ALL urban paper 1 (notes and case studies)
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
suburbanisation - Newcastle causes, affects on inner/outer city
causes: improved communication networks, local tax and land price increase meant more affordable and demanding homes
effects inner city - air pollution from congestion, more people wealthy outsides, a decline int he central city / donuts city
effects outer city - the green belt has had to be stretched, new development schemes e.g. 400m away from bus stop, communities split from new people
counter urbanisation - Sti Ives. causes, effect, adv dis
background - small rural town 100km from London, has a Victorian style look
causes - many people want a rural lifestyle close to large cities, the train ticket is cheaper than living in london (£3,200), the appeal of housing.
adv: more population means more tax and importance to the Uk, more designer shops have arrived
dis: house priced doubled in 14 years, split between young families and older generation, schools are full, housing developers are difficult to manage
Urban resurgance: London docklands L context, adv dis
context:
a former economical zone lost with the size of ships, becoming a derelict area
LDDC introduces to aid people
adv:
24,00 new homes
new transport and bike lanes in 1987
dis:
conflict between locals and new people due to introduction of premium apartments
many locals forced out due to high prices
enterprise zone - Merry hill: context, adv dis
context
the development created 217 stores
4,000 jobs
adv:
allowed for the regeneration fo a derelict area, creating economic opportunities in the Midlands
dis:
many people who had industrial skills were not needed, leading to poverty and people moving away
city challenge: hulme: context causes, consequences
context: a need for homes for the increasing population meant housing was needed, this rows of stacked flats where cheaply made to give people homes
causes:
Insulation issues due to cheap materials
The poor design lead to less efficient homes, which was a difficult issue during the oil crisis
consequences:
You were 30X more likely to be killed
Many of the homes became council housing, bringing in the poorest of households
The crime and drug use was common
Contrasting Urban form: LA
LA is mostly known for it’s history of holywood, this brings in the rich actors to live near or in LA
this leads to the creation of large, open rich neighbourhoods to suit the needs of actors and celebrities who want to afford luxury
This history had lead to mass tourism over the years, leading to the opening of Disneyland in 1955
the economic state - donut city, with rough areas and ganfs in the middle and more economic areas around the center
contrasting urban form: Mumbai
Mumbai is home to Bollywood, large Indain movies
Economic hub of India, with large tech companies such as TATA
there are higher numbers of povertiy due to the unsustainable growth
low tax means less supporgt and growth for people’s aid
dialy life is unhealthy due to smoke pollution and transport incidents
1000 new migrants a day
London diverse backgrounds: Harrow and Tower Hamlets
Harrow:
languages - Tamil, Polish, Somalian
birthplaces - Kenya, Somalia
population density - high density
life expectancy - above average
Tower Hamlets:
language - Polish, German
birthdplace - USA and Germany
population density - more cramped and above average
life expectancy: average
Air pollution - Beijing
issues:
extreme temperatures (-20 in winter and 26 in Summer)
57% (over half) of fuel from coal
6 million cars on the road
2008 Olympics, Olympians did not want to compete
Solutions:
transitioning away from coal to renewable and natural gas
introducing a car lottery
making sure a car is not used for at least 1 day a week
river restoration (removing hard engineering and returning to nature)- Darlington
1850 to 1945, the river was straightned for industrial purposes
made the river polluted with sewer water and leakages
1995, a plan to change the are into an attractive wetland environment, thriving with life was made
it was done to reduce the flood risk, treat water issues and increase biodiversity in Darlington
river conservation (planting wildlife) blue loop, Sheffield
rive rused for industrial purposes left it dirty and buildings near in derelict states
until the 1992 Sheffield development co-operation was formed
it aimed to rejuvenate the area for walking, encourage biodiversity and creating a community to aid the river
SUDS, Lamb Drove
a Euroean project to prove how SUDS can be used in new housing developments
they used:
water butts
permeable surfaces
filter strips
adv:
reduced metal found in the water
cost effective as maintenance was 10% less
created a mark-up due to USP
dis:
risks when it comes to large dips for SUDS cna be dangerous for people (especially children)
lower density of housing can be made
need specialised architects and builders who know waht to do
microclimate
a climate in a small or restricted area, especially when it differs to the surrounding areas.
Urban heat island effect
the increased temperature in urban areas compared to surrounding rural areas.
Albdedo effect
the reflectivity of certain services:
black surfaces such as roads and black buildings have low albedo
white surfaces have high albedo
absolute humidity
the mass of water vapour in a given volume of air, regardless of temp
relative humidity
a percentage / ratio of the actual amount of water vapour that is in the air.
different between relative and total humidity
relative - the percentage of water vapur
total - the quantity in the water
venturi effect
two buildings with a gap between them causing a sharp air wind speed
the formation of thunderstorms
ground surface heats and air rises
the air becomes unstable and causes of a ‘chimney’ of condensed air
causes ice crystals and they fall as precipitation
this causes electric charges of the positive crystals
causing thunder and lighting
downdraught effect
tall buildings cause the wind to mostly go down (some go up) and this air picks up speed and causes higher wind speeds.
fog
when visibility is less than 1000m and occurs when air colls to it’s dew point, causing invisible water vapour to condense around microscopic particles such as dust or salt
radiation fog
caused when there is cooling of land by thermal radiation cooling the close to the surface
the cooling reduces the ability to hold moisture and causes the dew point to be reached easier, causing fog
advection fog
caused by warm moist air blowing over a colder area, causing air to reach lower dew point.
Smog
a mixture of smoke and fog which occurs when smoke particulates and sulphur dioxide mix with fog.
photo chemical smog
occurs in drier areas and forms due to fossil fuels, and borning trees and organic waste
particle pollution
pollution which consists of particles suspended. these particles come from natural and human processes
smoke controlled areas: def adv dis
an areas where it is offence to emit smoke from a chimney, normally resulting in a fine.
adv: stops the emissions of gas within urban areas, better air quality, reduces risk of chimney fires
dis: the max offence charge is £1,000 meaning large businesses are mostly unaffected
clean air act: def adv dis:
the clean air act was brought in 1956 and dealt with smog issues, making smog contol areas where smoke is not allowed in domestic properties
adv: improving public health and environmental impact is reduced
dis: may lead to exportation from abroad, worsening the carbon footprint of products and reducing the UK’s economy
vehicle control: def adv dis:
introducing schemes to reduce cars in busy areas, whether that be from the design of cities reducing roads, to low emission zones being introduced
adv: encourages people to have cleaner habits in the way they commute
dis: leads to traffic on the outskirts of the city, with city expansion being an issue
vechile emissions: def adv dis:
car manufacturers have been made to make efficient fuel-burning engines
adv: reduces the impact of vechiles on the road and lowers fuel usage and price
dis: these new standards only apply to new cars, companies can still find ways around the emissions tests e.g. Volkswagen cars in diesel gate and the test showing 40X less emissions than what they did on the road
public transport: def adv dis:
introducing more public transport schemes such as bus and train stations and bike paths
adv: reduces traffic, reduces people’s carbon footprint getting to work
dis: can lead to overcrowding of services, can often be unreliable
industry zoning
forcing businesses to emit their pollutants above the immersion layer
adv: decreases fog and smoke, decreasing health issues and keeps businesses still in the city
dis: can have a negative look on a city and the emissions are still being released
the urban water cycle - neame the levels:
source - reservoirs, lakes
water treatment - raw water must be treated with methods such as filtering and disinfection
water distribution - clean water is put into pipes and pumps, where it is transported
use - can be used in many ways such as cleaning, drinking and bathing
wastewater collection - taken back for treatment
wastewater treatment - the physical, chemical and biological treatment processes and discharged into sources
Natural levees: def adv dis:
embankments (turns in the river) are made of concrete and riverbed materials
adv: relatively low costs to maintain and have a nice natural look
dis: can easily be over topped by flash floods
diversion spillways: def adv dis:
emergency areas which are opened when there is flooding
adv: reduce the pressures on the main channel
dis: expensive and can disrupt ecosystems r
river channelisation: def adv dis:
straightening channels with concerete to reduce friction
adv: improved navigation and more efficient flooding
dis: expensive and destroys habitats. can lead to flooding at the bottom of rivers
afforestation: def adv dis:
planting trees to increase interception and reduce water runoff
adv: more natural approach and little construction needed
dis: community not happy, takes long time for them to grow
riverbank conservation: def adv dis:
planting bushes and trees to reduce erosion and roots which stabilise riverbanks
adv: low maintenance and disruption needed
dis: takes a long time and does not reduce major flood impact
floodplain zoning: def adv dis:
restricts land use to a floodplain, allowing it to get flooded
adv: avoids people from being flooded, reducing risk
dis: can be difficult to implement and requires assessment of land
river straightening: def adv dis:
cutting through meanders to create a straight channel
adv: improved navigation, easier maintenance, more space for urban land
dis: can increase floods downstream and can destroy habitats
river restoration definition
removing all hard engineering and adaptations to restore meanders, wetlands and floodplains. this leads to flood management being returned to nature
river conservation
planting vegetation to reduce lateral erosion and riverbank collapse. this can also include introducing native species and awareness to the public
River restoration study - Darlington
the river was straightened in 1850 to accommodate industrialisation
in the 70’s the lake was highly polluted with gas and sewer pipes
in 1995 a plan was made to restore the area into an attractive wetland environment thriving with natural life
this was done to maintain biodiversity and reduce flood risks
river conservation study - Blue Loop Sheffield
throughout the 1800’s, the river was used for industrial purposes such as cooling and exporting coal and goods
this lead to the river becoming derelict, as well as the houses around the canal
this was until 1992 when the Sheffield development co-operation helped to conserve the river Don and canal
the aim was to: encourage biodiversity, create a community to help the river, reducing flood risk and making it a recreational area
SUDS definition
represent the ultimate in realistic yet environmentally friendly replication of natural drainage systems
SUDS: Swale

wide shallow drainage channels which collect and transport water
SUDS: permeable road and pavements

use of porous block paving and concrete
SUDS: infiltration trenches

bioretention basins

gravel / sand filtration beneath reed beds
SUDS: rain garden
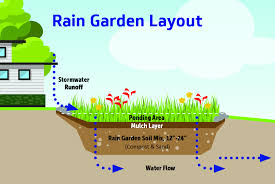
shallow landscape despressions planted with flowers and shrubs
SUDS: green roof

SUDS: adv dis
adv: slow down water runoff, provide wildlife homes i urban areas, reduced flooding risk, prevents water pollution
dis: lowered profit when developing, increased maintenance, high initial costs
Case study: Lamb Drove, Cambourne
this development was apart of a large scale project of introducing SUDS across Europe
this one included introducing methods such as: permeable surfaces for drives, under drained swale, water butts and filter strips
this lead to less metal in their water as well as maintenance being 10% less
however, it did lower profit’s for developers and concerns were made about exposed water
streategy: greener built environment. def adv dis:
initiatives to use energy and water more efficeintly as well as reducing waste in a more greener way
adv: can improve energy consumption in buildings, enhanced appeal of cities
dis: high initial costs, hard to change what is already implemented
strategy: planed expansion def adv dis
encouraging the conservation of historic buildings and green space.
adv: protects open spaces which act as carbon sinks, maintain hsitorical and tourism heritage.
dis: can be costly to maintain older buildings, restrictions on land use take a lot of time to gain
strategy: carbon neutral developments. def adv dis
building structures such as houses that produce as much energy as they need
adv: reduces impact on environment from all settlements, enhanced reputation
dis: can be challenging to maintain due to cost
strategy: economic opportunities. Adv dis
providing a range of economic opportunities outside of the fossil fuel department e.g. Quaternary sector
adv: can lead to a more sustainabel growth in demand and reduce reliance of fossil fuels
dis: can create economic inequalities due to loss of jobs needed
ecological footprint definition
the impact of a person or community on the environment, expressed as the amount of land required to sustain their use fo natural resources
biocapacity definition
refers to the capacity of a given biologically productive area to generate an on-going supply of renewable resources and to absorb its spill ober wastes
ecological defecit and surplus definition
the difference between the bio capacity and ecological footprint tor a region or country
defecit: when the footrpints exceeds the capacity in the area
surplus: when the capacity exceeds the footrprints in the area
Suburbanisation definition
The process of population movement from the central area of cities towards the suburbs on the outskirts or rural-urban fringe, (cities to suburbs).
Counter-urbanisation definition
The movement of people out of the city into surrounding villages and rural areas
Urban resurgence
Population movement from rural BACK to urban areas
Case study - Newcastle
causes - increase in communication means people don't need to live near areas such as London anymore
effects on inner city - inner city decline as richer people move away from the central areas into the suburbs, house prices become premium meaning high rise
Effects on outer city - green belt is pulled back to make space for housing, A scheme to make sure nobody is 400m away from a bus stop
decentralisation of government
the transfer of power and authority from higher to lower levels of the government / national to sub-national levels
decentralisation of retailing
retailers are moving their premises from CBD's to the outer suburbs of the city. this can cause the donut / polo affect, where the centre of cities is left in derelict, while the outskirts get all growth and wealth
Hiller's 3 steps of decentralisation
it started with the movement of superstores to outskirts.
next, it was large retail parks such as DIY stores
finally, it was large shopping centres being built e.g. merry hill
service economy def adv dis
when a country priotises providing services rather than goods adv: allows for economic growth from globalisation and allows for more tertiary jobs dis: the shutting of primary jobs has not been made up for yet, leaving more people unemployed due to itt.
urban policy Margaret Thatcher
she was the main ambassador for the service economy mindset of the UK, following in the USA's shoes (she liked them), this also included the growth of large, privatisation of regeneration schemes, with the hope of it 'trickling down to local schemes'
urban policy - John Major
a bidding scheme where local councils could bid on problems they want to fix
urban policy - Tomy Blair
more local decision being made on government redevelopment, allowed for the government ot send money for others to fix it
city challenge - hulme
rows of stacked flats were made in hulme, the poor production and design caused it to be a very poor housing area. this caused chaos as there was a high crime and drug use, makign it dangerous, as well as sitters getting hands on keys, causing a black market. you were 3x more likely to be killed in this area.
pre-industrial city
keeping it's traits, not being changed by modern urbanisation, having historical buildings and crafts as their functional areas e.g. York
modern city
little attention is spent on building aesthetics or ornate designs; improved transportation, multiple CBDs, and dispersal into the suburbs e.g. Birmingham
public transport oriented city
minimising the walk between housing areas and public transport. has railways over main roads and kepps things local e.g. Tokyo
African cities
a central CBD with sectors of activity out from that, and often a market sector or area adjacent to the CBD, nomrally high developed area next to derelict areas e.g. Nairobi
gentrified areas
An area of the inner city that has been regenerated by wealthier residents than would normally live there, bringing new life
fortress development
An urban area characterised by design with a high focus on security, such as the idea of 'defensible' space e.g. Beverly hills.
cultural and heritage corners
a cultural quarter to develop economic growth and revitalise local economy, normally done in derelict areas e.g. London with greener areas introduced and history activites.
postmodern western cities
More fragmented urban form with independent settlements, economies, societies and cultures. A greater emphasis on services, jobs in the Quaternary sector. and varied architecture Greater ethnic diversity but heightened economic, social and cultural inequalities.
Types of urban waste (name 3)
domestic - green and black bins commercial - hotels, stores, offices animal - crops, dead animals spoiled food institutional - needles from hospitals and waste from schools.
managing urban waste (name 3)
landfill incineration waste reduction schemes trade of waste
landfill adv dis
adv - helps store it in a inexpensive way dis - bad smell in local area, releases dangerous gases
incineration adv dis
adv - a good option do get rid of hazardous equipment e.g. needles dis - releases dangerous gases, needs lots of energy
waste reduction adv dis
adv - stops people throwing away items and takes little work from government councils dis - it may be cheaper to get a new one than repair it e.g. boiler or washing machine parts.
trade adv dis
adv - can help countries gain money which need it, as well as it can reduce waste in LIC's dis - there can be lack of regulation, leading to exploitation of materials, transporting long distances is bad for environment