Biology - B3 Living together (food and ecosystems)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
OCR GCSE
Last updated 3:57 PM on 3/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
1
New cards
enzymes
Biological catalysts that have a specific active site to match a substrate
2
New cards
Substrate
A molecule that is changed by a reaction. Fits into specific enzyme active sites
3
New cards
Enzyme substrate complex
When a substrate combines with the active site of an enzyme to react
4
New cards
Temperature
This effects the rate of enzyme substrate complexes as it can cause particles to speed up and increase collisions
5
New cards
How fast a product appears
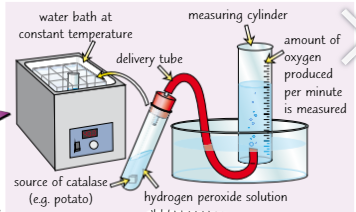
6
New cards
How fast substrate disappears
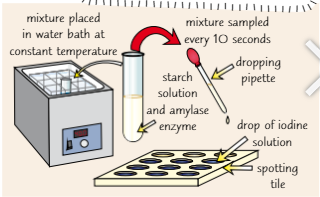
7
New cards
Photosynthesis
An endothermic reaction that creates glucose in plants and algae. Takes place in chlorophyll which contains enzymes that catalyse reactions inside of it.
8
New cards
testing if light is needed for photosynthesis
Place two plants in the dark for 48 hours so they use their starch stores. Move one into the light and do the starch test. Starch won’t be present in the dark plant
9
New cards
Limiting factors of Photosynthesis
Light → transfers energy needed for photosynthesis
Carbon Dioxide → substrate needed for photosynthesis
Temperature → Enzymes can only work at certain temperatures
Carbon Dioxide → substrate needed for photosynthesis
Temperature → Enzymes can only work at certain temperatures
10
New cards
Diffusion
The overall movement of particles from from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
11
New cards
Osmosis
The overall movement of water particles across a partially permeable cell membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
12
New cards
Active transport
The movement of particles across a membrane that goes against the concentration gradient using energy transferred during respiration
13
New cards
Exchanging substances across single celled organisms
E.g. prokaryotes → substances can diffuse straight across the cell membrane
14
New cards
Stomata
Little pores on the surface of a leaf that let CO2 and O2 diffuse in and out and water vapour to diffuse out. (aka transpiration). surrounded by guard cells which control the shape of the opening. They close when low on water or low on light.
15
New cards
Root hair cells
give plant roots greater surface area. Allows more water to diffuse in via osmosis. Allows minerals to diffuse in via Active transport.
16
New cards
Phloem
a column of living cells with perforated end plate which allow stuff to flow through. They have no nucleus so have a companion cell which also keeps them alive. food substances are translocated up and down the plant here.
17
New cards
Xylem
A column of dead cells with a lumen in the middle. Has thick walls made of cellulose and strengthened with lignin which supports the plant. Carries water and mineral ions up the stem into transpiration streams.
18
New cards
Transpiration
Caused by the evaporation and diffusion of water on plant surface. creates a slight shortage of water in the leaf so it draws more water from the roots which makes a stream of constant water throughout the plant.
19
New cards
Transpiration rate
This is effected by light intensity (brighter light, greater rate), Temperature (higher temperature, greater rate), and air movement (greater wind, greater rate)
20
New cards
Potometer
A potometer is a device used to measure the rate of water uptake by plants. It consists of a tube, a plant stem, and a reservoir of water. You remove one end of the capillary tube long enough for one air bubble to form which will travel along a scale as water is taken up by the plant.
21
New cards
Orginisation of ecosystems
Individual → a single organism
Population → all of one species in a habitat
Community → all organisms (every species) living in a habitat
Ecosystem → all organisms in a habitat including abiotic conditions
Population → all of one species in a habitat
Community → all organisms (every species) living in a habitat
Ecosystem → all organisms in a habitat including abiotic conditions
22
New cards
Competition factors
Plants → light, space, water, minerals from soil, seed distributors and pollinators
animals → space, shelter, food, water and mates
animals → space, shelter, food, water and mates
23
New cards
Abiotic
Factors that are non living such as Environmental conditions (average temperature, light intensity, moisture level and soil pH) or Toxic chemicals (bioaccumulation and eutrophication)
24
New cards
biotic
factors that are living such as the availability of food, number of predators or new pathogens.
25
New cards
Quadrat
A square frame enclosing a known area of land (e.g 1 metre^2) to compare how common organisms are in different areas.
26
New cards
Keys
A series of organisms to determine an unknown organism
27
New cards
Transect
A line across an area of land use to show how distribution of organisms change. Quadrats are used along the line to measure the amount of organisms
28
New cards
Producer
An organism that produces it’s own food i.e. plants
29
New cards
Primary consumers
Herbivores
30
New cards
Secondary consumers
Carnivores
31
New cards
Food chain
A diagram that shows what eats what in an ecosystem
32
New cards
Biomass
energy stored in the mass of the organisms that is eaten
33
New cards
trophic levels
levels in a food chain
34
New cards
Food webs
Diagrams that show how food chains are linked
35
New cards
Pyramids of mass
A pyramid displaying the biomass of every trophic level of a food chain. The producer at the bottom and the highest consumer at the top
36
New cards
Pyramids of number
A pyramid displaying the number of organisms on every trophic level of a food chain. The producer at the bottom and the highest consumer at the top
37
New cards
Loss of biomass
Energy is transferred through each organism on a food chain so not all of the biomass travels to the next trophic level.
38
New cards
Long chain carbohydrates
e.g starch is made of simple sugars
39
New cards
Proteins
made up of amino acids
40
New cards
Lipids
made up of fatty acids and glycerol
41
New cards
Benedict’s reagent
Heat reducing sugars mixed with this in a water bath and it will go from blue to brick red
42
New cards
Emulsion test
This is the test for lipids. Mix with ethanol and then pour into water. A milky white emulsion will for if lipids are present
43
New cards
Iodine
This tests for starch. Add this to the test sample and it will go blue-black if starch is present
44
New cards
Biuret test
This tests for proteins. Add a few drops of sodium hydroxide to make the solution alkaline then add Copper sulphate solution which will go from blue to purple if proteins are present
45
New cards
the Carbon cycle
* The process by which carbon moves between living organisms, the atmosphere, and the Earth.
* Carbon is absorbed by plants during photosynthesis and used to make food.
* Animals eat the plants and use the carbon to build their bodies.
* When organisms die, decomposers break down their bodies, releasing carbon back into the soil.
* Carbon can also be released into the atmosphere through respiration, combustion, and volcanic activity.
* The ocean absorbs and stores large amounts of carbon, but can also release it back into the atmosphere.
* Carbon is absorbed by plants during photosynthesis and used to make food.
* Animals eat the plants and use the carbon to build their bodies.
* When organisms die, decomposers break down their bodies, releasing carbon back into the soil.
* Carbon can also be released into the atmosphere through respiration, combustion, and volcanic activity.
* The ocean absorbs and stores large amounts of carbon, but can also release it back into the atmosphere.
46
New cards
the Water cycle
* The continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth.
* It involves several processes, including evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and transpiration.
* Evaporation occurs when water from oceans, lakes, and rivers turns into water vapor due to heat from the sun.
* Condensation happens when water vapor in the atmosphere cools down and turns into liquid water, forming clouds.
* Precipitation occurs when water droplets in clouds become too heavy and fall to the ground as rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
* Transpiration is the process by which plants release water vapor into the atmosphere through their leaves.
* This ensures the availability of water for all living organisms on Earth. It also helps to maintain the balance of the Earth's ecosystem by regulating temperature and weather patterns.
* Human activities such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change can disrupt the water cycle and have negative impacts on the environment.
* It involves several processes, including evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and transpiration.
* Evaporation occurs when water from oceans, lakes, and rivers turns into water vapor due to heat from the sun.
* Condensation happens when water vapor in the atmosphere cools down and turns into liquid water, forming clouds.
* Precipitation occurs when water droplets in clouds become too heavy and fall to the ground as rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
* Transpiration is the process by which plants release water vapor into the atmosphere through their leaves.
* This ensures the availability of water for all living organisms on Earth. It also helps to maintain the balance of the Earth's ecosystem by regulating temperature and weather patterns.
* Human activities such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change can disrupt the water cycle and have negative impacts on the environment.
47
New cards
decomposers
microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi which break down deceased organisms
48
New cards
Rate of decomposition
This is effected by:
* Oxygen availability → though some decomposers work anaerobically they work much slower so plenty of oxygen is needed
* Temperature → decomposers contain enzymes to help break down the organisms so higher temperatures are better
* Water availability → decomposers need water to survive but too much water means no oxygen, so moist conditions are best
* Oxygen availability → though some decomposers work anaerobically they work much slower so plenty of oxygen is needed
* Temperature → decomposers contain enzymes to help break down the organisms so higher temperatures are better
* Water availability → decomposers need water to survive but too much water means no oxygen, so moist conditions are best
49
New cards
Decomposers and global warming
landfill sites tend to be low in oxygen so decomposers respire anaerobically which produces methane, a powerful greenhouse gas more so that carbon dioxide