Dysphagia FINAL EXAM
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
#1
Material does not enter airway
#2
Material enters the airway, remains above the vocal folds, and is ejected from the airway
#3
Material enters the airway, remains above the vocal folds and is not ejected from the airway
#4
Material enters the airway, contacts the vocal folds, and is ejected from the airway
#5
Material enters the airway, contacts the vocal folds, and is not ejected from the airway
#6
Material enters the airway, passes below the vocal folds, and is ejected into the larynx or out of the airway
#7
Material enters the airway, passes below the vocal folds, and is not ejected from the trachea despite effort
#8
Material enters the airway, passes below the vocal folds, and no effort is made to eject
Do we typically use oral motor exercises with someone that has a progressive disease like Myasthenia Gravis?
no, instead we use things like puree consistencies and smaller meals throughout the day
Identify trach tube picture and what would you differently as the SLP if you now a patient has a trach?
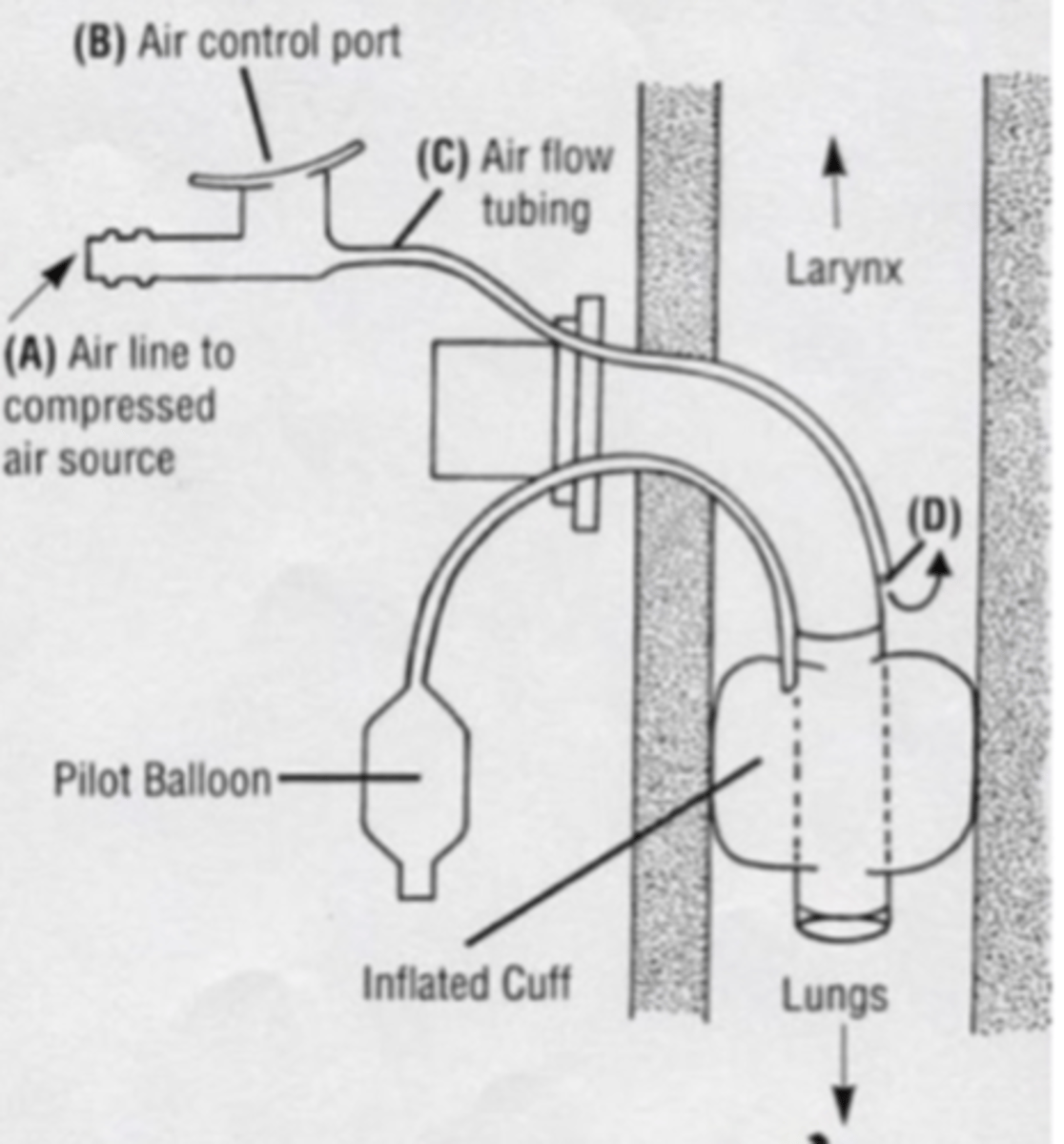
What are the 6 suprahyoid muscles?
1. digastric
2. stylohyoid
3. mylohyoid
4. geniohyoid
5. hyoglossus
6. genioglossus
What are the 4 infra hyoid muscles?
1. sternohyoid
2. sternothyroid
3. thyrohyoid
4. omohyoid
IDDSI level 0:
thin liquids (water, ice cream)
IDDSI level 1:
slightly thick liquids (thicker than water)
IDDSI level 2:
mildly thick liquids (flows off a spoon)
IDDSI level 3:
liquidized or moderately thick (sauces, gravies, fruit syrup)
IDDSI level 4:
pureed (pureed meat, mashed potatoes, baby food)
IDDSI level 5:
minced and moist (minced soft veggies, minced meat)
IDDSI level 6:
soft and bite sized (fruit, cooked veggies, rice, bananas)
IDDSI level 7:
regular, easy to chew (veggie sticks, cookies, crackers)
What are the 2 types of laryngectomy's?
1. supraglottic laryngectomy
2. total laryngectomy
Which type of laryngectomy is performed due to cancer of epiglottis, vallecula, posterior 1/3 of tongue, aryepiglottic folds, false vocal folds and upper pyriform sinuses? During these procedures one of the arytenoid cartilages must be removed, and the vocal folds are sutured to the cricoid cartilage?
supraglottic laryngectomy
Which type of laryngectomy consists of removal of the vocal folds, hyoid bone, thyroid, cricoid, epiglottis and several tracheal rings and separation of airway from mouth, nose and esophagus?
total laryngectomy
What is a mixed consistency?
contains both a solid and a liquid
What are the principles of neuroplasticity?
1. use it or lose it
2. use it and improve it
3. specificity - tailoring the activity or exercise to produce specific result
4. repetition matters
5. intensity matters
6. time matters
7. salience matters - must be relevant to the patient
8. age matters
9. generalization
10. interference - teach the patient to unlearn compensatory behaviors
What consistencies are used during a bedside evaluation?
begin with ice chips, small sips of water, puree, mechanical soft and regular consistencies
Who do we not use advanced solids with?
edentulous patients (no teeth)
If the patient does not have a gag reflex, what does this mean?
they have no sensation
What does damage to the trigeminal nerve result in?
- flaccid paralysis to one side of the jaw (deviates to the weak side)
- mastication dysfunction
- sensory problems w/ the face, lips, teeth, and tongue
What is the average amount of breaths per minute?
12-20
What does more than 12-20 breaths per minute indicate?
- respiratory difficulties
- inadequate abdominal and thoracic movement (poor breath support)
- results in a breathy vocal quality
What is a standardized scale used to describe a patient's performance on the MBS with the various consistencies?
Rosenbek Penetration/Aspiration Scale
What are the 8 different levels of the Rosenbek Penetration/Aspiration Scale?
1. material does not enter the airway
2. material enters airway, remains above the VF, and is ejected from the airway
3. enters, remains above, not ejected
4. enters, contacts folds, ejected
5. enters, contacts folds, not ejected
6. enters, passes below vocal folds, ejected into larynx or out of airway
7. enters, passes below, not ejected with effort
8. enters, passes below, no effort to eject
If you had a patient with altered mental status, but they were awake/alert) and you were ordered to do the bedside assessment what would you do?
- at least attempt the evaluation and see if they can mimic you
- could start po trials if you felt it was safe
If you ask a patient to open their mouth and you notice their jaw/tongue/velum deviates to one side, what does that indicate to you?
unilateral weakness (deviates to the weak side)
What are the different phases of the swallow?
1. oral phase
2. pharyngeal phase
3. esophageal phase
Oral Phase deficits:
1. drooling
2. anterior loss (food and/or liquid falls out front of mouth)
3. pocketing food in the anterior and lateral sulci
Pharyngeal Phase deficits:
1. delayed initiation of the swallow reflex
2. stasis in the vallecula or pyriform sinuses
3. penetration/aspiration
Esophageal Phase deficits:
1. GERD
2. globus
3. burping, heartburn, bad taste in mouth
4. halitosis (bad breath)
How do you know when a swallow is delayed?
if the bolus passes the ramus of the mandible and enters the vallecula/pyriform sinus and sits there, there is a delay
What is determined based on the behavior of the cells in question and what the cell looks like during microscopic inspection?
cancer grading
What are the different cancer grades?
I. normal
II. poorly differentiated
III. anaplastic
What determines how treatment will proceed whether it is radiation, chemotherapy or both?
cancer staging
What are the different cancer stages?
Level 0 = pre-cancer
Stage I = cancer is confined to the organ of origin
Stage II = cancer has invaded nearby tissue or organs
Stage III = cancer has spread to lymph nodes but remains near origin
Stage IV = cancer has metastasized to distant locations (much poorer prognosis)
What is the difference between compensation and restorative/facilitative therapy?
compensation = make them better by going around the missing function
restorative/facilitative = restoring the lost function
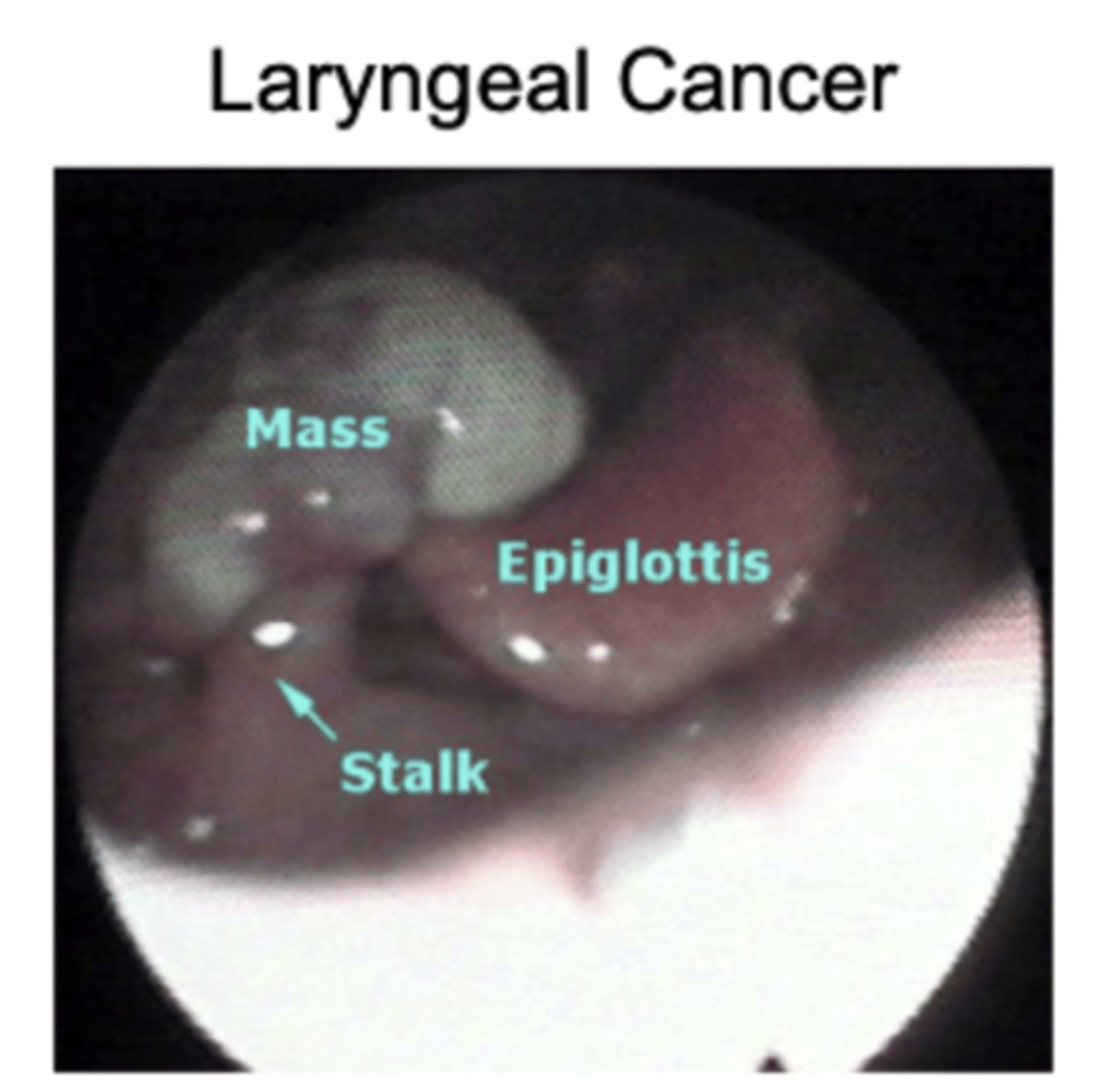
What are the symptoms of laryngeal cancer?
1. odinophagia (painful swallowing)
2. lumps/swelling in neck
3. change in vocal quality
4. weight loss
5. bad breath
6. difficulty swallowing
7. fatigue
What is an opening between pharynx and trachea and results in aspiration?
pharyngocutaneous fistula (PCF)
What are the changes you would expect to see as people age in terms of their swallowing?
- the initiation of laryngeal and pharyngeal events including laryngeal vestibule closure (and airway protection) are delayed significantly longer
- may take longer to chew foods
- may have some premature spillage
What are the different kinds of dysphagia?
1. oral phase
2. pharyngeal phase
3. esophageal phase
While performing an MBS, in what condition would you see a tongue pumping action where the tongue oscillates back and forth?
Parkinson's Disease
What is an example of a compensatory strategy you could use with a patient who has MG?
smaller meals throughout the day to help prevent fatigue
Cranial Nerves:
I. Olfactory - Sensory
II. Optic - Sensory
III. Oculomotor - Motor
IV. Trochlear - Motor
V. Trigeminal - Both
VI. Abducens - Motor
VII. Facial - Both
VIII. Vestibulocochlear - Sensory
IX. Glossopharyngeal - Both
X. Vagus - Both
XI. Spinal Accessory - Motor
XII. Hypoglossal - Motor
Which dysphagia exercises do we use for laryngeal elevation?
1. Effortful swallow
2. Mendelsohn Maneuver - patient is asked to swallow saliva several times while feeling "Adam's apple" moving up and down during swallow
3. Shakir - excursion
Why do we use thickened liquids?
clinicians are able to control how fast its moving and its more cohesive (greater viscosity)
If you have damage to the orbicularis oris and buccinator muscles what kind of problems would you have?
- anterior loss
- pocketing
- drooling
- stasis in oral cavities
What is Guillain-Barré syndrome?
- a disease that typically has a quick onset, the patient gets weaker globally and they have respiratory weakness (if they die its because of this)
- but they will start to get better eventually
If a patient has ALS, what is the best form of treatment for them?
PEG tube, because they will only get progressively weaker
What is typically used with those who demonstrate a delayed oral onset of pharyngeal swallow?
thermal stimulation
What does thermal stimulation do?
- can trigger a swallow
- uses a cold or sour bolus
- typically put a mirror in ice cold water and rub it against the faucial pillars to try and trigger a swallow
What are swallowing problems that would not be treated by an SLP?
- esophageal phase problems
- GERD/reflux
If you have a patient with reduced laryngeal closure what are some things to recommend?
thickened liquids
What are the different kinds of dysphagia exercises for tongue base weakness?
- tongue movement front to back - lick the roof of mouth from front to back
- tongue hold - lift tongue to roof of mouth and push for 3-5 seconds
- tongue pull back - pull tongue back in mouth and hold it for 3-5 seconds
- word repetition - repeat words 5 times saying them as hard as possible
- anchored swallows (Masako) - hold tongue between front teeth and try to swallow
If you have an older lady penetrate, is that pathological?
no, because penetration in older patients can be normal
Why do people pocket food?
poor buccal tension
What is known as a pocket in the posterior pharyngeal wall?
zenker's diverticulum
What is COPD and why do you get it?
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- smoking
What is the painful inflammation of mucus membranes of oral and pharyngeal cavities and leads to ulcers?
Mucositis
What may be the cause of leakage of prosthesis or yeast build up?
Tracheoesophageal puncture (TEP)
What is excessively dry mouth which is a result of reduced salivary secretions?
xerostomia
What is the contracture of muscles of mastication as a result of muscle spasm, or degeneration of temporomandibular joint?
trismus
What is excessive swelling caused by accumulation of lymphatic fluid in interstitial tissue?
lymphedema
What is increased production of fibrin, which is a protein that accumulates and damages radiated tissue over time?
Radiation Fibrosis Syndrome
If you do a chest x-ray where would you find signs of aspiration? and why is this?
right lower lobe; can also be a site of consolidation, where liquids accumulate.
Of the extrinsic muscles of the tongue, all are innervated by the hypoglossal nerve except the?
palatoglossus
Look at a picture of a patients tongue and say what happened:
the patient had a glossectomy of the left portion of her tongue with reconstructive repair from the underside of the right forearm
What exercises are used for poor hyolaryngeal excursion?
1. swallow hard - complete 1 swallow trying to swallow as hard as possible
2. pitch raises - say "ee" in a high pitch voice
3. pitch changes - use vowel sounds "ah" and "ee" and glide pitch up as high as possible
4. lowering pitch - use vowel sounds "ah" and "ee" and start at highest pitch and move to lowest pitch
5. Modified Valsalva - Press hands together hard and say "ee" as hard as possible
6. hyoid lifts - use a straw to pick up a small piece of paper and move it from one side to other
7. breath hold - hold breath as hard as they can
8. head lifts (Shakir) - lie down flat on back and gently lift head until feet are visible
Chin Tuck (compensatory)
- pharyngeal dysphagia
- enlarges vallecular space/narrows airway entrance
- prevents premature spillage
Chin Elevated (compensatory)
- oral dysphagia
- used for poor anterior transit/poor labial seal
- uses gravity to propel bolus back as patient tilts head backward, elevating chin
Head Rotation (compensatory)
- pharyngeal dysphagia
- used for patients w/ pharyngeal weakness and subsequent pharyngeal residue post swallow
- rotate head to weaker side to close the affected side off and direct bolus down stronger and more sensate side (used with chin tuck)
Head Tilt (compensatory)
- oropharyngeal dysphagia
- tilt head toward the stronger side
- stimulates oral and pharyngeal phases
- increases oral control and bolus formation
Hard/Effortful Swallow (swallowing exercises)
- used for patients who demonstrate pharyngeal residue caused by reduced pharyngeal contraction
- can be done with or without food
Supraglottic Swallow (swallowing exercises)
- used for patients with reduced closure of airway or a delayed pharyngeal trigger
- patient is asked to take a deep breath and to hold breath while swallowing, then exhales and produces a voluntary cough
- patient swallows again immediately after the cough
Super-supraglottic Swallow (swallowing exercises)
- patients who have poor VF closure and airway protection, along with poor tongue base retraction
- same as the supraglottic swallow but with extra effort
Dry Swallow
- used to clear residue from pharynx after initial swallow
- can be repeated as often as needed to clear residue
Voluntary Cough
- used to clear residue after initial swallow
- procedure is used with a patient who has a wet, gurgly voice after swallow
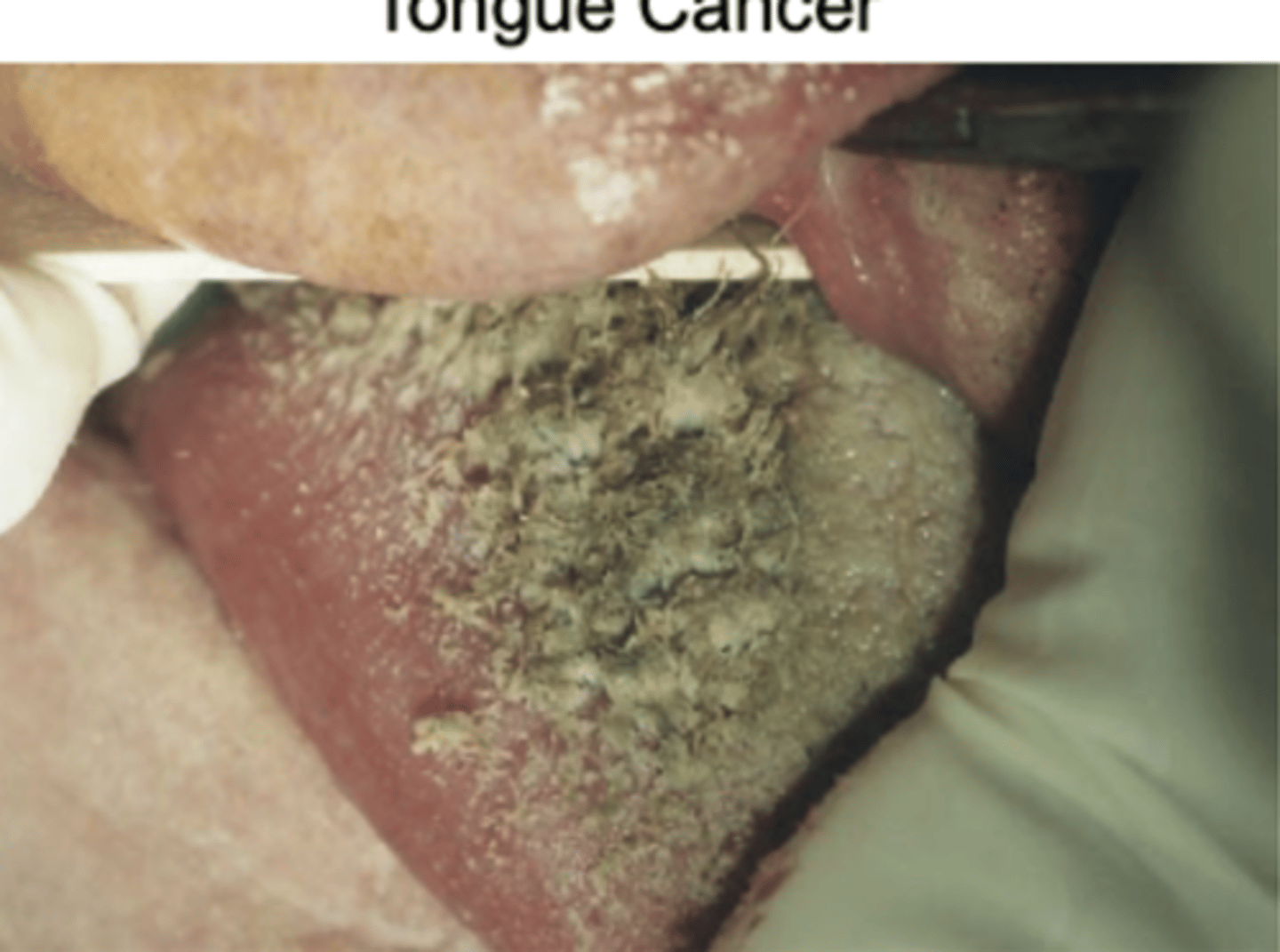
Tongue Cancer
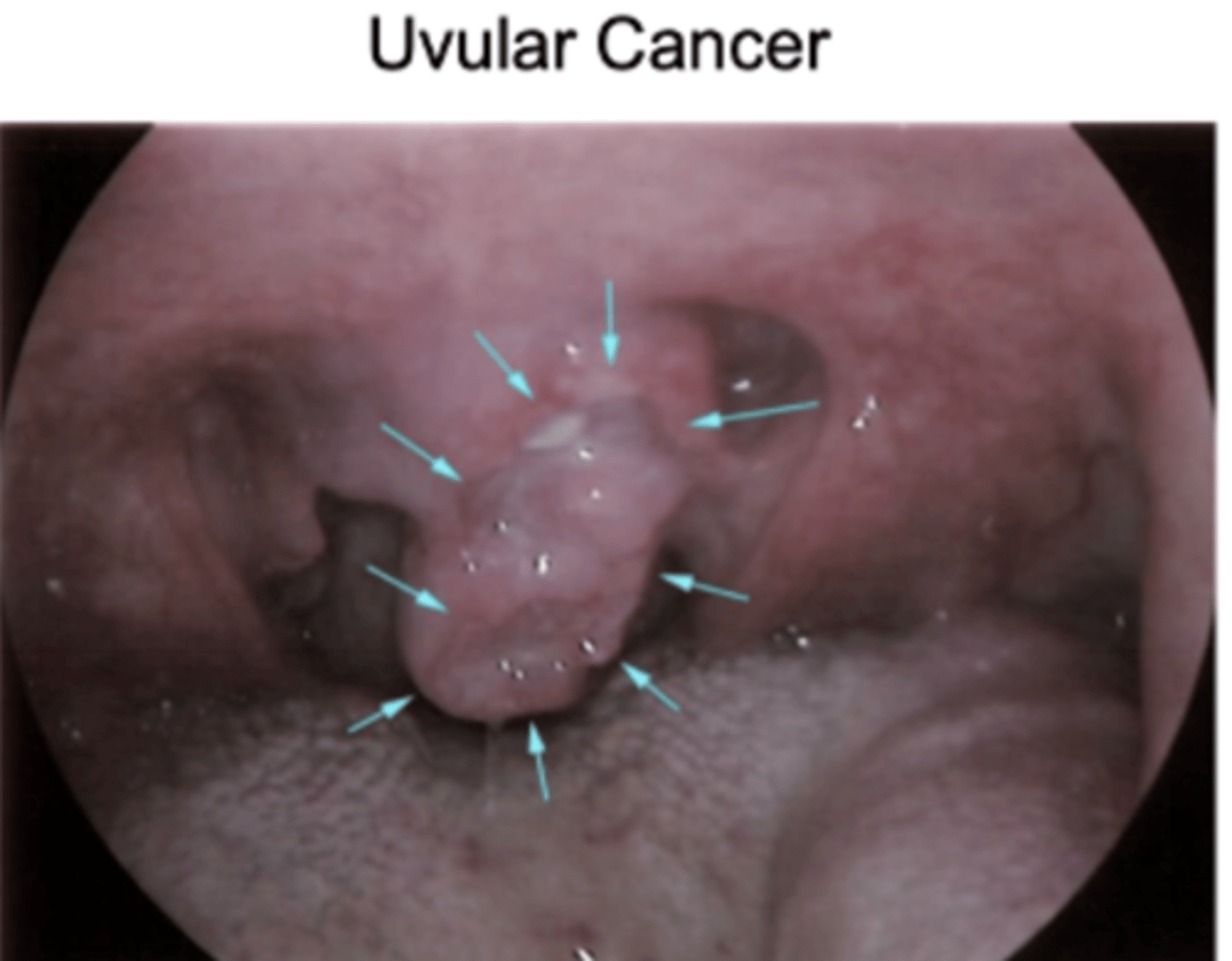
Uvular cancer
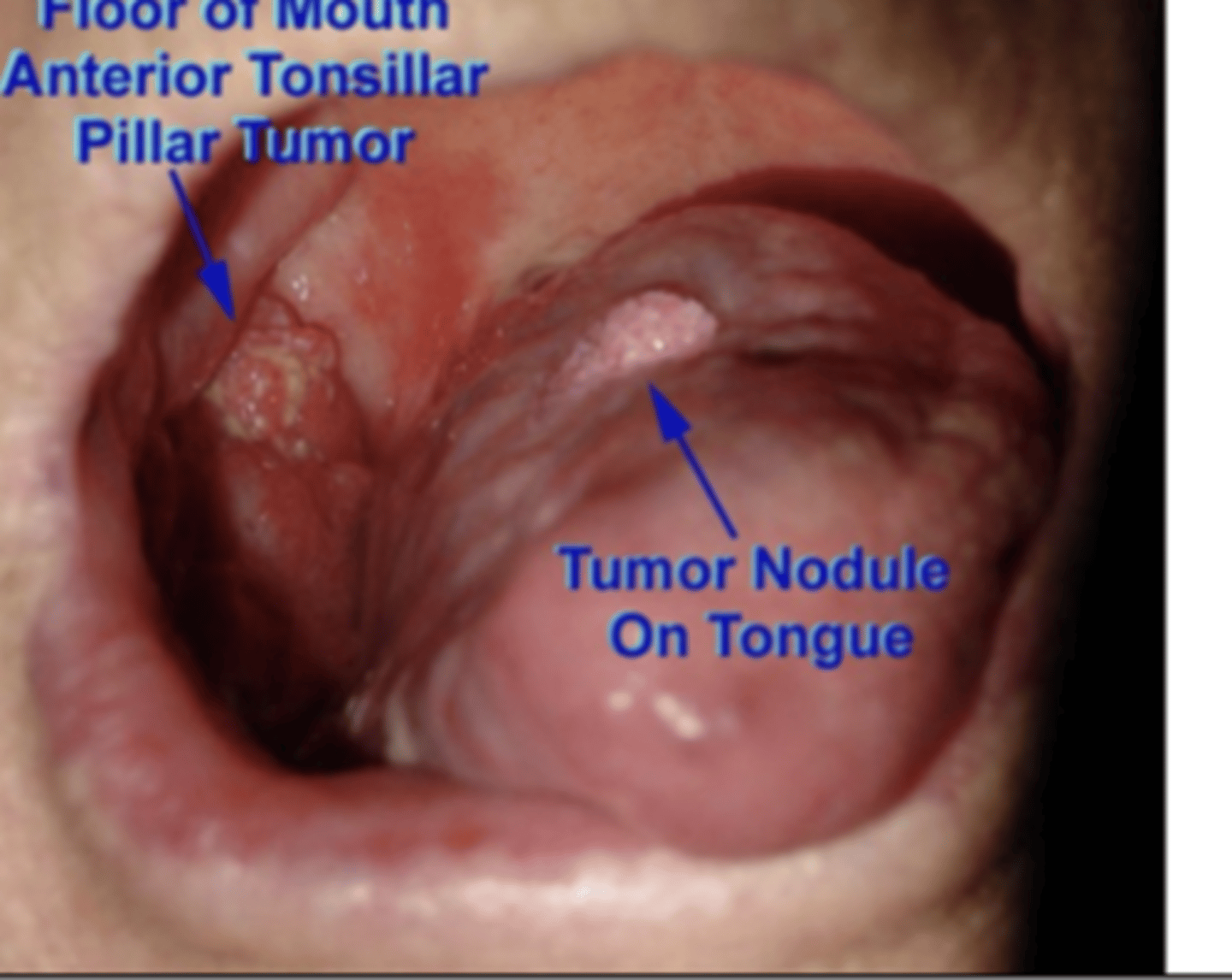
Tongue Cancer
Soft palate cancer (Velum)
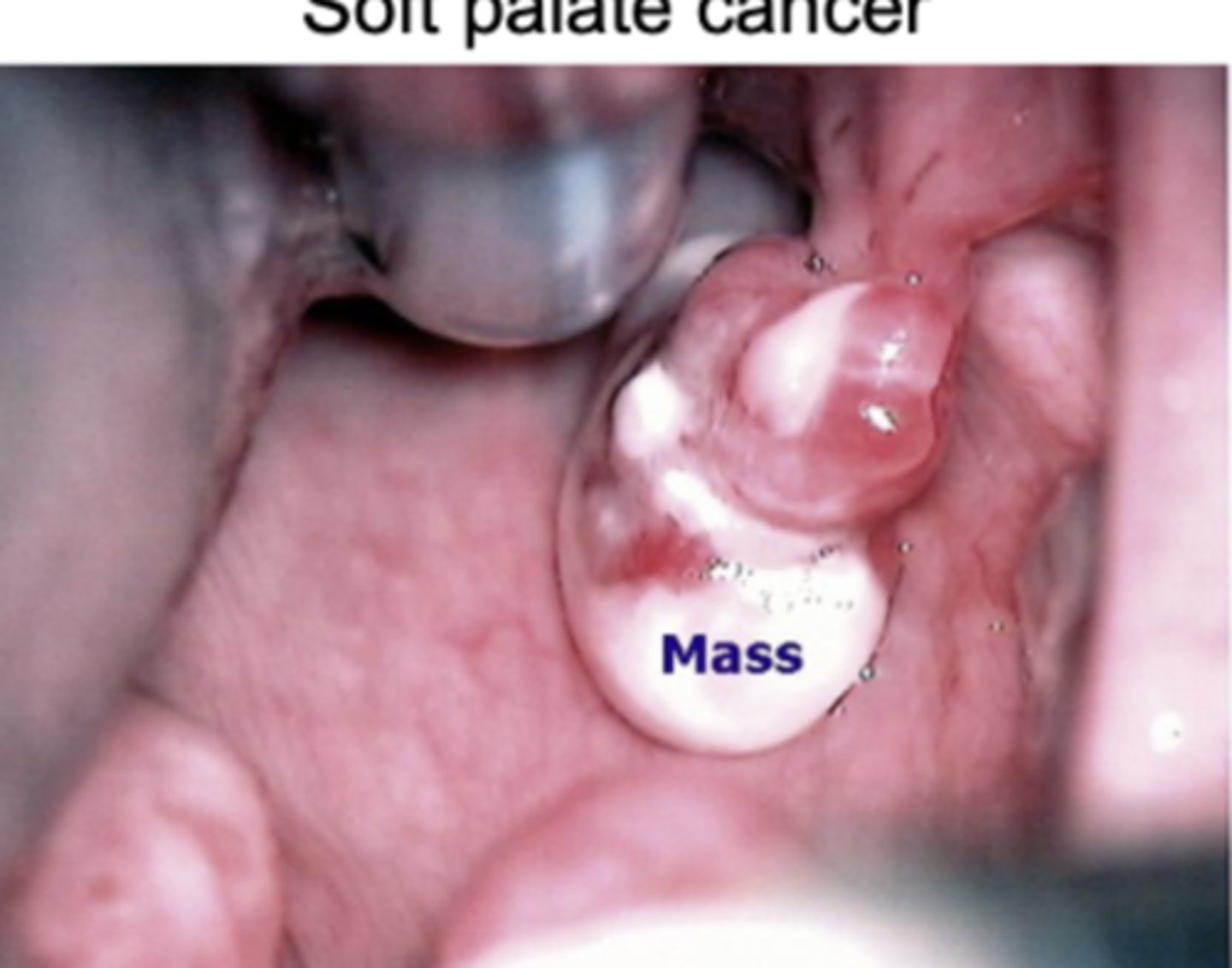
Laryngeal cancer
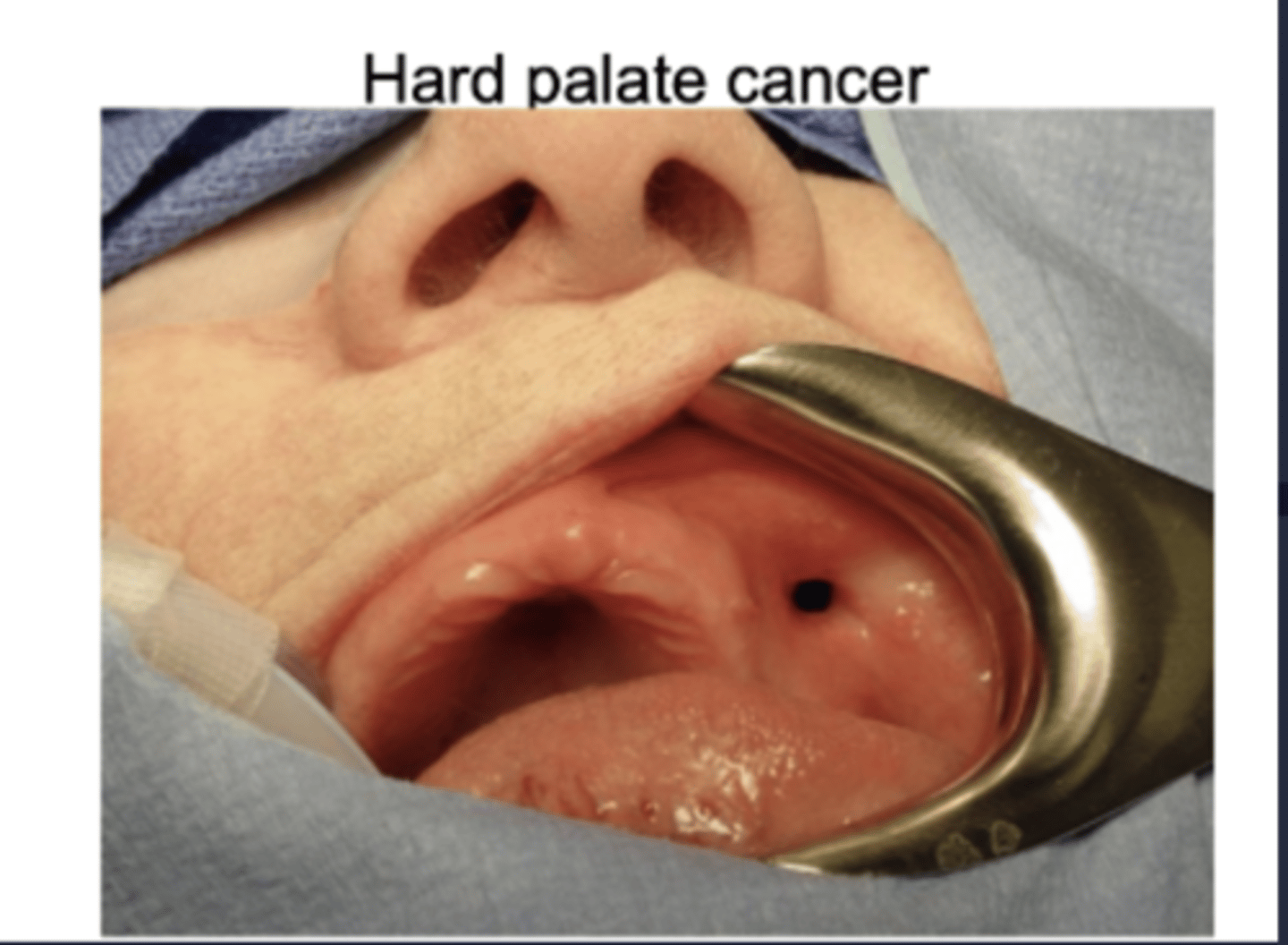
Hard palate cancer
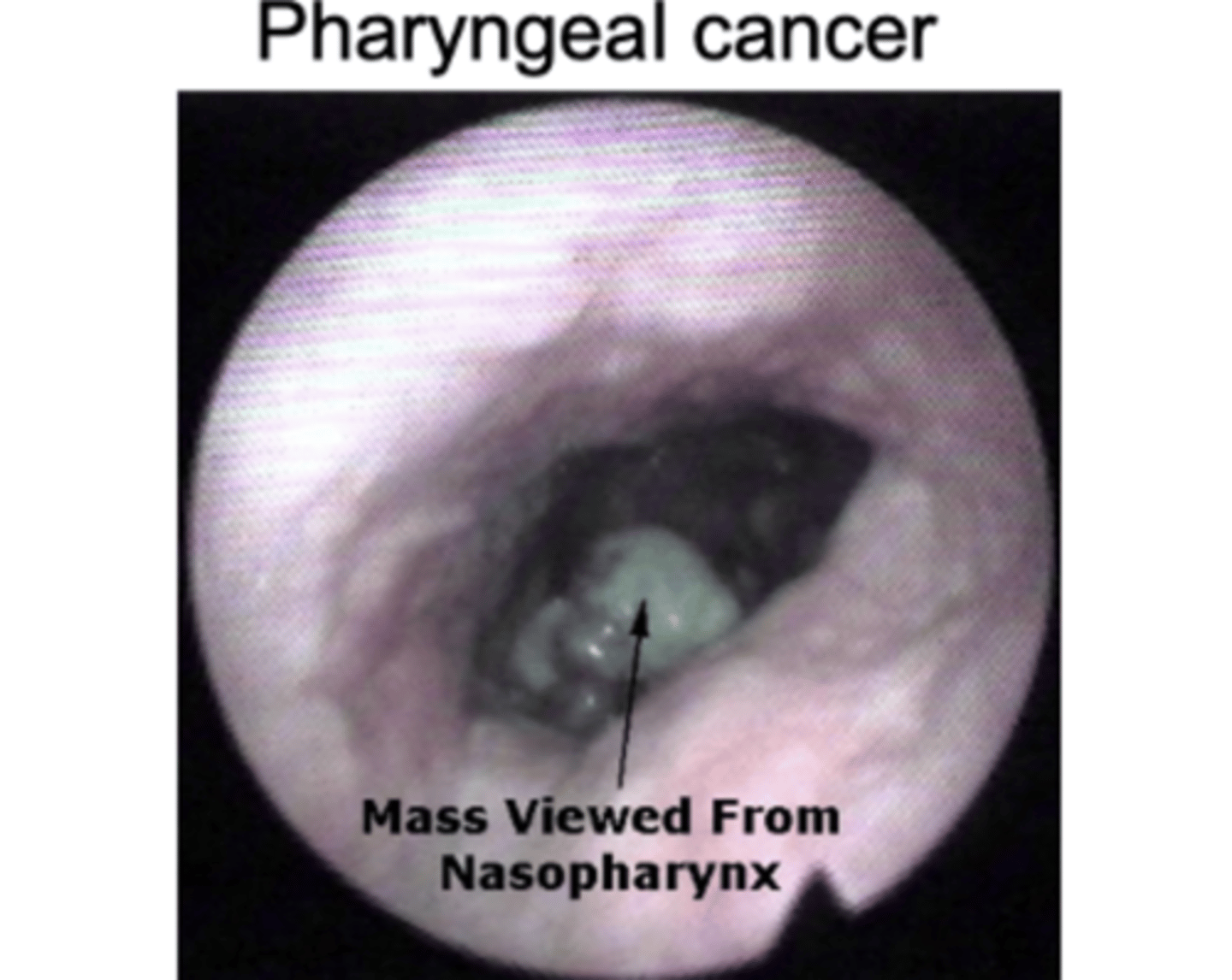
pharyngeal cancer
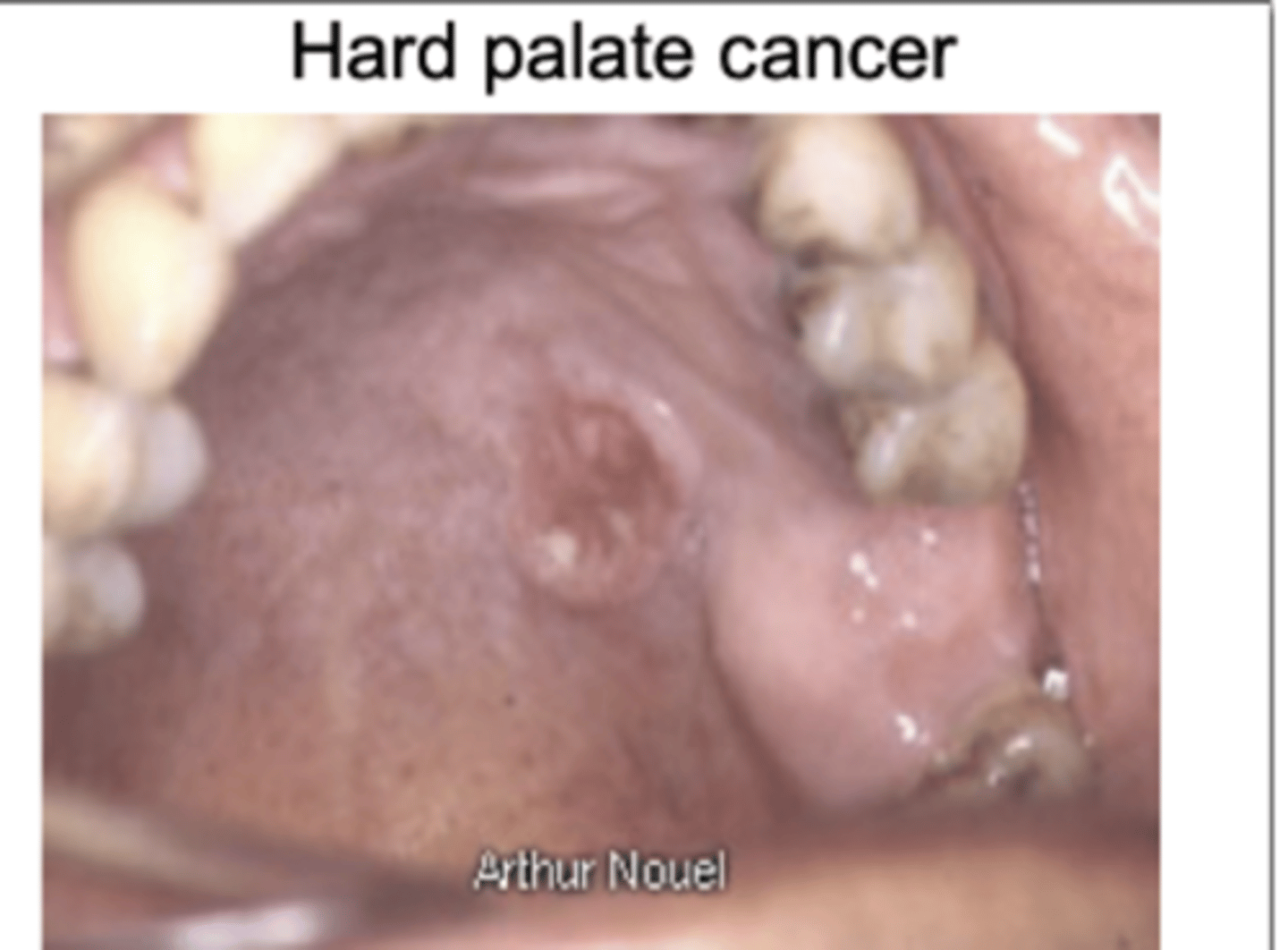
Hard palate cancer
What populations benefits from swallowing exercises to help prevent dysphagia?
pts with pharyngeal phase dysphagia; post stroke pts, head and neck cancer pts, neurological disorder pts, etc
Given a small case history, be able to recommend the best methods for treating the patient. Also, understand what a recommended treatment for the patient would not be based on s/s.
Which muscle that is mostly responsible for hyolaryngeal depression?
sternohyoid
Know which muscles can be affected by damage to certain cranial nerves/symptoms.
What would you do if you needed to evaluate a patient's swallowing and they were unable to follow directions/aphasic?
- at least attempt the evaluation and see if they can mimic you
- could start PO trials if you felt it was safe
If you are conduction a MBS and have a patient who is edentulous, what consistencies would you provide to them?
Advanced solids
As we age, what makes us more susceptible to dysphagia?
muscle loss
acid reflux
taking multiple medications reduce production of saliva