Angiosperms Lab
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Flower anatomy
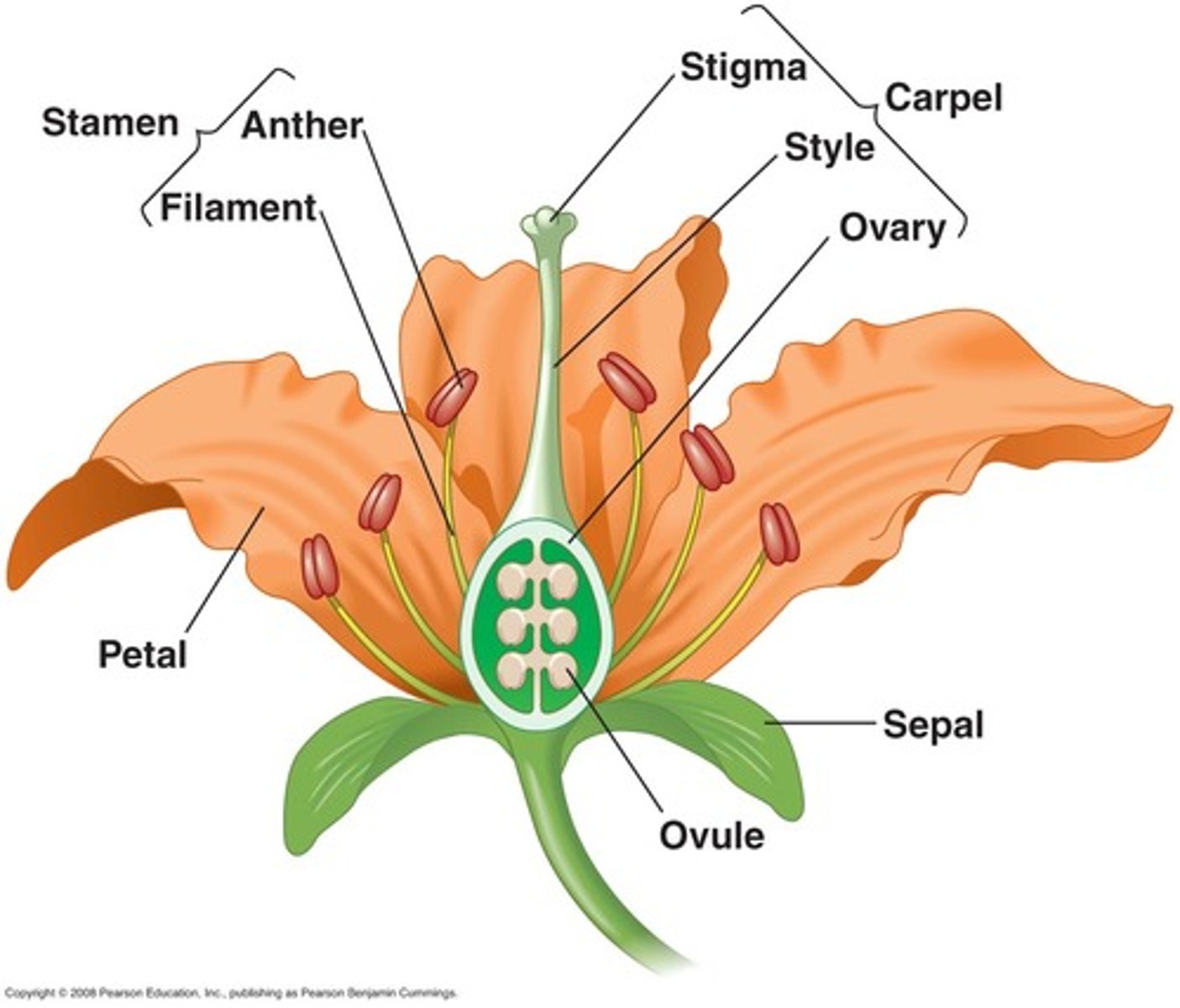
Petal is a unit of the
corrola
Sepal is the unit of the
calyx
Purpose of pistil/ carpels
◦the female reproductive structure of a flower composed of a stigma, style, ovary, and ovule
Purpose of stamen
the male reproductive structure of a flower, consisting of a filament and a anther, in which the pollen grains develop
Complete flower
flowers that contain sepals, petals, stamen, and pistils (carpels)
incomplete flowers
flowers that are missing one or more parts of a complete flower
Perfect flowers
flowers that contain stamen and pistils (carpels)
imperfect flowers
flowers that are missing either pistils (carpels) or stamen
Angiosperms are
heterosporous
Monocot characteristics
◦flower parts are in multiples of three
◦leaves with parallel veins
◦the embryo has one cotyledon
cotyledon: embryonic seed leaves
◦stem is a atactostele
atactostele: vascular tissue (xylem and phloem) is scattered throughout the stem
◦only primary growth no true secondary growth
◦fibrous root system
Dicot characteristics
◦leaves with net-like veins
◦flower parts in multiples of four or five
◦two cotyledons in the embryo
◦stem is a eustele
eustele: vascular bundles are arranged in a ring around the stem
◦many with secondary growth
◦tap root usually present
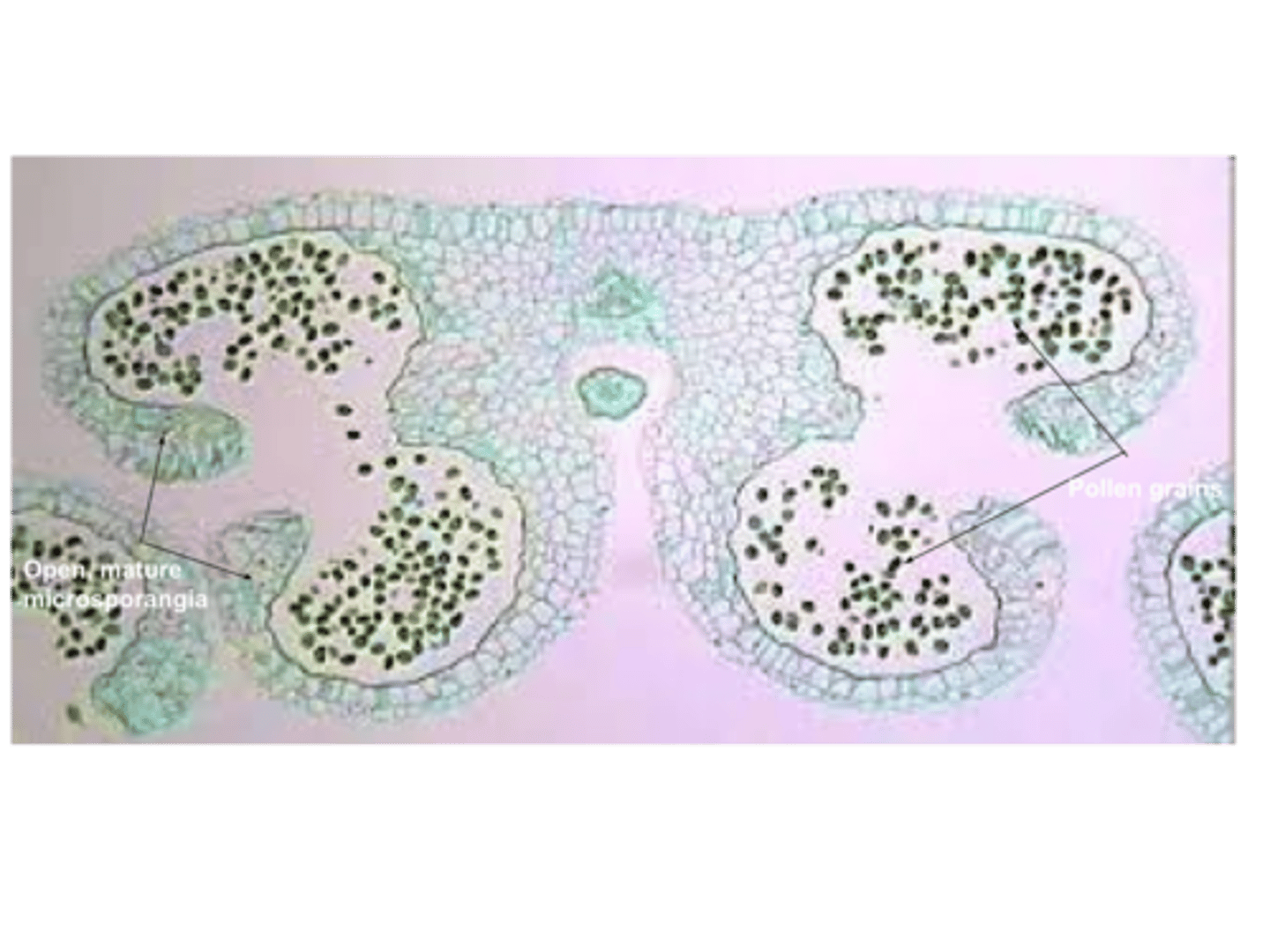
lily anther pollen tetrads
Lily anther pollen tetrads labeled
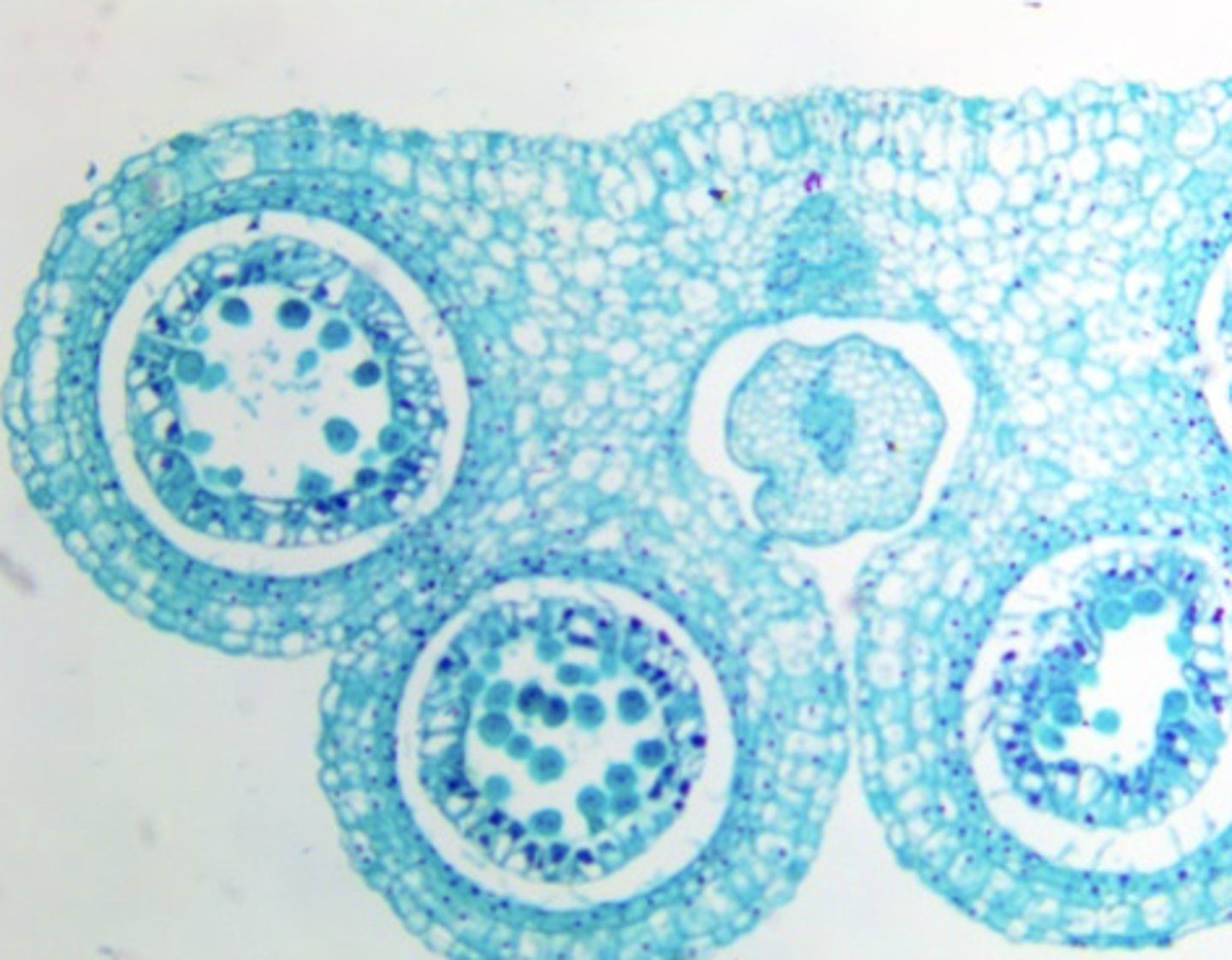
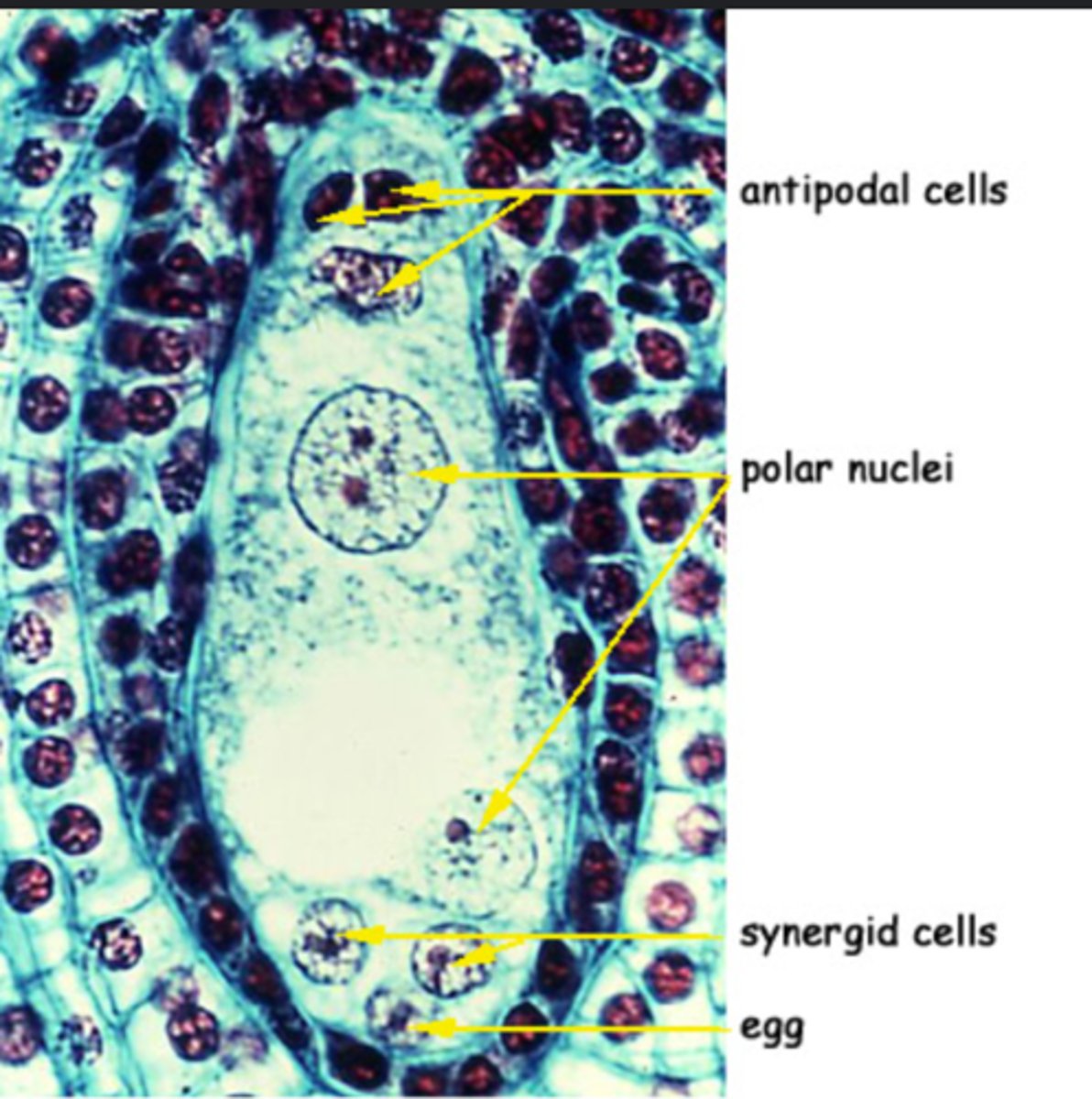
lily ovulatory mature female gametophyte
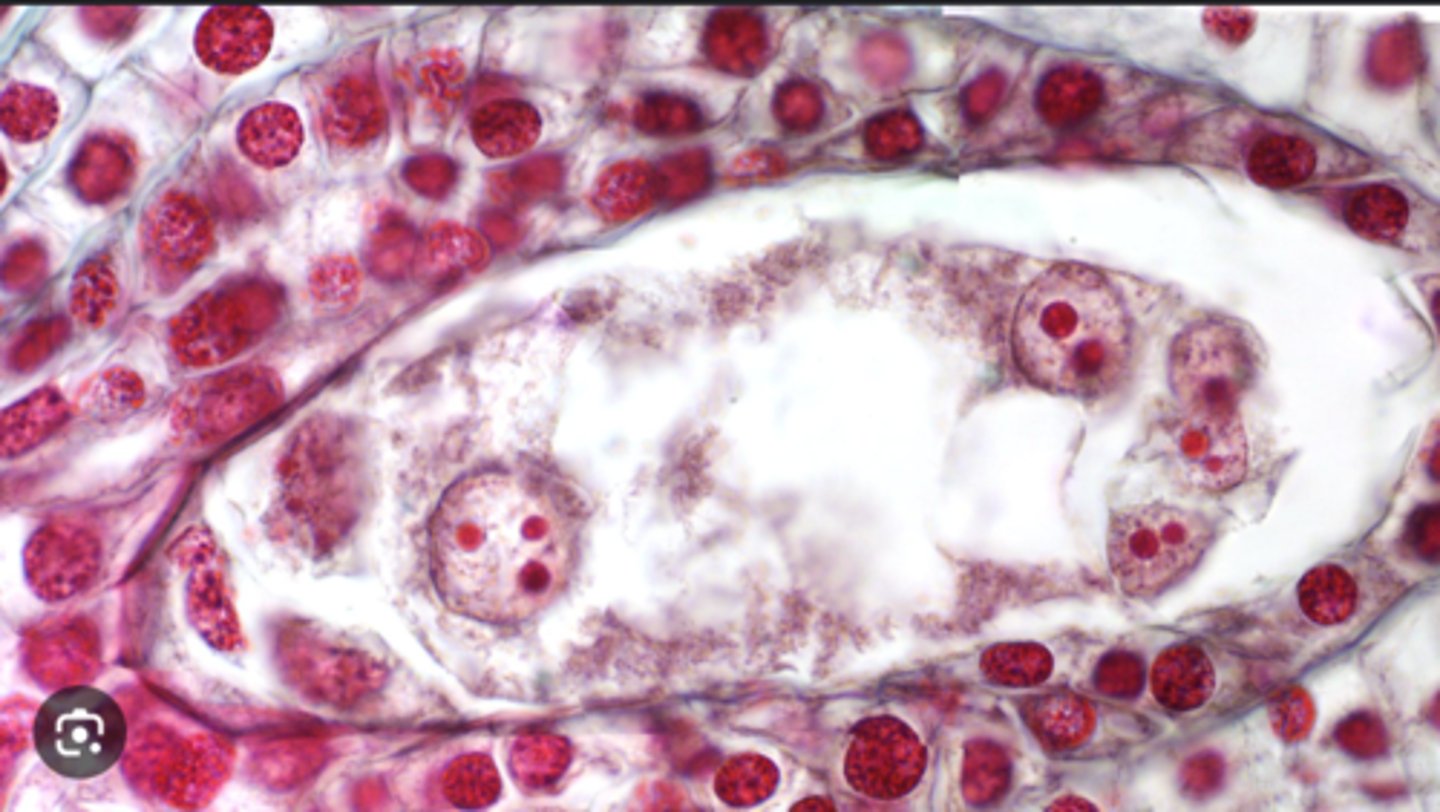
label lily ovulatory mature female gametophyte
Angiosperms belong to phylum
anthophyta