Balance of payments
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is the balance of payments?
a record of all financial transactions between one country and the rest of the world (record of all the money flowing in and out of a country)
What are the two main accounts in the Balance of Payments?
The two main accounts in the Balance of Payments are the Current Account and the Capital and Financial account.
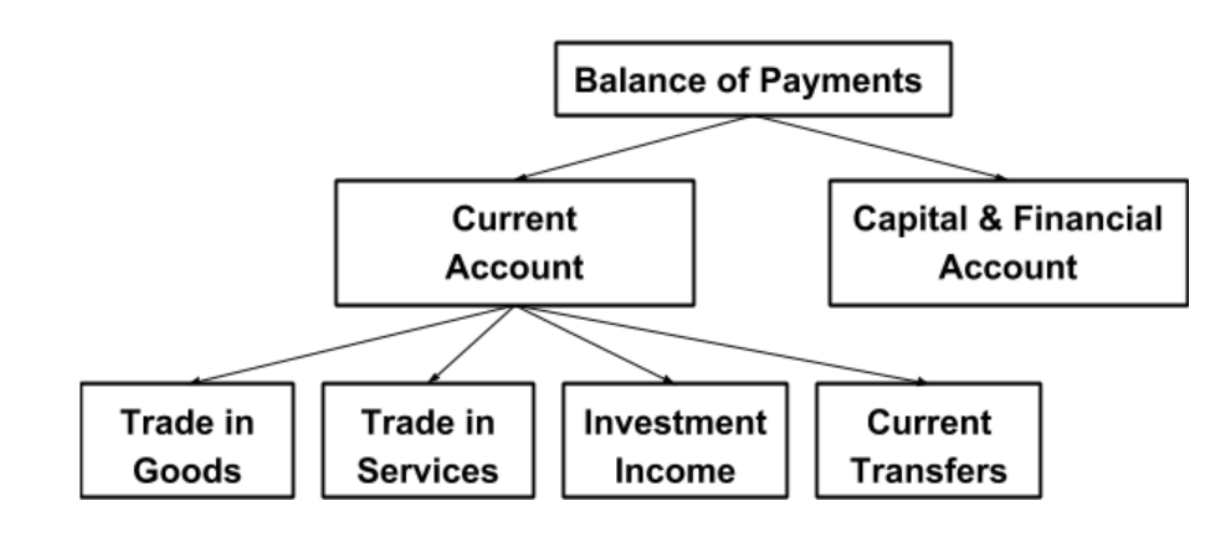
What are the components of the Current Account?
trade in goods e.g wine
trade in services e.g accounting
investment income
current transfers
What is the impact of an increase in imports on the UK Current Account?
It decreases due to an increase in withdrawals
What is the impact of an increase in exports on the UK Current Account?
It increases due to an increase in injections
How will Investment income earned by a UK investor abroad appear in the current account?
as a positive transaction because money is entering the UK so is increasing the current account.
Investment income paid from a British firm to an American investor will appear as
The investment income is leaving the UK. It will therefore be a negative on the UK Current Account, which will decrease. The same investment income is entering the US. It will therefore be a positive on the US Current Account, which will increase.
A Spanish woman invests in a British business. How are the profits from this investment recorded in the UK Balance of Payments?
he profits are recorded in the investment income part of the Current Account. No goods or services are being imported or exported in this transaction - it is only profit that is moving abroad.
The investment income is leaving the UK. It will therefore be a negative on the UK Current Account, which will decrease as a result. The same investment income is entering Spain.
It will therefore be a positive on the Spanish Current Account, which will increase.
With the aid of an example, explain the term ‘current transfers’.
Current transfers are when money is transferred abroad without getting any goods or services back in exchange. Common examples are aid which is sent abroad and workers wages which are sent back home (called remittances).
What is the term used to describe money transferred home from relatives working abroad?
a remittance.
What is investment income?
A component of the Current Account which includes any rent or profit earned on an investment made abroad.
What component of the Balance of Payments do Current Transfers fall under and what are they?
A component of the Current Account, which includes money that is transferred abroad without getting any goods or services back in exchange.
What is a current account deficit?
is negative and occurs when total inflows (money coming in) are less than total outflows (money leaving the economy).
What is a current account surplus?
when the current account is a positive number, which indicates that more money is entering the economy than leaving it.
What leads to a current account equilibrium?
when total inflows equal total outflows.
What is the trade balance?
Total value of exports minus total value of imports.
What is the Uk’s current account like?
is in a deficit of £111 billion. This means that the amount of money leaving the UK (outflows) is greater than the amount of money entering the UK from the rest of the world (inflows)
The UK’s Current Account is in a deficit of £111 billion, what does this mean for the financial and capital account?
The Capital & Financial Account will be in a surplus of £111 billion as money is invested into the UK
Why does the UK’s Balance of Payments balance?
n the UK, the Current Account is in deficit as more money is leaving the UK than is entering it. However, this means that the Capital & Financial Accountmust be in surplus as this money is reinvested back into the UK.
Warren Buffett is an American investor who buys shares in a British firm. How will the investment income for these shares appear in the UK Balance of Payments?
When Warren buys shares in the British company, this will be a positive in the British Capital & Financial Account as there is an inflow of money and a transfer of assets.
However, the income from these shares will appear in the Current Account as investment income is a component of the Current Account. It will be recorded as a negative in the current account as the investment income will leave the UK and go back to Warren Buffett in America.
What are the two types of investment into the capital and financial account?
FDI
hot money flows
What is FDI?
FDI stands for foreign direct investment. An FDI is an investment made by a firm in one country into a firm in another country in order to gain control over the foreign firm.
What is hot money?
money that investors move internationally between banks to maximise the interest that they receive.
What are the factors that affect a countries current account?
exchange rates
relative inflation
productivity and cost
quality
growth
protectionism
What happens if the value of the pound appreciates?
SPICEE - Strong Pound, Imports Cheaper, Exports (more) Expensive
if the pound appreciates (gets stronger), imports will get cheaper and exportswill get more expensive.
What is likely to occur with UK consumers if imports get cheaper and exports get more expensive?
UK consumers will buy more imports and so import expenditure will increase
What will happen if the UK pound depreciates?
weak pound, imports (more) expensive, exports cheaper.
UK imports will get more expensive and exports will get cheaper so import expenditure decreases, export revenue increases so the current account increases
What will happen to the UK’s Current Account deficit following a depreciation?
When the pound depreciates (gets weaker), imports get more expensive and exports get cheaper.
With more expensive imports, UK consumers will buy less, which will decrease import expenditure. There will be less money leaving the UK economy.
With cheaper exports, foreign consumers will buy more, which will increase export revenue. There will be more money entering the UK economy.
Outflows are decreasing and inflows are increasing, so the current account is increasing or improving.
Spain's inflation rate is 9% and Greece's inflation rate is 2%. What is the impact of these different inflation rates on Spain's Current Account?
Spain's high inflation rate means that their exports are comparatively more expensive than Greek exports. Therefore, fewer foreign consumers will choose to buy Spanish exports. This means that demand for Spanish exports will fall and so export revenue for Spain will decrease. This will worsen (decrease) their current account.
What is low productivities impact on the current account?
takes more time so higher cost per unit which will decrease the current account
What is the impact of a country that sells lower quality exports?
will sell fewer exports, which will cause export revenue to decrease. This will then decrease the current account.
What is likely to happen as a result of growth?
As an economy grows, spending on normal goods increases. If more normal goods are imported, import expenditure will increase and the current accountwill decrease.
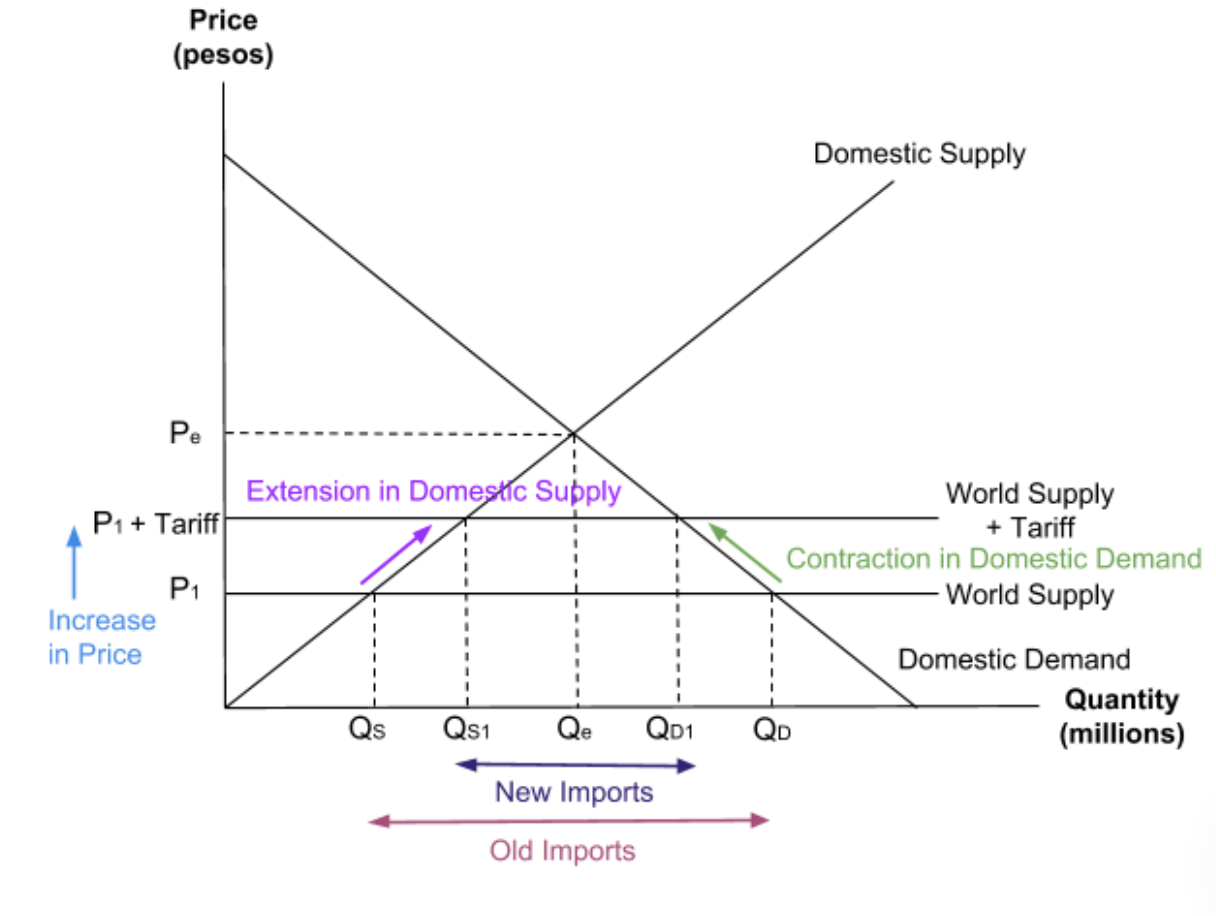
What is a tariff?
a tax on imports
What will the introduction of a tariff do to the price of imports?
increase the price of imports.
What does introducing protectionist policies do?
The introduction of protectionist measures like tariffs will increase the price of imports, causing consumers to switch from imports to domestic goods. This will lead to a decrease in import expenditure which will improve the country's current account.
Explain the impact that the quality of exports have on a country’s current account
A decrease in quality will decrease the current account. An increase in quality will increase the current account.
Explain the impact that growth has on a country’s current account
High economic growth will decrease the current account. Low levels of economic growth will put upward pressure on the current account.
Explain the impact of protectionism on the current account
The removal of protectionist measures will decrease the current account or the implementation of protectionist measures will increase the current account.
What are government bonds?
Government bonds, or treasury bills, are a method used by the government to borrow money. When a government issues government bonds, they sell a bondto an investor and then pay it back at a later date - with interest.
If a country moves from a balanced trade balance to a negative trade balance, what impact will it have on aggregate demand?
A negative trade balance means that import expenditure is greater than export revenue and so more money is leaving the economy than entering it. This means that AD is decreasing. In other words, if the trade balance decreases then the (X - M) part of the aggregate demand formula will decrease.This will in turn decrease AD overall.
A worsening of the Current Account deficit is caused by an increase in imports and a decrease in exports. Show the impact of this increase in imports and decrease in exports on the exchange rate diagram.
An increase in imports means UK consumers must supply more pounds. A decrease in exports means that foreign consumers are demanding fewer pounds. This will cause the exchange rate to depreciate
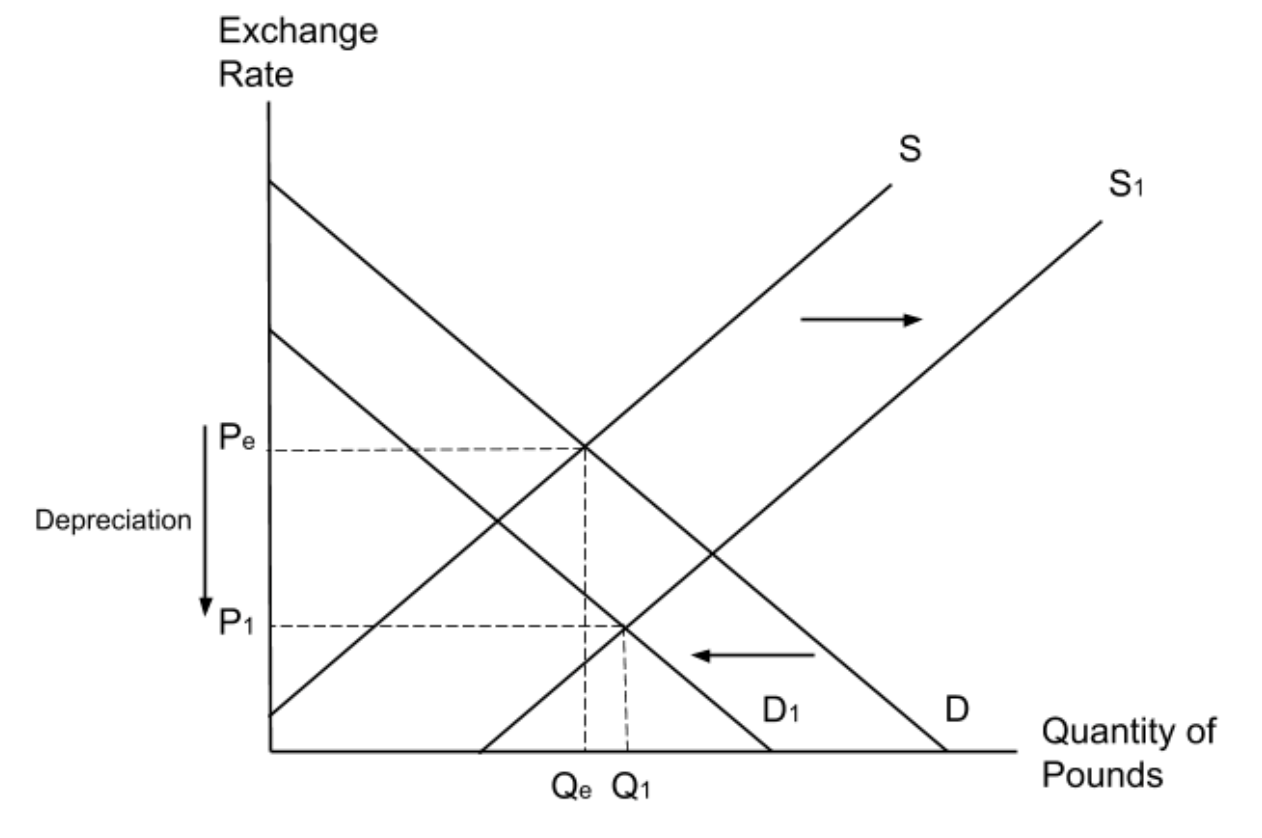
How does an increase in the supply of pounds affect the exchange rate?
An increase in the supply of pounds will cause further depreciation as shown below.
What is the impact of a severe depreciation of the pound on UK consumers?
A weak currency means that UK consumers must use a lot of pounds to purchase imports and so they become more expensive. This will decrease living standards as they can’t afford as much stuff.
How does a worsening of the current account deficit affect the exchange rate?
A worsening current account deficit is usually caused by an increase in import expenditure and/or a decrease in export revenue. This will increase the supply and reduce the demand for the country’s currency. This will cause a country’s exchange rate to depreciate.
How can a severe depreciation of the pound cause an appreciation?
A depreciation of the pound causes an increase in the price of imports and a decrease in the price of exports. This causes an increase in demand for exportswhich will increase the demand for pounds. This will cause the pound to appreciate again.
How is a worsening of the current account deficit most likely to affect aggregate demand and the exchange rate in the short run?
A worsening current account deficit is usually caused by an increase in import expenditure and/or a decrease in export revenue. This will lead to a decreasein aggregate demand which will lead to a reduction in real GDP which may cause lower living standards and higher unemployment.
An increase in imports means UK consumers must supply more pounds. A decrease in exports means that foreign consumers are demanding fewer pounds. This will cause the exchange rate to depreciate.
If a country moves from a balanced trade balance to a positive trade balance, what is the impact on aggregate demand?
A positive trade balance means that import expenditure is less than export revenue and so more money is entering the economy than leaving it. This means that AD must be increasing. In other words, if the trade balance increases the (X - M) part of the aggregate demand formula will increase. This will in turn increase AD overall.
An improvement of the Current Account deficit is caused by a decrease in imports and an increase in exports. How is this likely to affect the exchange rate?
A decrease in imports means domestic consumers must supply less of their currency. An increase in exports means that foreign consumers are demanding more pounds. This will cause the exchange rate to appreciate.
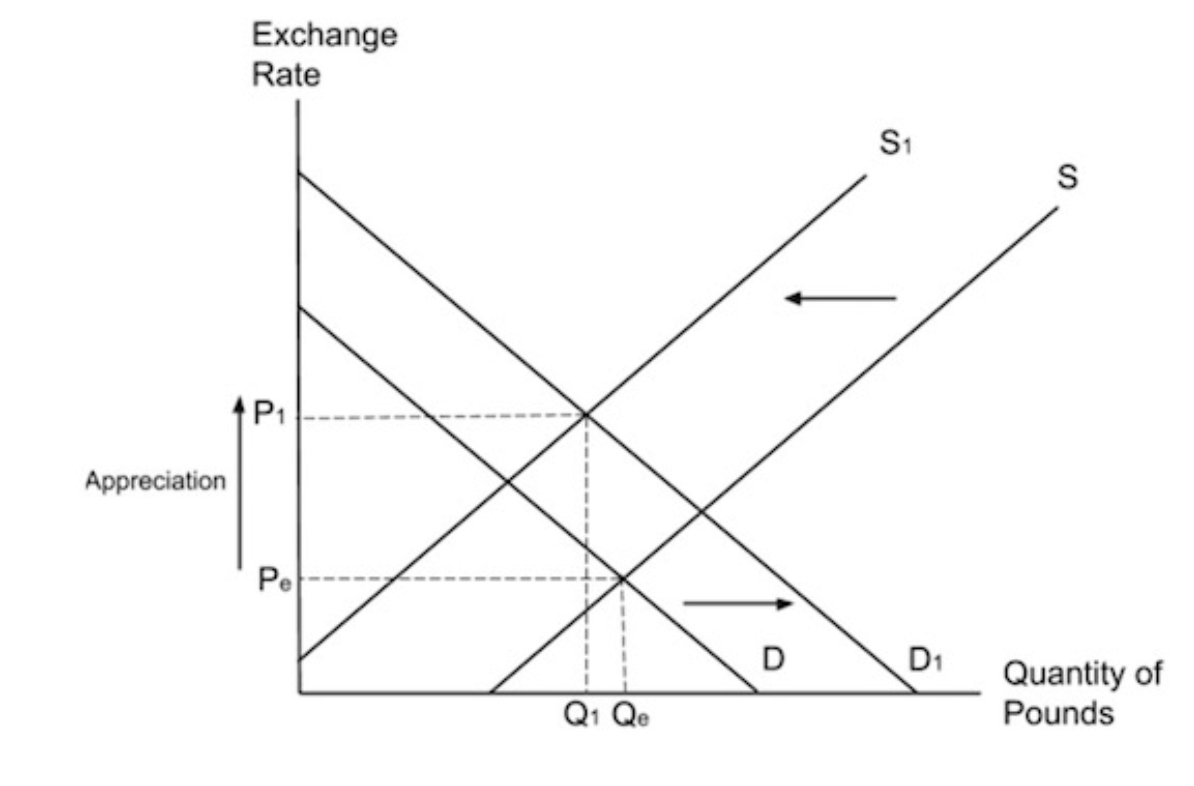
How is a worsening of the current account deficit most likely to affect aggregate demand and the exchange rate in the short run?
A worsening current account deficit is usually caused by an increase in import expenditure and/or a decrease in export revenue. This will lead to a decrease in aggregate demand which will lead to a reduction in real GDP which may in turn cause lower living standards and higher unemployment.
An increase in imports means that UK consumers must supply more pounds. A decrease in exports means that foreign consumers are demanding fewer pounds. This will cause the exchange rate to depreciate as shown below.
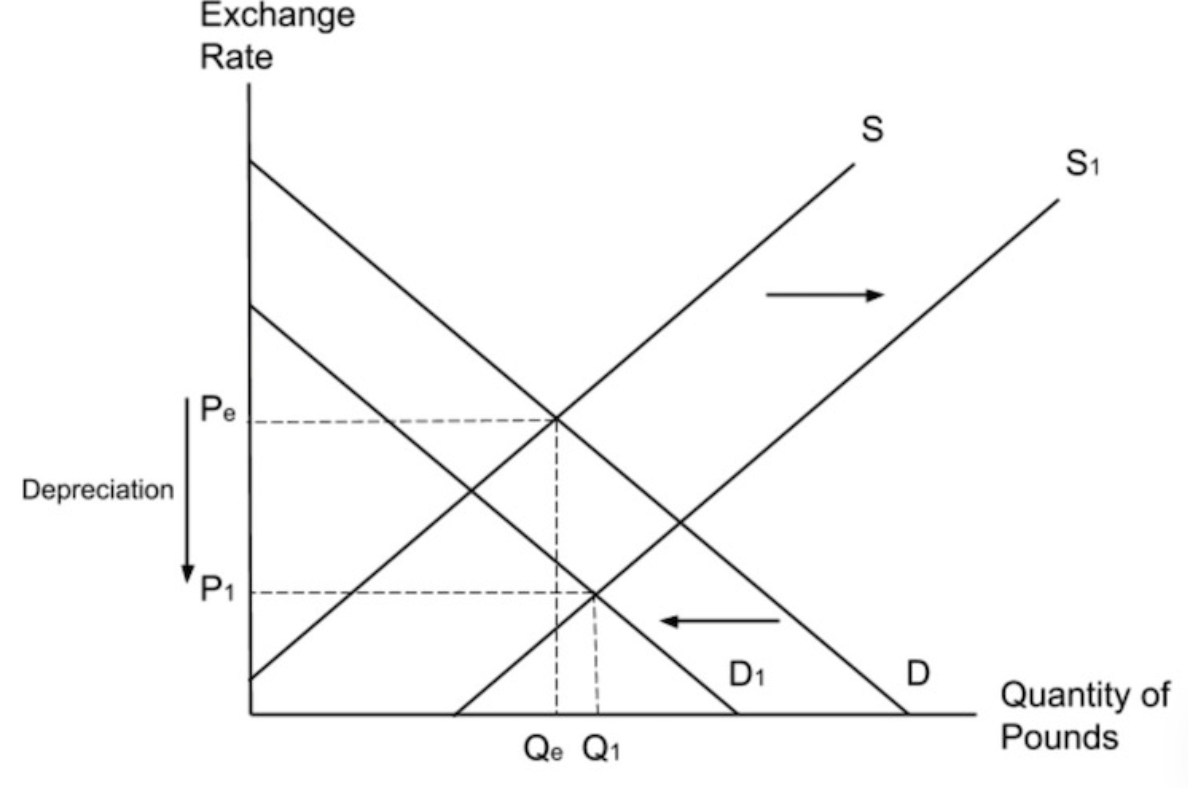
If a country moves from having a balanced trade balance to a positive trade balance, what will the impact be on aggregate demand?
A positive trade balance means that import expenditure is less than export revenue and so more money is entering the economy than leaving it. In other words, if the trade balance increases the (X - M) part of the aggregate demand formula increases resulting in an overall rise in AD.
What are the policies used to reduce the current account deficit
expenditure reducing policies
expenditure switching policies
How can a government reduce a current account deficit?
The government can attempt to reduce a Current Account deficit by reducing overall expenditure. This will have the effect of reducing expenditure on importswhich in turn should reduce the deficit by ensuring that less money is leaving the economy. The government can reduce overall expenditure by increasing income taxes or reducing government spending on benefits.
What are the two types of expenditure switching policies?
trade barriers
What are trade barriers?
Trade barriers are restrictions placed by a government on the imports of foreign goods. e.g tariffs
What is the impact of the introduction of tariffs on a tariff diagram?
An extension in domestic supply and a decrease in the quantity of imports