23 SARS, Anthrax, Campylobacter
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Related Coronavirus
What does SARS stand for?
SARS-CoV 1
Which SARS strand was most relevant around 2003-2004?
SARS-CoV 2 (COVID 19)
Which SARS strand was most relevant around 2019-present?
Coronaviridae family, Betacoronavirus sarbecovirus SARS
What is the scientific name for SARS?
Mainly affects humans, originated in bats
What species does SARS (CoV 1 and 2) MAINLY affect? In what animal did it originate?
SARS CoV 1 and 2
Which infections both originated in China and became worldwide outbreaks?
SARS CoV 1
Which infection resembles flu-like symptoms: fever, headache, chills, muscle aches, cough, and potentially pneumonia
Low morbidity and mortality
What is morbidity and mortality like in SARS CoV 1?
SARS-CoV-1
What infection can you diagnose with RT-PCR, FAT, and ELISA most commonly?
Respiratory droplets and inhaled aerosols coming in contact with mucous membranes
How is SARS CoV 1 transmitted?
Supportive therapy
How do you treat SARS CoV 1?
None
How many cases of SARS CoV 1 have been reported since the 2004 outbreak?
Woolsorter's Disease
What is another name for Anthrax?
Bacillus anthracis
What is the causative agent of Anthrax?
Humans, wildlife (deer), livestock (cattle)
What species does Anthrax infect?
Anthrax
Which infection is found in the soil, commonly in Asia, Africa, Middle east. Rare in U.S., and considered absent in Western Europe, North Africa, and east of the Mississippi river?
Cutaneous, respiratory, gastrointestinal, injection
What are the 4 clinical manifestations of Anthrax in humans?
Cutaneous
What is the most common form of anthrax in humans?
Cutaneous
This manifestation of Anthrax presents with skin lesions that have central scarring and marked non-pitting edema, fever, and leukocytosis
Respiratory
This manifestation of Anthrax presents with respiratory distress, muscle pain, fatigue, dyspnea, cyanosis, jaundice, elevated liver enzymes, and bleeding mediastinitis leading to fatal septicemia
Respiratory
Which manifestation of Anthrax is the most fatal and rare form in humans?
Gastrointestinal
This manifestation of Anthrax presents with fever, swollen lymph nodes, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain, and red eyes?
Injection
This manifestation of Anthrax is due to injection of illicit drugs, presenting deep under the skin or at muscle injection site
Peracute and acute
What are the two forms of Anthrax in animals?
Peracute
Which animal manifestation of Anthrax presents with dyspnea, convulsions, staggering when walking, all eventually leading to death?
Acute
Which animal manifestation of Anthrax presents with lethargy, seizures, staggering, difficult when breathing, death, colic, and swelling along dorsal side of the body (horses)?
HIGH (over 85%)
What is mortality rate like in Anthrax?
Anthrax
Which infection can be diagnosed with RT PCR, sputum culture, Anti-protective antigen antibodies, radiographs?
Exposure to spores within environment, opening animal carcasses exposed to bacterium, contact with infected animal products
How is Anthrax transmitted?
Human to human cases are RARE and RANDOM
What is human to human transmission like in Anthrax?
Anti-anthrax serum, vaccination, carcass management, antibiotics
How can you treat anthrax?
1. Tracing is difficult --> good bioterrorism agent
2. Increasing penicillin resistance
What is significant about Anthrax (2)?
Anthrax
What is this?
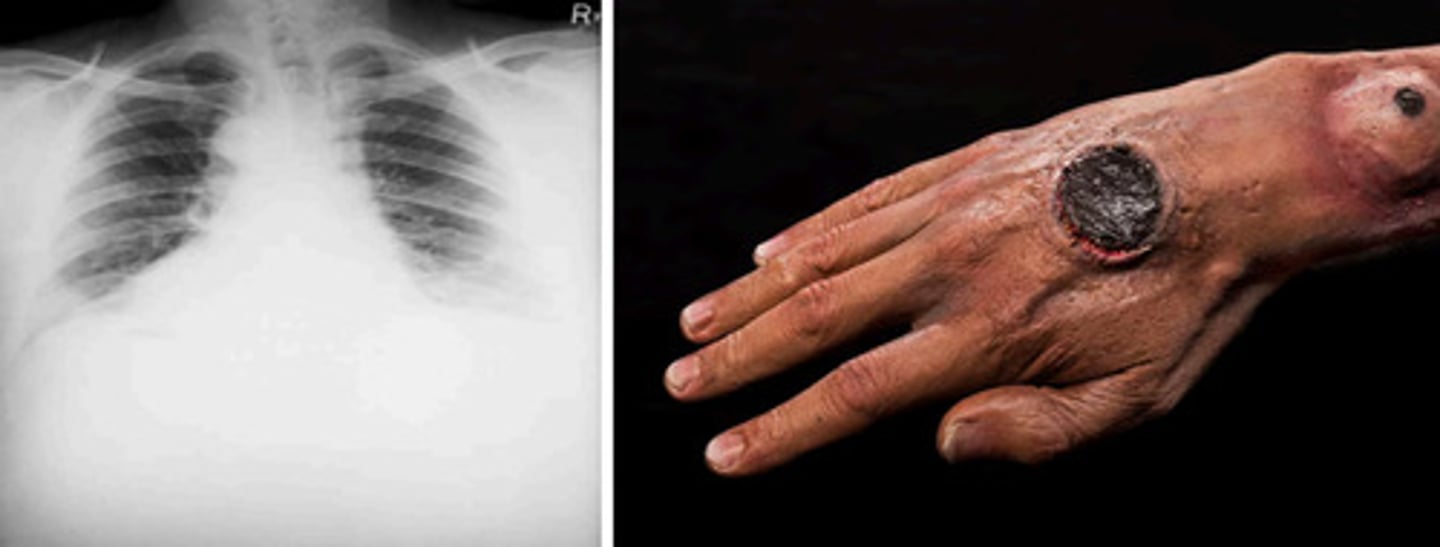
Yes
Is Anthrax zoonotic?
Campylobacter jejuni
What is the most common Campylobacter agent?
Campylobacter
Which infection involves infection with humans, domesticated, and wild animals?
Campylobacteriosis
Clinical signs of this infection include diarrhea, hematochezia, fever, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, potentially causing IBS, arthritis, and Guillain Barre syndrome.
Self Limiting and mild
What is the Campylobacter infection normally like in humans? Persistent and needing antibiotic treatment or self limiting and mild?
65 and older, children under 5, immunocompromised, pregnant, international travelers, stressed animals under 6 mo.
Who is at the highest risk for Campylobacter infection?
Campylobacter
This infection causes 1.5 million illnesses each year with 200 deaths in the U.S.
Campylobacter
This infection can be diagnosed using ELISA, stool sample, bacterial culture
Predominantly foodborne: contaminated/uncooked poultry, raw/contaminated milk, contaminated water/ice, RARELY fecal oral/person to person
How is Campylobacter transmitted?
Low infective dose, less than 500 organisms can cause disease
What is the infective dose for Campylobacter like?
Yes
Is Campylobacter zoonotic?
Antibiotics, hygiene management, supportive care, take food precautions
How can you treat Campylobacter?
Campylobacter
This is a gram negative curved/spiral rod bacterium. Many species exist but only few of them are pathogenic.
Campylobacter
What is the most common bacterial cause of human gastroenteritis worldwide?
Climate change
What change has been linked to increased emergence of Campylobacter?