Unit 1 - Chemistry of Life
1/142
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
covalent bond
the sharing of electrons between two atoms
ionic bond
the transfer of electrons (between a cation and an anion)
hydrogen bond
forms when a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is also attracted to another electronegative atom
van der waals interactions
attractions between molecules that are close together as a result of charges
what type of bonds form in water molecules?
polar covalent bonds
what type of bonds form between water molecules?
hydrogen bonds
why do water molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other?
because the polar covalent bonding in the water molecules causes the unequal sharing of electrons between the atoms of the molecule, allowing bonds to form between the slightly positive and slightly negative ends of water molecules
cohesion
water molecules sticking to other water molecules with hydrogen bonds
adhesion
the attraction between water and other substances or surfaces
capillary action
water moving against gravity by cohesion and adhesion working together
surface tension
how hard it is to break the surface of a liquid, water has high surface tension due to its hydrogen bonds (cohesion)
moderation of temperature by water
water absorbs heat from warmer air and releases stored heat to cooler air. water can absorb or release large amounts of heat with only a slight change in its own temperature
water’s high specific heat
water resists changing its temperature because of its high specific heat. the high specific heat of water minimizes temperature fluctuations to limits that permit life
evaporative cooling
as a liquid evaporates, its remaining surface cools. evaporative cooling in water helps stabilize temperatures in organisms and in bodies of water
density of ice
ice floats in water because hydrogen bonds in ice are more ordered, making ice less dense. ice creates a blanket on the surface of a body of water, insulating the temperature of the water for the survival of living organisms
solution
a liquid that is a completely homogeneous mixture of substances
solvent
does the dissolving
solute
is being dissolved
aqueous solution
water is the solvent
why is water the universal solvent of life?
due to its polarity
what happens when an ionic compound is dissolved in water?
each ion is surrounded by a sphere of water molecules called a hydration shell
hydrophilic
loves water
hydrophobic
hates water
hydrogen ion (H+)
the ion that loses one of its electrons and is transferred as a proton
hydroxide ion (OH-)
molecule that loses the proton
hydronium ion (H₃O+)
molecule with the extra proton
acid
a substance that increases the H+ of a solution
base
a substance that reduces the H+ of a solution
what happens to strong acids and bases in water?
they completely dissociate
buffers
substances that minimize changes in concentrations of H+ and OH- in a solution
what kinds of molecules is carbon able to form?
large, complex molecules
why can carbon form large, complex molecules?
because it has 4 available bonds
what does ‘organic’ in biology mean?
something contains carbon and hydrogen and comes from a living thing
vitalism
the belief that in a life force outside jurisdiction of physical and chemical laws
Redi
performed the maggot experiment, where he saw that maggots only formed when flies came in contact with the meat; disproving spontaneous generation.
Spallenzani
his experiment showed that it is not an inherent feature of matter that it can be destroyed by an hour of boiling. he realized that spontaneous generation could not happen without air.
Pasteur
boiled meat broth in a flask that prevented falling particles from coming in contact with the broth but allowed air to reach it. certain air particles caused the particles to spoil disproving spontaneous generation
when was vitalism disproved?
when chemists were able to synthesize organic molecules
Stanley Miller
demonstrated the abiotic synthesis of organic compounds
the Miller Urey experiment
Miller simulated Earth’s early atmosphere and oceans to test if organic molecules could be created abiogenically. organic molecules formed.
mechanism
the view that physical and chemical laws govern all natural phenomena
what does the electron configuration of carbon cause?
its compatibility with many different elements
what do carbon chains form?
the skeletons of most organic molecules
hydrocarbons
organic molecules consisting of only carbon and hydrogen
what happens when hydrocarbons undergo reactions?
they release large amounts of energy
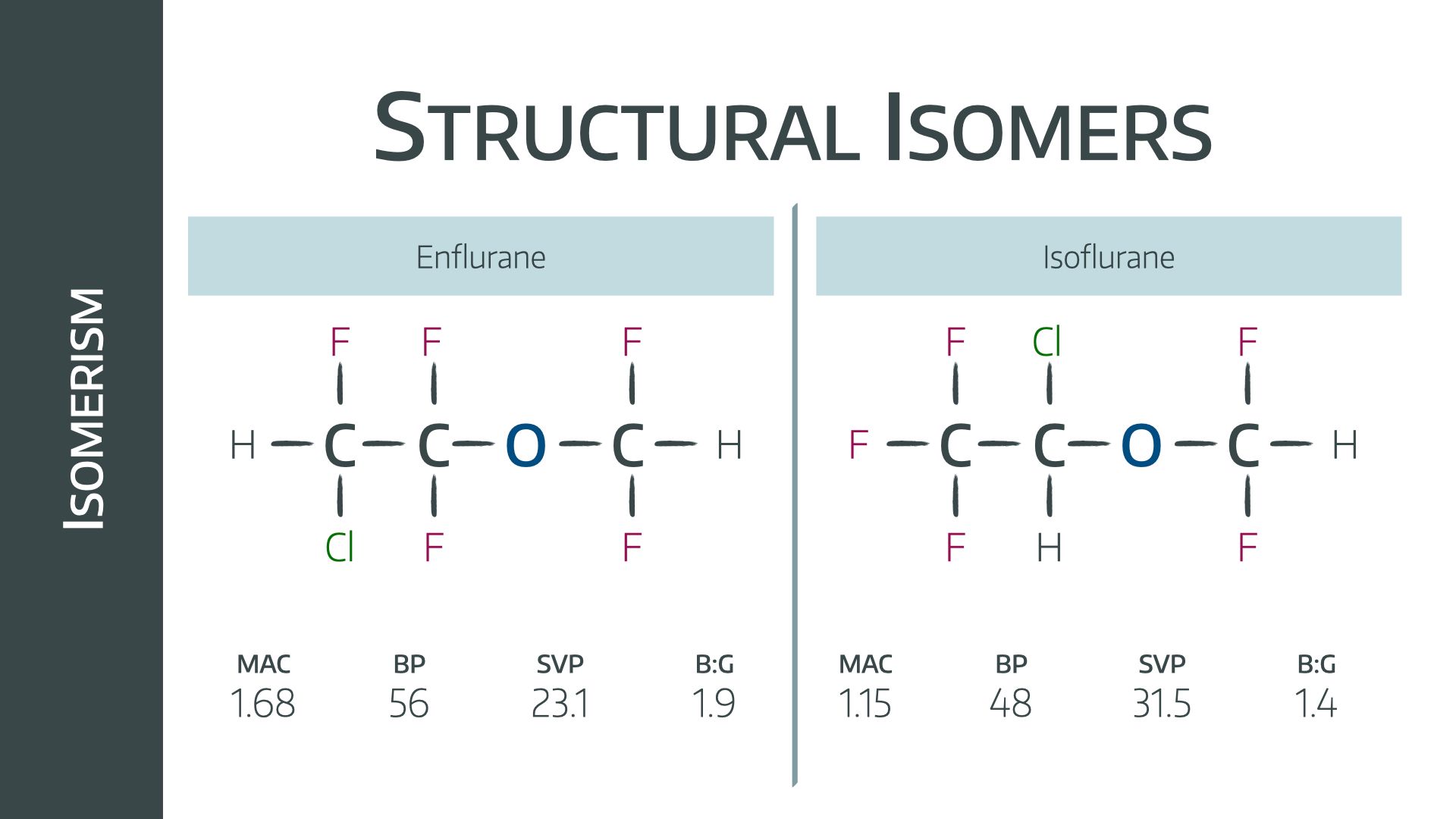
isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties
structural isomers
have different covalent arrangements of their atoms
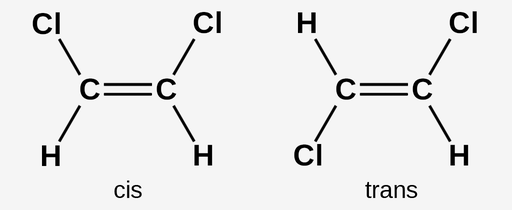
cis-trans isomers
have the same covalent bonds but differ in spatial arrangements
enantiomers
isomers that are mirror images of each other
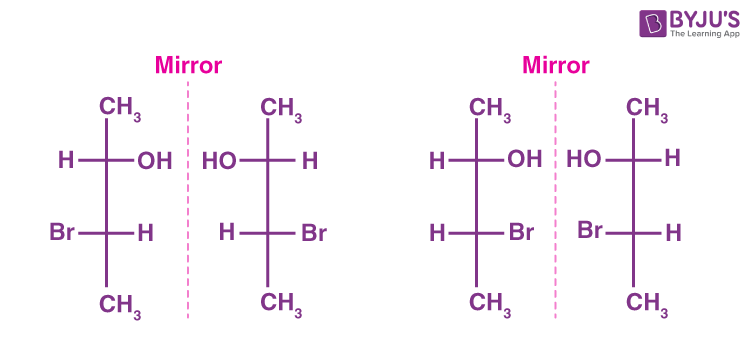
what industry are enantiomers important in?
the pharmaceutical industry
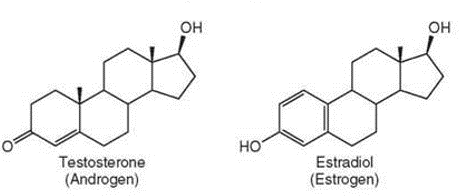
what is the form of the carbon skeletons' of estradiol and testosterone?
four fused carbon rings
how do testosterone and estradiol differ?
in the chemical groups attached to the rings of the carbon skeleton
functional groups
the components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions
what about the functional groups gives each molecule its unique properties?
the number and arrangement of the groups
what are the seven most important functional groups?
hydroxyl group
carbonyl group
carboxyl group
sulfhydryl group
phosphate group
methyl group
amino group
hydroxyl group (-OH) or (HO-)
polar due to electronegative oxygen
forms hydrogen bonds with water
compound name: alcohol

carbonyl group (>C=O)
ketoses - sugars with ketone groups
aldoses - sugars with aldehydes
compound name: ketone or aldehyde
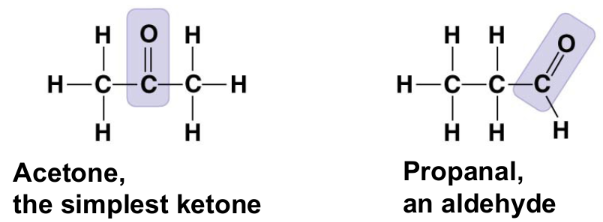
carboxyl group (-COOH)
acts as an acid
compound name: carboxylic acid or organic acid
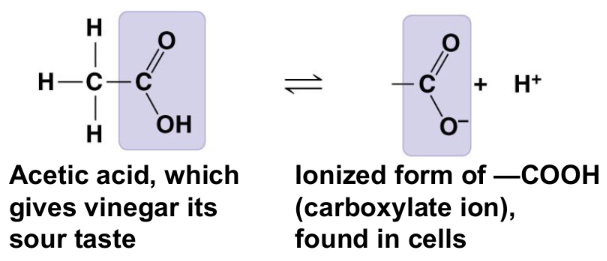
amino group (-NH₂)
acts as a base
compound name: amine
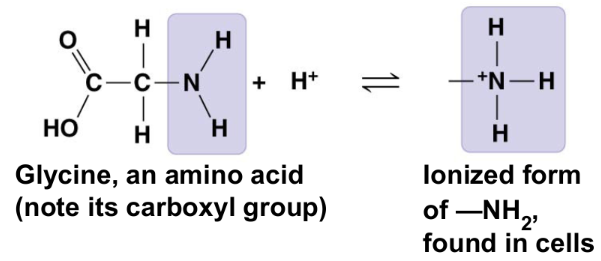
sulfhydryl group (-SH) or (HS-)
two (-SH) groups can react to form a disulfide bridge that helps stabilize proteins
compound name: thiol
phosphate group (-OPO₃⁻²)
contributes negative charge
when attached, confers on a molecule the ability to react with water, releasing energy
compound name: organic phosphate
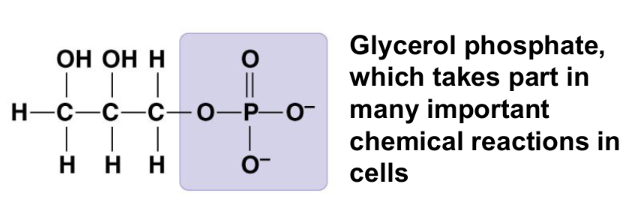
methyl group (-CH₃)
affects the expression of genes
affects the shape and function of sex hormones
compound name: methylated compound
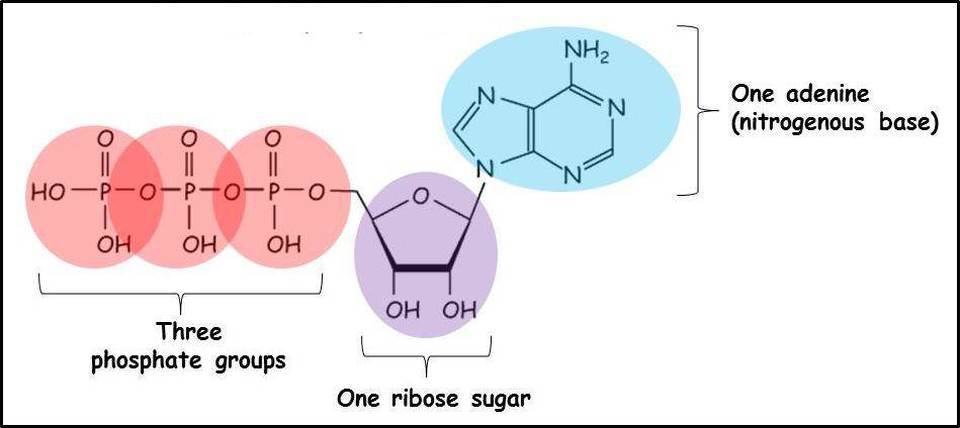
adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
an important organic phosphate
consists of an organic molecule (adenosine) attached to a string of three phosphate groups and one adenine
stores the potential to react with water, a reaction that releases energy to be used by the cell
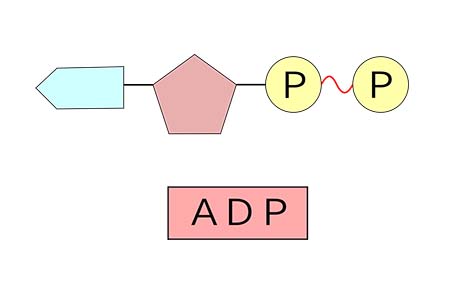
adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
consists of an organic molecule (adenosine) attached to a string of two phosphate groups and one adenine
what are the four biological macromolecules?
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
macromolecule
large and complex molecules
monomer
repeating units that serve as building blocks
polymer
a long molecule consisting of many similar monomers
enzymes
specialized molecules that speed up chemical reactions
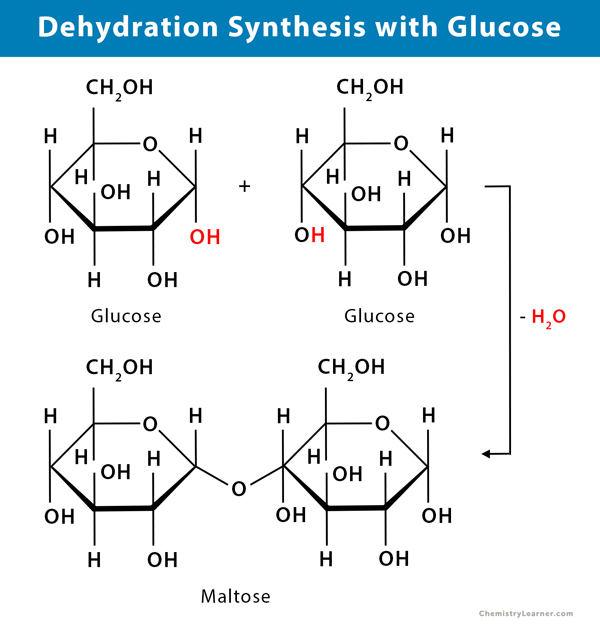
dehydration synthesis
occurs when two monomers bond together through the loss of water
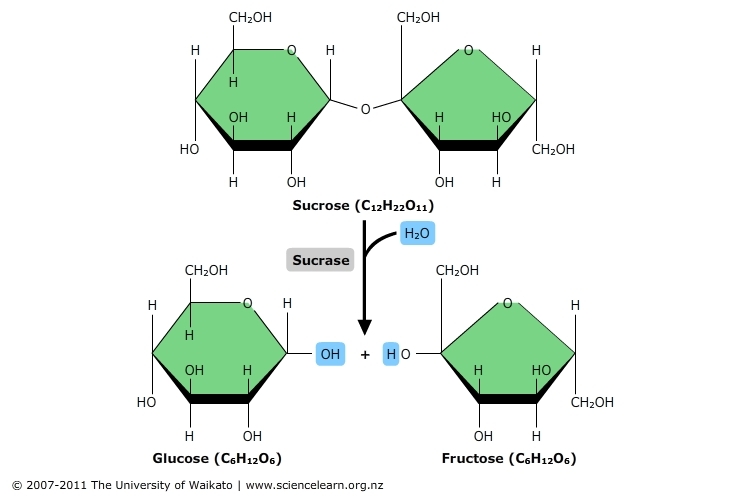
hydrolysis
occurs when a polymer breaks apart into monomers through the addition of water
carbohydrates
include sugars and the polymers of sugars
monosaccharides
simplest carbohydrates
polysaccharides
polymers composed of many sugar building blocks
what is the ratio of the molecular formulas for monosaccharides?
CH₂O (1:2:1)
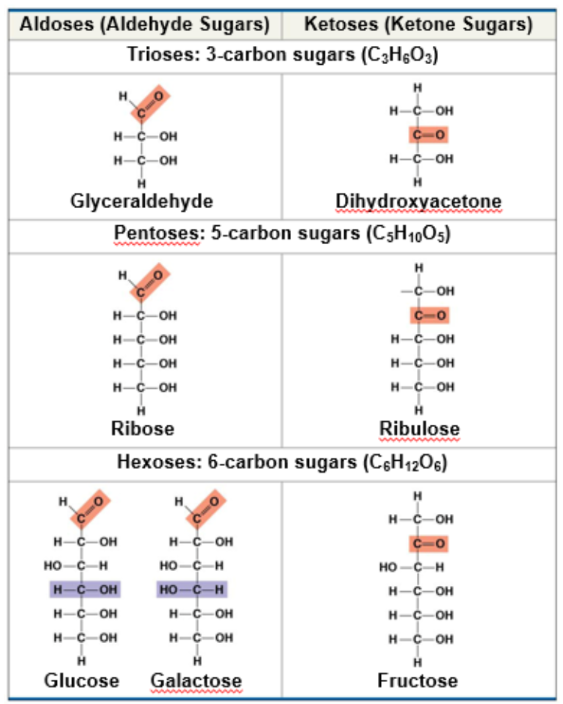
what are monosaccharides classified by?
the location of the carbonyl group as aldose or ketose
the number of carbons in the carbon skeleton
what is the function of carbohydrates?
to serve as major fuel for cells as raw material for building molecules
disaccharide
formed when a dehydration synthesis reaction joins two monosaccharides
what is kind of covalent bond joins a carbohydrate with another molecule?
a glycosidic bond
starch
a storage polysaccharide of plants, consist entirely of glucose monomers
plants store extra starch as granules in chloroplasts and other plastids
cellulose
a structural polysaccharide
a major component of the tough cell wall of plant cells
what is the difference of glycosidic linkages between starch and cellulose?
starch has alpha rings (glucose) and is largely helical
cellulose has beta rings (glucose) and is straight and unhinged
enzymes that digest starch by hydrolyzing alpha linkages cannot hydrolyze beta linkages in cellulose
chitin
a structural polysaccharide found in the exoskeleton of arthropods
provides structural support for the cell walls of many fungi
do lipids include true polymers?
no because they are not composed of repeating units of monomers
what is the unifying feature of lipids?
they do not mix well with water or they do not mix at all because they consist of mostly hydrocarbons
what are the three most important lipids?
fats, phospholipids, and steroids
what are fats constructed from?
glycerol and fatty acids
glycerol
a three carbon alcohol with a hydroxyl group attached to each carbon
fatty acid
consists of a carboxyl group attached to a long carbon skeleton
why do fats separate from water?
water molecules hydrogen bond to each other and exclude the fats
ester linkage
the bond between the hydrocarbon and the carboxylic ends of a fat
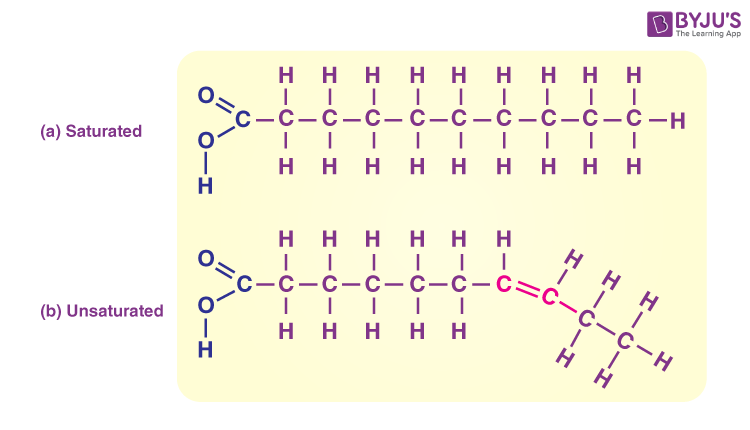
saturated fatty acids
have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible and NO double bonds
solid at room temp
most animal fats
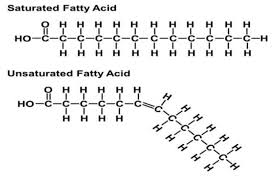
unsaturated fatty acids
have one or more double bonds
liquid at room temp
usually plants and fish fats
hydrogenation
the process of converting unsaturated fats to saturated fats by adding hydrogen
what does hydrogenating vegetable oils create?
unsaturated fats with trans double bonds (trans fats)
what is the major function of fats?
to store energy to use when its needed
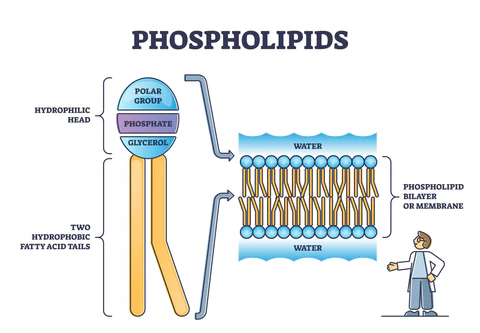
phospholipid
composed of two fatty acids and a phosphate group attached to glycerol
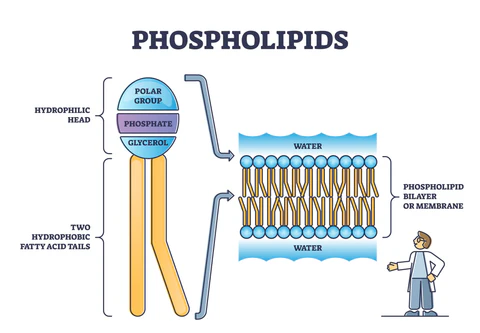
what happens when phospholipids are added to water?
they self-assemble into double-layered structures called bilayers
this allows them to form the cell membrane
steroids
lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings
cholesterol
a type of steroid, is a component in animal cell membranes and a precursor from which other steroids are synthesized