Part 4 - Hybridization
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
True about conditions for bonding:
a. Two electrons are needed to make a bond between two atoms.
b. Each of those atoms must have an unpaired orbital.
c. When they unify, their two unpaired orbitals become one paired/filled orbital.
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
f. All
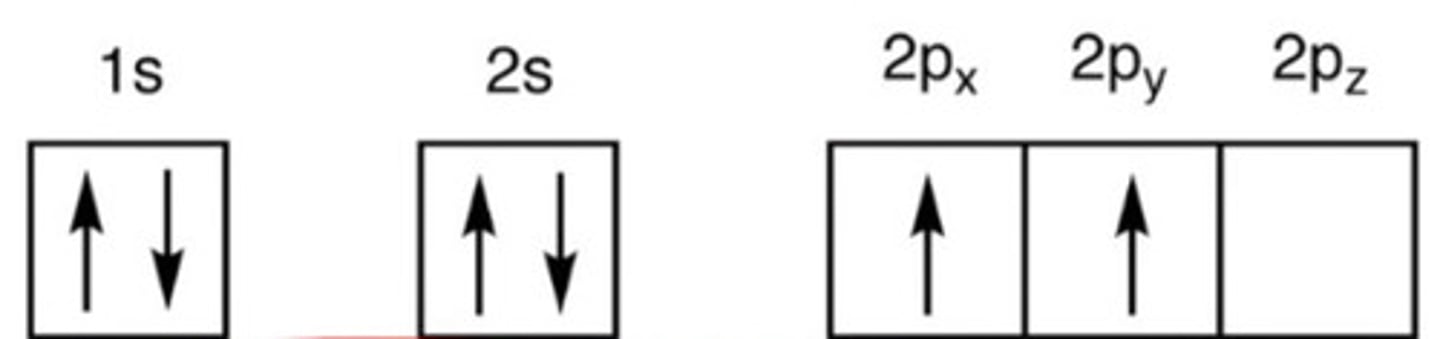
In this state, C has only 2 unpaired orbitals.
a. Ground
b. Excited
a. Ground
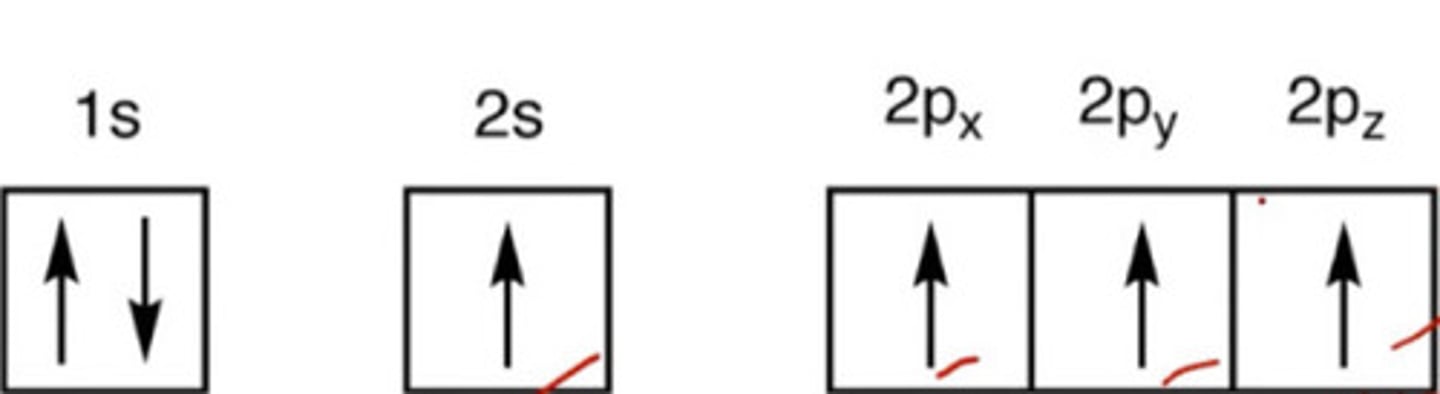
In this state, C will have 4 unpaired orbitals.
a. Ground
b. Excited
b. Excited
Bonding is headways overlap.
a. Sigma bond
b. Pi bond
a. Sigma bond
Bonding is sideways overlap.
a. Sigma bond
b. Pi bond
b. Pi bond
Stronger bond.
a. Sigma bond
b. Pi bond
a. Sigma bond
Weaker bond.
a. Sigma bond
b. Pi bond
b. Pi bond
First bond that forms.
a. Sigma bond
b. Pi bond
a. Sigma bond
Bond that is formed after the other.
a. Sigma bond
b. Pi bond
b. Pi bond
Formed by s or spx orbitals.
a. Sigma bond
b. Pi bond
a. Sigma bond
Formed by p orbitals only.
a. Sigma bond
b. Pi bond
b. Pi bond
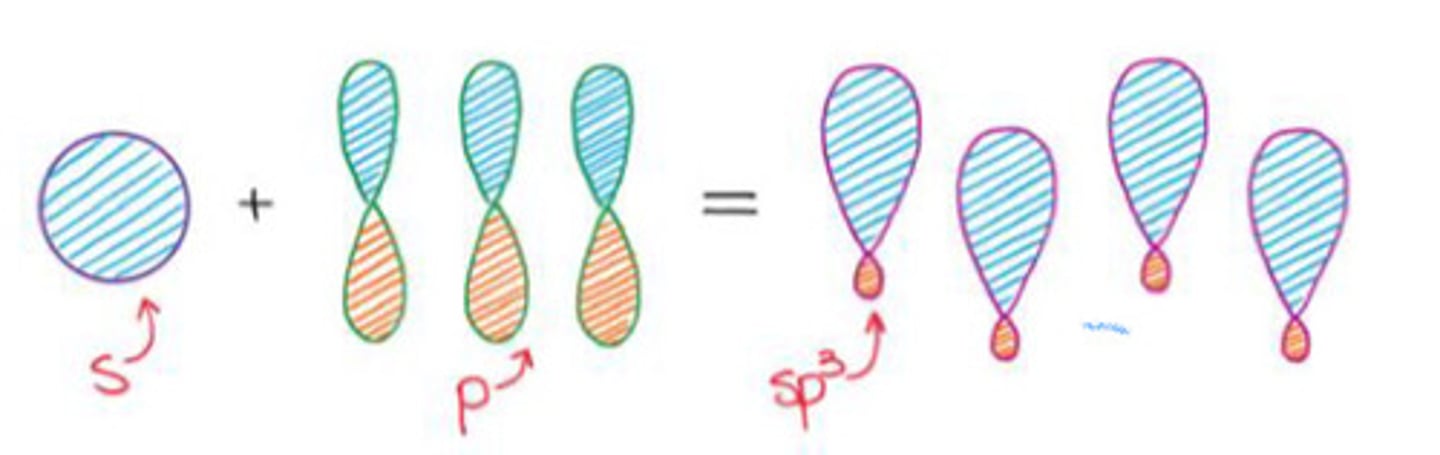
Mixing an s-orbital and three p-orbitals.
a. sp3 hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
c. sp hybridization
a. sp3 hybridization
Total substituents or attachments of sp3 hybridization.
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
d. 4
4 sp3 = sigma bonds
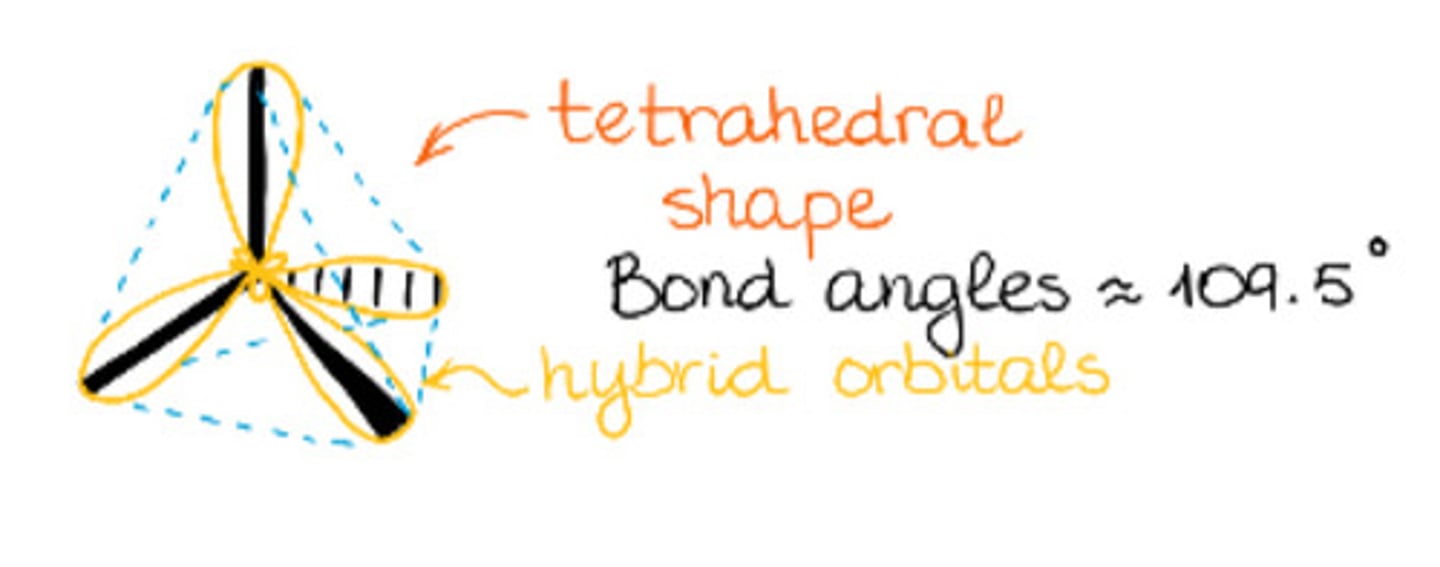
Bond angle of sp3 hybridization.
a. 109.5°
b. 120°
c. 180°
d. 240°
a. 109.5°
Has tetrahedral geometry.
a. sp3 hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
c. sp hybridization
a. sp3 hybridization
Three dimensional.
a. sp3 hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
c. sp hybridization
a. sp3 hybridization
Mixing of 1 s-orbital and 2 p-orbitals.
a. sp3 hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
c. sp hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization.
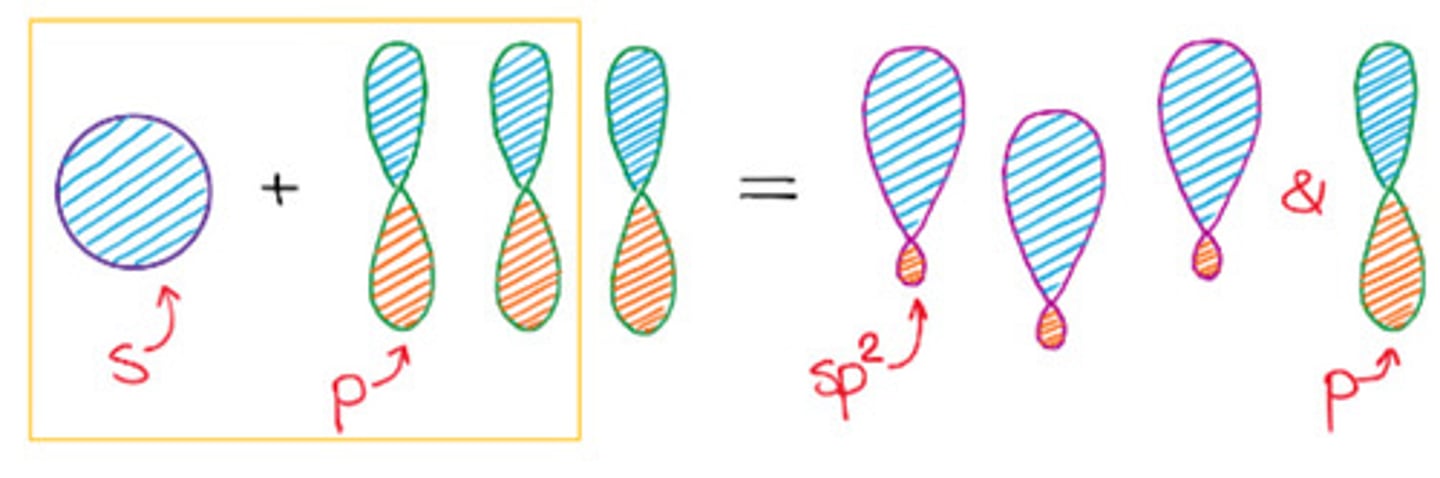
Total substituents or attachments of sp2 hybridization.
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
c. 3
3 sp2 orbitals = 3 sigma bonds
1 p orbital = 1 pi bond
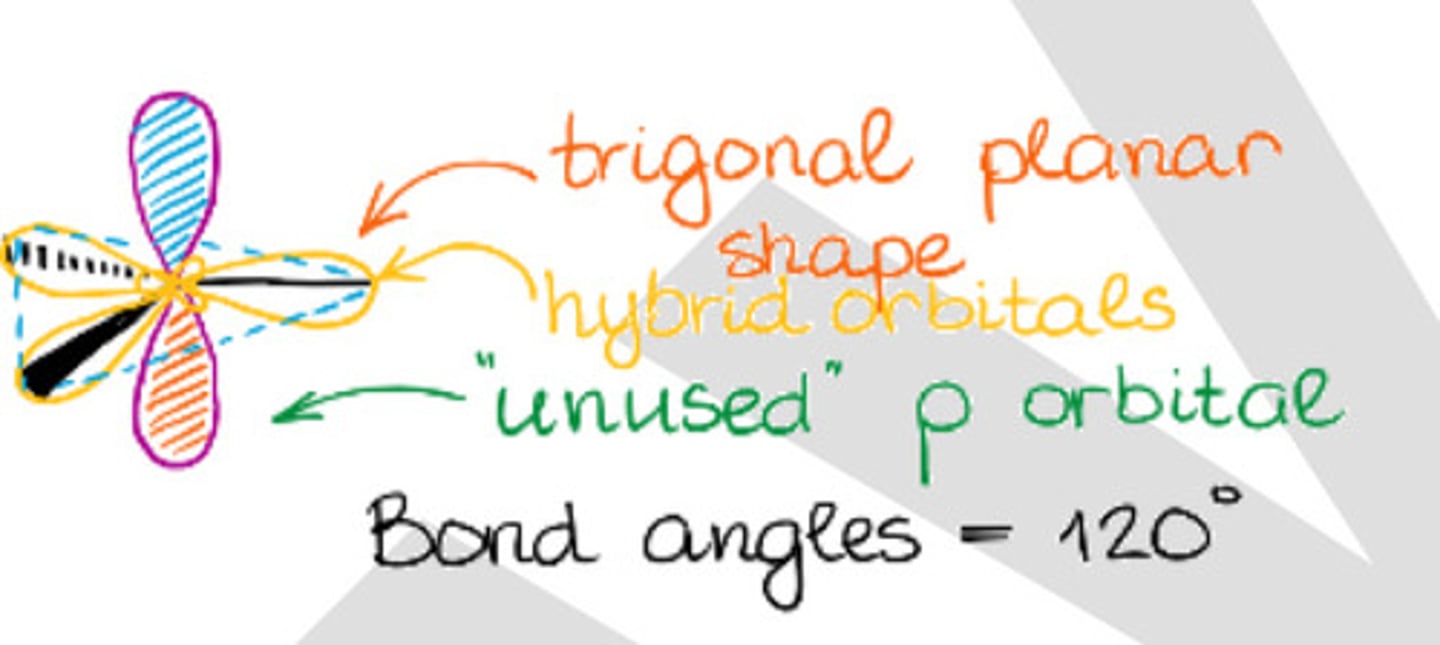
Bond angle of sp2 hybridization.
a. 109.5°
b. 120°
c. 180°
d. 240°
b. 120°
Has trigonal geometry.
a. sp3 hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
c. sp hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
Two dimensional.
a. sp3 hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
c. sp hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
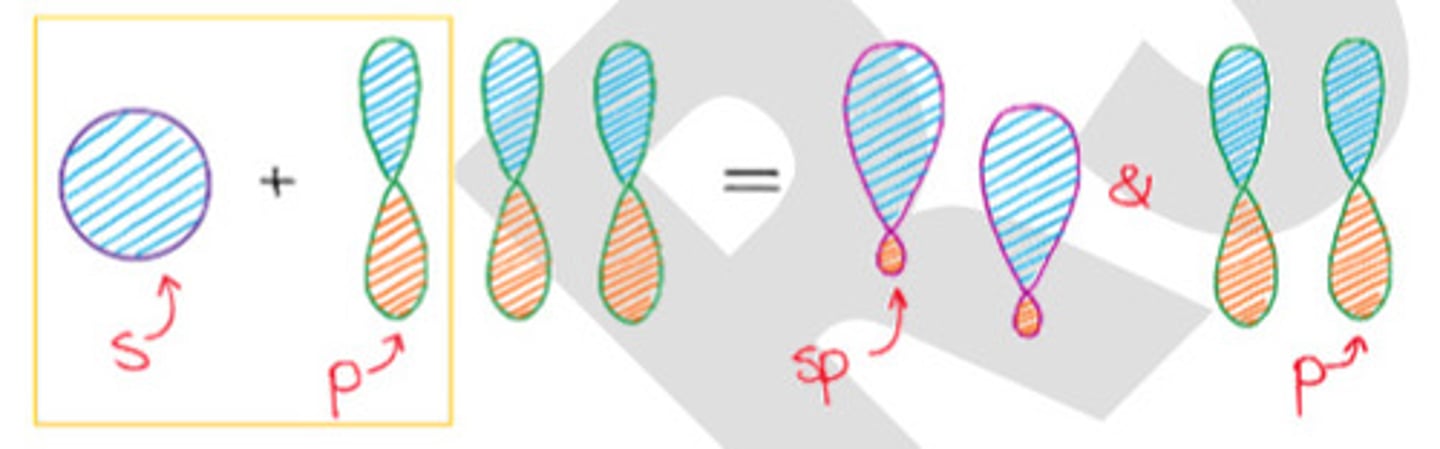
Mixing 1 s-orbital and 1 p-orbital.
a. sp3 hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
c. sp hybridization
c. sp hybridization
Total substituents or attachments of sp hybridization.
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
b. 2
2 sp = 2 sigma bonds
2 p = 2 pi bonds
Bond angle of sp hybridization.
a. 109.5°
b. 120°
c. 180°
d. 240°
c. 180°
Has liner geometry.
a. sp3 hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
c. sp hybridization
c. sp hybridization
Which will result to 4 sigma bonds?
a. sp3 hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
c. sp hybridization
a. sp3 hybridization
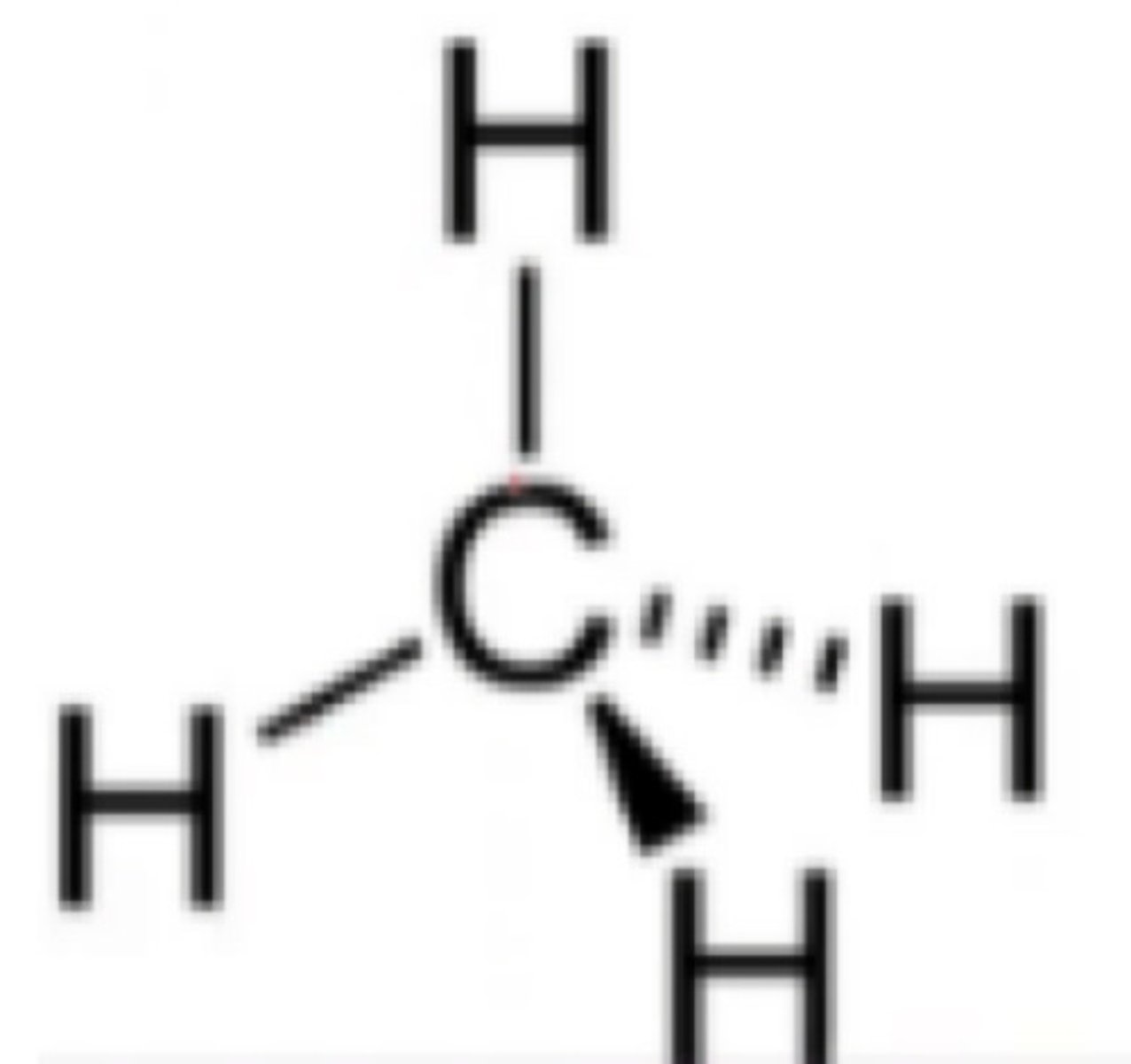
Which will result to 3 sigma bonds and 1 pi bond?
a. sp3 hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
c. sp hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
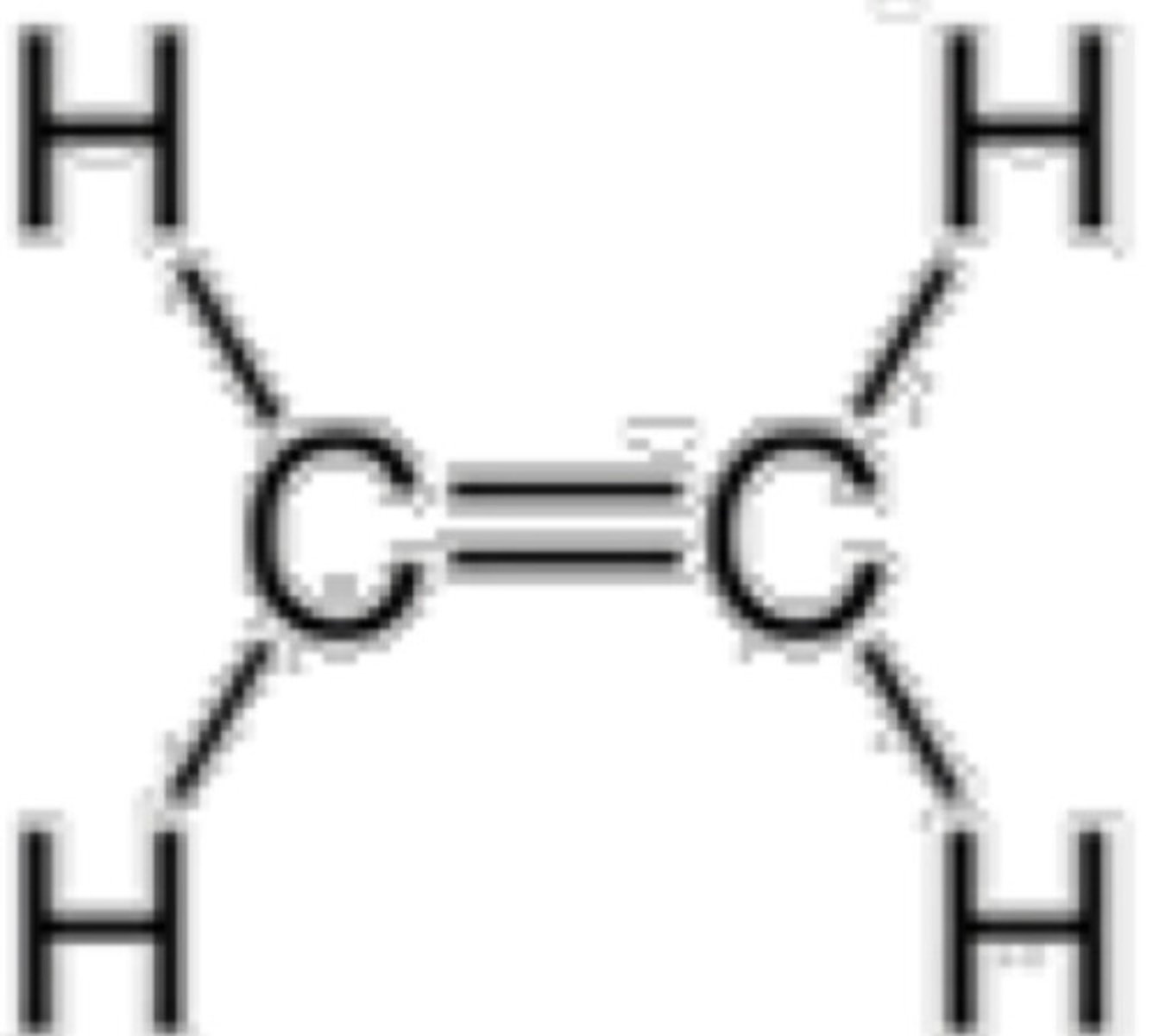
Which will result to 2 sigma bonds and 2 pi bonds?
a. sp3 hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
c. sp hybridization
c. sp hybridization
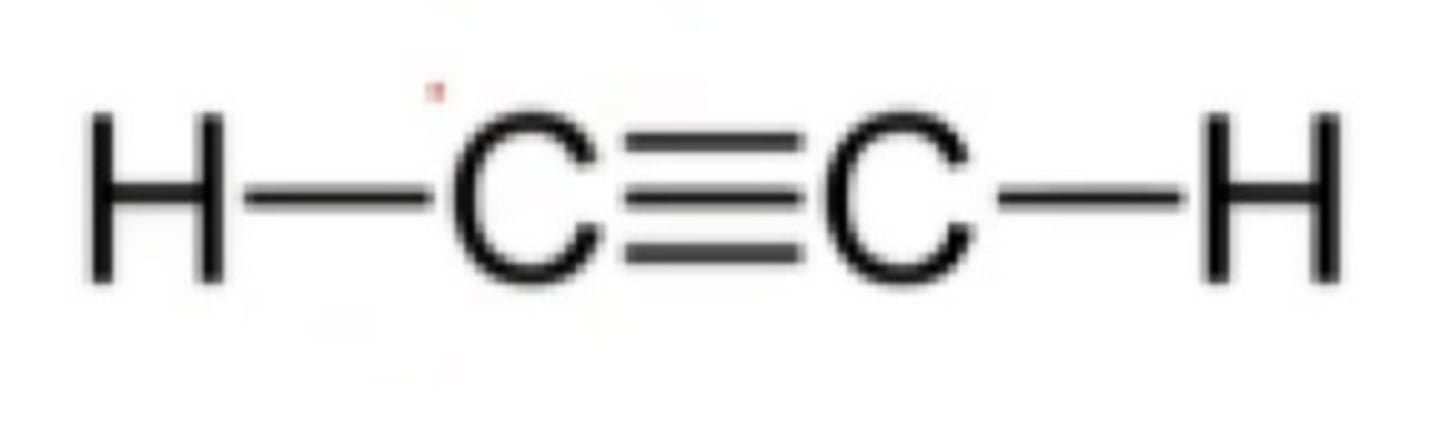
What is the hybridization of one C=C?
a. sp3 hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
c. sp hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
What is the hybridization of the middle carbon in C=C=C?
a. sp3 hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
c. sp hybridization
c. sp hybridization
It has 2 sigma and 2 pi bonds.
What is the hybridization of one C≡C?
a. sp3 hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
c. sp hybridization
c. sp hybridization
What is the hybridization of purely C-C?
a. sp3 hybridization
b. sp2 hybridization
c. sp hybridization
a. sp3 hybridization
Area in the molecular orbital where there is a zero probability of finding electron.
a. Node
b. Anode
c. Orbit
d. Positive region
a. Node
True about benzene except:
a. Shape is trigonal planar
b. Include pure sp2 hybridization
c. Each carbon can hold 3 sigma bonds
d. Hold 3 pi bonds
e. None
e. None