Topic 16 - Chemical Kinetics
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:47 PM on 5/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1
New cards
Rate expression
rate = k[A]^x[B]^y
2
New cards
rate constant
k
3
New cards
overall order of reaction
x + y
4
New cards
order of reaction
either x (with respect to A) or y (with respect to B)
5
New cards
Order of reactions
zero-order: the concentration does not affect the reaction rate
first-order: order of reaction = 1 (rate is proportional to concentration)
second-order: order of reaction = 2
first-order: order of reaction = 1 (rate is proportional to concentration)
second-order: order of reaction = 2
6
New cards
catalysts in activation energy
Alter a reaction mechanism by introducing a step with a lower activation energy
7
New cards
Reaction mechanism
A series of separate intermediate steps. All elementary steps summed together will give the overall balanced reaction.
8
New cards
heterogeneous reaction
a reaction involving reactants in two different phases
9
New cards
homogeneous reaction
a reaction whose reactants and products exist in a single phase
10
New cards
molecularity
the number of reactant particles involved in an elementary step
11
New cards
Unimolecular
describes a reaction that involves only one particle that goes on to form products
12
New cards
bimolecular
an elementary step in a reaction that involves two particles, either the same species or different, that collide and go on to form products
13
New cards
Relationship between reaction mechanism, order of reaction and rate-determining step
The slowest step in a reaction mechanism is known as the rate-determining step or the step with the highest activation energy
14
New cards
unit rate of reaction
mol dm-3 s-1
15
New cards
unit concentration
mol dm-3
16
New cards
Concentration-time graph zero order
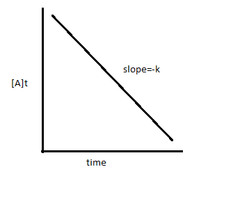
17
New cards
Concentration-time graph first order
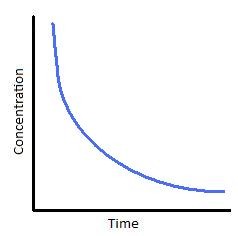
18
New cards
Concentration-time graph second order
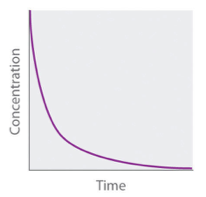
19
New cards
rate-concentration graph zero order
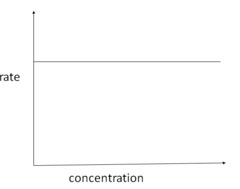
20
New cards
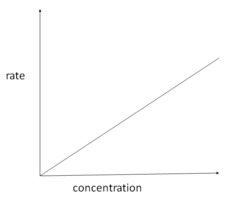
rate-concentration graph first order
21
New cards
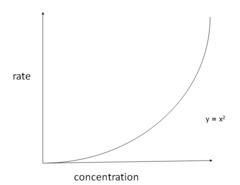
rate-concentration graph second order
22
New cards
Gradient of arrhenius graph
-Ea/R
23
New cards
y intercept (Arrhenius graph)
ln[A]
24
New cards
units in arrhenius equation
t = kelvin, Ea = J mol-1
25
New cards
What is A in the arrhenius equation
A = frequency factor (how many successful reactions occur)
26
New cards
What is your x value
1/T
27
New cards
What are the axis of an Arrhenius equation?
Y axis = ln k
\
X axis = 1/T
\
X axis = 1/T