Biomagnification and Cycles
1/58
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
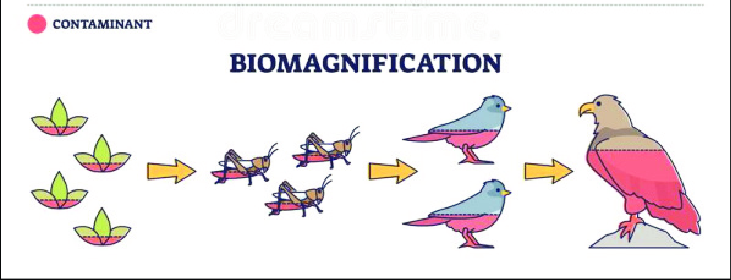
Biomagnification
Where toxins accumulate as you go up the food chain
The lower on the food chain, the less toxins are in it
Tends to collect/concentrate in fat tissue
Evaporation
Evaporation happens when a liquid substance becomes a gas.
When water is heated, it evaporates.
The molecules move and vibrate so quickly that they escape into the atmosphere as molecules of water vapor.
Condensation
Condensation is the change of water from its gaseous form (water vapor) into liquid water.
Condensation generally occurs in the atmosphere when warm air rises, cools and loses its capacity to hold water vapor.
As a result, excess water vapor condenses to form cloud droplets.
Precipitation
Precipitation is water released from clouds in the form of rain, freezing rain, sleet, snow, or hail.
It is the primary connection in the water cycle that provides for the delivery of atmospheric water to the Earth.
Most precipitation falls as rain.
Transpiration
Transpiration is the process by which plants lose water out of their leaves.
Transpiration gives evaporation a bit of a hand in getting the water vapor back up into the air.
Sublimation
The process of solids becoming a gas.
Ex. Dry ice
Deposition
The laying down of sediment carried by wind, flowing water, the sea or ice.
Infiltration
The downward entry of water into the soil.
Percolation
The downward movement of water through soil and rock under the force of gravity. This process follows infiltration.
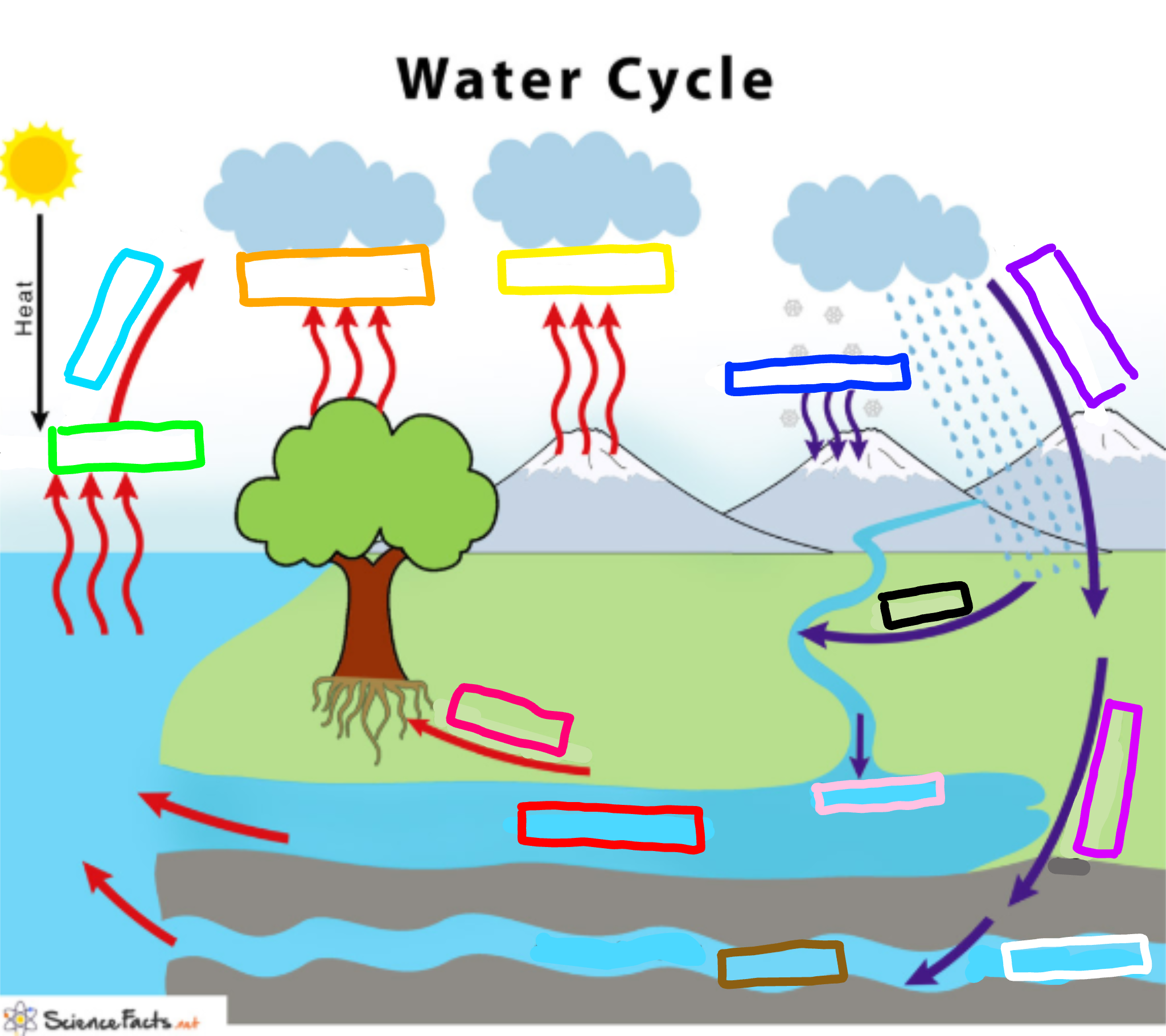
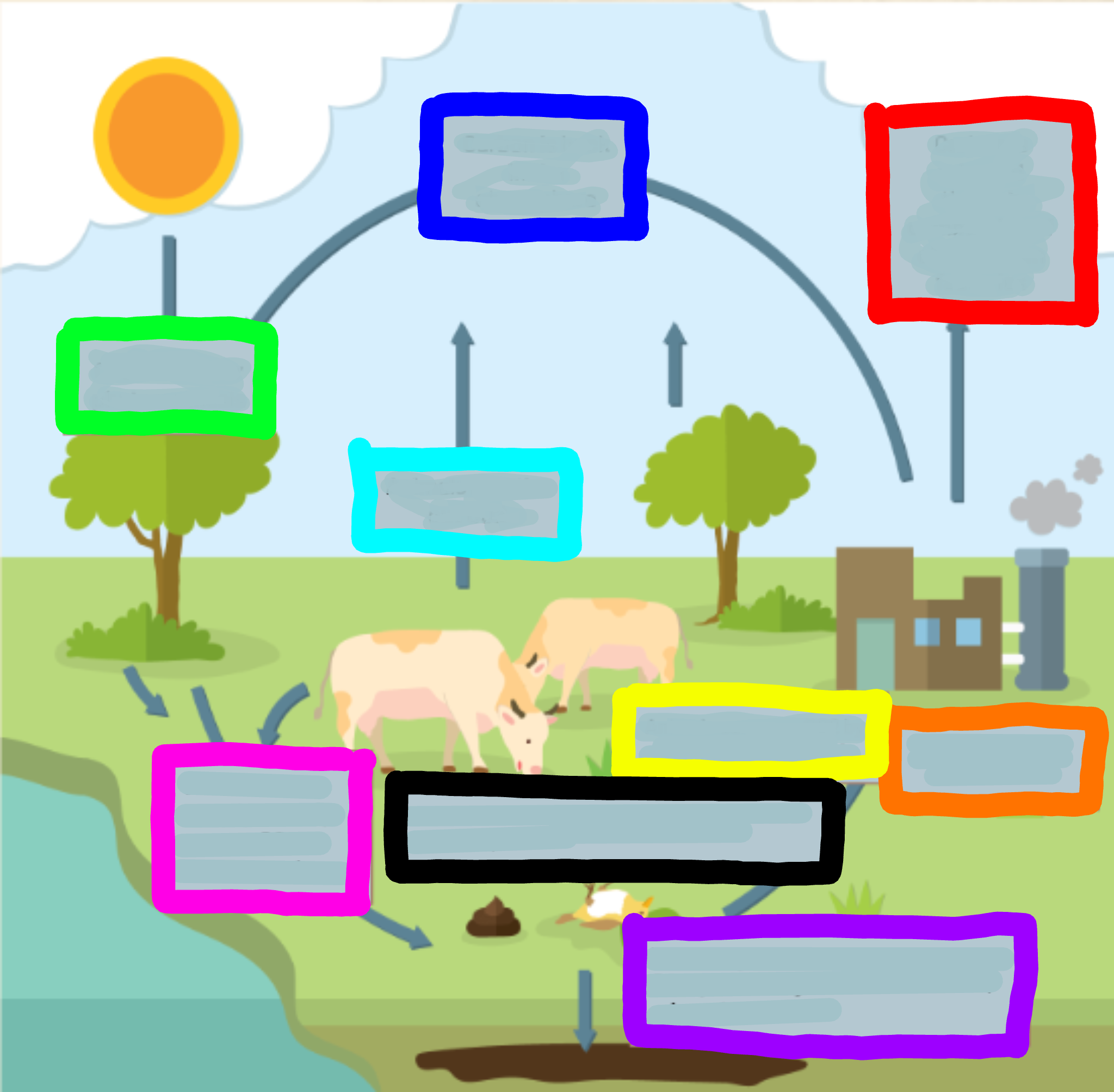
What is represented by the cyan box?
Condensation
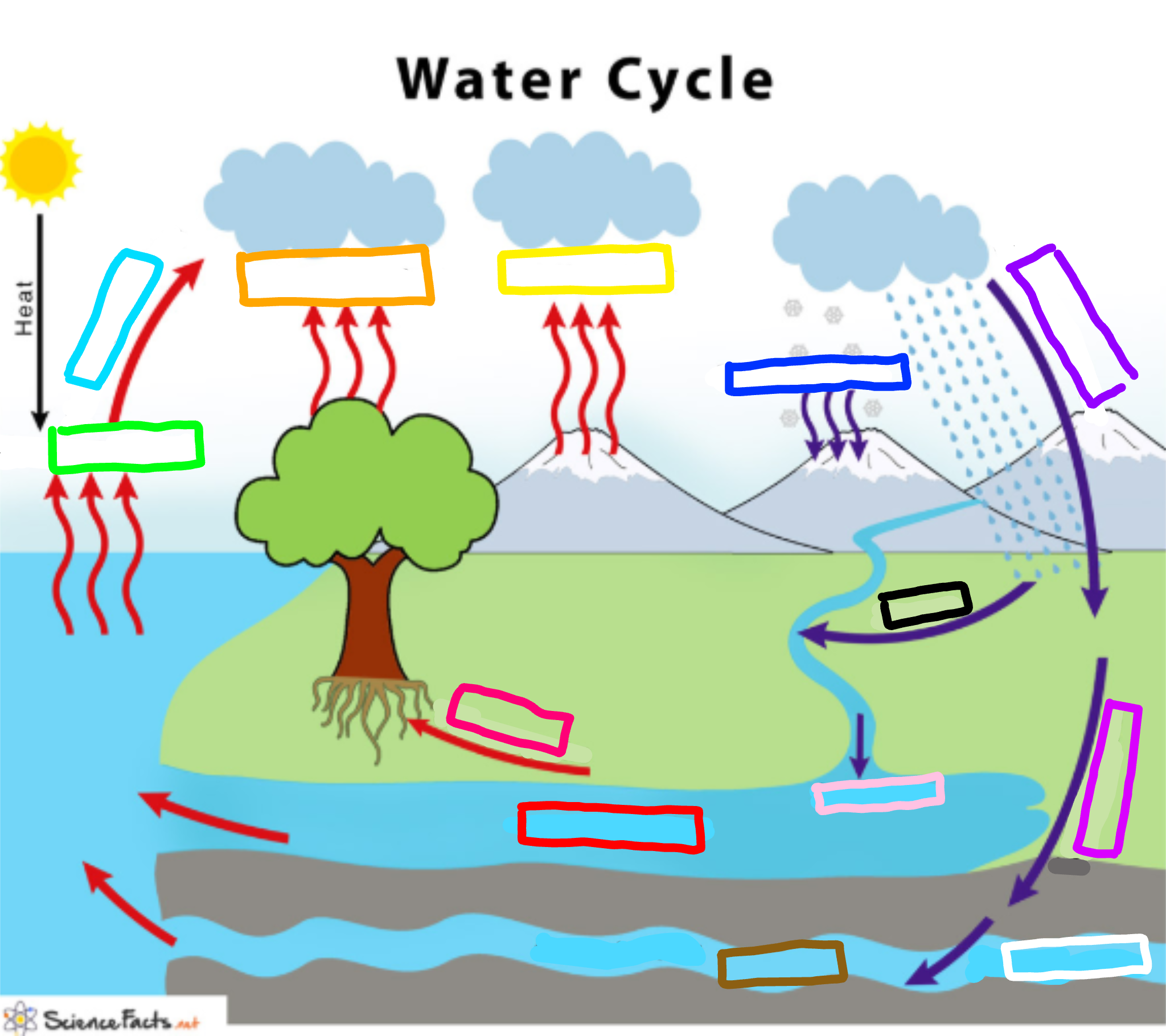
What is represented by the lime green box?
Evaporation
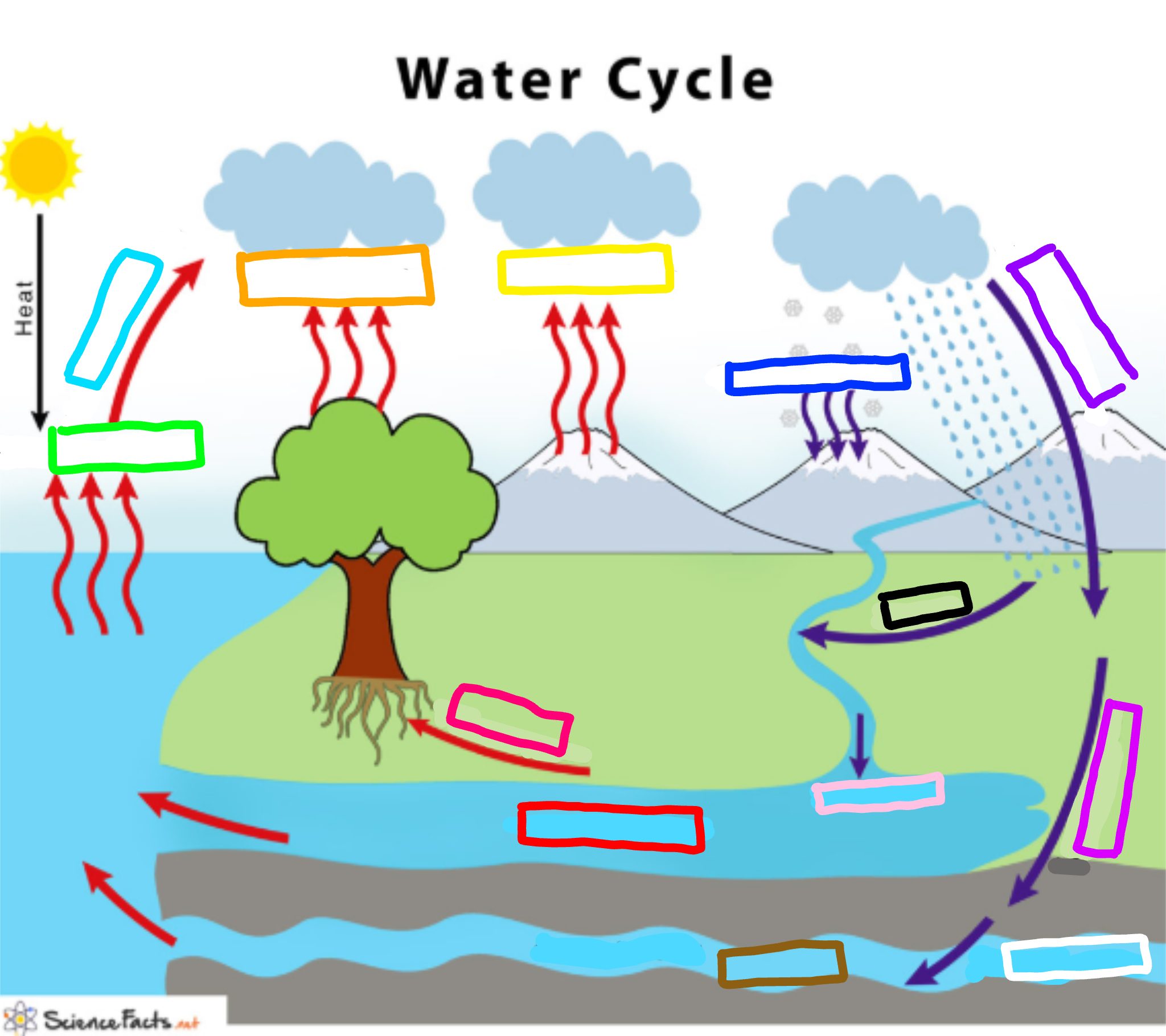
What is represented by the orange box?
Transpiration
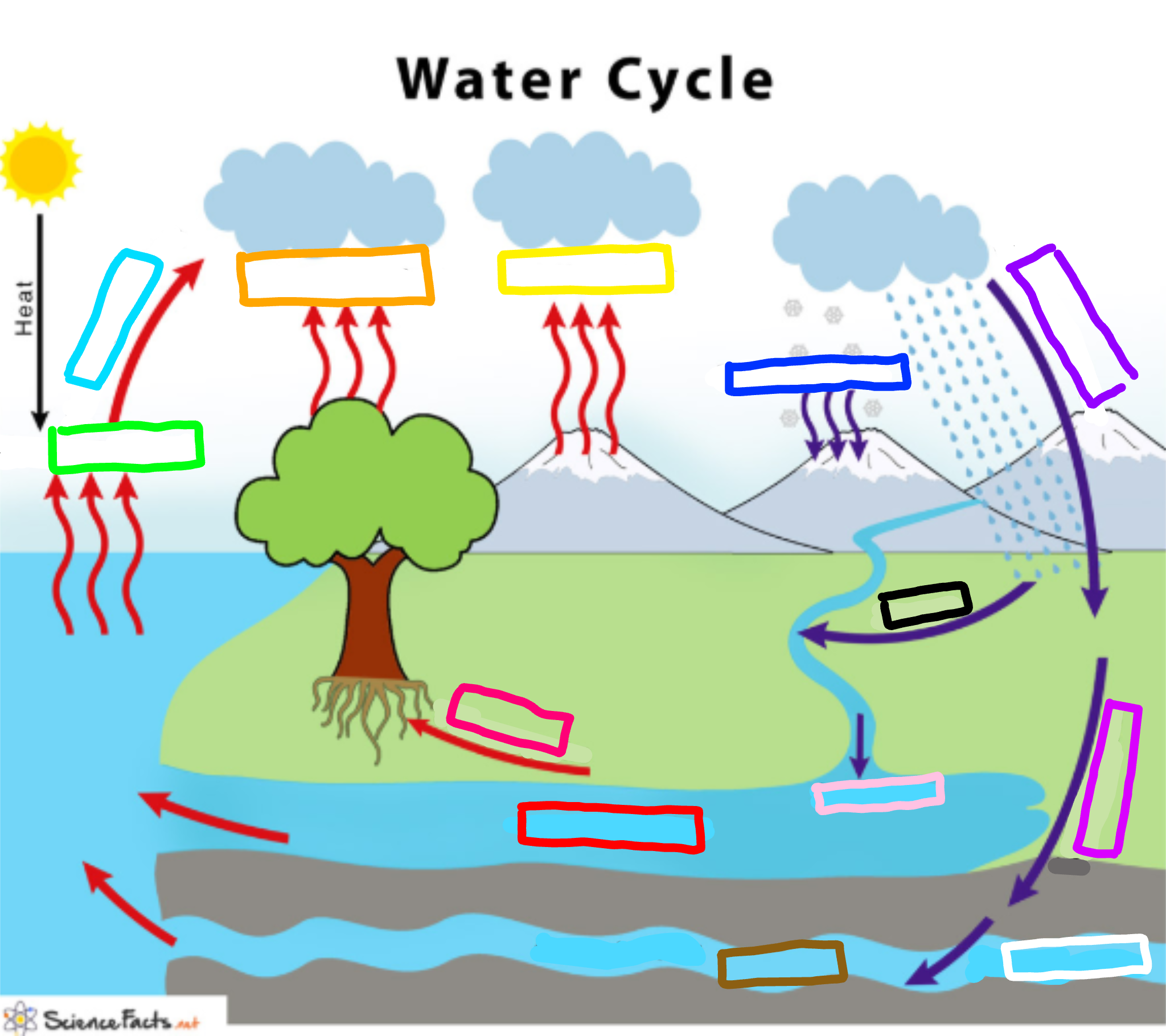
What is represented by the yellow box?
Sublimation
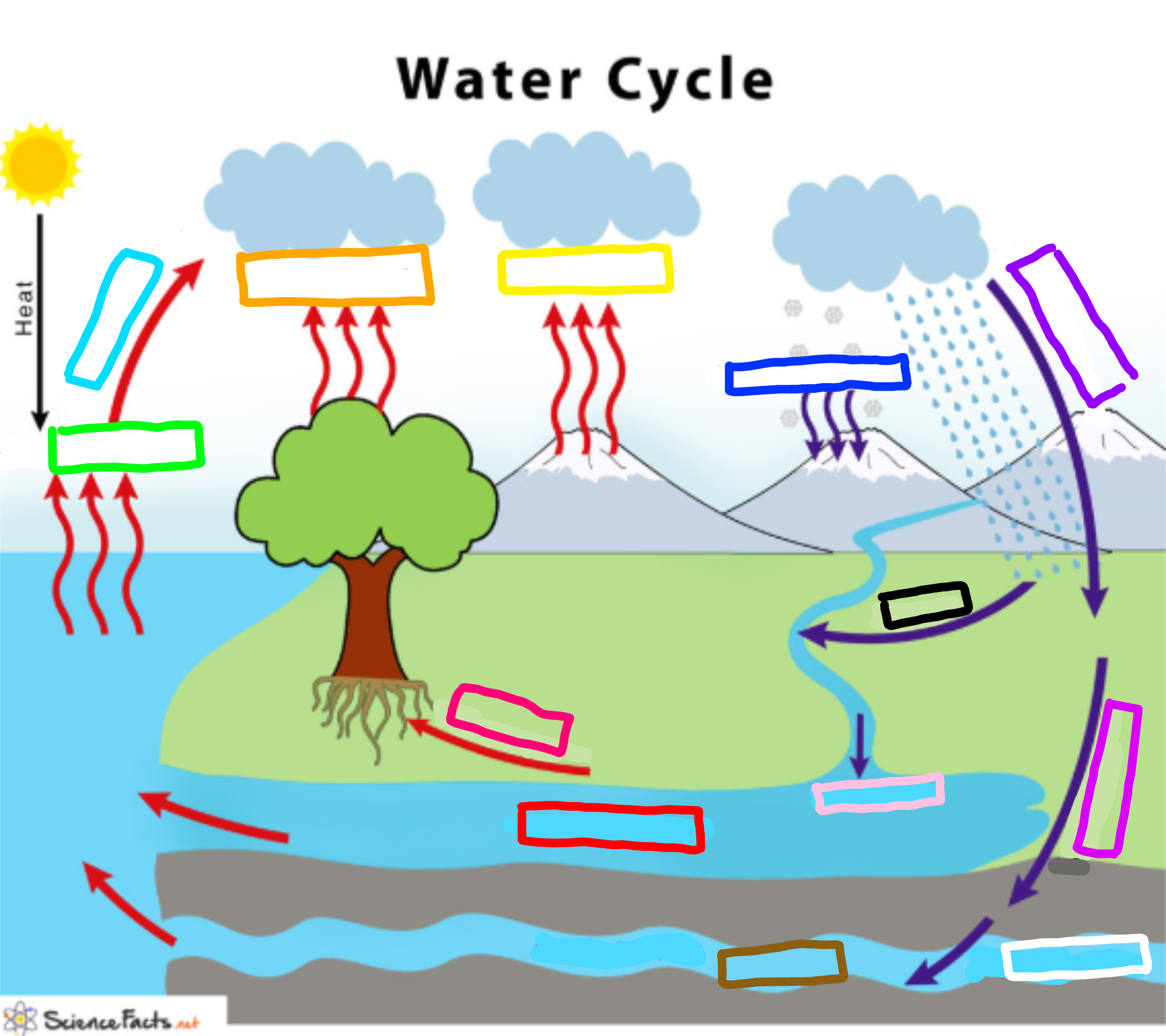
What is represented by the navy blue box?
Deposition
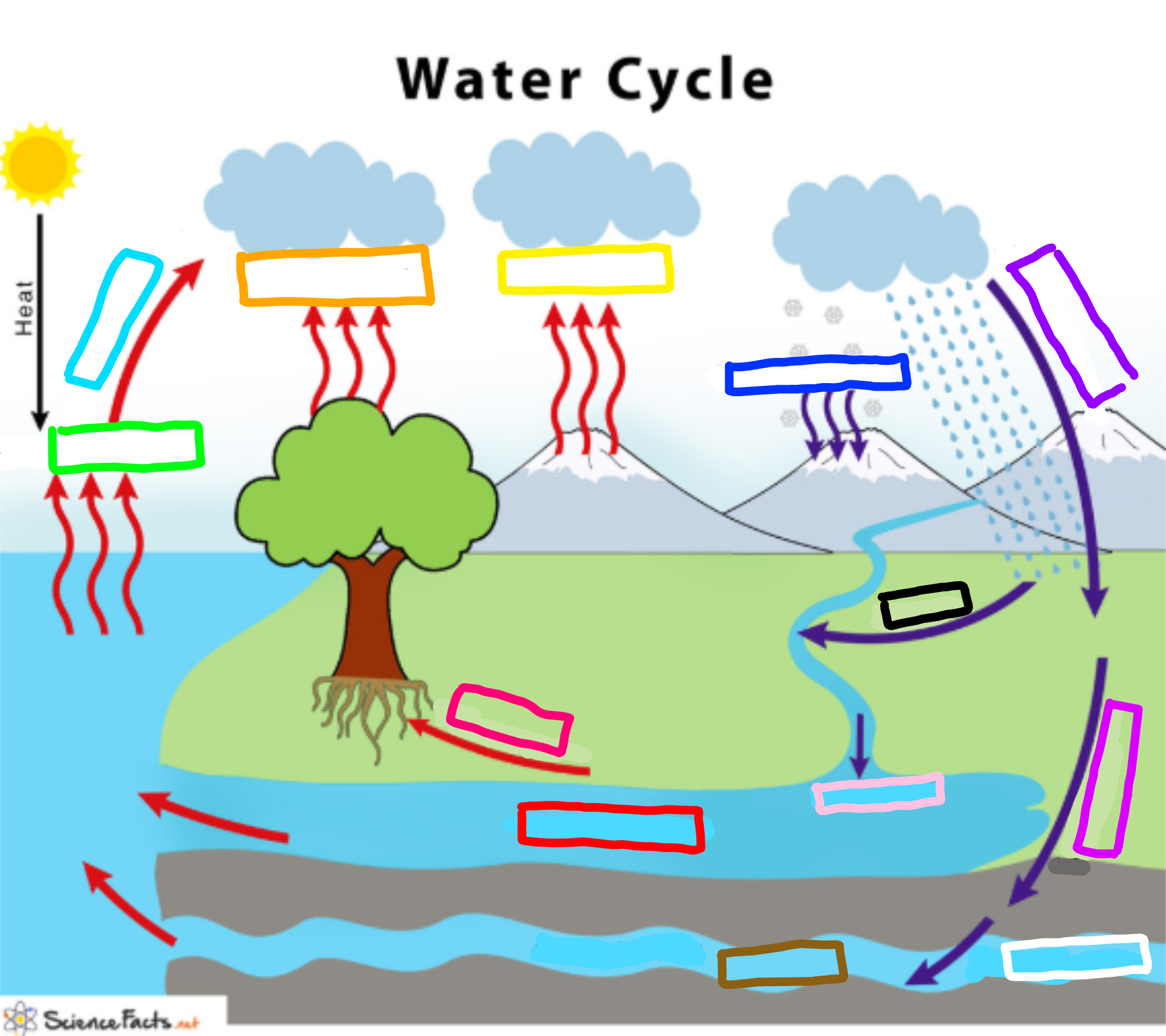
What is represented by the blue-violet box?
Precipitation
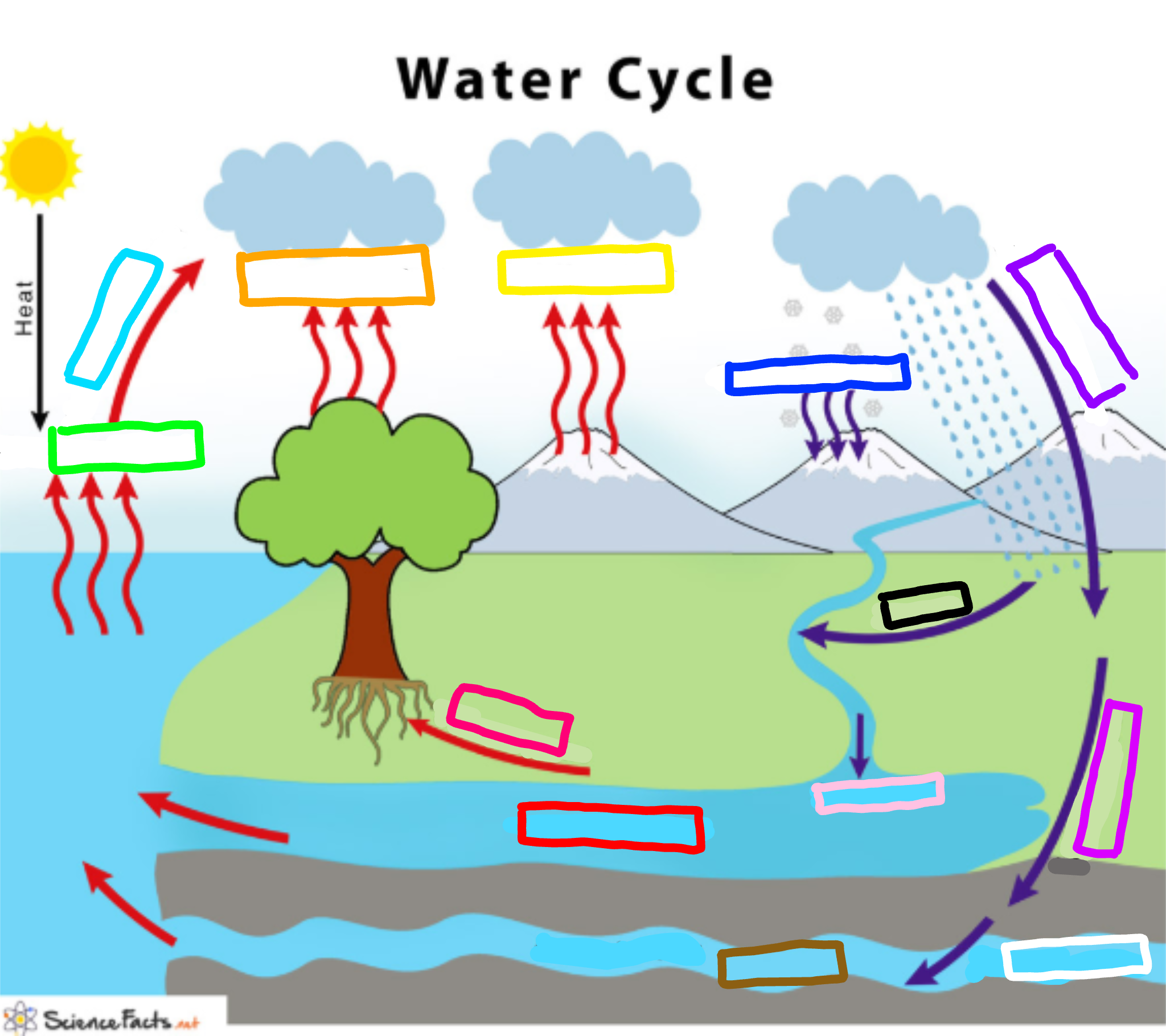
What is represented by the purple box?
Infiltration
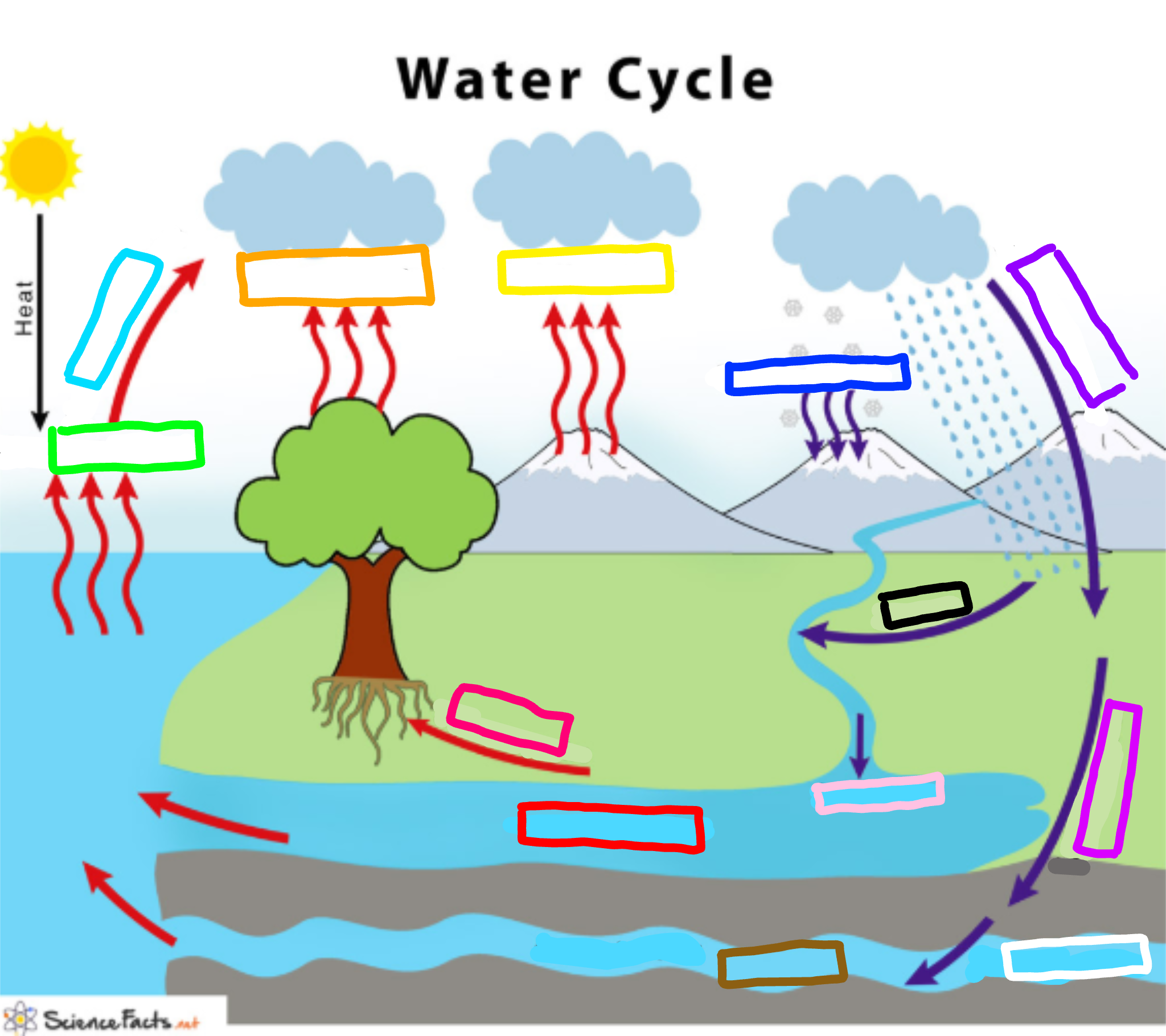
What is represented by the white box?
Percolation
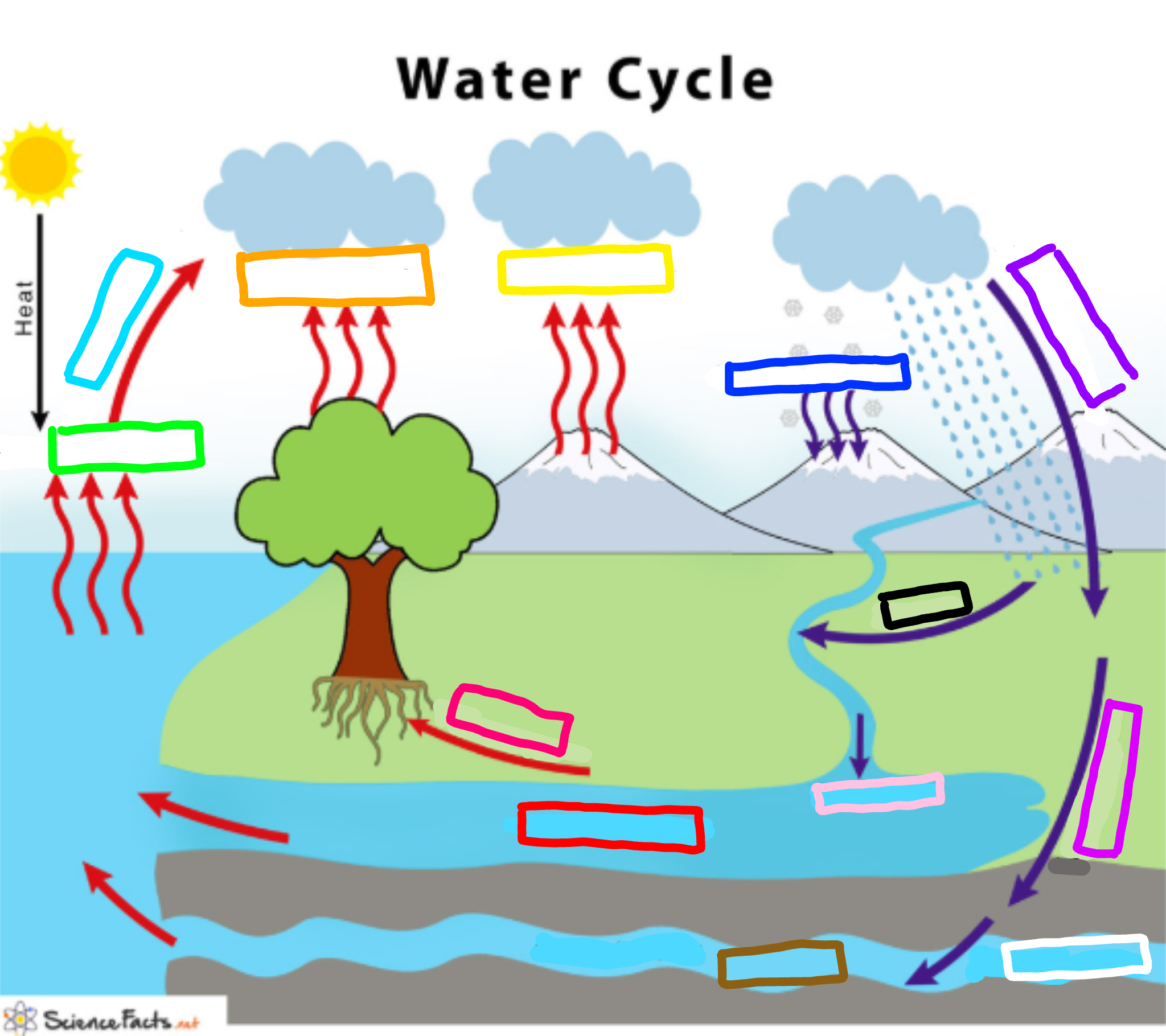
What is represented by the brown box?
Ground water
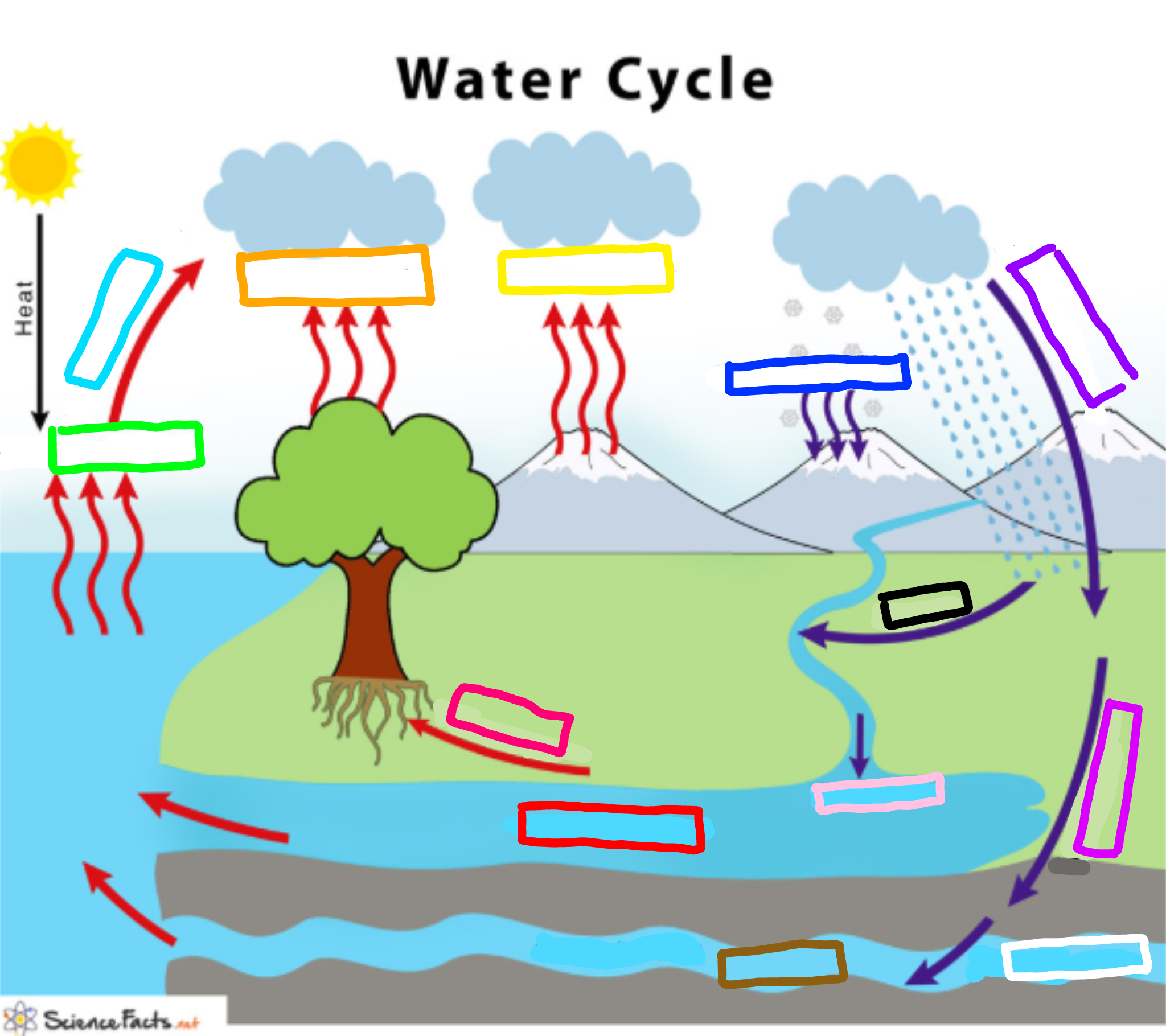
What is represented by the pink box?
Collection
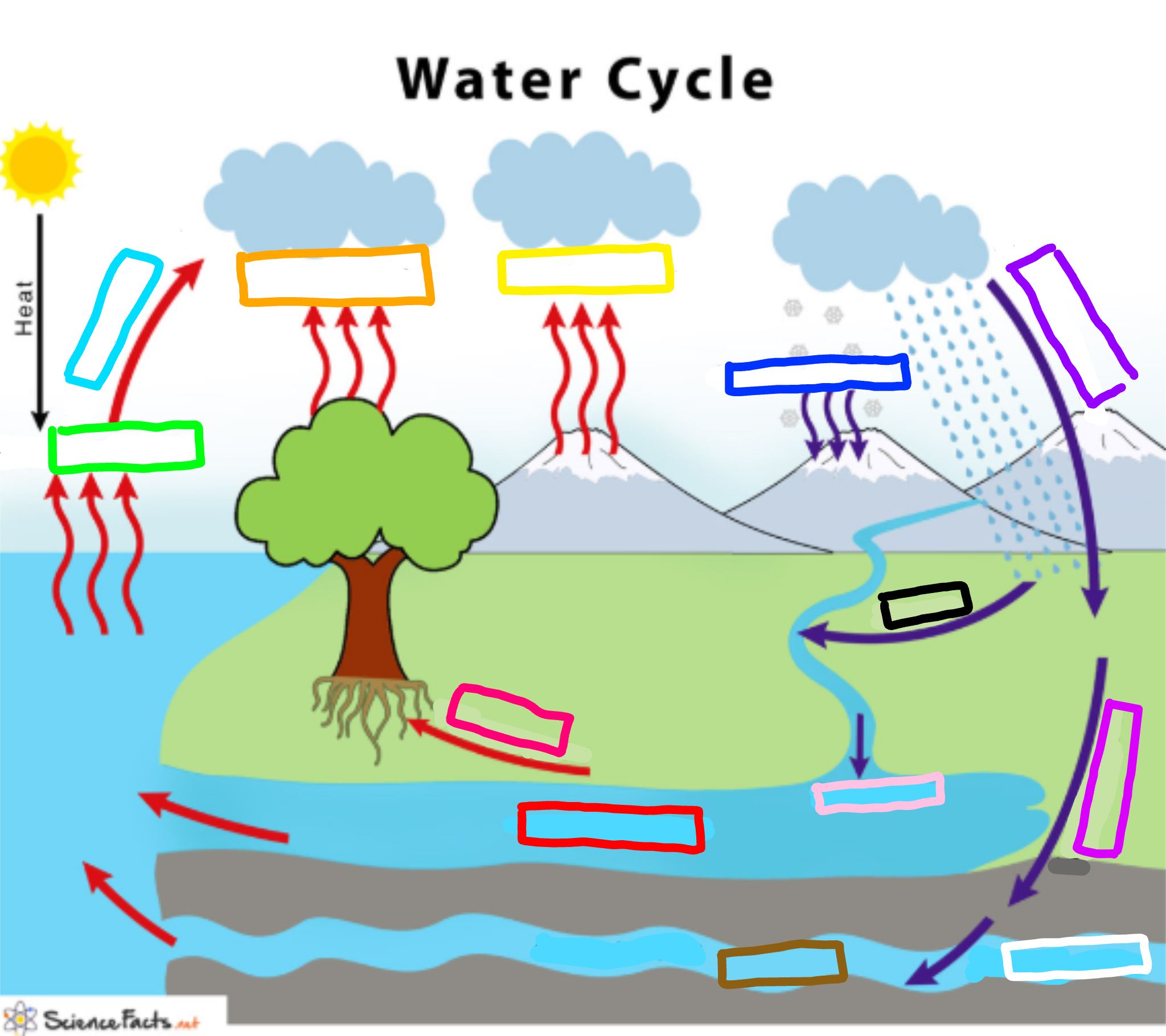
What is represented by the black box?
Runoff
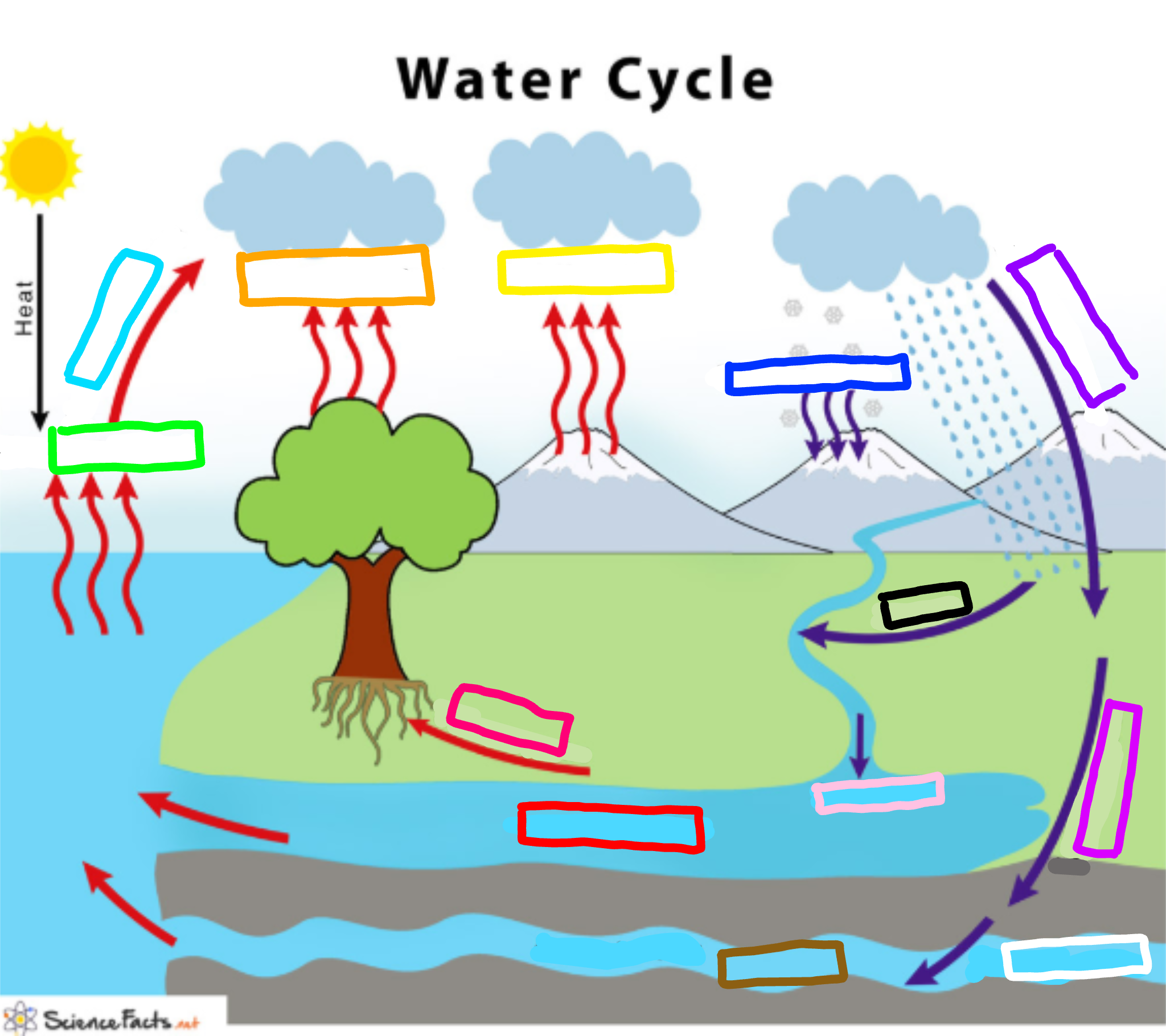
What is represented by the red box? (not the hot pink one!)
Surface water
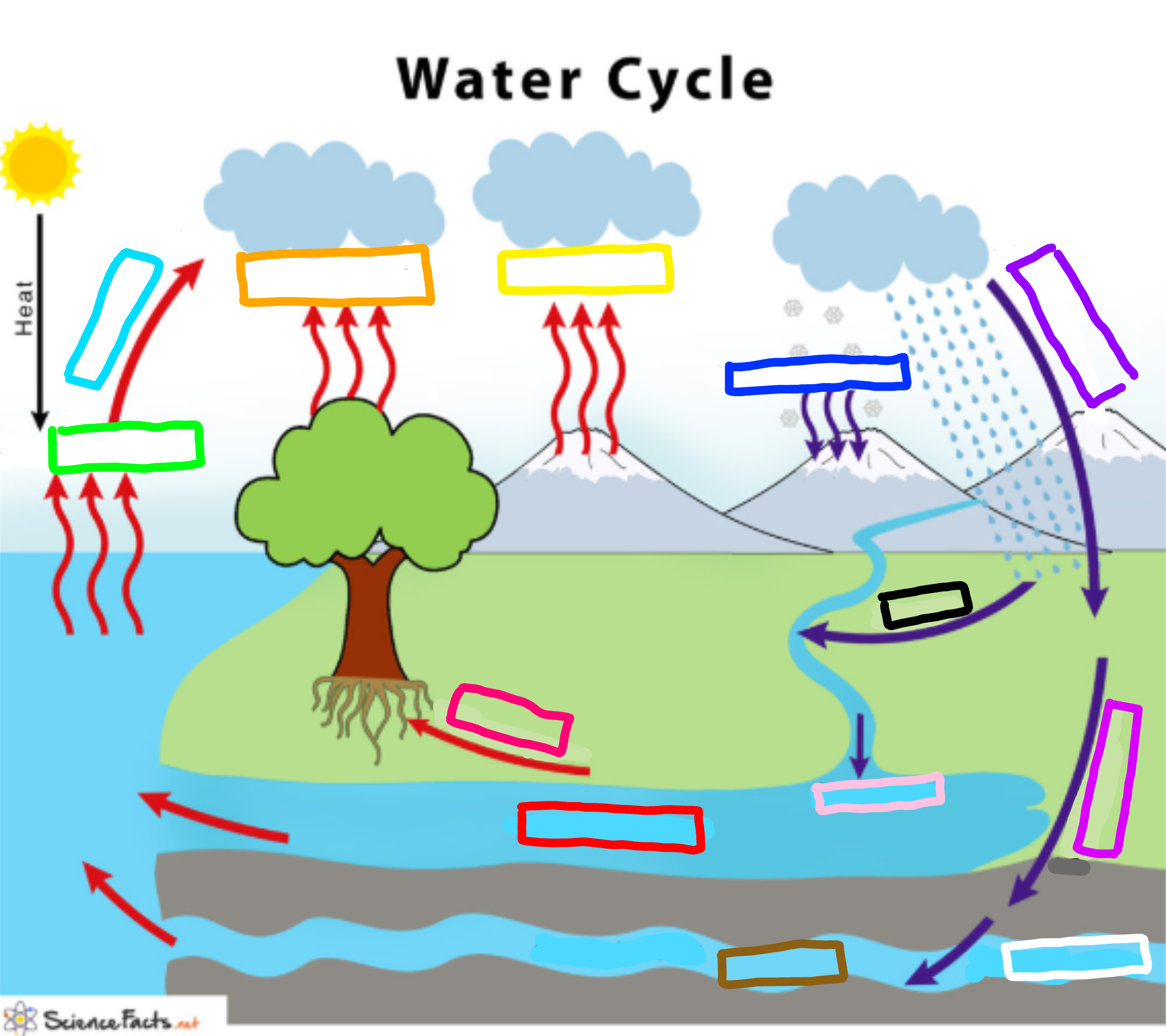
What is represented by the hot pink box? (not the red one!)
Plant Uptake
What is carbon?
6th element, the basis of life on earth, found in rocks, oceans, and the atmosphere
Carbon cycle
The cycling of carbon between the earth and the atmosphere
When organisms eat plants, they take in the carbon and some of it becomes part of their own bodies. What does this mean?
Carbon provides nutrients to make up the physical and chemical parts of the animal.
When plants and animals die…
Most of their bodies are decomposed and carbon atoms are returned to the atmosphere
Some are not fully decomposed and end in deposits underground (oil, coal, minerals)
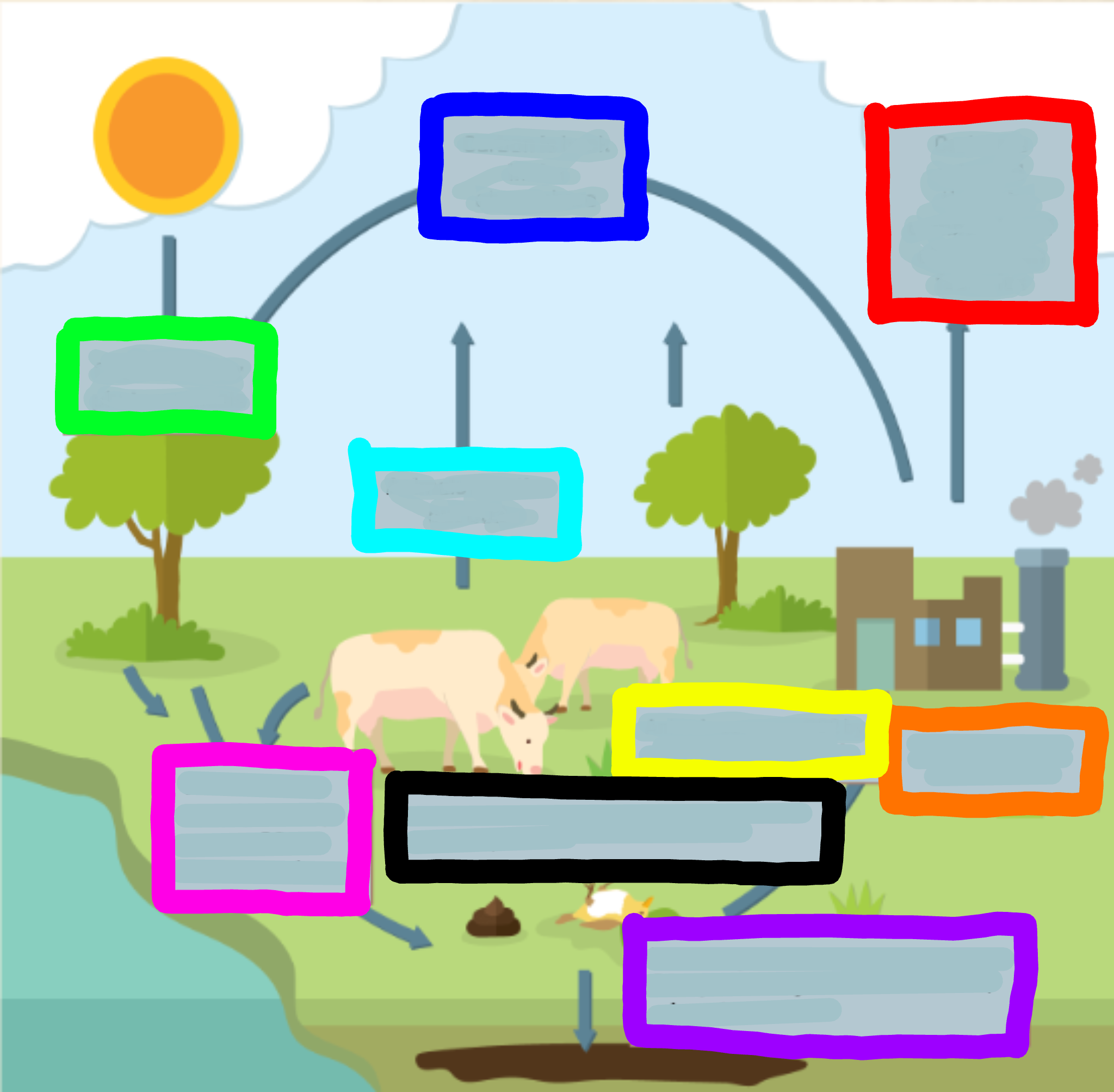
What does the red box represent?
Carbon is released through combustion of oi/coal from factories
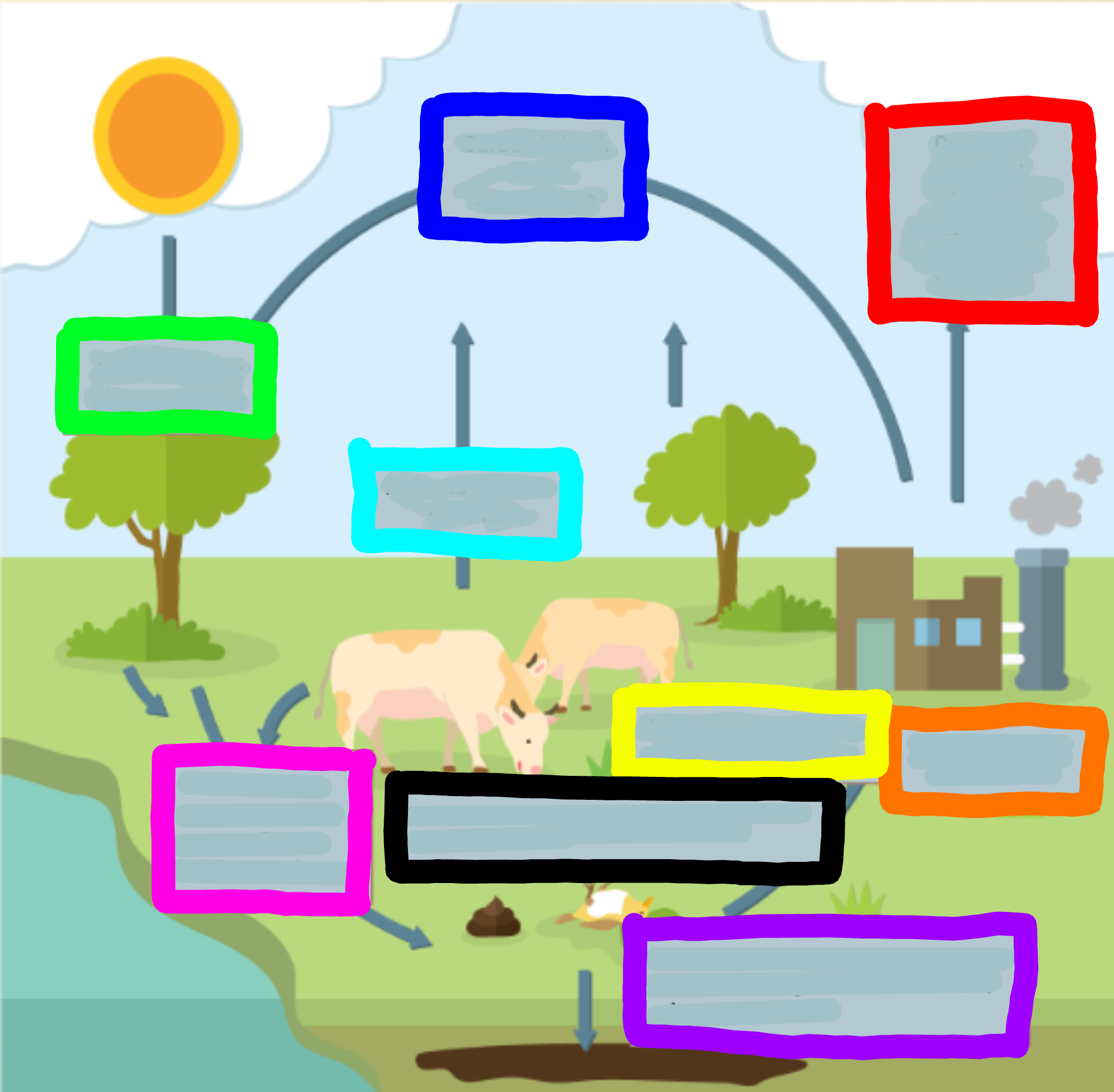
What does the orange box represent?
Factories burn oil and coal
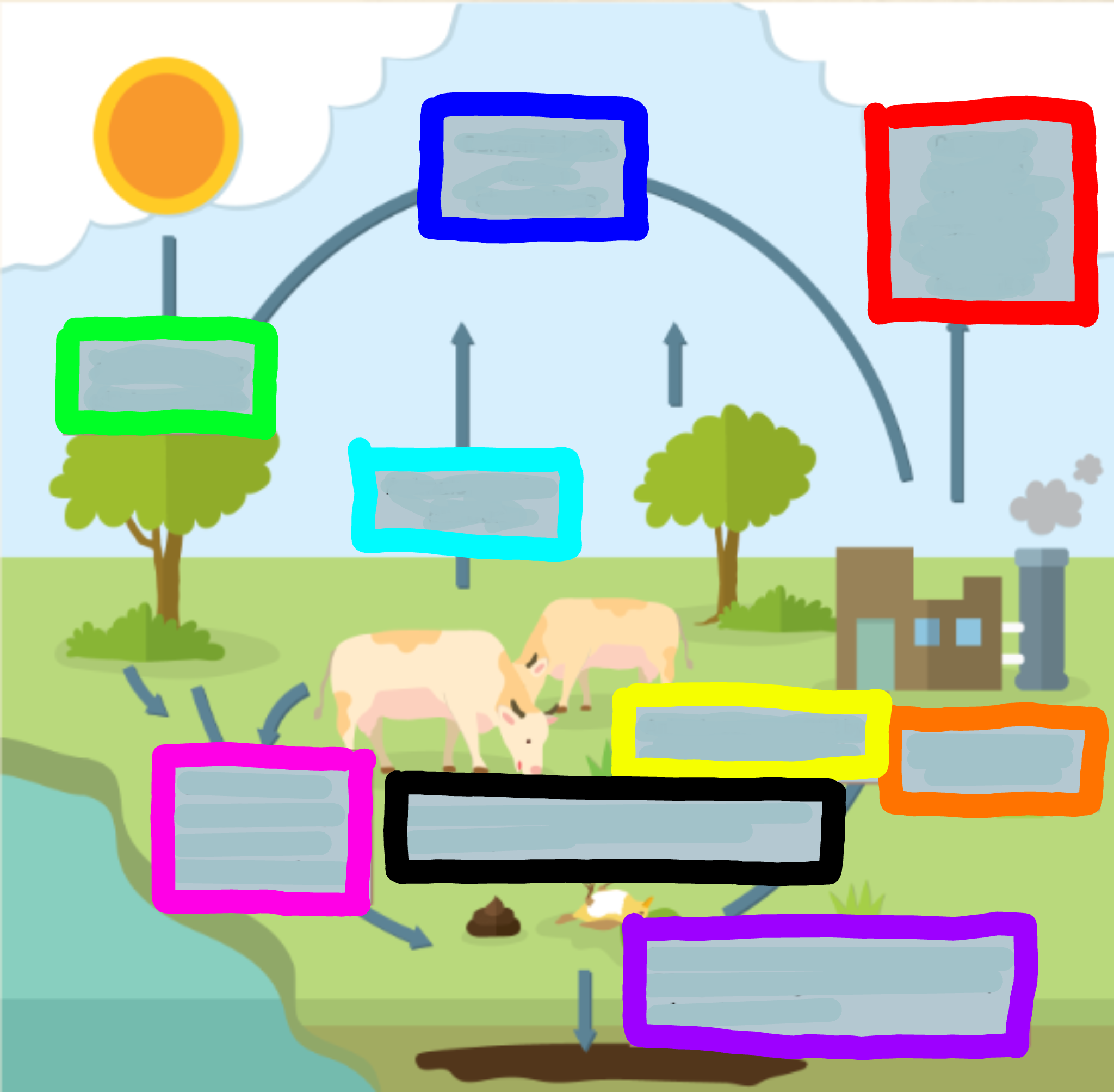
What does the yellow box represent?
Animals consume CO2 by eating it through plants
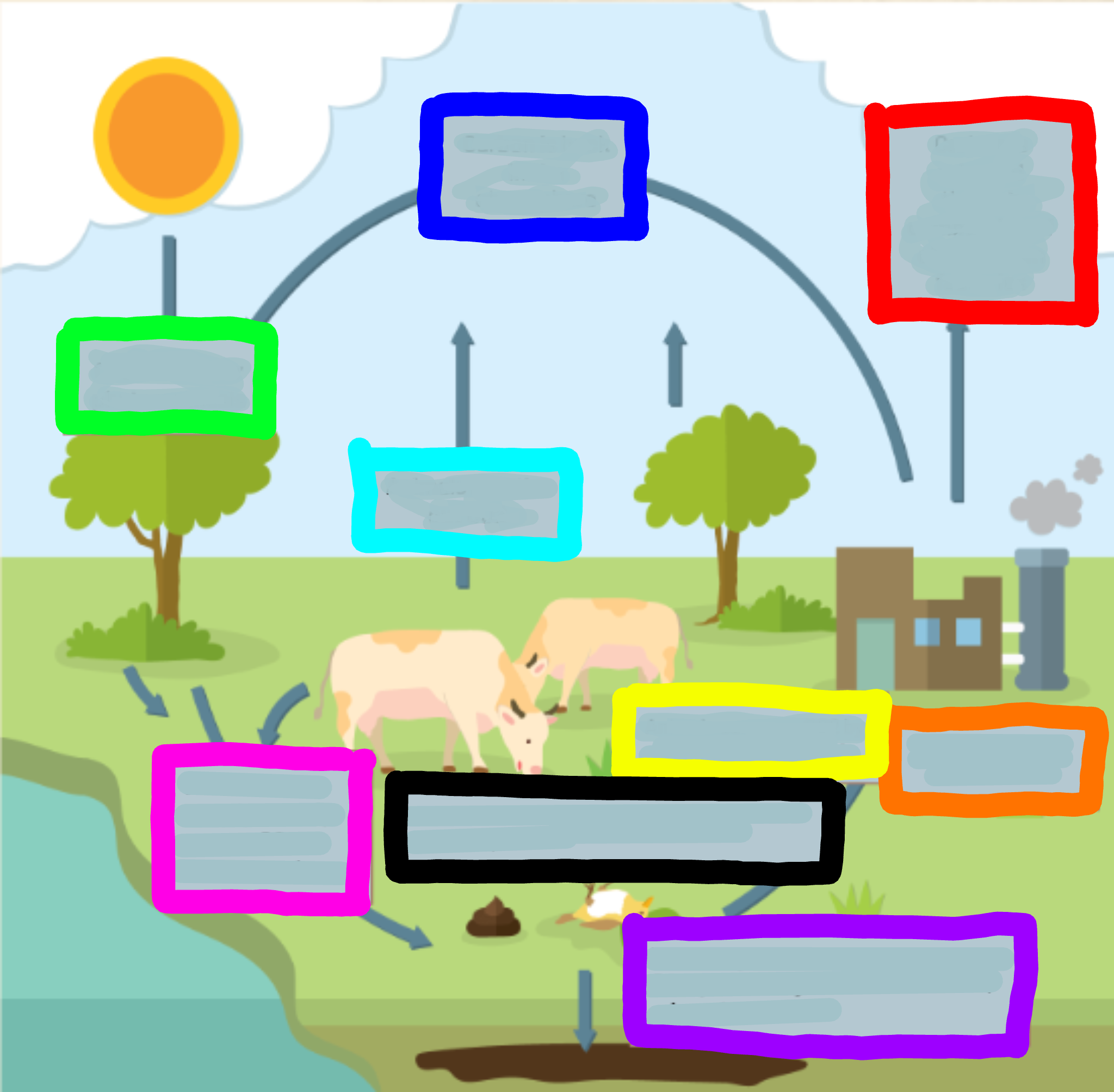
What does the green box represent?
CO2 is used for photosynthesis
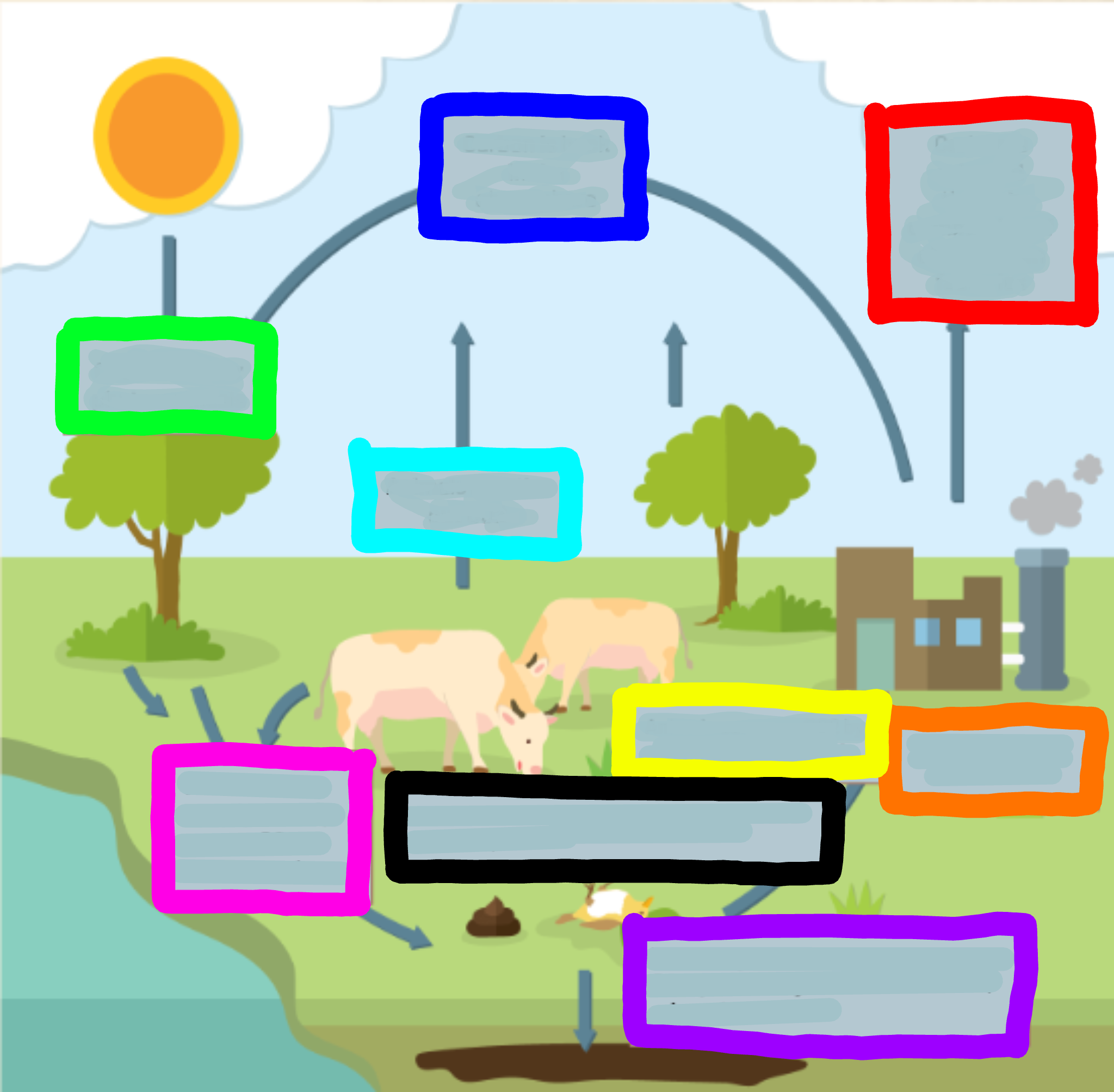
What does the cyan box represent?
Animals breathe out CO2
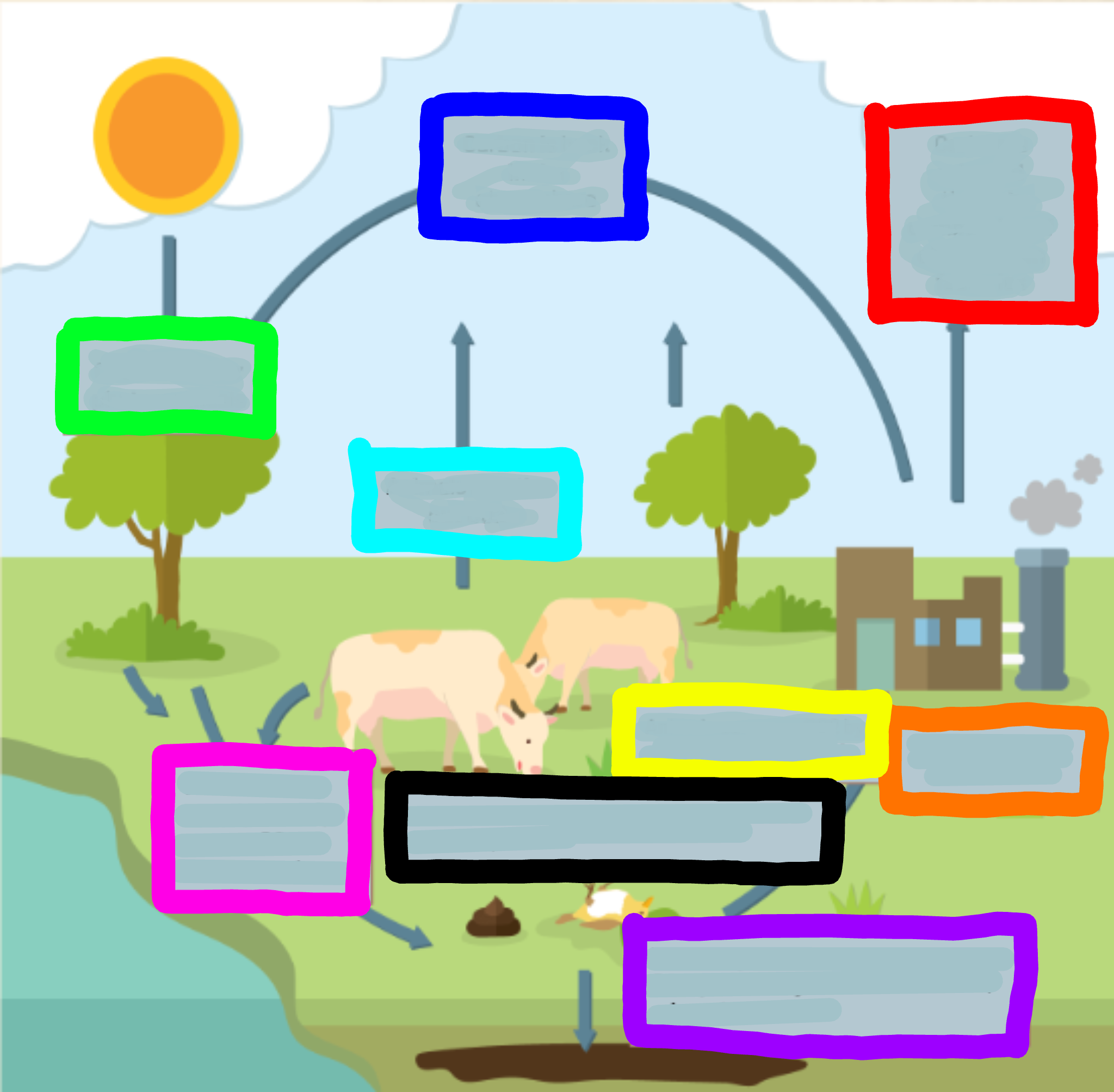
What does the blue box represent?
Carbon is back in the atmosphere
What does the purple box represent?
When organisms decompose, some CO2 joins the ground to make oils, minerals, and coal
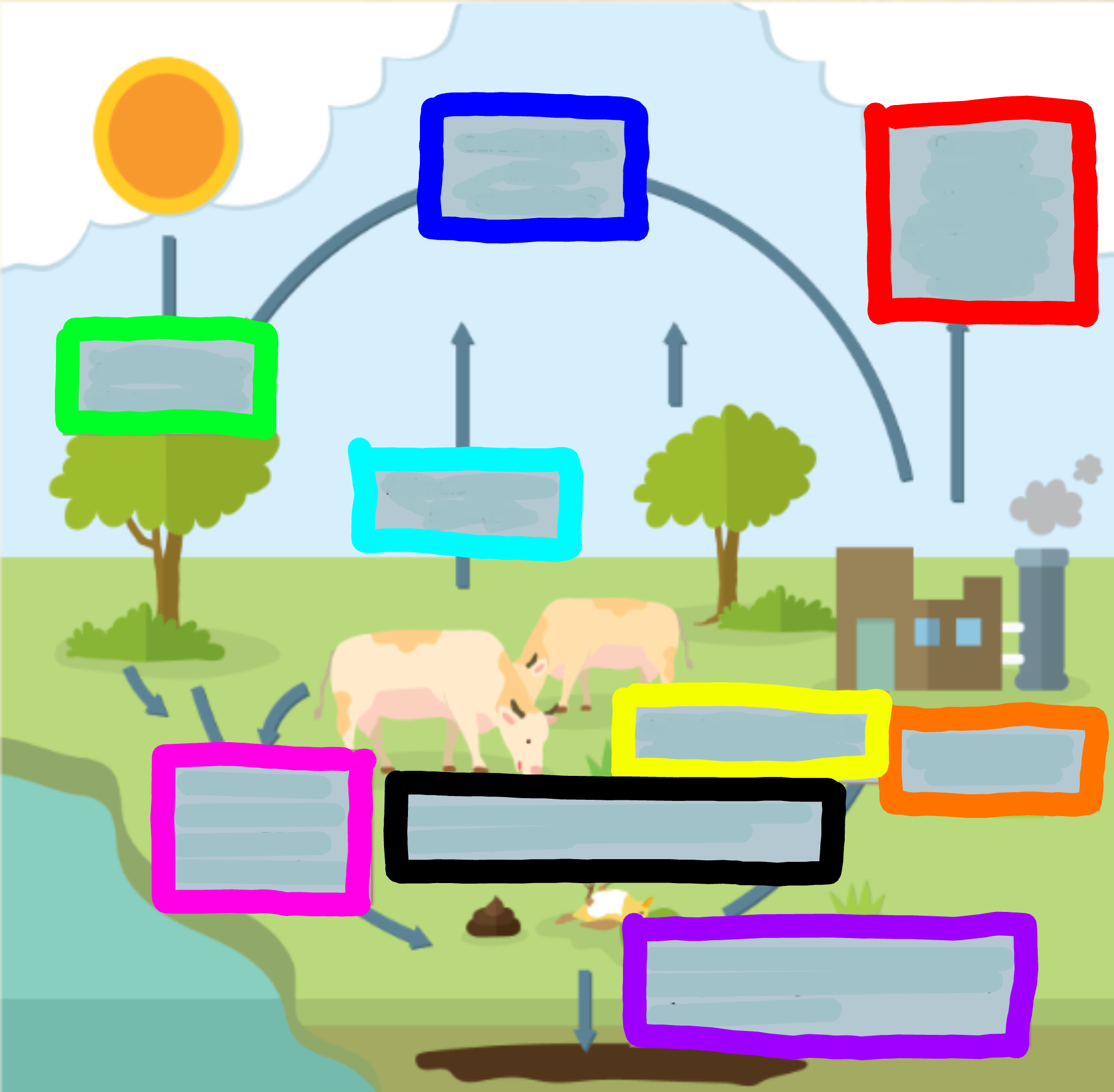
What does the pink box represent?
When animals excrete waste, they expose CO2 to the atmosphere
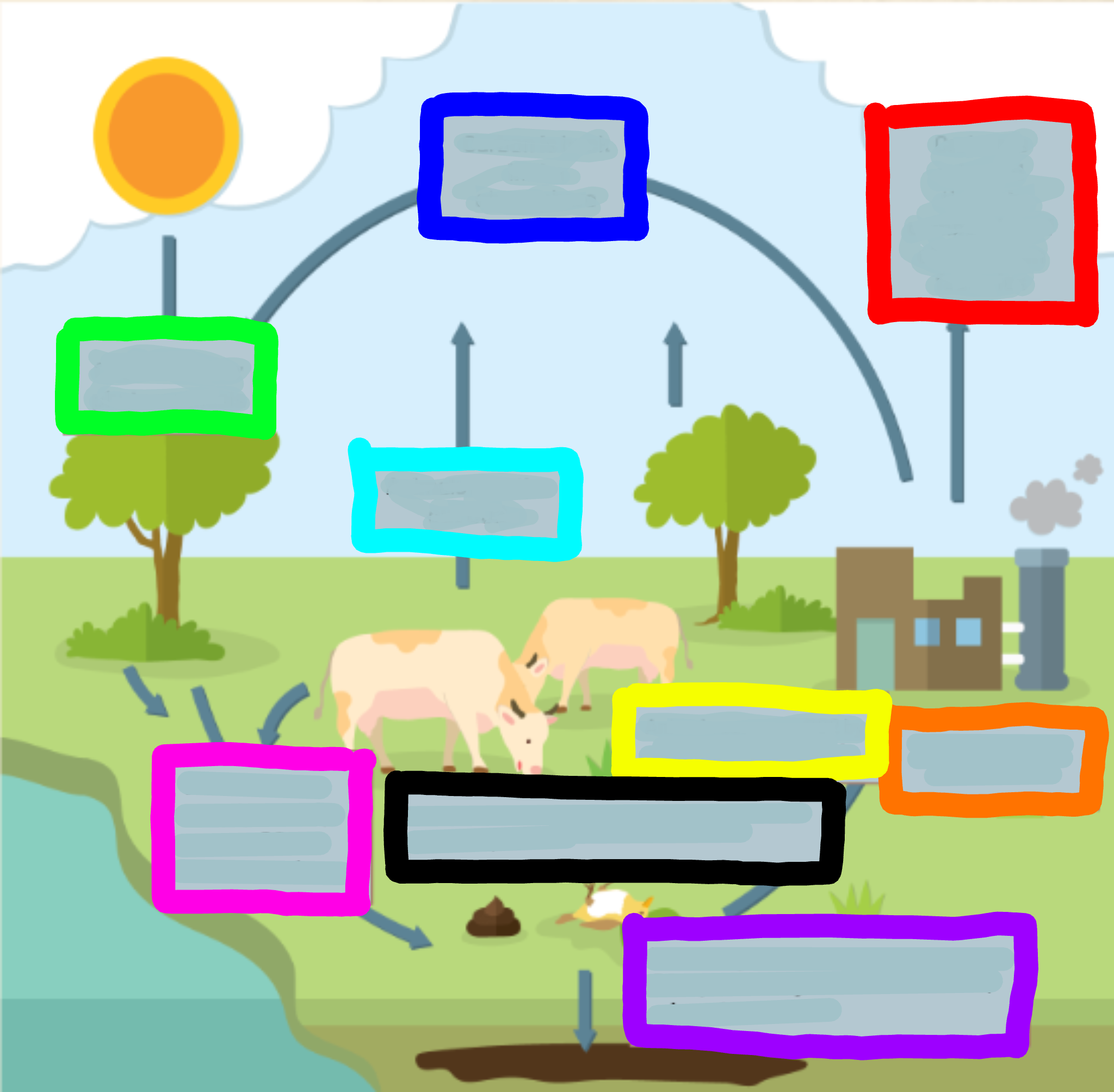
What does the black box represent?
When animals or plants die, they expose CO2 to the atmosphere
Where in the world is the largest store of carbon?
The ocean
How does the carbon cycle in the ocean? How is it used?
Animals pull carbon from the water to use in shells
Animals die and carbon substances are deposited at the bottom of the ocean
Nitrogen Cycle
The series of processes by which nitrogen and its compounds are converted in the environment and in living organisms, including nitrogen fixation and decomposition.
How do plants and animals obtain nitrogen?
Animals obtain nitrogen through consuming plants and animals
Plants have a harder time obtaining nitrogen, as they can only absorb nitrogen when it is mixed with hydrogen or oxygen
Nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen is mixed with oxygen or hydrogen changing it into ammonia
Ways nitrogen can be fixed
Lightning
Bacteria in the soil or bacteria found in nodules of legumes
Nitrification
This is the process by which ammonia gets changed into nitrates by bacteria.
Actually, ammonia is turned into nitrites first, THEN the nitrites are turned into nitrates via bacteria.
Nitrates are what the plants can then absorb and use as food.
Assimilation
This is how plants get nitrogen
They absorb nitrates from the soil into their roots
Then, the nitrogen gets used in amino acids, nucleic acids, and chlorophyll
Dentrification
Extra nitrogen in the soil gets put back in the air
There is a special bacteria that perform this as well - Pseudomonas
Ammonification
This is the part of the decaying process.
When a plant or animal dies, decomposers like fungi and bacteria turn the nitrogen back into ammonia, so it can reenter the nitrogen cycle.
Speed of decomposition is key to keeping the nitrogen cycle moving because it comes from bacteria breaking down dead matter and feces.
The (warmer/colder) an area is, the faster decomposition occurs.
Warmer
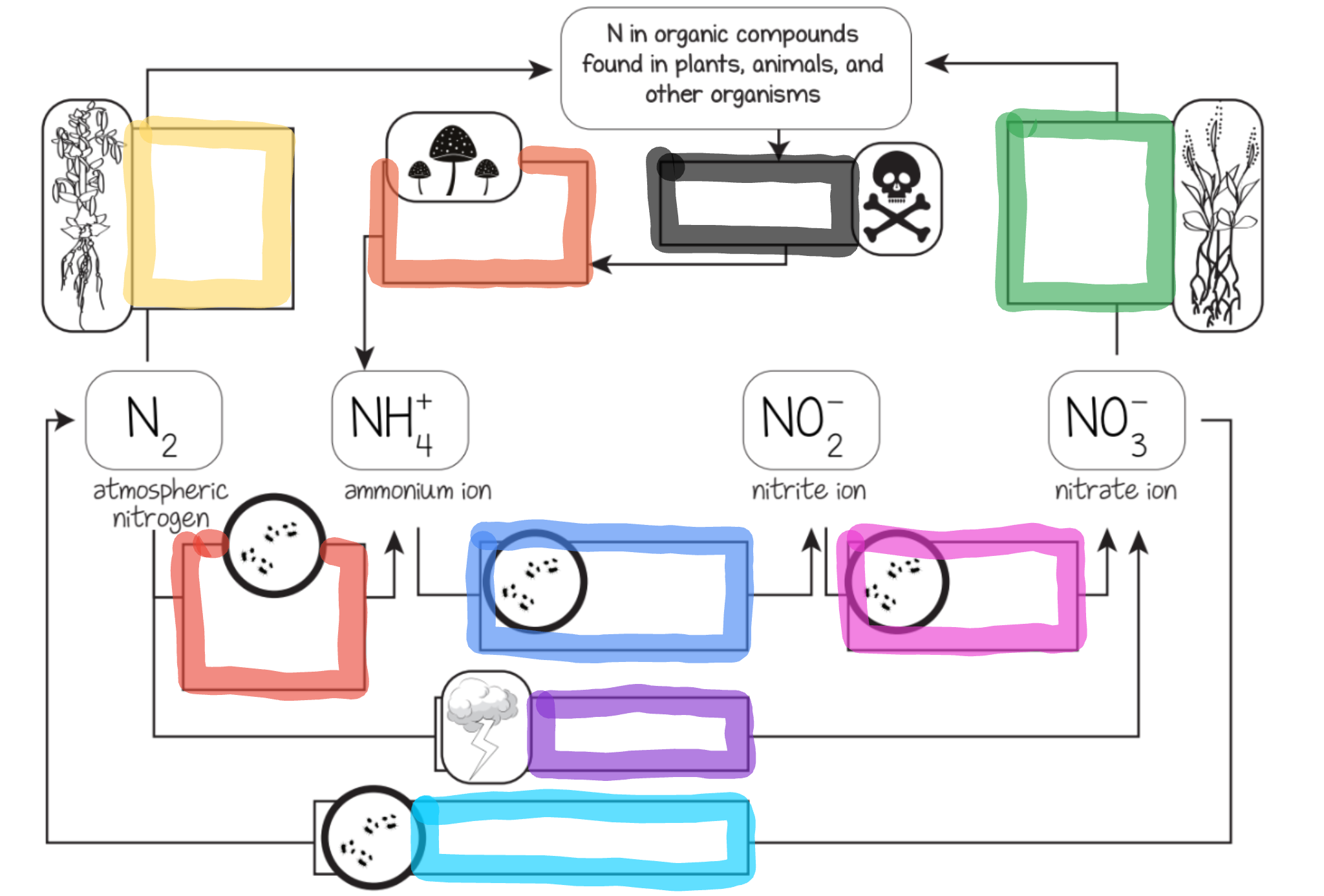
What does the red box represent?
Nitrogen fixing bacteria in soil
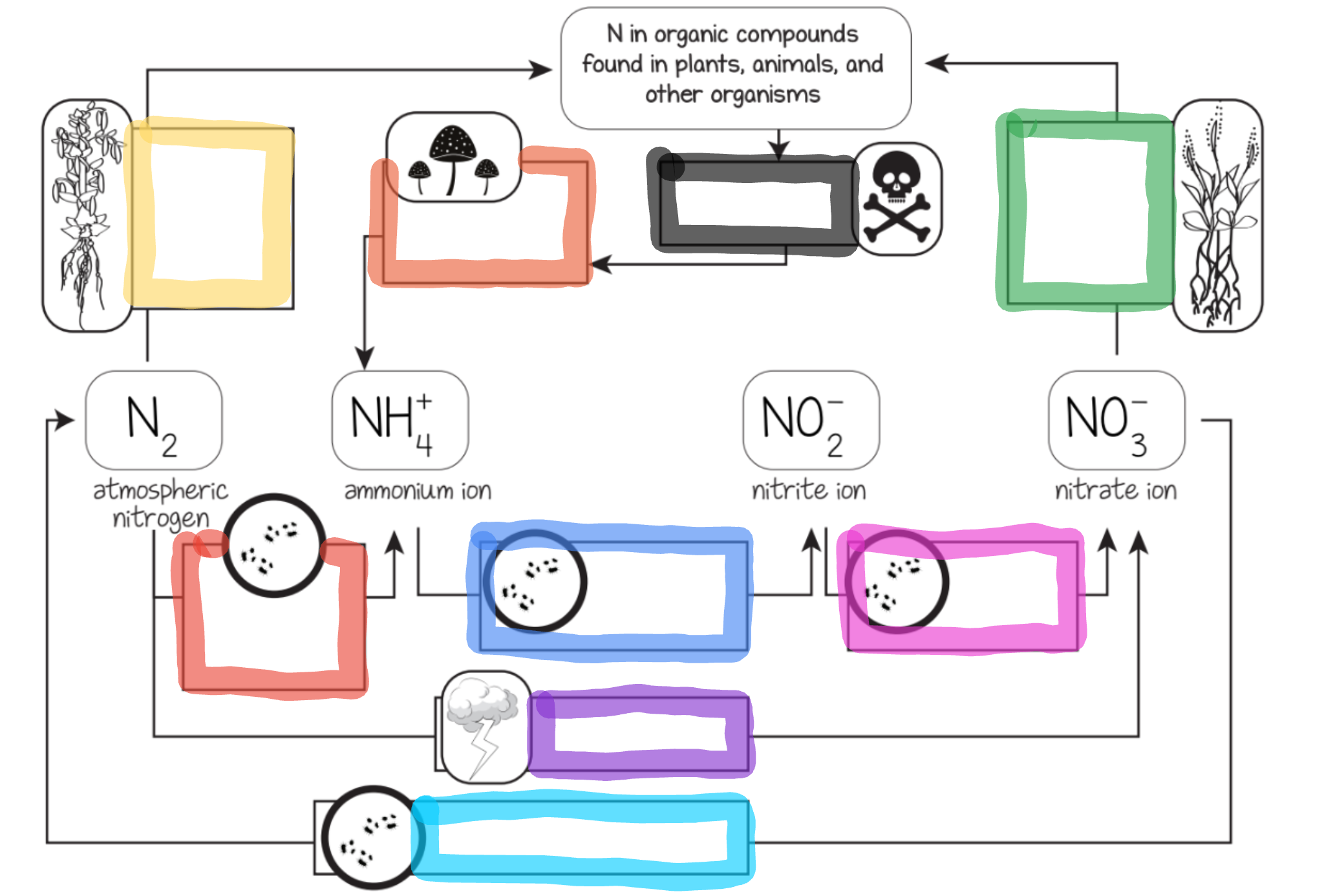
What does the orange box represent?
Decomposition by fungi and bacteria
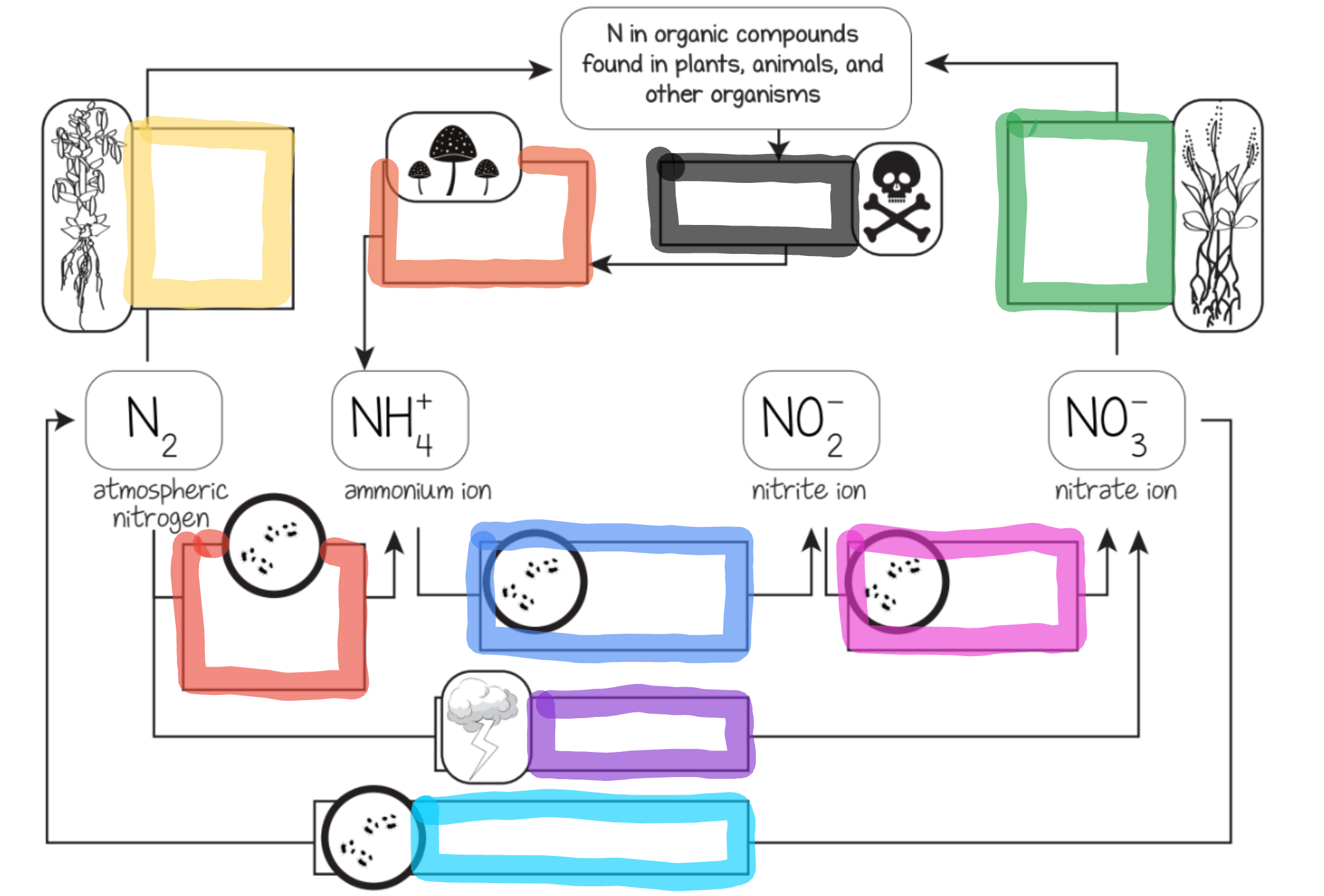
What does the yellow box represent?
Nitrogen fixing bacteria in legume root nodules
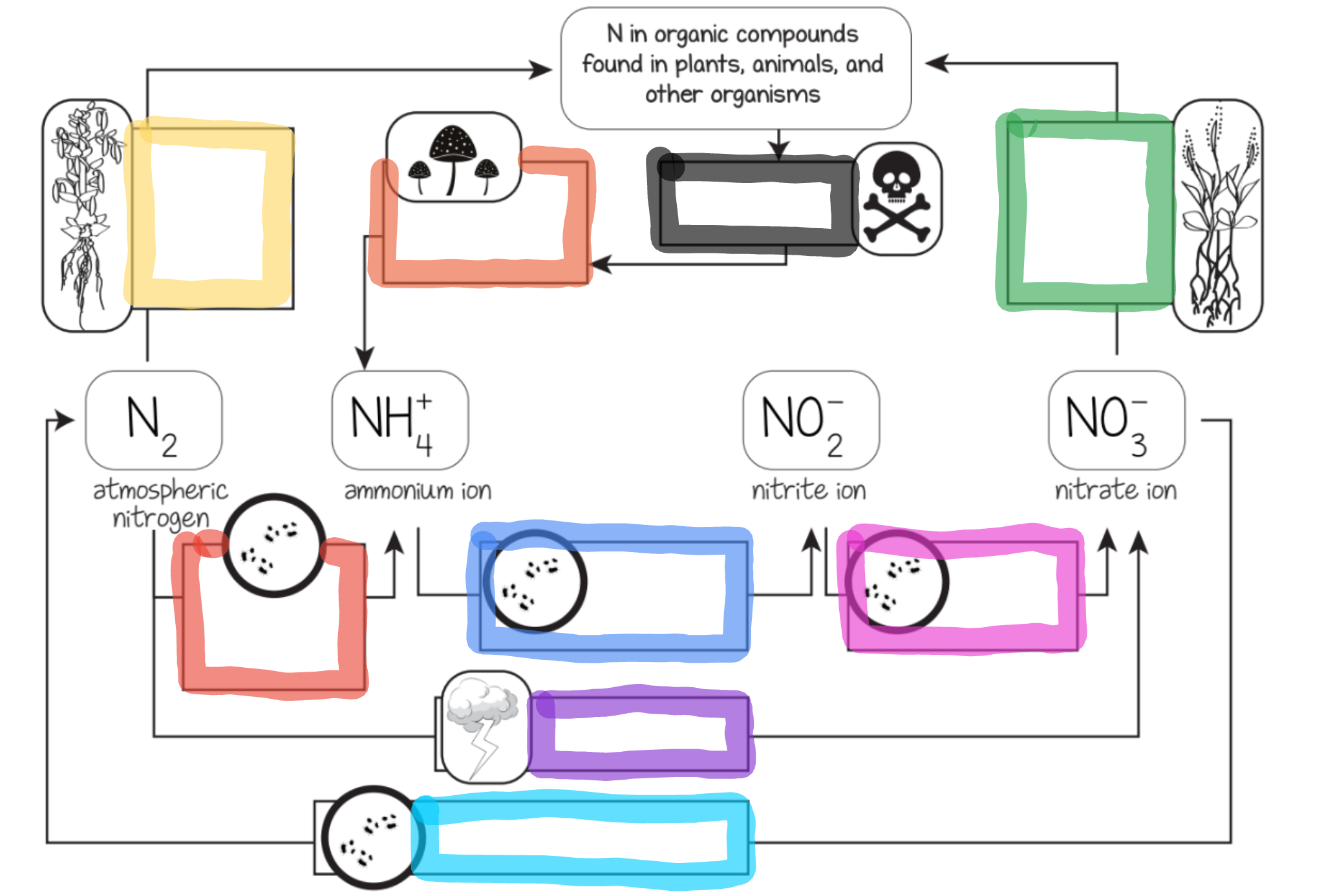
What does the green box represent?
Most plant uptake
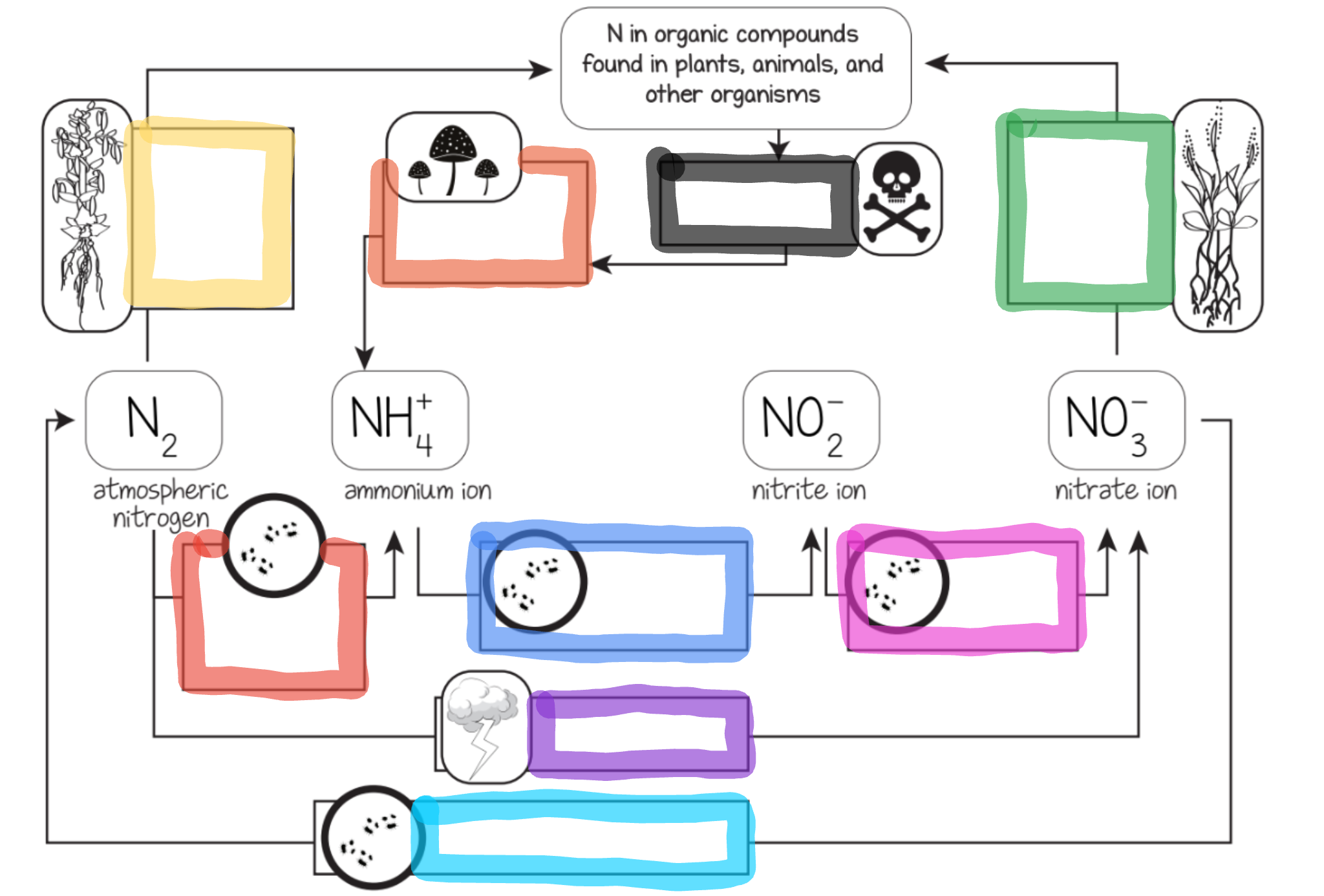
What does the cyan box represent?
Dentrifying bacteria
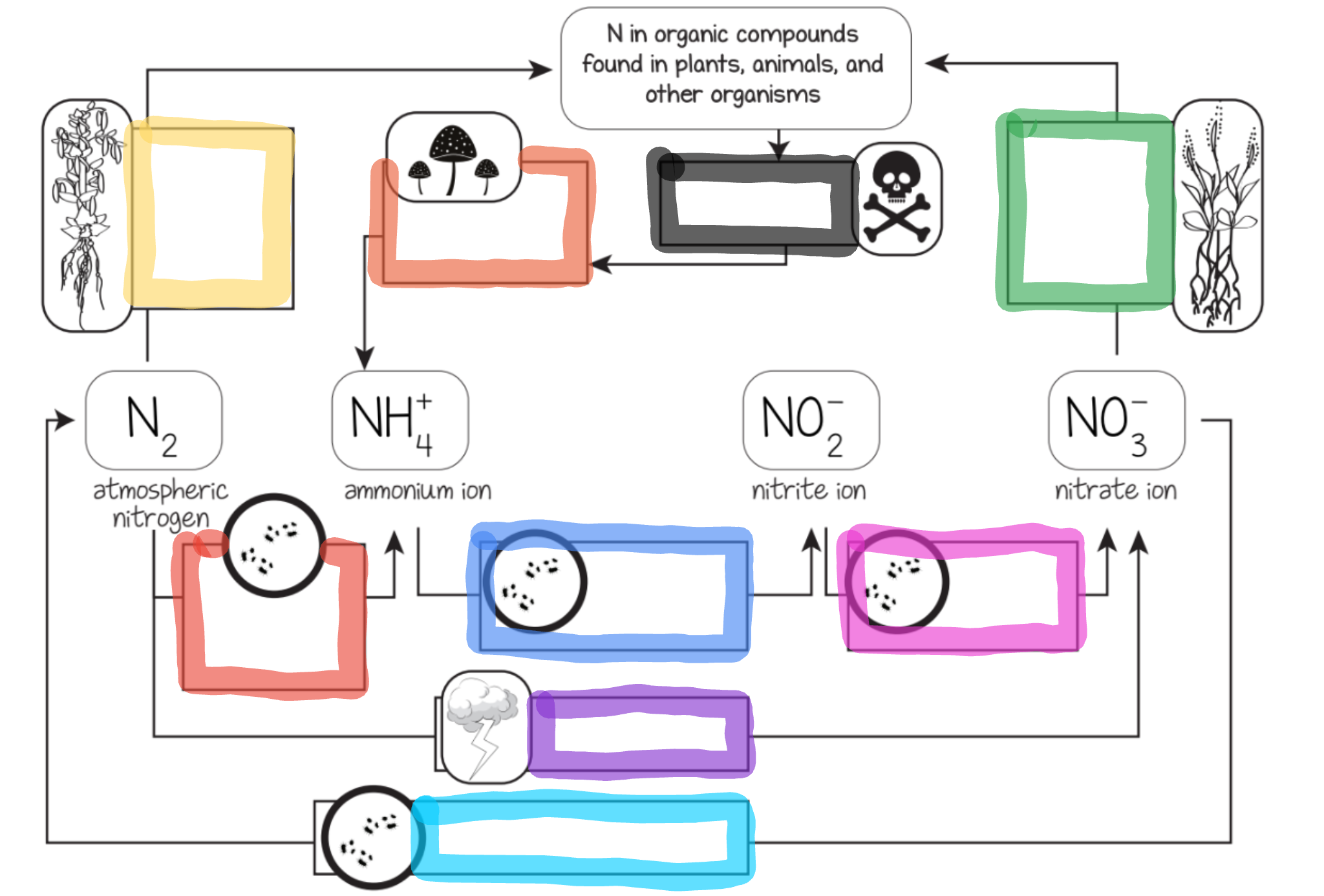
What does the blue box represent?
Ammonium oxidizing bacteria
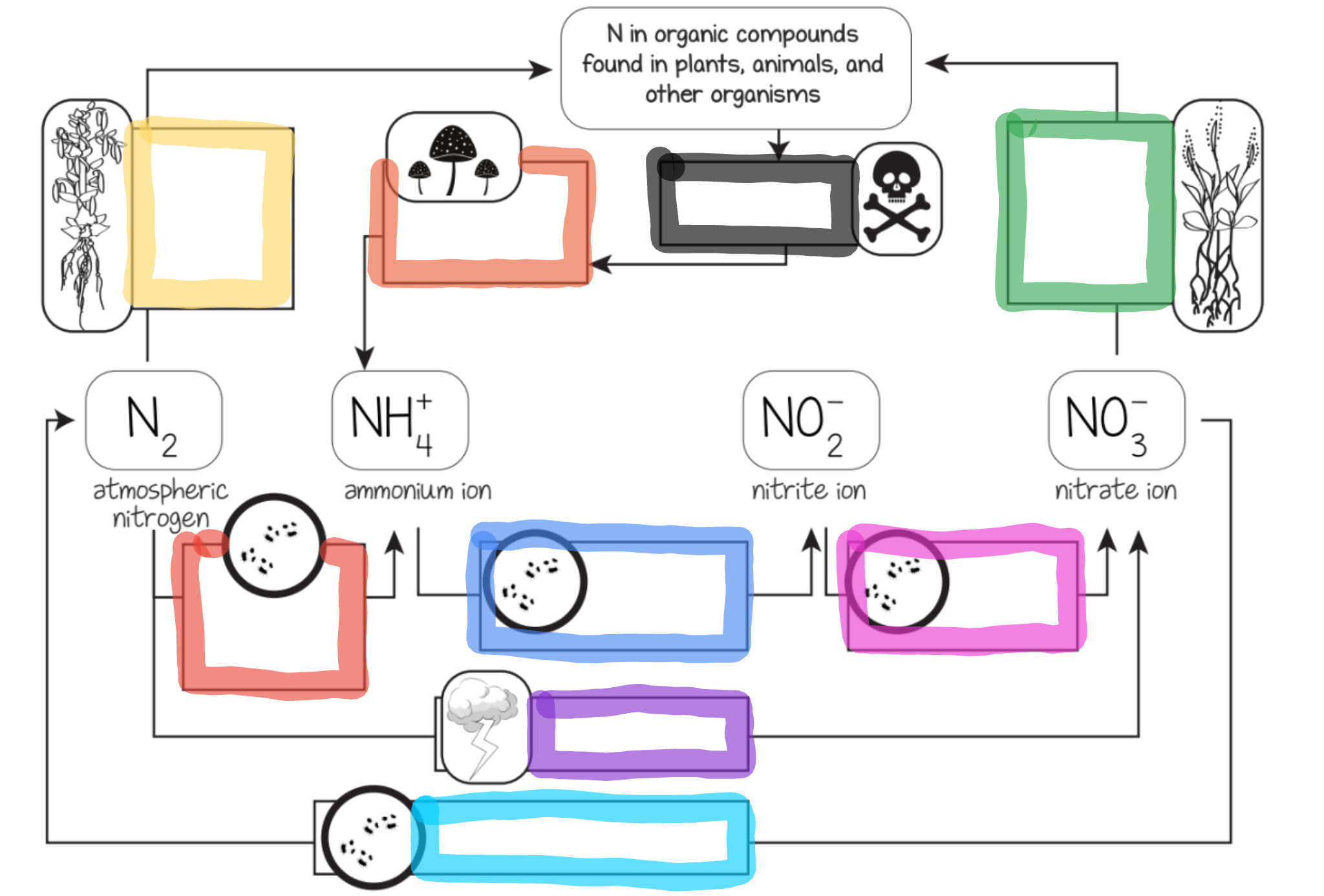
What does the purple box represent?
Lightning
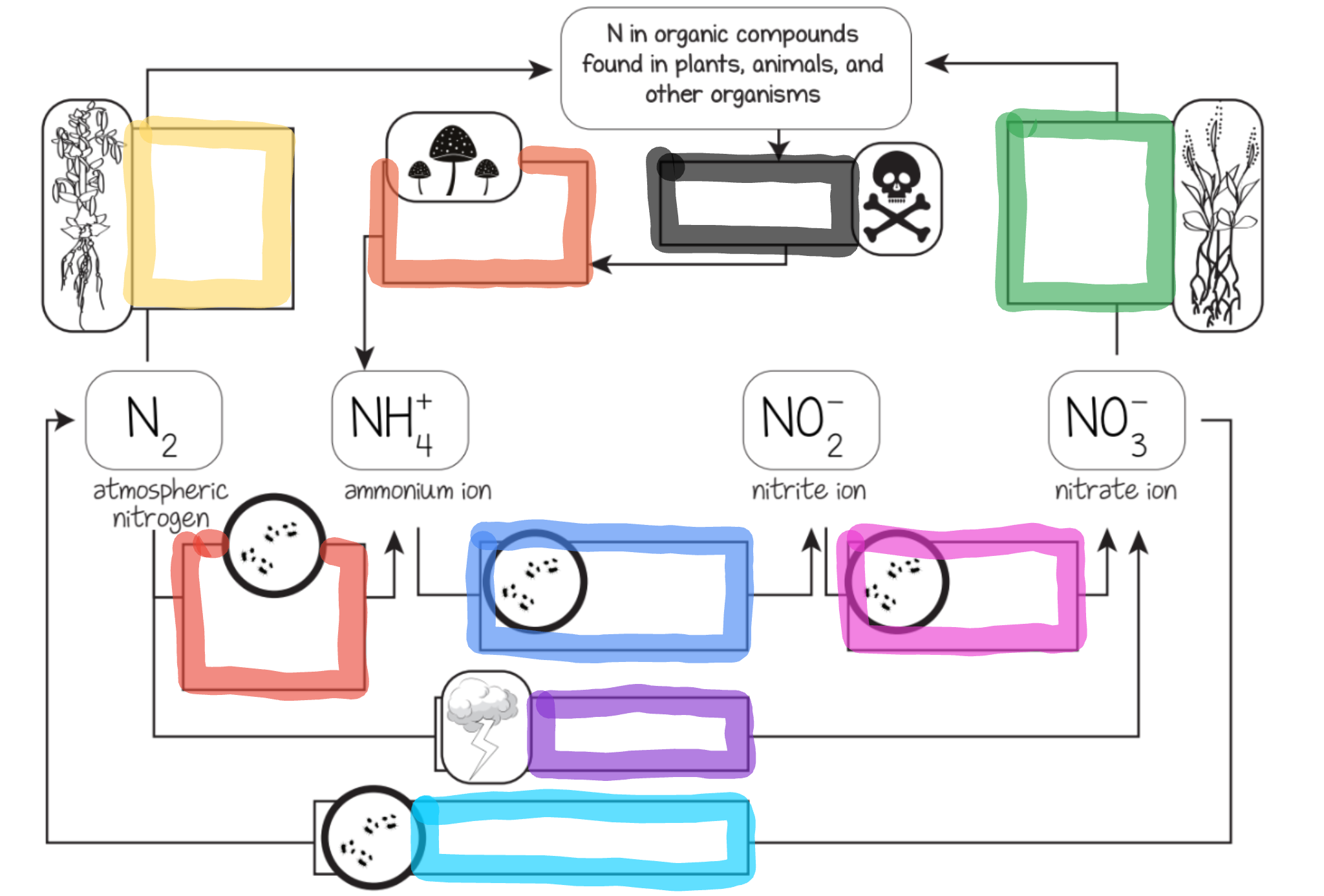
What does the pink box represent?
Nitrite oxidizing bacteria
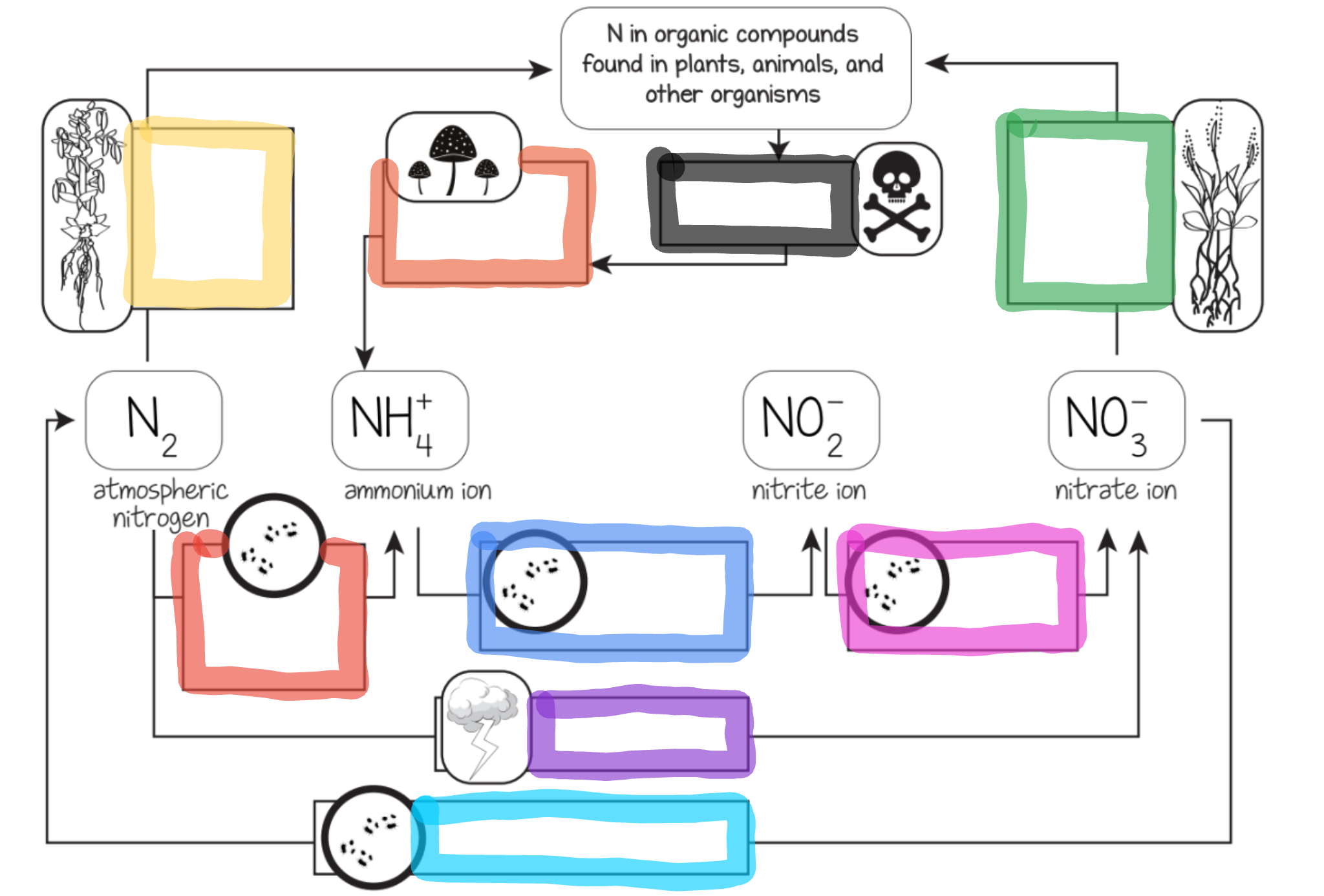
What does the black box represent?
Dead organisms and waste
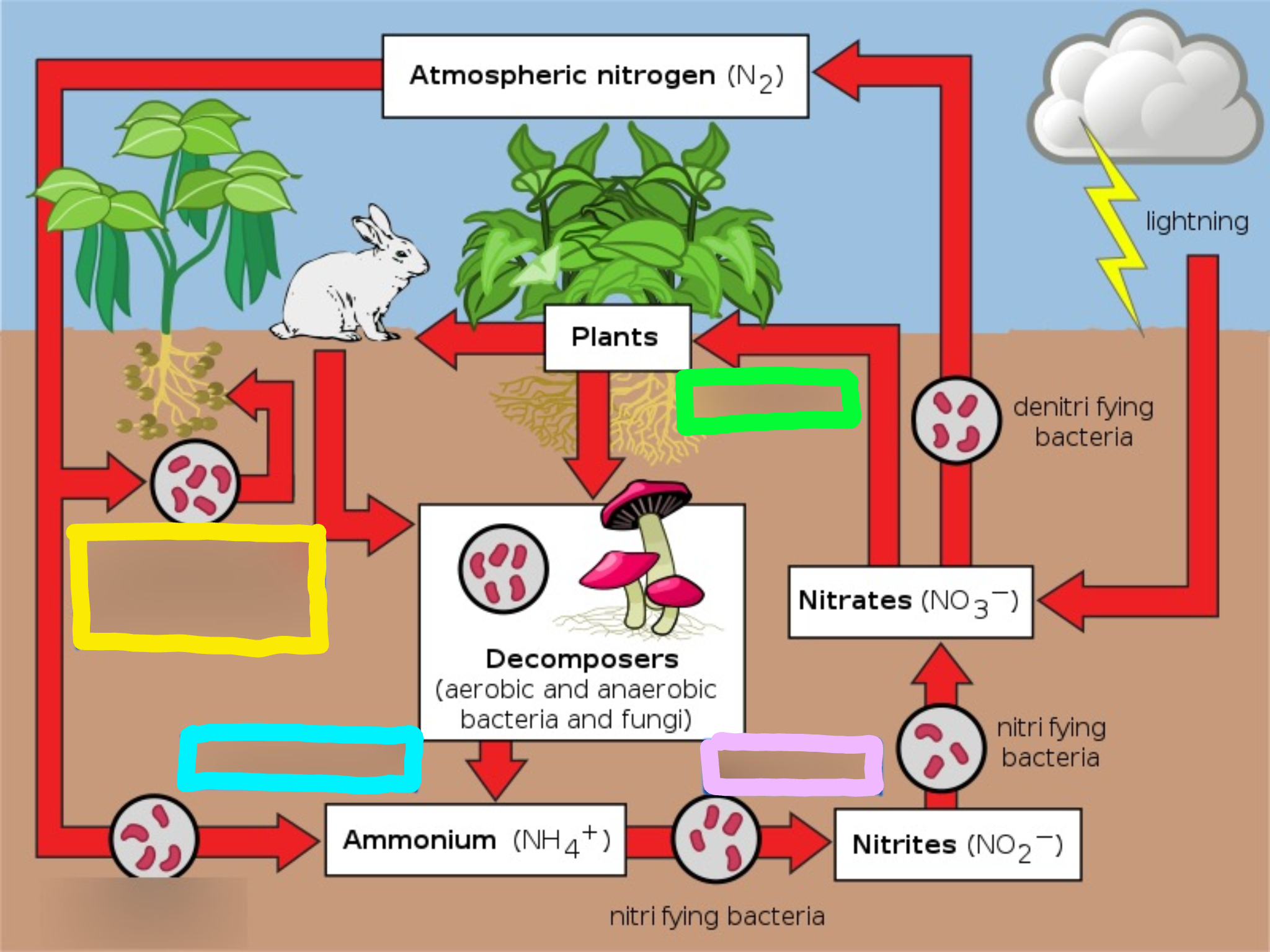
What does the yellow box represent?
Nitrogen fixing bacteria
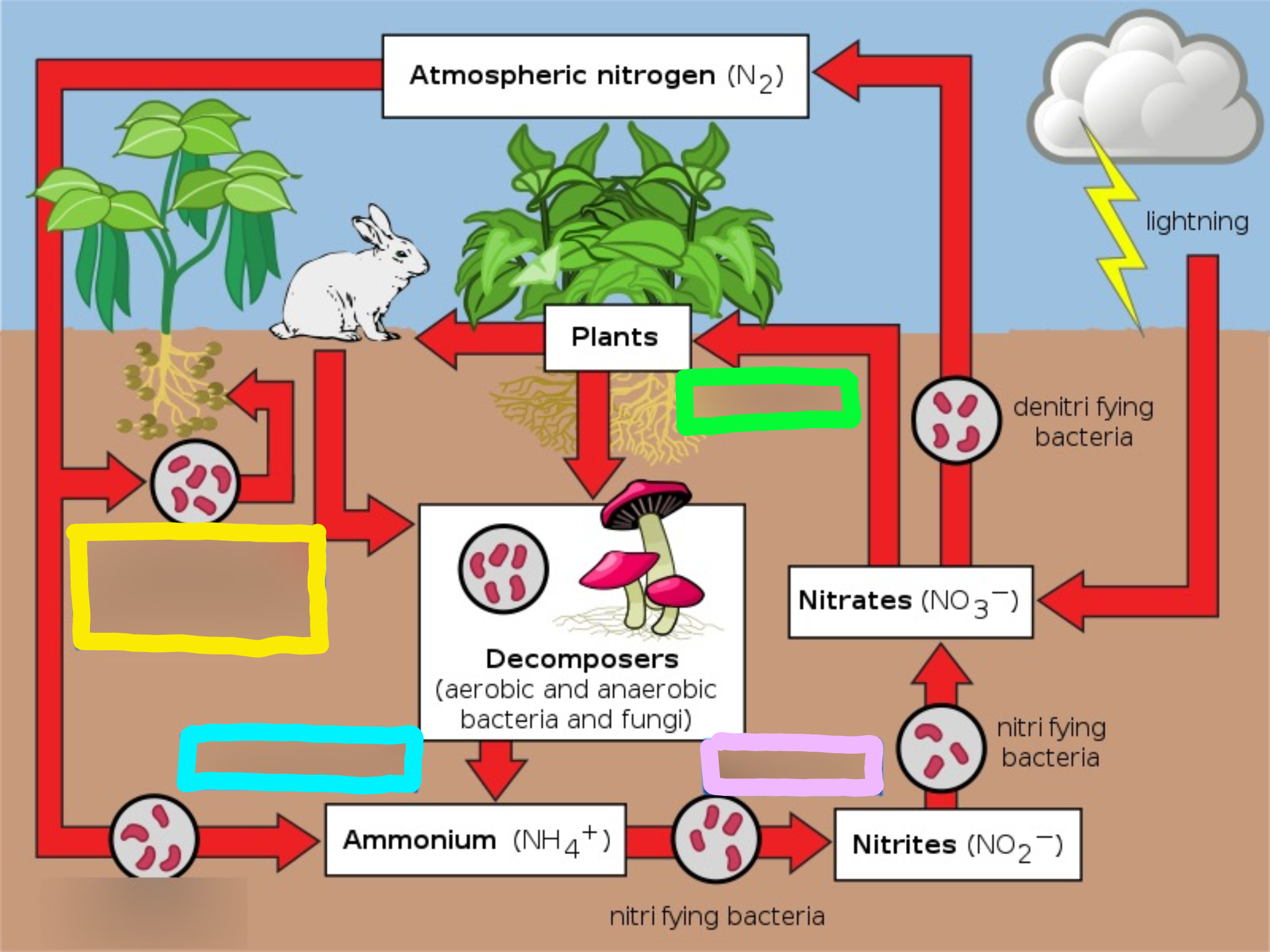
What does the cyan box represent?
Ammonification
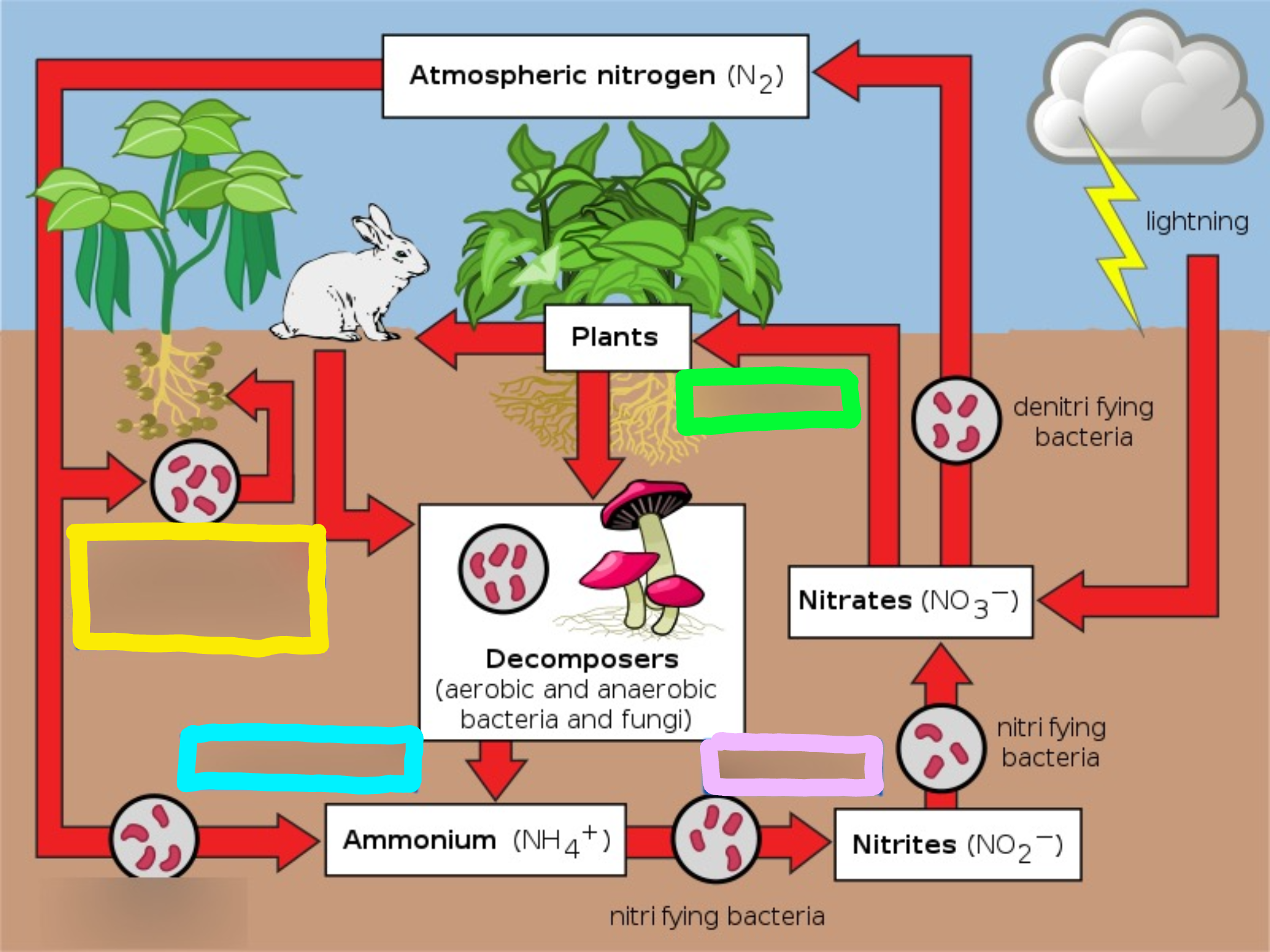
What does the green box represent?
Assimilation
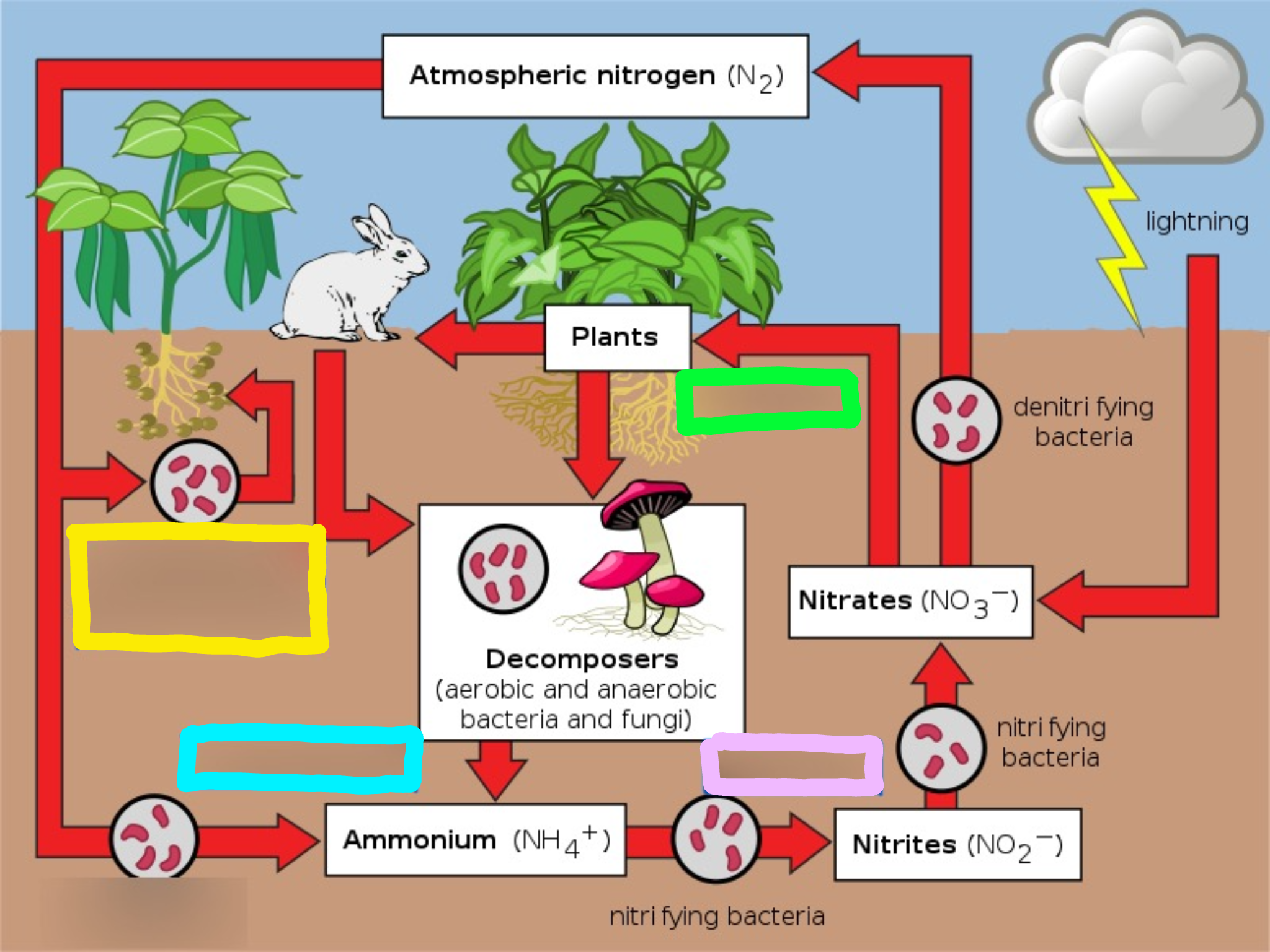
What does the lavender box represent?
Nitrification