Economics unit 1
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What is the business cycle?
The economy’s cycle of rising and falling activity over time
Characteristics of the expansion phase?
Rise in production/output, wages, consumer spending, and decrease in unemployment
Characteristics of the contraction phase?
Decrease in production/output, wages, consumer spending, and increase in unemployment
What is a recession
when the economy shrinks — for two quarters in a row (6 months) of negative GDP.
What is a depression and list 3 possible causes/ characteristics
A severe & prolonged downturn caused by falls in output, high unemployment and deflationary pressure.
Define economic growth.
The increase in a country’s production of goods and services over time.
Why is economic growth important?
Boosts jobs, income, living standards, and taxes, but it must grow faster than the population rate.
How is economic growth measured?
Growth GDP and GDP per capita
Formula for Aggregate Demand (GDP by expenditure)?
AD = C + I + G + (X - M) where C consumption, I investment, G government spending, X exports, M imports
What is the formula for GDP change (%)?
((GDP this year – GDP last year) ÷ GDP last year) × 100.
What is the target growth rate?
3-4% real GDP per year.
What are the limits of using economic growth as a performance measure?
GDP growth ignores inequality, unpaid work, environment, and quality-of-life
What is Natural Unemployment?
The normal joblessness from people changing jobs or skills not matching work available. (usually 4% of people)
Which types of unemployment make up Natural Unemployment?
Frictional unemployment
Structural unemployment
Define Frictional Unemployment. Give examples
Short-term joblessness when people switch, move, or re-enter work (e.g., graduates).
Define Structural Unemployment. Give examples
Job loss when skills don’t match new jobs (e.g., automation).
Define Cyclical Unemployment. Why is it serious?
Caused by long-term changes in the economy. (e.g. businesses failing)
Underemployment—definition + examples.
Workers have jobs but aren’t working to full potential or desired hours.
Identify type of unemployment:
A: - Fired from fast-food job (misconduct)
B - Factory closes due to outdated product
C - Recession layoffs in restaurants
D- Ski-lift operator loses job in spring
E - Rise in AI replacing jobs
A - Frictional
B - Structural
C - Cyclical
D - Seasonal
E - Structural
Effects of unemployment on living standards?
Lower output, falling GDP, loss of skills, & weaker innovation.
Effects of unemployment on national production?
Less output, slower growth, reduced competitiveness, fewer foreign investors/skilled migrants.
Effects of unemployment on government budget?
Unemployment reduces tax, limits infrastructure, health, education.
Define inflation.
The general rise in prices over time, reducing money’s purchasing power
Describe Demand‑pull inflation.
When aggregate demand exceeds supply, pushing prices up.
Describe Cost‑push inflation.
When production costs rise, reducing supply and raising prices
What does SRAS stand for?
Short-Run Aggregate Supply
CPI index formula?
Cost of goods in current period (t)
——————————————— x 100
Cost of that good in base year
Australia’s target rate of inflation?
2–3% CPI on average over time.
Consequences of high inflation?
Inflation reduces purchasing power, creates uncertainty, shifts income and raises costs.
How is the labour force participation rate calculated?
(Labour Force / Working-Age Population) × 100
How do you calculate the labour force?
Number of Employed + Number of Unemployed (who are actively seeking work)
Fill in the Following diagram:
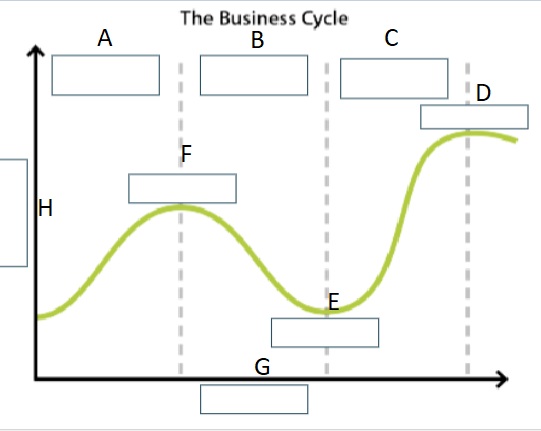
A = Expansion
B = Contraction
C = Expansion
D = Peak
E = Trough
F= Peak
H= Output
G= Time
During what stage of the business cycle are we likely to see wages decreasing?
Contraction (Recession phase) – businesses cut jobs, unemployment rises, and wages usually decrease.
During which stage of the business cycle are we most likely to see production and output increasing?
Expansion – businesses grow, demand rises, production and output increase, and unemployment falls.
Unemployment is most likely to peak during a ___?
Trough – the lowest point in the business cycle.
Unemployment is most likely to be the lowest during a ___?
Peak
What are examples of investment spending?
New factories and machinery
Technology and equipment
New buildings and offices
People losing their jobs because the economy has gone into recession is known as?
Options:
A) Seasonal unemployment
B) Structural unemployment
C) Frictional unemployment
D) Cyclical unemployment
D
What is meant by real GDP per capita?
Average goods and services each person produces, adjusted for inflation.
According to the ABS, Australia’s GDP rate for the last quarter of 2024 was 0.6%. Explain why this is not considered ideal.
because it causes slow economic expansion, limited jobs, income, and confidence.
Describe 2 limitations of using GDP to measure economic growth.
GDP can rise even if most people stay poor.
unpaid work and pollution are excluded.
What are the 2 main types of inflation?
Demand-pull inflation – occurs when demand exceeds supply, pushing prices up.
Cost-push inflation – occurs when production costs rise, leading businesses to increase prices.
What is the calculation for inflation?
CPI last year - CPI this year / CPI last year×100
What are 2 consequences of inflation?
Erodes purchasing power – money buys less over time.
Creates uncertainty – makes planning, saving, and investment more difficult.
Give an example of who is not in the labor force.
People not working and not seeking work, such as:
Full-time students
Retirees
What are the 4 ABS criteria for someone to be considered unemployed?
Not working at all
Actively seeking work
Available to start work
Of working age (15+ in Australia)
Effect of unemployment on the economy as a whole?
Less spending and demand, wasted labor resources, lower production, and slower economic growth overall.
How do you measure the unemployment rate?
Unemployed/ labor force × 100
What is an example of Australian imports?
Australians going to Bali
Explain why it is more meaningful to compare 2 economies to GDP per capita rather than on GDP?
GDP per capita is better as it adjusts for population, showing average living standards, unlike total GDP.
Explain why inflation may cause firms to make capital for labor substitutions.
Inflation raises labor costs as wages increase, leading firms to substitute capital and technology for expensive human labor.
What is a boom? And what can it lead to?
A period of strong economic expansion (businesses full capacity or above). It can lead to rapid growth in prices.
What are 3 business cycle indicators?
Lagging
Leading
Coincident
What are lagging indicators in the business cycle?
Confirm trends after they occur. e.g., consumer debt, & bankruptcies
What are leading indicators in the business cycle?
Predict future economic activity, changing before the economy does e.g., employment vacancies & inventory levels.
What are coincident indicators in the business cycle?
Move simultaneously with the economy, reflecting activity e.g., retail sales, real GDP.
How frequently is the unemployment level measured?
Seasonally adjusted
How have productivity and working conditions changed over time?
It has increased slowly as knowledge, skills, and human capital embedded in production expanded.
What is headline inflation?
Measures total inflation, comparing current prices to last year, without adjusting extenuating factors.
What is underlying inflation?
Removes one- off seasonal or volatile factors, revealing the true, long term inflationary trend.
Give an example of underlying inflation adjustment.
The effect of Covid- 19 on temporary price falls is removed to show genuine inflationary movement.
What is the typical length of a business cycle?
5-7 years.
Fill in
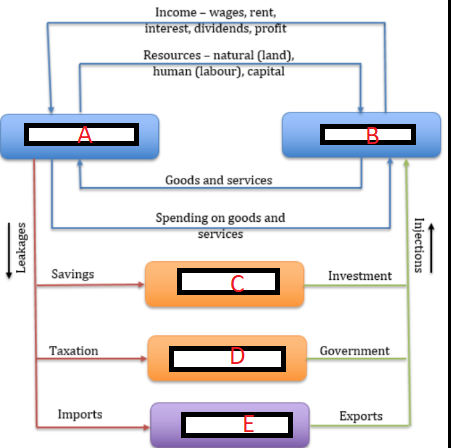
A- Household sector
B- Firms sector
C- Financial sector
D- Government sector
E- Overseas sector