Chapter 10 Economics: Monopoly
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Market Power
the ability to alter the market price of a good or service
Does a monopoly have total market power?
Yes!
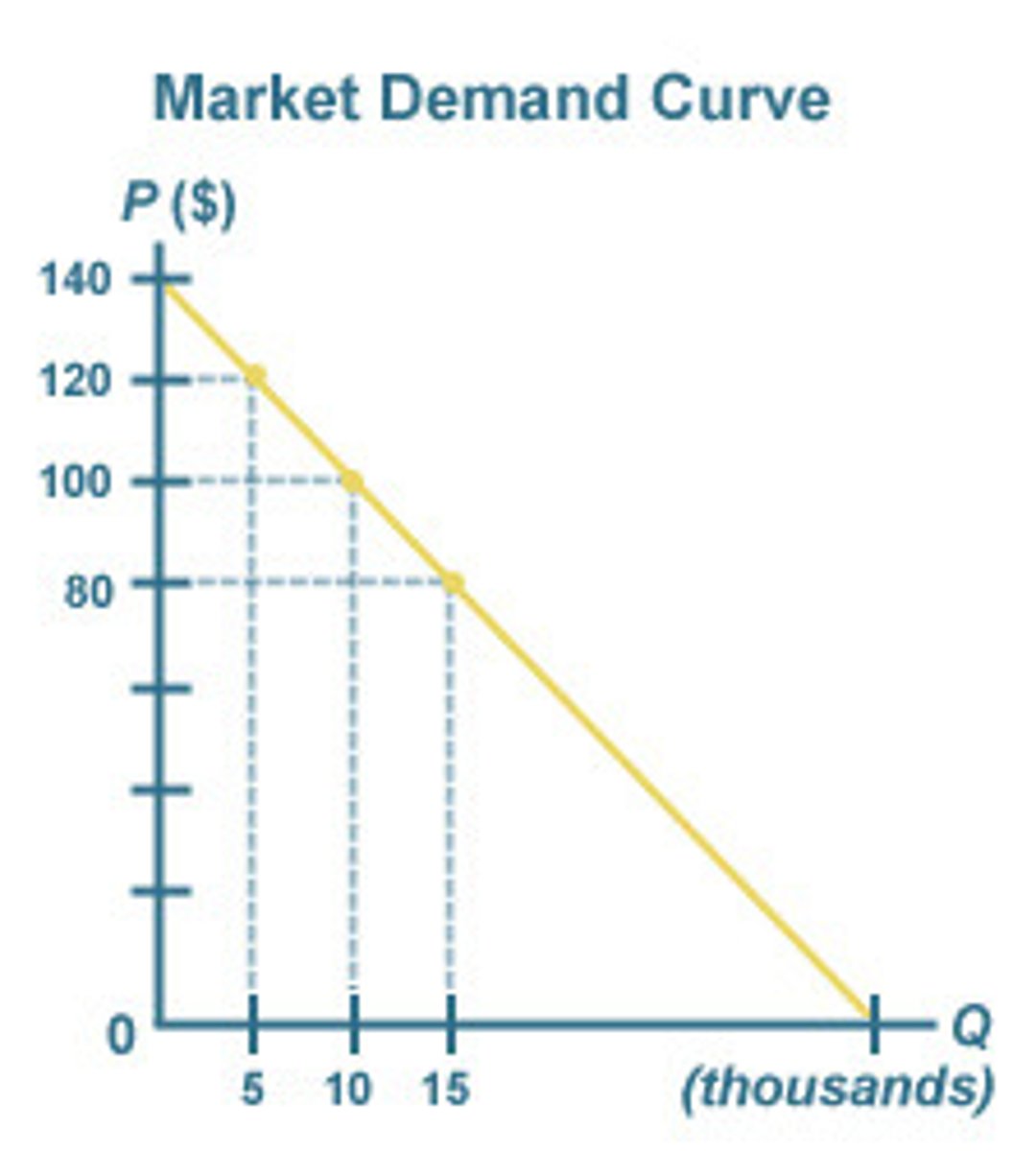
What type of curve does a monopolist have?
confronts a downward sloping market demand curve for its output
Imperfect competition
a market structure that does not meet the conditions of perfect competition (MR no longer equals price)
How do I find Profit Maximization?
1. Find where the MR curve intersects the MC curve
2. Drop down to the output to find the PROFIT MAXIMIZING QUANTITY
3. Go up to the demand curve and then left to the price axis to find the PROFIR MAXIMIZING PRICE
What is compatible with profit maximizing output?
ONLY ONE PRICE
The monopolist will charge that price
If higher or lower price, profit falls!
If MR>MC
increase output and profit rise
If MR
decrease output and profit rise
MR=MC
this is the profit maximizing output
Charactristics of Monopoly
-must be total barrier to entry, if not another firm will enter and end the monopoly
-no close substitutes
-no competitive pressure (charge higher prices and produce smaller quantity)
-no profit squeeze
-no increased quantity even if consumer demand increases
Competitive Industry
-High profits attract more suppliers.
-Supply shifts right and price falls.
-Economic profits go to zero.
-P = MC.
-Profits are squeezed, so there is great pressure to reduce costs and improve quality.
Monopoly
-High profits, but barriers to entry exclude new suppliers
-Want high barriers ---> earns them market power
-no product change, so price does not fall
-P>MC
-No profit squeeze, no pressure to reduce cost or improve quality
Where does market power come from?
-high entry barriers --> keep competitors out
-patients
-exclusive franchises
-political appointment
-considerable market power ---> generate products used by the firm to exert political power
Does a monopoly have absolute power?
No! The customer does not have to buy from the monopolist
Monopolists in any event would not gouge the customer, it will set its prices in accordance with the profit maximizing rules
Price Discrimination
the business practice of selling the same good at different prices to different customers
pros of market power
-greater ability to pursue research and development
-tremendous incentive for invention and innovation
-large companies can produce more efficiently
-act accordingly to competition
Cons of Market Power
-R&D. No competition = little incentive to improve their product
-Invention and innovation --> new products come from entrepreneurs who weren't allowed to pursue their dreams so they break away from the firm.
Economies of Scale
When bigger means cheaper
-As production increases, the average cost per unit decreases
-increasing scale does not lower costs as economies of scale kick in. However, there is no incentive for the monopolist to expand to achieve this advantage
(creates natural monopolies)
Natural Monopoly
an industry in which one firm can achieve economies of scale over the entire range of the market
-economies of scale acts as a natural barrier to entry
-utilities have been examples of natural monopolies (cable, water, gas)
Government sets up natural monopolies
-describes the rate quality and area of service
-sets the rate(price) the natural monopoly can charge its customers
-the rate is set so there is no economic profit
-normal profit is allowed
Contestable Market
an imperfectly competitive industry subject to potential entry if prices or profits increase
-monopolies may be constrained by potential competition
-entry barriers become important
-one firm may seem to monopolize an industry, but if other firms can enter the monopoly must compete
Sherman Act of 1890
Makes trusts and conspiracies in restraint of trade illegal; makes monopolies and attempts to monopolize misdemeanors
Clayton Antitrust Act
prohibits price discrimination, exclusice dealing agreements, certain types of merger, and interlocking boards of directors among competing firms
FTC (Federal Trade Commission)
studies industry structures and behaviors to identify anti competitive practices