🌏 ANTH 111BA EXAM 1 Flashcards
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Introduction to anthropology and the aspects associated
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
1
New cards
What is Anthropology?
The study of humans and cultures around the globe and how they’ve evolved throughout time
2
New cards
How is anthropology different from other fields that study human beings?
* Considered a holistic science
* Studies non-Western societies from the past and present
* Offers cross-cultural perspectives by comparing the customs of one society with others
* Studies non-Western societies from the past and present
* Offers cross-cultural perspectives by comparing the customs of one society with others
3
New cards
Why is Franz Boas relevant to the field of anthropology?
He influenced anthropologists to approach the study as a holistic science and established the idea of cultural relativism
4
New cards
What is cultural relativism?
The idea that one society should not judge the customs of another society based on their own traditions and values; understand how that society functions and adapts through looking at their history, traditions, and values.
5
New cards
How does cultural relativism differ from ethnocentrism?
Cultural relativism = seeing all cultures as valuable and equal
Ethnocentrism = seeing your own culture as superior while others inferior or wrong; close-mindedness
Ethnocentrism = seeing your own culture as superior while others inferior or wrong; close-mindedness
6
New cards
Define culture
Customs, traditions, and/or values that are learned/passed down to future generations
7
New cards
Name the four fields of anthropology
1. Cultural = focuses on societies’ cultures
2. Archaeology = analyzes human behavior through material remains
3. Biological anthropology = observes human biological adaptations from past and present and development of human diversity
4. Linguistic anthropology = examines the multiple ways people communicate across the globe
8
New cards
Why are there four fields in anthropology?
They all coexist to answer life’s key questions of our origins and evolutionary changes that affect how we live today
9
New cards
Why is anthropology considered a science?
It relies on the scientific method to make accurate predictions and offer credible explanations
10
New cards
What is the scientific method?
Method of finding out how nature works through making observations, asking questions, and testing ideas
11
New cards
What are the steps of the scientific method?
1. Start with a question
2. Develop a hypothesis
3. Test hypothesis
4. Collect data from test
5. Devise a conclusion
6. Contribute to a larger society
12
New cards
What are the characteristics of scientific research?
* Hypothesis = a proposition that requires testing
* Association = a relationship between variables; if one variable changes, the other must change
* Theory = collective ideas that aid to explain something
* Law = a statement of an observation of something that occurs everytime if certain conditions are met
* Association = a relationship between variables; if one variable changes, the other must change
* Theory = collective ideas that aid to explain something
* Law = a statement of an observation of something that occurs everytime if certain conditions are met
13
New cards
THEORY VS LAW
Theory = a collection of ideas that were used to explain something
Law = a statement of fact; states how something works rather than why something works
Law = a statement of fact; states how something works rather than why something works
14
New cards
Is evolution a theory or a law? Why?
Evolution is a theory because it contains numerous ideas that explain why we do what we do
15
New cards
What is evolution?
Transformation of species over time
16
New cards
What does natural selection do?
Selects traits that are the most adaptive to an organism’s environment and passes down those traits to future generations
17
New cards
What is the goal of natural selection?
Strong fitness; success in surviving and reproduction to maintain variation
18
New cards
Define fitness
The ability to survive and reproduce in a given environment
19
New cards
Who established the idea of natural selection?
Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace
20
New cards
What results in natural selection?
Competition between individual vs individual (self vs self)
21
New cards
What does Lamarck’s inheritance of acquired characteristics state?
Physiological modifications produced by the organism get passed down to their offspring
22
New cards
Why is Lamarck’s idea of inheritance of acquired characteristics incorrect?
* Goes against basic principles of genetics and genetic variation
* Traits are based on genetics that you inherit from your parents
* Mutations are the only way a gene can change
* Traits are based on genetics that you inherit from your parents
* Mutations are the only way a gene can change
23
New cards
Is evolution directed? Or is there an end goal?
There is no end goal. Evolution will always happen as we continue to change to adapt to our environment
24
New cards
Catastrophism vs Uniformitarianism
Catastrophism was an idea composed by George Curvier that states that earth’s current geological landscape is the result of violent and sudden cataclysmic events. Uniformitarianism was a concept produced by Charles Lyell stating that long-term natural processes continue to form earth’s features.
25
New cards
Who is George Mendel and what did he do?
The “father” of genetics; used his pea plants to establish basic units of inheritance, genetics, and variation
26
New cards
Where are genes located?
On a segment of DNA
27
New cards
What does a gene do?
Code for a specific trait
28
New cards
What is a trait?
Observational characteristics on a person-eye color, hair color, height, etc.
29
New cards
Dominant vs Recessive
Dominant = genes that mask a hidden gene or present themselves in all generations
\
Recessive = a hidden gene
\
Recessive = a hidden gene
30
New cards
Gene vs allele
Gene = segment of DNA that codes for a trait
Allele = variant of the gene
\
Gene - eye color
Allele - variations of eye color (brown, blue, etc.)
Allele = variant of the gene
\
Gene - eye color
Allele - variations of eye color (brown, blue, etc.)
31
New cards
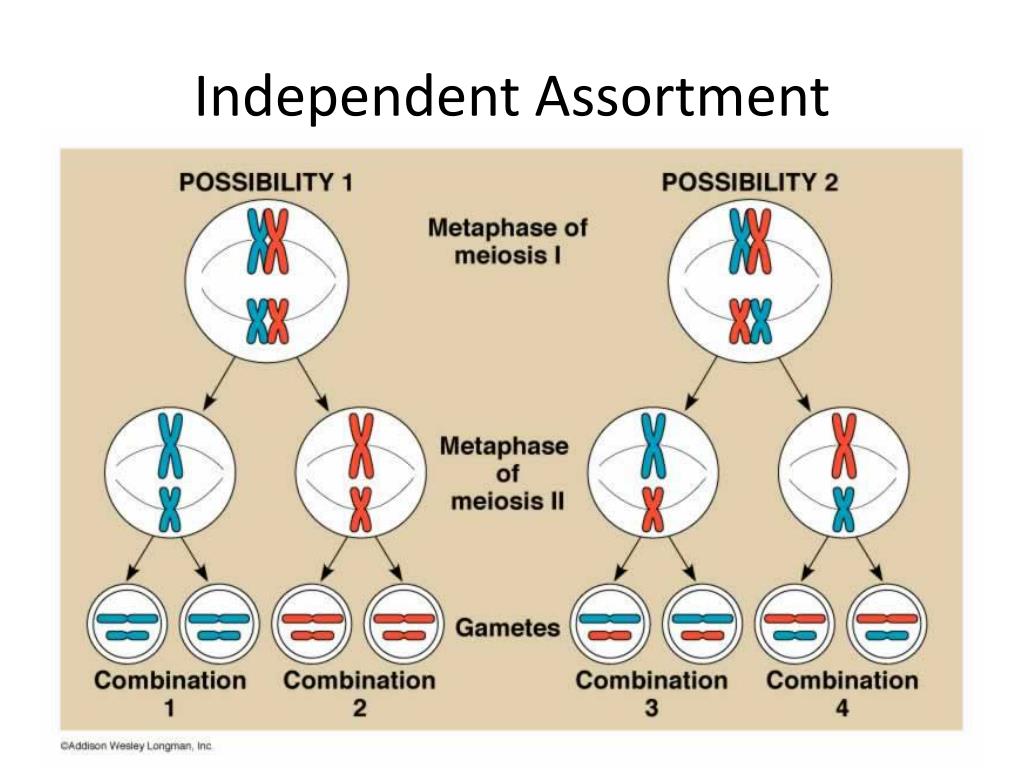
Principle of independent assortment
A concept produced by Mendel declaring that pairs of alleles assort themselves independently. The distribution of one pair of alleles has no influence over the other pair of alleles, it is randomized to create a 50/50 chance, so it generates more variation in gametes.
32
New cards
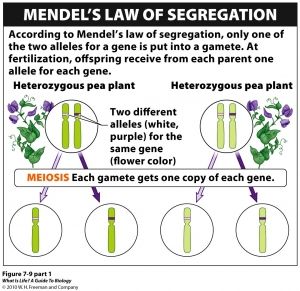
Principle of segregation
Another principle created by Mendel stating that each gamete will receive one allele for a specific gene from their parents that posses two alleles
33
New cards
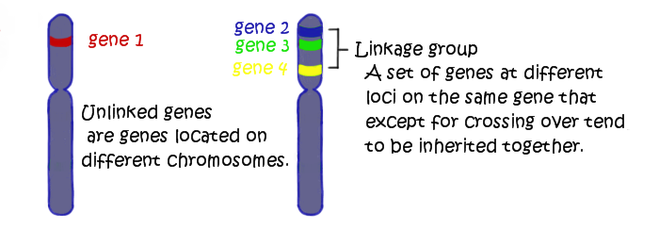
What is linkage?
A violation of independent assortment in which genes are on the same chromosome at different loci that tend to be inherited together, which decreases variation.
34
New cards
Genotype vs Phenotype
Genotype = genetic makeup
Phenotype = physical expression of genetic makeup
Phenotype = physical expression of genetic makeup
35
New cards
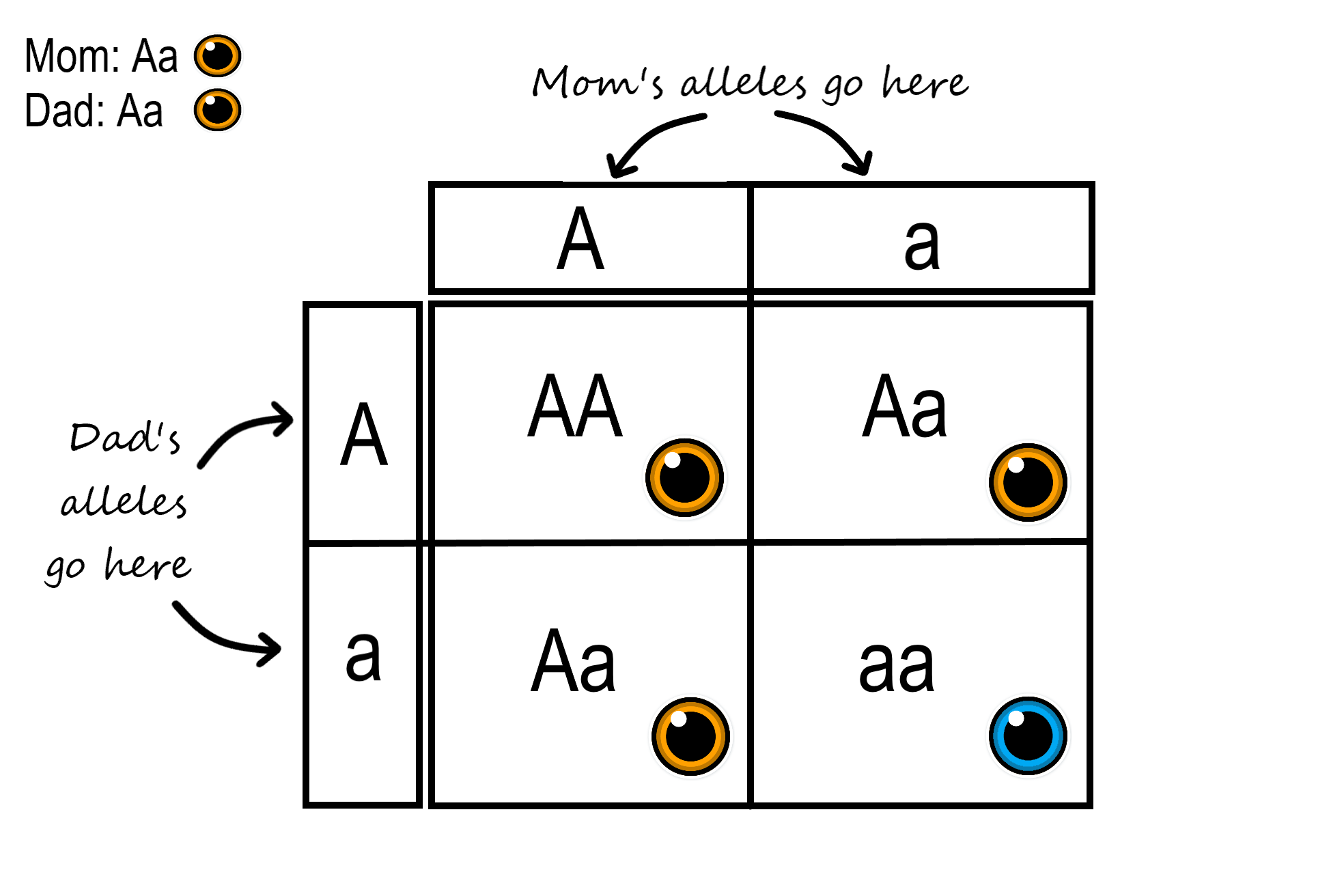
How would you use a Punnett square?
To calculate genotypes and possible phenotypes
36
New cards
What is the relationship between genetic variation and evolution?
Without variation, natural selection wouldn’t have any alleles to choose from to determine prime adaptiveness and survival, and without natural selection, there would be no evolution
37
New cards
Why is the Scientific Revolution important for biological anthropology?
The renounced discovery and exploration of science changed people’s perspectives on evolution. New navigation systems that stemmed from the revolution allowed scientists and explorers to observe new wildlife, experiment in biological diversity, and discover fossils from the past, which made them realize that things change and always haven’t been the same.
38
New cards
Why is blending inheritance considered wrong?
Genes don’t “blend”. There is a dominant and recessive gene, and the dominant gene is the only that shows up. Plus, it goes against natural selection since any gene that would’ve been beneficial would be blended in, therefore losing genetic variation.
39
New cards
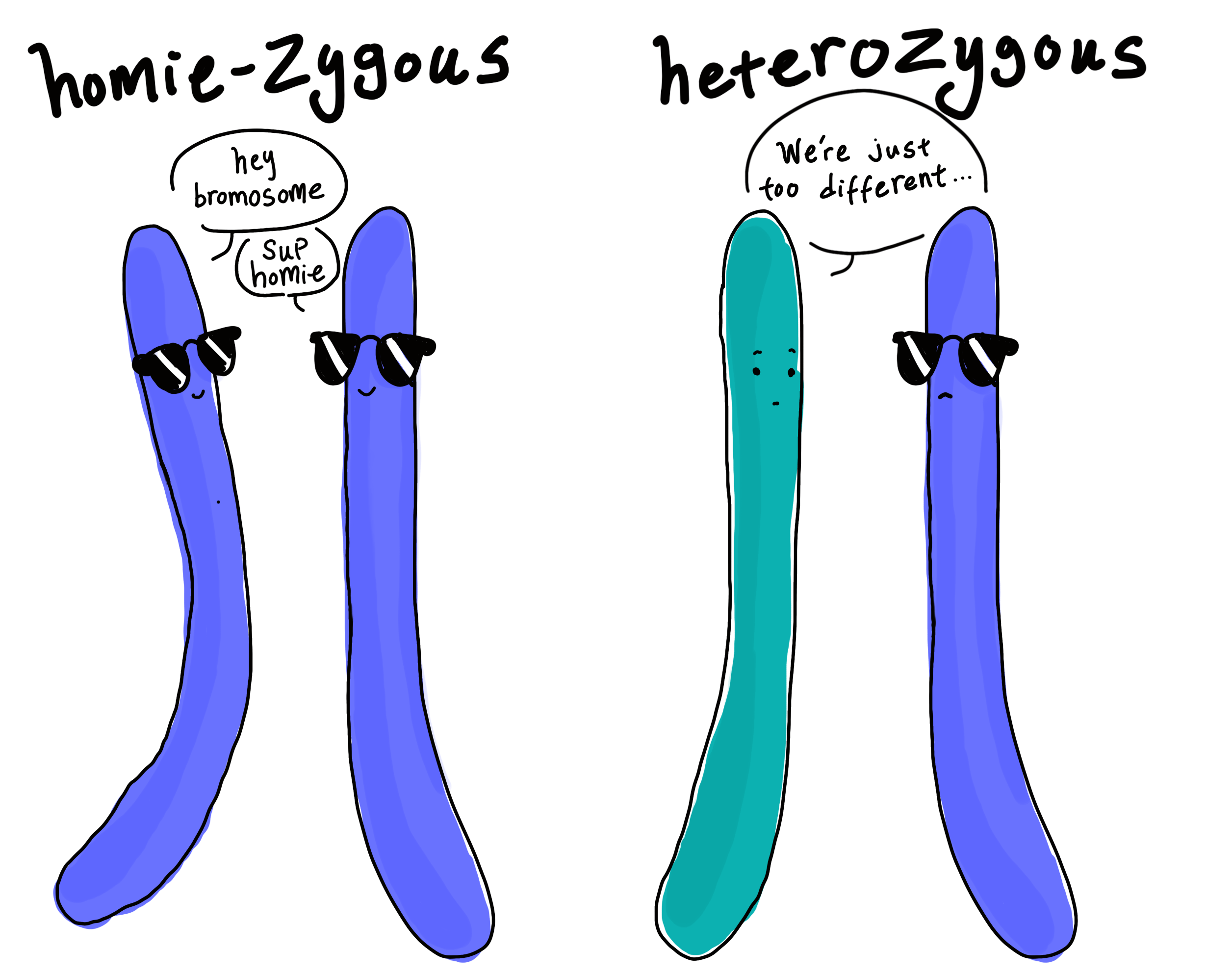
Homozygous vs Heterozygous
Homozygous = having the same allele (AA or aa)
Heterozygous = having different alleles (Aa)
Heterozygous = having different alleles (Aa)
40
New cards
What are eye color, hair color, and skin color considered to be?
Polygenic traits
41
New cards
What are polygenic traits?
2 or more genes influence one trait/phenotype, which produce variation
42
New cards
Define Mendelian traits
Traits that follow Mendel’s principles of genetic inheritance--determined by a single gene with two alleles that are either dominant or recessive
43
New cards
Blood types, sickle-cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, and Tay-Sachs disease would be called what?
Mendelian traits
44
New cards
What does the modern synthesis state?
States that evolution happens in two stages:
1. Production and redistribution of variations
2. Natural selection acts on variations, and such variations among individuals affect their ability to successfully reproduce
Combination of Darwinian evolution and Mendelian genetics
1. Production and redistribution of variations
2. Natural selection acts on variations, and such variations among individuals affect their ability to successfully reproduce
Combination of Darwinian evolution and Mendelian genetics
45
New cards
What is the definition of population genetics?
The study of genetics in a breeding population
46
New cards
What are the 3 parts of population genetics?
Genotypic frequency, phenotypic frequency, and allele frequency
47
New cards

The # of allele combinations/genotypes is what?
genotypic frequency
48
New cards

The # of traits presented is what?
phenotypic frequency
49
New cards

The # of alleles is called what?
allele frequency
50
New cards
Microevolution vs Macroevolution
Microevolution = small genetic changes that occur within a species in a short time frame that usually doesn’t cause speciation
Macroevolution = large-scale changes that can result in speciation
Macroevolution = large-scale changes that can result in speciation
51
New cards
What is hidden variation?
Inherited differences that hid in recessive alleles and only show up if there are two copies of the recessive gene
52
New cards
What are the aspects of population genetics that maintain and produce variation?
Mutation, natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow
53
New cards
How does mutation produce variation?
Changing the DNA sequence of one gene caused new genes to form
54
New cards
How does recombination/crossing over produce variation?
Intertwining of chromosomes allows for exchange of new combinations of alleles in offspring
55
New cards
How does natural selection produce variation?
It favors different alleles or combination of alleles that suit the organism’s situation
56
New cards
How does genetic drift maintain variation?
Random changes in allele frequencies create differences among populations that are isolated from each other
57
New cards
How does genetic drift reduce variation?
Usually happens in smaller populations, and allele combinations with lower frequency can either become fixed/permanent or be lost
58
New cards
How does gene flow produce variation?
The exchange of genes btw populations either introduces new alleles or changes the frequencies of existing alleles
59
New cards
What are some examples of mutations?
Blond hair, lactose tolerance, and color blindness
60
New cards
Is lactose tolerance a bad or good mutation?
Good mutation b/c digesting lactose gives us the ability to consume more calories needed for survival
61
New cards
What are the principles of genetic inheritance that maintain and product variation?
Principle of segregation, principle of independent assortment, and crossing over/recombination
62
New cards
Define nature vs nurture
Nature: your genetics
Nurture: your environment/situation that can impact your genetics
\
Is this how you are or did your environment play a role?
Nurture: your environment/situation that can impact your genetics
\
Is this how you are or did your environment play a role?
63
New cards
How can the environment impact genetics?
If you live in a place where there are no adequate food, shelter, or sources for you to grow, then your genetics will change based on the lack of nutrient and comfort from your surroundings
64
New cards
What is the process of natural selection
1. All species have variation and produce offspring faster than food supply increase
\
2. Limited food = competition among individuals
\
3. Individuals with beneficial traits have a better chance of surviving and successfully reproducing
\
4. Nature perceives traits as either beneficial or harmful, and the beneficial traits stay
\
5. Those traits are passed down to the offspring
\
6. Variations accumulate over time to the point where current generations may differ from ancestral ones
\
7. As populations respond to the environment, they may become distinct and descend from a common ancestor
\
8. Later generations or new species may be distinct from ancestral generations
65
New cards
The creation of a new species is classified as what?
Speciation
66
New cards
When does speciation occur?
During macroevolution
67
New cards
Biological vs Ecological species
biological = species cannot breed with each other due to varying genes; reproductive isolation
\
ecological = species that live in the same geographic region, but have distinct niches; can still breed but offspring becomes infertile
\
ecological = species that live in the same geographic region, but have distinct niches; can still breed but offspring becomes infertile

68
New cards
A role that a species plays in their local environment is a ______
niche
69
New cards
How did species form during allopatric speciation?
New species formed from geographically isolated populations; some barrier prevents gene flow between populations
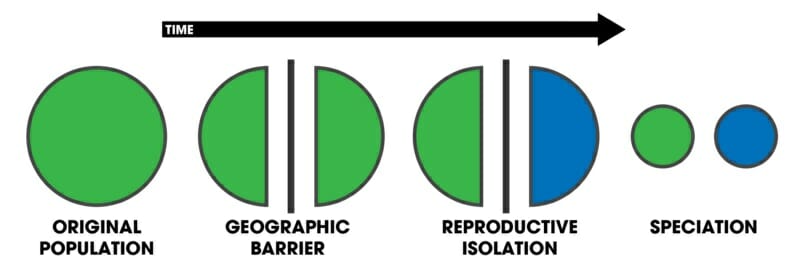
70
New cards
How did species form through parapatric speciation?
Two populations that have different roles share a common border called the “hybrid zone” that allow for some gene flow
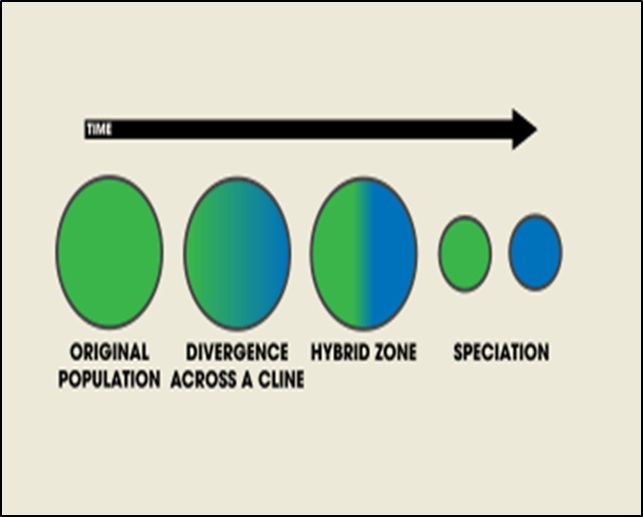
71
New cards
Define adaptive radiation
Organisms filling open niches
72
New cards
When might an animal need to perform adaptive radiation?
After an extinction of a former species, environmental changes, or migration to a new region
73
New cards
What does punctuated equilibrium have to do with speciation and evolution?
It can speed up evolution by disrupting long periods of stability with evolutionary leaps to help keep a species alive
74
New cards
How do we classify species?
Through phylogeny and systematics; name their genus and species
75
New cards
Define taxonomy
Science of classifying living things into groups based on their similarities; based on an idea that all living things share a common ancestor and evolved from that ancestor
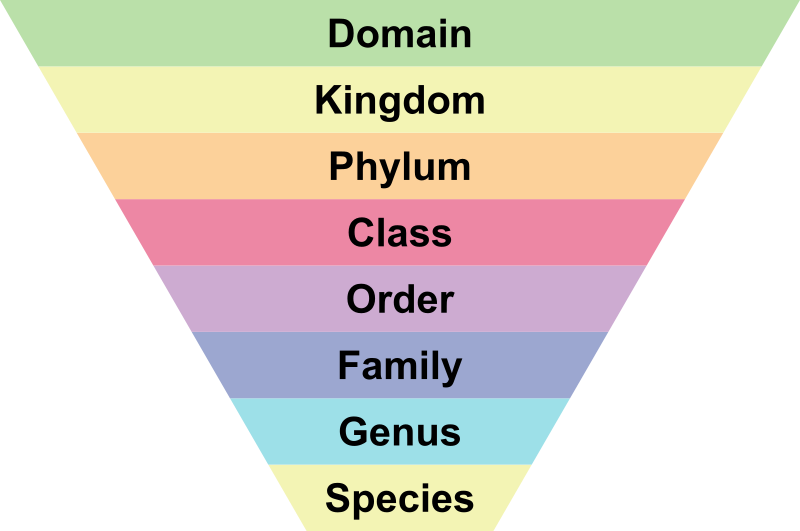
76
New cards
The “family tree” or history of evolutionary descent is called _____.
Phylogeny
77
New cards
What is the procedure for constructing phylogeny?
Systematics
78
New cards
Why are phylogenies important?
* Helps identify and classify organisms
* Determines why a species is involved in certain adaptations and not others
* Compares morphological traits and behaviors in different species
* Determines why a species is involved in certain adaptations and not others
* Compares morphological traits and behaviors in different species