HGAP unit 1 vocab
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Absolute location
The exact position of a place on the Earth's surface, often given in coordinates such as latitude and longitude.
Census data
Statistical data collected from a population, typically used for demographic analysis.
Clustering
The grouping of people or phenomena in a certain area.
Distortion
The misrepresentation of the shape, area, distance, or direction (SADD) of geographic features on a map.
Environmental determinism
The theory that the physical environment predisposes human social development. (env was here bf us, it determines our lifestyle)
Field Observation
The act of watching, recording, and analyzing phenomena in their natural setting.
Flows (migration)
The movement of people from one area to another.
Formal region
An area defined by official boundaries and characteristics, such as a country or city.
Functional region
An area defined by a function or more central focus, such as a metropolitan area.
ex. trains
Geographic Information System (GIS)
A system that captures, stores, analyzes, and presents spatial or geographic data.
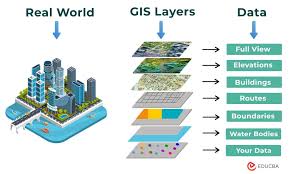
Geographical data
Information about the Earth's surface and its features.
Land Use
The management and modification of natural environment or wilderness into built environment.
Ex. agri, commercial, residential
Landscape Analysis
The assessment and evaluation of physical features, land use, and social aspects of a region.
Map projection & distortion
A method of representing the curved surface of the earth onto a flat map, which creates distortions.
Toponym
A place name, especially one derived from a topographical feature.
Friction of distance
The idea that distance has a limiting effect on human interaction.
Natural Resources
Materials or substances occurring in nature which can be exploited for economic gain.
Perceptual/vernacular region
An area defined by the informal sense of place that people ascribe to them. Ex. midwest
Place
A specific point on Earth distinguished by a particular character.
Possibilism
The theory that the environment sets certain constraints or limitations, but humans can adapt and overcome environmental challenges.
Reference maps
Maps that show the relative locations of geographic features.
Regional analysis
The study of the unique characteristics and patterns found in particular areas.
Regional scale
The level of analysis in geographic studies that focuses on large areas and their interrelations.
Relative location
The position of a place in relation to other places. (to the left, to the north)
Remote sensing
The acquisition of information about an object or area from a distance, typically using satellites.
Satellite imagery
Pictures of Earth or other planets collected by satellites.
Satellite navigation system (GPS)
A system that uses satellites to determine the precise location of a device on Earth.
Scale (map scale)
The relationship between distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground.
Scale (scale of analysis)
The scope or level at which geographical analysis is conducted.
Space
The physical gap or interval between two objects.
Spatial Pattern
The arrangement of various elements in space.
Sustainability
The ability to maintain certain processes or states indefinitely.
Thematic maps
Maps that focus on specific themes or topics. Tell a story
Time-distance decay
The decline in the intensity of an interaction as the distance between places increases. Travel more often to a grocery store 5 min away, than a huge mall a hour away…
Site
The specific location of a place, characterized by physical or human-made features.
Situation
The location of a place relative to its surroundings and other places.
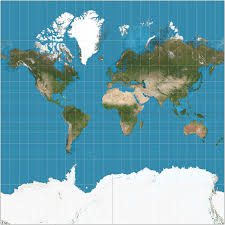
Mercator Map
Distorts size and distance but maintains correct shapes and angles, commonly used for navigation.
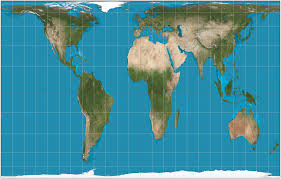
Gall Peters
accurately represents area but distorts shape, often used to emphasize equatorial regions.
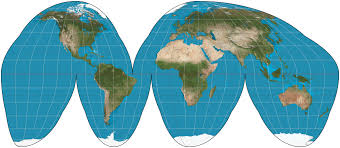
Goode’s Homolosine
minimizes distortion of land area but sacrifices shape. It is designed to represent the distribution of phenomena on Earth's surface.
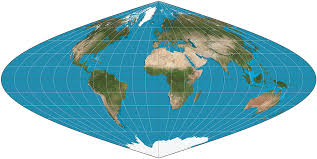
Sinusoidal
accurately represents land area while distorting shapes and distances, often used for global thematic mapping.
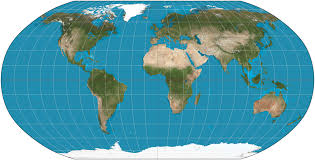
Robinson
attempts to balance distortions in area, shape, distance, and direction, making it visually appealing for world maps.
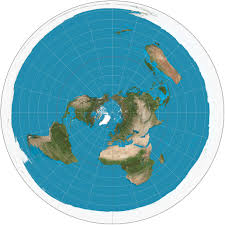
Polar Projection
displays the Earth's northern or southern hemisphere from a viewpoint directly above the pole, often used for aviation and meteorology.
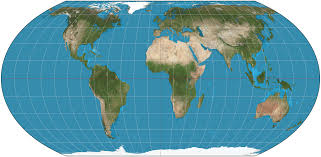
Equal Earth
visually balances area and shape distortions, making it useful for accurate land area representation.