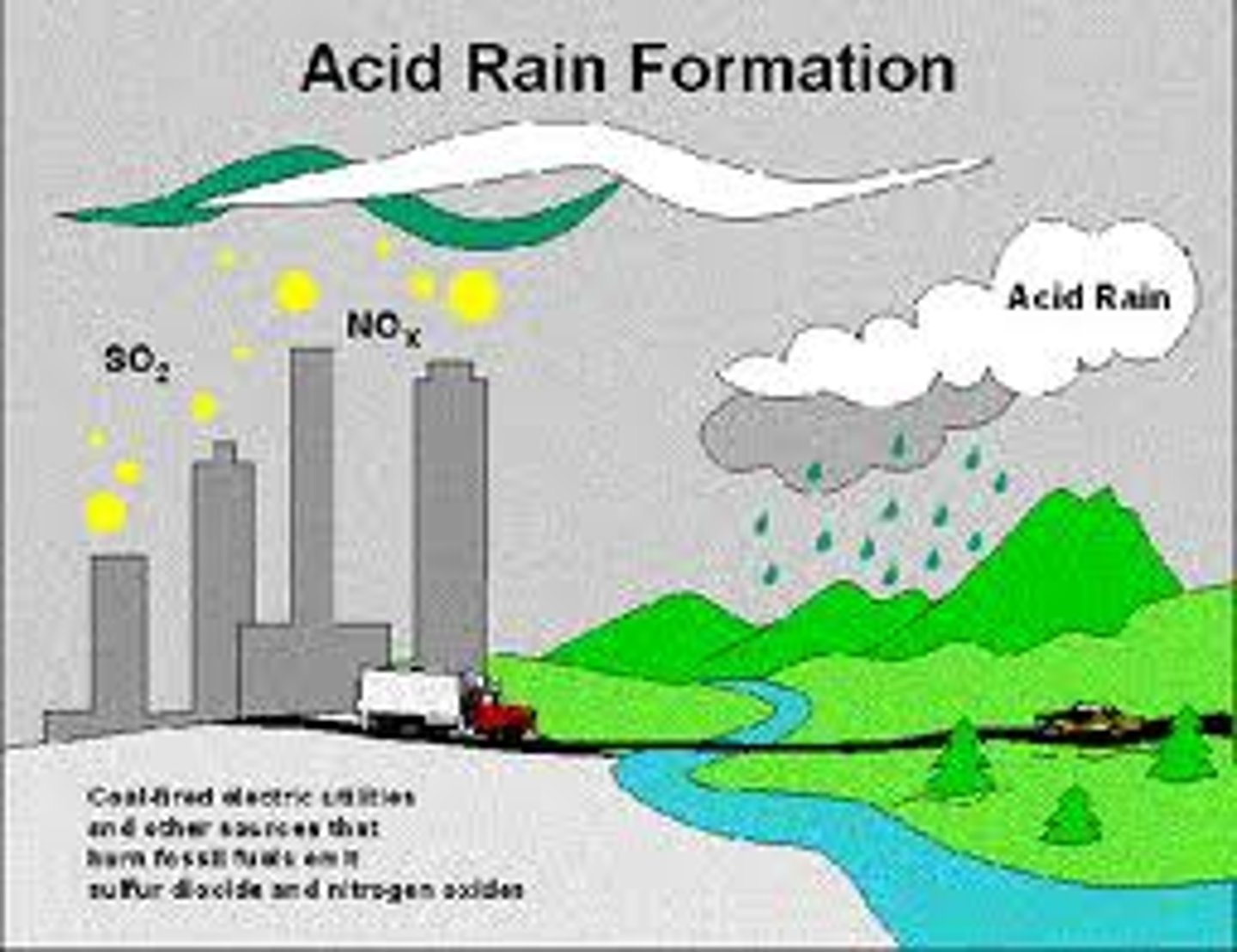
measures that are taken to reduce sulfur dioxide pollution (acid rain)
-Low sulphur fuels
-flue gas desulphurisation: uses limestone to react with gases before being released into atmosphere
-catalytic converters: reduces nitrogen oxides in fumes of cars
How increases in carbon dioxide and
methane leads to climate change?
Carbon dioxide is a heavy gas that traps heat in the atmosphere
Methane absorbs heat increasing temperature of atmosphere

negative impacts of female contraceptive hormones in water courses
- reduced sperm count in men
- feminisation of aquatic organisms
sustainable resource
produced as rapidly as it is removed from the environment so that it does not run out

sustainable development
development providing for the needs of an
increasing human population without harming the environment

sustainable development requirement
- management of conflicting demands
- planning and co-operation at local, national
and international levels
Explain the need to conserve fossil fuel
It is a unrenewable fuel source that takes long time to produce
How forests and fish stocks can be sustained?
- education
- legal quotas
- re-stocking
Safe sewage treatment process
-Stone and sand filter to remove large impurities
-activated sludge process where air is pumped through sewage in which bacteria use to break down organic matter in water
-sludge is produced and used as starter culture for the next secondary treatment

Why organisms become endangered or extinct?
- climate change
- habitat destruction
- hunting
- pollution
- introduced species

risks to a species if the population size drops, reducing variation
-loss in vigor
-loss in individuals with resistance to diseases
-loss individuals with resistance to change in enviroment
-loss in biodiversity
How endangered species can be conserved?
- monitoring and protecting species and habitats
- education
- captive breeding programmes
- seed banks
reasons for conservation programmes
- reducing extinction
- protecting vulnerable environments
- maintaining ecosystem functions for nutrient cycling and resource provision