Physical Assessment Unit 3- Male GU, Rectosigmoid Area, and Prostate
1/209
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
210 Terms
what history questions do you ask before PE?
sexual orientation, relationship status, sexual response (function), anal or oral (associated symptoms for those areas)
what ROS questions do you ask before PE?
penile discharge or lesions, scrotal swelling or pain and STIs, risk of HIV
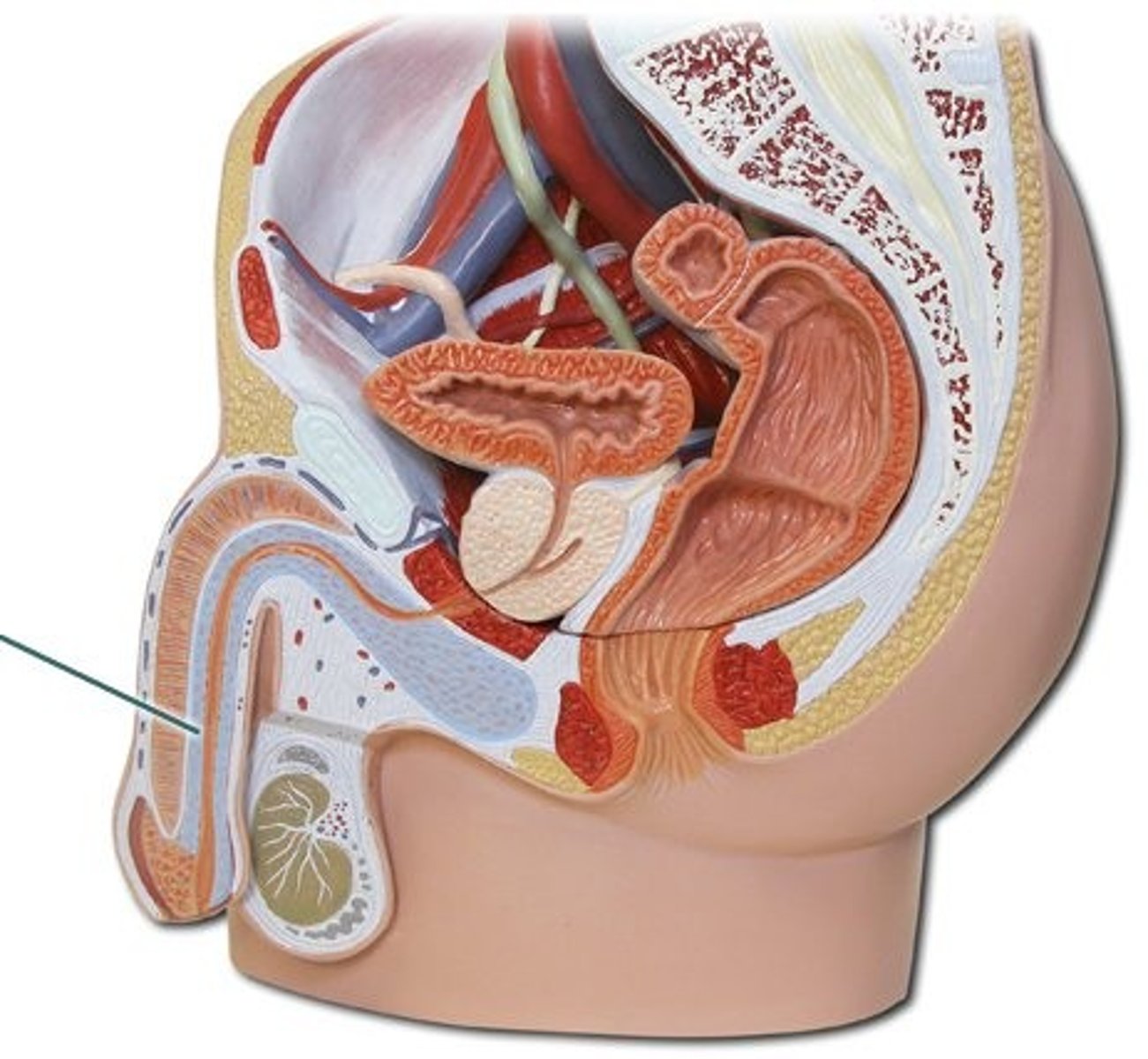
corpus spongiosum
identify this structure
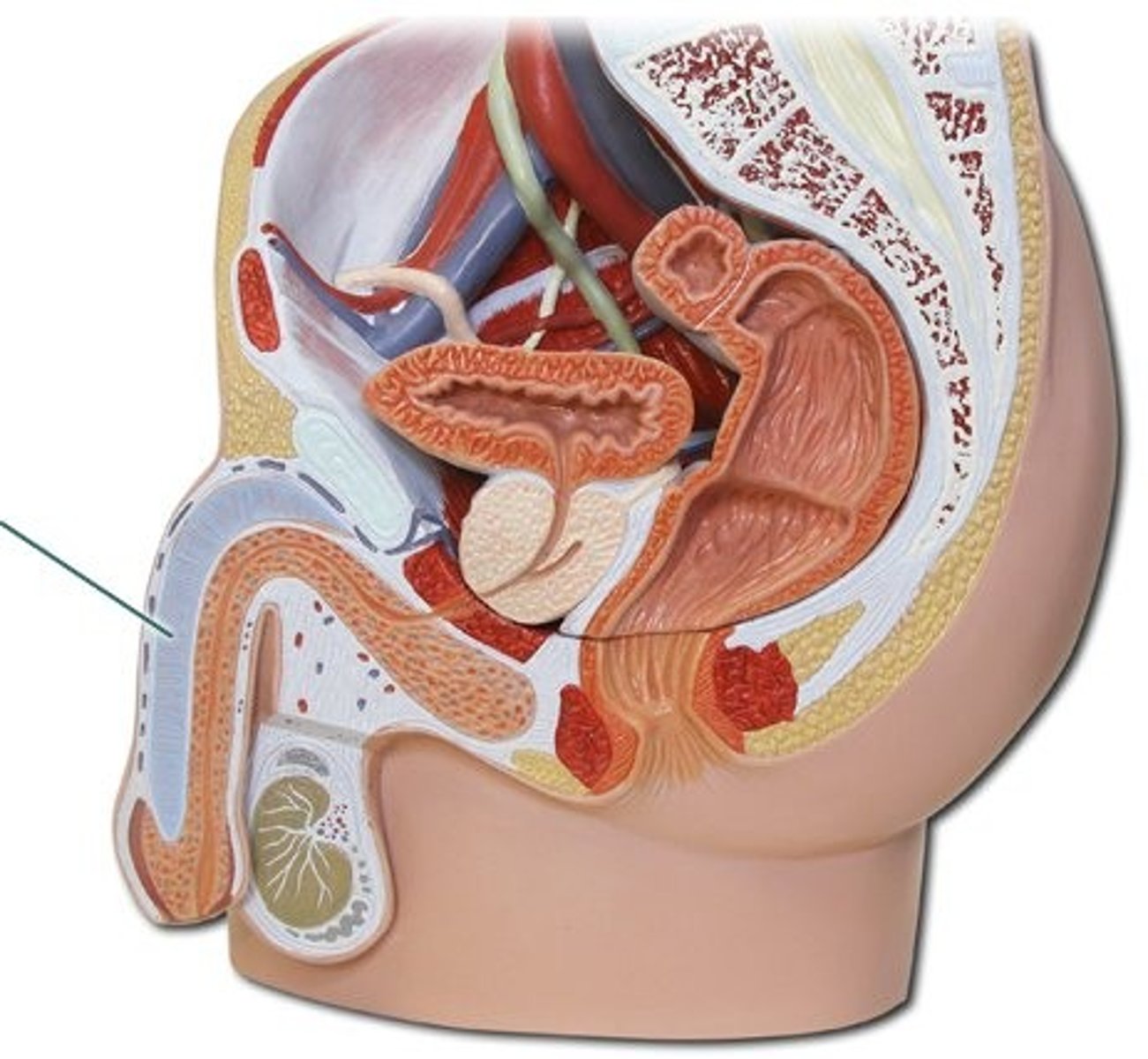
corpora cavernosa
identify this structure
glans penis
identify this structure
foreskin
identify this structure
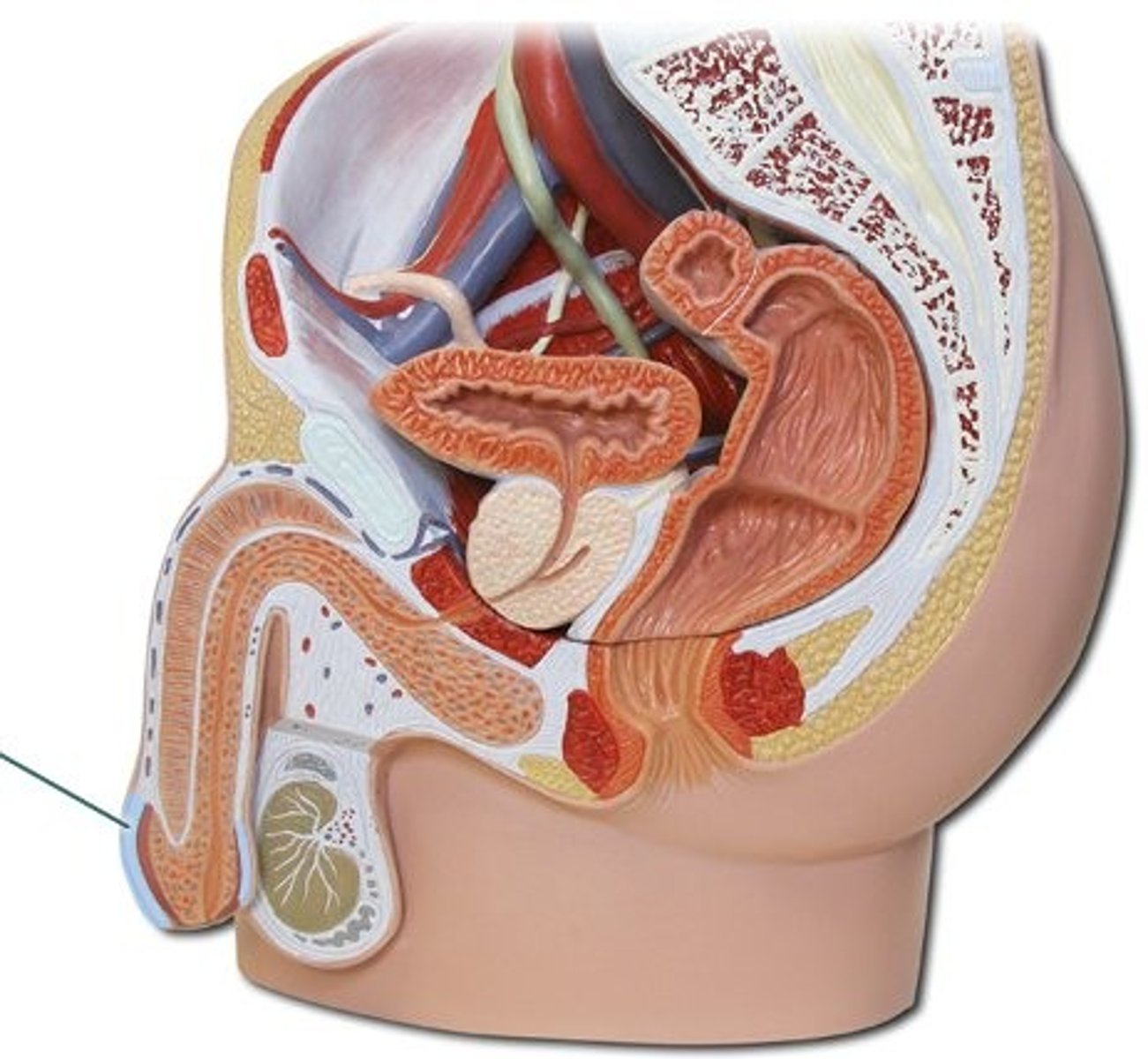
what is the mechanism of creating testosterone in the testes?
GRH, LH + Leydig cells, testosterone
what is the mechanism of triggering puberty?
testosterone, 5a reductase, 5a dihydrotestosterone, triggers pubertal growth
what hormone regulates sperm production?
FSH
In order to trigger pubertal growth in men, testosterone is converted by what?
5a reductase
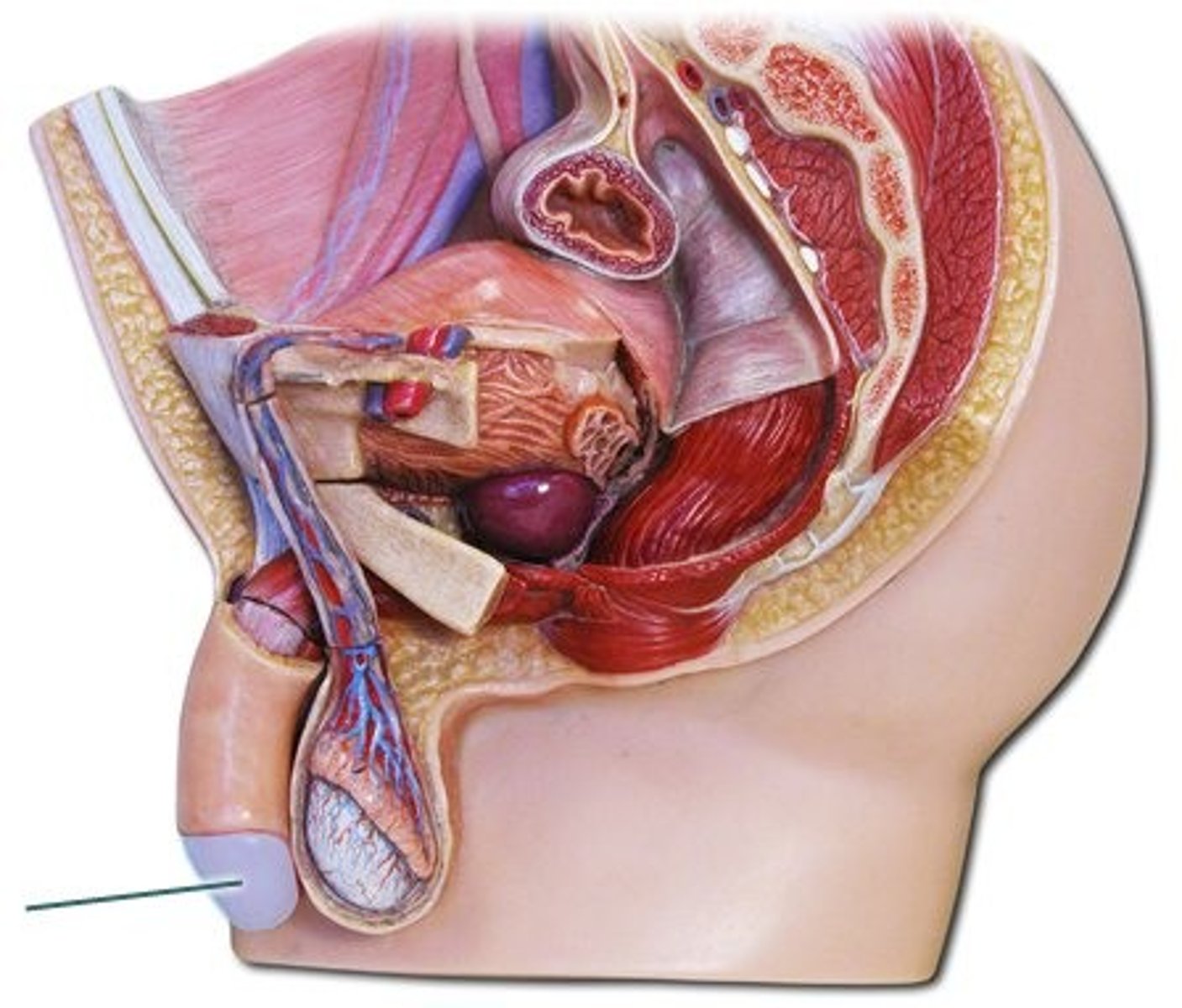
scrotum
identify this structure
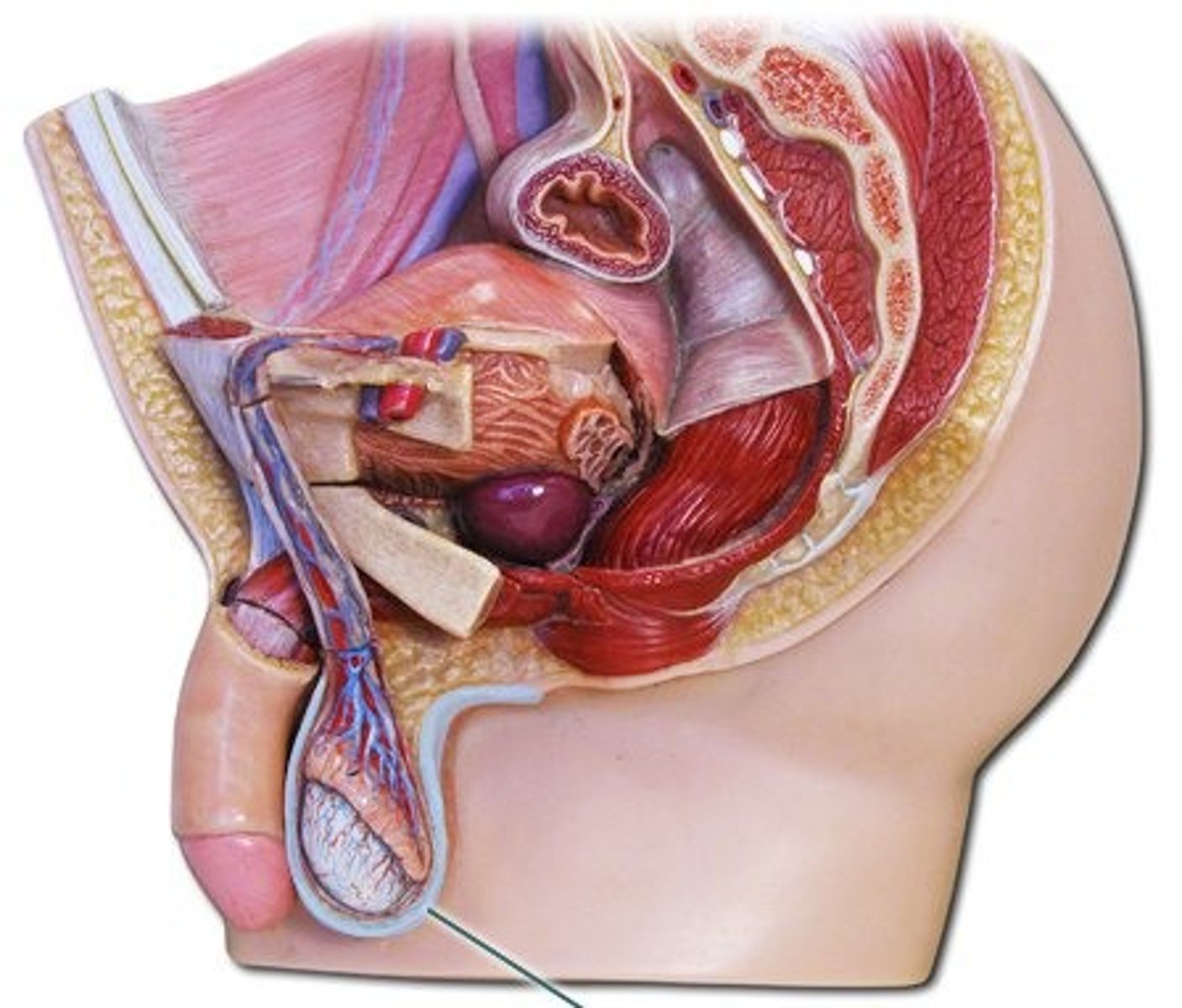
describe the divided pouch of the scrotum
each contains a testicle covered by tunica vaginalis (except posterior aspect)
epididymis
identify this structure
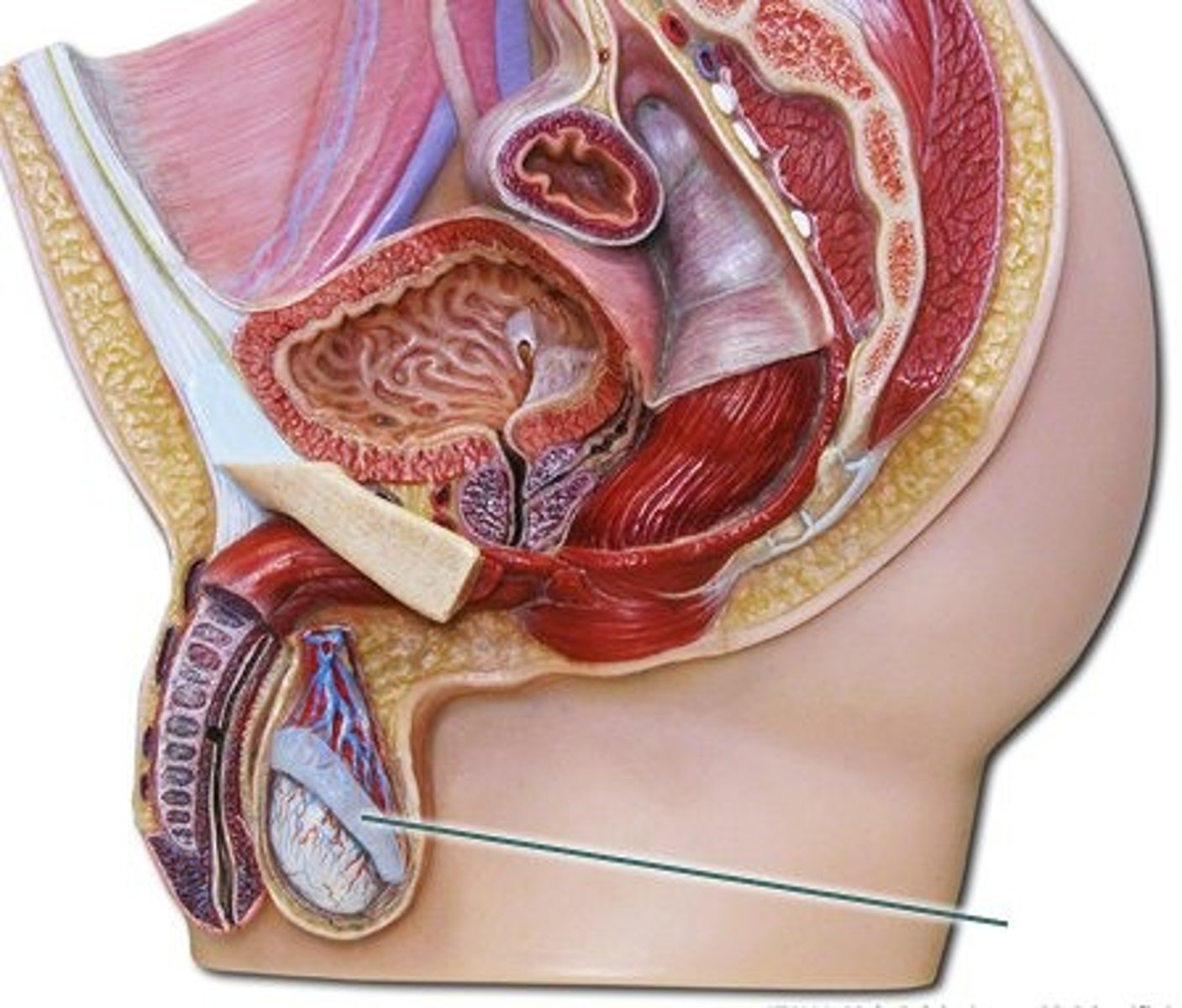
this structure is a tightly coiled spermatic duct on the posterolateral surface of the scrotum and serves as a route for sperm to the vas deferens
epididymis
vas deferens
identify this structure
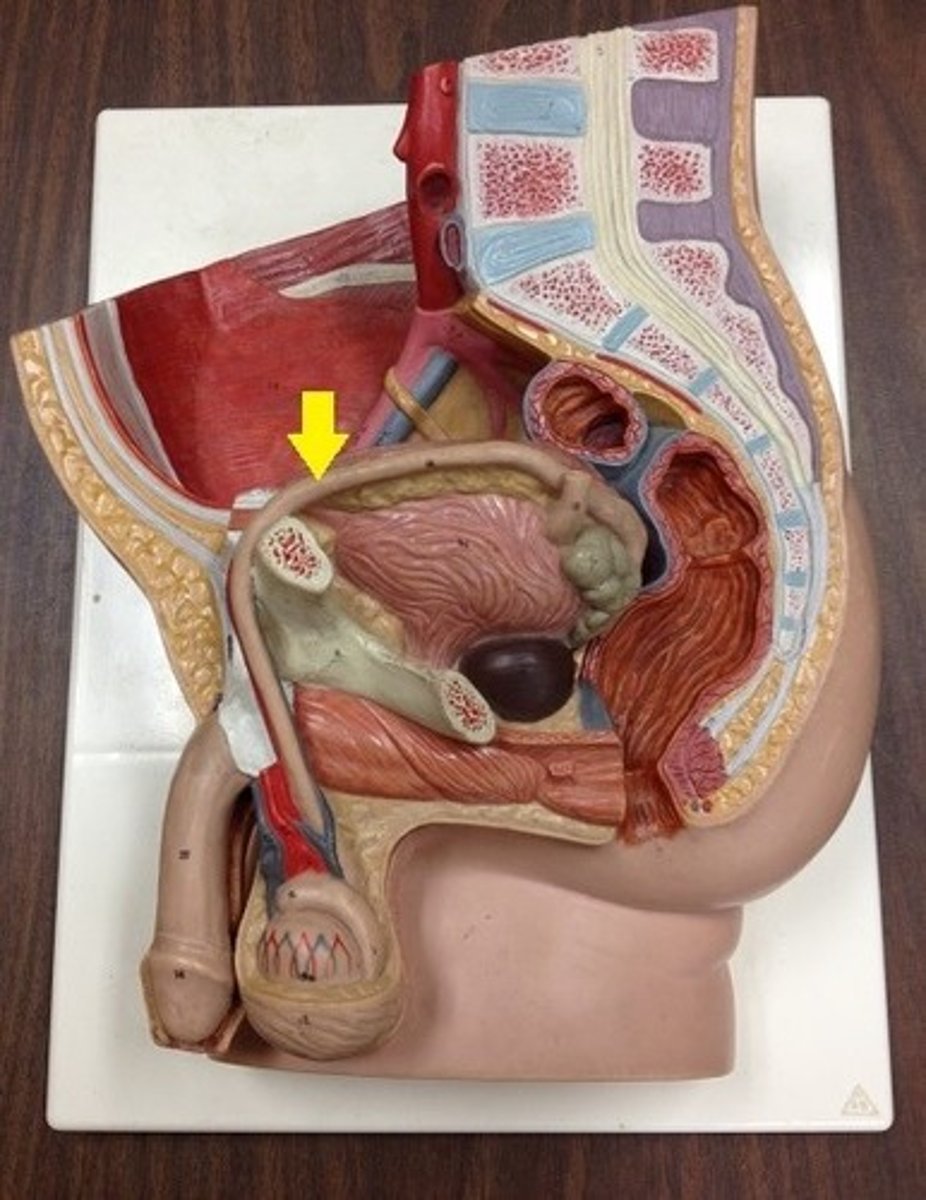
Where is GRH produced?
Hypothalamus
This is the name of the pouch of serous membrane covering the testes.
Tunica vaginalis
The tunica vaginalis covers the entirely aspect of the testicle, except for which paart?
Posterior aspect
what makes up the spermatic cord?
vas deferens, seminal vesicle, ejaculatory duct, seminal fluid
how do sympathetic and parasympathetic signals reach the male genitalia?
pudendal nerve
Does increased nitrous oxide and cGMP cause local vasoconstriction or vasodilation?
Vasodilation
In regards to the lymphatics, the scrotal and penile areas drain into which set of lymph nodes?
Inguinal lymph nodes
if there is a lesion present in the scrotum or penis, this is concerning for what in regards to lymphatics?
inflammation or possible malignancy
In regards to the lymphatics, the testicular lymphatics drain into what?
Abdomen
Can we clinically assess the inguinal lymph nodes?
Yes
Can we clinically assess the abdomen lymph nodes?
No
ASIS
identify this structure
inguinal ligament
identify this structure
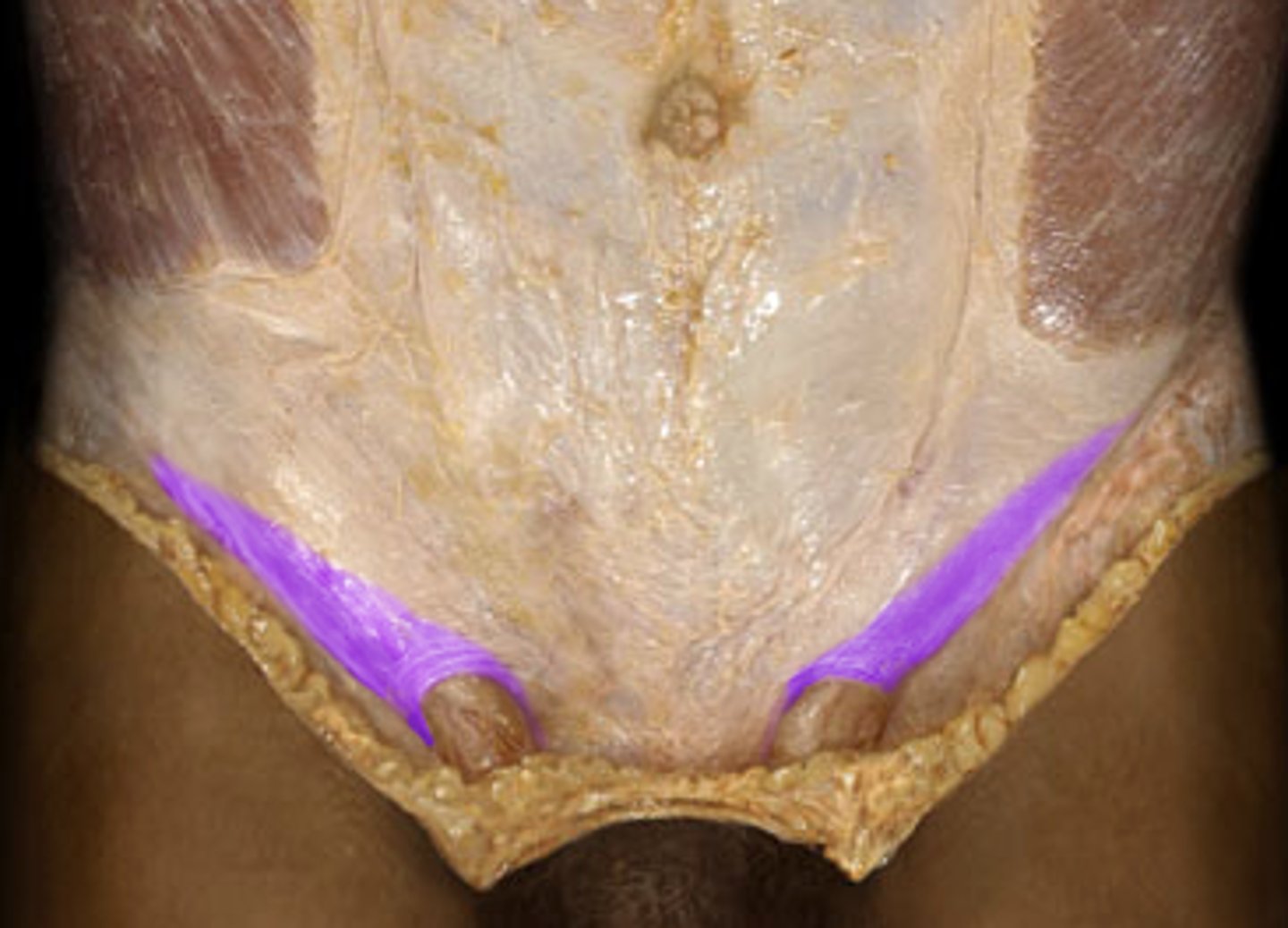
internal inguinal ring
identify this structure
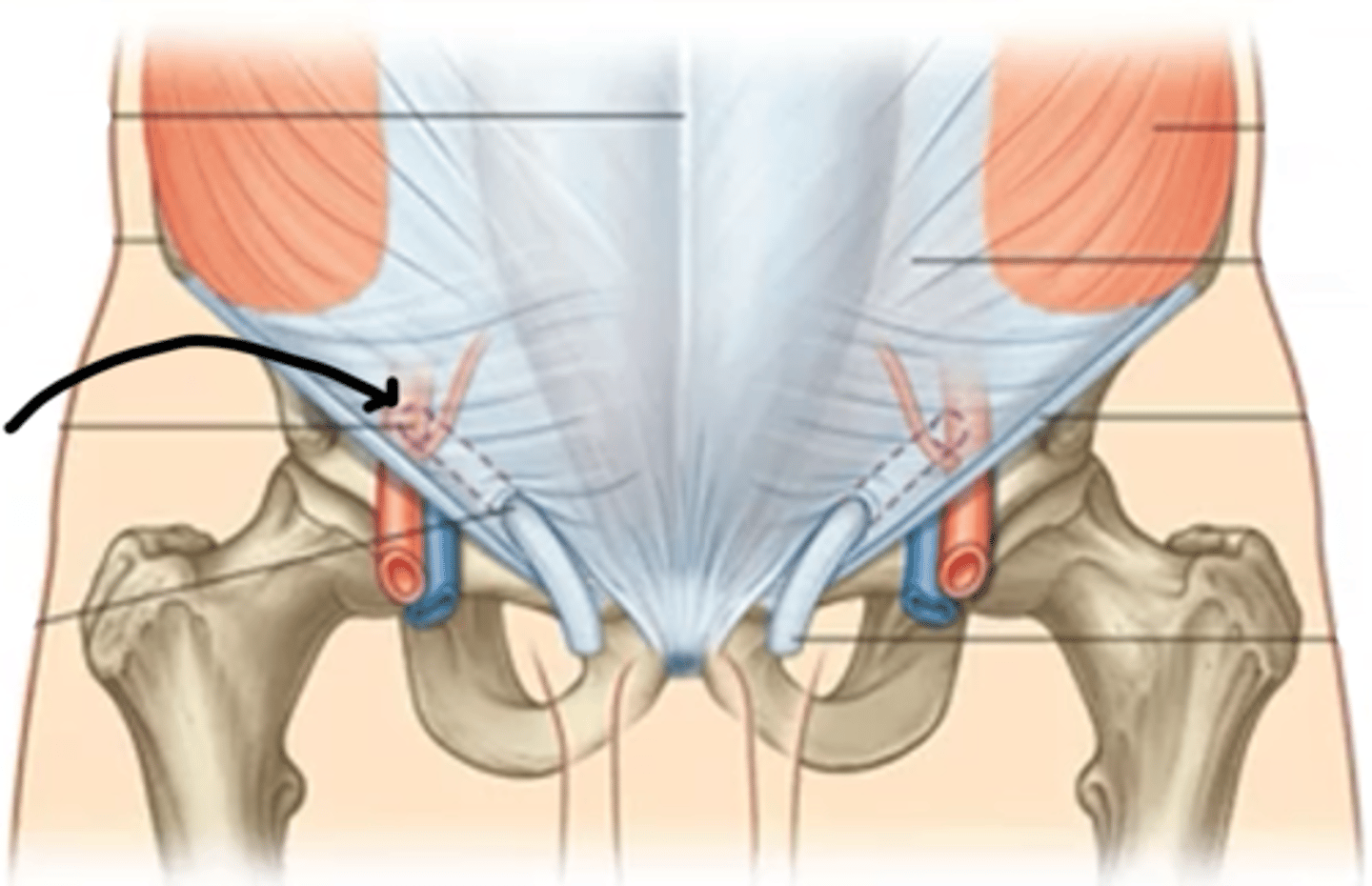
external inguinal ring
identify this structure
spermatic cord
identify this structure
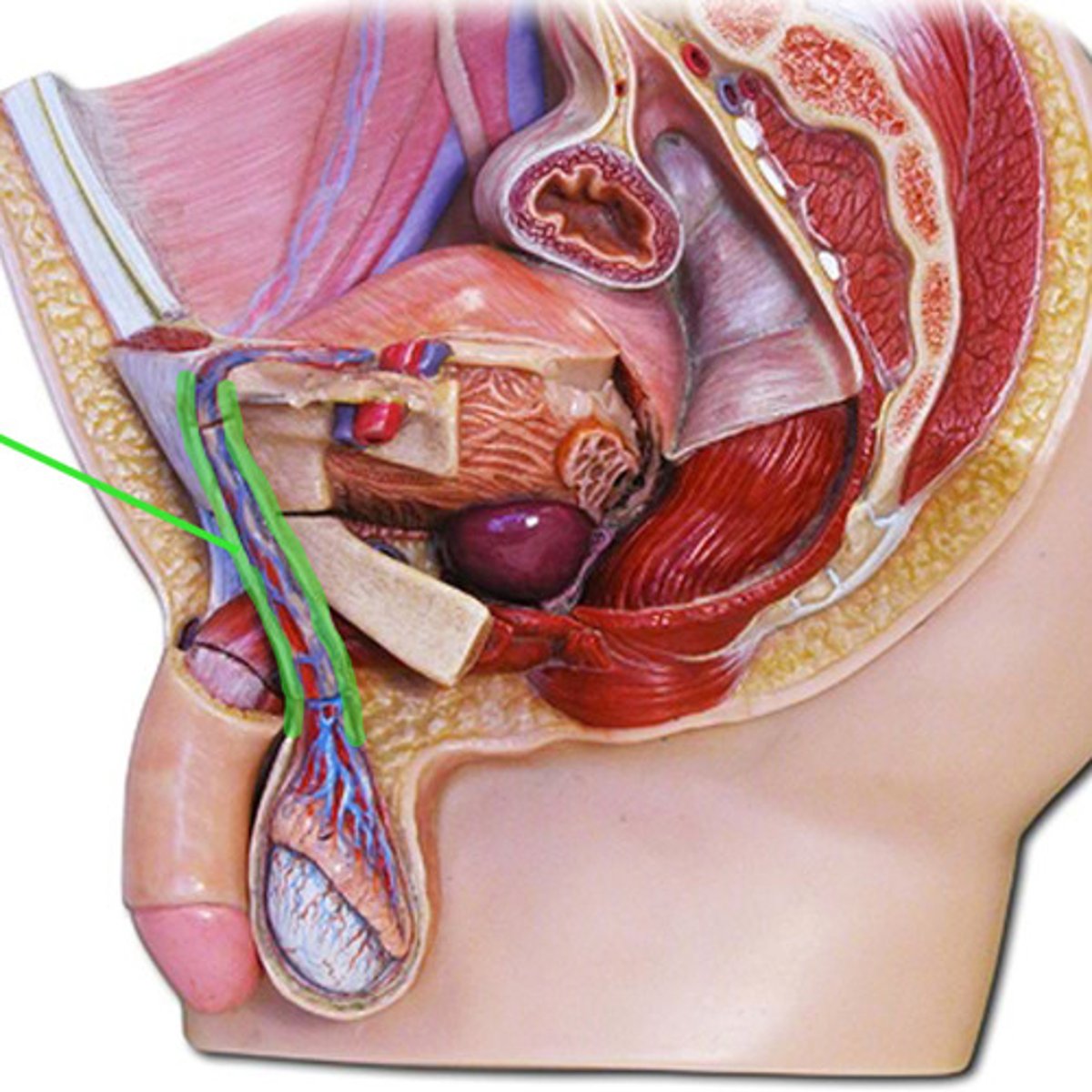
pubic tubercle
identify this structure
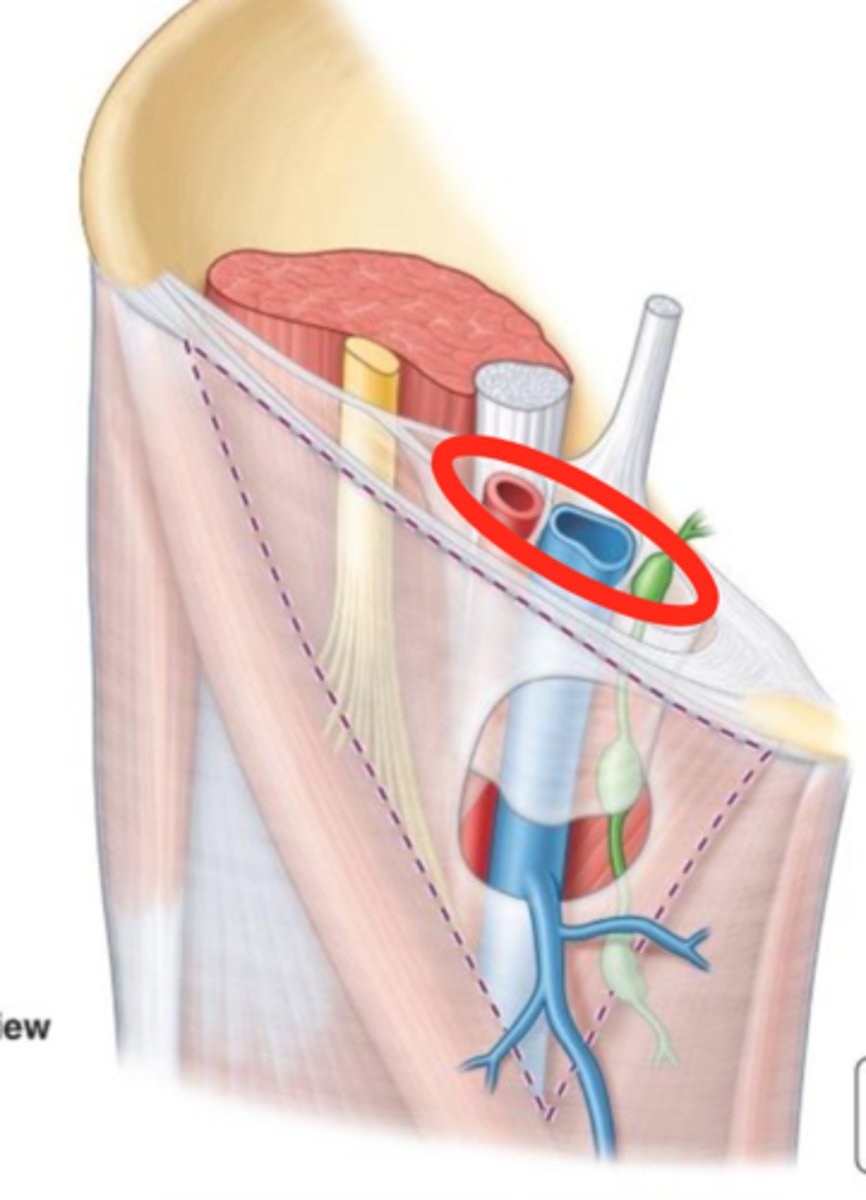
femoral canal
identify this structure
when inspecting the penis, what are we looking for?
skin abnormalities and smegma
This is the term for sebaceous secretions under the foreskin.
rashes, cysts, masses, Smegma
when palpating the penis, what are we looking for?
lumps, veins, tenderness
Is skin cancer on the scrotum common?
No
what are we noting when palpating the epididymis?
size, shape, consistency, nodules, tenderness
This is the term for pain located superior to the pubic tubercle.
Suprapubic pain
This is the term for pain in the CVA region.
Flank pain
This is the term for dribbling after the completion of urination.
Dribbling
This is the term for the need to urinate more often than usual.
Frequency
This is the term for difficulty starting or maintaining a urine stream.
Hesitancy
This is the term for sudden, compelling urge to urinate.
Urgency
This is the term for a spurt-like leakage of urine during moments of physical activity, such as coughing, sneezing, laughing, jumping, or exercise and with walking, changing position from sitting to standing, or with sexual activity.
Stress incontinence
This is the term for a strong, sudden need to urinate due to bladder spasms or contractions.
Urge incontinence
This is the term for blood-tinged or bloody semen.
Hemospermia
This is the term for secretions seeping from penis which may indicate infection.
Penile discharge
This is the term for inability to achieve or maintain an erection with decreased sex drive.
Impotence
This is the term for inability or diminished ability to produce offspring.
Infertility
This is the term for inability to achieve or maintain an erection without decreased sex drive.
Erectile dysfunction
This is the term for absence of urine.
Anuria
This is the term for reduced amount of urine production.
Oliguria
This is the term for excessive production and discharge of urine.
Polyuria
This is the term for excessive urination during the night.
Nocturia
This is the term for pain with urination.
Dysuria
This is the term for bloody urine.
Hematuria
This is the term for excretion of urine containing free gas.
Pneumaturia
what most often causes nocturia?
enlarged prostate compressing the urethra, so bladder never fully empties
what most often causes pneumaturia?
fistula/diverticulitis
This is the term for atrophied testis that may be located in the inguinal canal or abdomen.
Cryptochidism
Is the scrotum filled with cryptochidism?
no
Cryptochidism increases a man's risk for what?
Testicular cancer
is cryptochidism congenital or acquired?
congenital
which side of the penis is the ventral surface?
the side you see when it is erect
This is the term for displacement of the urethral meatus to the ventral surface of the penis.
Hypospadias
This is the term for the displacement of the urethral meatus to the dorsal surface of the penis.
Epispadias
is hypospadias congenital or acquired?
congenital
is epispadias congenital or acquired?
congenital
Which is more common? Hypospadias or epispadias?
Hypospadias
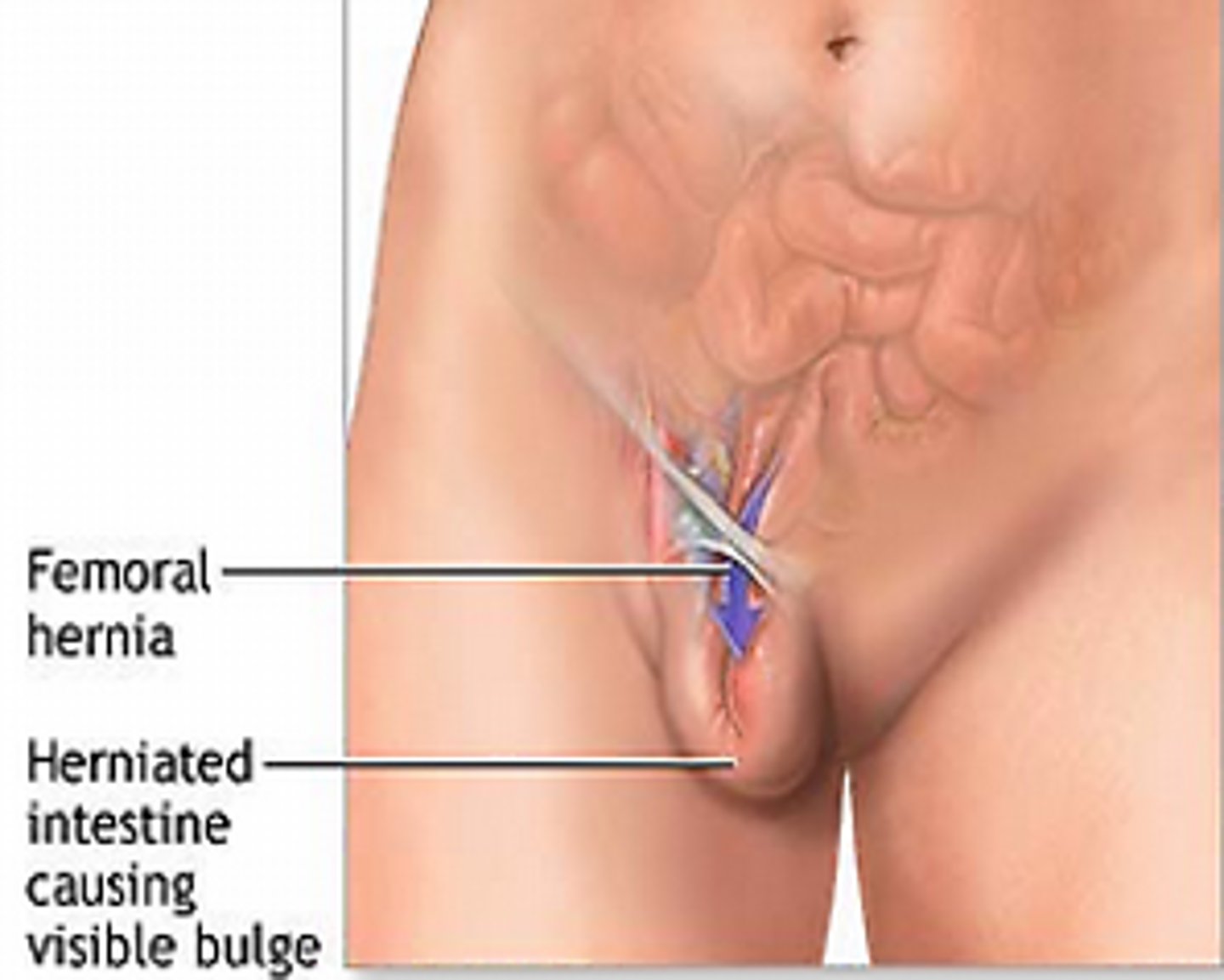
femoral hernia
identify this structure
direct inguinal hernia
identify this structure
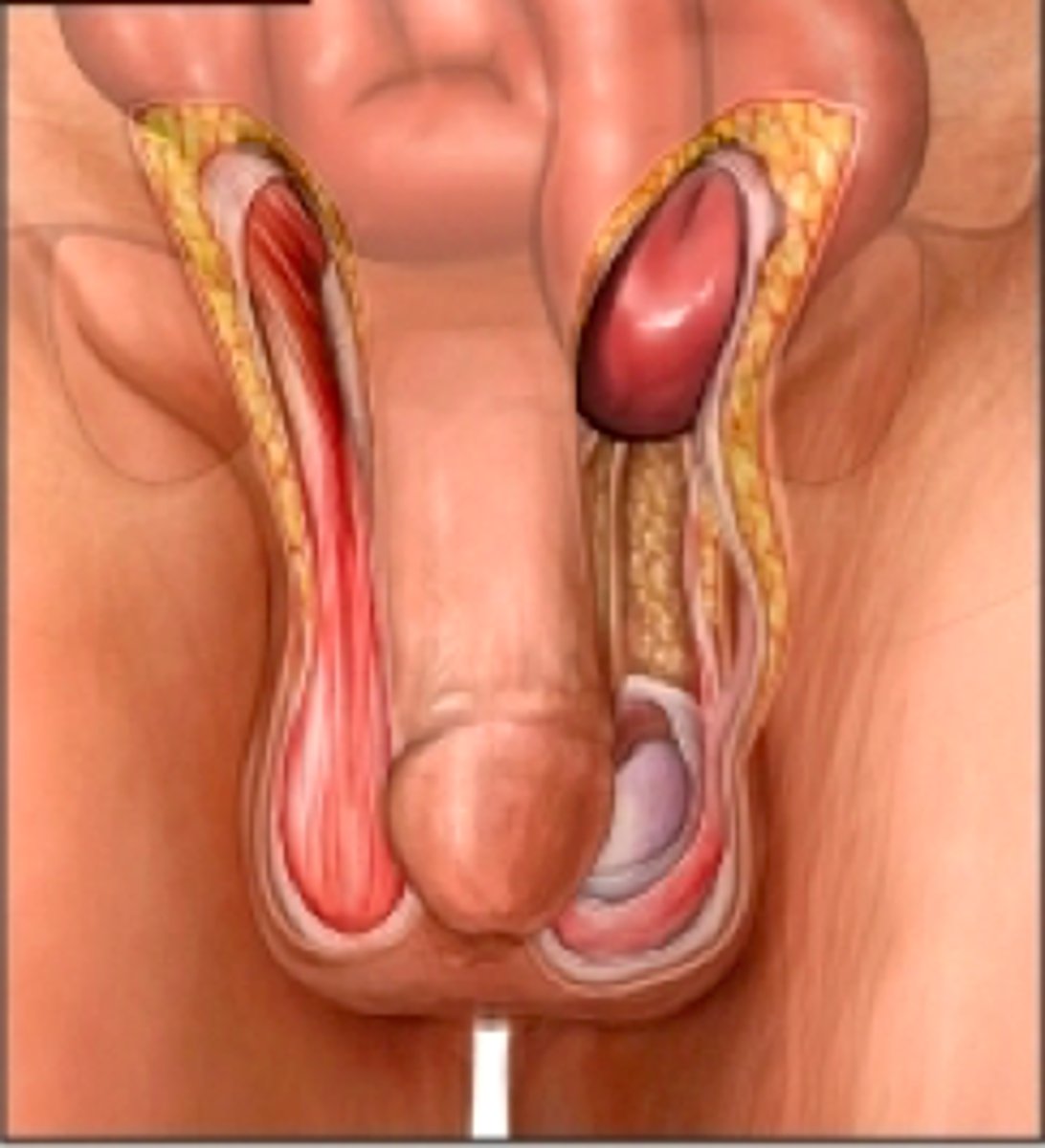
what kind of hernia is most common, all ages and sexes. often in children?
indirect
what hernia has an origin of above inguinal ligament, near midpoint, internal inguinal ring?
indirect
what hernia often goes into the scrotum, comes down inguinal canal, touches examining finger?
indirect
what hernia is less common, usually in men older than 40, rare in women?
direct
what hernia has its origin above the inguinal ligament, close to pubic tubercle, near external inguinal ring?
direct
what hernia rarely goes into the scrotum, and normally bulges anteriorly and pushes the side of the examining finger foreward?
direct
what is the least common hernia, more common in women than men?
femoral
what hernia originates below the inguinal ligament, appears more lateral, can be hard to differentiate from lymph nodes?
femoral
what hernia does not travel into the scrotum, and the inguinal canal is empty?
femoral
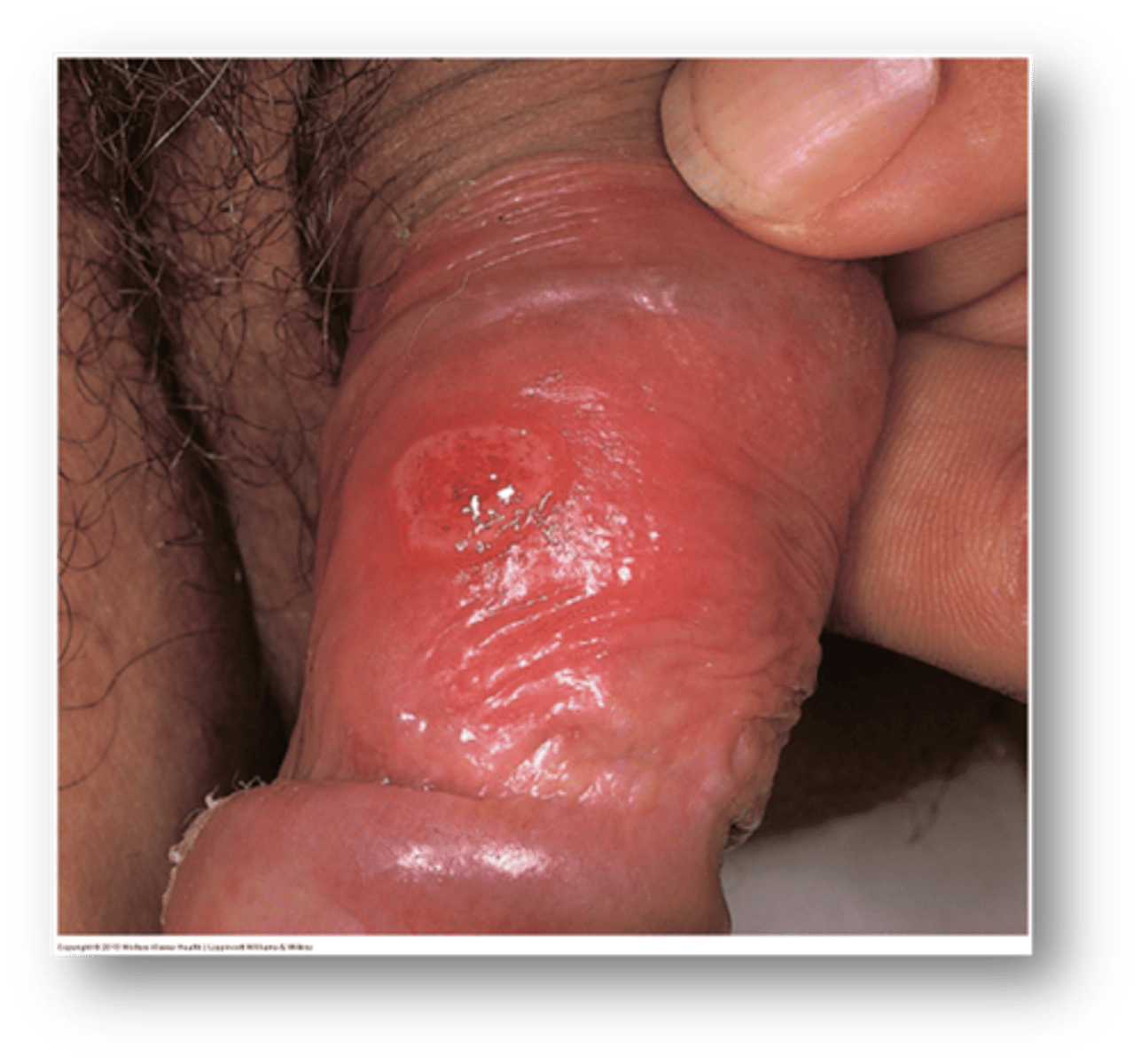
This is a small, red papule on the penis that has painless erosion.
Syphilitic chancre
how to examine and test for hernias?
tip of index finger at anterior inferior margin of scrotum, superficial to testes, move finger upward toward external inguinal ring, follow spermatic cord upward to inguinal ligament, find opening of external inguinal ring, ask patient to cough
bulge near external inguinal ring suggests what kind of hernia?
direct
bulge near internal inguinal ring suggests what kind of hernia?
indirect
this condition due to STI exposure is a small red papule with chancre (painless erosion)
syphilitic chancre
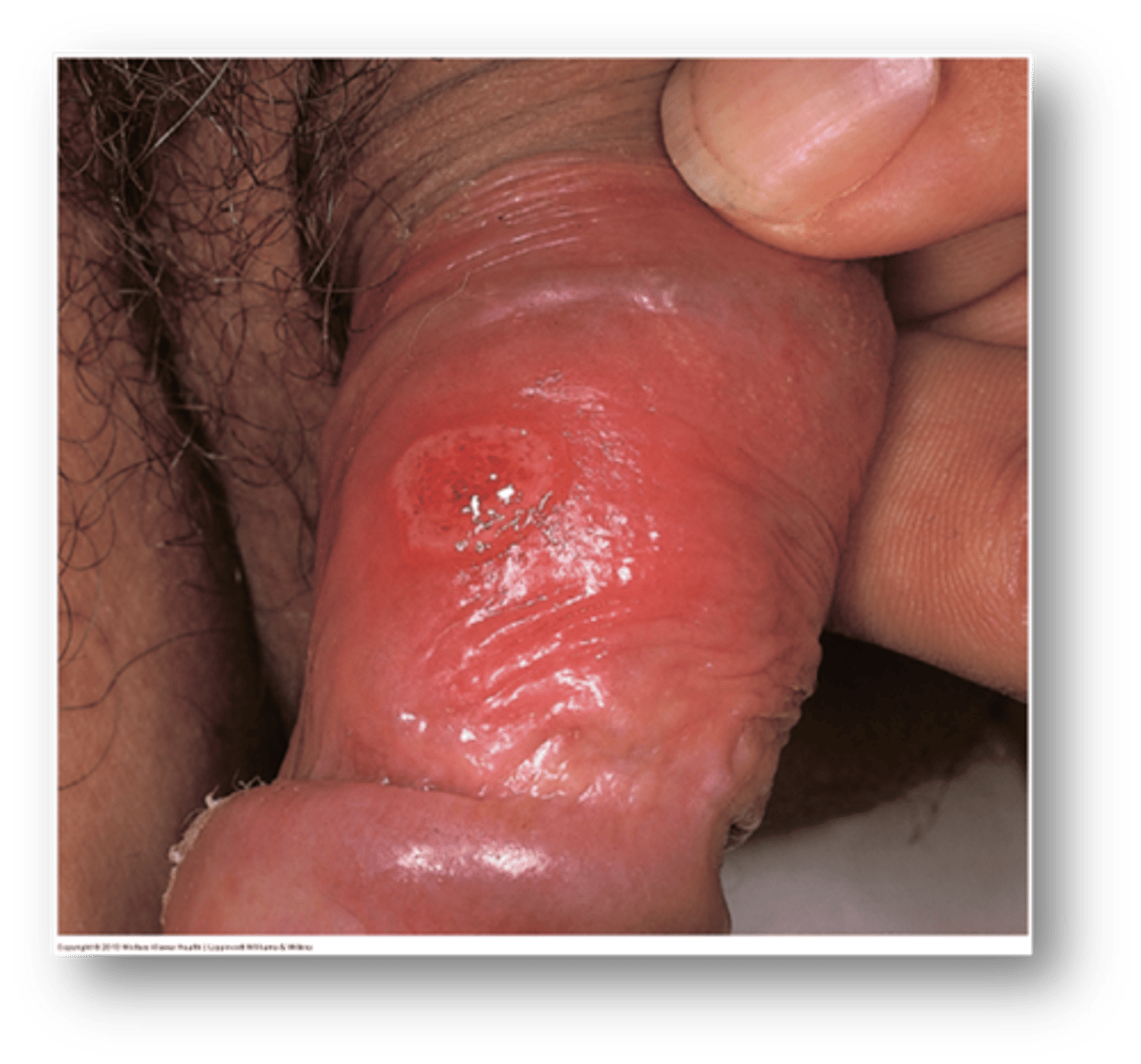
Do syphilitic chancres usually heal on their own? time frame?
Yes, 3-8 weeks
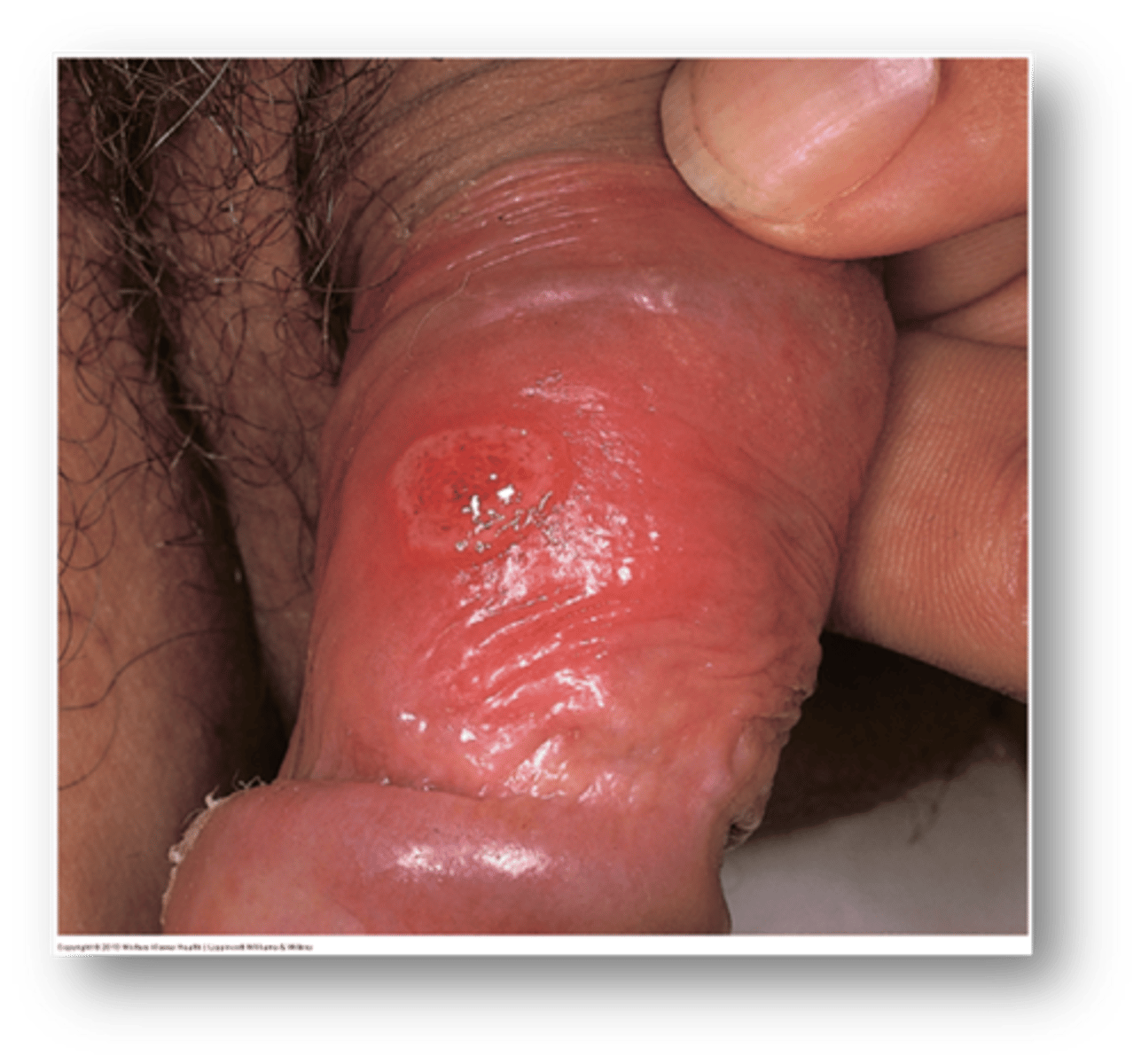
If secondary syphilis develops while a syphilitic chancre is present, what does this suggest?
Co-infection with HIV
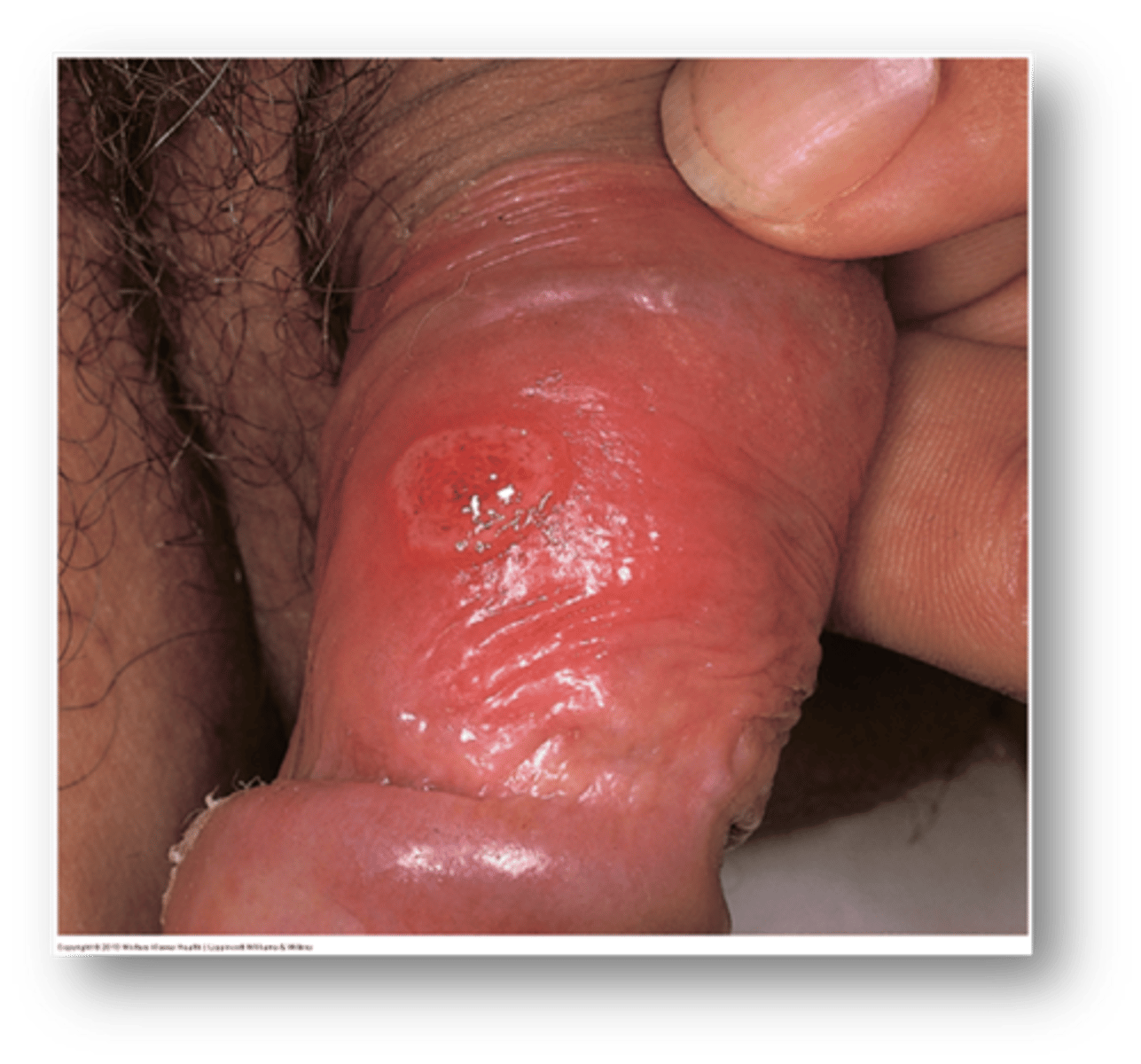
Treponema pallidum will cause what disease?
Syphilis
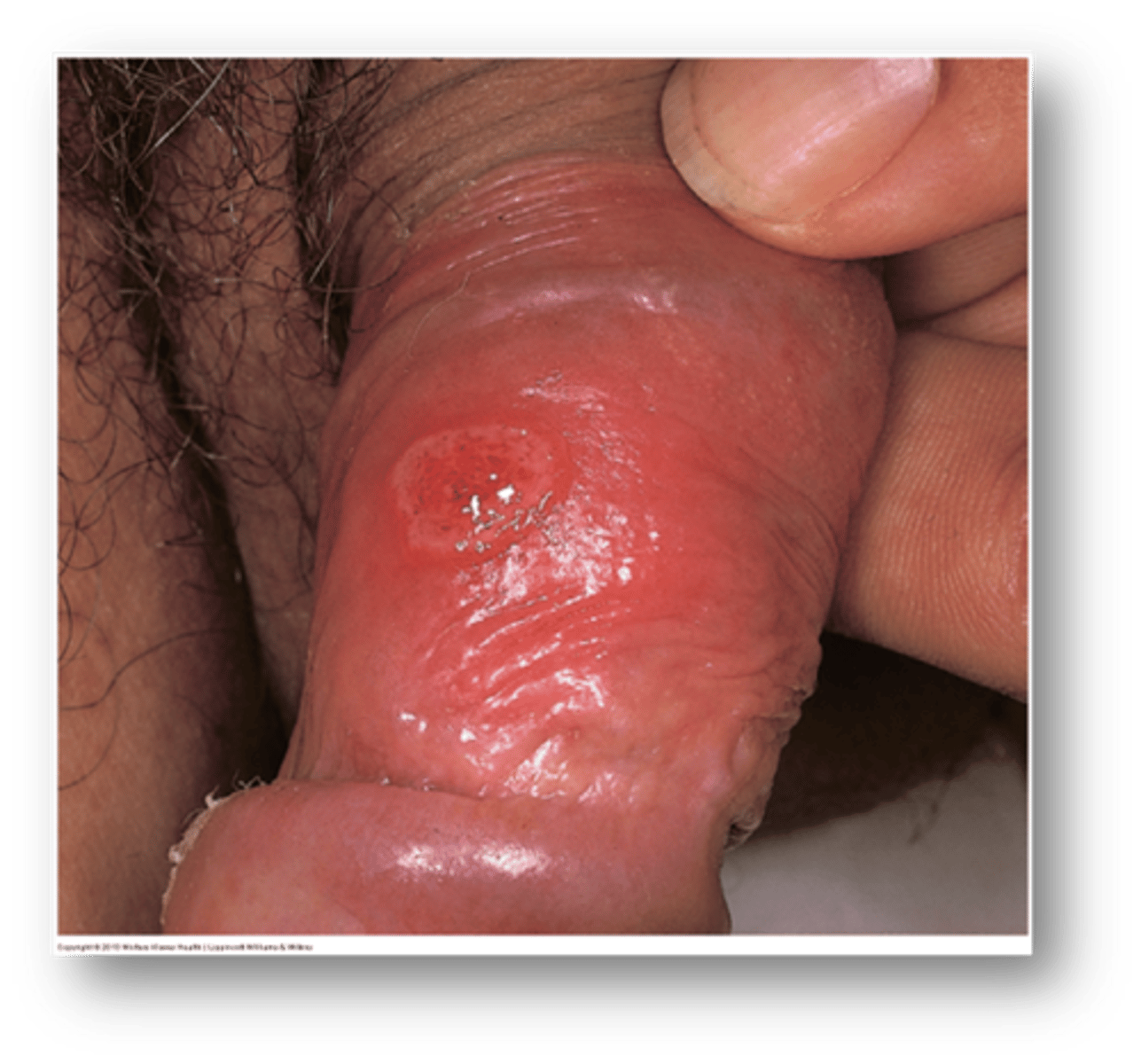
how long after exposure to treponema pallidum does syphilitic chancre occur?
9-90 days
About 7 days after exposure to treponema pallidum, what will you notice?
Inguinal lymphadenopathy
lymph nodes of the inguinal region are mobile, non-tender, and rubbery. condition?
inguinal lymphadenopathy
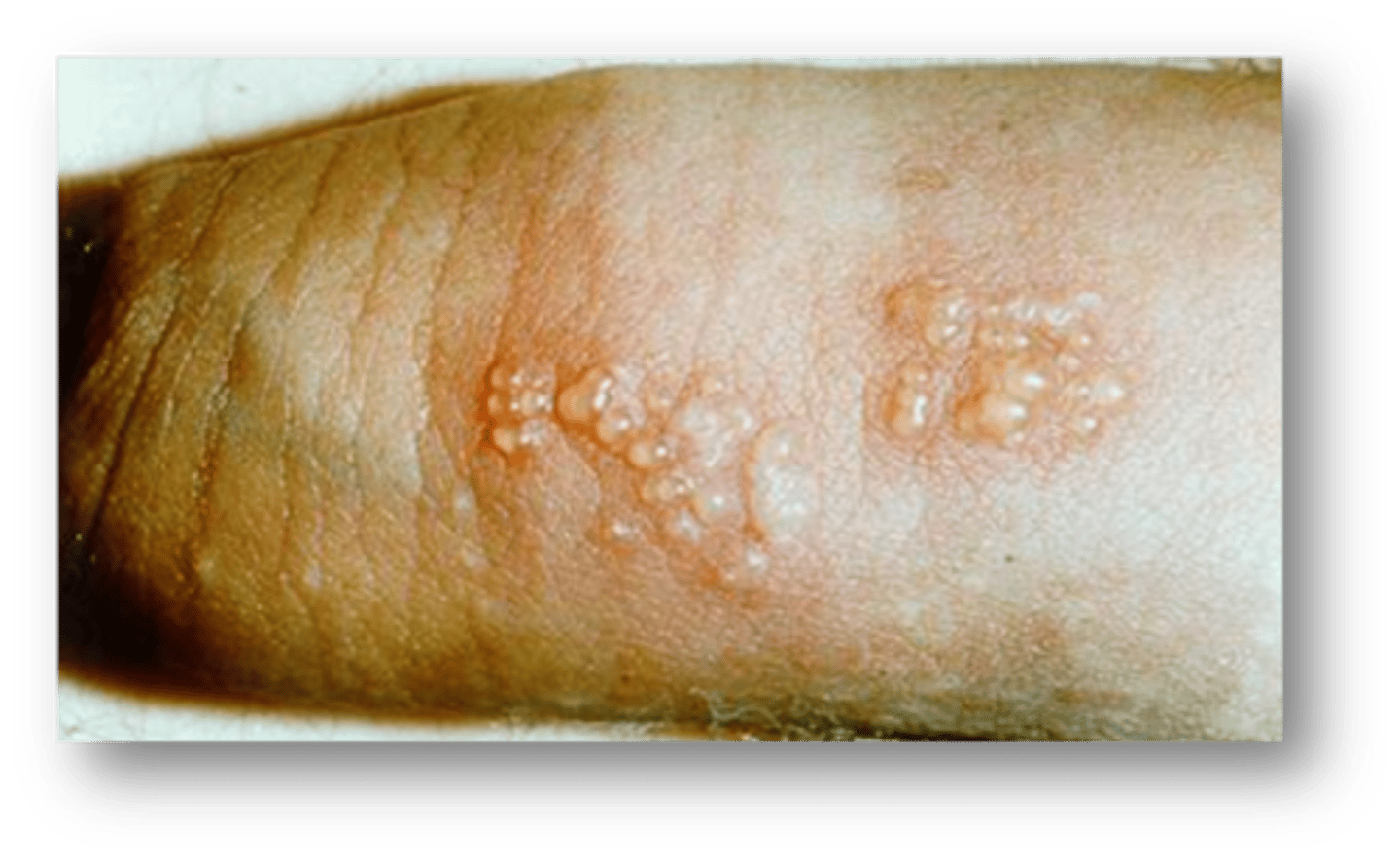
This condition caused by STI exposure is small, scattered, or grouped vesicles 1-3mm in size on the glans or shaft. They will appear as erosion if the vesicles break.
Genital herpes
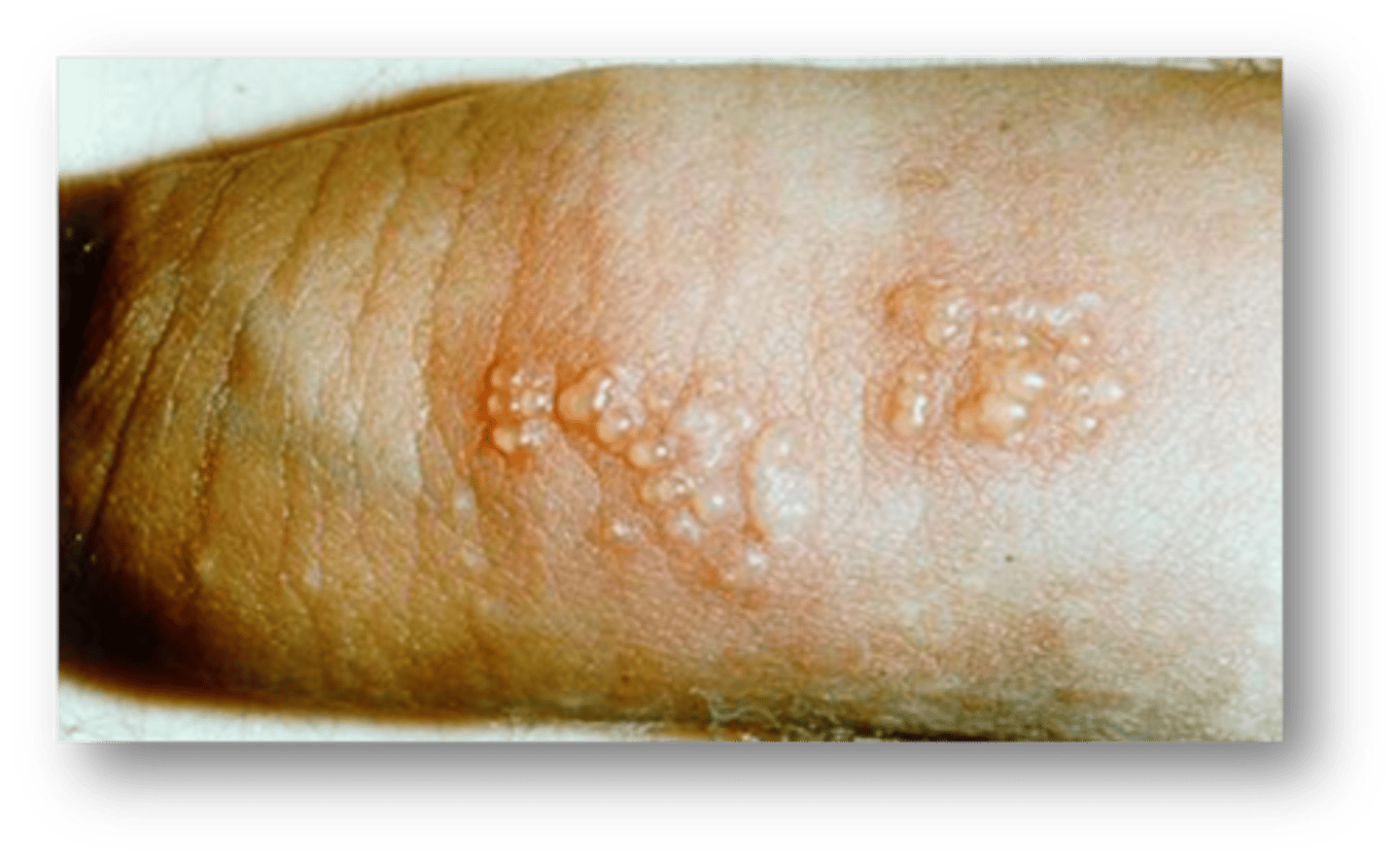
Genital herpes is more often caused by what strain of the virus?
HSV2 (2 double stranded DNA virus)
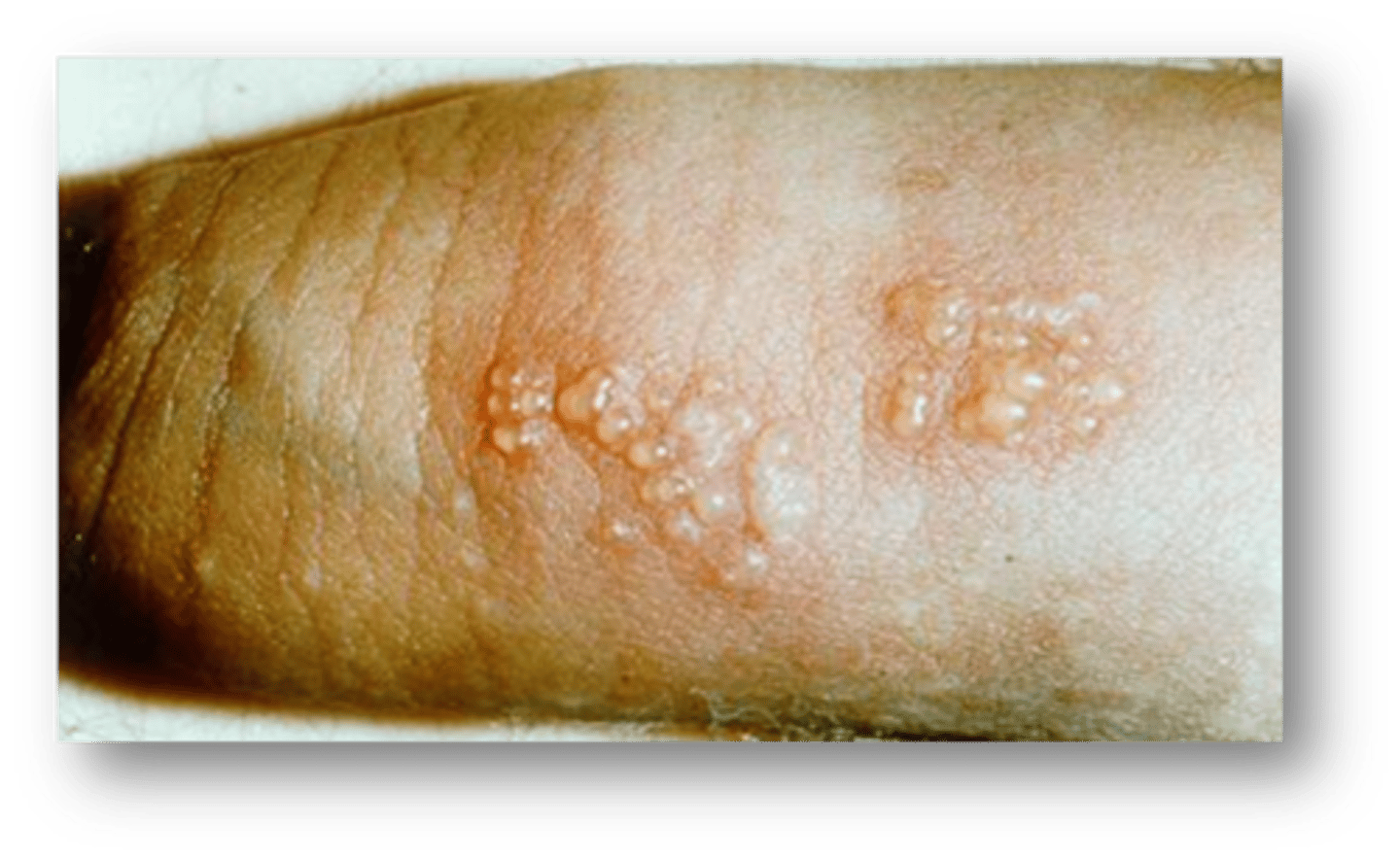
The vesicles from genital herpes usually appear how many days after exposure?
2-7 days
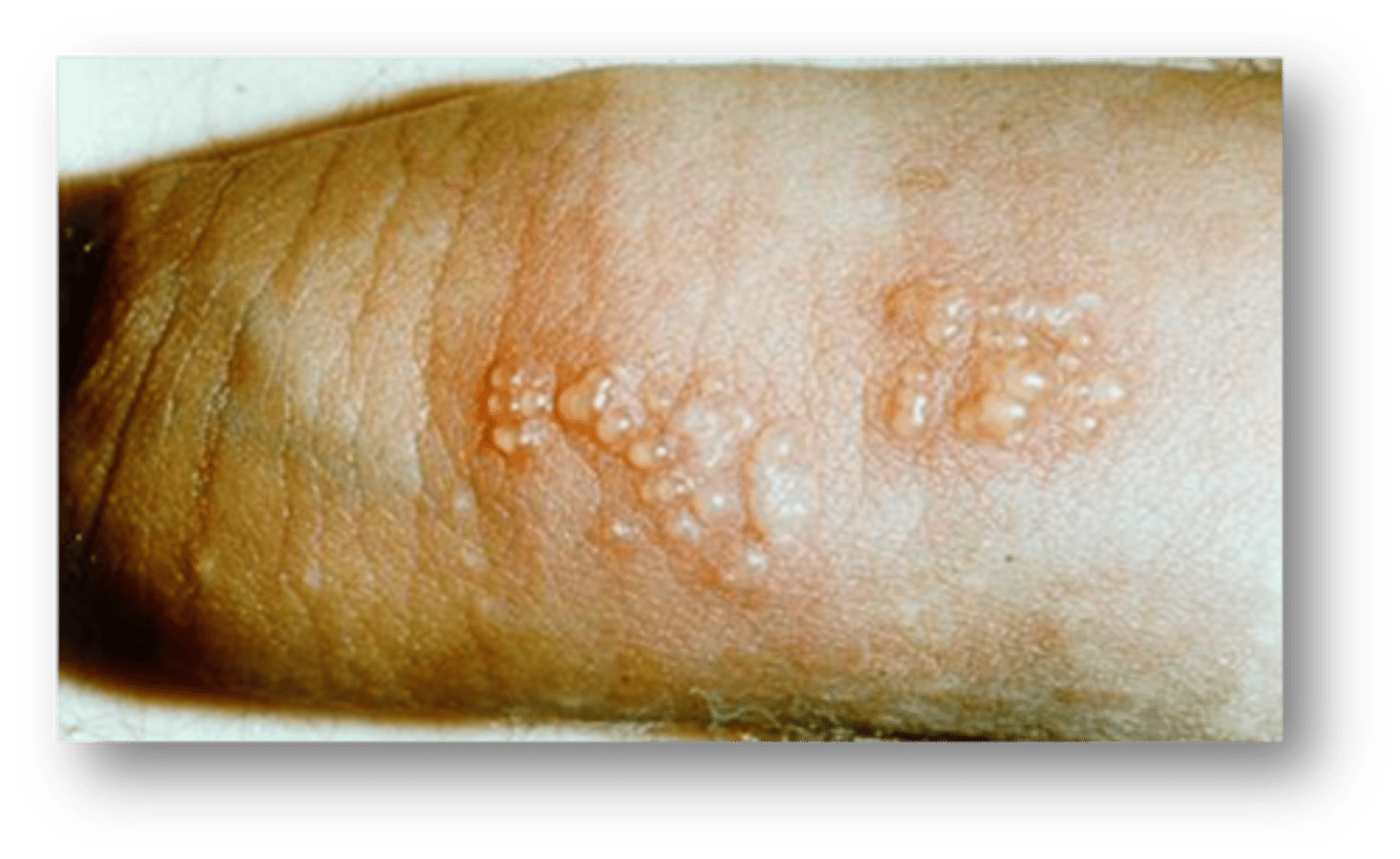
What are associated symptoms of primary episode of genital herpes? Are subsequent episodes of herpes usually more or less painful? longer or shorter?
asymptomatic. less painful/shorter
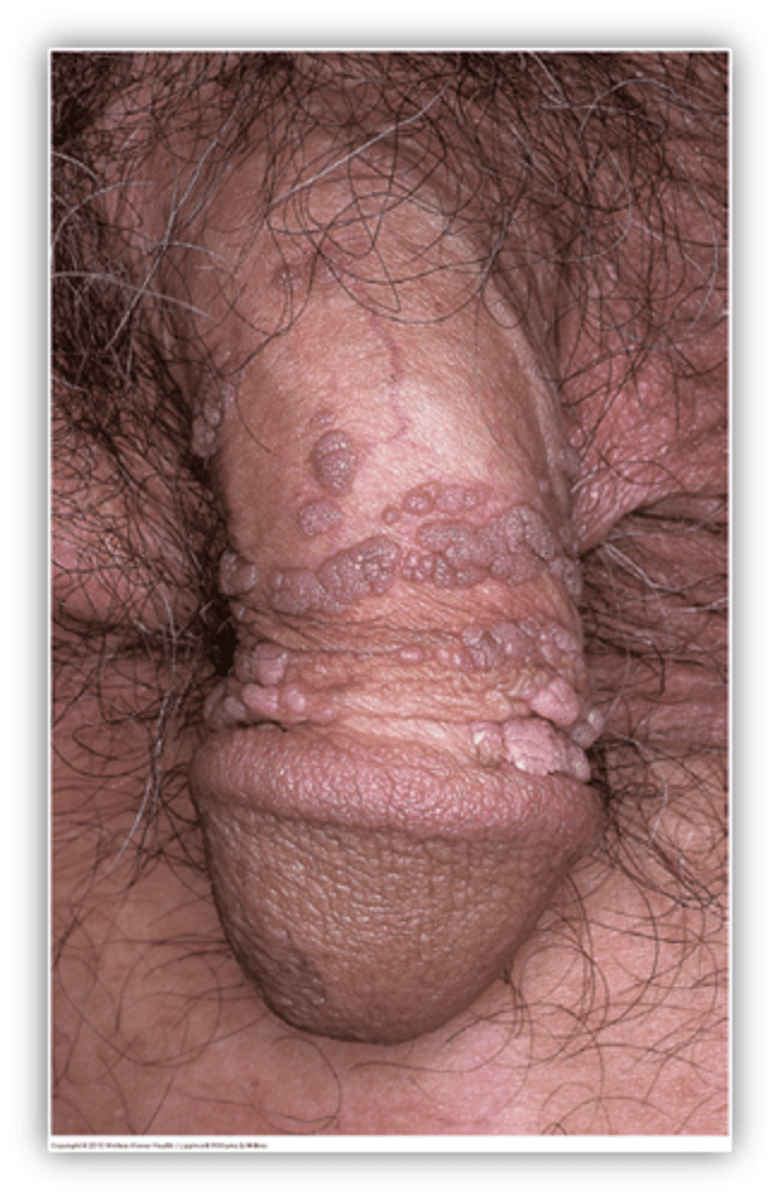
This is single/multiple papules/plaques that may be raised or cauliflower like (verrucous)
Condyloma acuminatum
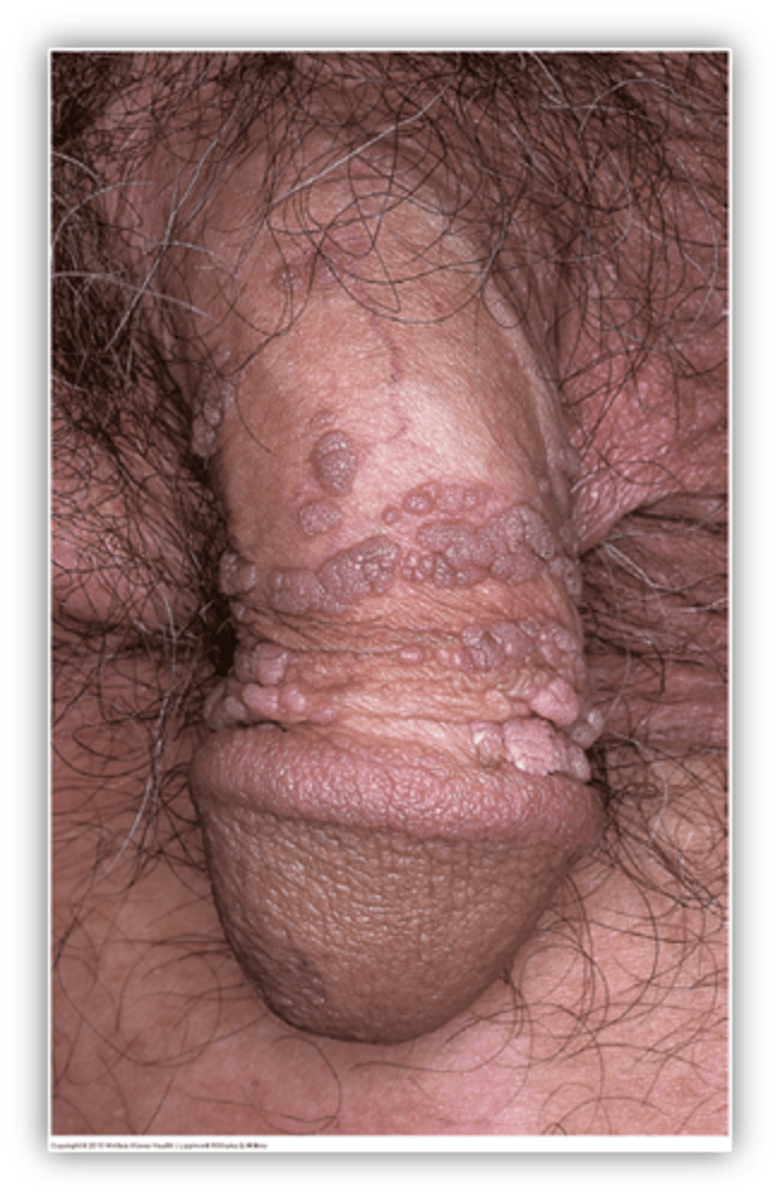
Condyloma acuminatum is caused by what?
HPV subtypes 6,11
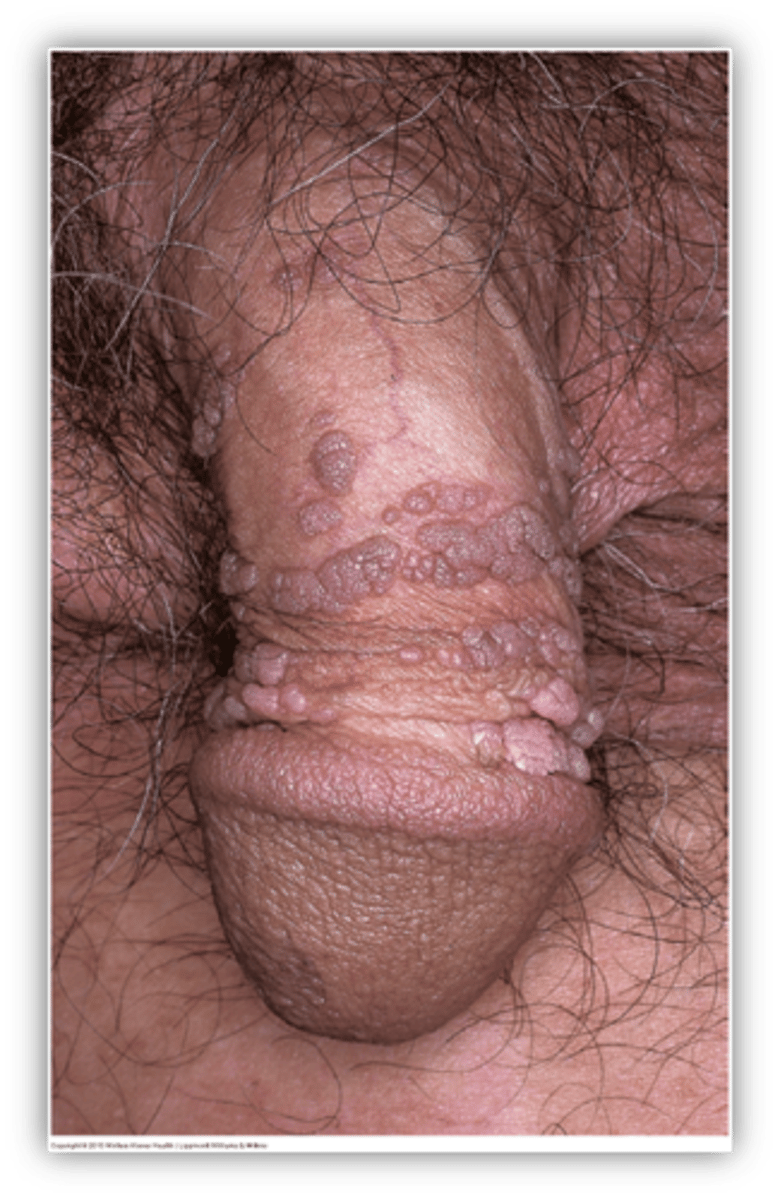
Condyloma acuminatum occurs how often after exposure to HPV?
Weeks to months
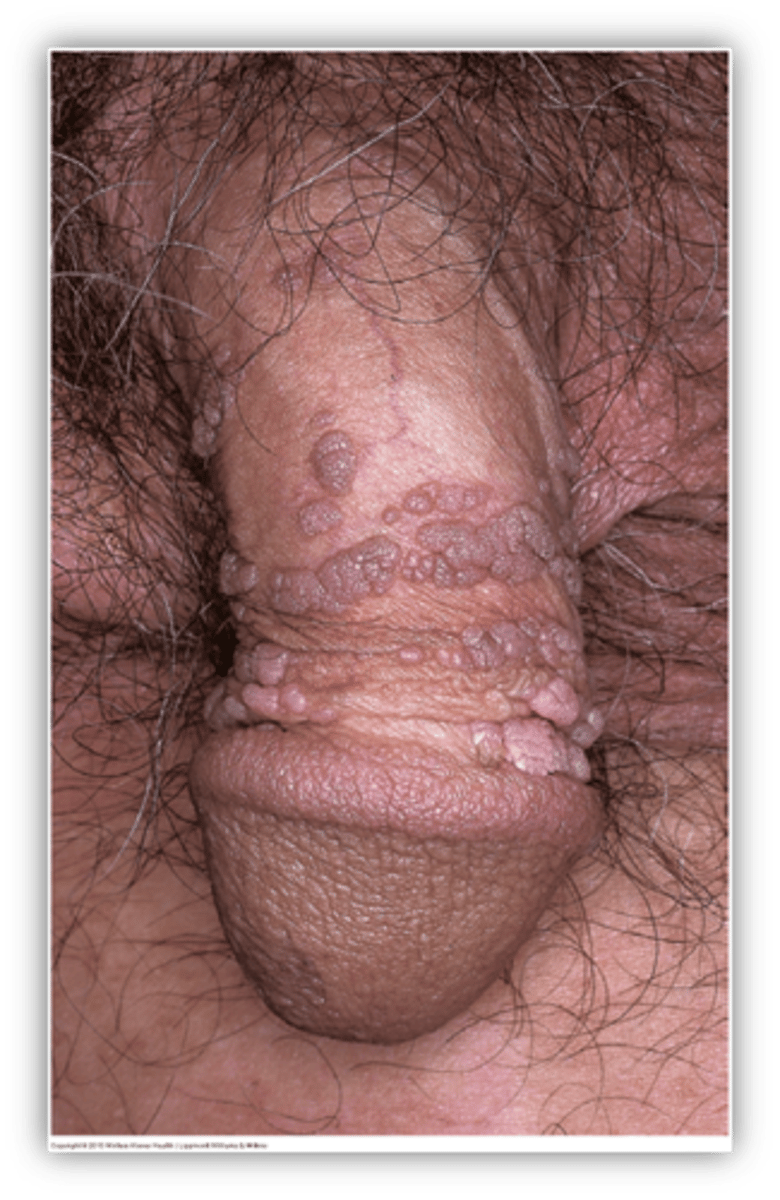
what are associated symptoms of condyloma acuminatum?
itching, pain