BIOl 3200 mehari exam 4 (antimicrobial therapy)
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
antimicrobial vs antibiotic
antimicrobials - anything that can kill microbes
antibiotics - products of other organisms known to kill bacterial cells
leading cause of pneumonia in humans
S. pneumoniae
75% of all antibiotics are used in
animal feed
60-70% of nosocomial staphylococcus infects are a result of
MRSA (methicillin resistant S. aureus)
Ernest Duchesne
proposed that bacteria and molds engaged in a perpetual battle for survival
looked at the effect of fungus
Alexander Fleming
rediscovered penicillin
the mold was identified as Penicillium notatum
the penicillin we use today came from a moldy melon that has strains of penicillin
Howard Florey and Ernst Chain
purified penicillin
Gerhard Domagk
discovered sulfa drugs
discovered the first commercially available antimicrobial drug
look at antimicrobials, not antibiotics
Selman Waksman + student Albert Schatz
father of antibiotics
discovered 20+ antibiotics
- most successful is Streptomycin
discovered streptomycin from Streptomycin griseus in soil
two criteria for antimicrobial therapy
antibiotic must affect target organism
it must not affect humans
broad spectrum antibiotics
an antibiotic that is able to affect both Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria
narrow spectrum antibiotics
sensitive to only a few types of bacteria
penicillin spectrum
narrow?? (in class he said broad)
is more effective against Gram positive than Gram negative cells because Gram negative have an extra lipid layer that makes their cell wall more protected
bactericidal
antibiotic that kills bacteria
bacteriostatic
antibiotic that inhibits bacterial growth
cannot kill organism, if removed then organism will resume growth
minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)
smallest concentration of drug that visibly inhibits growth
may still have living (nongrowing) organisms
only requirement is that tube growth is NEGATIVE
minimal lethal concentration (MLC)
lowest concentration of drug that kills pathogen
requires tube growth to be NEGATIVE and subculture plate to be NEGATIVE
MLC/MIC ratio
MLC > MIC
Kirby-Bauer
test is used to determine the susceptibility of a microorganism to an antibiotic
zone of inhibition cannot be assumed as susceptible or not, must be measured, and compared to chart
leading causes of death
CVD > cancer > covid19 > accidents > stroke
penicillin inhibitor type
cell wall
cephalosporins inhibitor type
cell wall
vancomycin inhibitor type
cell wall
cell wall inhibitors - goal
inhibit peptidoglycan synthesis
interfere with synthesis
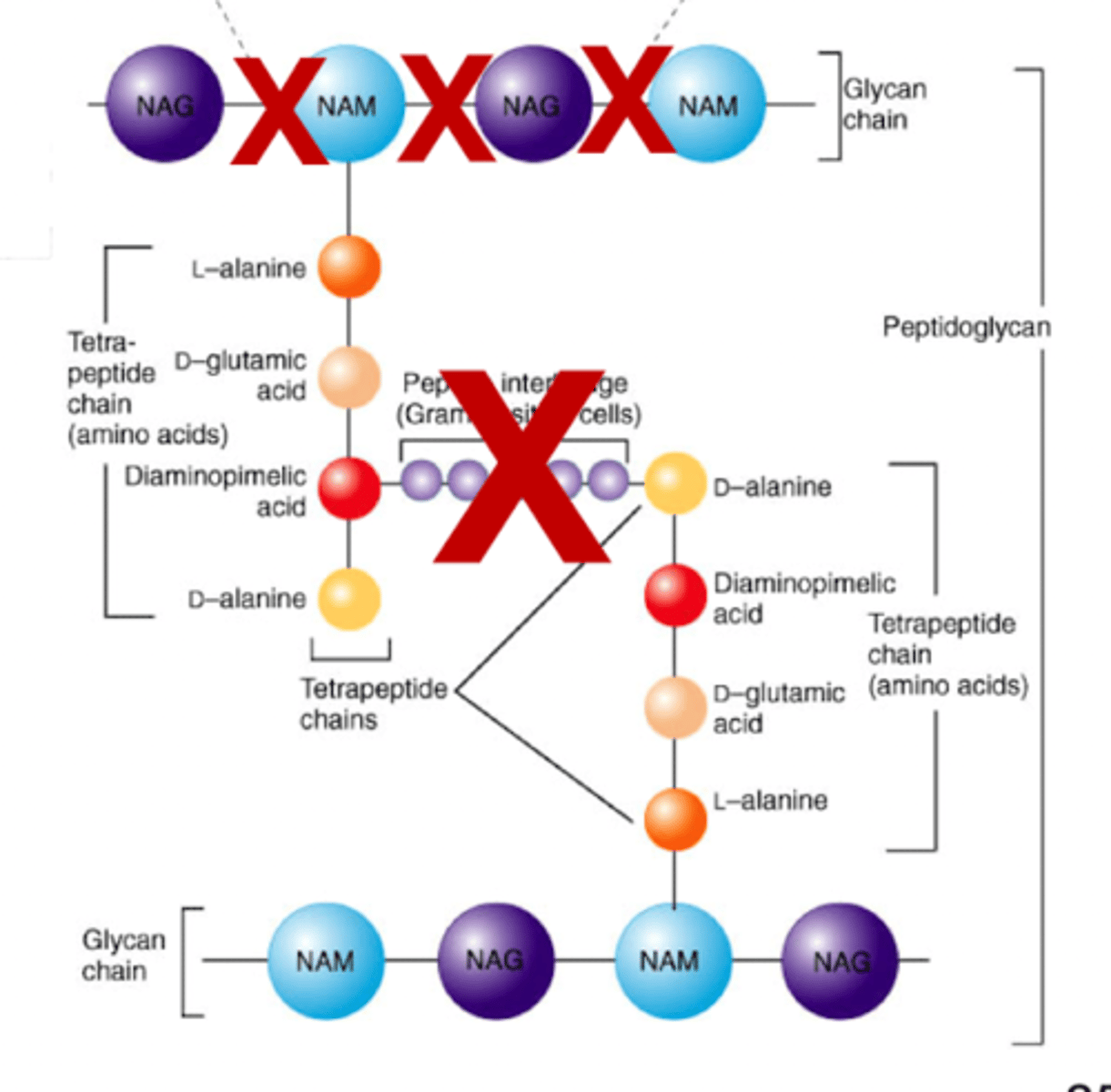
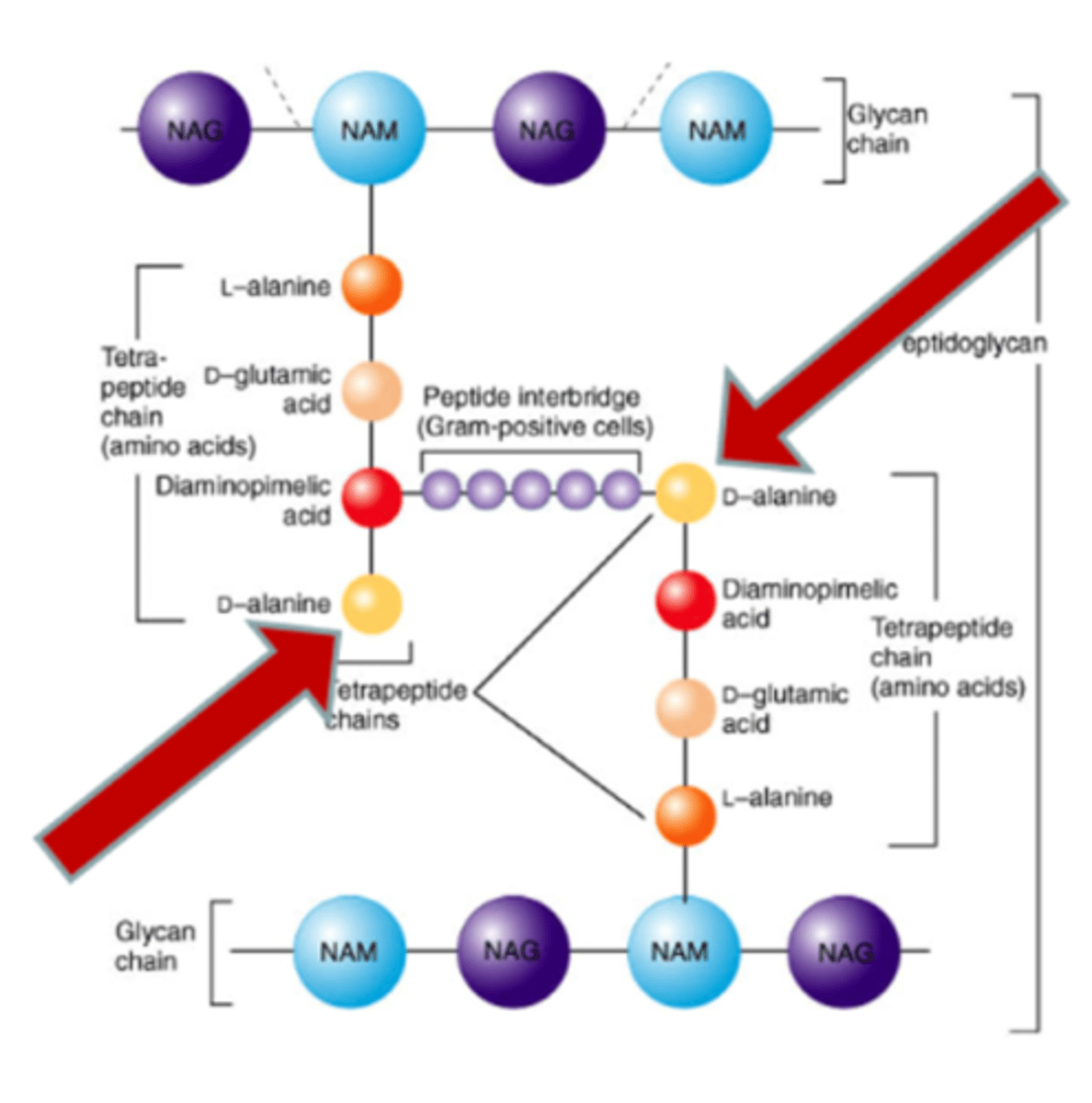
cell wall - peptidoglycan makeup
NAG and NAM peptide
cell wall - transglycosylases
enzymes that form the B 1,4 linkages between NAG-NAM
attaches precursors to existing cell wall structure
cell wall - transpeptidases
cross-linking of linear peptidoglycan chains
forms amino acid links between NAM sugars of different layers
penicillin and cephalosporin - inhibition
mimicry via beta lactam ring that resembles D-Al-D-Al piece of peptidoglycan
inhibit the cross-bridge formation by transpeptidase!!
penicillin and cephalosporin - affect to humans
no toxicity
humans lack cell walls
peptidoglycan does not exist in mammalian cells
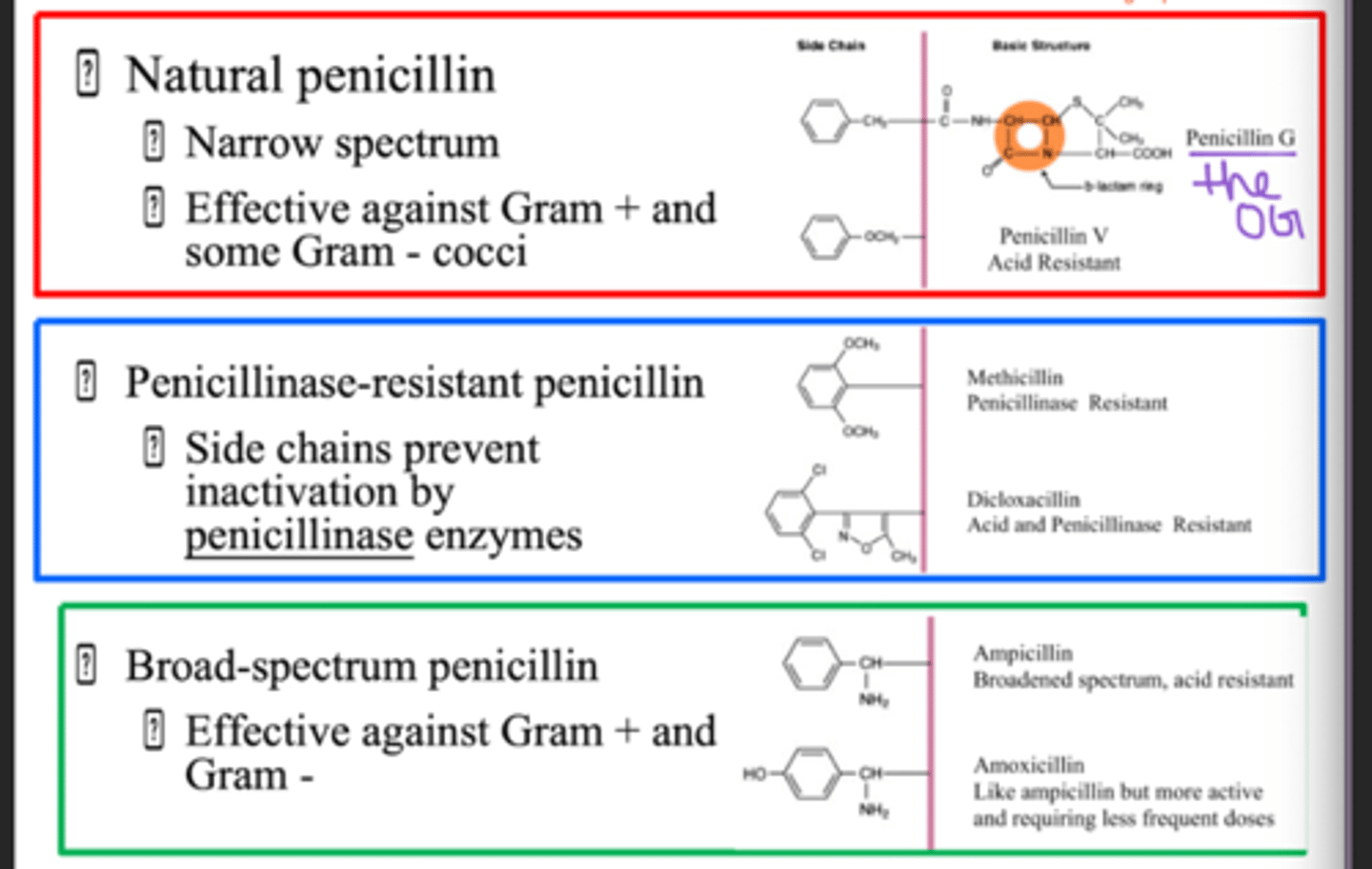
semisynthetic penicillin differ in
R groups
vancomycin - inhibition
blocks transglycosylases and transpeptidases by binding to D-Ala-D-Ala terminal
blocks transglycosylation!!
"last resort" for penicillin resistant Gram positive organisms
given intravenously due to poor absorption
- to big to diffuse through Gram negative cell wall
vancomycin - affect to humans
no toxicity
polymyxins inhibitor type
cell membrane
gramicidin inhibitor type
cell membrane
cell membrane inhibitors - availability
fewest available antibiotics due to similarity between bacteria and human cell membranes
cell membrane inhibitors - goal
interfere with cell membrane
gramicidin - inhibition
forms cyclic cation channel
allows ions leakage out of cell to disrupt membrane polarity
lyse
polymyxin (colistin) - inhibition
detergent like
destroyed cell membrane
lyse
only topical use
gramicidin and polymyxin - affect to human
toxicity
humans have similar membranes to bacteria
applied topically
- internal application would be harmful
quinolone inhibitor type
DNA replication
DNA synthesis & integrity
sulfonamide (sulfa drugs) inhibitor type
metabolic
DNA synthesis & integrity
DNA synthesis & integrity inhibitor - goal
inhibit DNA synthesis
quinolone (fluoroquinolones) - inhibition
block bacterial DNA gyrase and therefore prevents DNA replication
quinolone (fluoroquinolones) - affect to humans
no toxicity
humans have a different topoisomerase
DNA gyrase is unique to bacteria
sulfonamide - inhibition
mimicry via SFA that resembles PABA for folic acid synthesis
inhibits folic acid synthesis which is needed for DNA synthesis
sulfonamide - affect to humans
no toxicity
humans are able to get folic acid from dietary sources
humans do not synthesize folic acid in the body
rifamycin B (rifampin) inhibitor type
RNA polymerase
RNA polymerase inhibitors - goal
inhibit transcription
most active agent against growing bacteria
actinomycin D inhibitor type
RNA polymerase
RNA polymerase inhibitors are all
bactericidal
rifamycin B (rifampin) - inhibition
binds to beta subunit of RNA polymerase
does not allow RNA polymerase to bring in more nucleotides to elongate chain
prevents the elongation step of transcription
rifamycin B (rifampin) - affect to humans
no toxicity
humans have a different RNA polymerase
actinomycin D - affect to humans
toxic
we all share the same DNA
actinomycin D - inhibition
binds to DNA from any source
prevents the initiation step of transcription
aminoglycosides (streptomycin) inhibitor type
30S ribosome subunit
protein synthesis
tetracyclines inhibitor type
30S ribosome subunit
protein synthesis
macrolide (erythromycin) inhibitor type
50S ribosome subunit
protein synthesis
chloramphenicol inhibitor type
50S ribosome subunit
protein synthesis
clindamycin and metronidazole inhibitor type
50S ribosome subunit
protein synthesis
30S & 50S ribosome subunit/protein synthesis inhibitors - goal
inhibit translation of mRNA
affects 30S and 50S subunit
aminoglycosides (streptomycin) - inhibition
causes the translational misreading of mRNA
tetracyclines - inhibition
blocks the binding of charged tRNA to the A-site of the ribosome
is bacteriostatic
macrolide (erythromycin) - inhibition
inhibits translocation
chloramphenicol - inhibition
inhibits peptide transferase activity
clindamycin and metronidazole - inhibition
bind at the same ribosomal site as chloramphenicol
active in anaerobic environments
30S & 50S ribosome subunit/protein synthesis - affect to humans
can be toxic
due to human relation to our inherited mitochondria from ancient bacteria
tetracycline - affect to humans
toxicity
mitochondrial ribosomes of humans are susceptible
common cold caused by
Rhinovirus
rhinovirus and antibiotics
no antibiotic designed for bacteria can touch it
why are there fewer antiviral agents
antivirals target host cell machinery and have bad side effects
hard to get selective toxicity to kill viruses and nothing else
antivirals - goal
inhibit DNA synthesis
amantadine inhibitor type
antiviral, preventing virus uncoating/release
neuraminidase inhibitor type
antiviral, preventing virus uncoating/release
xofluza inhibitor type
antiviral, preventing virus uncoating/release
amantadine - inhibition
prevents entry of virus into host cell
- is intact before virus enters the cell
- finds virus before cell entry
- prevents viral uncoating
has developed resistance
neuraminidase - inhibition
prevents release of mature viruses
traps virus inside infected human cell
tamiflu was previously the most commonly prescribed for the flu
xofluza - inhibition
targets viral RNA polymerase
inhibits the activity of influenza cap-dependent endonuclease, which will prevent cap-snatching and stop viral replication
most effective against growing number of flu viruses
zidovudine - inhibition
mimicry via zidovudine (DNA with -N3 ) that resembles thymine (DNA with -OH) for normal DNA polymerase to use to bind nucleotides too
causes growing chain termination, inhibit new DNA synthesis
inhibits reverse transcriptase
most common anti-HIV drug
zidovudine inhibitor type
antiviral, prevents DNA synthesis
zidovudine - affect to humans
can be toxic but human DNA polymerase has proofreading ability
why are fungal infections more difficult to treat than bacterial infections
fungi are eukaryotes, and so selective toxicity issues arise
fungi have an efficient drug detoxification system that modifies and inactivates many drugs
fungal physiology is more similar to that of humans than bacterial physiology is
are unable to have selective toxicity
antifungal - affect to humans
toxic
both human and fungal cells are eukaryotes
antifungal superficial mycoses
treated topically
antifungal deep mycoses
treated systematically
why are there fewer antiviral drugs than antibacterial drugs
there are fewer viral specific drug targets in viruses
viruses are intracellular
ALL antibiotics listed on the lecture slides are bactericidal except
TETRACYLINES
erythromycin
macrolide
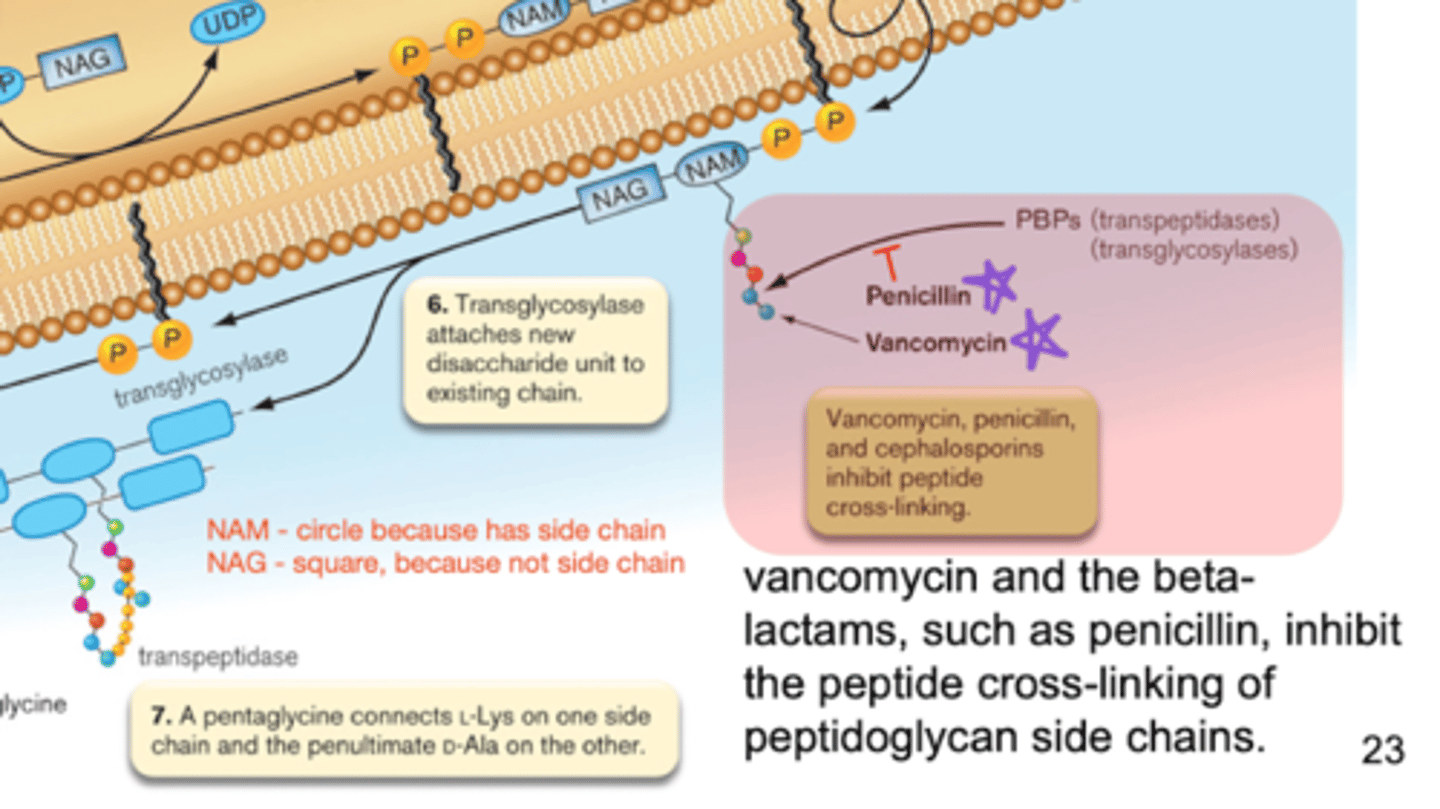
4 key steps of peptidoglycan synthesis of Gram positive bacteria
amino acids are added to NAM
D-Ala peptide attach
NAM pentapeptide transfer to bactoprenol on Gram positive cell membrane
NAG links to NAM
- NAM contains the side chain
NAM-NAG chain flips to be on the outside of the cell membrane
transglycosylase attaches new disaccharide units to the NAM-NAG chain
pentaglycine connects L-Lys one one side and penultimate D-Ala on the other
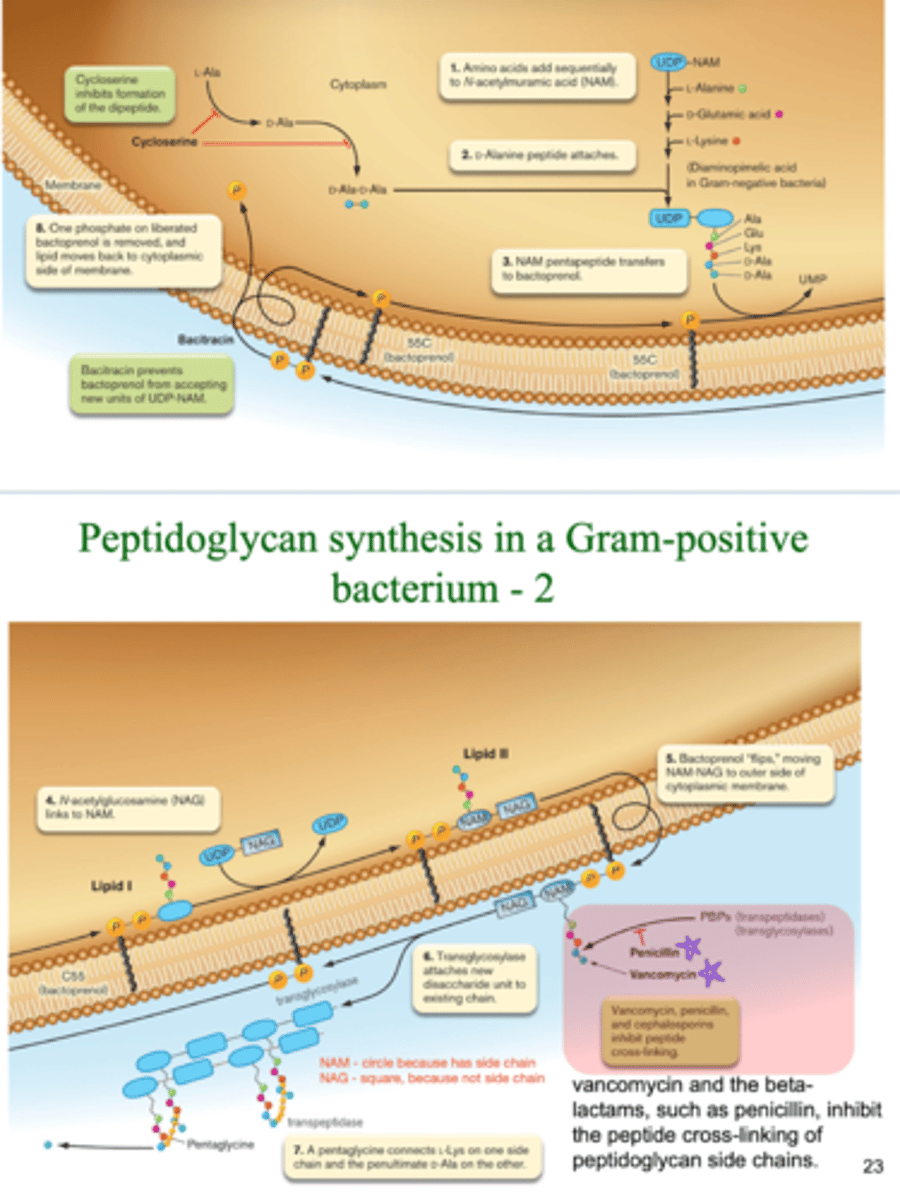
antibiotics that affect peptidoglycan synthesis in Gram positive bacteria
penicillin, cephalosporins, and vancomycin inhibit peptide cross-linking
interfere with PBPs
- pencillin mimicry prevents PBP function of peptide cross linking by binding to PBP active site