Nucleic Acids A1.2 SL/HL
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
IB Biology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Double Stranded
Double Helix
Antiparallel
Deoxyribose sugar
Hereditary information passed to offspring
Polymer mad eof monomers called nucleotides
RNA
Ribonucleic acid
Single-stranded
Ribose Sugar
(is used by some viruses instead of DNA, but viruses are not living organisms)
Components of nucleotides
pentose sugar (5 sided)
Phosphate group
nitrogenous base
Bases in DNA
Adenine
Thymine
Cytosine
Guanine
Bases in RNA
Adenine
Uracil
Cytosine
Guanine
Purines (double rings)
Adenine
Guanine
Pyrimidines (single rings)
Cytosine
Uracil
Thymine
Condensation Reaction
Removal of water to create a bond
Complimentary Base Pairing
A→ T
G → C
(Hydrogen Bonds between them)
DNA Replication is…
Semiconservative
Each resulting copy is made of one parent strand and one new strand
Parent strands are used as templates to make the new strands
Follows the rules of complimentary base pairing
Gene Expression
using the codes in DNA to synthesize a protein
Protein synthesis happens in steps….
DNA → RNA → Protein
Diversity of DNA sequences
DNA molecules can vary in length
Many possibilities for unique sequences
Universal genetic code
all life arose from a common ancestor
the same codons on RNA code for the same amino acids in almost every organism
Directionality of RNA and DNA
Carbons are numbered
5’ and 3’ ends
Antiparallel
New nucleotides can only be added to the 3’ end
Each complementary pair has…
one purine and one pyrimidine
All pairs are the same length
this increases stability of DNA molecule
Nucleosome
DNA wrapped twice around a core of 8 histone proteins
Hershey-Chase Experiment
Trying to figuire out whether DNA or Proteins were reaponsible for transmitting genetic information
(Protein adherance) Sulfur → virus was in the supernatant
(incorporated into DNA) Phosphorous → virus was in the pellet
Bacteriophages
Centrifuges (separates things based on weight)
Pellet (stuff that sinks to the bottom)
Supernatant (Virus Particles)
Realized that DNA IS THE GENETIC MATERIAL
Chargaffs experiement
Looking for data on the relative amounts of pyrimidine and purine bases across diverse life forms
Tetranucleotide hypothesis: DNA consisted of a repeating sequence of 4 nucleotides in equal amounts and proyteins were the genetic material
Chargaffs rule of complimentary base pairing
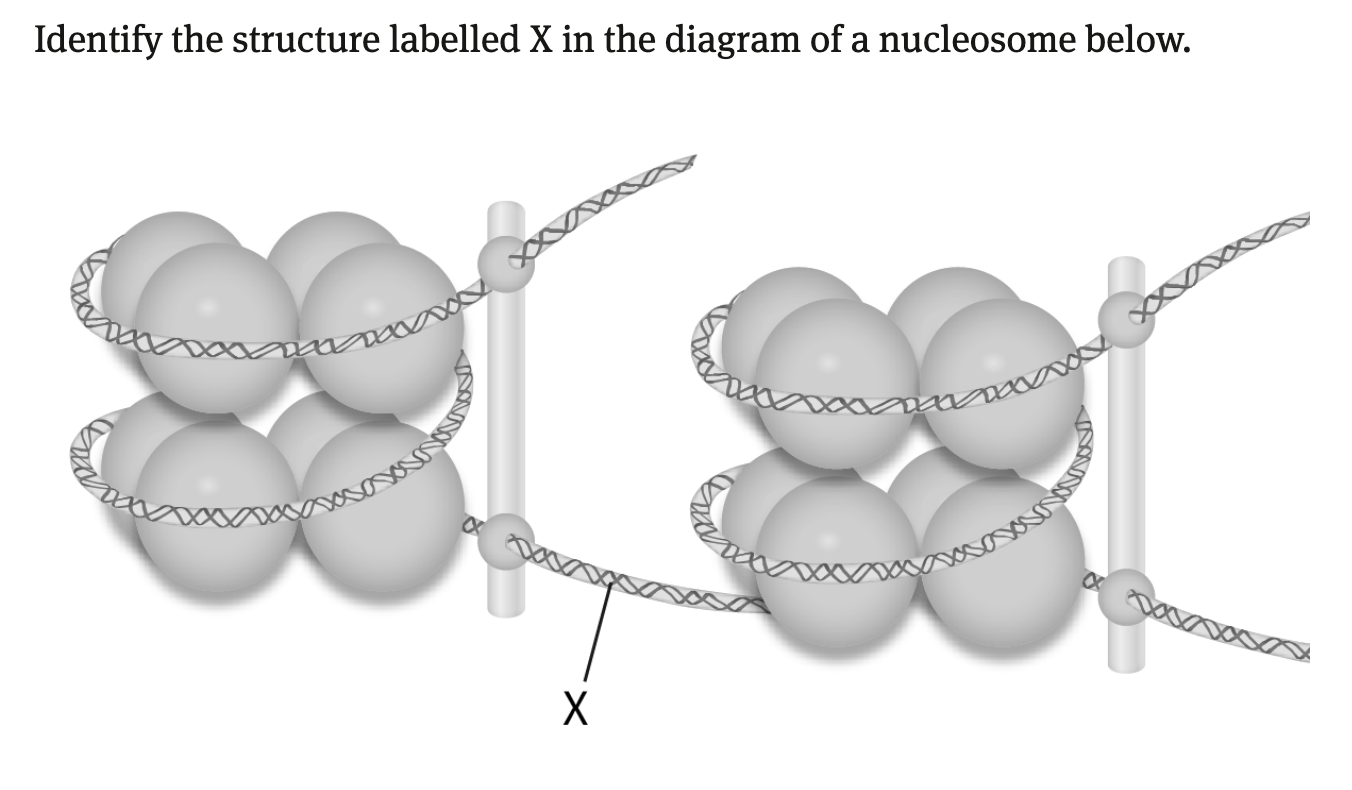
linker DNA
What makes up a nucleosome?
DNA and histone proteins
What provides the strongest evidence for universal common ancestry amongst living species?
highly conserved sequences of DNA amongst living organisms
Reactions
Photosynthesis: Plants convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose, producing oxygen as a byproduct.
Cellular respiration: Cells break down glucose to produce energy, releasing carbon dioxide and water.
Anabolism: The synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones, such as proteins and nucleic acids.
Catabolism: The breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy.
Condensation reactions, also known as dehydration synthesis, build larger molecules from smaller ones by removing water,
Hydrolysis reactions break down large molecules into smaller ones by adding water.
Types of bonds
Covalent Bonds:
.Opens in new tab
These strong bonds are formed when atoms share electrons, allowing them to achieve a stable electron configuration. They are common in biomolecules like proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
Ionic Bonds:
.Opens in new tab
These bonds occur when one atom donates electrons to another, resulting in oppositely charged ions that attract each other. They are important in maintaining the structure and function of biomolecules like proteins.
Hydrogen Bonds:
.Opens in new tab
These weak interactions occur when a hydrogen atom is attracted to an electronegative atom (like oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine) in another molecule. They play a crucial role in the structure of proteins, DNA, and water.