Respiratory System
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
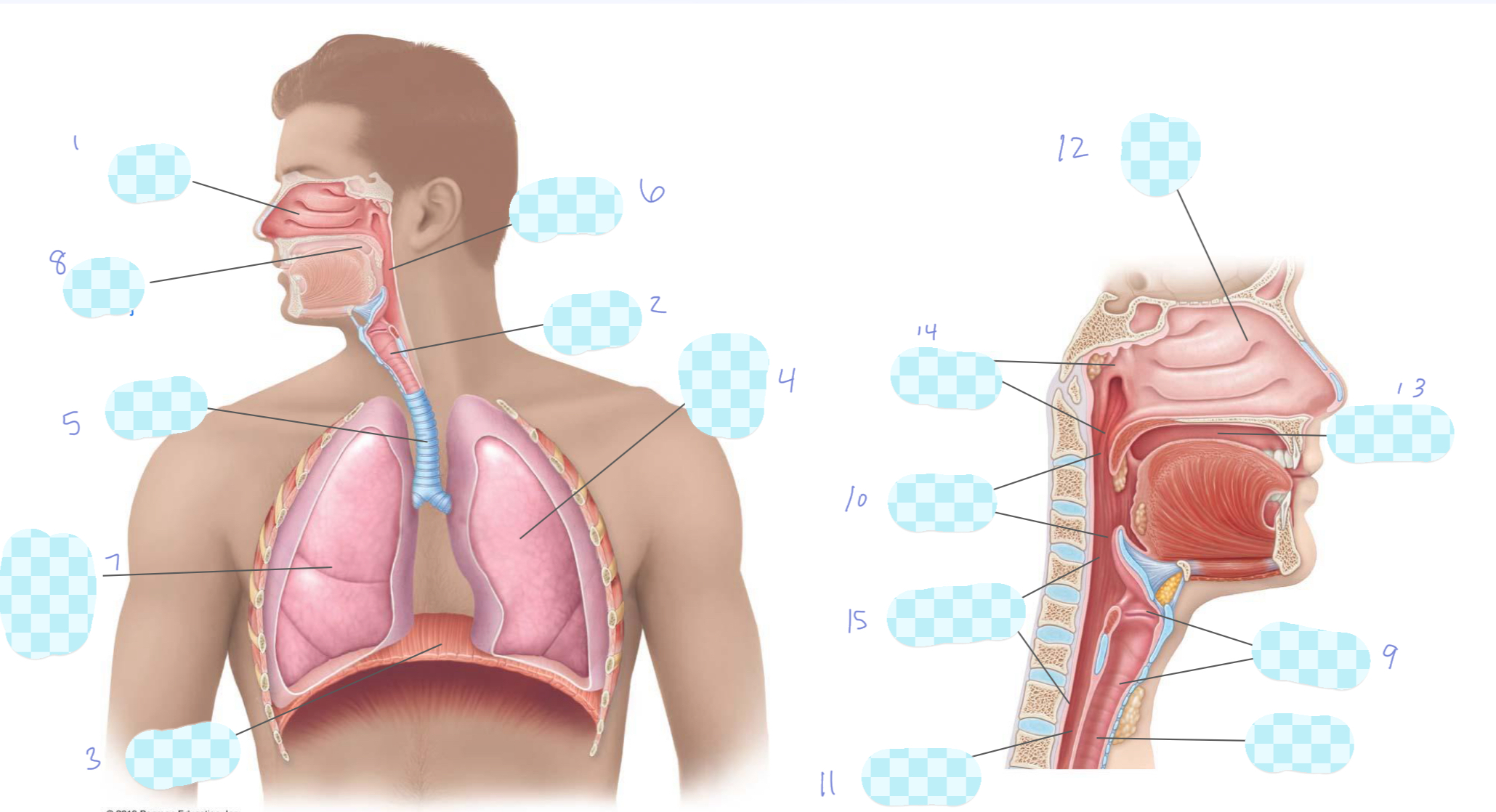
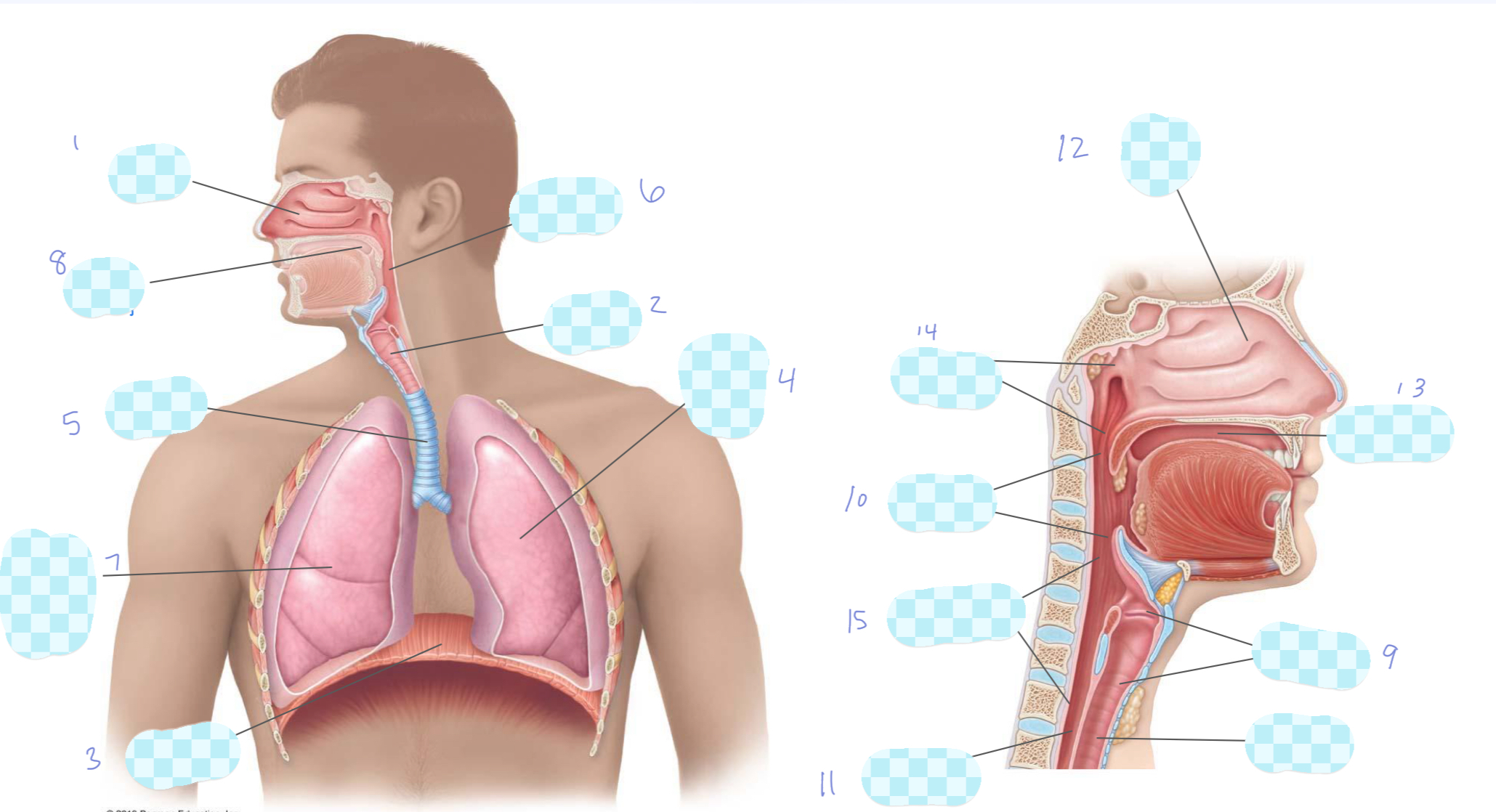
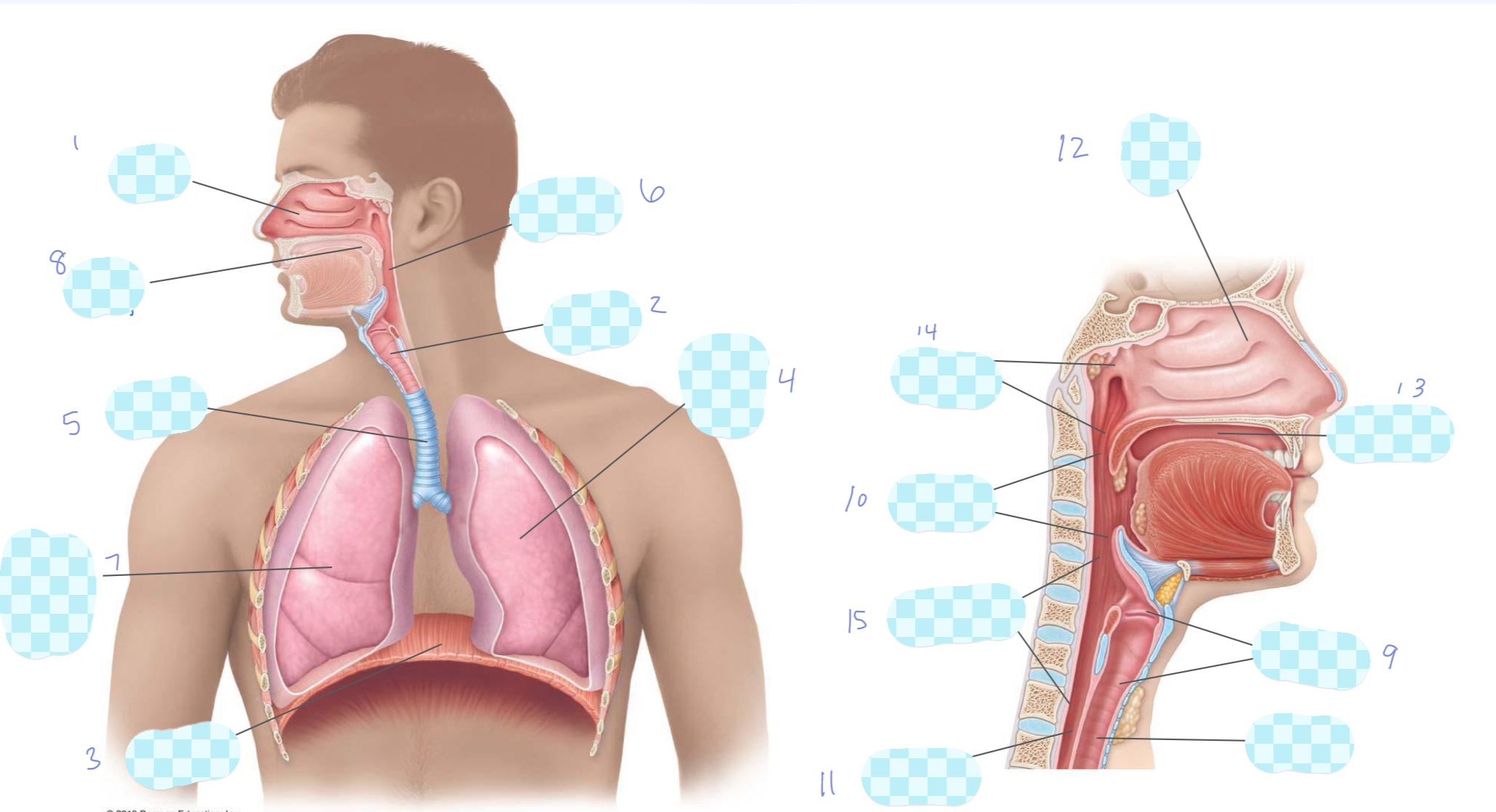
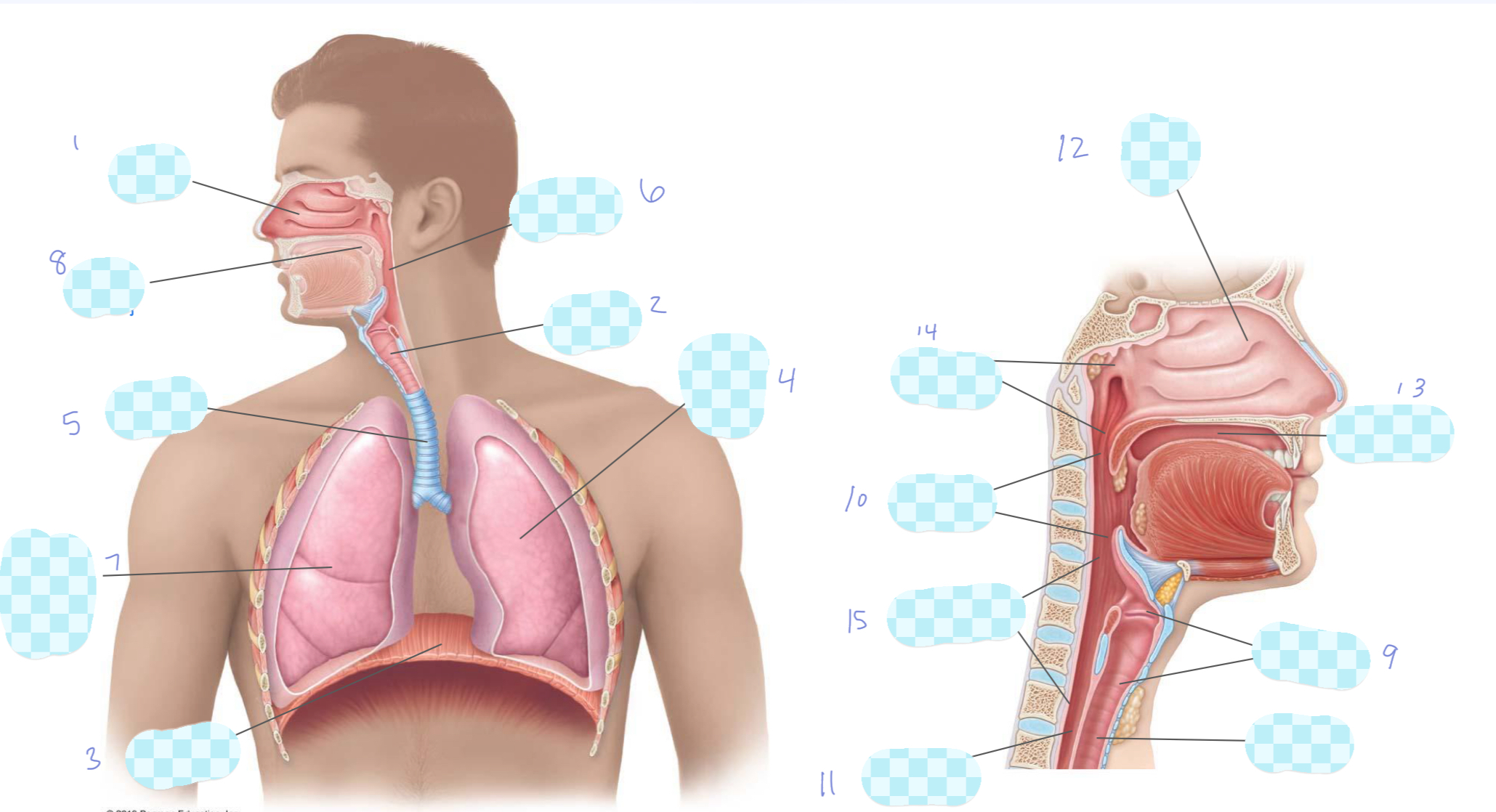
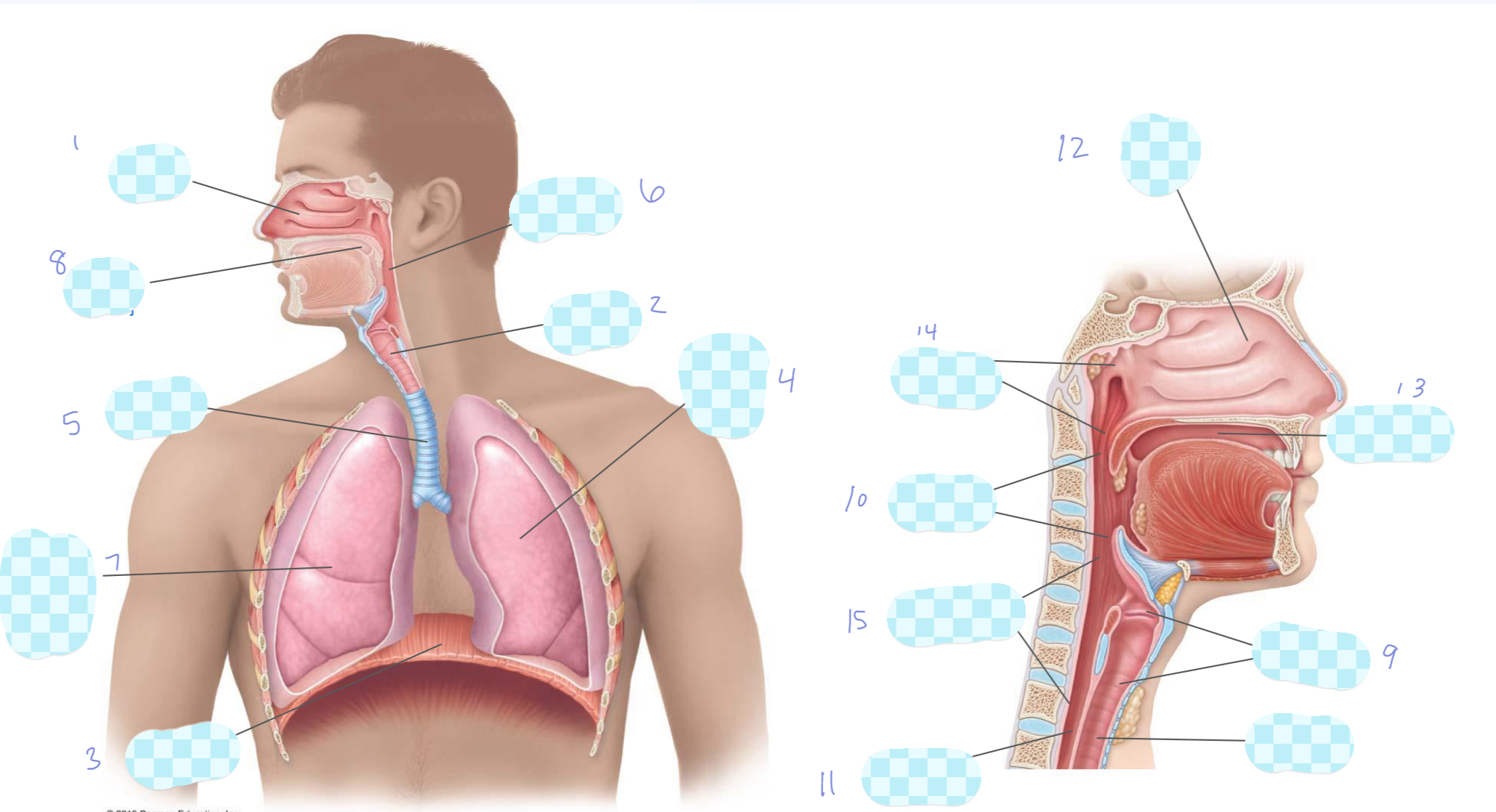
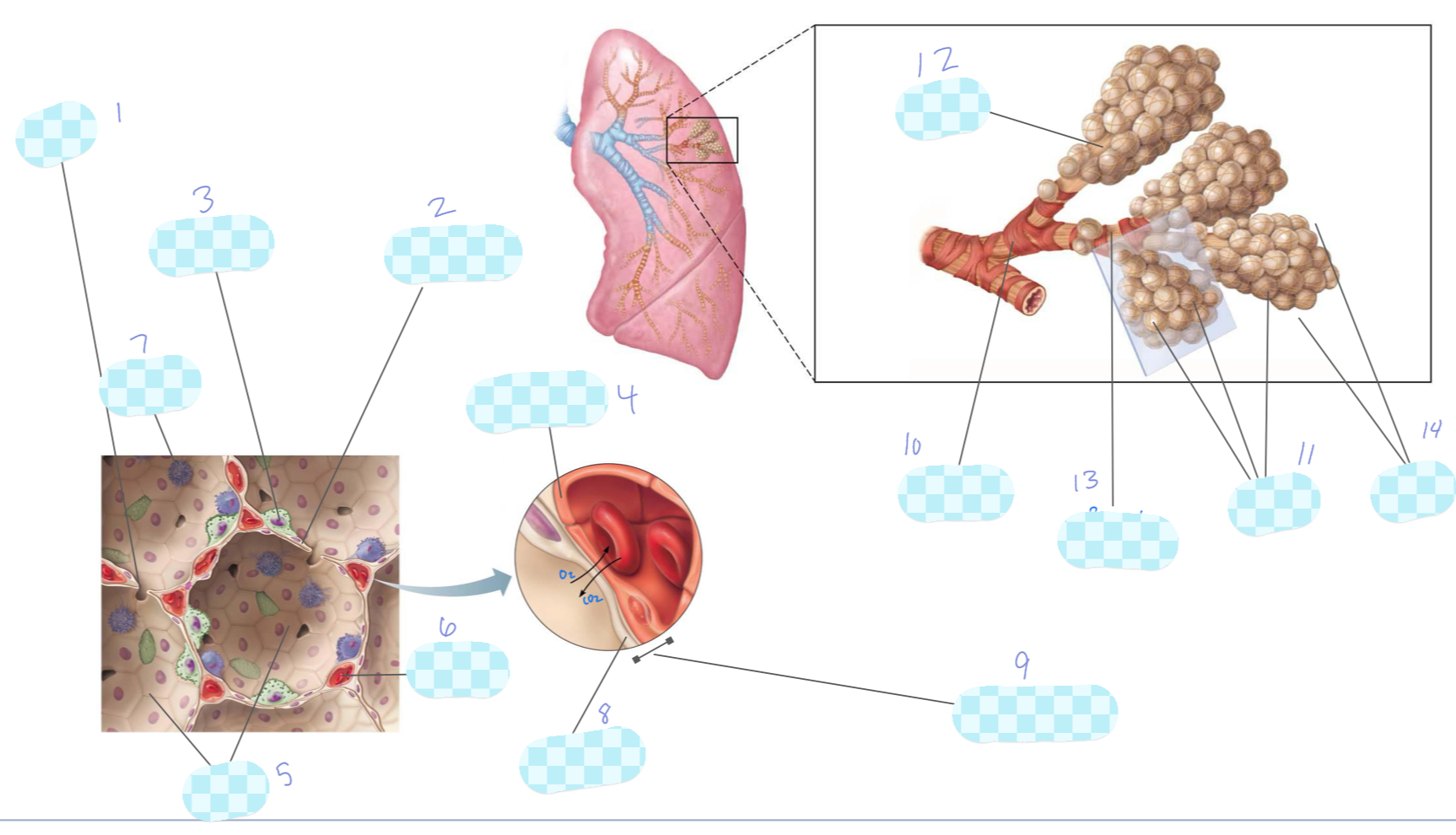
What is 1?
nasal cavity
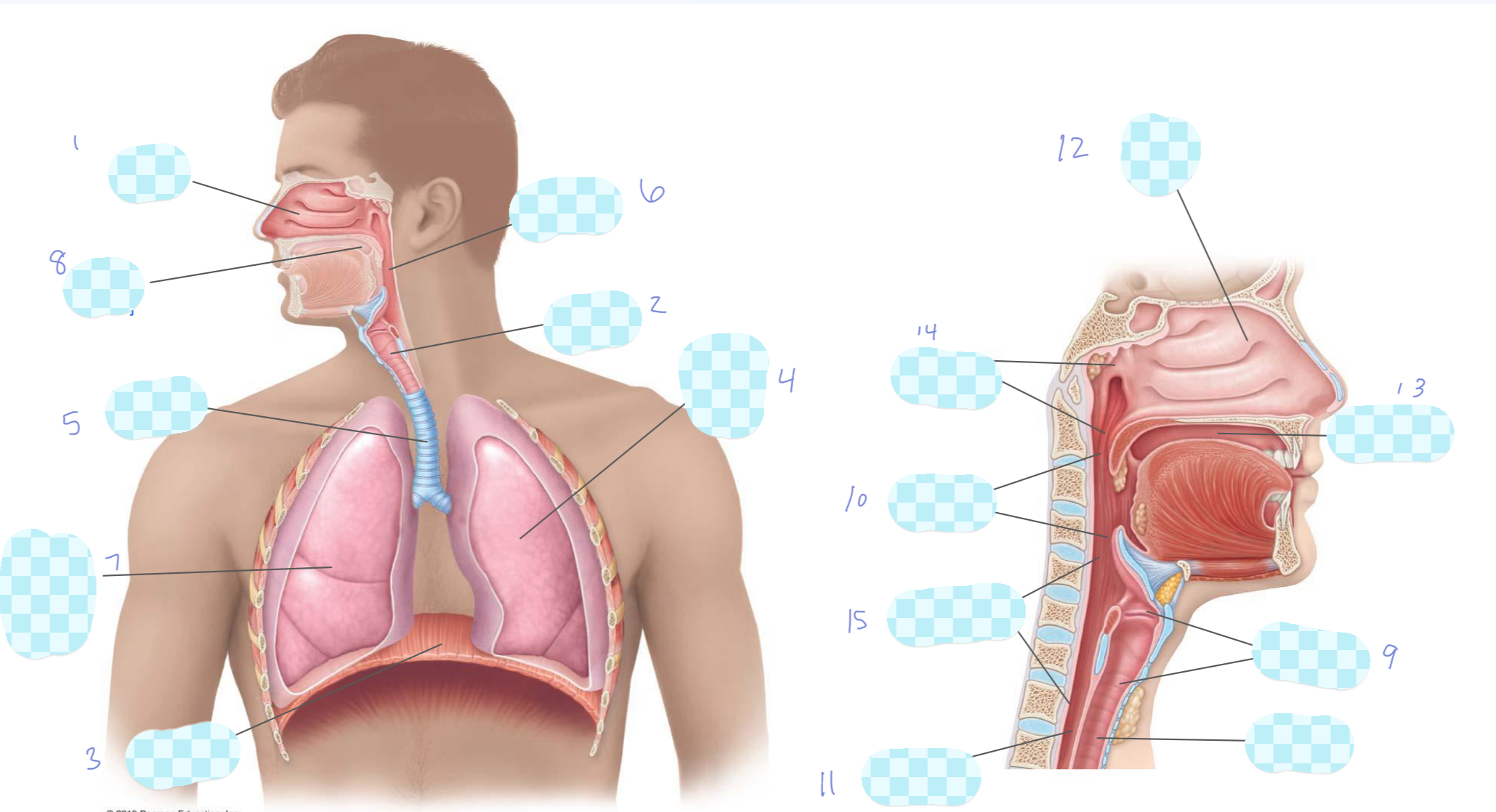
What is 2?
larynx
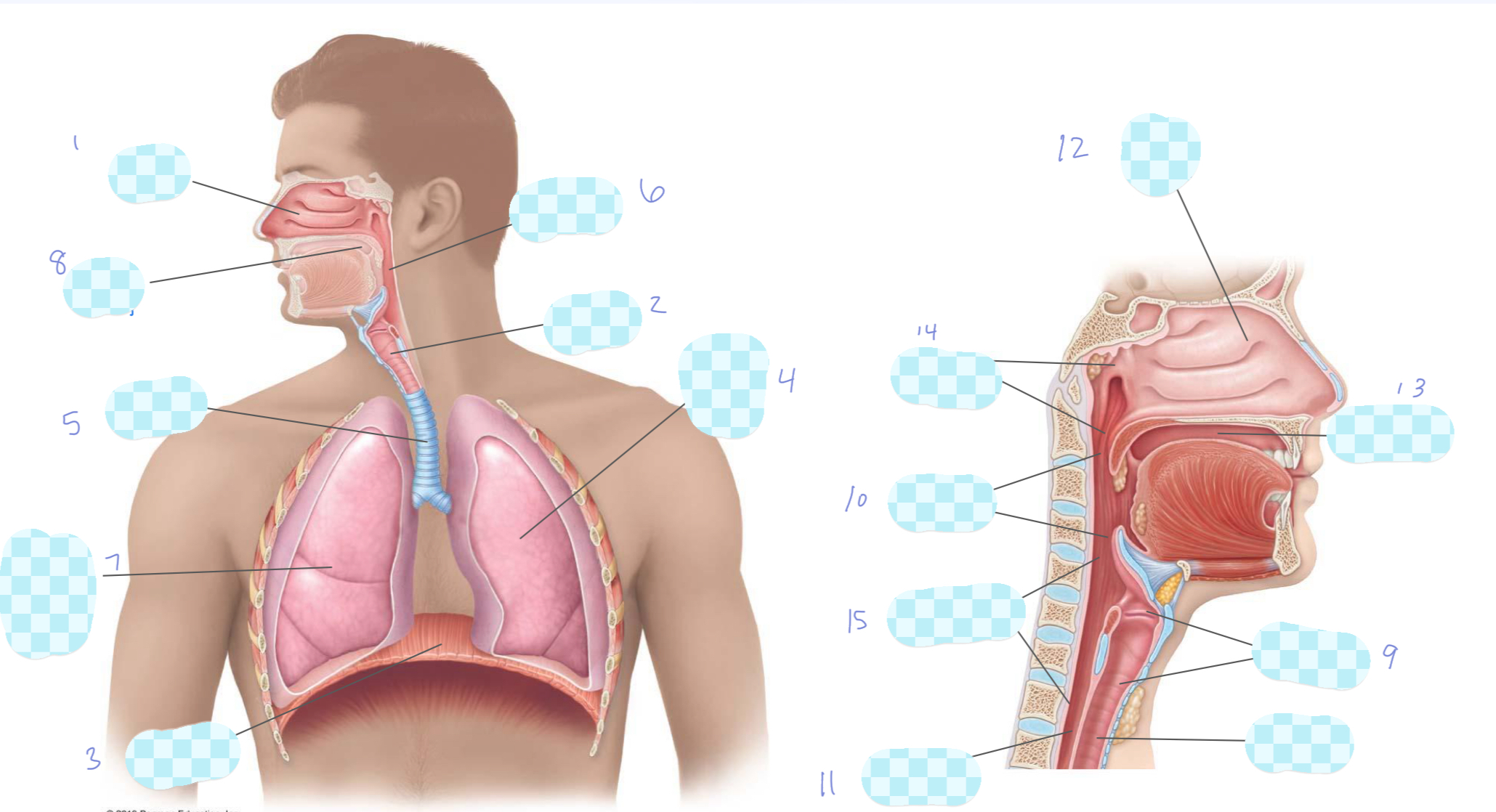
What is 3?
diaphragm
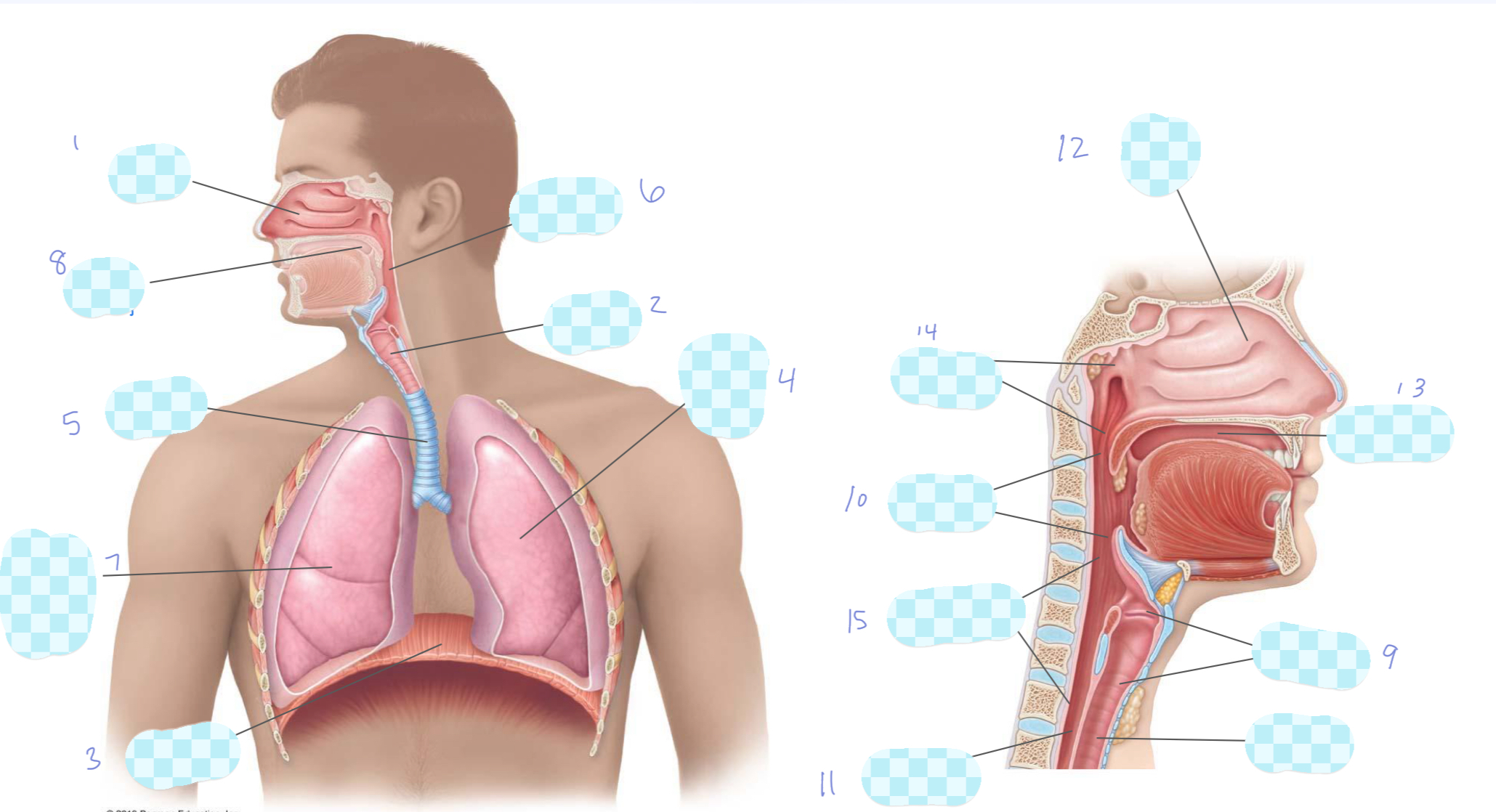
What is 4?
left lung
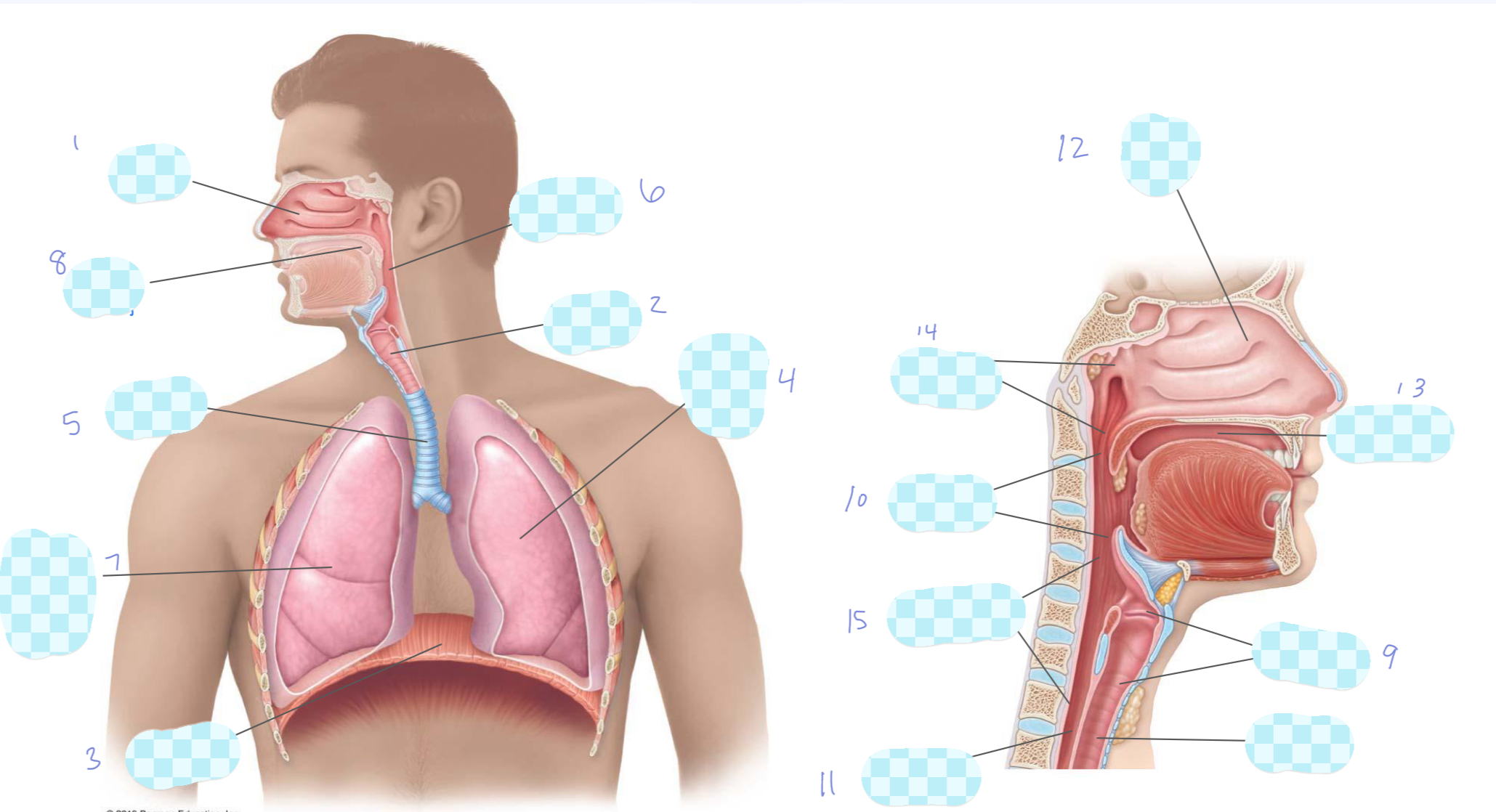
What is 5?
trachea
What is 6?
pharynx
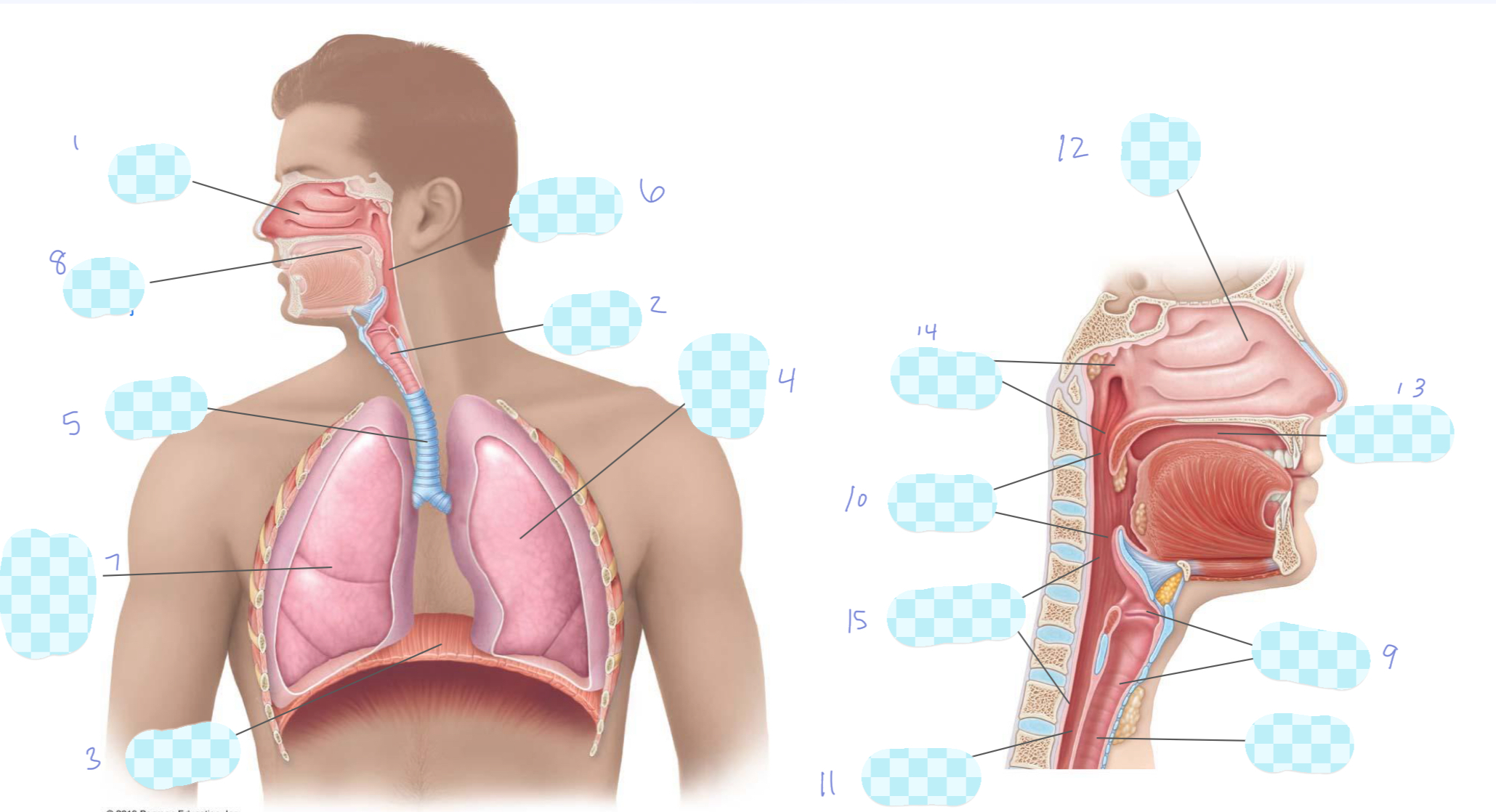
What is 7?
right lung
What is 8?
oral cavity
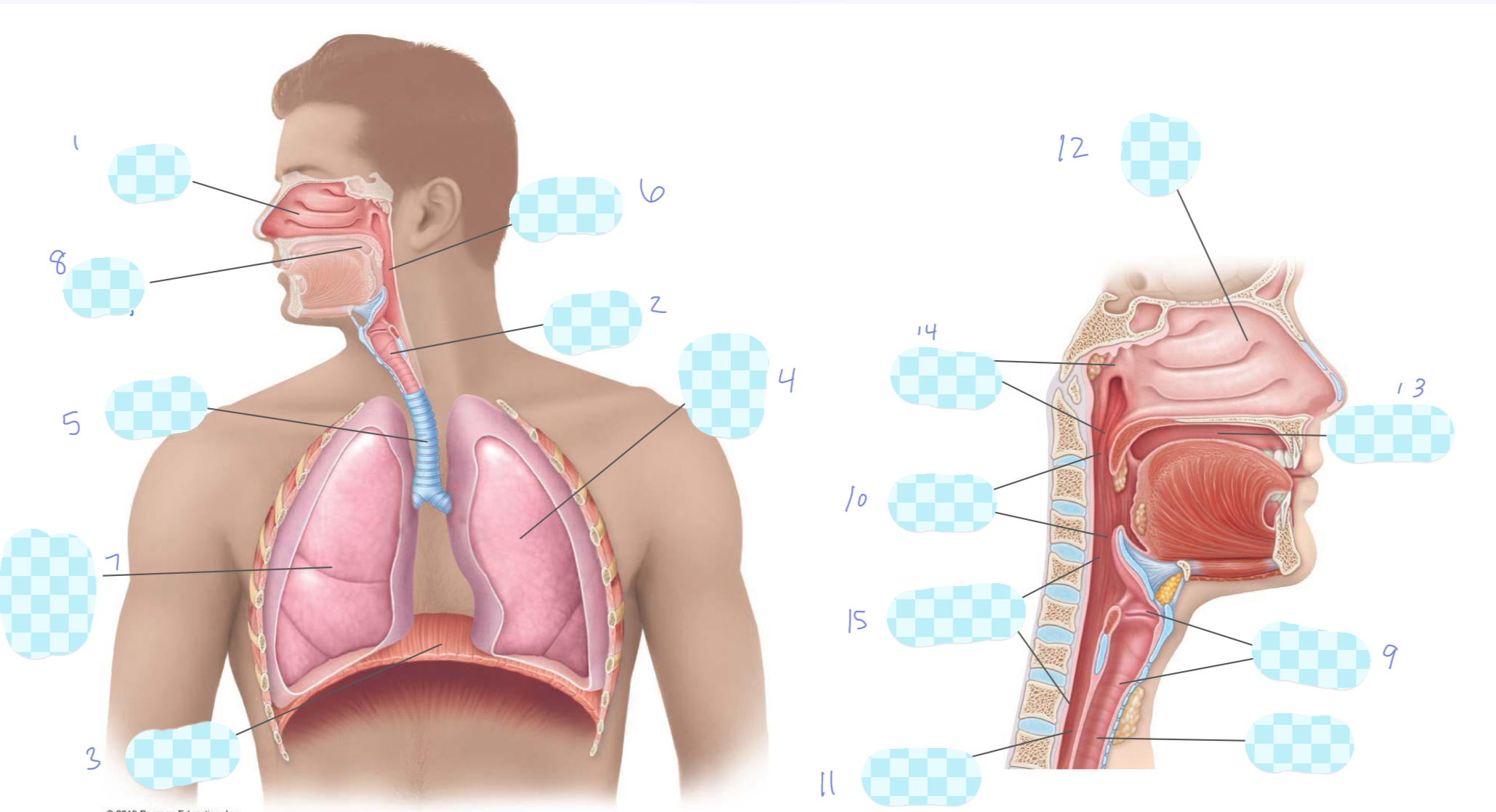
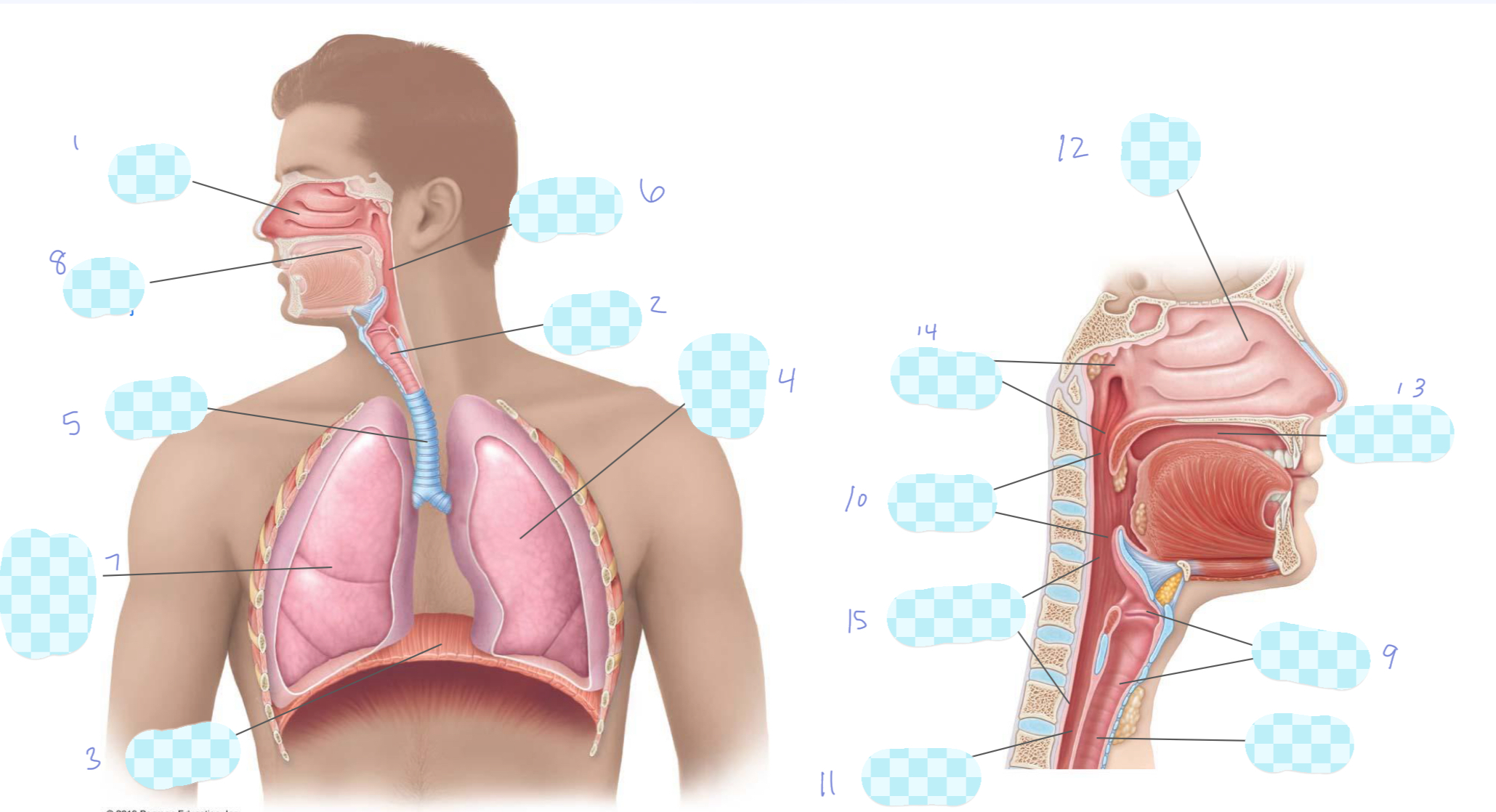
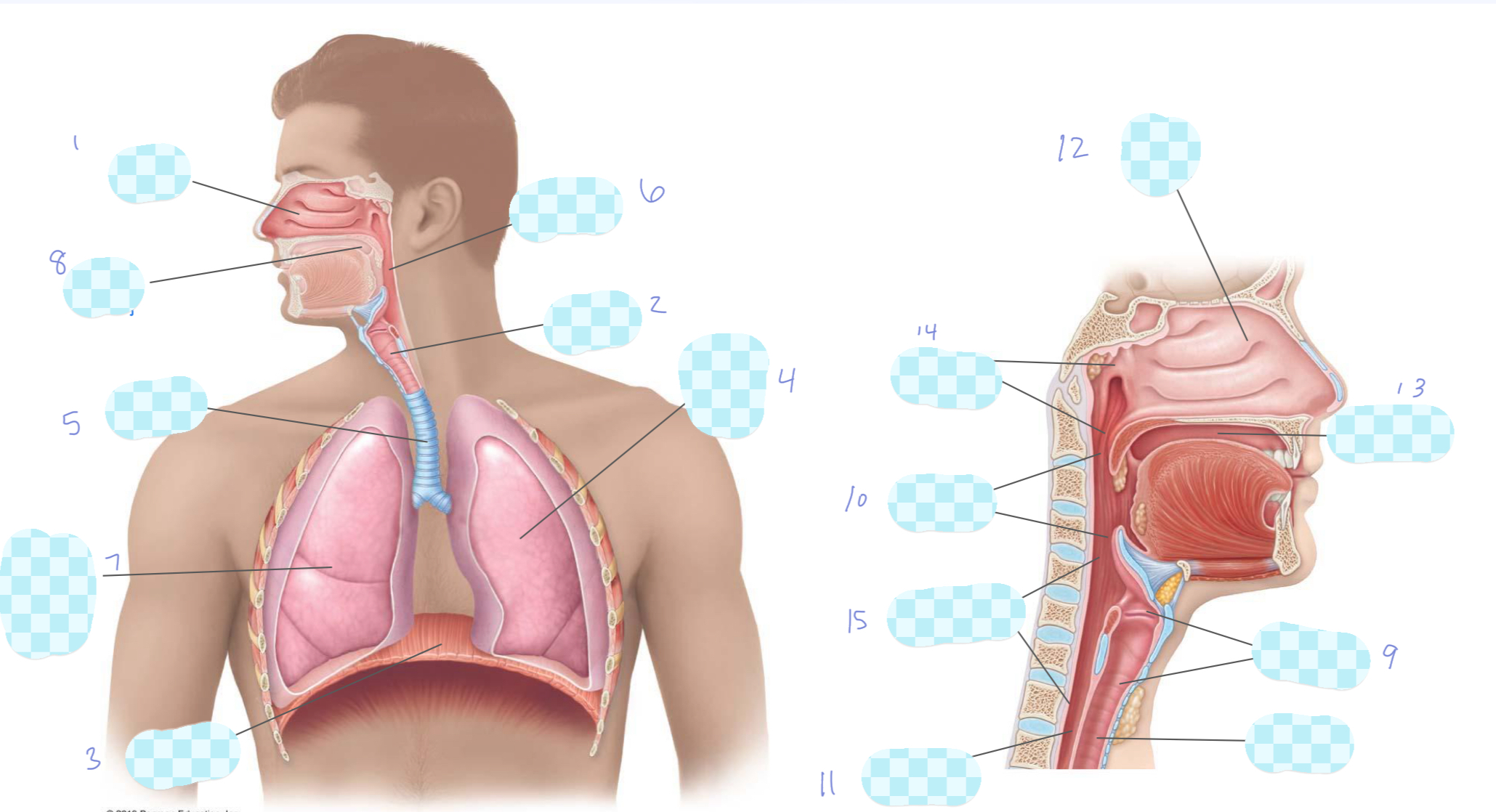
What is 9?
larynx
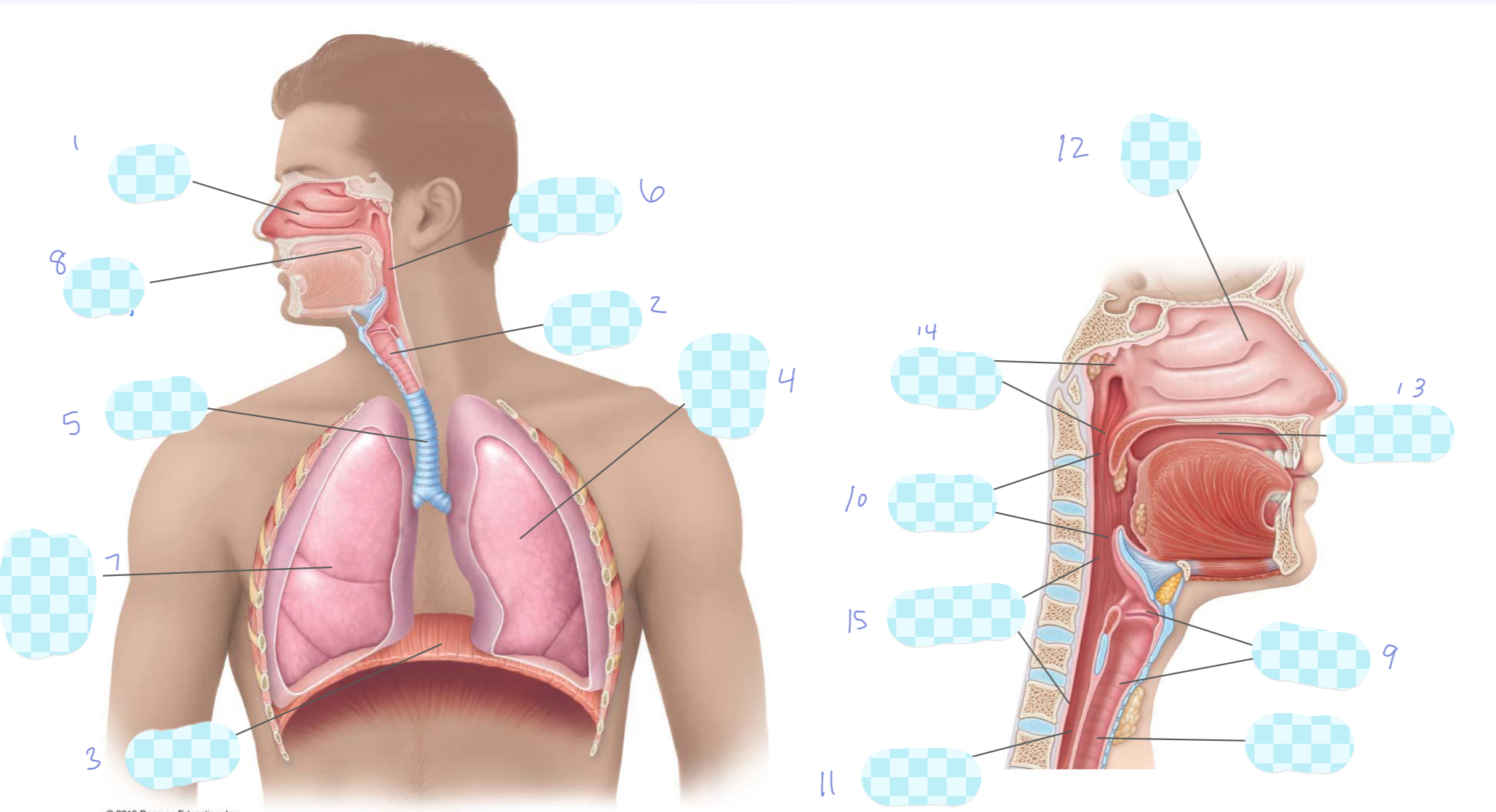
What is 10?
oropharynx
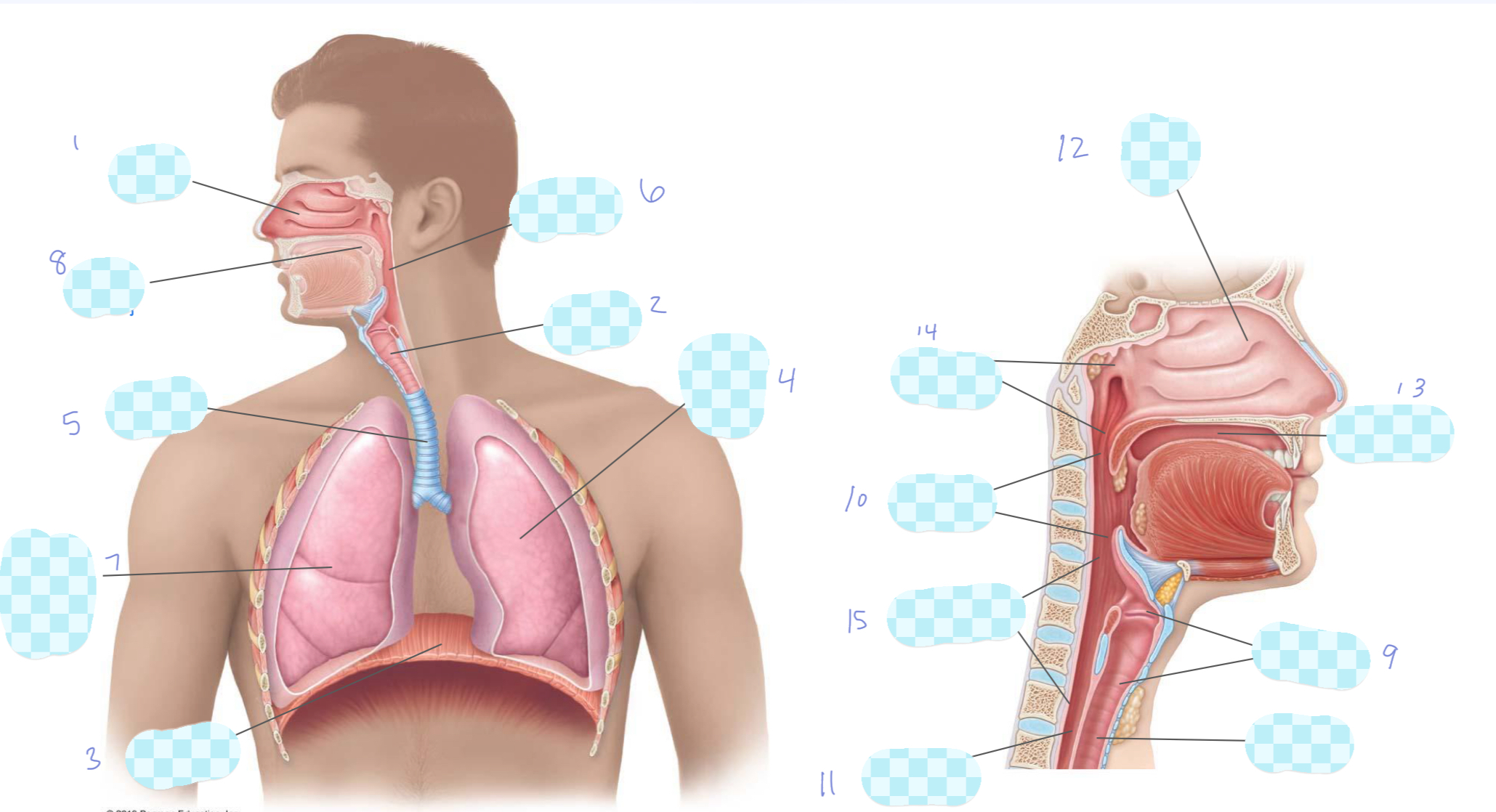
What is 11?
esophagus
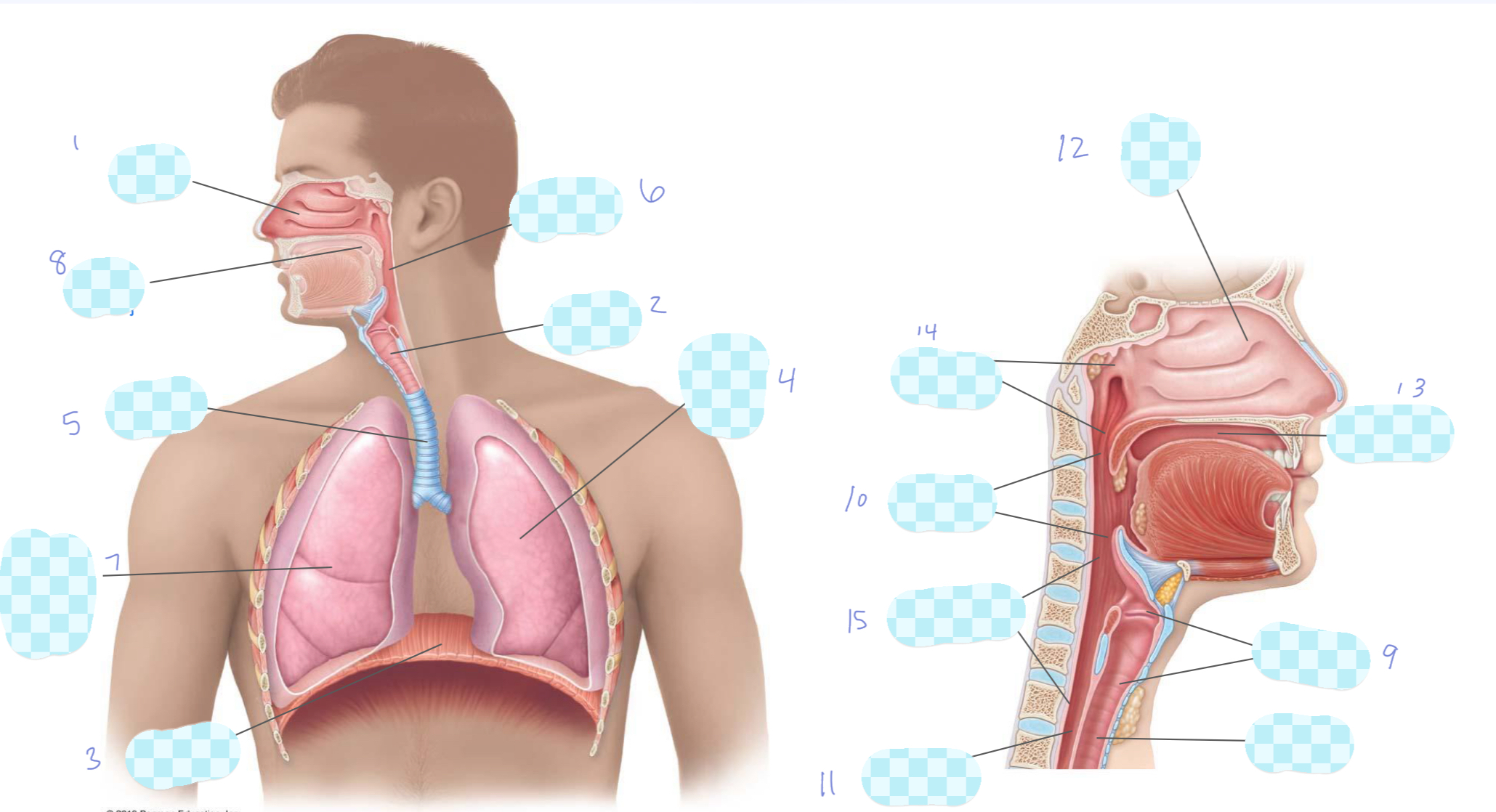
What is 12?
nasal cavity
What is 13?
oral cavity
What is 14?
nasopharynx
What is 15?
laryngopharynx
What is the unlabeled one?
trachea
What is 1?
alveolar pore
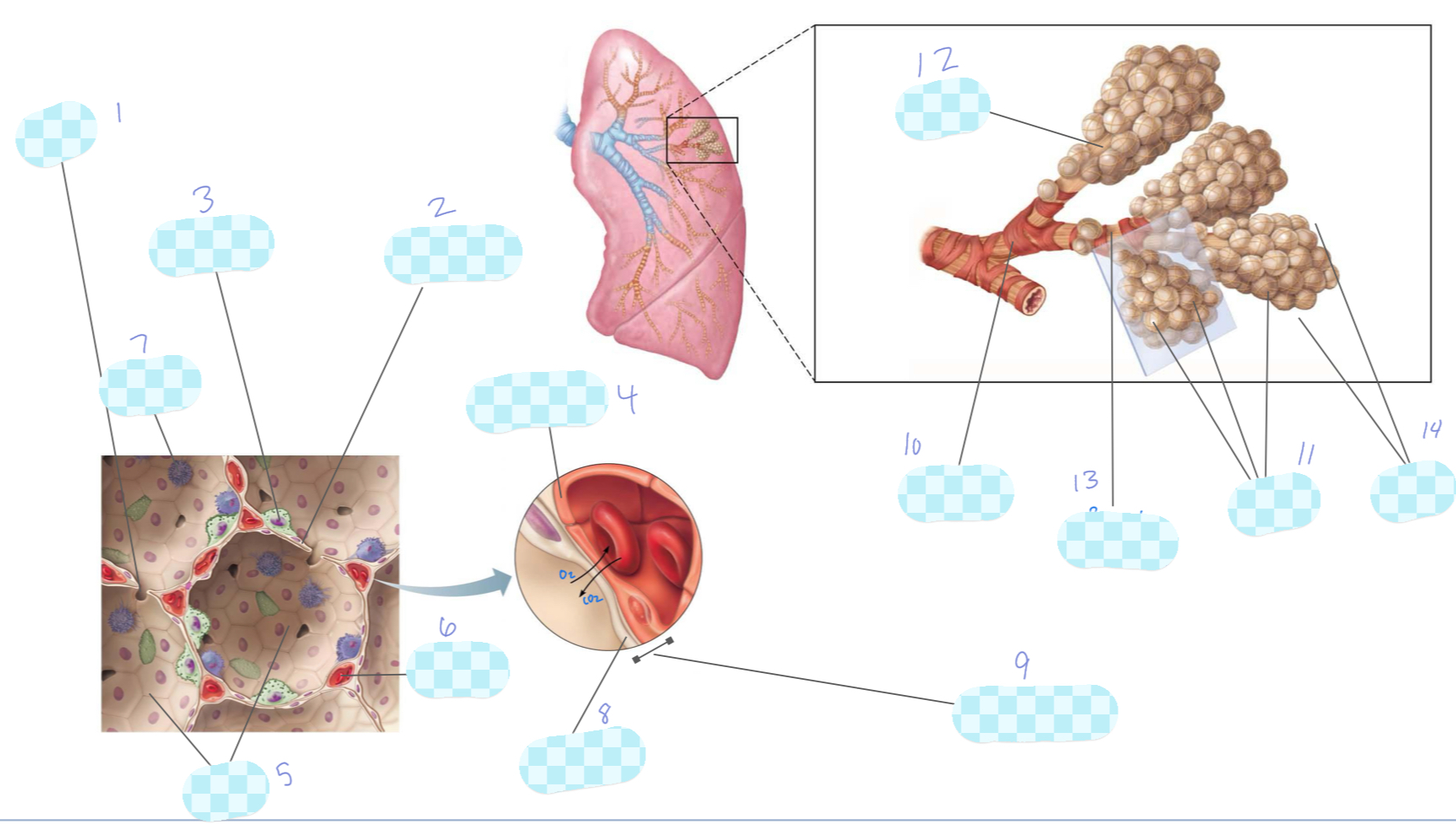
What is 2?
type I alveolar cell
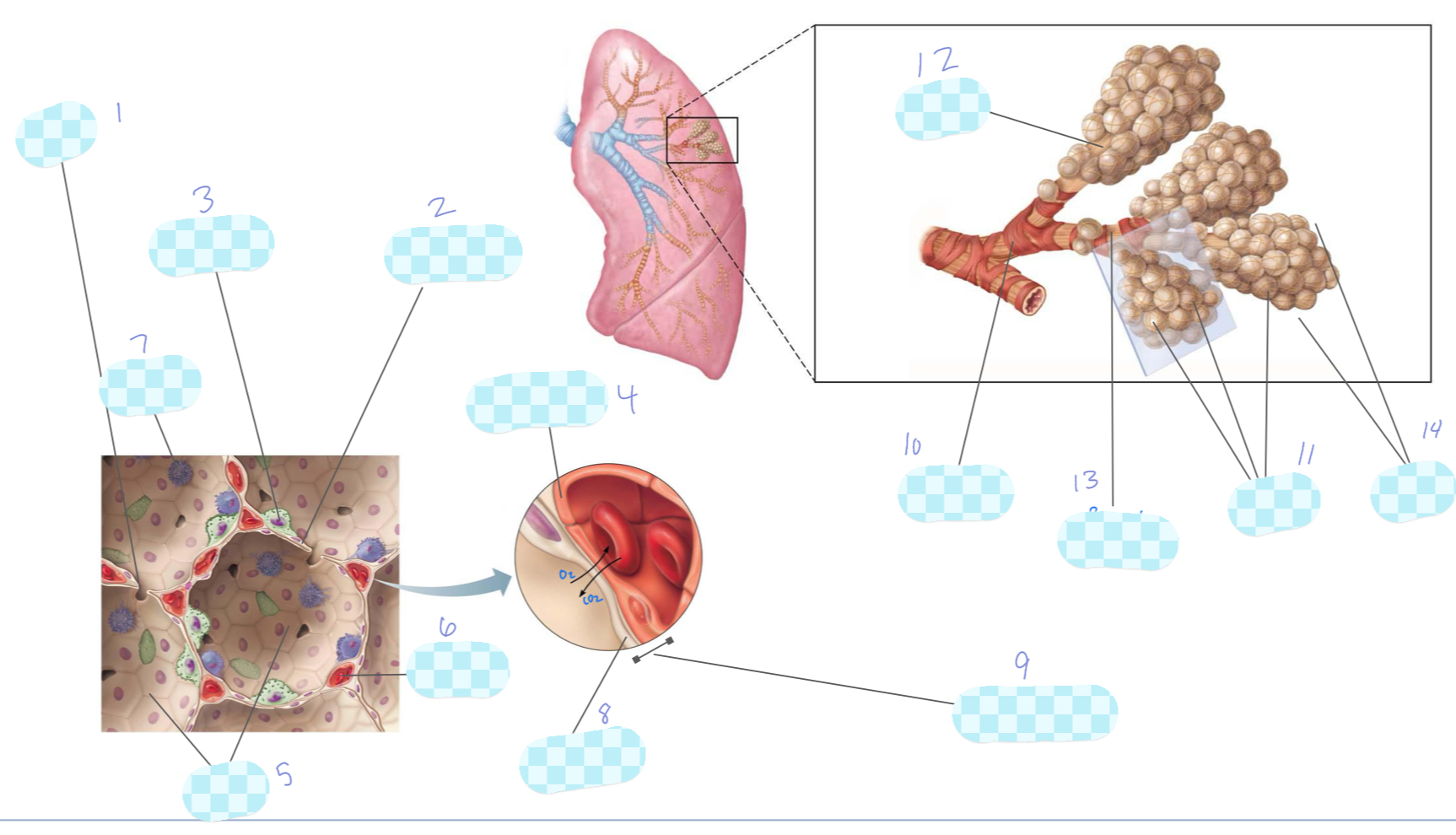
What is 3?
type II alveolar cell
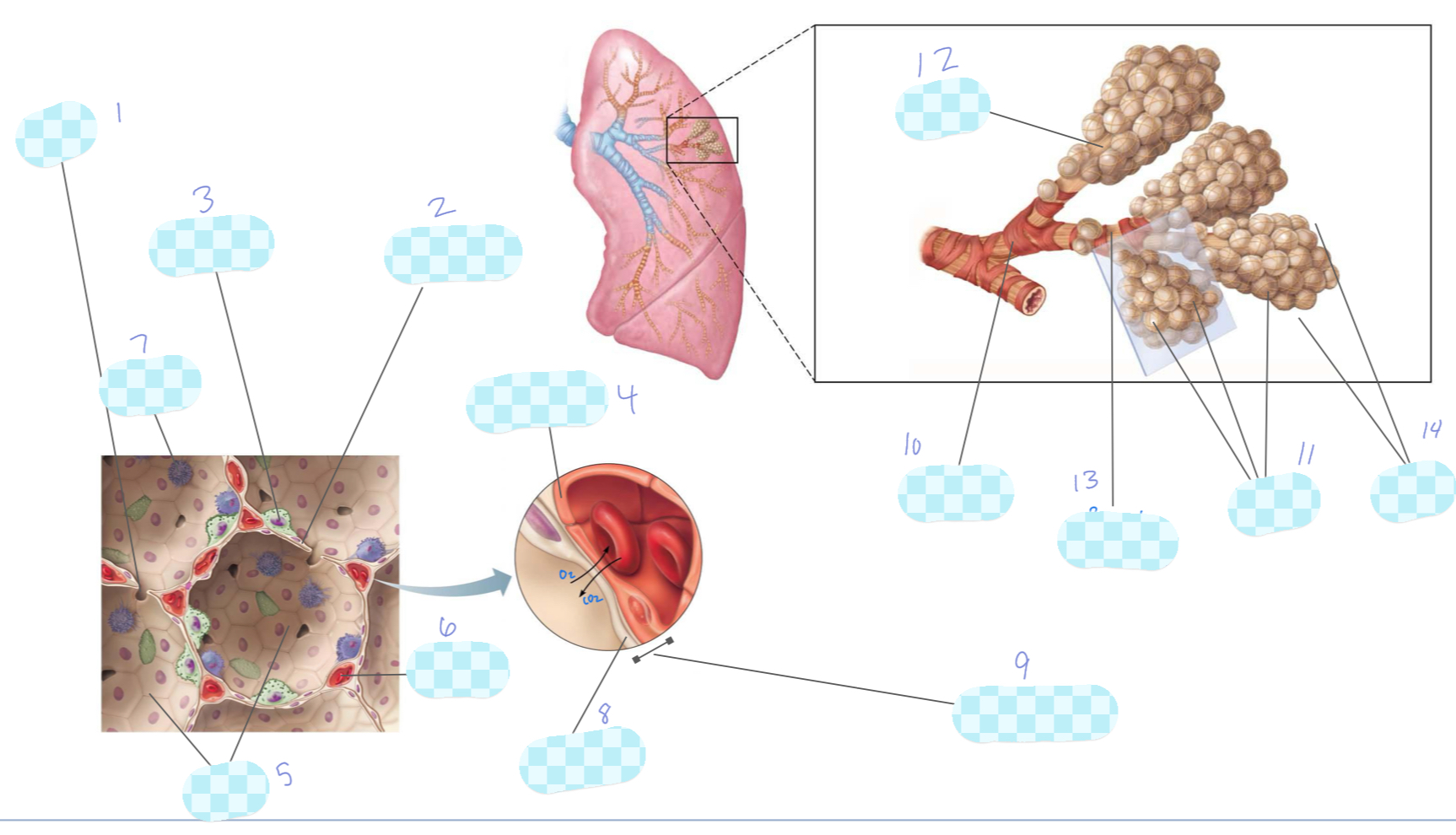
What is 4?
capillary endothelium
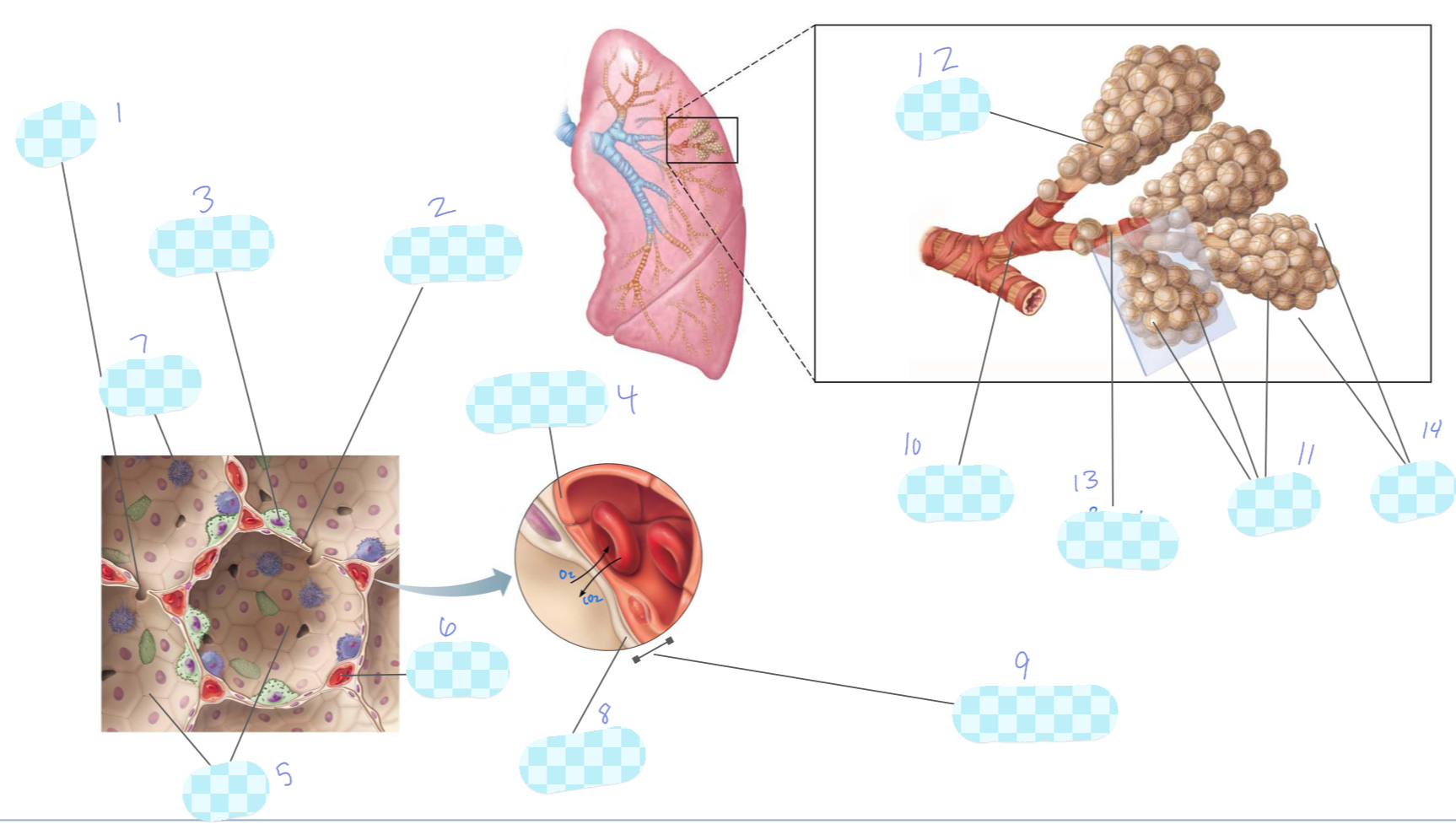
What is 5?
alveoli
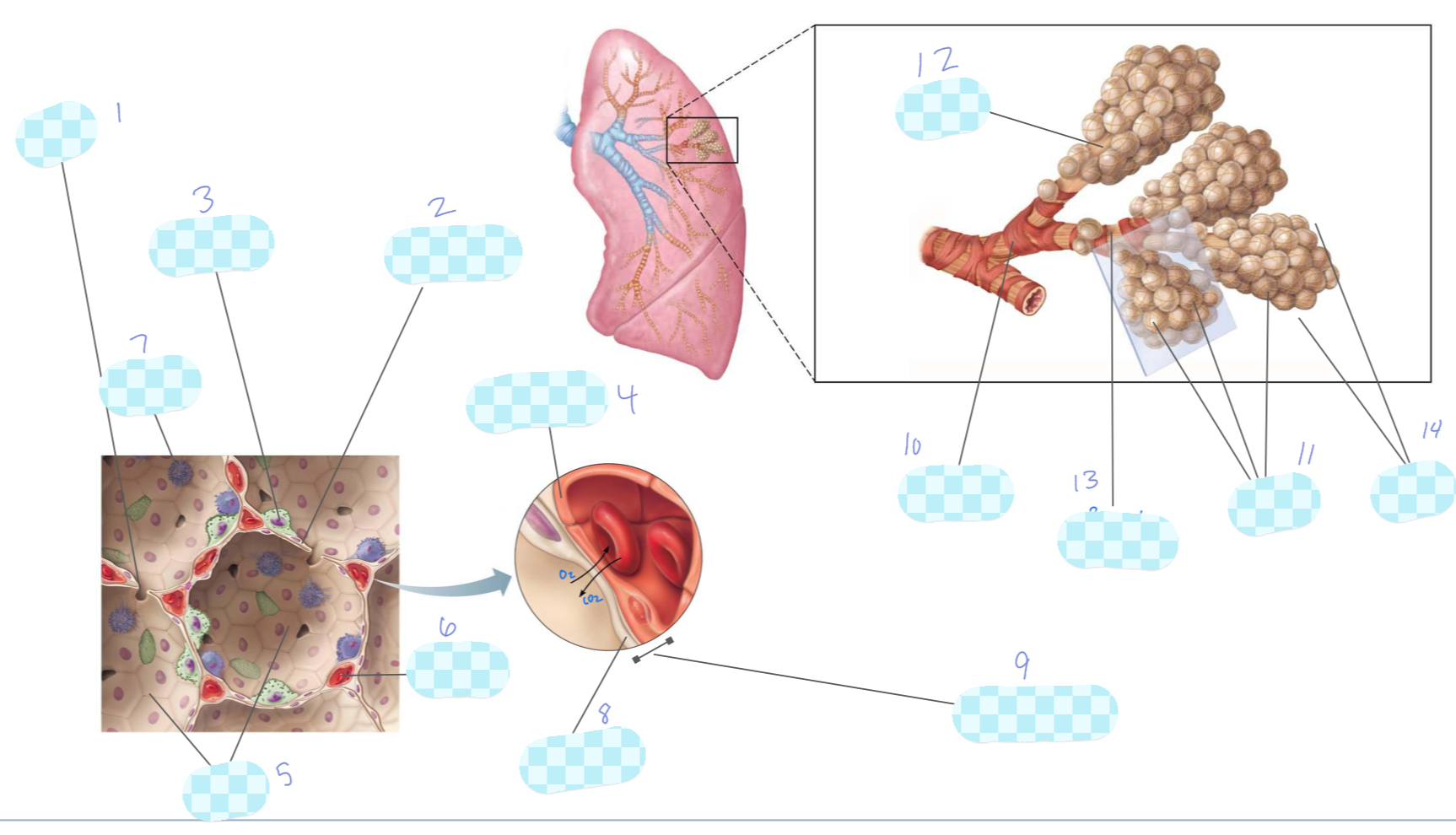
What is 6?
capillary
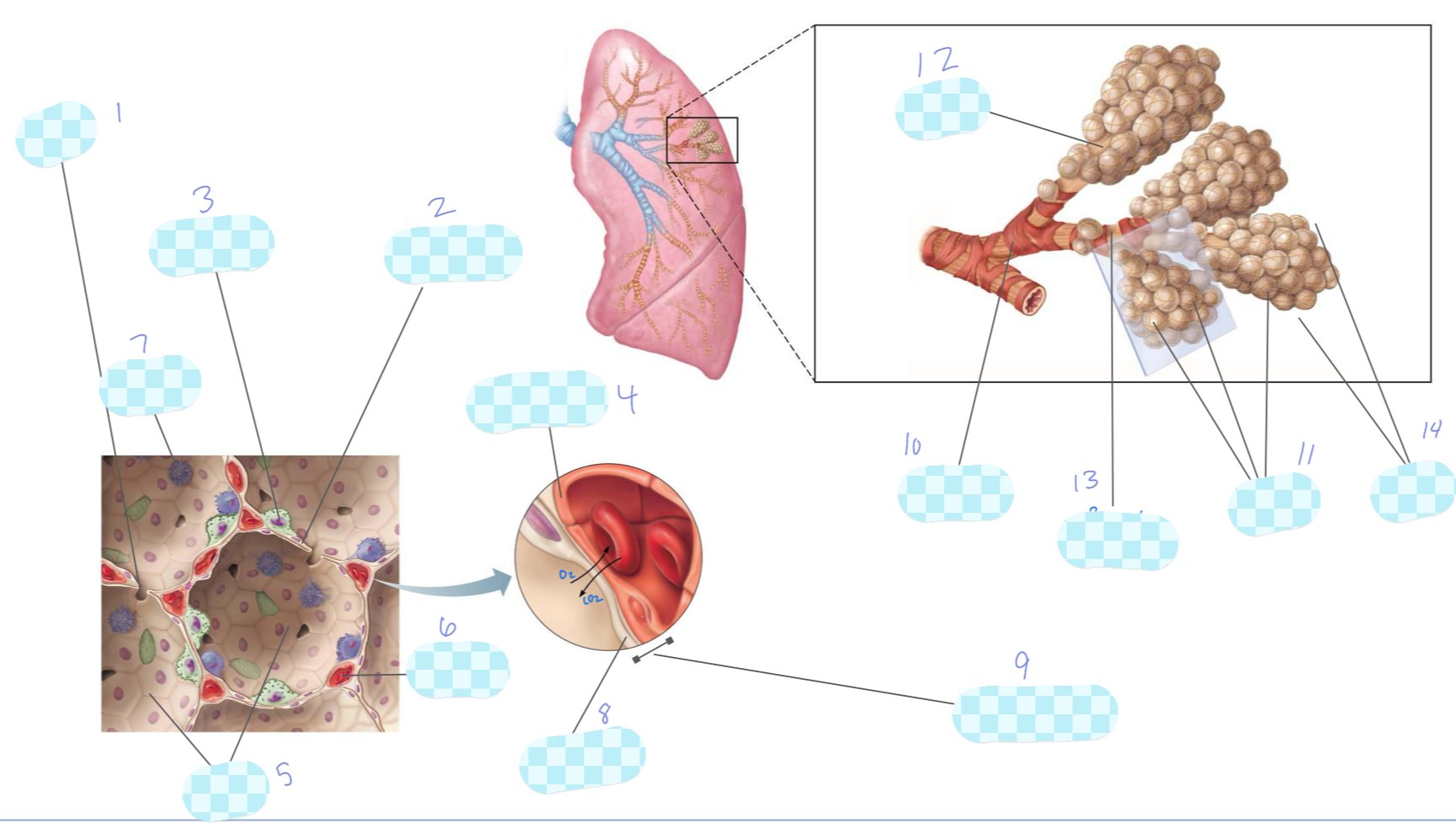
What is 7?
macrophage
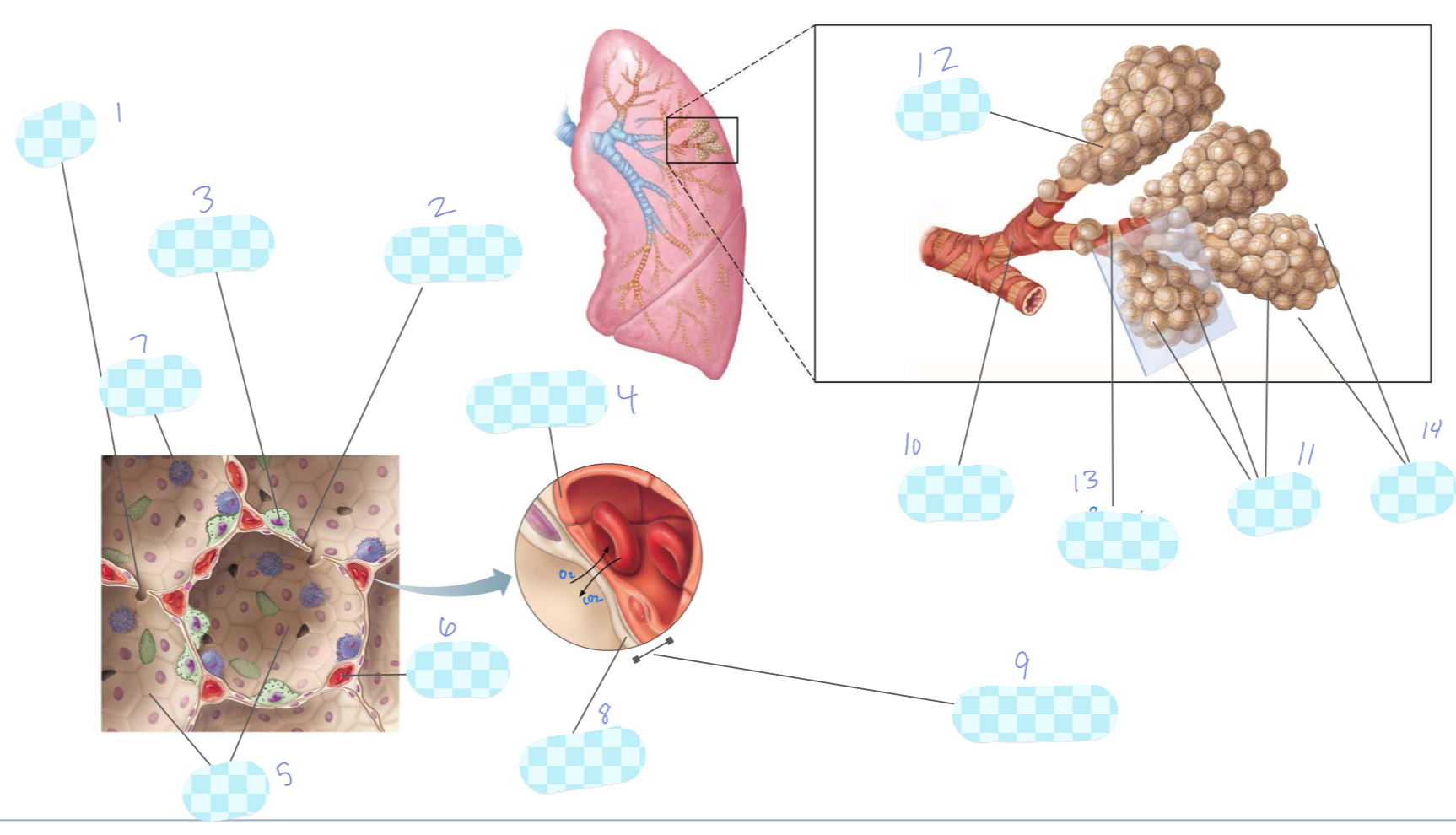
What is 8?
alveolar epithelium
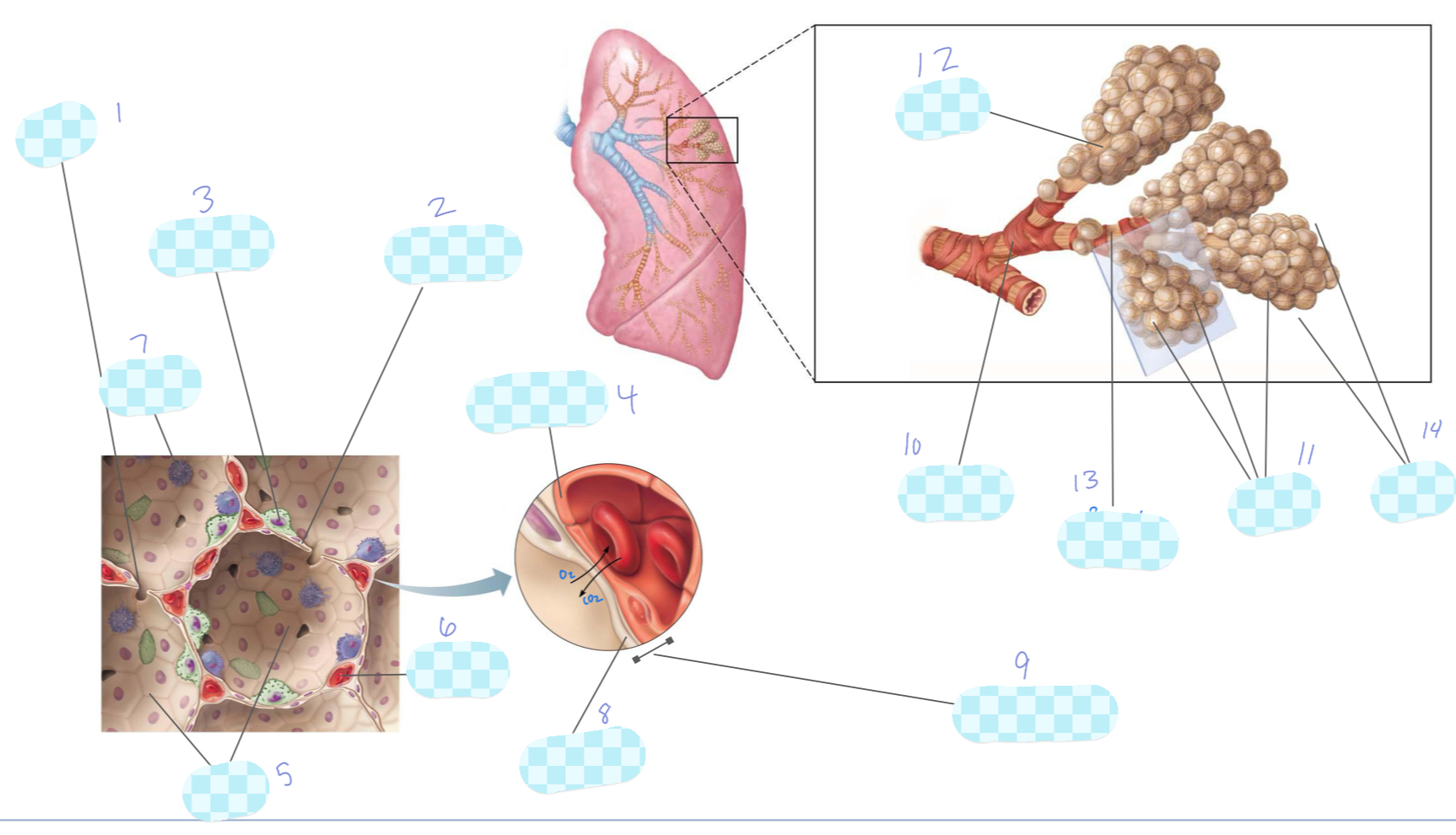
What is 9?
respiratory membrane
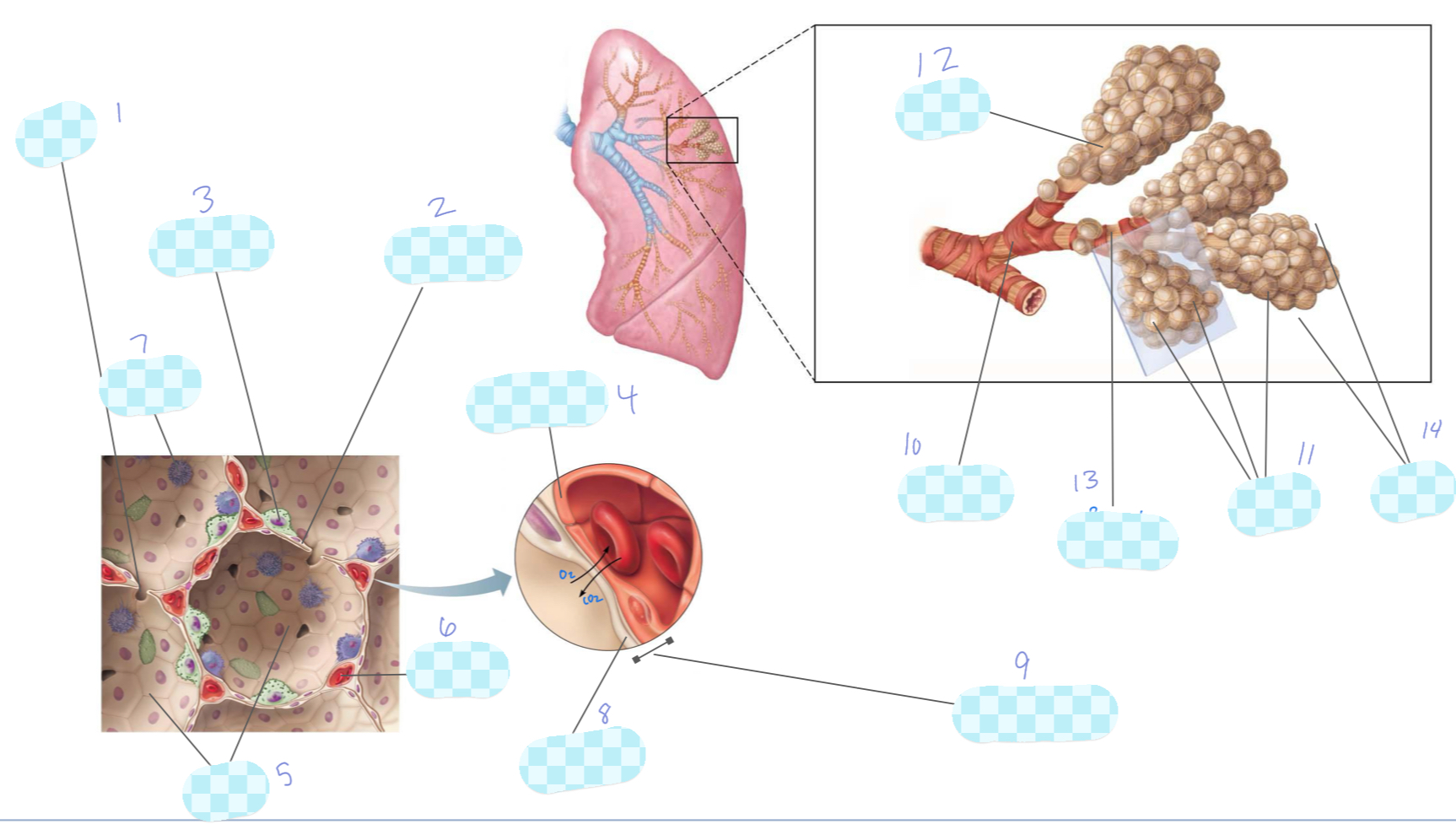
What is 10?
terminal bronchiole
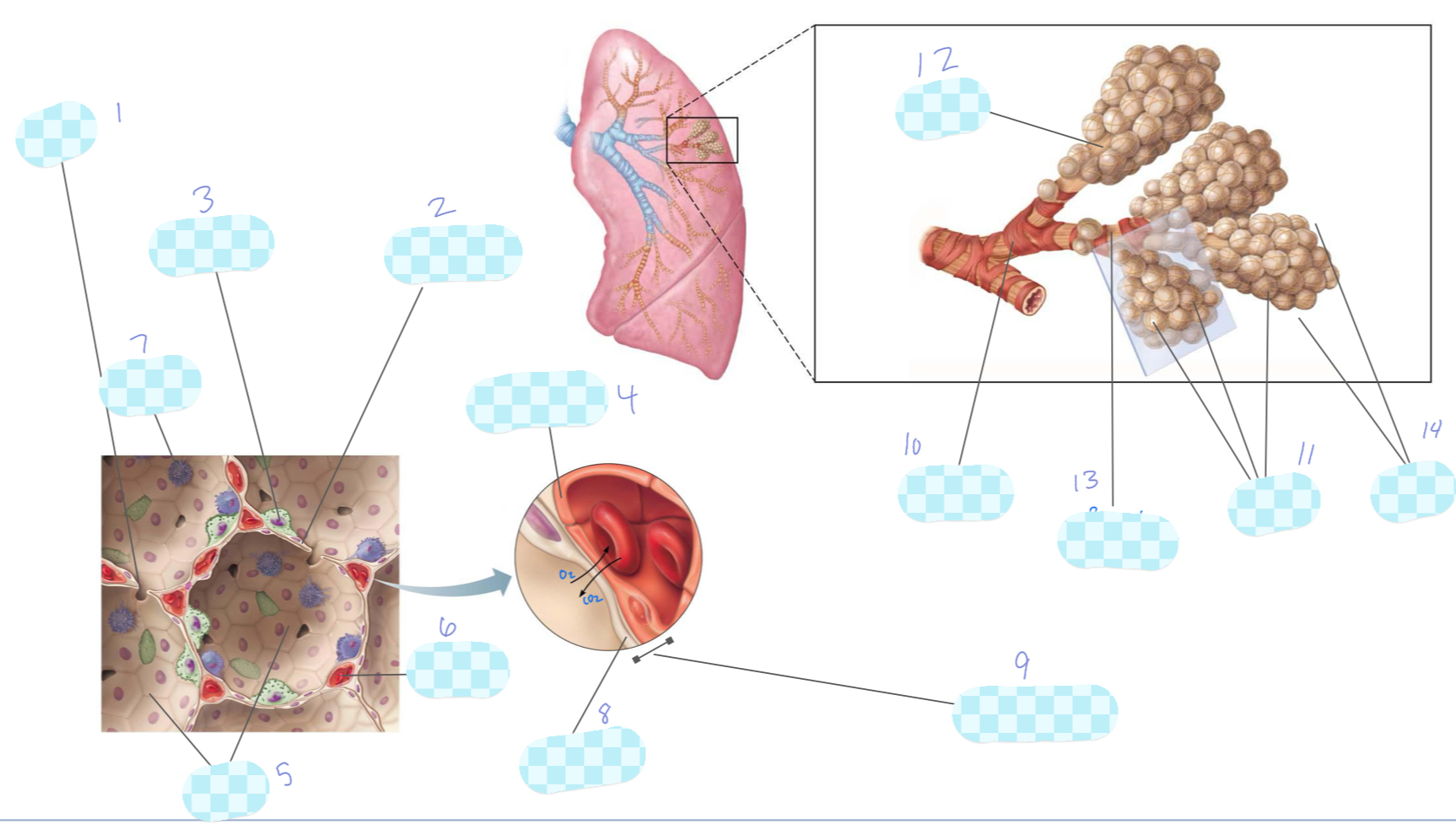
What is 11?
alveoli
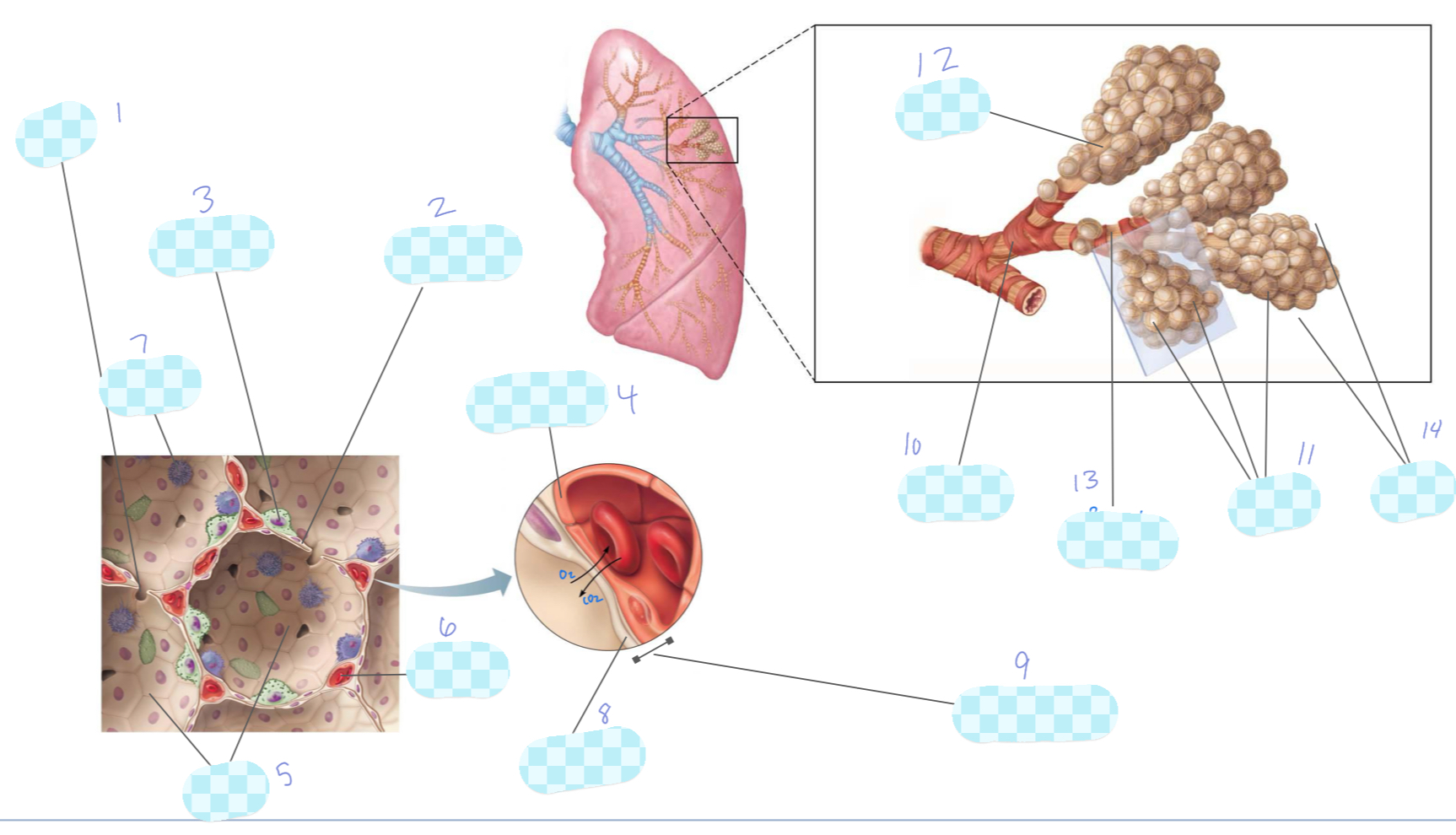
What is 12?
alveolar duct
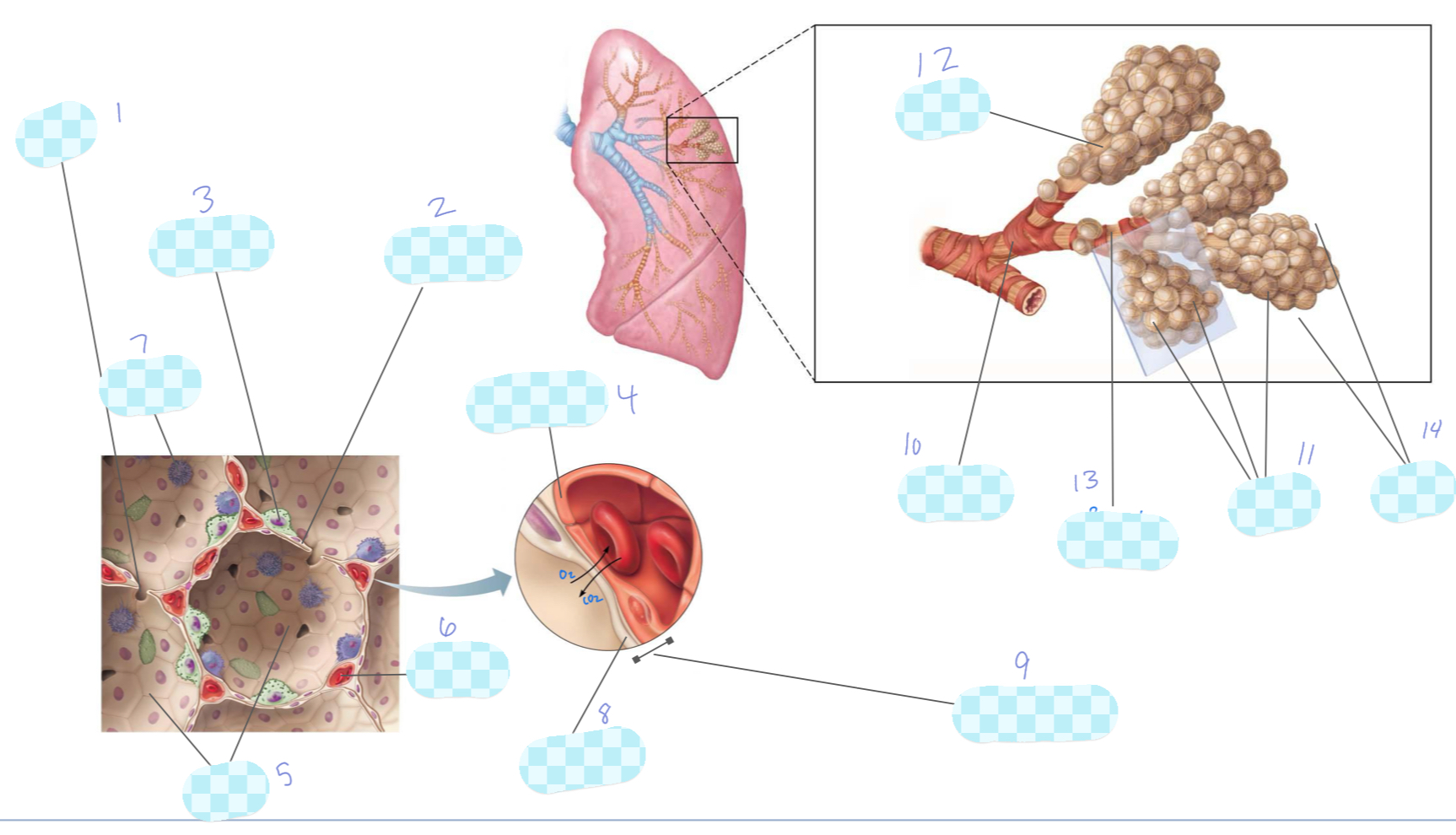
What is 13?
respiratory bronchiole
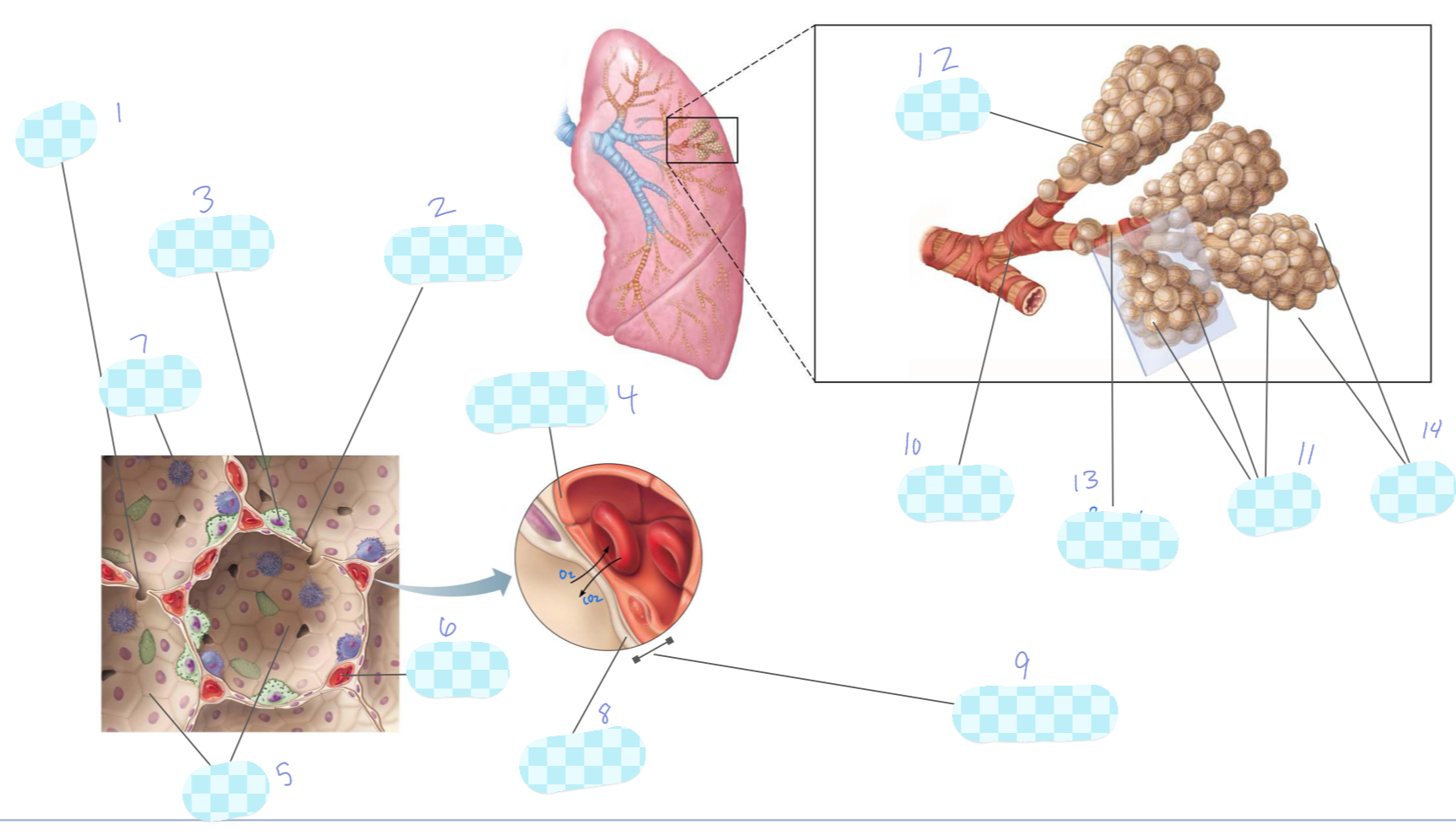
What is 14?
alveolar sac
What is the major function of the respiratory system?
gas exchange (supplying oxygen to the blood and removing carbon dioxide)
What are the four processes that make up respiration?
ventilation
transportation of respiratory gases
external and internal respiration
What is ventilation?
moving air in and out of the lungs
Where does oxygen diffuse during external respiration?
lungs to blood
Where does carbon dioxide diffuse during external respiration?
blood to lungs
Where does oxygen diffuse during internal respiration?
blood to tissues
Where does carbon dioxide diffuse during internal respiration?
tissues to blood
During transportation of respiratory gases where does oxygen start and then go?
lungs to tissues/cells
During transportation of respiratory gases where does carbon dioxide start and then go?
tissues/cells to lungs
What epithelium is alveoli I?
squamous epithelium
What is the function of alveoli I?
form alveolar walls
Is alveoli I or alveoli II more abundant?
alveoli I
What epithelium is alveoli II?
cuboidal epithelium
What is the function of alveoli II?
secrete surfactant and antimicrobial proteins
What does surfactant do?
prevents alveoli from sticking together and collapsing
What do alveolar macrophages do?
immune surveillance of inhaled pathogens
What characteristics of the respiratory membrane allows for gas exchange?
thin and large surface areas
allows for rapid gas exchange
barrier
ensure that concentration gradient stays consistent for simple diffusion to occur
How does pressure and volume change during inspiration and what does the diaphragm and ribcage do?
diaphragm contracts
rib cage expands
V goes up
P goes down
Patm is higher than P in lungs so air goes down concentration gradient into the lungs
How does pressure and volume change during inspiration and what does the diaphragm and ribcage do?
diaphragm relaxes
rib cage condenses
V goes down
P goes up
Patm is lower than P in lungs so air travels down the concentration gradient out of the lungs
IC =
IRV+TV
FRC =
ERV+RV
VC =
IC+FVC
IRV+TV+ERV
TLC =
IRV+TV+ERV+RV
How does pressure gradients drive gas exchange in the body?
Gas exchange occurs because of simple diffusion
Pressure gradients are important because for simple diffusion to occur, the substance travels high to low pressure gradients
Pressure gradients for oxygen needs to be higher in the tissue than the blood in order for oxygen to get to the tissue
How is ventilation and perfusion related?
they must be the same for efficient gas exchange in the lungs
What is ventilation in terms of gas exchange?
amount of gas reaching the alveoli
What is perfusion?
amount of blood circulating pulmonary capillaries
How is O2 transported?
carried on Hb of erythrocyte
How is CO2 transported?
dissolved in plasma
carried Hb
transported as bicarbonate ions
What is the importance of CO2 maintaining blood pH?
low level of CO2 maintain a low concentration of H+ ions in the blood. This allows for the blood to remain slightly basic
Where are the chemoreceptors involved in neural regulation breathing?
carotid and aorta arch
Where are the mechanoreceptors involved in neural regulation breathing?
muscles and joints
stretch receptors in lungs
irritant receptors in lungs
How do muscles and joints signal lack of CO2 in the body?
pain signals not enough oxygen
How does neural regulation of breathing occur?
receptors sense CO2 levels either increasing or decreasing
that sensory information is sent to the medulla oblongata and pons
How do stretch receptors in the lungs signal neural regulation of breathing?
too much stretch leads to more expiration to avoid the lungs from overinflating
How do irritant receptors in the lungs signal neural regulation of breathing?
signals the lungs to exhale more to get rid of particulets
How does ventilation change due to an increase of CO2 or a decrease in O2?
increase the rate of breathing (air flowing in)