Pulmonary - Physical Examination of Respiratory System
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
how do you test the frontal sinuses?
by pressing above & Ethmoid sinuses by pressing below eyebrows
how do you test the maxillary sinuses?
Apply gentle pressure over the cheeks
what will a patient complain of in sinusitis?
facial pain and nasal congestion
what should you always rule out in the presence of UNILATERAL maxillary sinusitis?
dental cause
how to generally palpate the sinuses
directly, gently press & percuss on the sinuses to elicit tenderness and/or swelling
inspecting for acute sinusitis:
• Have the patient flex the neck & bend the head towards the chest
• When head becomes dependent, significant pain is experienced if sinusitis exists
when tapping on the teeth around the maxillary sinus, what are you checking for?
maxillary sinus inflammation
- if discomfort occurs, the sinus is inflamed
Describe what happens during a trans-illumination test.
• Dim the room lights & place a lighted flashlight on the face just below the eye
• Look for light glowing through the mucosa of the upper mouth
• Maxillary sinus are fluid filled with inflammation & do not allow this trans-illumination
describe what you are looking for during the inspection aspect off assessment of the respiratory system.
Posture, shape, movement & dimensions of the chest, flared nostrils, use of accessory muscles, skin & nail color, rate, rhythm and depth of respiration & ability to speak
describe what you are looking for during the palpation aspect off assessment of the respiratory system.
Respiratory excursions, masses and tenderness
describe what you are looking for during the percussion aspect off assessment of the respiratory system.
Resonant, dull, hyper-resonant sounds
describe what you are looking for during the auscultation aspect off assessment of the respiratory system.
Breath sounds, voice sounds, rales/crackles, rhonchi, wheezes
What 7 pieces of information should you gather from watching a patient?
• General comfort and breathing pattern of the patient
• Does the patient appear distressed, diaphoretic/sweating, or has labored breathing?
• Is there nasal flaring (nostrils widen) while breathing?
• Are the breaths regular and deep?
• Are accessory muscles (e.g. Scalene, SCMs) being used? Signifies respiratory difficulty
• Is the patient breathing through pursed lips?
• What is the color of the patient, especially around the lips and nail beds?
you will often see pursed lips in what pulmonary abnormality?
emphysema
nostrils flaring when breathing indicates what?
respiratory distress
how will patients with severe pulmonary dysfunction often sit?
up-right
in cases of real respiratory distress, how will patients position themselves?
they will lean forward, resting their hands on their knees
- tripod position
what effect does very high RR and/or labored breathing have on a patient's ability to speak? what should be done as an assessment?
patient is unable to speak in full sentences and you should not how many words the patient can speak
- the fewer words per breath, the worse the problem
what conclusion can be drawn from having a patient with RR and or labored breathing speak?
the fewer words per breath, the worse the problem
what are some audible noises that are associated with breathing?
Occasionally wheezing or gurgling from secretions in large airways
normally, the diaphragm pushes intra-abdominal contents ______ and the abdominal wall _______.
down (contents) and outward (wall)
in cases of severe diaphragm flattening, in what direction will the abdominal wall move?
the abdominal wall may move inward during inspiration
severe diaphragm flattening is seen in...
emphysema or paralysis
what is paradoxical breathing?
the abdominal wall moving inward during inspiration
What is pectus excavatum?
Congenital posterior displacement of lower aspect of sternum
- gives the chest a somewhat "hollowed-out" appearance
normally, what is the Anterior-Posterior Diameter?
shoulder-to-shoulder dimensions are always greater than the back-to-front dimensions
what do you expect to see in barrel shaped chest?
back-to-front chest dimensions are greater than shoulder-to-shoulder dimensions
what is barrel-shaped chest caused by?
chronic air trapping with emphysema and advanced COPD
what will the x-ray of someone with barrel chest show?
increased anterior-posterior diameter
what happens at the sternal angle?
- the second rib joins the sternum
- tracheal bifurcation
- bronchial breach sounds
are bronchial breath sounds normal at the sternal angle?
YES
lung collapse will do what to the trachea
pull toward the affected side
pleural effusion or pneumothorax will do what to the trachea?
push trachea away from the affected side
what do you expect to happen normally when palpating for chest excursions?
hands should lift symmetrically outward when patient take a deep breath
when will you have asymmetric lung exapnsion?
when air/fluid fills the pleural space
normally, when palpating for chest excursion, hands should lift symmetrically outward when the patient takes a deep breath. Describe abnormal findings during palpation for chest excursion
the hand on the affected side will move outward to a lesser degree
a collapsed apex in an adult is often due to what?
Tuberculosis (TB)
how to palpate the apex of the lungs
• Place your palms on the patient's shoulders
• Press down firmly & ask the patient to breath deeply
• Note if the apex of both lungs rise up equally
a Normal lung transmits what sensation to the chest wall?
a palpable vibration
what is fremitus?
palpable vibration on the chest wall when talking
how is fremitus detected?
by placing the ulnar aspects of both hands firmly against the chest on either-side of the spine while patient says the words “99"
- the bony aspects of the hands are particularly sensitive for detecting these vibrations
you should repeat the movement to detect fremitus until what point?
until the entire posterior thorax is covered
when does consolidation occur?
when normally air filled lung parenchyma becomes engorged with fluid or tissue, most commonly due to pneumonia
as a result of consolidation, what becomes more pronounced/increased?
fremitus
pleural effusion can collect in the pleural space, affecting the lungs how
displaces them upwards
as a result of pleural effusion, what becomes less pronounced/decreased?
fremitus
when is fremitus more pronounced/increased?
consolidation
when is fremitus less pronounced/decreased?
pleural effusion
how do you do percussion?
Allow your hand to swing freely at the wrist, hammering your finger onto the target
percussion over normal air-filled lung parenchyma produces what sound?
resonant note
Percussion over a fluid or tissue filled cavity generates what sound?
dull note
effusion or pneumonia will generate what tone?
a dull tone
emphysema or acute pneumothorax causes what?
air trapping and hyper-resonant notes
emphysema or acute pneumothorax will generate what sound?
hyper-resonant notes
instructions to patient for construction:
• Patient crosses hands in front of their chest grasping opposite shoulder with each hand
• This helps to pull the scapulae laterally & away from the percussion field
In what position is auscultation usually done?
when the patient is sitting upright
what is examined first in auscultation?
the posterior fields toward the top of the patient's back
• Listen over one spot & then move to the same position on the opposite side & repeat
• This again makes use of one lung as a source of comparison for the other
what should be done when auscultation of the posterior field is completed?
move around to the front and listen to the anterior fields in the same fashion
adventitious sounds are abnormal sounds heard over the lungs and airways and include:
• Rales/Crackles
• Wheezes
• Rhonchi
• Stridor
what are the normal breath sounds?
• Vesicular
• Bronchial
• Broncho-Vesicular
• Tubular
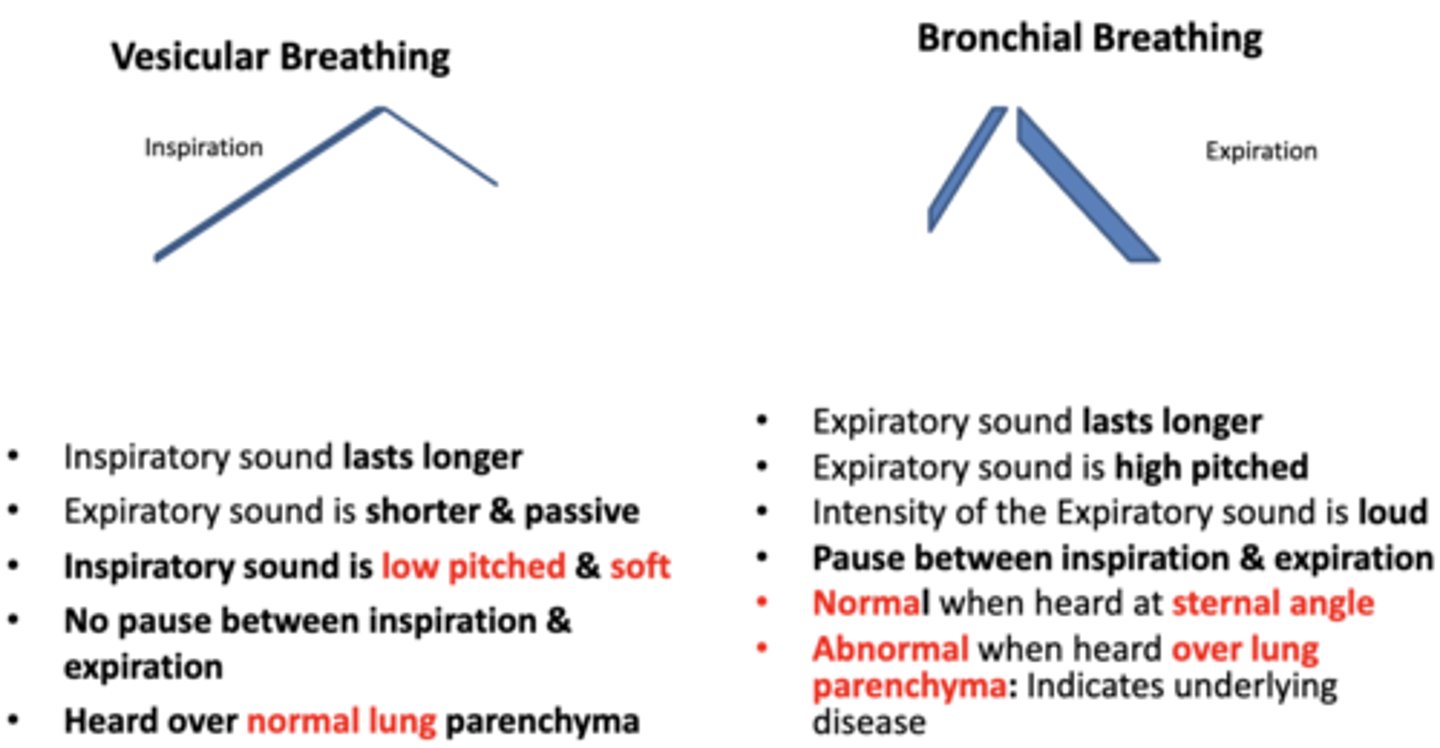
Vesicular sounds produce what type of sound?
a soft inspiratory sound as air rushes into the lungs
do you expect to normally hear a lot of noise on expiration?
NO
• Very little noise occurs on expiration: NORMAL pattern over lung parenchyma
describe normal bronchial breath sounds
Bronchial sounds are tubular, hollow, louder & high-pitched than Vesicular sounds
- There is a pause between inspiration and expiration
what sounds are normal when heard over lung parenchyma? what sounds are abnormal?
normal when heard over lung parenchyma: vesicular breath sounds
abnormal when heard over lung parenchyma:
bronchial breath sounds
are bronchial breath sounds normal when heard over lung parenchyma?
NO
- normal bronchial breath sounds are heard over the large airways
bronchial breath sounds are normally heard where?
over the large airways
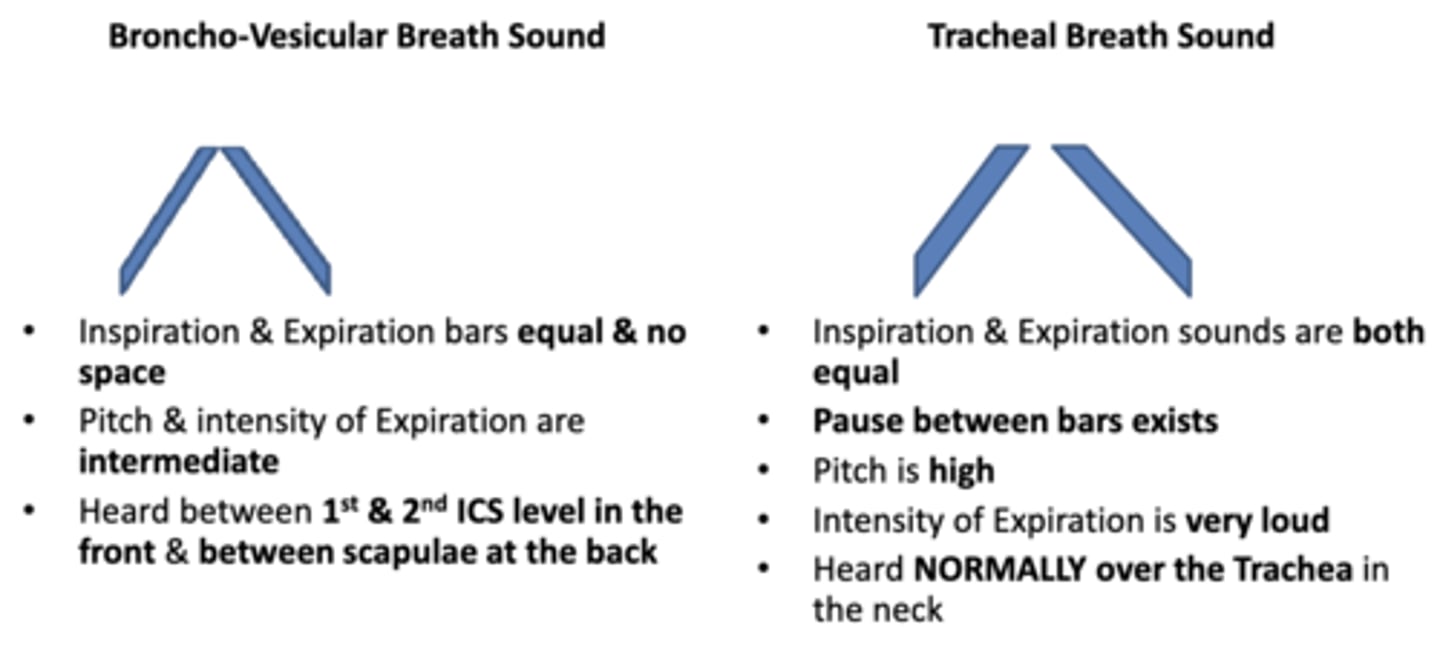
describe normal tracheal breath sounds
bronchial breath sounds over the trachea
compare tracheal breath sounds to other breath sounds
they are higher pitch and are louder
- inspiration and expiration bars are equal
is there a pause between inspiration and expiration bars in tracheal breath sounds?
YES
compared to vesicular breath sounds, describe the sound of broncho-vesicular sounds
broncho-vesicular sounds they have an intermediate intensity and pitch compared to vesicular breath sounds
where are bronchovesicular sounds normally heard?
in the 1st and 2nd intercostals
compare:
- inspiratory sound duration
- expiratory sound duration
- inspiration sound quality
- presence of pauses between inspiration and expiration
- location the sound is heard
between vesicular and bronchial breathing
compare:
- inspiration and expiration bars
- pitch and intensity of expiration
- location of sound
between broncho-vesicular breath sounds and tracheal breath sounds
rales/crackles are scratchy sounds caused by...
fluid accumulation in alveolar and interstitial spaces
what is the most common cause of rales/crackles?
pulmonary edema
rales/crackles are most common in what population?
in the elderly and results in systemic findings
where do rales/crackles first occur? how do they progress?
Occurs first in the lower lobes & then extends towards apices as disease progresses
rales/crackles is similar in sound to what?
rubbing strands of hair together close to your ear
consolidated lung transfers what?
central sounds directly to the edges
describe the sounds produced by pneumonia
crackles restricted to a specific region of the lung
what is egophony? what does this indicate?
"Aaaa" is heard during auscultation as the patient says "eeee"
- indicates consolidation
wheezes are...
high-pitched whistling sounds produced by air going through narrowed airways
wheezes are most often heard when?
when the patient breathes out
causes of wheezing:
bronchoconstriction, secretions and or mucosal edema
are wheezes restricted to certain parts of the lung?
no they can occur in any lobe of the lung
what is expected of the expiratory phase with severe bronchoconstriction?
expiratory phase becomes noticeably prolonged
finish the sentence:
the greater the obstruction,...
the longer the expiration time relative to the inspiration time
when does focal wheezing occur?
airway narrowing that is restricted to a single anatomic area
what is the cause of focal wheezing?
an obstructing tumor or bronchoconstriction induced by pneumonia
what is stridor?
wheezing ONLY heard on inspiration
what is stridor associated with?
mechanical obstruction at the level of the trachea/upper airway
is stridor emergent?
YES
ronchi are also known as...
low-pitched wheezes
rhonchi cause what type of sound?
a gurgling-type noise similar to sucking on the last sips through a straw
rhonchi is often caused by...
secretions in larger airways or from obstruction
- Pneumonia, chronic bronchitis, cystic fibrosis or COPD
to patients with severe, stable emphysema produce sound
produce very little sound
These patients have significant lung destruction and air trapping
emphysema patients
patients with emphysema have significant lung destruction and air trapping, what does this mean for their tidal volume?
means they are breathing at small tidal volume and generate almost no noise
usually, there are little to no sounds heard with emphysema, when you hear wheezing in a patient with emphysema, what does this mean?
there is a superimposed acute inflammatory process
dullness on percussion can be from...
consolidation or effusion