Global Earth Systems Exam 1 (Jamie’s flashcards)
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
Littoral Desert
where cold ocean currents reduce evaporation and cool the air on nearby coastlines, normally on west coasts
Where is precipitation inhibited?
areas of subsidence, like the interior of large landmasses
Leeward side of mountain ranges
Littoral deserts
Where are heavy precipitation zones associated with uplift?
along polar front zone
ITCZ
Warm land masses in summer
Where air is mechanically forced up, like mountain ranges
Cloud condensation nuclei
organic or inorganic, natural or anthropogenic particles that water condenses on, causing rain
Without these, the air can become supersaturated
Relative humidity
Ratio of actual vapor pressure to saturation pressure at the temperature at 100%, it normally rains
Where is water on land?
~ 75% in ice sheets (Greenland and Antarctica)
<1% in lakes, soils, and rivers
Rest in groundwater
Energy needed to heat water from 0C to 100C
419 kJ/kg
Water on earth
Oceans >70%
Clouds cover ~50%
Only natural substance to exists in 3 states at surface
Cycles readily between different components of the Earth system
Monsoons
a pattern of wind circulation that changes with the season
Generally wet summers, dry winters
Linked to different heat capacities of land and water and the north- south movement of the ITCZ
Ex: in Southeast Asia, there is a large landmass north of the Indian Ocean near the equator
Radiation incident of land vs water and what it means
Land: radiation absorbed or reflected at the surface
Ocean: radiation penetrates further than on land
this means the ocean absorbs more energy over the same area as land with less temperature change (but more volume in ocean)
Thermal conductivity
rate at which energy passes through a column of a given material
Albedo of ocean vs. land
Ocean is less than land, so it absorbs more and reflects less solar radiation
Latitudinal distribution of incoming solar radiation is modified by
seasonal changes of temperature input
Land- ocean contrasts in thermal behavior
Solar radiation at high latitudes
energy spread out over more area
Energy passes through more area
Incident angle causes lower intensity which causes the poles to be cooler
3 qualities of incoming radiation
varies with latitude (causes temperature differences)
Radiation comes in parallel waves
Incident angle varies with latitude
Why does land distribution affect airflow? What does this cause?
land changes temperature more rapidly than water due to lower heat capacity
ITCZ more narrow and consistent over oceans
Greater season differences in Northern Hemisphere (Earth’s top heavy)
Specific Heat
4.186 J/gK of water
Residence time (constituents)
amount in the oceans / flux in or out of the ocean
Average length of time on elements spends in the ocean
Heat budget
the total amount of heat received by Earth and lost by radiation and reflection; the amount in is the amount lost
Latent heat of evaporation
amount of heat required to change 1g of water from liquid to gas
Water has the highest of any known liquid
Heat capacity
The amount of heat/energy required to raise the temperature of a quantity of matter by 1C
latent heat of fusion
amount of heat required to change 1g of water from ice to liquid
Seasonality and N-S (or US) temperature gradient
season change weakens or strengthens the N-S temperature gradient in different hemispheres
Why are wind patterns considered simplified
winds are not continuous around the globe
Wind do not blow continuously
Convective uplift in ITCZ occurs in clusters of small cells
Areas of subsidence are concentrated in localized zones that vary with season
Winds in polar regions
easterly winds circulating around a polar high pressure area
Winds at mid-lats, subtropics, equator
Mid-lats: westerly winds
Subtropic: easterly trade winds
Equator: doldrums
Coriolis effect
-opponent force acting on a body in motion
Caused by rotation of earth
Deflection right in Northern Hemisphere and left in Southern (from equator)
Inertial force
What causes coriolis effect
rotation of Earth (once per day)
If earth is broken down into discs, the ones at the equator move faster than the ones at higher latitudes; circumference is longer but the same 360 must be covered in the same time
Intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ)
region of weak and variable winds where trade winds of the two hemispheres converge
Generally associated with the zone of the highest surface temperature and as the climate equator between 3N and 10N
Coriolis effect near equator
to weak to generate rotation air masses
Polar Front Zone
~ 60 latitude
Where air from the poles meets air from the tropics
Sharp temperature gradient
Doldrums
nautical term for a belt of light, variable winds near the equator
How is heat moved
ocean and air currents (equator to poles)
Solar radiation
Change in state
Evaporation: heat loss
Condensation: heat gain
Atmospheric convergence vs. divergence
Convergence: where winds meet at the bottom of the troposphere
Divergence: where winds separate at the bottom of the troposphere
What stops air from continuing to rise in areas of uplift?
tropopause forms a barrier due to density stratification in the stratosphere
Coriolis effect and atmospheric circulation
air affected because it has mass
Air is deflected before reaching pole from equator (sinks about 1/3 the way there)
Descending air deflected right, back to equator
Heats up at the equator and rises again
Atmosphere structure
Bottom: troposphere
Stratosphere
Mesosphere
Thermosphere
How is it moved: sensible vs latent heat
Sensible: convection and conduction
Latent: change in state
Where is there a solar radiation on surplus? A deficit?
Surplus: equator (~30S to ~30N)
Deficit: above and below equator (-30S + and ~30 N+)
thermosphere
O2 absorbs short wavelength UV
mesosphere
ozone and heating decline
Temperature decreases with altitude
Stratosphere
the stratified second layer of atmosphere ~10 to 50 km in altitude
Lower pressure than troposphere
No convection due to stable thermal structure (warmer higher up)
Ozone blocks UV radiation
Troposhere
constrains ~ 80 % of atmospheric mass
Well mixed by convection
Temperature decreases with altitude
Thermal instability leads to atmospheric circulation
Causes of horizontal atmospheric circulation
caused by uneven solar heating with respect to latitude and powered by sunlight
Effect of pressure on vertical air movement
compressed air becomes warmer and rises
Decompressed air becomes cooler and sinks
Rising air experiences less pressure and cools
Descending air experiences more pressure and warms
Describe air movement
air warms and rises at the equator
Loses moisture at it expands and cools
Cool air moves toward equator to replace it
Creates zones of low and high pressure
3 global changes on short timescales
greenhouse gases and global warming
Stratospheric ozone depletion
Deforestation and biodiversity loss
2 causes for global warming
primarily fossil fuel combustion
Some deforestation
Evidence that global warming is caused by humans
Carbon isotopes in the atmosphere, 13^C/12^C and radioactive 14^C
What do ice cores show?
Unprecedented increase in greenhouse gases
Why do we know the increase in greenhouse gases is due to humans?
Ocean circulation and configuration of landmasses
Why do we know climate change data is not wrong
Multiple data sets are independent of each other, so problems with one is not applicable to the others
What absorbs UV-B radiation?
Stratospheric Ozone
What caused the hole in the ozone?
Chlorine containing compounds formed from anthropogenic CFCs
Why does ozone hole primarily occur over Antarctica in spring?
atmospheric circulation
Chemistry
Availability of sunlight
How do human impacts reduce landscape complexity?
Clearing forests and grasslands reduces biodiversity, resulting in extinctions
Tropical rainforests
Most biodiversity terrestrial habitats that are rapidly being cleared
What does rainforest clearing result in?
Largest and most significant loss of species
Time needed to recover stratospheric ozone depletion atmospheric CO2 increase mass extinction of species
Ozone depletion: ~50 to 150 years
CO2 increase: over 1 million years at current rates
Mass extinction: tens of million years to never
How to determine which global scale change is most concerning?
Based on the time it takes to recover
3 global changes on long timescales
Glacial-interglacial cycles in Quaternary (ka)
Mass extinction at K-T boundary (Ma)
Solar luminosity changes (Ga)
Order of geologic time intervals
eons>eras>periods>epochs
Why do temperature, CO2, and CH4 vary over glacial-interglacial cycles?
Atmospheric CO2 increase mass
Milankovitch cycles
Alvarez Impact hypothesis
too much indium at K-T boundary to be deposited in normal circumstances
~200km crater near chicxulub supports impact hypothesis
Causes in changes in solar luminosity
-Stellar nucleosynthesis, which is H to He to Fe
4 H —> 4^He + energy
He takes less space than 4H, causing the core to contract and heat up
Why is solar luminosity increase?
The rate of nuclear fusion and emission of energy from the sun is increasing
Faint young sun paradox
solar luminosity was too low for liquid water before 2 billion years ago
BUT! We had liquid water
Thought that greenhouse gases made earth warm enough for liquid water
Gaia hypothesis
posits Earth is a self regulating system in which biota play an integral role in optimizing conditions for their continued survival; does not require a collective consciousness
Problems with Gaia hypothesis
Difficult to test
Unlikely biota can cope with all possible disturbances
System
An entity composed of diverse but interrelated parts that function as a complex whole
Types of system components
reservoirs of matter
Reservoirs of energy
Attributes of a system
Subsystems composed of sub components
State of a system
set of attributes characterizing a system at a particular time
Couplings
links between components of a system in which changes to one affects the other
Stable vs unstable equilibrium
stable needs a large disturbance to affect equilibrium state, while unstable is easily permanently changed
Perturbation vs forcings
Perturbations are temporary and forcings are more persistent
Ex: volcanic eruption vs solar luminosity
Daisy world climate system
a very simple hypothetical planet used to show how the biota can self regulate
essence of Gaia
evolution of the biota and its material environment is tightly coupled process
Active feedback processes operate
Positive and negative feedback
Solar energy sustains the Earth system geophysology
Biological regulation occurs in the context of physical changes in the environment
Essence of Gaia active feedback processes
arises from coupling between biotic and physical/geological processes
Essence of Gaia Geophysiology
term also used to explain this global self-regulation
Essence of Gaia biological regulation occurs in the context of physical changes in the environment
increase in solar luminosity changes tectonic activity
Not really at homeostasis, fluctuates around a fixed point
Better considered homeorrhesis (or homeostasis I can’t read it)
Daisyworld stats
gray soil and white daisies
No clouds or greenhouse gases
Surface temperature determined by albedo
Daisy growth dependent on planet temperature
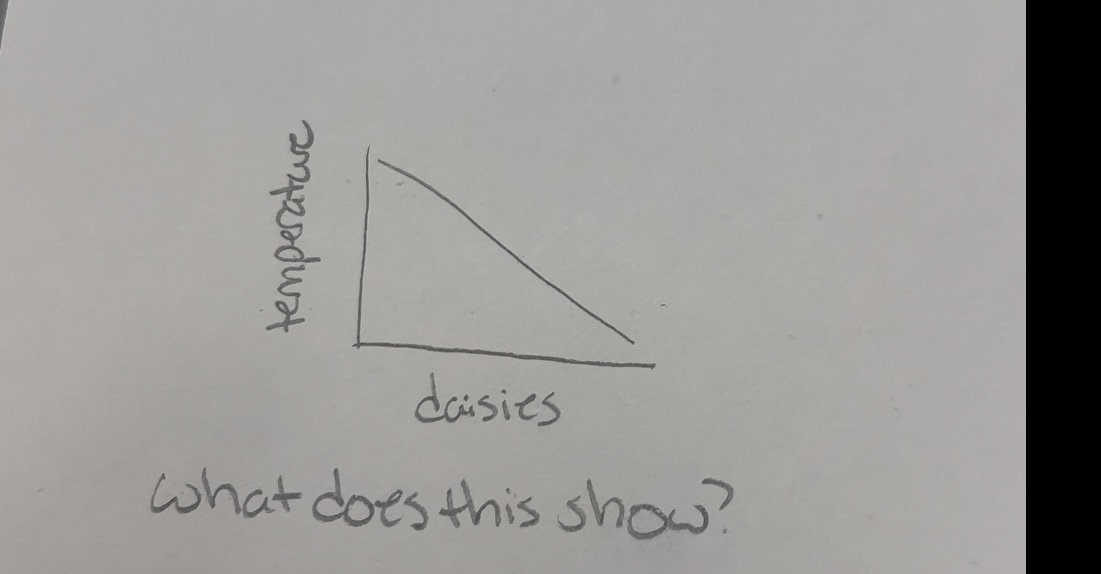
What does this show
More daisies increases albedo and lowers temperature
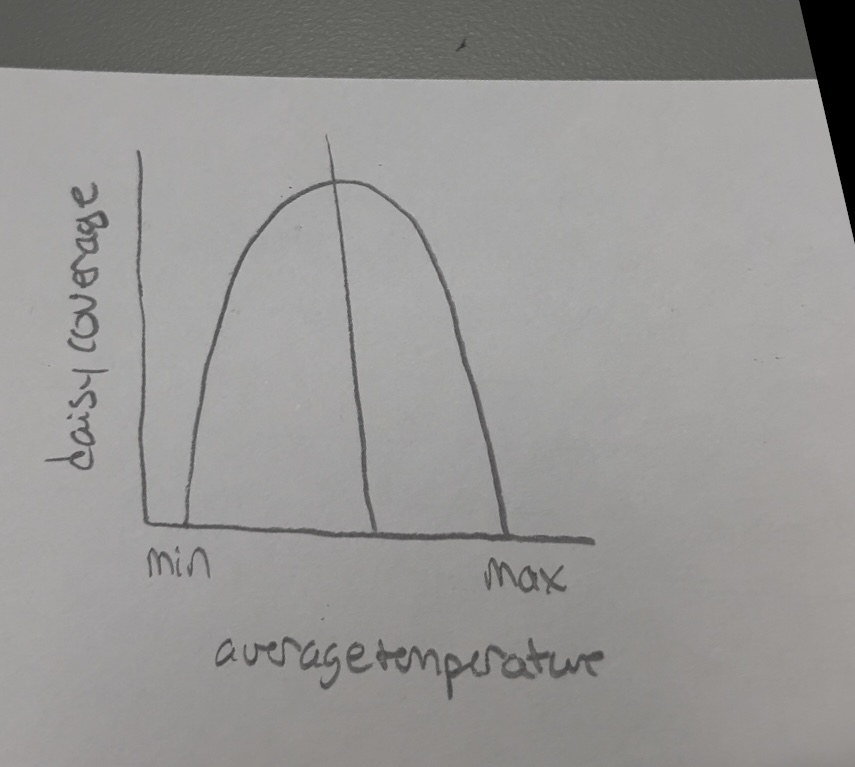
What does this show
Shows that daisies have an optical temperature range
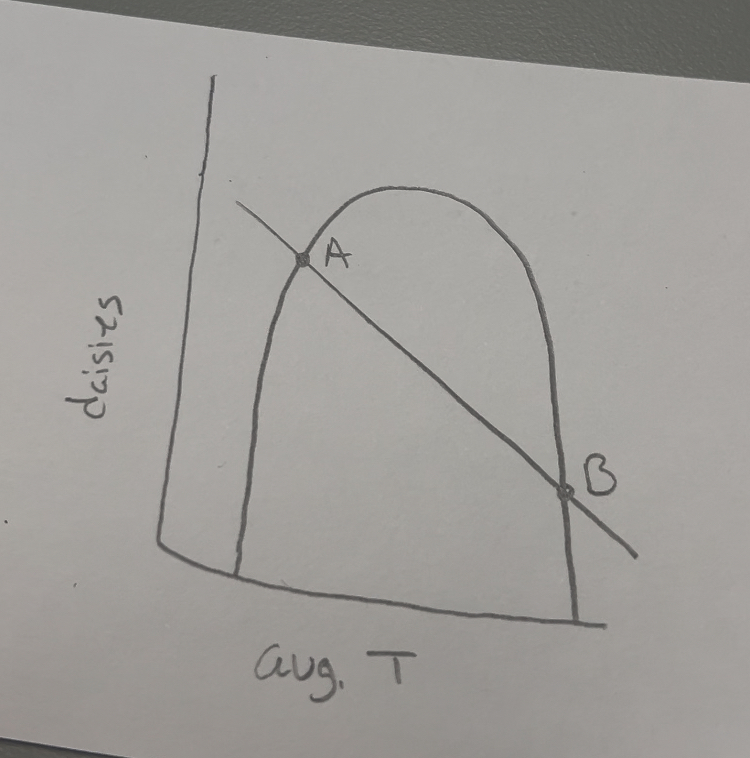
What does this show?
Shows daisy and temperature relationship with the interactions of optimal daisy growth
A is stable equilibrium while B is unstable
If temperature changes, the line will move
Lessons from Daisyworld
Planetary climate systems are not necessarily passive in response to internal and external influences
Responses are feedback loops
What causes Earth’s moderate temperature?
Greenhouse effect
Planetary albedo
Convection
Process in which heat energy is transferred by motions of a fluid, bottoms particles warm and move up, cooler particles sink to warm
Radiation movement
moves as a stream of photons from an energy source
What is the speed of electromagnetic radiation?
Speed of light, 3×10^8 m/s
Blackbody radiation
an object emits radiation with a 100% efficiency across the entire electromagnetic spectrum
Stefan-Boltzmann Law
the energy flux emitted by a black body is related to the fourth power of the body’s absolute temperature
Flux
amount of energy or material that passes across a given area per unit time
A vector quantity, so the only part that matters is perpendicular to a given area
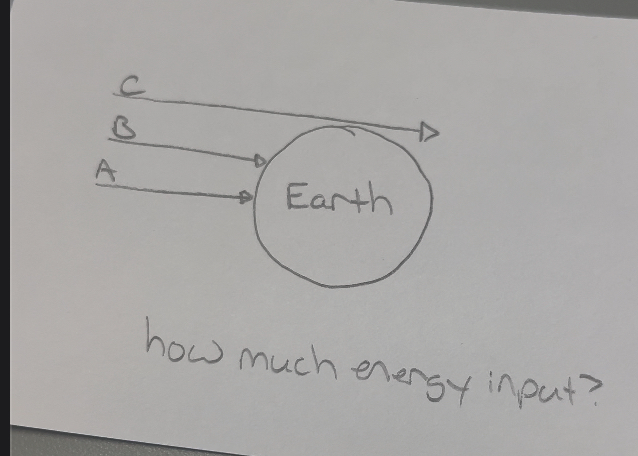
How much energy input?
A- highest solar energy input
B- moderate solar energy input
C- very little solar energy input
Differences in latitudinal albedo
tropics have low albedo due to oceans
Polar regions have high albedo due to ice
Albedo and solar energy input
albedo differences amplify differences in solar energy input as a function of latitude
Solar constant for Earth(s) and other planets
S earth: 1360 W/m²
Other planets: varies by 1/r²
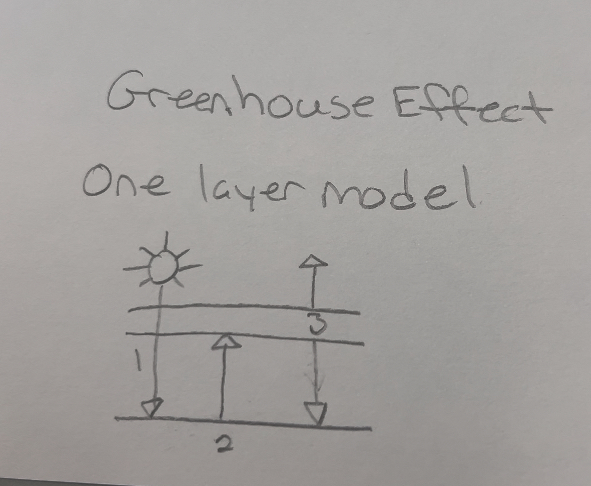
Greenhouse Effect One Layer model
Atmosphere transparent to visible photons
Planetradiates heat (infrared photons upwards; atmosphere opaque to infrared photons
Atmosphere radiates infrared protons equally in all directions
Why are CO2 and water vapor greenhouse gases?
Infrared radiation absorption and emissions affects the rate of molecular rotation and vibration
Greenhouse gases
water vapor
Carbon dioxide
Methane
Nitrous oxide
Ozone
Freons
Why are minor greenhouse gases still important?
They absorb wavelengths CO2 and water vapor do not